
漢德百科全書 | 汉德百科全书
 No personal income tax
No personal income tax
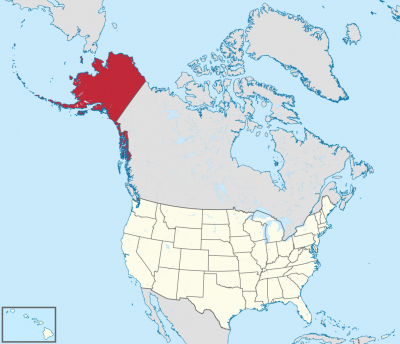


アラスカ州(英: State of Alaska [əˈlæskə] (![]() 音声ファイル))は、アメリカ合衆国最北端にある州。アリューシャン列島を含む。北アメリカ大陸北西の端にあり、合衆国本土とはカナダを挟んで飛地になっている。アラスカでは、合衆国本土を"lower 48"(直訳:南方の48州。アメリカ50州からアラスカ州とハワイ州を除いたもの)と呼ぶことがある[2]。
音声ファイル))は、アメリカ合衆国最北端にある州。アリューシャン列島を含む。北アメリカ大陸北西の端にあり、合衆国本土とはカナダを挟んで飛地になっている。アラスカでは、合衆国本土を"lower 48"(直訳:南方の48州。アメリカ50州からアラスカ州とハワイ州を除いたもの)と呼ぶことがある[2]。
アメリカ合衆国の州の中では面積最大、東はカナダ、北は北極海、西と南は太平洋と接し、西のベーリング海を隔ててロシアとも海上の国境がある。2010年国勢調査による人口は710,231人であり[3]、その約半分はアンカレッジ都市圏に居住。州都はジュノー市で、最大都市はアンカレッジ市である。海港アンカレッジはかつてアジアとアメリカおよびヨーロッパを結ぶ航空路線の寄港地として知られた。アメリカ合衆国の州の中では人口密度が最小の州でもある[4]。
アラスカは1867年3月30日にロシア帝国からアメリカ合衆国が買収した。その後幾つかの管理形態の変遷を経て、1912年5月11日にアラスカ準州、1959年1月3日にアラスカ州となった。
Alaska (/əˈlæskə/ (![]() listen); Aleut: Alax̂sxax̂; Inupiaq: Alaasikaq; Alutiiq: Alas'kaaq; Tlingit: Anáaski; Russian: Аля́ска, romanized: Alyáska) is a U.S. state located on the northwest extremity of the country's West Coast, just across the Bering Strait from Asia. An exclave of the U.S., it borders the Canadian province of British Columbia and territory of Yukon to the east and southeast and has a maritime border with Russia's Chukotka Autonomous Okrug to the west. To the north are the Chukchi and Beaufort seas of the Arctic Ocean, while the Pacific Ocean lies to the south and southwest.
listen); Aleut: Alax̂sxax̂; Inupiaq: Alaasikaq; Alutiiq: Alas'kaaq; Tlingit: Anáaski; Russian: Аля́ска, romanized: Alyáska) is a U.S. state located on the northwest extremity of the country's West Coast, just across the Bering Strait from Asia. An exclave of the U.S., it borders the Canadian province of British Columbia and territory of Yukon to the east and southeast and has a maritime border with Russia's Chukotka Autonomous Okrug to the west. To the north are the Chukchi and Beaufort seas of the Arctic Ocean, while the Pacific Ocean lies to the south and southwest.
Alaska is the largest U.S. state by area and the seventh-largest subnational division in the world. It is the third-least populous and the most sparsely populated state, but by far the continent's most populous territory located mostly north of the 60th parallel, with an estimated population of 738,432 as of 2015—more than quadruple the combined populations of Northern Canada and Greenland.[3] Approximately half of Alaska's residents live within the Anchorage metropolitan area. The state capital of Juneau is the second-largest city in the United States by area, comprising more territory than the states of Rhode Island and Delaware.
Alaska was occupied by various indigenous peoples for thousands of years before the arrival of Europeans. The state is considered the entry point for the settlement of North America by way of the Bering land bridge. The Russians were the first Europeans to settle the area beginning in the 18th century, eventually establishing Russian America, which spanned most of the current state. The expense and difficulty of maintaining this distant possession prompted its sale to the U.S. in 1867 for US$7.2 million, or approximately two cents per acre ($4.74/km2). The area went through several administrative changes before becoming organized as a territory on May 11, 1912. It was admitted as the 49th state of the U.S. on January 3, 1959.[4]
While it has one of the smallest state economies in the country, Alaska's per capita income is among the highest, owing to a diversified economy dominated by fishing, natural gas, and oil, all of which it has in abundance. United States armed forces bases and tourism are also a significant part of the economy; more than half the state is federally owned public land, including a multitude of national forests, parks, and wildlife refuges.
Alaska's indigenous population is proportionally the highest of any U.S. state, at over 15 percent.[5] Close to two dozen native languages are spoken, and Alaskan Natives exercise considerable influence in local and state politics.
L’Alaska (prononcé /a.las.ka/ Écouter (Fr.) en français et /ə.ˈlæs.kə/ Écouter (É.-U.A) en anglais) est le 49e État des États-Unis, dont la capitale est Juneau et la plus grande ville Anchorage, où habite environ 40 % de la population de l'État. Avec une superficie totale de 1 717 854 km2, il est l'État le plus étendu et le plus septentrional du pays, mais l'un des moins peuplés, ne comptant que 731 545 habitants en 20191.
Comme Hawaï, l'Alaska est séparé des États-Unis contigus et se situe au nord-ouest du Canada. Bordé par l'océan Arctique au nord et la mer de Béring et l'océan Pacifique au sud, ce territoire est séparé de l'Asie par le détroit de Béring. En outre, ses divisions administratives ne sont pas des comtés mais des boroughs.
Alaska signifie « grande Terre » ou « continent » en aléoute3. Cette région, que l'on appelait au XIXe siècle l'« Amérique russe », tire son nom d'une longue presqu'île, au nord-ouest du continent américain, à environ 1 000 kilomètres au sud du détroit de Bering, et qui se lie, vers le sud, aux îles Aléoutiennes. Le surnom de l'Alaska est « la dernière frontière » ou « la terre du soleil de minuit ».
Peuplé par des Aléoutes, Esquimaux (notamment Iñupiak et Yupiks) et peut-être d'autres Amérindiens depuis plusieurs millénaires, le territoire est colonisé par des trappeurs russes à la fin du XVIIIe siècle. Les ressources de l'Alaska proviennent alors essentiellement du commerce du bois et de la traite des fourrures. Le 30 mars 1867, les États-Unis l'achètent à la Russie pour la somme de 7,2 millions de dollars (environ 120 millions de dollars actuels), et celui-ci adhère à l'Union le 3 janvier 1959. Les secteurs économiques prédominants aujourd'hui sont la pêche, le tourisme, et surtout la production d'hydrocarbures (pétrole, gaz) depuis la découverte de gisements à Prudhoe Bay dans les années 1970.
Le Denali (6 190 mètres d'altitude), point culminant des États-Unis, se trouve dans la chaîne d'Alaska et constitue le cœur du parc national et réserve du Denali.
Le climat y est de type polaire, et la faune caractéristique des milieux froids (grizzli, caribou, orignal, ours blanc).
Les territoires limitrophes sont le territoire du Yukon et la province de Colombie-Britannique au Canada. Le Kraï du Kamtchatka et le district autonome de Tchoukotka en Russie se trouvent à quelques dizaines de kilomètres, de l'autre côté du détroit de Bering.
Bastion du Parti républicain, l'Alaska est gouverné depuis 2018 par Mike Dunleavy.
L'Alaska (pron. /aˈlaska/[3]; in inglese , /əˈlæskə/), italianizzata in Alasca[4][5] (in aleutino Alax̂sxax̂; in inupiaq Alaasikaq; in alutiiq Alas'kaaq; in tlingit Anáaski; in russo Аляска, Aljaska), è uno Stato federato degli Stati Uniti d'America. Situato nella estremità nordoccidentale del continente nordamericano è separato da qualsiasi altro stato degli USA, confina a est con il Canada ed è bagnato a nord dal Mar Glaciale Artico e a sud dall'oceano Pacifico; a ovest lo stretto di Bering lo separa dalla Čukotka, nella regione storica della Siberia. Con 1717854 km² è lo Stato più grande degli Stati Uniti ma, visto il clima rigido, è scarsamente popolato: nel 2019 la popolazione dello Stato era di 731 545 abitanti[1]; il dato lo rende il 47º stato per popolazione. Circa la metà di questi abitanti vive nell'area metropolitana di Anchorage, centro principale dello Stato. L'economia dell'Alaska è dominata dalle riserve di petrolio, gas naturale e dall'industria della pesca, risorse di cui dispone in abbondanza. Anche il turismo occupa una parte significativa dell'economia.
Anche se era stato occupato per migliaia di anni dalle popolazioni indigene, dal XVIII secolo in poi le potenze europee considerarono il territorio dell'Alaska pronto per essere sfruttato. Gli Stati Uniti acquistarono l'Alaska dalla Russia il 30 marzo 1867, per 7,2 milioni di dollari (120 milioni di dollari al netto dell'inflazione), a circa due centesimi per acro (4,74 $/km²). L'area ha attraversato diversi cambiamenti amministrativi prima di essere organizzata come un territorio l'11 maggio 1912. È stato ammesso come 49º Stato degli Stati Uniti d'America il 3 gennaio 1959.
Il toponimo Alaska è derivato dalla parola alaxsxaq che ha come significato «grande paese» o «terraferma» nella lingua degli Aleutini o Unangan (come essi si chiamavano nella propria lingua)[6].
Il soprannome dell'Alaska è The Last Frontier (usato anche nelle targhe automobilistiche), e l'animale scelto come simbolo dello Stato è l'alce.
Alaska es uno de los cincuenta estados que forman los Estados Unidos de América. Su capital es Juneau y su ciudad más poblada es Anchorage. Está ubicado en el extremo noroeste de América del Norte, en la región Oeste del país, división Pacífico. Limita al norte con el océano Ártico, al este con Canadá, al sur con el océano Pacífico y al oeste con el mar de Bering (océano Pacífico). Con 1 717 856 km² es el estado más extenso del país y la séptima entidad subnacional más grande del mundo, por detrás de la república de Sajá (Rusia), Australia Occidental, Krai de Krasnoyarsk (Rusia), Groenlandia (Dinamarca), Nunavut (Canadá) y Queensland (Australia); con 710 231 habs. en 2010, el cuarto menos poblado —por delante de Dakota del Norte, Vermont y Wyoming, el menos poblado— y con 0,41 hab/km², el menos densamente poblado. Fue el penúltimo en ser admitido en la Unión, el 3 de enero de 1959, como el estado número 49, solo antes que Hawái. Es el estado con mayor proporción de empleados públicos respecto de la población.4
Alaska recibe el nombre del vocablo aleutiano alyeska o alaxsxaq, que significa «tierra grande», o más literalmente, «el objeto contra el que la acción del mar es dirigida».5 La bandera de Alaska representa, sobre fondo azul, las estrellas que forman la constelación de la Osa Mayor y, en la esquina superior derecha, la estrella polar.
El 30 de marzo de 1867, Estados Unidos compró Alaska del Imperio ruso, por 7 200 000 dólares.6 Estados Unidos trató, durante las primeras décadas del siglo XX, de mejorar las comunicaciones (sobre todo para conectar Alaska con el resto de los Estados Unidos por ferrocarril), y promover la colonización del valle de Matanuska. Sin embargo, la Segunda Guerra Mundial y las batallas navales en las islas Aleutianas con Japón cambiaron el rumbo de la política de los EE. UU. en los asuntos de Alaska. Así, en 1942, se construyó en meses una carretera de comunicación (la Autopista Alaska) para garantizar la defensa del Territorio de Alaska, a la vez que establecieron nuevas bases militares (por ejemplo, de radares) y se promovieron asentamientos civiles. El final de la guerra mundial y el comienzo de la Guerra Fría aceleraron la necesidad de integrar este territorio a la Unión. En 1959, Alaska fue finalmente aceptada como el 49.º estado de los Estados Unidos de América.
El descubrimiento de yacimientos petrolíferos ha permitido un enorme crecimiento económico en Alaska durante las últimas décadas, pese al aislamiento geográfico y a las duras condiciones de vida. El mayor hito de su desarrollo ha sido la construcción, a partir de 1974, del Trans-Alaska Pipeline, un oleoducto de 1269 km que une la Bahía Prudhoe con el puerto de Valdez. Pero el petróleo también ha sido el origen de ciertos desastres, como el accidente ocurrido en 1989 cuando el superpetrolero Exxon Valdez encalló en las aguas de Alaska y provocó una marea negra que ha sido calificada como uno los mayores desastres ecológicos de la historia, el desastre del Exxon Valdez.
Аля́ска[2][3] (англ. Alaska [əˈlæskə], эским. Alaskaq, Aqłuq) — самый северный и крупнейший по территории штат[4] США; расположен на северо-западе Северной Америки. В Беринговом проливе имеет морскую границу с Россией.
Включает территорию Северной Америки западнее 141-го меридиана западной долготы, в том числе одноимённый полуостров с прилегающими островами, Алеутские острова и собственно территорию Северной Америки к северу от полуострова, а также узкую полосу тихоокеанского побережья вместе с островами архипелага Александра вдоль западной границы Канады.
Площадь территории — 1 717 854 км², из которых 236 507 км² приходится на водную поверхность. Население — 737 438[1] чел. (2018). Столица штата — город Джуно.
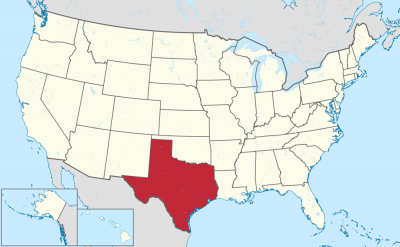


Texas (englisch [ˈtʰɛksəs] ![]()
![]() oder [ˈtʰɛksɪs], von cadd. táyshaʔ ‚Freunde‘ oder ‚Verbündete‘[2]) ist ein Bundesstaat im mittleren Süden der Vereinigten Staaten von Amerika. Texas hat den Beinamen Lone Star State (Staat des einsamen Sterns), da auf seiner Flagge nur ein Stern zu sehen ist. Texas hat von allen US-Bundesstaaten nach Alaska die zweitgrößte Fläche und nach Kalifornien die zweitgrößte Bevölkerungszahl. Mit seinen 254 Countys hat Texas die meisten Countys eines Bundesstaats der Vereinigten Staaten.
oder [ˈtʰɛksɪs], von cadd. táyshaʔ ‚Freunde‘ oder ‚Verbündete‘[2]) ist ein Bundesstaat im mittleren Süden der Vereinigten Staaten von Amerika. Texas hat den Beinamen Lone Star State (Staat des einsamen Sterns), da auf seiner Flagge nur ein Stern zu sehen ist. Texas hat von allen US-Bundesstaaten nach Alaska die zweitgrößte Fläche und nach Kalifornien die zweitgrößte Bevölkerungszahl. Mit seinen 254 Countys hat Texas die meisten Countys eines Bundesstaats der Vereinigten Staaten.
Texas grenzt im Süden an Mexiko. Dies macht etwa die Hälfte der Grenze zwischen den Vereinigten Staaten und Mexiko aus. Daneben grenzt Texas an die Bundesstaaten New Mexico im Westen, nördlich an Oklahoma, nordöstlich an Arkansas und an Louisiana im Osten.
得克萨斯州(英语:State of Texas,/ˈtɛksəs/,当地 /ˈtɛksɪz/; 西班牙语: Texas , Tejas),简称得州,旧译德沙士;是全美国土地面积和人口第二大的州(面积仅次于阿拉斯加州;人口次于加利福尼亚州)。得克萨斯州位于美国中南部地区,东部与路易斯安那州,东北部与阿肯色州,北部与俄克拉荷马州,西部与新墨西哥州接壤,同时与墨西哥的奇瓦瓦州、科阿韦拉州、新莱昂州、塔毛利帕斯州共享边界,在东南部还有一段墨西哥湾海岸线。
得州因其曾经是一个独立的共和国而被称为“孤星之州”,同时也是对该州从墨西哥独立出来的纪念。在得克萨斯州州旗和得克萨斯州州徽上可以看到“孤星”。
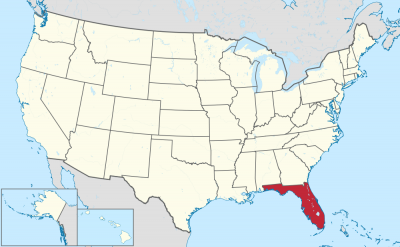


Florida besteht aus der Halbinsel Florida sowie dem Festlandteil Florida Panhandle und liegt im Südosten der Vereinigten Staaten. An der Ostküste liegt der Atlantische Ozean, an der West- und an der Südküste der Golf von Mexiko.
Der Bundesstaat besitzt am südlichen Ende eine Inselkette, deren Inseln „Keys“ genannt werden. Die bekanntesten sind die Florida Keys, die durch 42 Brücken miteinander verbunden sind. Am Ende dieser Inselkette liegt Key West. Von dort aus sind es nur 140 Kilometer bis nach Kuba. In Key West befindet sich auch der südlichste Punkt der kontinentalen USA.
佛罗利达州(英语:State of Florida)是美国本土东南端的一个州,亦属于墨西哥湾沿岸地区,是美国人口第三多的州,为著名的度假、避寒圣地。中文俗称为佛州,佛罗里达。州府位于塔拉哈西,最大的城市为杰克逊维尔,最大的都会区为迈阿密都会区。佛罗利达吸引了不少名人和运动员来这里度假,以高尔夫球、网球、水上活动、赛车著称。
早于欧洲人抵达佛罗里达州前几千年,该地已经有人类居住。利玛窦曾在坤舆万国全图中将之译为“花之屿”。西班牙航海家胡安·庞塞·德莱昂在1513年4月2日,发现这片地方。时值西班牙人称为Pascua Florida(花的复活节)的节日,所以此地被德莱昂命名为La Florida。传说德莱昂是为了找寻青春之泉而发现了佛罗里达。
随后西班牙和法国殖民者逐渐在佛罗里达半岛上建立占据地。其中在1559年建立的彭萨科拉和1565年建立的圣奥古斯丁成为欧洲人在北美洲建立的最早的聚居地。而彭萨科拉和圣奥古斯丁亦分别成为当时西班牙统治下的西佛罗里达和东佛罗里达的首府。而西班牙殖民者在17世纪已成功占领整个佛罗里达半岛和附近地区。
至18世纪,英国在七年战争中占据西班牙的殖民地古巴,西班牙为取回古巴,于1763年将佛罗里达割让予英国作交换条件。西班牙割让佛罗里达予英国后,当地的西班牙移民也一并迁走,而英国也大量在当地殖民。美国独立战争期间,佛罗里达仍效忠于英国,但英国在战败后让美国独立,也于1783年将佛罗里达交回给西班牙,但佛罗里达的英国移民却不愿受西班牙人统治,纷纷起事对抗。西班牙在拿破仑战争后转衰,在1819年西班牙与美国签定条约,将西班牙属佛罗里达割让给美国,以换取美国承认西班牙在得克萨斯的利益。
佛罗里达于1845年3月3日正式成为美利坚合众国第27个州。
1861年,美国南北战争爆发,佛罗里达州于1861年1月10日宣布脱离联邦,随后加入美利坚联盟国,与联邦政府对抗。1865年美利坚联盟国战败,佛罗里达州国会代表团在1868年6月25日重新加入国会,佛州恢复在联邦政府地位。在重建时期后,与其他美国南方州相同,佛罗里达州近一个世纪一直支持民主党,近年逐渐成为共和党的重要根据地。著名的华特迪士尼世界位于本州的奥兰多市内,迪士尼世界是目前六个迪士尼度假区面积最大的。
フロリダ州(英: State of Florida [ˈflɒrɪdə] (![]() 音声ファイル) )は、アメリカ合衆国南東部の州である。メキシコ湾と大西洋に挟まれるフロリダ半島の全域を占め、北はジョージア州とアラバマ州に接しており、サンベルトと呼ばれる比較的気候が温暖な州の1つである。
音声ファイル) )は、アメリカ合衆国南東部の州である。メキシコ湾と大西洋に挟まれるフロリダ半島の全域を占め、北はジョージア州とアラバマ州に接しており、サンベルトと呼ばれる比較的気候が温暖な州の1つである。
フロリダ州の面積は170,306 km2 (65,758 mi2) で、50州の中で22位であるが、海岸線の長さは約1900 kmあり、大陸48州の中では最長である。
フロリダ州は北部と中部が亜熱帯、南部は熱帯に属して概して暖かいので、「サンシャインステート(日光の州)」という渾名がある[1]。2009年の推計人口は18,537,969人となっており、全米50州の中で第4位である[2][3]。州都はタラハシー (Tallahassee) 、人口最大の都市はジャクソンビル (Jacksonville)、その他主な都市としてはマイアミ (Miami)、タンパ (Tampa)、オーランド (Orlando)などがあり、マイアミ都市圏は人口500万人以上を抱える州内最大の都市圏になっている。
ケネディ宇宙センター、スペースポート・フロリダ、ウォルト・ディズニー・ワールド・リゾート、ユニバーサル・オーランド・リゾート、シー・ワールド・オブ・フロリダなどがあることで有名で、アメリカでも有数の観光地として知られている。
Florida (/ˈflɒrɪdə/ (![]() listen),[14] Spanish pronunciation: [floˈɾiða]) is a state located in the southeastern region of the United States. With a population of over 21 million, Florida is the third-most populous and the 22nd-most extensive of the 50 United States. The state is bordered to the west by the Gulf of Mexico, to the northwest by Alabama, to the north by Georgia, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, and to the south by the Straits of Florida. The state's capital is Tallahassee and its most populous municipality is Jacksonville. The Miami metropolitan area, with a population of almost 6.2 million, is the most populous urban area in Florida and the seventh-most populous in the United States. Other urban areas in the state with a population of more than one million are Tampa Bay, Orlando, and Jacksonville. Florida's $1.0 trillion economy is the fourth-largest of any U.S. state, and if it were a country, Florida would be the 16th-largest economy in the world.[15]
listen),[14] Spanish pronunciation: [floˈɾiða]) is a state located in the southeastern region of the United States. With a population of over 21 million, Florida is the third-most populous and the 22nd-most extensive of the 50 United States. The state is bordered to the west by the Gulf of Mexico, to the northwest by Alabama, to the north by Georgia, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, and to the south by the Straits of Florida. The state's capital is Tallahassee and its most populous municipality is Jacksonville. The Miami metropolitan area, with a population of almost 6.2 million, is the most populous urban area in Florida and the seventh-most populous in the United States. Other urban areas in the state with a population of more than one million are Tampa Bay, Orlando, and Jacksonville. Florida's $1.0 trillion economy is the fourth-largest of any U.S. state, and if it were a country, Florida would be the 16th-largest economy in the world.[15]
The first European contact was made in 1513 by Spanish explorer Juan Ponce de León, who called it la Florida ([la floˈɾiða] "the land of flowers") upon landing there.[16] At various points in its colonial history, Florida was administered by Spain and Great Britain. Florida was admitted as the 27th state on March 3, 1845. Florida was the principal location of the Seminole Wars (1816 – 1858), the longest and most extensive of Indian Wars in United States history. Florida declared its secession from the Union on January 10, 1861, and was one of the seven original Confederate States. After the Civil War, Florida was restored to the Union on June 25, 1868.
Today, Florida is distinctive for its large Cuban expatriate community and high population growth, as well as for its increasing environmental issues. The state's economy relies mainly on tourism, agriculture, and transportation, which developed in the late 19th century. Florida is also renowned for amusement parks, orange crops, winter vegetables, the Kennedy Space Center, and as a popular destination for retirees. It is the flattest state in the United States,[17] and Lake Okeechobee is its largest freshwater lake.[18]
The state's close proximity to the ocean influences many aspects of Florida culture and daily life. Florida is a reflection of influences and multiple inheritance; African, European, indigenous, Latino, and Asian heritages can be found in the architecture and cuisine. Florida has attracted many writers such as Marjorie Kinnan Rawlings, Ernest Hemingway and Tennessee Williams, and continues to attract celebrities and athletes. It is internationally known for golf, tennis, auto racing, and water sports. Several beaches in Florida have turquoise and emerald-colored coastal waters.[19]
About two-thirds of Florida occupies a peninsula between the Gulf of Mexico and the Atlantic Ocean. Florida has the longest coastline in the contiguous United States, approximately 1,350 miles (2,170 km), not including the contribution of the many barrier islands.[20] Florida has a total of 4,510 islands that are ten acres (4 ha) or larger in area.[21][22] This is the second-highest number of islands of any state; only Alaska has more.[21] It is the only state that borders both the Gulf of Mexico and the Atlantic Ocean. Much of the state is at or near sea level, and is characterized by sedimentary soil. Florida has the lowest high point of any U.S. state. The American alligator, American crocodile, American flamingo, Roseate spoonbill, Florida panther, bottlenose dolphin, and manatee can be found in Everglades National Park in the southern part of the state. The climate varies from subtropical in the north to tropical in the south.[23] Along with Hawaii, Florida is one of only two states that have a tropical climate, and is the only continental state that has both a tropical climate and a coral reef. The Florida Reef[24] is the only living coral barrier reef in the continental United States,[25] and the third-largest coral barrier reef system in the world (after the Great Barrier Reef and Belize Barrier Reef).[26]
La Floride (en anglais : Florida /ˈflɔɹ.ɪ.də/ ; en espagnol : Florida /floˈɾi.ða/) est un État américain situé dans le sud-est des États-Unis, sur la côte dite du Golfe. Elle est bordée à l’ouest par le golfe du Mexique, au nord par l'Alabama et la Géorgie et à l’est par l’océan Atlantique. Avec plus de 21 millions d'habitants en 2019, il s'agit du troisième État le plus peuplé du pays (après la Californie et le Texas). Avec une superficie de 170 451 km2, la Floride se classe au 22e rang des États américains. Sa capitale politique est Tallahassee, mais l'agglomération la plus peuplée est Miami, qui compte plus de 6,1 millions d'habitants (estimations de 2017).
La Floride est constituée à l'est d'une péninsule d'environ 630 km de long et à l'ouest d'une bande côtière étroite d'environ 330 km de long en forme de « queue de poêle » (panhandle). Sa géographie est marquée par un littoral étendu, par l'omniprésence de l'eau et par la menace des ouragans. Le relief se caractérise par de faibles altitudes — le point culminant atteignant seulement 105 m d'altitude — et des terrains sédimentaires, le climat variant de subtropical au nord, à tropical au sud. Ses animaux emblématiques, comme le lamantin et l'alligator, peuvent être aperçus dans les Everglades, l'un des parcs nationaux les plus connus au monde.
Depuis sa découverte, en 1513, par l'Espagnol Juan Ponce de León qui la baptise « la Pascua florida » (« les Pâques fleuries » en référence au dimanche des Rameaux), la Floride est un enjeu pour les puissances coloniales européennes avant d'intégrer les États-Unis en 1845. Elle est le théâtre des guerres séminoles, contre les Amérindiens, puis de la ségrégation raciale, après la guerre de Sécession ; elle se distingue par son importante communauté cubaine et une forte croissance démographique soulevant des problèmes environnementaux. Son économie repose principalement sur le tourisme, l'agriculture et les transports, qui se développèrent à la fin du XIXe siècle. Elle est connue pour ses parcs d'attractions, la production d'oranges et le Centre spatial Kennedy.
La culture floridienne est le reflet d'influences et d'héritages multiples, amérindiens, afro-américains, anglo-saxons et hispaniques, héritages que l'on retrouve dans l'architecture et la gastronomie. La Floride attire de nombreux écrivains comme Marjorie Kinnan Rawlings, Ernest Hemingway, ou encore Tennessee Williams et continue de séduire les vedettes et les sportifs. Elle est internationalement réputée pour le tennis, le golf, les courses automobiles et les sports liés à la mer.
La Florida (/ˈflɔːrida/ o /floˈriːda/, in inglese: /ˈflɒɹɪdə/ o 'flɔː-, in spagnolo: /floˈɾiða/)[2] è uno stato degli Stati Uniti d'America. Si estende su buona parte dell'omonima penisola ed è bagnata ad ovest dal Golfo del Messico, mentre a nord confina con gli Stati della Georgia e dell'Alabama e ad est si affaccia sull'Oceano Atlantico. È il 22º stato per superficie degli Stati Uniti e il 4° per popolazione. La sua capitale è Tallahassee ma la città più conosciuta è Miami. La sua geografia è segnata da un'estesa linea costiera, dall'onnipresenza delle acque e della minaccia degli uragani. Il terreno è caratterizzato dalla bassa elevazione, costituito prevalentemente da rocce sedimentarie. Il clima varia dal subtropicale a nord, al tropicale a sud. Animali caratteristici sono il lamantino e l'alligatore.
Fin dalla sua scoperta nel 1513 ad opera dello spagnolo Juan Ponce de León, la Florida è stata una sfida coloniale per le potenze europee, prima di essere integrata dagli Stati Uniti nel 1845. Fu teatro di guerre contro gli indiani Seminole, e della segregazione razziale dopo la guerra civile. Oggi si distingue per la sua grande comunità cubana e la forte crescita della popolazione solleva questioni ambientali. La sua economia, che si è andata sviluppando dal tardo XIX secolo, si basa principalmente sul turismo, sull'agricoltura e sui trasporti. È anche nota per i suoi parchi di divertimento, per la produzione di arance e per il Kennedy Space Center
La cultura della Florida riflette diverse influenze, quella anglosassone, indios, afro-americana e ispanica che si trova riflessa nell'architettura e nella gastronomia. La Florida ha attirato molti scrittori, come Marjorie Kinnan Rawlings, Ernest Hemingway, e Tennessee Williams. Il soprannome della Florida è Sunshine State (usato anche nelle targhe delle auto) e gli animali simbolo sono la pantera della Florida, che però è sempre più rara nel territorio della Florida, e l'alligatore, invece molto presente.
Florida o la Florida (esta última denominación empleada sobre todo por hispanohablantes de EE. UU., así como cubanos y dominicanos)3 es uno de los cincuenta estados que, junto con Washington D. C., forman los Estados Unidos de América, ubicado en la región meridional del país. Limita al occidente con el golfo de México y Alabama, al norte con Alabama y Georgia, al oriente con el océano Atlántico y al sur con el estrecho de Florida. Florida ocupa el puesto 22 en cuanto a extensión y el tercero en cuanto a población.4
Jacksonville es la ciudad más poblada del estado y la ciudad más extensa por superficie en el territorio continental de los Estados Unidos (debido a la consolidación de Jacksonville con el condado de Duval). El Área Metropolitana de Miami es el área más urbanizada del estado. Tallahassee es la capital del estado.
Cerca de dos tercios del estado conforman una península entre el golfo de México y el océano Atlántico. Florida tiene la costa más extensa del territorio continental de Estados Unidos, aproximadamente 1350 millas, sin incluir la contribución de las Islas Barrera. Es el único estado que limita tanto con el golfo de México como con el océano Atlántico. Gran parte del estado se encuentra al nivel del mar o cerca de él y se caracteriza por el suelo sedimentario. El clima varía de subtropical en el norte a tropical en el sur.5
El cocodrilo americano, la pantera de Florida y el manatí se pueden encontrar en parque nacional de los Everglades en la parte sur del estado. Florida, por el gran territorio costero, es el único estado continental de los Estados Unidos con clima tropical (el otro estado con este tipo de clima es Hawái).
Desde la llegada de exploradores españoles al mando de Juan Ponce de León, quién la nombró La Florida, en 1513; el territorio fue un reto para el colonialismo europeo antes de convertirse en un estado de la Unión en 1845. Fue el principal teatro de las Guerras Seminolas y se caracterizó por la existencia de segregación racial después de la Guerra de Secesión.
En el sigo XXI, Florida se distingue por su gran comunidad de expatriados cubanos y su alto crecimiento poblacional, así como por sus crecientes problemas ambientales. La economía del estado se basa principalmente en el turismo, la agricultura y el transporte, que se desarrolló a fines del siglo XIX. Florida también es reconocida por sus parques de atracciones (como Walt Disney World, Bush Gardens y Universal Studios Florida), sus cultivos de cítricos, sus verduras de invierno, el Centro Espacial Kennedy, y como un destino turístico popular entre los jubilados estadounidenses.
La cultura de Florida es un reflejo de múltiples influencias; la herencia africana, europea, indígena e hispanoamericana se puede encontrar en la arquitectura y la cocina. Florida ha atraído a muchos escritores como Marjorie Kinnan Rawlings, Ernest Hemingway y Tennessee Williams. Es internacionalmente conocida por la práctica de deportes como el golf, el tenis, el automovilismo y los deportes acuáticos.
Флори́да[1][2][3] (англ. Florida , МФА [ˈflɒrɪdə], от исп. florida «цветущая») — штат[4] на юго-востоке США; столица — город Таллахасси.
Расположен на одноимённом полуострове между Мексиканским заливом на западе и Атлантическим океаном на востоке, с юга омывается Флоридским проливом. На севере граничит со штатами Алабама и Джорджия. Морские границы проходят вдоль всего полуострова, захватывая немного территории к северу от него и группу островов Флорида-Кис к югу.
Население — 20 271 272 чел. (2015 год): 3-й по численности населения штат США (после Калифорнии и Техаса)[5].
Площадь территории — 170 304 км²: 22-й по площади территории штат США.Крупнейший город — Джэксонвилл, крупные города — Майами, Тампа, Орландо.
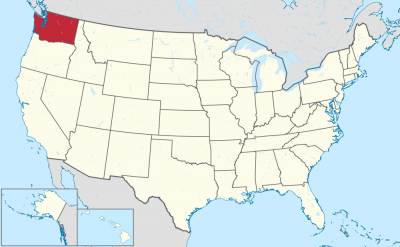


Washington (engl. Aussprache [ˈwɒʃɪŋtən]) ist ein Bundesstaat der Vereinigten Staaten von Amerika. Er liegt im Nordwesten der USA an der Küste des Pazifischen Ozeans, nördlich von Oregon, westlich von Idaho und südlich von British Columbia in Kanada.
Gemessen an seiner Fläche steht Washington unter den US-Bundesstaaten mit 184.665 Quadratkilometern an 18. Stelle, gemessen an seiner Bevölkerung von 6.724.540 Einwohnern an 13. Stelle (Stand 2010). Der Großteil der Bevölkerung konzentriert sich rund um den Puget Sound, eine etwa 150 km lange, inselreiche und weitverzweigte Bucht im Westen des Staates, an der auch die Hauptstadt Olympia sowie die mit Abstand größte Stadt Seattle liegen.
Der Staat wurde nach dem ersten US-Präsidenten, George Washington, benannt und als 42. Staat im Jahr 1889 in die Vereinigten Staaten aufgenommen. Aufgrund der Vielzahl von Nadelbäumen trägt der Staat den Spitznamen Evergreen State (deutsch Immergrüner Staat).
Um den Bundesstaat von der ebenfalls nach George Washington benannten, an der Ostküste befindlichen Hauptstadt der USA, Washington, D.C., abzugrenzen, wird für den Staat oft die Bezeichnung Washington State verwendet.
ワシントン州(英: State of Washington, 英語発音: [ˈwɑʃɪ̞ŋʔn̩])は、アメリカ合衆国西海岸最北部の州。州都はオリンピアであるが、規模・経済の面での中心都市はシアトルである。北はカナダのブリティッシュコロンビア州、南はオレゴン州、東はアイダホ州と接している。1846年にオレゴン境界紛争を解決するためのオレゴン条約が結ばれた結果、イギリスから割譲されたワシントン準州の西側が現在のワシントン州になった。1889年にアメリカ合衆国42番目の州として認められた。
カリフォルニア州、オレゴン州と共にリベラルな気風で、保守的な中西部に対して「レッドウッド・カーテンの向こう側」と称される。
近年ではマイクロソフトの本拠地であり、スターバックスの発祥の地などとして知られる。州の中心都市シアトルがMLBシアトル・マリナーズの本拠地である。
2010年国勢調査によると、州の人口は6,724,540人となっている。そのおよそ60%はセイリッシュ海のピュージェット湾に沿った交通、事業、産業の中心であるシアトル都市圏に集中している。ピュージェット湾は太平洋からの入江であり、氷河が侵食した多くの島、深いフィヨルドおよび湾がある。州の西部は深い温帯雨林があり、西部、中部、北東部および最南東部には山脈がある。東部の亜乾燥盆地は徹底した農業が行われている。アメリカ合衆国の西海岸や西部ではカリフォルニア州に次いで2番目に人口の多い州である。
州の名はアメリカ建国の父で初代アメリカ合衆国大統領ジョージ・ワシントンに由来しており、大統領の名前が付けられたことでは合衆国の中で唯一の州である。首都ワシントンD.C.と区別するためにワシントン州と呼ばれるが、州民、近在の州およびカナダのブリティッシュコロンビア州南部の住人は単に「ワシントン」と呼び、首都の方は「ワシントンD.C.」あるいは単純に「D.C.」のみで呼んでいる。元々ワシントン州のある地域はコロンビア川にちなんで「コロンビア」と呼ばれており、ワシントンD.C.がコロンビア特別区と呼ばれることから、混乱を避けるためにワシントン州とされた。
Washington (/ˈwɒʃɪŋtən/ (![]() listen)), officially the State of Washington, is a state in the Pacific Northwest region of the United States. Named for George Washington, the first U.S. president, the state was made out of the western part of the Washington Territory, which was ceded by the British Empire in 1846, in accordance with the Oregon Treaty in the settlement of the Oregon boundary dispute. The state, which is bordered on the west by the Pacific Ocean, Oregon to the south, Idaho to the east, and the Canadian province of British Columbia to the north, was admitted to the Union as the 42nd state in 1889. Olympia is the state capital; the state's largest city is Seattle. Washington is often referred to as Washington state to distinguish it from the nation's capital, Washington, D.C.
listen)), officially the State of Washington, is a state in the Pacific Northwest region of the United States. Named for George Washington, the first U.S. president, the state was made out of the western part of the Washington Territory, which was ceded by the British Empire in 1846, in accordance with the Oregon Treaty in the settlement of the Oregon boundary dispute. The state, which is bordered on the west by the Pacific Ocean, Oregon to the south, Idaho to the east, and the Canadian province of British Columbia to the north, was admitted to the Union as the 42nd state in 1889. Olympia is the state capital; the state's largest city is Seattle. Washington is often referred to as Washington state to distinguish it from the nation's capital, Washington, D.C.
Washington is the 18th largest state, with an area of 71,362 square miles (184,827 km2), and the 13th most populous state, with more than 7.6 million people. Approximately 60 percent of Washington's residents live in the Seattle metropolitan area, the center of transportation, business, and industry along Puget Sound, an inlet of the Pacific Ocean consisting of numerous islands, deep fjords, and bays carved out by glaciers. The remainder of the state consists of deep temperate rainforests in the west; mountain ranges in the west, central, northeast, and far southeast; and a semi-arid basin region in the east, central, and south, given over to intensive agriculture. Washington is the second most populous state on the West Coast and in the Western United States, after California. Mount Rainier, an active stratovolcano, is the state's highest elevation, at almost 14,411 feet (4,392 meters), and is the most topographically prominent mountain in the contiguous U.S.
Washington is a leading lumber producer; its rugged surface is rich in stands of Douglas fir, hemlock, ponderosa pine, white pine, spruce, larch, and cedar. Washington is the nation's largest producer of apples, hops, pears, red raspberries, spearmint oil, and sweet cherries, and ranks high in the production of apricots, asparagus, dry edible peas, grapes, lentils, peppermint oil, and potatoes. Livestock and livestock products make important contributions to total farm revenue, and the commercial fishing of salmon, halibut, and bottomfish makes a significant contribution to the state's economy. Washington ranks second only to California in wine production.
Manufacturing industries in Washington include aircraft and missiles, shipbuilding, and other transportation equipment, food processing, metals and metal products, chemicals, and machinery. Washington has more than a thousand dams, including the Grand Coulee Dam, built for a variety of purposes including irrigation, power, flood control, and water storage.
Washington is one of the wealthiest and most socially liberal states in the country.[4] The state consistently ranks among the best for life expectancy and low unemployment.[5] Along with Colorado, Washington was one of the first to legalize medicinal and recreational cannabis, was among the first thirty-six states to legalize same-sex marriage, doing so in 2012, and was one of only four U.S. states to have been providing legal abortions on request before the 1973 Supreme Court decision in Roe v. Wade loosened abortion laws nationwide. Similarly, Washington voters approved a 2008 referendum on legalization of physician-assisted suicide, and is currently one of only five states, along with Oregon, California, Colorado and Vermont, as well as the District of Columbia to have legalized the practice. The state is also one of eight in the country to have criminalized the sale, possession and transfer of bump stocks, with California, Florida, New Jersey, New York, Vermont, Maryland, and Massachusetts also having banned these devices.
Washington (/ˈwɑʃ.ɪŋ.tən/3 Écouter) est un État des États-Unis situé à l'extrême nord-ouest du Mainland, soit les États-Unis contigus, (l'Alaska étant l'État à l'extrême nord-ouest de tous les États-Unis).
Il est bordé au nord par la province canadienne de la Colombie-Britannique, à l'est par l'Idaho, au sud par l'Oregon et à l'ouest par l'océan Pacifique.
Il ne faut pas confondre l'État de Washington et la capitale des États-Unis, Washington (district de Columbia), située à l'est du pays, qui tiennent tous les deux leurs noms du président américain George Washington.
Washington è uno stato federato del nord-ovest degli Stati Uniti d'America, posto sulla costa del Pacifico ad est, a nord dell'Oregon, a ovest dell'Idaho e a sud della provincia canadese della Columbia Britannica. Prende il nome da George Washington, primo presidente degli Stati Uniti, e deriva dalla parte occidentale del Territorio di Washington che era stato ceduto dalla Gran Bretagna nel 1846 con il Trattato dell'Oregon, annesso poi all'Unione come 42º stato nel 1889. La città più grande è Seattle, situata a ovest, seguita da Spokane, situata ad est, mentre la capitale è Olympia. È il 18° più esteso e il 13° più popoloso dei 50 Stati membri: dopo la California è il secondo Stato più popoloso sulla West Coast e negli Stati Uniti nord-occidentali, con circa il 60% dei residenti dello Stato che vive nella zona metropolitana di Seattle, il centro dei trasporti, del commercio e dell'industria lungo lo stretto di Puget (Puget Sound), un'insenatura del Pacifico costituita da numerose isole, profondi fiordi e valli scavate da ghiacciai. Il resto dello Stato è costituito da foreste pluviali temperate ad ovest, catene montuose nella parte occidentale, centrale, nordorientale e sudorientale, e una regione semi-arida a est, al centro e al sud, dedita all'agricoltura intensiva.
È uno dei principali produttori di legname essendo la sua superficie frastagliata ricca di foreste di abete di Douglas, cicuta, ponderosa e pino bianco, abete rosso, larice e cedro; è inoltre il più grande produttore di mele, luppoli, pere, lamponi rossi, olio di menta e ciliegie, e si colloca ai primi posti anche nella produzione di albicocche, asparagi, piselli, uva, lenticchie e patate; inoltre, animali e prodotti derivati danno un contributo importante al fatturato totale delle aziende agricole e la pesca commerciale del salmone, dell'halibut, e dei pesci dei fondali dà un contributo significativo all'economia dello Stato.
Anche se il suo nome inequivocabile è "The State of Washington", il nome dello Stato è spesso invertito e definito come "Washington State"' per evitare di confonderlo con Washington DC, il territorio della capitale degli Stati Uniti d'America che è invece situato nella parte opposta del paese (East Coast).
Washington, también llamado estado de Washington para diferenciarlo de Washington D. C., es uno de los cincuenta estados que, junto con Washington D. C., forman los Estados Unidos de América. Su capital es Olympia y su ciudad más poblada, Seattle. Está ubicado en la región Oeste del país, división Pacífico, limitando al norte con Canadá, al este con Idaho, al sur con Oregón y al oeste con el océano Pacífico. Fue admitido en la Unión el 11 de noviembre de 1889, como el estado número 42.
Fue nombrado en homenaje al líder de las fuerzas estadounidenses de la Guerra de la Independencia de EE. UU. de 1776 y primer presidente de Estados Unidos, George Washington. Los nombres de muchas ciudades y condados de Estados Unidos rinden homenaje a diversos presidentes estadounidenses, pero el estado de Washington es el único estado en ser nombrado en homenaje a un presidente estadounidense. Para diferenciarla de la capital de Estados Unidos, Washington D. C., en Estados Unidos, se suele llamar "estado de Washington" al estado y "D. C." (abreviatura de "Distrito de Columbia", District of Columbia en inglés), "ciudad federal" o "ciudad de Washington" o a la capital nacional.
Washington cuenta con enormes bosques de coníferas, que le han valido el apodo de Evergreen State (estado siempre verde, o estado de la hoja perenne). Estos bosques hacen de Washington un líder de la industria maderera estadounidense. Se encuentra cortado por varios ríos y salpicado por varios lagos, lo que crea un terreno propicio para la instalación de presas. Aquí se localiza la mayor del país, la presa Grand Coulee, en el río Columbia. Su economía, sin embargo, se centra principalmente en el turismo y en la industria aeroespacial. El segundo mayor fabricante de aviones del mundo, Boeing, tiene su sede en este estado, así como varias de sus fábricas.
Los primeros europeos en explorar esta región fueron los castellanos, y posteriormente, los británicos fundaron los primeros asentamientos. La región formaba parte originalmente de una mayor llamada Oregon Country, un territorio disputado entre los estadounidenses y los británicos entre las décadas de 1810 y 1840. En 1846, el Tratado de Oregón establece que todas las tierras al sur del paralelo 49 del Oregon Country pasarían al control de Estados Unidos (a excepción de la isla de Vancouver). Hasta 1859, Washington formó parte del territorio de Oregón, creado a partir de la parte estadounidense del Oregon Country. En 1859, se crea el territorio de Washington, que fue nombrado en homenaje a George Washington.
Вашингто́н[1][2] (англ. Washington, американское произношение: [ˈwɒʃɪŋtən] (![]() слушать)) — штат[3] на северо-западе США, 42-й штат в составе страны. Столица — город Олимпия, крупнейший город — Сиэтл. Население — 7 546 410 человек (2019 г.).
слушать)) — штат[3] на северо-западе США, 42-й штат в составе страны. Столица — город Олимпия, крупнейший город — Сиэтл. Население — 7 546 410 человек (2019 г.).
Во избежание путаницы со столицей США, название последней обычно сопровождают словосочетанием «округ Колумбия» (в англоязычном варианте — «Washington, D.C.»). Официальное прозвище — «Вечнозелёный штат».



Wyoming (engl. Aussprache [wai̯ˈoʊ̯mɪŋ]) ist mit 579.315 Einwohnern[1][2] (2017) der bevölkerungsärmste Bundesstaat der Vereinigten Staaten von Amerika und, nach Alaska, der Bundesstaat mit der zweitgeringsten Bevölkerungsdichte.[3][4] Er liegt im Westen der Vereinigten Staaten und steigt von den Great Plains Ost-Wyomings zu den Rocky Mountains hin an.
Der Name stammt aus der Sprache der Algonkin-Indianer und bedeutet „Große Ebenen“. Er wurde der poetischen Erzählung Gertrude of Wyoming entnommen, die Thomas Campbell 1809 geschrieben hatte.
Der größte Ort ist die Hauptstadt Cheyenne. Der Spitzname ist Equality State nach dem Motto des Staates: „Equal Rights“ (deutsch: gleiche Rechte).
Mit seinen 253.336 km² ist Wyoming flächenmäßig der zehntgrößte Bundesstaat der USA. Nach Colorado ist er mit 2044 m auch der durchschnittlich am zweithöchsten gelegene Staat des Landes. Er befindet sich im westlichen Zentrum des US-Staatsgebiets und zählt somit durch seine Lage (wie auch seine Kultur) zum legendären sogenannten (Wilden) Westen (daher auch der Kosename Cowboy State).
Wyoming erstreckt sich auf einer Breite von 450 km zwischen etwa 41° N und 45° N und einer Länge von 550 bis 580 km zwischen etwa 104° W und 111° W und gehört gemeinsam mit seinen südlichen und westlichen Nachbarstaaten Colorado und Utah zu den Bundesstaaten, deren Grenzen fast ausschließlich nach geographischen Längen- und Breitengraden definiert wurden. Die Grenzziehung entspricht (auf einem entsprechenden Kartennetzentwurf, etwa der Mercator-Projektion) mit geringfügigen Abweichungen einem Rechteck.
Im Prinzip ist das Gebiet von Wyoming ein weites, gebrochenes Plateau, aus dem verschiedene Bergkämme der Rocky Mountains aufragen. Aus einer Querschnittsperspektive gesehen, befindet sich dieses Plateau in einer Schräglage, die von einem höher gelegenen Westen in einen tieferen Osten übergeht. Diese Neigung beschreibt auch den Übergang von den weiten östlichen Ebenen der Prärien über zentrale Beckenlandschaften zum westlich gelegenen Felsengebirge. Wyoming ist ein Staat, der die großen Kulturlandschaften der Great Plains und der Rocky Mountains verbindet – eine Position, die er nur mit drei der 50 weiteren Bundesstaaten teilt: Montana im Norden sowie Colorado und New Mexico im Süden.
Eine weitere geographische Bedeutsamkeit ist Wyomings Lage an der Great Continental Divide, der großen kontinentalen Wasserscheide des nordamerikanischen Kontinents, die die Bundesstaatsfläche in nordwestlich-südöstlicher Richtung durchzieht. Sie verläuft entlang der Absaroka Range und Wind River Ranges und setzt sich im Great Divide Basin, und später der Park Range (großteils in Colorado), fort. Alle Flüsse, die östlich dieser Linie entspringen, entwässern Richtung Osten und münden irgendwann alle in den Missouri River, der in den Mississippi River und schließlich in den Atlantischen Ozean (Golf von Mexiko) fließt. Jene Flüsse, die westlich der Wasserscheide ihren Lauf beginnen, enden im Pazifik (entweder im offenen Ozean, wenn sie dem Columbia River westwärts folgen, oder im Golf von Kalifornien, wenn sie nach Süden in den Green River und später den Colorado River entwässern).
Wyoming kann in drei große geographische Räume gegliedert werden, die alle grob ein Drittel des Staatsgebiets umfassen: die Great Plains, die Intermountain Basins (Gebirgsbecken) und die Rocky Mountains.
ワイオミング州(英: State of Wyoming [waɪˈoʊmɪŋ] (![]() 音声ファイル))は、アメリカ合衆国西部の山岳地域にある州である。
音声ファイル))は、アメリカ合衆国西部の山岳地域にある州である。
州都はシャイアン市。陸地面積は全米50州の中で第10位だが、人口は563,626人(2010年国勢調査)[1]と全米50州の中で最も少なく[2]、州都シャイアンからわずか160km南にあるコロラド州の州都デンバーを含む、全米の31都市よりも少ない。人口密度は2人/km2で、全米50州の中では、アラスカ州に次いで2番目に低い。ワイオミングとはアルゴンキン語族インディアンの言葉で「大平原」を意味し、州の東側3分の1はハイプレーンズと呼ばれ、広大なグレートプレーンズの西部にあたる標高の高い平原地帯が広がっている。西側3分の2はロッキー山脈東部の山岳地帯と丘陵の牧草地帯である。州の愛称は「平等の州 (Equality State)」、「カウボーイ州 (Cowboy State)」である。
Wyoming (/waɪˈoʊmɪŋ/ (![]() listen)) is a doubly landlocked state in the western United States. The 10th largest state by area, it is also the least populous and second most sparsely populated state in the country. It is bordered by Montana to the north and northwest, South Dakota and Nebraska to the east, Colorado to the south, Utah to the southwest, and Idaho to the west. The state population was estimated at 578,759 in 2019, which is less than 31 of the most populous U.S. cities.[6] The state capital and the most populous city is Cheyenne, which had an estimated population of 63,957 in 2018.[7]
listen)) is a doubly landlocked state in the western United States. The 10th largest state by area, it is also the least populous and second most sparsely populated state in the country. It is bordered by Montana to the north and northwest, South Dakota and Nebraska to the east, Colorado to the south, Utah to the southwest, and Idaho to the west. The state population was estimated at 578,759 in 2019, which is less than 31 of the most populous U.S. cities.[6] The state capital and the most populous city is Cheyenne, which had an estimated population of 63,957 in 2018.[7]
Wyoming's western half is mostly covered by the ranges and rangelands of the Rocky Mountains, while the eastern half of the state is high-elevation prairie called the High Plains. Almost half of the land in Wyoming is owned by the U.S. government, leading Wyoming to rank sixth by area and fifth by proportion of a state's land owned by the federal government.[8] Federal lands include two national parks—Grand Teton and Yellowstone—two national recreation areas, two national monuments, several national forests, historic sites, fish hatcheries, and wildlife refuges.
Original inhabitants of the region include the Arapaho, Crow, Lakota, and Shoshone. Southwest Wyoming was claimed by the Spanish Empire and then as Mexican territory until it was ceded to the U.S. in 1848 at the end of the Mexican–American War. The region acquired the name "Wyoming" when a bill was introduced to Congress in 1865 to provide a temporary government for the territory of Wyoming. The name had been used earlier for the Wyoming Valley in Pennsylvania, and is derived from the Munsee word xwé:wamənk, meaning "at the big river flat".[9][10]
The main drivers of Wyoming's economy are tourism and extraction of minerals such as coal, oil, natural gas, and trona. Agricultural commodities include livestock, hay, sugar beets, grain (wheat and barley), and wool. The climate is semi-arid and continental, drier and windier than the rest of the country with greater temperature extremes. Wyoming has been a politically conservative state since the 1950s, with the Republican nominee carrying the state in every presidential election since 1968.[11] Donald Trump won it by 46 points in 2016, which was the best performance in the 21st century in the state and Trump's best performance in any state.
Le Wyoming /wi.o.miŋ/ (prononciation en anglais : /waɪ.ˈoʊ.mɪŋ/) est un État de l'Ouest des États-Unis, bordé à l'ouest par l'Idaho, au nord par le Montana, à l'est par le Nebraska et le Dakota du Sud et au sud par le Colorado et l'Utah. Le tiers de l’État est situé dans les Grandes Plaines, mais le Wyoming est montagneux sur tout le reste de son territoire. C'est aussi l'État le moins peuplé des États-Unis avec ses 563 626 habitants. Sa capitale et plus grande ville est Cheyenne.
Il Wyoming è uno Stato degli Stati Uniti, quello con minore popolazione. Confina a nord con il Montana, a est con il Dakota del Sud e il Nebraska, a sud con il Colorado e a ovest con lo Utah e l'Idaho. La capitale dello Stato è Cheyenne. Il nome Wyoming deriva dalla parola in lingua munsee xwé:wamənk che significa presso il grande fiume calmo usata in origine per denominare la Wyoming Valley in Pennsylvania.
Wyoming (pronunciación en inglés: /waɪˈoʊmɪŋ/ (![]() escuchar)) es uno de los cincuenta estados que, junto con Washington D. C., forman los Estados Unidos de América. Su capital y ciudad más poblada es Cheyenne (63 335 habs. en 2015). Está ubicado en la región Oeste del país, división Montañas Rocosas, limitando al norte con Montana, al este con Dakota del Sur y Nebraska, al sur con Colorado, al suroeste con Utah y al oeste con Idaho.
escuchar)) es uno de los cincuenta estados que, junto con Washington D. C., forman los Estados Unidos de América. Su capital y ciudad más poblada es Cheyenne (63 335 habs. en 2015). Está ubicado en la región Oeste del país, división Montañas Rocosas, limitando al norte con Montana, al este con Dakota del Sur y Nebraska, al sur con Colorado, al suroeste con Utah y al oeste con Idaho.
Con 586 107 habitantes en 2015 es el estado menos poblado, con 253 336 km², el décimo más extenso —por detrás de Alaska, Texas, California, Montana, Nuevo México, Arizona, Nevada, Colorado y Oregón— y con 2,2 hab/km², el segundo menos densamente poblado, por detrás de Alaska. Fue admitido en la Unión el 10 de julio de 1890, como el estado número 44.2 Con una tasa de 449 empleados cada 10 000 habs., es el estado con mayor proporción de empleo público no federal del país.3
Dos tercios del territorio oeste están cubiertos, mayormente, por las sierras y montañas de las Montañas Rocosas, mientras que el resto este del estado son praderas de grandes alturas sobre el nivel del mar conocidas como High Plains. Casi la mitad de la tierra de Wyoming es propiedad del gobierno estadounidense, haciendo de Wyoming el sexto estado con mayor número de acres en manos del gobierno federal. Estas tierras federales incluyen dos parques nacionales —Grand Teton y Yellowstone— dos áreas recreativas nacionales, dos monumentos nacionales, así como varios bosques nacionales, sitios históricos, zonas de pescas y áreas protegidas para la vida silvestre.
Las naciones indias Crow, Arapajó, Lakota y Shoshón son algunos de los pobladores originales de la región. La región suroeste del estado fue incluida en el Imperio Español y, consecuentemente, en territorio mexicano, hasta que fue cedido a los Estados Unidos en 1848 como resultado de la intervención estadounidense en México. La región adquirió el nombre de Wyoming cuando un proyecto de ley fue introducido al Congreso en 1865 para proveer "un gobierno temporal al territorio de Wyoming". El territorio fue nombrado por el Valle de Wyoming en Pensilvania, siendo el nombre derivado de la palabra xwé:wamənk, en idioma munsee, que significa "en el gran río plano".45
La industria de extracción de minerales—especialmente carbón, petróleo, gas natural y trona—junto con el turismo son los principales motores de la economía de Wyoming. La agricultura ha sido históricamente un importante componente de la economía del estado. El clima es generalmente semiárido y continental, siendo más seco y con más vientos que el resto de los Estados Unidos, con temperaturas extremas comunes.
Exceptuando las elecciones de 1964, Wyoming ha sido un estado políticamente conservador desde la década de 1950, con el Partido Republicano ganando todas las elecciones presidenciales en el estado desde entonces.
Вайо́минг[1][2] (англ. Wyoming, американское произношение: [waɪˈoʊmɪŋ] (![]() слушать)) — штат[3] на западе США, входящий в группу так называемых Горных штатов. Столица и крупнейший город — Шайенн. Официальное прозвище — «Штат равноправия» (англ. Equality State). Официальный девиз — «Равные права» (англ. Equal Rights). Занимает в государстве последнее место по численности населения.
слушать)) — штат[3] на западе США, входящий в группу так называемых Горных штатов. Столица и крупнейший город — Шайенн. Официальное прозвище — «Штат равноправия» (англ. Equality State). Официальный девиз — «Равные права» (англ. Equal Rights). Занимает в государстве последнее место по численности населения.


South Dakota (englische Aussprache [ˌsaʊ̯θ dəˈkʰoʊ̯ɾə], deutsch Süddakota) ist einer der nordwestlichen Prärie-Bundesstaaten der Vereinigten Staaten. Er umfasst 199.731 km². Im Westen befinden sich die Black Hills, östlich davon die Badlands und im Osten des Staates das Coteau des Prairies. Die größte Stadt ist Sioux Falls, die Hauptstadt ist Pierre. South Dakota beheimatet mehrere Indianerreservate, insbesondere der Lakota. Der Staat hat innerhalb der USA nach Alaska und New Mexico den dritthöchsten Bevölkerungsanteil von Indianern.[2]
Der Name Dakota leitet sich von der indianischen Ethnie der Dakota ab, die vor der Unterwerfung durch die Weißen in diesem Gebiet lebte. Spitzname von South Dakota ist The Mount Rushmore State.
南达科他州(英语:State of South Dakota),简称南达州,是美国中西部平原上地势较高的一州,过去曾是美国印地安人苏族中拉科他族(Lakota)的聚落所在。南达科他州在1889年11月2日加入美国联邦,也是在同一天被命名的。
南达科他州的北边是北达科他州,南边是内布拉斯加州,东边则紧邻艾奥瓦州与明尼苏达州,西边是怀俄明州和蒙大拿州,它同时也是美国上被称为边疆带六州中的一州。
美国战舰南达科他号就是以此州命名的。
サウスダコタ州(英: State of South Dakota [ˌsaʊθ dəˈkoʊtə] (![]() 音声ファイル))は、アメリカ合衆国の中西部にある州である。グレートプレーンズ(大平原)にあり、南西部はハイプレーンズと呼ばれる標高の高い平原地帯である。州の北はノースダコタ州に、東側はミネソタ州とアイオワ州に、西側はモンタナ州とワイオミング州に、南側はネブラスカ州に接している。州の中央にはミズーリ川が南北に流れているので、その東側と西側には地理的にも社会的にもはっきりとした特徴があり、州民は「イーストリバー」「ウェストリバー」と呼んでいる[2]。
音声ファイル))は、アメリカ合衆国の中西部にある州である。グレートプレーンズ(大平原)にあり、南西部はハイプレーンズと呼ばれる標高の高い平原地帯である。州の北はノースダコタ州に、東側はミネソタ州とアイオワ州に、西側はモンタナ州とワイオミング州に、南側はネブラスカ州に接している。州の中央にはミズーリ川が南北に流れているので、その東側と西側には地理的にも社会的にもはっきりとした特徴があり、州民は「イーストリバー」「ウェストリバー」と呼んでいる[2]。
州都はピア市であり、人口最大の都市は、ミネソタ州、アイオワ州との州境に近いスーフォールズ市である。「ダコタ」という名前はインディアン部族のダコタ族(スー族)の言葉「ダコタ(仲間)」に由来する。面積ではアメリカ合衆国50州の中で第17位だが、人口では第46位、人口密度も第46位と過疎である。19世紀後半にできたダコタ準州の南側半分であり、1889年11月2日に40番目の州に昇格した。
州内東側には州民の大半が住んでおり、その肥沃な土壌で様々な農作物が栽培されている。西側は牧畜業が盛んであり、その経済は観光業と防衛費に依存している。州南西部にはブラックヒルズと呼ばれる低木の松に覆われた山脈があり、スー族の聖地である。ここには4人の大統領の顔のモニュメントで有名な観光地ラシュモア山国立記念公園がある。他にもバッドランズ国立公園、クレイジー・ホース記念碑、ウインドケーブ国立公園、ジュエルケーブ国定記念物、カスター州立公園、また歴史ある町のデッドウッドなどが、訪れる人の多い観光地である。ウォール・ドラッグストアなど、民間主導で運営されている観光地・名所も少なくない。はっきりとした四季のある大陸性気候であり、雨量は東部で中程度、西部でやや少ない亜乾燥気候である。生態系は北アメリカ草原に典型的な様相を示している。
自然が豊富で多くの観光客が訪れる州という華やかな面がある一方、ゴールドラッシュ期にはインディアンと白人との激しい抗争が繰り返された州でもある。全米で最も経済的に貧しい地域がある州であり、現在でも、インディアン居留地の貧困は、サウスダコタ州が抱える大きな問題として残っている。
South Dakota (/- dəˈkoʊtə/ (![]() listen)) is a U.S. state in the Midwestern region of the United States. It is named after the Lakota and Dakota Sioux Native American tribes, who comprise a large portion of the population and historically dominated the territory. South Dakota is the seventeenth largest by area, but the fifth smallest by population and the 5th least densely populated of the 50 United States. As the southern part of the former Dakota Territory, South Dakota became a state on November 2, 1889, simultaneously with North Dakota. It was either the 39th or 40th state admitted to the union. Before signing the statehood papers, President Benjamin Harrison shuffled the papers so that no one could tell which became a state first.[8] Pierre is the state capital and Sioux Falls, with a population of about 187,200,[9] is South Dakota's largest city.
listen)) is a U.S. state in the Midwestern region of the United States. It is named after the Lakota and Dakota Sioux Native American tribes, who comprise a large portion of the population and historically dominated the territory. South Dakota is the seventeenth largest by area, but the fifth smallest by population and the 5th least densely populated of the 50 United States. As the southern part of the former Dakota Territory, South Dakota became a state on November 2, 1889, simultaneously with North Dakota. It was either the 39th or 40th state admitted to the union. Before signing the statehood papers, President Benjamin Harrison shuffled the papers so that no one could tell which became a state first.[8] Pierre is the state capital and Sioux Falls, with a population of about 187,200,[9] is South Dakota's largest city.
South Dakota is bordered by the states of North Dakota (to the north), Minnesota (to the east), Iowa (to the southeast), Nebraska (to the south), Wyoming (to the west), and Montana (to the northwest). The state is bisected by the Missouri River, dividing South Dakota into two geographically and socially distinct halves, known to residents as "East River" and "West River".[10]
Eastern South Dakota is home to most of the state's population, and the area's fertile soil is used to grow a variety of crops. West of the Missouri River, ranching is the predominant agricultural activity, and the economy is more dependent on tourism and defense spending. Most of the Native American reservations are in West River. The Black Hills, a group of low pine-covered mountains sacred to the Sioux, are in the southwest part of the state. Mount Rushmore, a major tourist destination, is there. South Dakota has a temperate continental climate, with four distinct seasons and precipitation ranging from moderate in the east to semi-arid in the west. The state's ecology features species typical of a North American grassland biome.
Humans have inhabited the area for several millennia, with the Sioux becoming dominant by the early 19th century. In the late 19th century, European-American settlement intensified after a gold rush in the Black Hills and the construction of railroads from the east. Encroaching miners and settlers triggered a number of Indian wars, ending with the Wounded Knee Massacre in 1890. Key events in the 20th century included the Dust Bowl and Great Depression, increased federal spending during the 1940s and 1950s for agriculture and defense, and an industrialization of agriculture that has reduced family farming.
While several Democrats have represented South Dakota for multiple terms in both chambers of Congress, the state government is largely controlled by the Republican Party, whose nominees have carried South Dakota in each of the last 13 presidential elections. Historically dominated by an agricultural economy and a rural lifestyle, South Dakota has recently sought to diversify its economy in areas to attract and retain residents. South Dakota's history and rural character still strongly influence the state's culture.
Le Dakota du Sud /dakɔta dy syd/3 Écouter (en anglais : South Dakota /ˌsaʊθ dəˈkoʊtə/4 Écouter) est un État du Nord des États-Unis, bordé à l'ouest par le Wyoming et le Montana, au nord par le Dakota du Nord, à l'est par le Minnesota et l'Iowa et au sud par le Nebraska. État situé dans l'ouest des plaines du Midwest, il possède un climat continental. Il compte 814 180 habitants en 2010 (soit le 46e État américain au regard de la population). Sa capitale est Pierre et sa plus grande ville Sioux Falls, avec environ 154 000 habitants.
Le Dakota du Sud est coupé en deux par la rivière Missouri : à l'est de la rivière se trouvent la plupart des habitants et les exploitations agricoles, tandis qu'à l'ouest prédominent l'élevage et le tourisme. Le mont Rushmore, les Black Hills et les parcs nationaux de l'État sont des destinations appréciées.
Le Dakota du Sud est traditionnellement dirigé par des élus du Parti républicain. Si la ruralité influence grandement la culture de l'État, il a, ces dernières décennies, diversifié son économie afin d'attirer et de fixer de nouveaux habitants, ce qui a permis une augmentation modérée de la population ; le Dakota du Sud se trouve cependant confronté à l'exode rural et à de fortes disparités économiques, notamment entre les centres urbains et les réserves amérindiennes.
Il Dakota del Sud (AFI: [daˈkɔta][3]; in inglese , [ˌsaʊθ dəˈkoʊtə]) è uno stato federato degli Stati Uniti d'America, situato nelle alte pianure del Midwest. Prende il nome dalla tribù di Nativi Americani Lakota (Sioux) e venne ammesso nell'Unione il 2 novembre 1889, assieme al Dakota del Nord, quando in precedenza, dal 2 marzo 1861 era stato costituito il Territorio del Dakota[4].
Costituito da 66 contee, la capitale è Pierre e confina a nord con il Dakota del Nord, a sud con il Nebraska, ad est con Iowa e Minnesota, ad ovest con Wyoming e Montana. L'unità navale USS South Dakota prese questo nome in onore dello Stato.
Dakota del Sur (en inglés, South Dakota) es uno de los cincuenta estados que, junto con Washington D. C., forman los Estados Unidos de América. Su capital es Pierre y su ciudad más poblada, Sioux Falls. Está ubicado en la región Medio Oeste del país, división Centro Noroeste, limitando al norte con Dakota del Norte, al este con Minnesota, al sureste con el río Big Sioux que lo separa de Iowa, al sur con Nebraska, al oeste con Montana y al noroeste con Wyoming. Con 814 180 habs. en 2010 es el quinto estado menos poblado —por delante de Alaska, Dakota del Norte, Vermont y Wyoming, el menos poblado— y con 4,1 hab/km², el quinto menos densamente poblado, por delante de Dakota del Norte, Montana, Wyoming y Alaska, el menos densamente poblado. Fue admitido en la Unión el 2 de noviembre de 1889, como el estado número 40.
Su nombre proviene de las tribus amerindias lakota y dakota (sioux). Alberga el Monte Rushmore (Colinas Negras) donde están esculpidos los bustos de cuatro Presidentes de los Estados Unidos. Esta enorme escultura es una de las atracciones turísticas más conocidas del mundo, y que da al estado el sobrenombre de The Mount Rushmore State.
Su territorio está dividida por el río Misuri, que lo separa en dos mitades social y económicamente distintas, conocidas por los residentes como "este del río" y "oeste del río". La agricultura ha sido históricamente su principal fuente de riqueza. Es uno de los líderes nacionales en la producción de trigo. Posee, también, una de las mayores cabañas de ganado bovino del país. Dominado por una economía basada en la agricultura, ha procurado diversificarse para atraer y mantener a sus residentes. Sigue siendo sin embargo mayoritariamente rural, con una de las densidades de población más bajas del país.1
La región que forma actualmente Dakota del Sur fue una de las últimas zonas de Estados Unidos continental en ser explorada y asentada por los estadounidenses. En 1858, el gobierno federal crearía el Territorio de Dakota, que incluyó las actuales Dakotas, hasta entonces parte del de Minnesota. Estuvo escasamente poblado hasta el siglo XIX, cuando lo atravesaron las primeras líneas ferroviarias, lo que incentivó la agricultura. Inicialmente, solo algunos pocos latifundistas dominaban la economía del territorio. Sin embargo, el éxito de estos latifundistas y los ferrocarriles atrajeron a miles de personas a la región. El 2 de noviembre de 1889, el Territorio de Dakota fue dividido en las actuales Dakota del Norte y Dakota del Sur, y ambas fueron elevadas a la categoría de estados, incorporándose a la Unión.
Ю́жная Дако́та[1][2] (англ. South Dakota, МФА: /ˌsɑʊθ dəˈkoʊtə/ ![]() слушать) — штат, расположенный на Среднем Западе США. Назван в честь индейских племён Лакота и Дакота (Сиу). Южная Дакота стала штатом 2 ноября 1889 года (одновременно с Северной Дакотой). Столица штата — город Пирр, крупнейший город — Су-Фолс.
слушать) — штат, расположенный на Среднем Западе США. Назван в честь индейских племён Лакота и Дакота (Сиу). Южная Дакота стала штатом 2 ноября 1889 года (одновременно с Северной Дакотой). Столица штата — город Пирр, крупнейший город — Су-Фолс.



Nevada (englisch [nəˈvæːdə])[2][3] ist ein Bundesstaat im Westen der Vereinigten Staaten von Amerika. Er umfasst den größten Teil des Großen Beckens östlich der Sierra Nevada und wird von Kalifornien, Oregon, Idaho, Utah sowie Arizona umschlossen.
Nevada trat im Jahr 1864 als 36. Bundesstaat den Vereinigten Staaten bei und ist flächenmäßig deren siebtgrößter. Hauptstadt ist Carson City.
Teile Nevadas sind militärisches Sperrgebiet, vor allem die Nellis Range im Süden, in der sich die Nevada Test Site befindet, auf der während des Kalten Krieges Atomwaffen getestet wurden.
内华达州(英语:State of Nevada),简称内州,是美国西部的一个州,以其发达的赌博业而著称。该州的邮政缩写是NV。“内华达”来源于西班牙语,意思是“被雪覆盖”,原本是用来形容该州西部的内华达山的寒冷。多艘美国海军的军舰也被叫作“内华达号”,名字就来源于内华达州。在南部林肯县区域是美国秘密研发和测试飞行器的地点,也曾发生过不明飞行物坠毁事件,该地点为51区。
ネバダ州(英: State of Nevada)は、アメリカ合衆国の西部に位置する州である。地域区分としてはロッキー山脈西部およびアメリカ合衆国南西部にも含められる。面積は110,561平方マイル (286,350 km2) であり、全米50州の中で第7位である。人口は2010年時点で約270万人であり、全米第35位である。人口の3分の2以上がラスベガス都市圏に住んでいる[1]。この都市圏にはネバダ州の人口の多い都市上位3つが入っている[2]。
ネバダ州はカナダにもメキシコにも境を接しておらず、アメリカの内陸州としては面積最大である。
Nevada (/nɪˈvædə/ or /nɪˈvɑːdə/, Spanish: [neˈβaða]) is a state in the Western United States.[5] It is bordered by Oregon to the northwest, Idaho to the northeast, California to the west, Arizona to the southeast, and Utah to the east. Nevada is the 7th most extensive, the 32nd most populous, but the 9th least densely populated of the U.S. states. Nearly three-quarters of Nevada's people live in Clark County, which contains the Las Vegas–Paradise metropolitan area,[6] including three of the state's four largest incorporated cities.[7] Nevada's capital is Carson City.
Nevada is officially known as the "Silver State" because of the importance of silver to its history and economy. It is also known as the "Battle Born State" because it achieved statehood during the Civil War (the words "Battle Born" also appear on the state flag); as the "Sagebrush State", for the native plant of the same name; and as the "Sage-hen State".[8]
Nevada is largely desert and semi-arid, much of it within the Great Basin. Areas south of the Great Basin are within the Mojave Desert, while Lake Tahoe and the Sierra Nevada lie on the western edge. About 86% of the state's land is managed by various jurisdictions of the U.S. federal government, both civilian and military.[9]
Before European contact — and still today, American Indians of the Paiute, Shoshone, and Washoe tribes inhabited the land that is now Nevada. The first Europeans to explore the region were Spanish. They called the region Nevada (snowy) because of the snow which covered the mountains in winter. The area formed part of the Viceroyalty of New Spain, and became part of Mexico when it gained independence in 1821. The United States annexed the area in 1848 after its victory in the Mexican–American War, and it was incorporated as part of Utah Territory in 1850. The discovery of silver at the Comstock Lode in 1859 led to a population boom that became an impetus to the creation of Nevada Territory out of western Utah Territory in 1861. Nevada became the 36th state on October 31, 1864, as the second of two states added to the Union during the Civil War (the first being West Virginia).[10]
Nevada has a reputation for its libertarian laws. In 1940, with a population of just over 110,000 people, Nevada was by far the least-populated state, with less than half the population of the next least-populated state, Wyoming.[11] However, legalized gambling and lenient marriage and divorce laws transformed Nevada into a major tourist destination in the 20th century.[12][13] Nevada is the only U.S. state where prostitution is legal, though it is illegal in its most populated regions — Clark County (Las Vegas), Washoe County (Reno) and Carson City (which, as an independent city, is not within the boundaries of any county). The tourism industry remains Nevada's largest employer,[14] with mining continuing as a substantial sector of the economy: Nevada is the fourth-largest producer of gold in the world. [15]
Le Nevada /n̪e.va.d̪a/2 (en anglais : /nəˈvædə/3 ou /nəˈvɑdə/ ; en espagnol : /neˈβaða/4) est un État de l'Ouest des États-Unis, bordé à l'ouest et au sud-ouest par la Californie, au nord par l'Oregon et l'Idaho, et à l'est par l'Utah et au sud-est par l'Arizona.
Il Nevada (in inglese: , /nəˈvædə/) è uno Stato federato situato negli Stati Uniti occidentali. Viene collocato tradizionalmente nella regione del sudovest e talvolta in quella delle Montagne Rocciose degli Stati Uniti d'America. Lo Stato è il 7° più ampio, il 35° più popoloso, e il 9° meno densamente popolato dei 50 stati degli Stati Uniti. Quasi tre quarti delle persone del Nevada vivono nella Contea di Clark, che contiene l'area metropolitana di Las Vegas-Paradise in cui si trovano le tre più grandi città dello Stato fuse insieme. La capitale del Nevada è Carson City. Lo Stato è ufficialmente conosciuto come The Silver State ("Lo Stato d'argento") e il motto è All for our Country ("Tutto per il nostro Paese").
Il Nevada è in gran parte desertico e semiarido, trovandosi quasi interamente all'interno del Gran Bacino. Le aree a sud di esso si trovano all'interno del deserto del Mojave, mentre il Lago Tahoe e la Sierra Nevada si trovano sul confine occidentale. Circa l'86% del territorio dello Stato è gestito da varie giurisdizioni del governo federale degli Stati Uniti, sia civili che militari.
"Nevada" è un aggettivo che in spagnolo significa innevato, coperto di neve. Il nome deriva dalla catena montuosa della Sierra Nevada nell'ovest dello Stato. Gli abitanti di questo Stato si chiamano "nevadani" (Nevadans). Prima del contatto con gli europei, il territorio che oggi comprende lo Stato era abitato dai nativi americani delle tribù dei Paiute, Shoshone, e Washoe. Lo Stato faceva parte del Vicereame della Nuova Spagna, diventato in seguito Messico nel 1821 (anno dell'indipendenza messicana). Gli Stati Uniti ottennero il territorio nel 1848 dopo la vittoria nella Guerra messicano-americana e l'area fu poi incorporata come parte del Territorio dello Utah nel 1850. La scoperta del filone d'argento di Comstock nel 1859 portò ad un boom demografico che determinò la creazione del Territorio del Nevada, separato dalla parte occidentale del Territorio dello Utah nel 1861. Il 31 ottobre 1864 il Nevada divenne il 36º Stato dell'unione.
Il Nevada è noto per le sue leggi libertarie. Con una popolazione di poco più di 40.000 persone, il Nevada era di gran lunga lo Stato meno popolato nel 1900. Tuttavia, la legalizzazione del gioco d'azzardo ed i veloci procedimenti di matrimonio e divorzio nel XX secolo trasformarono il Nevada in un'importante destinazione turistica. Lo Stato è l'unico in cui la prostituzione è legale in 12 contee, escluse quelle di Clark e di Washoe, comprendenti rispettivamente Las Vegas e Reno, nonché a Carson City. L'industria del turismo rimane la più grande fonte di occupazione e guadagno del Nevada, con il settore minerario che continua ad essere un settore particolarmente rilevante nell'economia locale, facendo del Nevada il quarto più grande produttore di oro al mondo.
Nevada es uno de los cincuenta estados que, junto con Washington D. C., forman los Estados Unidos de América. Su capital es Carson City y su mayor ciudad es Las Vegas, famosa por sus casinos y la legalización del juego. Está ubicado en la región Oeste del país, división Montañas Rocosas. Limita al noroeste con Oregón, al noreste con Idaho, al este con Utah, al sureste con Arizona (parte de esta frontera la forma el río Colorado) y al oeste y suroeste con California. Con 286 351 km² es el séptimo estado más extenso —por detrás de Alaska, Texas, California, Montana, Nuevo México y Arizona— y con 9,43 hab/km² es el noveno menos densamente poblado, por delante de Nebraska, Idaho, Nuevo México, Dakota del Sur, Dakota del Norte, Montana, Wyoming y Alaska, el menos densamente poblado. Fue admitido en la Unión el 31 de octubre de 1864, como el estado número 36, en plena Guerra de Secesión; ello le ha valido el apodo de El estado nacido en la batalla.
Nevada posee las mayores tasas de crecimiento demográfico —66,3% entre 1990 y 2000— de todo Estados Unidos, en gran medida gracias a la gran inmigración de mexicanos. No obstante, la mayor parte de Nevada está casi despoblada. La mayoría de la población del estado se concentra en los núcleos urbanos de Las Vegas, Henderson y Reno.
Los primeros exploradores europeos en explorar la zona de Nevada fueron los españoles, quienes le dieron el nombre de Nevada, a causa de la nieve que cubría los montes en invierno. Fue parte del Virreinato de Nueva España hasta 1821, fecha de la independencia de México, pasando a formar parte de México. En 1848, con el final de la Guerra entre México y Estados Unidos, pasa a formar parte de Estados Unidos.
Durante la década de 1870 se encontraron en Nevada grandes yacimientos de plata, lo que le valió el apodo de The Silver State. Actualmente, la minería aún posee cierta importancia en su economía, aunque mucho menos que antaño. Además de plata, es un gran productor de oro, petróleo y arena. Sin embargo, en la actualidad la mayor fuente de ingresos es el turismo (Las Vegas y Reno)
Нева́да[1][2] (англ. State of Nevada, (IPA: /nɨˈvæːdə/)) — штат[3] в западной части США. Столица штата — город Карсон-Сити, самый большой город — Лас-Вегас.
Невада вошла в состав США во время Гражданской войны между южными и северными штатами. Слово Невада переводится с испанского языка как «заснеженный» и происходит от названия гор Сьерра-Невада («заснеженные горы»). «Штат, рождённый в боях» (англ. The Battle Born State) — официальный слоган Невады. На флаге штата присутствует надпись «Рождённый в боях» (англ. Battle Born).
В честь штата был назван тип линейных кораблей ВМС США, а также первый корабль в этой серии.
 Alaska-AK
Alaska-AK

 Florida-FL
Florida-FL
 No personal income tax
No personal income tax

 Nevada-NV
Nevada-NV

 South Dakota-SD
South Dakota-SD

 Texas-TX
Texas-TX

 Washington-WA
Washington-WA

 Wyoming-WY
Wyoming-WY

 Geography
Geography
 Economy and trade
Economy and trade