
漢德百科全書 | 汉德百科全书
 Japan
Japan
 Egypt
Egypt
 Australia
Australia
 Belgium
Belgium
 Brunei Darussalam
Brunei Darussalam
 China
China
 Germany
Germany
 Djibouti
Djibouti
 France
France
 Greece
Greece
 Guangdong Sheng-GD
Guangdong Sheng-GD
 Hongkong Tebiexingzhengqu-HK
Hongkong Tebiexingzhengqu-HK
 India
India
 Indonesia
Indonesia


 IT-Times
IT-Times
 Late Classical, Romantic (Early, Middle, Late)
Late Classical, Romantic (Early, Middle, Late)
 Italy
Italy
 Japan
Japan
 Malaysia
Malaysia
 Morocco
Morocco
 Myanmar
Myanmar
 Oman
Oman
 Pakistan
Pakistan
 Philippines
Philippines
 Portugal
Portugal
 Republic of Korea
Republic of Korea
 Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia
 Shanghai Shi-SH
Shanghai Shi-SH
 Singapore
Singapore
 Singapore
Singapore
 Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka
 Taiwan Sheng-TW
Taiwan Sheng-TW
 Thailand
Thailand
 Turkey
Turkey
 United Arab Emirates
United Arab Emirates
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 Vietnam
Vietnam
 Cyprus
Cyprus
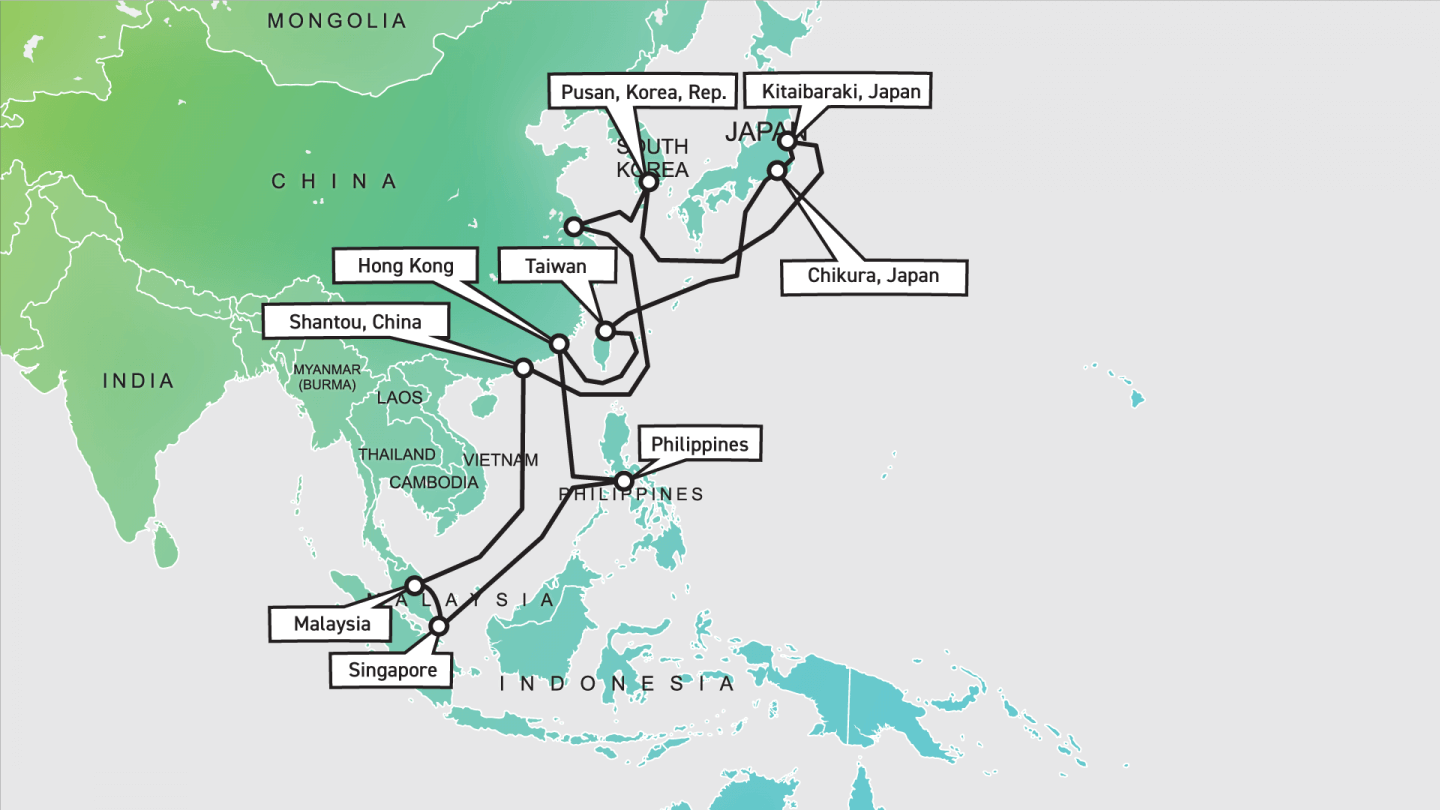
 China
China
 Guangdong Sheng-GD
Guangdong Sheng-GD
 Hongkong Tebiexingzhengqu-HK
Hongkong Tebiexingzhengqu-HK


 IT-Times
IT-Times
 Modern music impressionism
Modern music impressionism
 Japan
Japan
 Malaysia
Malaysia
 Philippines
Philippines
 Republic of Korea
Republic of Korea
 Shanghai Shi-SH
Shanghai Shi-SH
 Singapore
Singapore
 Taiwan Sheng-TW
Taiwan Sheng-TW
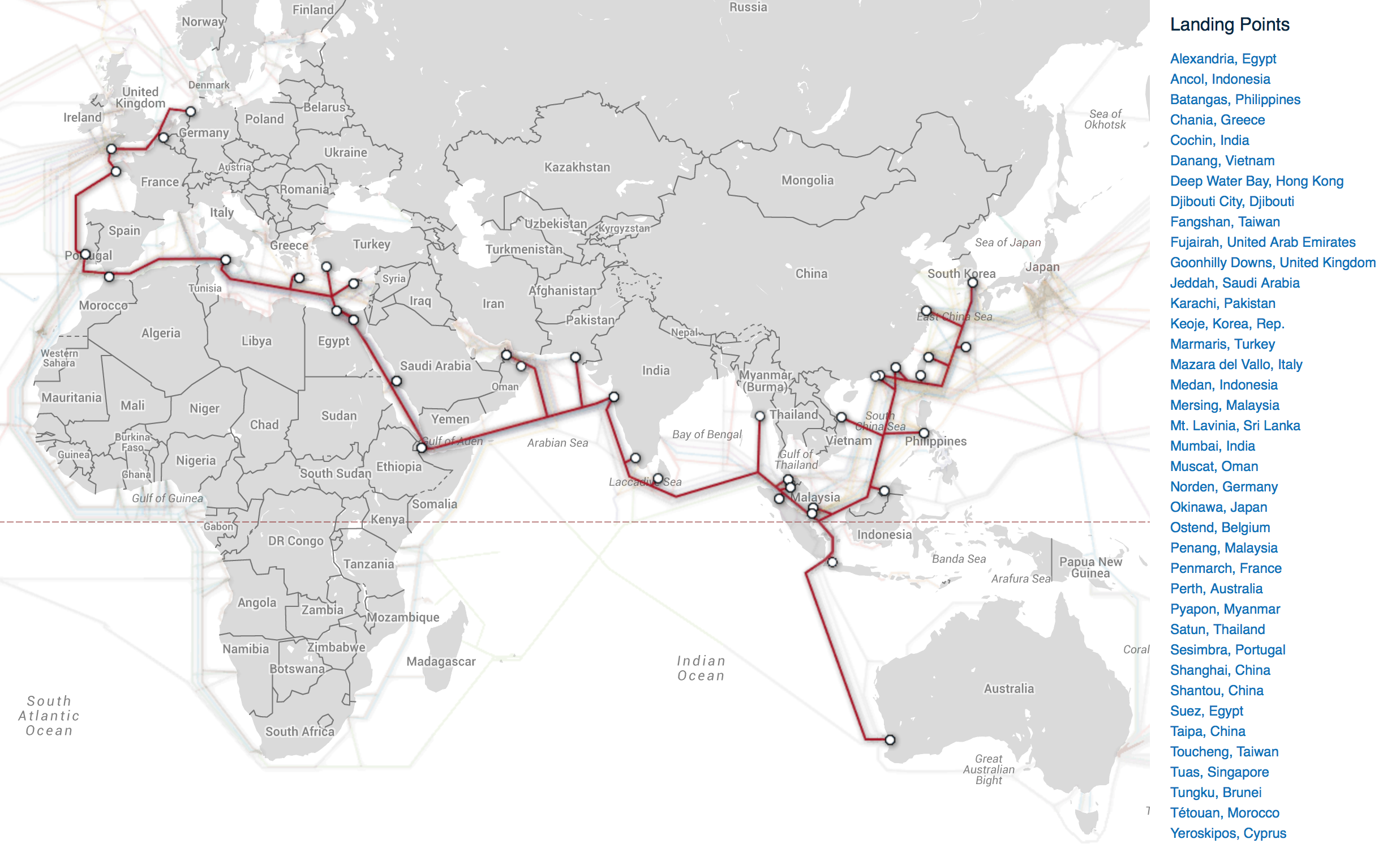
Cable System:
- Asia Pacific Cable Network 2, or APCN-2
Cable Length:
- 19,000 Km
Design Capacity:
- 2.56 Tbps
- 4 fiber pairs, each of 64x10 Gbps DWDM
- upgrade to 40 Gbps DWDM in September 2011
Lit Capacity:
- 80 Gbps (as of RFS in Dec. 2001)
- 160 Gbps (first upgrade in 2002)
- 280 Gbps (2nd upgrade in 2006)
Ready for Service Date:
- December 20, 2000
Investment Type:
- Consortium
Owner(s):
- The APCN-2 consortium members consist of 45 carriers in Asia Pacific region, including following 26 initial parties:
| KDD (Japan) Advantel(Hong Kong) Chunghwa Telecom (Taiwan) C&W Global Network (Ireland) KPN (Netherlands) Metromedia Fiber Network (USA) PLDT (Philippines) Taiwan Fixed Net (Taiwan) Telecom Malaysia (Malaysia) | NTT Communications (Japan) China Telecom (China) Concert (Bermuda) Global One (Japan) Layer 2 Communications (British Virgin Is.) New Century Infocomm Co. (Taiwan) Singapore Telecom (Singapore) Teleglobe (United States) Williams Communications (USA) | Japan Telecom (Japan) China Unicom (China) C&W HKT (Hong Kong) Korea Telecom (Korea) MCII (United States) OneLink Cable Network (Hong Kong) Starhub (Singapore) Telstra Global Networks (Bermuda) |
 *Think Tanks in Japan
*Think Tanks in Japan

 Financial
Financial
 *Japan economic data
*Japan economic data
 Kantō
Kantō

 Party and government
Party and government
 *Think Tank
*Think Tank

 Economy and trade
Economy and trade
 Economic and political research
Economic and political research
 AFC Champions League 2015
AFC Champions League 2015
 AFC Champions League 2016
AFC Champions League 2016
 AFC Champions League 2017
AFC Champions League 2017
 AFC Champions League 2018
AFC Champions League 2018
 AFC Champions League 2019
AFC Champions League 2019
 AFC Champions League 2020
AFC Champions League 2020
 AFC Champions League 2021
AFC Champions League 2021
 AFC Champions League 2022
AFC Champions League 2022
 AFC Champions League 2023
AFC Champions League 2023
 AFC Champions League 2024
AFC Champions League 2024
 AFC Champions League 2025
AFC Champions League 2025
 Australia
Australia
 China
China
 Iran
Iran
 Israel
Israel
 Japan
Japan
 Katar
Katar
 Republic of Korea
Republic of Korea
 Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia
 Thailand
Thailand
 United Arab Emirates
United Arab Emirates


 Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation,APEC
Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation,APEC

 Australian Capital Territory-ACT
Australian Capital Territory-ACT
 Australia
Australia
 Beijing Shi-BJ
Beijing Shi-BJ

 British Columbia-BC
British Columbia-BC
 Brunei Darussalam
Brunei Darussalam
 Chile
Chile
 China
China

 Hand in Hand
Hand in Hand

 Hawaii-HI
Hawaii-HI
 Hongkong Tebiexingzhengqu-HK
Hongkong Tebiexingzhengqu-HK
 Indonesia
Indonesia
 Japan
Japan
 Canada
Canada
 Kantō
Kantō
 Kinki
Kinki
 Malaysia
Malaysia
 Mexico
Mexico
 New Zealand
New Zealand

 New South Wales-NSW
New South Wales-NSW
 Papua-Neuguinea
Papua-Neuguinea

 Party and government
Party and government

 Party and government
Party and government
 Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation,APEC
Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation,APEC
 Peru
Peru
 Philippines
Philippines
 Republic of Korea
Republic of Korea
 Russia
Russia
 Shanghai Shi-SH
Shanghai Shi-SH
 Singapore
Singapore
 Taiwan Sheng-TW
Taiwan Sheng-TW
 Thailand
Thailand
 United States
United States
 Vietnam
Vietnam

 Washington-WA
Washington-WA

 Important International Organizations
Important International Organizations

Die Asiatisch-Pazifische Wirtschaftsgemeinschaft (für englisch Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation, kurz APEC, auch übersetzt als Asiatisch-Pazifische Wirtschaftskooperation oder Asien-Pazifik-Forum) ist eine internationale Organisation, die es sich zum Ziel gesetzt hat, im pazifischen Raum eine Freihandelszone einzurichten.
In den 21 APEC-Staaten lebt knapp die Hälfte der Weltbevölkerung. Der Wirtschaftsraum erbringt mehr als die Hälfte der Weltwirtschaftsleistung und ist eine der am schnellsten wachsenden Wirtschaftsregionen der Welt.
亚太经济合作组织(简称亚太经合组织;英语:Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation,缩写:APEC),是亚太区内各地区之间促进经济成长、合作、贸易、投资的论坛。此组织的创办在历史上取代了该区域的冷战结构,但由于日本在该区域会因过去历史记忆引发负面评价,所以由澳大利亚主导创始事项[1]。
始设于1989年,现有21个经济体成员。亚太经合组织是经济合作的论坛平台,其运作是通过非约束性的承诺与成员的自愿,强调开放对话及平等尊重各成员意见,不同于其他经由条约确立的政府间组织。“APEC”与“Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation”均是亚太经济合作组织的注册商标。[2]
アジア太平洋経済協力会議(アジアたいへいようけいざいきょうりょくかいぎ、英: Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation)は、環太平洋地域における多国間経済協力を進めるための非公式なフォーラム[2]である。略称、APEC(エイペック[3][4])。
「アジア太平洋」という概念が最初に打ち出されたのは、永野重雄が1967年に発足させた太平洋経済委員会(PBEC)という経済団体の設立時であるとされるが[5][6][7]、具体的にこうした地域概念が政府レベルの協力枠組みに発展する萌芽は、1978年、日本の大平正芳首相が就任演説で「環太平洋連帯構想」を呼びかけたことにある。これを具体化した大平政権の政策研究会「環太平洋連帯研究グループ」(議長:大来佐武郎、幹事佐藤誠三郎)の報告を受け、大平がオーストラリアのマルコム・フレイザー首相に提案して強い賛同を得たことが、1980年9月の太平洋経済協力会議(PECC)の設立につながった。PECCは地域における様々な課題を議論し研究するセミナーといった趣のものであったが、これを土台にして、各国政府が正式に参加する会合として設立されたのが、APECである[8][9]。
APECは、1989年にオーストラリアのホーク首相の提唱で、日本・アメリカ合衆国・カナダ・韓国・オーストラリア・ニュージーランド及び当時の東南アジア諸国連合(ASEAN)加盟6か国の計12か国で発足し、同国のキャンベラで閣僚会議(Ministerial Meeting)を開催した。また、1993年には米国のシアトルで初の首脳会議(Economic Leaders' Meeting)がもたれた。現在は、首脳会議、及び、外相、経済担当相による閣僚会議をそれぞれ年1回開いている。シンガポールに常設事務局を置き、開催国から任期1年で事務局長が選任されている[10]。 参加しているメンバーは、21カ国・地域で、2012年現在、人口では世界の41.4%、GDP(国内総生産)では57.8%、貿易額では47%を占めている。
APECは、開かれた地域協力によって経済のブロック化を抑え、域内の貿易・投資の自由化を通じて、世界貿易機関(WTO)のもとでの多角的自由貿易体制を維持・発展することを目的としてきたが、近年のWTOの新ラウンドの停滞や自由貿易協定締結の動きの活発化などによって、その存在意義が問われている。
Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC) is an inter-governmental forum for 21 Pacific Rim member economies[2] that promotes free trade throughout the Asia-Pacific region. Inspired from the success of Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN)’s series of post-ministerial conferences launched in the mid-1980s, the APEC was established in 1989 in response to the growing interdependence of Asia-Pacific economies and the advent of regional trade blocs in other parts of the world; and to establish new markets for agricultural products and raw materials beyond Europe.[3][4][5] Headquartered in Singapore, the APEC is recognised as one of the oldest forums and highest-level multilateral blocs in the Asia-Pacific region, and exerts a significant global influence.[6][7][8][9][10][11]
An annual APEC Economic Leaders' Meeting is attended by the heads of government of all APEC members except Republic of China (Taiwan) (which is represented by a ministerial-level official under the name Republic of China as economic leader).[12] The location of the meeting rotates annually among the member economies, and a famous tradition, followed for most (but not all) summits, involves the attending leaders dressing in a national costume of the host country. APEC has three official observers: the Association of Southeast Asian Nations Secretariat, the Pacific Economic Cooperation Council and the Pacific Islands Forum Secretariat.[13] APEC's Host Economy of the Year is considered to be invited in the first place for geographical representation to attend G20 meetings following G20 guidelines.[14][15][16][17]
La Coopération économique pour l'Asie-Pacifique (en anglais : Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation, APEC) est un forum économique intergouvernemental visant à faciliter la croissance économique, la coopération, les échanges et l'investissement de la région Asie Pacifique. Elle se réunit chaque année1.
L'Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC), ossia Cooperazione Economica Asiatico-Pacifica, è un organismo nato nel 1989 allo scopo di favorire la cooperazione (o, più in generale, la crescita) economica, il libero scambio e gli investimenti nell'area asiatico-pacifica. Tale area (come suggerisce il logo stesso dell'APEC) coincide non solo con l'Asia Pacifica, ma potenzialmente con l'intero Pacific Rim.
L'APEC ha sede a Singapore, Paese considerato una delle tigri dell'Asia.
Dal punto di vista del diritto internazionale l'APEC si definisce organismo e non organizzazione internazionale perché, essendo composto da economie e non da Stati, è privo di una piena personalità giuridica. Ciò spiega, fra l'altro, come mai possano farne parte contemporaneamente la Cina continentale, Hong Kong e Taiwan, ossia tre realtà che, territorialmente (secondo Pechino e secondo tutti i governi che intrattengono relazioni diplomatiche con Pechino), appartengono a un unico Stato: la Repubblica Popolare di Cina.
APEC (Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation, en español Foro de Cooperación Económica Asia-Pacífico) es un foro multilateral creado en 1989, con el fin de consolidar el crecimiento y la prosperidad de los países del Pacífico, que trata temas relacionados con el intercambio comercial, coordinación económica y cooperación entre sus integrantes.1
Como mecanismo de cooperación y concertación económica, está orientado a la promoción y facilitación del comercio, las inversiones, la cooperación económica y técnica y al desarrollo económico regional de los países y territorios de la cuenca del océano Pacífico. Fomentando un crecimiento económico inclusivo, equitativo, sustentable e innovador.2
La suma del Producto Nacional Bruto de las veintiuna economías que conforman el APEC equivale al 56 % de la producción mundial, en tanto que en su conjunto representan el 46 % del comercio global.
La APEC no tiene un tratado formal. Sus decisiones se toman por consenso y funciona con base en declaraciones no vinculantes. Tiene una Secretaría General, con sede en Singapur, que es la encargada de coordinar el apoyo técnico y de consultoría. Cada año uno de los países miembros es huésped de la reunión anual de la APEC. La vigésimo novena cumbre se realizó en noviembre de 2017 en Da Nang, Vietnam; y la próxima será en Santiago, Chile.
Азиатско-Тихоокеанское экономическое сотрудничество (АТЭС) (англ. Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation, APEC) — форум 21 экономики Азиатско-Тихоокеанского региона для сотрудничества в области региональной торговли и облегчения и либерализации капиталовложений.
Целью АТЭС является повышение экономического роста, процветания в регионе и укрепление азиатско-тихоокеанского сообщества. В экономиках-участницах проживает около 40 % мирового населения, на них приходится приблизительно 54 % ВВП и 44 % мировой торговли[1].
 Asian Football Confederation
Asian Football Confederation
 Australia
Australia
 Iraq
Iraq
 Iran
Iran
 Iran
Iran
 Iran
Iran
 Israel
Israel
 Japan
Japan
 Japan
Japan
 Japan
Japan
 Japan
Japan
 Katar
Katar
 Kuwait
Kuwait
 Republic of Korea
Republic of Korea
 Republic of Korea
Republic of Korea
 Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia
 Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia
 Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia


Die Fußball-Asienmeisterschaft (engl. AFC Asian Cup oder Asian Nations Cup), auch kurz nur Asien Cup genannt, ist ein seit 1956 ausgetragenes kontinentales Turnier für Fußball-Nationalmannschaften zur Ermittlung des Asienmeisters im Fußball und nach der Copa América (erstmals 1916 ausgetragen), der zweitälteste Wettbewerb seiner Art. Organisiert wird der neben den Asienspielen bedeutendste Wettbewerb des Kontinents von der asiatischen Fußball-Konföderation AFC. Der Sieger der Asienmeisterschaft qualifiziert sich jeweils für den nächsten FIFA-Konföderationen-Pokal.

 Afghanistan
Afghanistan
 Armenia
Armenia
 Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan
 Asian Development Bank,ADB
Asian Development Bank,ADB
 Asian Development Bank,ADB
Asian Development Bank,ADB
 Haruhiko Kuroda
Haruhiko Kuroda
 Asian Development Bank,ADB
Asian Development Bank,ADB
 Kimimasa Tarumizu
Kimimasa Tarumizu
 Asian Development Bank,ADB
Asian Development Bank,ADB
 Masao Fujioka
Masao Fujioka
 Asian Development Bank,ADB
Asian Development Bank,ADB
 Masatsugu Asakawa
Masatsugu Asakawa
 Asian Development Bank,ADB
Asian Development Bank,ADB
 Mitsuo Sato
Mitsuo Sato
 Asian Development Bank,ADB
Asian Development Bank,ADB
 Shiro Inoue
Shiro Inoue
 Asian Development Bank,ADB
Asian Development Bank,ADB
 Tadao Chino
Tadao Chino
 Asian Development Bank,ADB
Asian Development Bank,ADB
 Takehiko Nakao
Takehiko Nakao
 Asian Development Bank,ADB
Asian Development Bank,ADB
 Takeshi Watanabe
Takeshi Watanabe
 Asian Development Bank,ADB
Asian Development Bank,ADB
 Taroichi Yoshida
Taroichi Yoshida
 Australia
Australia
 Bangladesh
Bangladesh
 Bhutan
Bhutan
 Brunei Darussalam
Brunei Darussalam
 China
China
 Denmark
Denmark
 Germany
Germany

 European Union
European Union

 Financial
Financial
 International Bank for Cooperation
International Bank for Cooperation
 Finland
Finland
 France
France
 Georgia
Georgia
 Hongkong Tebiexingzhengqu-HK
Hongkong Tebiexingzhengqu-HK
 India
India
 Indonesia
Indonesia
 Ireland
Ireland
 Italy
Italy
 Japan
Japan
 Cambodia
Cambodia
 Canada
Canada
 Kasachstan
Kasachstan
 Kyrgyzstan
Kyrgyzstan
 Laos
Laos
 Luxembourg
Luxembourg
 Malaysia
Malaysia

 Mongolei
Mongolei
 Myanmar
Myanmar
 Nepal
Nepal
 New Zealand
New Zealand
 Netherlands
Netherlands
 Austria
Austria
 Pakistan
Pakistan
 Papua-Neuguinea
Papua-Neuguinea
 Philippines
Philippines
 Portugal
Portugal
 Republic of Korea
Republic of Korea
 Salomonen
Salomonen
 Sweden
Sweden
 Singapore
Singapore
 Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka
 Taiwan Sheng-TW
Taiwan Sheng-TW
 Takehiko Nakao
Takehiko Nakao
 Thailand
Thailand
 Tonga
Tonga
 Turkey
Turkey
 Turkmenistan
Turkmenistan
 Uzbekistan
Uzbekistan
 United States
United States
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 Vietnam
Vietnam

 Important International Organizations
Important International Organizations

 Economy and trade
Economy and trade
 Economic and political research
Economic and political research


亚洲开发银行(英语:Asian Development Bank,缩写:ADB,简称亚银、亚行、亚开行),香港旧译亚洲发展银行,属于亚太地区的政府之间金融机构,其目的是为了促进亚洲经济与社会的发展。1966年12月19日成立,有31个创始会员国,目前有68个成员体,其中亚太有49个。总部设置于菲律宾马尼拉并在世界各地拥有31个办事处。亚洲开发银行仿照世界银行的股权制度,依照成员体的资本比例,得到相应比例的投票权。2014年以来,亚洲开发银行发布亚太创意生产指数年度报告。[3][4]亚洲开发银行为联合国观察员。
The Asian Development Bank (ADB) is a regional development bank established on 19 December 1966,[4] which is headquartered in the Ortigas Center located in the city of Mandaluyong, Metro Manila, Philippines. The company also maintains 31 field offices around the world[5] to promote social and economic development in Asia. The bank admits the members of the United Nations Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific (UNESCAP, formerly the Economic Commission for Asia and the Far East or ECAFE) and non-regional developed countries.[6] From 31 members at its establishment, ADB now has 68 members.
The ADB was modeled closely on the World Bank, and has a similar weighted voting system where votes are distributed in proportion with members' capital subscriptions. ADB releases an annual report that summarizes its operations, budget and other materials for review by the public.[7] The ADB-Japan Scholarship Program (ADB-JSP) enrolls about 300 students annually in academic institutions located in 10 countries within the Region. Upon completion of their study programs, scholars are expected to contribute to the economic and social development of their home countries.[8] ADB is an official United Nations Observer.[9]
El Banco Asiático de Desarrollo (BAsD) es una organización financiera para el desarrollo económico de Asia y el Pacífico. Su objetivo principal es la erradicación de la pobreza y facilitar ayudas para mejorar el nivel de vida de la población de la región a través de préstamos y colaboración técnica.
Creado en 1966 por 31 países. Hoy cuenta con 67 miembros (48 regionales y 19 no regionales). Estados Unidos y Japón son sus principales accionistas, con el 15,6% del capital cada uno.
El Banco tiene como su principal objetivo la lucha contra la pobreza. Para ello busca promover el crecimiento económico y la cooperación en la región de Asia-Pacífico, y acelerar el proceso de desarrollo económico de sus países miembros. Las dos terceras partes de personas pobres del mundo (aquellos que viven con menos de dos dólares diarios por persona), cerca de 1.800 millones de pobres, viven en esta región. El BAsD aprobó una nueva Estrategia a Largo Plazo (2008-2020) centrada en un crecimiento económico, medioambientalmente sostenible e integración regional.
Азиа́тский банк разви́тия (англ. Asian Development Bank) — банк, основанный в 1966 году, его главной задачей является стимулировать рост экономики в Азии и на Дальнем Востоке, направляя в эти регионы прямые займы и оказывая техническое содействие.
Штаб-квартира в Маниле (Филиппины). Президентом АБР с 28 апреля 2013 года является японец Такэхико Накао. 17 января 2020 года президентом станет Масацугу Асакава, избранный 2 декабря 2019 года[1].
 Beijing Shi-BJ
Beijing Shi-BJ
 China
China
 China
China
 Chūgoku
Chūgoku
 Guangdong Sheng-GD
Guangdong Sheng-GD
 India
India
 India
India
 India
India
 Indonesia
Indonesia
 Iran
Iran
 Japan
Japan
 Japan
Japan
 Kantō
Kantō
 Katar
Katar
 National Capital Territory
National Capital Territory
 Philippines
Philippines
 Philippines
Philippines
 Republic of Korea
Republic of Korea
 Republic of Korea
Republic of Korea
 Republic of Korea
Republic of Korea
 Thailand
Thailand
 Thailand
Thailand
 Thailand
Thailand
 Thailand
Thailand

亚洲运动会(简称亚运会、亚运;英语:Asian Games,简写:Asiad)是亚洲的综合性运动会,为国际奥委会承认的地区性大型综合运动会,由亚洲奥林匹克理事会(亚奥理事会)主办,每4年一届。
Die Asienspiele (englisch Asian Games), auch Panasiatische Spiele genannt, sind sportliche Wettkämpfe asiatischer Staaten mit olympischem Charakter.


岩手县(日语:岩手県/いわてけん〔いはてけん〕 Iwate ken */?)是日本本州东北地方东北部的一个县,首府为盛冈市。岩手县位于本州的东北部,东临太平洋,内陆部多山岳,与秋田县交接。山上有北上川,是东北地方第一大河。主峰岩手山高约海拔2,041米;东部为北上山地,其最高峰早池峰山位山地中部,海拔1,914米。岩手县占地15,279平方公里,是除北海道以外面积最大的一级行政区。
盛冈市 - 宫古市 - 大船渡市 - 花卷市 - 北上市 - 久慈市 - 远野市 - 一关市 - 陆前高田市 - 釜石市 - 江刺市 - 二户市 - 八幡平市 - 奥州市 - 泷泽市
Die Präfektur Iwate (japanisch 岩手県, Iwate-ken) ist eine der 47 Präfekturen Japans und liegt in der Region Tōhoku. Sitz der Präfekturverwaltung ist Morioka. Iwate ist Partnerpräfektur des deutschen Bundeslandes Rheinland-Pfalz.
Die Präfektur Iwate liegt im Norden der Hauptinsel Honshū, südlich der Präfektur Aomori, östlich der Präfektur Akita und nördlich der Präfektur Miyagi. Die Präfektur besteht hauptsächlich aus Bergen und Hochplateaus (Ōu-Gebirge und Kitakami-Bergland), die sich bis zur Küste im Osten ziehen. Im Westen an der Grenze zu Akita wird die Präfektur von dem Ōu-Gebirge abgeschlossen. Das ansonsten gebirgige Iwate wird in Nord-Süd-Richtung von einem Tal (Fluss Kitakami) durchschnitten, in dem Morioka und die meisten anderen Städte der Präfektur liegen.
Die Präfektur Iwate ist bestimmt durch landwirtschaftliche Nutzung und landschaftliche Schönheit. Die Industrialisierung ist gering.
In Iwate gibt es sieben Präfekturnaturparks (kenritsu shizen kōen). Außerdem liegen ganz oder teilweise in der Präfektur die Quasi-Nationalparks Kurikoma und Hayachine sowie die Nationalparks (kokuritsu kōen) Towada-Hachimantai und Sanriku-Fukkō. Zusammen umfassen die Naturparks in Iwate eine Fläche von 72.061 ha.[1]

Diese Burg aus der Edo-Zeit führt ihren Ursprung auf das Jahr 1603 zurück, als Ii Naokatsu, der Sohn des früheren Daimyo Ii Naomasa, ihren Bau anordnete. Die Befestigung wurde ursprünglich 1575, als Teil der Burg Ōtsu erbaut und dann von den Ii nach Hikone verbracht. Sie wurde 1622 fertiggestellt. Naokatsus Ländereien waren ihm in dieser Zeit vom Tokugawa-Shogunat weggenommen worden und als sein Bruder Naotake die Kontrolle über das Gebiet um die Provinz Ōmi erlangte, konnte er die Burg mit Hilfe von Steinen der früheren Burg Sawayama fertigstellen. Ein bedeutender Vertreter der Familie war Ii Naosuke, der dem Shogunat in der Mitte des 19. Jhd. als Kanzler (Tairō) diente. Die Familie führte das obenstehende Familienzeichen, die Tachibana-Blüte. Der citrus tachibana ist heute Baum der Stadt Hikone.
Als 1868 die Meiji-Zeit begann, wurden viele Burgen zerstört. Nur auf Intervention des Kaisers selbst, der die Gegend bereiste, blieb die Burg Hikone intakt. Heute ist sie eine der ältesten im Originalzustand erhaltenen Burgen Japans. 1985-85 hat man den repräsentativen vorderen Teil der ehemaligen Residenz (表御殿, omote goten) unterhalb des Burghügels einschließlich einer Noh-Bühne mit einer Fläche von 4851 m² zur Nutzung als Museum rekonstruiert. Das Museum besitzt als Nationalschatz den sechsteiligen Hikone-Stellschirm.
Der Hauptturm der Burg Hikone wurde 1952 vom Ministerium für Bildung, Kultur, Sport, Wissenschaft und Technologie zum Nationalen Kulturgut erklärt.
 Sport
Sport
 Fashion world
Fashion world
 Life and Style
Life and Style
 Companies
Companies
 Geography
Geography
 Architecture
Architecture