
Deutsch-Chinesische Enzyklopädie, 德汉百科
 Important port
Important port



 Financial
Financial
 M 1500 - 2000 AD
M 1500 - 2000 AD

 Financial
Financial
 ***Global Financial Center
***Global Financial Center

 Geography
Geography

 Geography
Geography
 *World's Most Livable Cities
*World's Most Livable Cities

 History
History
 N 2000 - 2100 AD
N 2000 - 2100 AD

 History
History
 M 1500 - 2000 AD
M 1500 - 2000 AD

 International cities
International cities
 ***Global Urban Economic Competitiveness
***Global Urban Economic Competitiveness
 Japan
Japan
 Kantō
Kantō
 Olympic Summer Games
Olympic Summer Games
 1964 Summer Olympics
1964 Summer Olympics
 2020 Summer Olympics
2020 Summer Olympics
 Silk road
Silk road

 Important port
Important port

东京(日语:東京/とうきょう Tōkyō)是位于日本关东地方的都市,狭义上指东京都、或东京都区部(即东京市区),亦可泛指东京都及周边卫星都市群相连而成的“首都圈”(东京都会区)。目前(2017年8月)东京都区部人口数达946万,首都圈的人口数则达3千6百万,是目前全球规模最大的都会区[1],亦为亚洲最重要的世界级城市。东京是传统上的全球四大世界级城市[2]之一,在2016年GDP达9472.7亿美元,超越纽约(9006.8亿)成为全球第一,同时全球城市指数排名中排名第三。
东京古称江户,自德川幕府时代以来开始成为日本主要都市之一,明治维新时期改为现名后,更发展为日本政治、经济、文化、交通等众多领域的枢纽中心。经过二战后的继续发展,东京不仅成为世界商业金融、流行文化与时尚重镇,亦为世界经济发展度与富裕程度最高的都市之一。此外,东京还有目前全球最复杂、最密集的城市轨道交通系统,其中单就计算东京的地铁系统管辖区段每日平均运量达880万人次,繁忙程度居全球地铁第三位(如含地铁直通运转路线、私铁通勤路线及JR东日本通勤路线,则每日平均运量位居世界城市轨道交通运输系统第一位)。
在正式的行政区划定义上,东京仅限于东京都,与道、府、县同为日本的一级行政区,辖区包含东京都区部、多摩地方与伊豆群岛、小笠原群岛等离岛;其中,东京都区部为日本中央政府所在地。东京都同时也囊括了日本最南端(冲之鸟礁)和最东端(南鸟岛)等地理极点,拥有日本各都道府县中最多的人口数,同时也是日本人口密度最高的都道府县。
Tokio (auch Tokyo, japanisch 東京 Tōkyō  [to̞ːkjo̞ː]) ist eine Weltstadt[3] in der Kantō-Region im Osten der japanischen Hauptinsel Honshū. Mit 9.508.776 Einwohnern ist sie nicht nur die bevölkerungsreichste Metropole des Landes, sondern als Sitz der japanischen Regierung und des Tennō auch die Hauptstadt Japans. Sie umfasst die 23 Bezirke auf dem Gebiet der 1943 als Verwaltungseinheit abgeschafften Stadt Tokio und ist damit keine eigene Gebietskörperschaft mehr; stattdessen bilden die Bezirke zusammen mit den Städten und Gemeinden der westlich gelegenen Tama-Region und den südlichen Izu- und Ogasawara-Inseln die Präfektur Tokio. Diese bildet wiederum das Zentrum der Metropolregion Tokio-Yokohama, in der mehr als 37 Millionen Menschen leben (Stand 2014), was die Region zum größten Ballungsraum der Welt macht.
[to̞ːkjo̞ː]) ist eine Weltstadt[3] in der Kantō-Region im Osten der japanischen Hauptinsel Honshū. Mit 9.508.776 Einwohnern ist sie nicht nur die bevölkerungsreichste Metropole des Landes, sondern als Sitz der japanischen Regierung und des Tennō auch die Hauptstadt Japans. Sie umfasst die 23 Bezirke auf dem Gebiet der 1943 als Verwaltungseinheit abgeschafften Stadt Tokio und ist damit keine eigene Gebietskörperschaft mehr; stattdessen bilden die Bezirke zusammen mit den Städten und Gemeinden der westlich gelegenen Tama-Region und den südlichen Izu- und Ogasawara-Inseln die Präfektur Tokio. Diese bildet wiederum das Zentrum der Metropolregion Tokio-Yokohama, in der mehr als 37 Millionen Menschen leben (Stand 2014), was die Region zum größten Ballungsraum der Welt macht.
Die Stadtgeschichte beginnt im Jahr 1446, als Ōta Dōkan in einem Sumpfgebiet am Nordufer der heutigen Bucht von Tokio mit dem Bau der Burg Edo begann, umgeben von einigen Fischerdörfern. 1590 ging diese Burg an Tokugawa Ieyasu, der hier nach seinem Sieg in der Schlacht von Sekigahara sein neues Shōgunat und damit die Edo-Zeit begründete. Edo wurde neben Kyōto zum politischen und kulturellen Zentrum des Landes. Mit der Meiji-Restauration 1868 wurde das Shōgunat abgeschafft und der Sitz des Tennō nach Edo verlegt, die Burg wurde zum Kaiserpalast und Edo bekam seinen neuen Namen Tokio, der „Östliche Hauptstadt“ bedeutet. Von da an wuchs auch die Bevölkerung der Stadt, die bereits um 1910 mit rund zwei Millionen Einwohnern zu den größten der Welt zählte. Im Zweiten Weltkrieg war Tokio zahlreichen Luftangriffen durch die USA ausgesetzt, bei denen rund die Hälfte der Stadtfläche zerstört wurde. Nach dem Ende der amerikanischen Besatzungszeit folgte ein rasanter wirtschaftlicher Aufschwung, einhergehend mit einem erneuten Bevölkerungszuwachs.
Tokio ist heute das Industrie-, Handels-, Bildungs- und Kulturzentrum Japans mit zahlreichen Universitäten, Hochschulen, Forschungsinstituten, Theatern und Museen. Mit den Flughäfen Narita und Haneda und als Ausgangspunkt der meisten Shinkansen-Linien ist es auch das Verkehrszentrum des Landes. Der Finanzplatz Tokio ist nicht nur der größte Japans, sondern zählt neben London, New York und Hongkong auch zu den fünf größten der Welt. Zudem weist die Stadt ein hohes Preisniveau auf und lag in einer Studie 2014 auf Platz 9 der teuersten Städte weltweit.[4][5] Neben modernen Sehenswürdigkeiten wie dem Tokyo Tower oder Tokyo Skytree bietet sie auch historische Anlagen wie die Kaiserlichen Gärten in Chiyoda, den Ueno-Park oder den Asakusa-Kannon-Tempel. In den vergangenen Jahren wurde Tokio zu einem zunehmend beliebten Tourismusziel und befindet sich mit jährlich bis zu acht Millionen Besuchern aus dem Ausland unter den 20 meistbesuchten Städten.[6] In einer Rangliste der Städte nach ihrer Lebensqualität belegte Tokio im Jahre 2018 den 50. Platz unter 231 untersuchten Städten weltweit.[7]
東京(とうきょう、英: Tokyo)は、日本の関東平野中央部に位置し、東京湾に面する都市。日本の首都である[1][注 1]。現在、その域内には23特別区・26市・5町・8村の基礎自治体がある[2]。
日本における政治・経済・文化の中心である。政治面では、日本政府が本拠地としている。立法府である国会の議事堂、司法府の頂点である最高裁判所、行政府の長である内閣総理大臣の官邸、中央省庁街(「霞が関」)などは、いずれも東京の中心部である東京23区にある。経済面では、日本の株式上場企業の本社のほとんどが東京に集中し、(東京圏では)購買力平価(PPP)を基にしても東京都市圏のGDPは1兆5369億ドル(2014年)であり[3]、世界的な経済都市であり、大消費地でもある。文化面では、たとえば現在では(東京都内に)千数百におよぶ劇場・ホール・ライブハウス類があり[4]多数のアーティストたちが活動する場であり、ポップカルチャーなどの新しい文化の発信地でもあり、ミシュランガイドの星つきの飲食店の数は世界最多で[5]食文化が華開いている場所でもある。
東京には、日本国内からだけでなく近隣の様々な国や世界各国から外国人が観光に訪れるようになった他、東京に移住した外国人が移民街を形成している。関東大震災や東京大空襲で焼け野原となったが、戦後の発展により現在は世界最大級のメトロポリス・世界都市となっている。東京は明治期にも課題が山積みの都市であったが(#明治維新後の課題と都市政策を参照)、現在もさまざまな課題を抱えている都市である(#近年の東京が都市としてかかえる課題を参照)。 東京都(とうきょうと、英: Tokyo Metropolis)は、日本の首都[注 1]。関東地方に位置する広域地方公共団体(都道府県)のひとつ。都庁所在地は新宿区[注 2]。最大の都市は世田谷区[注 3]。 管轄する領域は東京都区部(東京23区)、多摩地域(26市[注 4]と西多摩郡3町1村)および東京都島嶼部(大島、三宅、八丈、小笠原)の4支庁(2町7村)からなっている。東京都区部(東京23区)は、一つの都市として「東京」とも呼ばれる。沖ノ鳥島、南鳥島を含む小笠原諸島を含むため、日本最南端および最東端に位置する都道府県でもある。都公認の「東京都」の英語表記はTokyo Metropolis(Tokyo Met.)。他には Tokyo Prefecture と Tokyo Metropolitan Prefecture がある。
Tokyo (東京 Tōkyō, /ˈtoʊkioʊ/;[7] Japanese: [toːkʲoː] ( listen)), officially Tokyo Metropolis (東京都 Tōkyō-to), is one of the 47 prefectures of Japan and has been the capital since 1869.[8][9] The Greater Tokyo Area is the most populous metropolitan area in the world.[10] It is the seat of the Emperor of Japan, the Japanese government and the National Diet. Tokyo is in the Kantō region on the southeastern side of the main island Honshu and includes the Izu Islands and Ogasawara Islands.[11] Tokyo was formerly named Edo when Shōgun Tokugawa Ieyasu made the city as his headquarters in 1603. It became the capital after Emperor Meiji moved his seat to the city from Kyoto in 1868; at that time Edo was renamed Tokyo. Tokyo Metropolis was formed in 1943 from the merger of the former Tokyo Prefecture (東京府 Tōkyō-fu) and the city of Tokyo (東京市 Tōkyō-shi).
listen)), officially Tokyo Metropolis (東京都 Tōkyō-to), is one of the 47 prefectures of Japan and has been the capital since 1869.[8][9] The Greater Tokyo Area is the most populous metropolitan area in the world.[10] It is the seat of the Emperor of Japan, the Japanese government and the National Diet. Tokyo is in the Kantō region on the southeastern side of the main island Honshu and includes the Izu Islands and Ogasawara Islands.[11] Tokyo was formerly named Edo when Shōgun Tokugawa Ieyasu made the city as his headquarters in 1603. It became the capital after Emperor Meiji moved his seat to the city from Kyoto in 1868; at that time Edo was renamed Tokyo. Tokyo Metropolis was formed in 1943 from the merger of the former Tokyo Prefecture (東京府 Tōkyō-fu) and the city of Tokyo (東京市 Tōkyō-shi).
Tokyo has 39 million residents, 50% more people than any other urban area, with a $2.5 trillion economy larger than that of any other city; if it were a country, Tokyo would be the 8th largest economy in the world. Tokyo is often referred to as a city, but is officially known and governed as a "metropolitan prefecture", which differs from and combines elements of a city and a prefecture, a characteristic unique to Tokyo. The Tokyo Metropolitan Government administers the 23 Special Wards of Tokyo (each governed as an individual city), which cover the area that was the city of Tokyo before it merged and became the metropolitan prefecture in 1943, the 30 municipalities in the western part of the prefecture, and the two outlying island chains. The population of the special wards is over 9 million people, with the total population of the prefecture exceeding 13 million. The prefecture is part of the world's most populous metropolitan area with upwards of 37.8 million people and the world's largest urban agglomeration economy. In 2011, the city hosted 51 of the Fortune Global 500 companies, the highest number of any city in the world at that time.[12] Tokyo ranked third (twice) in the International Financial Centres Development Index. The city is also home to various television networks such as Fuji TV, Tokyo MX, TV Tokyo, TV Asahi, Nippon Television, NHK and the Tokyo Broadcasting System.
Tokyo is ranked first in the Global Economic Power Index and third in the Global Cities Index. The city is considered an alpha+ world city – as listed by the GaWC's 2008 inventory[13] – and in 2014, Tokyo was ranked first in the "Best overall experience" category of TripAdvisor's World City Survey (the city also ranked first in the following categories: "helpfulness of locals", "nightlife", "shopping", "local public transportation" and "cleanliness of streets").[14] In 2015, Tokyo was ranked as the 11th most expensive city for expatriates, according to the Mercer consulting firm,[15] and also the world's 11th most expensive city, according to the Economist Intelligence Unit's cost-of-living survey.[16] In 2015, Tokyo was named the Most Liveable City in the world by the magazine Monocle.[17] The Michelin Guide has awarded Tokyo by far the most Michelin stars of any city in the world.[18][19] Tokyo was ranked first out of all sixty cities in the 2017 Safe Cities Index.[20] The QS Best Student Cities ranked Tokyo as the 3rd-best city in the world to be a university student in 2016[21] and 2nd in 2018.[22] Tokyo hosted the 1964 Summer Olympics, the 1979 G-7 summit, the 1986 G-7 summit, and the 1993 G-7 summit, and will host the 2019 Rugby World Cup, the 2020 Summer Olympics and the 2020 Summer Paralympics.
Tokyo (東京(とうきょう), Tōkyō?, littéralement « Capitale de l'est »), anciennement Edo (江戸(えど)?), officiellement la préfecture métropolitaine de Tokyo (東京都(とうきょうと), Tōkyō-to?), est la capitale actuelle du Japon. Elle est la plus peuplée des préfectures du Japon, avec plus de 13 831 421 habitants intra-muros en 2018 et 42 794 714 dans l'agglomération2, et forme l'aire urbaine la plus peuplée au monde. Située sur la côte est de l'île principale de l'archipel japonais, Honshū, Tokyo est l'une des quarante-sept préfectures du Japon. Principal centre politique de l'archipel depuis le XVIIe siècle, la ville accueille la plupart des institutions du pays : la résidence de l'empereur du Japon, du Premier ministre, le siège de la Diète (le parlement japonais), du Cabinet, les ministères qui le constituent ainsi que toutes les ambassades étrangères.
À l'origine, Tokyo était un petit village de pêcheurs nommé Edo (« l'estuaire »). Fortifié au XVe siècle, Edo devient la base militaire du shogun Tokugawa Ieyasu à la fin du XVIe siècle, puis la capitale de son gouvernement. Durant l’époque d'Edo (1603-1868), la ville se développe et devient l'une des plus peuplées au monde à la fin du XVIIIe siècle, avec une population de près d'un million d'habitants. Avec la restauration de l'Empire en 1868, elle est confortée dans son rôle de cœur politique du Japon : le château d'Edo devient la résidence de l'empereur Meiji (Kōkyo), et la ville acquiert son nom actuel par opposition à Kyoto, l'ancienne capitale. Elle est ravagée en 1923 par un séisme de magnitude 7,9 qui fait plus de 100 000 morts. Durant la Seconde Guerre mondiale, elle est détruite pour moitié par des bombardements aériens américains, mais est rapidement reconstruite. Dans la seconde moitié du XXe siècle, Tokyo devient une métropole de rang mondial grâce à un fort développement industriel — notamment dans l'électronique —, et voit sa population multipliée par dix en cinquante ans.
Principal centre économique et financier du Japon, Tokyo est l'une des principales places financières asiatiques et mondiales. Elle est la première ville mondiale en termes de produits urbains bruts. Le dynamique arrondissement de Shinjuku comporte de nombreux gratte-ciels, dont la mairie de la ville, et plusieurs grands magasins du Japon. Minato-ku accueille les sièges sociaux de nombreuses entreprises japonaises et étrangères, ainsi qu'une cinquantaine d'ambassades. Chiyoda concentre quant à lui les institutions politiques japonaises. Enfin, Shibuya est réputé être l'un des quartiers les plus animés de la ville, grâce à la présence de grands centres commerciaux comme le 109. Malgré la modernité de son architecture, dont témoigne la tour Tokyo Skytree, de nombreux sanctuaires shinto et temples bouddhistes ont été préservés ou reconstruits après les bombardements, comme le Sensō-ji, le sanctuaire Yasukuni, le Zōjō-ji ou les portes Hōzōmon.
Située au fond de la baie de Tokyo, la commune de Tokyo dispose d'un statut administratif particulier parmi les préfectures du Japon, la ville de Tokyo ayant été supprimée en tant qu'entité politique ou administrative en 1943. L'agglomération de Tokyo, qui s'étend bien au-delà des limites de la préfecture, s'étend sur une large frange de la baie de Tokyo ainsi que sur la région du Kantō. Elle constitue en outre un des pôles de la mégalopole japonaise, avec notamment Ōsaka et Nagoya. La préfecture a organisé les Jeux olympiques d'été de 1964, et les accueillera à nouveau en 2020.
Tokio (東京都 Tōkyō-to?, lit. ‘capital del este’; pronunciación japonesa:  [toːkʲoː] (?·i)) es la capital de facto6 de Japón, localizada en el centro-este de la isla de Honshu, concretamente en la región de Kanto. En conjunto forma una de las 47 prefecturas de Japón, aunque su denominación oficial es metrópolis o capital (都 -to). La ciudad es el centro de la política, economía, educación, comunicación y cultura popular del país. Cuenta también con la mayor concentración de sedes corporativas, instituciones financieras, universidades y colegios, museos, teatros, y establecimientos comerciales y de entretenimiento de todo Japón.
[toːkʲoː] (?·i)) es la capital de facto6 de Japón, localizada en el centro-este de la isla de Honshu, concretamente en la región de Kanto. En conjunto forma una de las 47 prefecturas de Japón, aunque su denominación oficial es metrópolis o capital (都 -to). La ciudad es el centro de la política, economía, educación, comunicación y cultura popular del país. Cuenta también con la mayor concentración de sedes corporativas, instituciones financieras, universidades y colegios, museos, teatros, y establecimientos comerciales y de entretenimiento de todo Japón.
Con una población que supera los 13 millones de habitantes, se subdivide en 23 barrios (区 -ku); 26 ciudades (市 -shi); un distrito (郡 -gun) subdividido en tres pueblos (町 -chō o -machi) y una villa (村 -son o -mura); y cuatro subprefecturas (支庁 -shichō) subdivididas en dos pueblos y siete villas, que representan a varias pequeñas islas al sur de Honshu que se extienden más allá de 1800 km de Shinjuku, capital de la metrópoli y sede de la gobernación. El centro de Tokio, con sus 23 barrios, ocupa un tercio de la metrópoli, con una población cercana a los 13,23 millones de habitantes; esta área es lo que se conoce internacionalmente como la ciudad de Tokio. En su área metropolitana viven más de 37 millones de habitantes, lo que la convierte en la mayor aglomeración urbana del mundo.
A pesar de que Tokyo es la romanización más común del nombre en japonés, el nombre de la ciudad es Tokio en español y otros idiomas —entre ellos el alemán y el neerlandés—. En inglés y otros idiomas se escribe Tokyo, aunque antiguamente también se escribía Tokio. En el pasado, la ciudad se denominaba como Tokei, Edo o Yedo. El gentilicio de Tokio es tokiota.
Tokio fue sede de los Juegos Olímpicos de 1964 y será sede de los Juegos Olímpicos de 2020.7
То́кио (яп. 東京 То:кё: (инф.), «Восточная столица»[4][5]) — столица Японии, её административный, финансовый, промышленный и политический центр. Крупнейшая городская экономика мира[6]. Расположен в юго-восточной части острова Хонсю, на равнине Канто в бухте Токийского залива Тихого океана.
Помимо столицы, Токио также является одной из сорока семи префектур страны. Площадь префектуры составляет 2188,67 км²[7], население — 13 742 906 человек (1 октября 2017)[8], плотность населения — 6279,11 чел./км². По состоянию на 1 мая 2020 года население Токио составляло 14 002 973 человека, что делает Токио префектурой с самым большим населением в Японии.[9] Большой Токио является городской территорией с самым большим населением в мире, с населением по состоянию на 2016 год в 38 140 000 человек.[2]
Токийский столичный округ — административная единица Японии, включающая в себя специальные районы Токио, область Тама и островные территории Токийского столичного округа (острова Идзу и Огасавара).


多伦多[注 1](英语:Toronto)是加拿大安大略省首府,也是加拿大最大的城市,坐落在安大略湖西北岸的南安大略地区。根据2021年的加拿大人口普查,多伦多市人口达2,794,356人,为加拿大最大城市。多伦多市是大多伦多地区的核心地区,也是安大略省南部人口稠密区(称作“金马蹄地区”)的一部分。[9][10][11]都会区有6,202,225名居民,[12]而覆盖范围较广的大多伦多地区则有9,765,188名居民。[10]作为加拿大的经济中心,多伦多是一个世界级城市,[13]也是世界上最大的金融中心之一。[14][15]多伦多在经济上的领先地位在于金融、商业服务、电信、航太、交通运输、媒体、艺术、电影、电视制作、出版、软件、医药研究、教育、旅游、体育等产业。[16][17]多伦多证券交易所是世界第七大交易所,总部设于市内,有多数加拿大公司在这里上市。
多伦多的国际性人口[18]体现出它是前往加拿大移民的重要落脚点。[19]而市内49%的人口是在加拿大以外诞生[20],也造就多伦多成为世上种族最多样化的城市之一。目前多伦多的低犯罪率、洁净的环境、高生活水准、以及对多样文化的包容性,令该市被多个经济学智囊团列为世界上最宜居的城市之一。[21][22]另一方面,多伦多于2006年被列为加拿大生活成本最高的城市。
多伦多(英语/法语:Toronto),是北美洲国家加拿大安大略省首府,加拿大的最大城市。
多伦多坐落在安大略湖西北岸的南安大略地区。根据2012年七月的加拿大人口普查,多伦市人口达2,790,060,为加拿大最大城市。多伦多市是大多伦多地区的心脏地区,也是安大略省南部人口稠密区(称作“金马蹄地区”)的一部分。[1][2][3]城市区有5,132,794名居民。[4]在2011年人口普查中,多伦多人口普查区有5,583,064名居民,而覆盖范围较广的大多伦多地区则有6,054,191名居民。[2]
作为加拿大的经济中心,多伦多是一个世界级城市,[5]也是世界上最大的金融中心之一。[6][7] 多伦多在经济上的领先地位在于金融、商业服务、电信、航太、交通运输、媒体、艺术、电影、电视制作、出版、软件、医药研究、教育、旅游、体育等产业。[8][9]多伦多证券交易所是世界第七大交易所,总部设于市内,有多数加拿大公司在这里上市。
多伦多的国际性人口[10] 体现出它是前往加拿大移民的重要落脚点。[11]而市内49%的人口是在加拿大以外诞生[12],也造就多伦多成为世上种族最多样化的城市之一。目前多伦多的低犯罪率、洁净的环境、高生活水准、以及对多样文化的包容性,令该市被多个经济学智囊团列为世界上最宜居的城市之一。[13][14]另一方面,多伦多于2006年被列为加拿大生活成本最高的城市。[15]
大约1/3的加拿大人居住在距多伦多两小时车程的郊区。加拿大大约1/6的就业机会在该市。
多伦多当地的华侨及华裔人口多达四十万,相当于加拿大全国约百分之一的人口,该城市也是加拿大华人最多的城市。除此之外也有大量世界各地的移民,加拿大安大略省多伦多市的人口统计资料使多伦多成为世界上最多元文化和多种族的城市之一。2016年,该市居民的51.5%属于明显的少数族裔,而2011年这一比例为49.1%,和1981年为13.6%。多伦多还建立了多个社区,例如唐人街,意大利的Corso,小意大利,小印度,希腊城,韩国城,小牙买加,小葡萄牙和朗塞瓦勒,以庆祝该市的多元文化主义的成功。
Toronto (englische Aussprache [təˈɹɒn(t)oʊ̯]; regional auch  [təˈɹɒnə] oder [ˈtɹɒnoʊ̯]) ist mit 2,6 Millionen Einwohnern[2] die größte Stadt Kanadas und die Hauptstadt der Provinz Ontario. Sie liegt im Golden Horseshoe (Goldenes Hufeisen), einer Region mit über 8,1 Millionen Einwohnern, die sich halbkreisförmig um das westliche Ende des Ontariosees bis zu den Niagarafällen erstreckt. Rund ein Drittel der Bevölkerungszunahme des ganzen Landes lebte in den letzten Jahren in diesem Großraum. Die Einwohnerzahl der Metropolregion (Census Metropolitan Area) stieg von 4,1 Millionen im Jahr 1992 auf 5,6 Millionen im Jahr 2011.[3] Die Greater Toronto Area hatte 2010 über 6,2 Millionen Einwohner.[4]
[təˈɹɒnə] oder [ˈtɹɒnoʊ̯]) ist mit 2,6 Millionen Einwohnern[2] die größte Stadt Kanadas und die Hauptstadt der Provinz Ontario. Sie liegt im Golden Horseshoe (Goldenes Hufeisen), einer Region mit über 8,1 Millionen Einwohnern, die sich halbkreisförmig um das westliche Ende des Ontariosees bis zu den Niagarafällen erstreckt. Rund ein Drittel der Bevölkerungszunahme des ganzen Landes lebte in den letzten Jahren in diesem Großraum. Die Einwohnerzahl der Metropolregion (Census Metropolitan Area) stieg von 4,1 Millionen im Jahr 1992 auf 5,6 Millionen im Jahr 2011.[3] Die Greater Toronto Area hatte 2010 über 6,2 Millionen Einwohner.[4]
Die Stadt liegt am nordwestlichen Ufer des Ontariosees, dem mit 18.960 km² Fläche[5] kleinsten der fünf Großen Seen. Durch die Eingemeindung einer Reihe von Vorstädten, die bereits mit Toronto verschmolzen waren (Etobicoke, Scarborough, York, East York und North York), wurde Toronto Ende der 1990er Jahre mehrfach vergrößert. Das Zentrum mit dem Einkaufs- und Bankendistrikt befindet sich in der Nähe des Sees. Die Haupteinkaufsstraße ist die Yonge Street. Toronto ist seit ungefähr den 1970er Jahren, nachdem Montreal über Jahrzehnte hinweg diese Rolle zugefallen war, Kanadas Wirtschaftszentrum und weltweit einer der führenden Finanzplätze.
トロント(英語: Toronto、標準音:[təˈɹɒntoʊ]、現地音:[ˈtɹɒnoʊ, təˈɹɒnoʊ])は、カナダのオンタリオ州の州都であり、同国最大の都市である。オンタリオ湖岸の北西に位置し、2016年の統計で人口273万人[1]。
国際影響力の強い世界都市であり、2016年の都市圏人口は624万人[2]。またヒューロン語で「集まる場所」という意味がある。
オンタリオ湖西岸を囲むゴールデン・ホースシュー(Golden Horseshoe)と呼ばれる都市化された地域の人口はおよそ924万人とされ、カナダ随一の金融センターとしてその中心を成している。1834年までの旧名はヨーク(Town of York)。
Toronto is the provincial capital of Ontario and the most populous city in Canada, with an estimated population of 2,956,024 (2018) and an estimated population of 6,341,935 in the Toronto Region (2018.)[14] Located on the shores of the western end of Lake Ontario, Toronto is also the anchor of the Golden Horseshoe, an urban agglomeration of 9,245,438 (2016)[15] that accounts for a significant portion of Canada's economic activity and more than 20% of Canada's population. Toronto is an international centre of business, finance, arts, and culture. Its large population of immigrants from around the globe has also made Toronto one of the most multicultural and cosmopolitan cities in the world.[16][17][18]
People have travelled through and inhabited the Toronto area, located on a broad sloping plateau interspersed with rivers, deep ravines, and urban forest, for more than 10,000 years.[19] After the broadly disputed Toronto Purchase, when the Mississauga surrendered the area to the British Crown,[20] the British established the town of York in 1793 and later designated it as the capital of Upper Canada.[21] During the War of 1812, the town was the site of the Battle of York and suffered heavy damage by American troops.[22] York was renamed and incorporated in 1834 as the city of Toronto. It was designated as the capital of the province of Ontario in 1867 during Canadian Confederation.[23] The city proper has since expanded past its original borders through both annexation and amalgamation to its current area of 630.2 km2 (243.3 sq mi).
The diverse population of Toronto reflects its current and historical role as an important destination for immigrants to Canada.[24][25] More than 50 percent of residents belong to a visible minority population group,[26] and over 200 distinct ethnic origins are represented among its inhabitants.[27] While the majority of Torontonians speak English as their primary language, over 160 languages are spoken in the city.[28]
Toronto is a prominent centre for music,[29] theatre,[30] motion picture production,[31] and television production,[32] and is home to the headquarters of Canada's major national broadcast networks and media outlets.[33] Its varied cultural institutions,[34] which include numerous museums and galleries, festivals and public events, entertainment districts, national historic sites, and sports activities,[35] attract over 43 million tourists each year.[36][37] Toronto is known for its many skyscrapers and high-rise buildings,[38] in particular the tallest free-standing structure in the Western Hemisphere, the CN Tower.[39]
The city is home to the Toronto Stock Exchange, the headquarters of Canada's five largest banks,[40] and the headquarters of many large Canadian and multinational corporations.[41] Its economy is highly diversified with strengths in technology, design, financial services, life sciences, education, arts, fashion, aerospace, environmental innovation, food services, and tourism.[42][43][44]
Toronto (/tɔ.ʁɔ̃.to/1 ; en anglais : /təˈɹɒntoʊ̯/2 Écouter voire localement /təˈɹɒnə/ ou /ˈtɹɒnoʊ̯/ Écouter) est la plus peuplée des villes du Canada et la capitale de la province de l'Ontario. Elle se situe dans le Sud-Est du Canada, sur la rive nord-ouest du lac Ontario. Selon le recensement de 2016, Toronto compte plus de 2,7 millions d'habitants, faisant d'elle la quatrième ville la plus peuplée en Amérique du Nord. Son aire métropolitaine compte 5,9 millions d'habitants, et la mégalopole du Golden Horseshoe, dont elle est le cœur, plus de 8,7 millions d'habitants en 2011, soit le quart de la population canadienne. Ville mondiale, Toronto est le centre bancaire, financier, commercial et artistique du Canada anglophone, et l'une des villes les plus multiculturelles et cosmopolites au monde.
La région de Toronto, située sur un vaste plateau en pente jalonné de rivières, de ravins et de forêts, est habitée depuis plus de 10 000 ans. Après la brève installation d'un fort par les Français puis l’achat contesté de la région au peuple Mississauga par la Couronne britannique, les colons anglais fondent en 1793 la ville d'York, qui devient la capitale du Haut-Canada. Pendant la guerre de 1812, la ville est le théâtre de la bataille d'York et subit de lourds dégâts par les troupes américaines. York est renommée Toronto en 1834. Elle est désignée capitale de la province de l'Ontario en 1867 par la Confédération canadienne. La ville s'est depuis étendue au-delà de ses frontières d'origine, à la suite de plusieurs fusions, jusqu'à atteindre la superficie actuelle de 630,2 km2.
La population particulièrement cosmopolite de Toronto reflète son rôle historique de destination des immigrants au Canada. Plus de 50 % des résidents appartiennent à un groupe de minorités visibles et plus de 200 origines ethniques distinctes sont représentées parmi ses habitants. Bien que la majorité des Torontois parlent l'anglais principalement, plus de 160 langues sont parlées dans la ville.
Toronto est devenu un important centre de musique, théâtre, de production cinématographique et télévisuelle. Elle abrite le siège des principaux réseaux de diffusion et des médias nationaux du Canada. Ses institutions culturelles variées, qui comprennent de nombreux musées et galeries d'art, des festivals et événements publics, des quartiers de divertissement, des lieux historiques nationaux et des activités sportives, attirent plus de 25 millions de touristes chaque année. Toronto est connue pour ses nombreux gratte-ciel, en particulier la plus haute structure autoportante de l' hémisphère occidental, la tour CN.
La ville abrite la Bourse de Toronto, le siège des cinq plus grandes banques du Canada et de nombreuses autres grandes sociétés canadiennes et multinationales, de tous les secteurs économiques. Elle abrite aussi de nombreux établissements d'enseignement supérieur réputés, dont l'université de Toronto qui figure parmi les plus réputées au monde.
Toronto apparaît régulièrement dans les classements des meilleures villes en termes de qualité de vie, malgré un coût de la vie important. Ses habitants s'appellent les Torontois.
Toronto (IPA: [təˈɹɒntoʊ̯]; pronuncia locale: [ˈtrɒnoʊ] oppure [təˈɹɒnə], ascolta[?·info]) è una città dell'estremo Sud-Est del Canada, capoluogo della provincia dell'Ontario e centro più popoloso del Canada con i suoi 3 120 668 abitanti[1] (5 928 040 nell'area metropolitana[2]).
Motore economico del Canada, Toronto è, assieme a Montréal, la città del paese nordamericano più conosciuta nel mondo, seguita da Ottawa. Caratteristica della città è quella di essere una delle più multiculturali nel mondo, con circa il 36% degli abitanti di origine non canadese. Per dare un'idea di ciò basti pensare che il 911 (numero telefonico di emergenza) di Toronto è attrezzato per rispondere in oltre 150 lingue[3]. La seconda più grande comunità, superata da qualche anno da quella cinese, è costituita dagli italiani che hanno dato un enorme contributo allo sviluppo di questo paese. Si stima che le persone di origine italiana residenti a Toronto siano superiori a 500 000. Il primo quartiere dove si insediarono gli italiani fu quello di College, successivamente si spostarono a Saint Clair denominata col nome aggiuntivo di Corso Italia[4] dal 1988.
Toronto è suddivisa in 240 quartieri all'interno dei suoi confini, raggruppati in sei distretti (Old Toronto, East York, Etobicoke, Scarborough, North York e York (dove si trova anche il quartiere di Weston). Nella parte centrale di Toronto (Downtown Toronto) c'è una città sotterranea, chiamata PATH (in inglese: il sentiero o il percorso), costituita da una rete di collegamenti che mettono in collegamento i grattacieli della città. Il percorso è lungo più di 30 km. Secondo il Guinness dei primati, con i suoi 371600 m² di estensione, il PATH è più esteso centro commerciale sotterraneo del mondo.[5]
I residenti considerano questi 27 km di strade sotterranee come parte della città stessa, come se la città iniziasse non dal suolo, ma dal piano -3. Venne creata agli inizi degli anni sessanta perché in inverno, spazzata da venti nordici, Toronto è molto fredda in rapporto alla latitudine, mentre sotto ci si può muovere in abiti primaverili, sulle strade superiori, durante straordinarie irruzioni gelide ci possono essere temperature di −25/−30 °C al primo mattino o di sera. Di notte si può scendere un po' più in basso ed in tali casi le massime rimangono spesso a -20 sotto lo zero. Ovviamente il traffico automobilistico convenzionale è bandito nella città sotterranea, gli spostamenti sono previsti a piedi o con mezzi per disabili, ma il path ha numerosi punti di contatto con la viabilità esterna (parcheggi) o, molto più frequentemente, con una fitta rete di stazioni del trasporto pubblico di superficie o sotterraneo (subway).
Per muoversi nella parte sotterranea è molto importante fare riferimento a elementi di identificazione degli incroci (come elementi architettonici, facciate di banche, negozi tipici, ecc.), dato che non sempre il percorso sotterraneo (pedonale) corrisponde a quello (stradale) di superficie; o meglio, se non si è pratici, bisogna usare la mappa. La città sotterranea è completamente attrezzata come una città comune: ci sono banche, uffici postali, locali pubblici, ristoranti, uffici e supermercati. Le maggiori istituzioni (stazioni ferroviarie, aziende pubbliche, aziende commerciali, ecc.) hanno accesso multiplo: di superficie e sotterraneo.
Toronto (pronunciación en inglés: /tʲəˈɹɑntʲoʊ/ (![]() escuchar), localmente /tʲəˈɹɑnoʊ/, /ˈtʲɹɑnoʊ/) es la capital de la provincia de Ontario3 y, con una población de 2 615 060 habs.4 es la ciudad más grande de Canadá,5 además del centro financiero de dicho país.
escuchar), localmente /tʲəˈɹɑnoʊ/, /ˈtʲɹɑnoʊ/) es la capital de la provincia de Ontario3 y, con una población de 2 615 060 habs.4 es la ciudad más grande de Canadá,5 además del centro financiero de dicho país.
Localizada en la orilla noroeste del lago Ontario,6 es la quinta ciudad más grande de Norteamérica.7 Toronto se encuentra en el corazón del Área Metropolitana de Toronto (Greater Toronto Area en inglés y abreviado como GTA), la mayor área metropolitana de Canadá, y es parte de una región densamente poblada en el centro-sur de Ontario conocida como Golden Horseshoe (Herradura Dorada), donde residen ocho millones de habitantes.8910
Al ser la capital económica de Canadá, Toronto es considerada una ciudad global y una de las principales ciudades financieras del mundo.11 Lidera los sectores económicos de finanzas, servicios empresariales, telecomunicaciones, transporte, medios de comunicación, arte, cine, investigación médica, educación, y turismo de Canadá.1213 El Toronto Stock Exchange es la mayor bolsa de valores del país y la séptima del mundo.12
Toronto es famosa por la Torre CN, con 553 metros de altura. La ciudad se considera el centro de la cultura canadiense anglófona y es la anfitriona de muchas celebraciones nacionales.
La población de Toronto es cosmopolita,1415 y es un importante destino para muchos inmigrantes a Canadá.16 Toronto es la mayor ciudad del mundo en porcentaje de residentes no nacidos en el propio país; sobre un 49 % de los habitantes de la ciudad no ha nacido en Canadá.141516 Debido al bajo índice de criminalidad,17 el cuidado medio ambiente y el alto nivel de vida, Toronto, es considerada con asiduidad una de las ciudades mejor habitables del mundo.1819 Además, en 2006 fue clasificada como la ciudad más cara de Canadá.20 Los nacidos en Toronto reciben el gentilicio de torontonianos.21
En enero de 2005, Toronto fue escogida por el gobierno canadiense como una de las capitales culturales de Canadá. Toronto posee una de las mejores calidades de vida de América del Norte, y es considerada por muchos como una de las mejores metrópolis del mundo para vivir.22 Es una de las ciudades más seguras de América —su tasa de criminalidad es menor que la de cualquier gran ciudad del continente, y una de las menores de Canadá.23
En la ciudad vecina de Mississauga está el Aeropuerto Internacional Toronto Pearson. Además, en 'las islas de Toronto' dentro de la ciudad está el Billy Bishop Toronto City Airport, que es más pequeño.
Торо́нто (англ. Toronto [təˈrɒntoʊ], местн. [təˈrɒnoʊ], [ˈtrɒnoʊ], [-nə]) — крупнейший город Канады, административный центр провинции Онтарио. Население — 2 731 571 чел. (2016); вместе с городами Миссиссога, Брамптон, Маркем и другими образует агломерацию Большой Торонто с населением 5928 тыс. жителей.
Торонто является частью «золотой подковы» — густонаселённого региона вокруг западной части озера Онтарио с населением около 7 млн человек. Приблизительно одна треть всего населения Канады живёт в радиусе 500 км от Торонто. Около шестой части всех рабочих мест Канады находятся в пределах городской черты.
Город Торонто известен также как «экономический двигатель» Канады, считается одним из ведущих мегаполисов мира и имеет большой вес как в регионе, так и на государственном и международном уровне. В ежегодном рейтинге Global Liveability Ranking журнала The Economist, оценивающем совокупное качество жизни, Торонто занимает четвёртое место в мире среди 140 городов — участников рейтинга[1].
В Торонто располагается главный офис Всемирного конгресса украинцев. В июне 2010 года в Торонто прошла встреча глав государств и правительств «Большой двадцатки».
К северо-востоку от Торонто в городе Пикеринг находится атомная электростанция АЭС Пикеринг с восемью ядерными реакторами.





图尔库(芬兰语:Turku,发音:[ˈturku] (ⓘ);瑞典语:Åbo,发音:[ˈoːbu] (ⓘ),奥布)是芬兰西南部芬兰本部区的城市,为该国第六大城市,也是最古老的城市(在1154年已有记载),人口188,584人(2017年8月底)。
图尔库是芬兰第一个首都(1812年以前),也是第一个教区(成立于1300年,后来成为大主教区),还是芬兰第一所大学(奥布皇家学院,建于1640年)的所在地。
1741年瑞典王国进攻俄罗斯帝国,企图夺回芬兰湾地带,但俄军占领了芬兰全境。1743年,瑞典屈辱求和,俄国迫使之签定《奥布和约》,割让包括维堡在内的芬兰东南部地区。


 Valencian Community
Valencian Community

 International cities
International cities
 *World Design Capital
*World Design Capital
 Spain
Spain

 Cities founded by the Romans
Cities founded by the Romans

 World Heritage
World Heritage

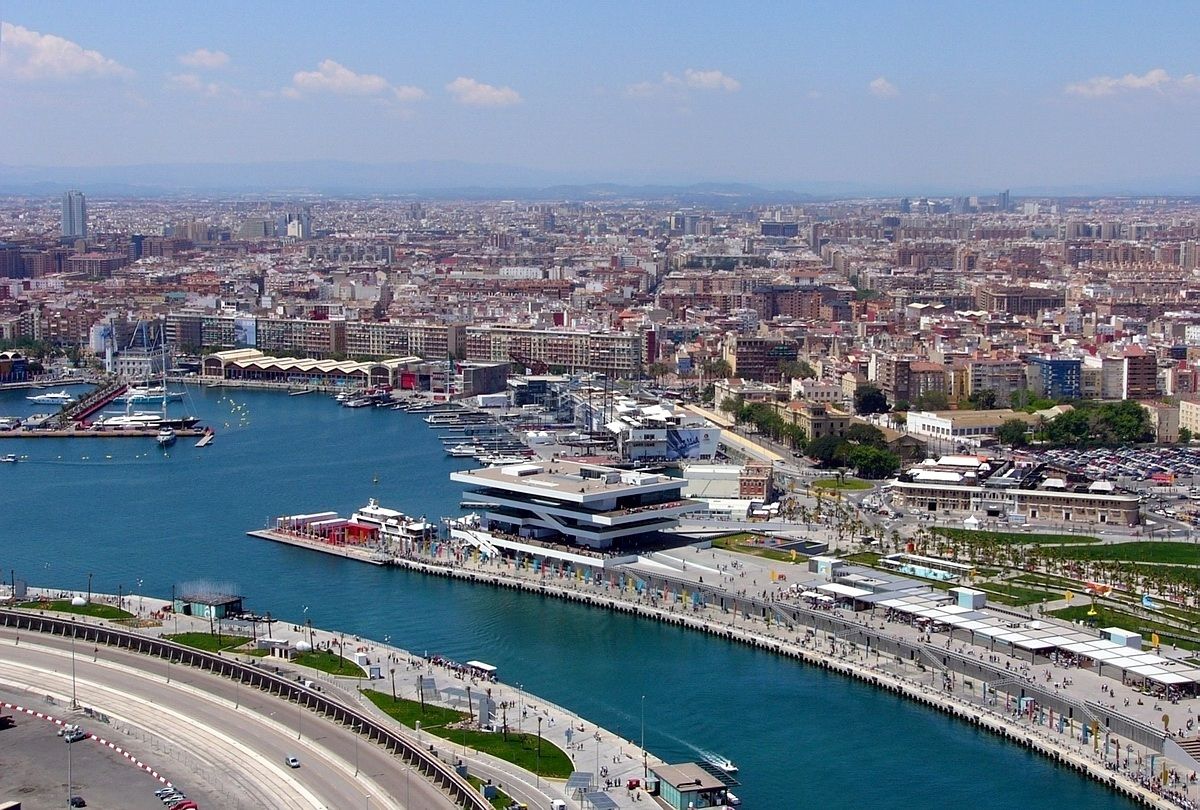
 Important port
Important port



 British Columbia-BC
British Columbia-BC

 FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 2026
FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 2026
 Women's Soccer World Cup 2015
Women's Soccer World Cup 2015

 Geography
Geography

 Geography
Geography
 *World's Most Livable Cities
*World's Most Livable Cities
 ITU World Championship Series
ITU World Championship Series
 Canada
Canada
 Winter Olympics
Winter Olympics
 Ski vacation
Ski vacation

 Sport
Sport
 Triathlon
Triathlon

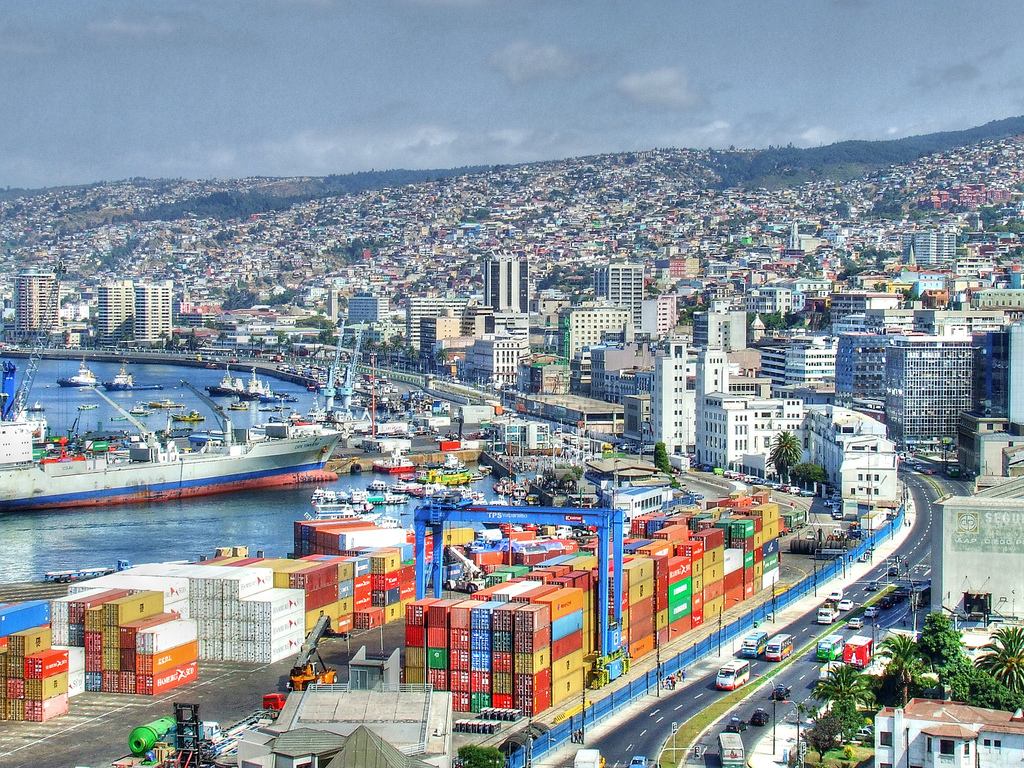
 Important port
Important port

一般所说的”温哥华”泛指”大温地区”(请参考温哥华概况介绍)。温哥华市中心位于一个半岛上,主要分成几块区域:西尾区与水滨(West End & Waterfront)、耶鲁镇(Yaletown)、盖士镇与华埠(Gastown & Chinatown)。市中心往南的温哥华市以Carrall街与Ontario街分成温西(West Side)与温东(East Side)。外地人常把温西与西温哥华(West Vancouver)搞混,后者是温哥华北岸的一个城市,从温哥华市中心向北跨越狮门大桥(Lions Gate Bridge)即可抵达。
西尾区(West End)在市中心西端,北与史丹利公园、南与市中心商业区紧邻,是由整片新兴的高级住宅大楼与罗布森街(Robson Street)购物区、各国风味餐厅、海滩、游艇码头等所组成的热闹区域。到温哥华旅游如果不自行开车,在西尾区住宿是明智选择。
耶鲁镇(Yaletown)是位于市中心东缘的新兴小区,这里有许多杂错的红砖仓库改建成精致典雅的新购物娱乐区与艺术家工作室。一栋栋平房红砖墙的建筑 及巷道上的石板路,将素有“Funky Town"之称的耶鲁镇特色表露无遗。耶鲁镇有电影制片公司、美发沙龙、室内设计工作室、小型设计师家具店、古董店、精品服饰店,加上各种特色美食与露天 咖啡座、小酒馆,让耶鲁镇的雅痞色彩十足,成为温哥华时尚一族抢着进驻的地区。
盖士镇(Gastown)是温哥华的发源地,是个以2条横街和3条直街组成的三角地带。卑诗省政府将盖士镇规划程成为独特的观光区与历史维护区。如今这里 保存完好的19世纪初维多利亚式建筑、铺满圆石的悠长街道、别致的露天咖啡屋,复古的路灯及一座座低矮的历史建筑,行走其间宛如时空错置。也是游客来温哥 华必至之处。(Quelle:http://www.usatrip.cn/jdjs/jdjs_Vancouver.asp)
温哥华市(City of Vancouver)是加拿大不列颠哥伦比亚省低陆平原地区一沿岸城市。根据2016年加拿大统计局人口普查,温哥华市人口有631,486人,而大温哥华地区的人口为246万,[1]是不列颠哥伦比亚省以至加拿大西部最大的都会区,以及全国第三大都会区;市内人口则在全国排行第八。[2][3]
温哥华以英国航海家乔治·温哥华命名,欧洲人抵达温哥华一带后,区内经济早期主要依赖于林木业。加拿大太平洋铁路于1887年延至温哥华后,温哥华成为北美西岸水陆路交通的主要枢纽之一,更构成远东地区、加拿大东部和英国之间贸易往来的重要一环。[4][5]温哥华港现时是加拿大最大和最繁忙的港口,以货物总吨数计也是北美第四大港口。[6]此外,温哥华的自然环境深受游客欢迎,令旅游业成为市内第二大经济支柱。[7]温哥华也是北美第三大制片中心,有“北方好莱坞”之称。[8][9]也是20世纪后,与美国旧金山同为华人在北美最集中的地区。
温哥华近年经常在各项世界最佳居住城市的调查中名列前茅。[10][11]温哥华亦曾于2010年与125公里以外的惠斯勒联手举办冬季奥运会和冬季残奥会。[12]此外温哥华还曾举办2015年女子世界杯足球赛,决赛场地即设在不列颠哥伦比亚体育馆。
Vancouver (englische Aussprache [væŋˈkuːvɚ] oder [vænˈkuːvɚ]) ist eine Stadt im Südwesten von British Columbia an der Westküste Kanadas. Sie liegt zwischen der Straße von Georgia und den Coast Mountains, rund 45 Kilometer nordwestlich der Grenze zu den USA. Die Stadt gehört zum Regionaldistrikt Metro Vancouver, der mit 2.463.431 Einwohnern[1] die größte Metropolregion Westkanadas und nach Toronto und Montreal die drittgrößte des Landes bildet. Die Bevölkerungszahl der eigentlichen Stadt Vancouver beträgt 631.486.[2] Benannt ist die Stadt nach dem britischen Kapitän George Vancouver, der die Region Ende des 18. Jahrhunderts erforschte und vermaß. Der Name Vancouver selbst stammt vom niederländischen „van Coevorden“, abgeleitet von der Stadt Coevorden.
Die Stadt entstand in den 1860er Jahren als Folge der Einwanderungswelle während des Fraser-Canyon-Goldrauschs und entwickelte sich nach der Eröffnung der transkontinentalen Eisenbahn im Jahr 1887 innerhalb weniger Jahrzehnte von einer kleinen Sägewerkssiedlung zu einer Metropole. Die Wirtschaft basierte zu Beginn auf der Ausbeutung der natürlichen Ressourcen von British Columbia: Forstwirtschaft, Bergbau, Fischerei und Landwirtschaft. Der Hafen Vancouver erlangte nach der Eröffnung des Panamakanals internationale Bedeutung. Er ist heute der größte in Kanada und exportiert mehr Güter als jeder andere Hafen in Nordamerika.
Vancouver wandelte sich mit der Zeit zu einem Dienstleistungszentrum und (insbesondere nach der Weltausstellung Expo 86) zu einem Reiseziel für Touristen. Die Stadt ist darüber hinaus hinter Los Angeles und New York der drittwichtigste Standort der nordamerikanischen Filmindustrie und wird daher auch als „Hollywood North“ bezeichnet. Die Finanzwirtschaft spielt ebenfalls eine bedeutende Rolle. In einer Rangliste der wichtigsten Finanzzentren weltweit belegt Vancouver den 15. Platz (Stand: 2018).[3]
Vancouver veranstaltete vom 12. bis 28. Februar 2010 die XXI. Olympischen Winterspiele. Einige Wettbewerbe der Spiele fanden im 125 Kilometer von Vancouver entfernten Whistler statt. Nach Montreal im Jahr 1976 und Calgary im Jahr 1988 war Vancouver die dritte kanadische Stadt, die Olympische Spiele veranstaltet hat.
バンクーバー(英語: Vancouver)は、カナダ連邦ブリティッシュコロンビア州南西部にある都市。同州最大の都市である。ヴァンクーヴァーと表記されることもある[3]。
バンクーバーを中心とする都市圏人口は210万人とカナダ国内第3位の都市圏を形成している[4]。バンクーバー市のみの人口では同国内で第8位の約64万人[5]である。民族や言語が多様で、人口のおよそ52%は第一言語が同州の公用語にあたる英語ではない[6]。北米有数の世界都市であり、2016年に発表された「世界の都市総合力ランキング」では、世界28位と評価された[7]。
1867年に製材所ができ、これらを中心とする入植地であったギャスタウンは発展を続け、グランビルとして町は拡大した。東カナダから続く鉄道の終着駅が町まで敷かれることになった1886年に町はバンクーバーとして改名され市政となる。
林業が同市最大の産業で、都市部ながら自然に囲まれた都市として知られていることから、観光業が発達しており、同市第2の産業となっている[8]。同市にあるメトロバンクーバー港は同国最大の港であり、北米においても積載量で第4位の規模を持つ[9]。同市および隣のバーナビー市には、主要な各映画製作会社が拠点を置いており、ロサンゼルス、ニューヨークに続く北米第3位の規模となる映画製作拠点となっている。このため、通称ハリウッドノースとも呼ばれる[10][11]。国際会議や国際競技が数多く開催されており、2010年には第21回冬季オリンピック(バンクーバーオリンピック)が開催された。
Vancouver (/vænˈkuːvər/ ( listen)) is a coastal seaport city in western Canada, located in the Lower Mainland region of British Columbia. As the most populous city in the province, the 2016 census recorded 631,486 people in the city, up from 603,502 in 2011. The Greater Vancouver area had a population of 2,463,431 in 2016, making it the third-largest metropolitan area in Canada. Vancouver has the highest population density in Canada with over 5,400 people per square kilometre,[5][6] which makes it the fifth-most densely populated city with over 250,000 residents in North America behind New York City, Guadalajara, San Francisco,[7] and Mexico City according to the 2011 census. Vancouver is one of the most ethnically and linguistically diverse cities in Canada according to that census; 52% of its residents have a first language other than English.[8][9] Roughly 30% of the city's inhabitants are of Chinese heritage.[10] Vancouver is classed as a Beta global city.
listen)) is a coastal seaport city in western Canada, located in the Lower Mainland region of British Columbia. As the most populous city in the province, the 2016 census recorded 631,486 people in the city, up from 603,502 in 2011. The Greater Vancouver area had a population of 2,463,431 in 2016, making it the third-largest metropolitan area in Canada. Vancouver has the highest population density in Canada with over 5,400 people per square kilometre,[5][6] which makes it the fifth-most densely populated city with over 250,000 residents in North America behind New York City, Guadalajara, San Francisco,[7] and Mexico City according to the 2011 census. Vancouver is one of the most ethnically and linguistically diverse cities in Canada according to that census; 52% of its residents have a first language other than English.[8][9] Roughly 30% of the city's inhabitants are of Chinese heritage.[10] Vancouver is classed as a Beta global city.
Vancouver is consistently named as one of the top five worldwide cities for livability and quality of life,[11][12] and the Economist Intelligence Unit acknowledged it as the first city ranked among the top-ten of the world's most well-living cities[13] for five consecutive years.[14] Vancouver has hosted many international conferences and events, including the 1954 British Empire and Commonwealth Games, UN Habitat I, Expo 86, the World Police and Fire Games in 1989 and 2009; and the 2010 Winter Olympics and Paralympics which were held in Vancouver and Whistler, a resort community 125 km (78 mi) north of the city.[15] In 2014, following thirty years in California, the TED conference made Vancouver its indefinite home. Several matches of the 2015 FIFA Women's World Cup were played in Vancouver, including the final at BC Place.[16]
The original settlement, named Gastown, grew up on clearcuts on the west edge of the Hastings Mill logging sawmill's property, where a makeshift tavern had been set up on a plank between two stumps and the proprietor, Gassy Jack, persuaded the curious millworkers to build him a tavern, on July 1, 1867. From that first enterprise, other stores and some hotels quickly appeared along the waterfront to the west. Gastown became formally laid out as a registered townsite dubbed Granville, B.I. ("B.I" standing for "Burrard Inlet"). As part of the land and political deal whereby the area of the townsite was made the railhead of the Canadian Pacific Railway (CPR), it was renamed "Vancouver" and incorporated shortly thereafter as a city, in 1886. By 1887, the Canadian Pacific transcontinental railway was extended westward to the city to take advantage of its large natural seaport to the Pacific Ocean, which soon became a vital link in a trade route between the Orient / East Asia, Eastern Canada, and Europe.[17][18] As of 2014, Port Metro Vancouver is the third-largest port by tonnage in the Americas (recently displacing New York City), 27th in the world,[19] the busiest and largest in Canada, and the most diversified port in North America.[20] While forestry remains its largest industry, Vancouver is well known as an urban centre surrounded by nature, making tourism its second-largest industry.[21]
Major film production studios in Vancouver and nearby Burnaby have turned Greater Vancouver and nearby areas into one of the largest film production centres in North America,[22][23] earning it the nickname "Hollywood North".[24][25][26]
Vancouver /vãkuvaɛ̯ʁ/a Écouter ou /vɑ̃kuvɛʁ/b (en anglais : /væŋˈkuvɚ/c Écouter) est une cité1 portuaire du pourtour du Pacifique située dans les basses-terres continentales de la province de Colombie-Britannique, au Canada. Avec 631 486 habitants selon le recensement du Canada de 2016, elle est la huitième plus grande municipalité canadienne3. Son agglomération de 2 463 431 est la troisième aire urbaine du pays, et la plus peuplée de l'Ouest canadien. Vancouver est une des villes les plus cosmopolites du Canada, 52 % des résidents ont une autre langue maternelle que l'anglais4. Vancouver est considérée comme une ville mondiale de classe beta. La superficie de Vancouver est de 114,97 km2, donnant une densité de population de 5 493 au kilomètre carré, faisant d'elle la municipalité canadienne la plus densément peuplée et la quatrième en Amérique du Nord, après New York, San Francisco et Mexico5. Elle est la vingt-troisième ville la plus peuplée d'Amérique du Nord6.
Le premier établissement, nommé Gastown, s'est développé autour d'une scierie appelé Hastings Mills, en 1867. Le site fut renommé Vancouver et incorporé comme cité en 1886. En 1887, le chemin de fer transcontinental a été étendu jusqu'à elle pour profiter de son grand port naturel, qui est rapidement devenu un maillon essentiel d'une route commerciale entre la côte est du Canada, l'Orient et l'Europe7,8. En 2009, Port Metro Vancouver est le port le plus grand et le plus achalandé du Canada, et le plus diversifié d'Amérique du Nord9. Même si l'exploitation forestière demeure sa plus grande industrie, Vancouver est réputée pour être un centre urbain entouré par la nature, faisant du tourisme sa deuxième industrie10. Les studios de production cinématographique de Vancouver et de Burnaby ont fait de la métropole l'un des plus grands centres cinématographiques en Amérique du Nord11,12, ce qui lui a valu le surnom de Hollywood North13,14,15.
Vancouver est régulièrement citée comme l'une des cinq meilleures villes au monde pour sa qualité de vie16,17, et l'Economist Intelligence Unit l'a classée parmi les dix villes les plus agréables durant cinq années consécutives18,19. Vancouver fut l'hôte de nombreux évènements internationaux, comme les Jeux de l'Empire britannique et du Commonwealth de 1954, la conférence Habitat I par l'Organisation des Nations unies en 1976, l'Exposition internationale de 1986 et les Jeux olympiques d'hiver de 201020. En 2015, elle a accueilli la finale de la Coupe du monde féminine de football21. La ville accueillera en 2018 le Congrès ornithologique international.
Vancouver (AFI: [vanˈkuver][1]) è una città canadese, sulla costa Pacifica della provincia canadese della Columbia Britannica (British Columbia). È situata nella parte meridionale della provincia e rappresenta uno dei maggiori porti dell'Oceano Pacifico. È delimitata dallo Stretto di Georgia (Georgia Strait), dal fiume Fraser, e dalla catena montuosa delle Montagne Costiere. Il nome è in onore del capitano George Vancouver, esploratore britannico.
La popolazione della città è di 603 502 abitanti, mentre l'area urbana ne conta 2 135 201. Vancouver fa parte della regione metropolitana, conosciuta come la "Greater Vancouver Regional District" (GVRD) o Metro Vancouver, nella quale vivono 2 463 700 (stima del 2012)[2]. Questo la rende la più grande area metropolitana nel Canada occidentale, e la terza più grande nel paese. Come in buona parte del Canada, anche Vancouver etnicamente è molto diversificata, basti pensare che il 52% dei residenti[3][4] della città e il 43% dell'area metropolitana hanno come prima lingua un idioma diverso dall'inglese[5].
La popolazione metropolitana è proiettata a raggiungere i 3 milioni di abitanti entro il 2021[6]. La densità di popolazione è tra le più alte del Nord America, e la pone al quarto posto dopo New York, San Francisco e Città del Messico. Il trend porta a stimare che possa raggiungere il secondo posto entro il 2021[7].
L'economia di Vancouver ha tradizionalmente fatto leva sulle risorse della Columbia Britannica: forestali, minerarie, pesca e agricoltura. Ma tuttavia è andata diversificandosi nel tempo, ed oggi Vancouver ha un'importante e vitale industria nel settore dei servizi e del turismo. La città è diventata il terzo più grande polo di produzione cinematografico del Nord America dopo Los Angeles e New York, tanto da guadagnarsi il soprannome di Hollywood del Nord[8][9][10]. Vancouver ha avuto un'espansione nell'industria dell'high-tech, in particolare nello sviluppo dei videogiochi.
Vancouver è costantemente classificata fra le prime tre città più vivibili del mondo[11][12][13]. Secondo il rapporto 2010 della Mercer Human Resource Consulting, ad esempio, Vancouver è considerata la prima città al mondo per qualità della vita. Nel 2007 Vancouver era la seconda città più cara del Canada dopo Toronto e la 89ª a livello globale.
Nel 2010 Vancouver, insieme a Whistler, situata 125 km a nord della città, ha ospitato i Giochi olimpici invernali e i Giochi Paralimpici invernali.
Vancouver (en inglés:  /væŋ'ku:vɚ/ (?·i), en español /baŋ'kuβ̞eɾ/) es una ciudad de la costa pacífica de Canadá, ubicada en el suroeste de la provincia de Columbia Británica, entre el estrecho de Georgia y las Montañas Costeras. La ciudad fue llamada así en honor del capitán George Vancouver, un explorador inglés.
/væŋ'ku:vɚ/ (?·i), en español /baŋ'kuβ̞eɾ/) es una ciudad de la costa pacífica de Canadá, ubicada en el suroeste de la provincia de Columbia Británica, entre el estrecho de Georgia y las Montañas Costeras. La ciudad fue llamada así en honor del capitán George Vancouver, un explorador inglés.
Es parte del área metropolitana del Distrito Regional del Gran Vancouver, el cual, con una población de 2 313 328 habitantes (2011),1 constituye el área metropolitana más grande del oeste canadiense y la tercera en el país después de Toronto y Montreal.2 Vancouver en sí mismo cuenta con 603 502 habitantes.1 El gentilicio utilizado para referirse a los residentes de Vancouver es vancuverita o vancouverense,3 (en inglés Vancouverite).
Vancouver, en los últimos años, siempre ha sido considerada como una de las cinco ciudades con mejor calidad de vida en el mundo.4567 En 2013, obtuvo el puesto 21º entre las ciudades en que es más caro vivir y resultó ser la más cara de Norteamérica. 8 También es una de las ciudades más seguras del mundo, debido a sus bajísimas tasas de criminalidad.
Los Juegos Olímpicos y Paralímpicos de invierno de 2010 se llevaron a cabo en Vancouver y en la cercana localidad de Whistler.91011
Ванку́вер (англ. Vancouver) — город на западе Канады, крупнейший населённый пункт провинции Британская Колумбия и третий по величине в Канаде. В 2010 году в Ванкувере проводились XXI зимние Олимпийские игры. Исследовательская группа Economist Intelligence Unit (EIU) британского издания The Economist трижды — в 2005, 2007, 2009 годах — присваивала Ванкуверу звание «лучшего города Земли»[2][3][4].
Население самого города — 631 486 чел. (на 2016 год). В агломерации Большой Ванкувер (англ.)русск. проживает свыше 2 463 431 чел. (на 2016 год) — это третья по величине агломерация в Канаде. Ванкувер является наиболее этнически и лингвистически разнообразным городом страны — 52 % его жителей считают своим родным языком не английский[5].

威尼斯(威尼斯语︰Venezsia;意大利语︰Venezia;弗留利语︰Vignesie;拉丁语︰Venetia;英文:Venice)是意大利东北部著名的旅游与工业城市,也是威尼托地区的首府。威尼斯城由被运河分隔并由桥梁相连[1]的118座小岛组成。[2]威尼斯潟湖是位于波河与皮亚韦河河口之间的一个封闭的海湾,威尼斯城就坐落在威尼斯潟湖的浅滩上。威尼斯以其优美的环境、建筑和艺术品珍藏而闻名。[1]潟湖和城市的一部分被列为世界遗产。[1]Luigi Barzini曾在纽约时报形容它“无疑是最美丽的人造都市”[3],时代线上也称赞威尼斯是欧洲最浪漫的城市之一。
2014年,共有264,579人居住在威尼斯市镇,其中约55,000人居住在老城区。威尼斯与帕多瓦和特雷维索一起,组成了帕多瓦-特雷维索-威尼斯大都市区(PATREVE),总人口260万。PATREVE只是一个统计学意义上的大都市区,不是行政区划的等级。[4]
威尼斯这个名字源于公元前十世纪居住在该地区的古威尼蒂人。[5][6]这个城市历史上曾经是威尼斯共和国的首府。威尼斯同时被誉为“主之城”、“尊贵之城”、“亚得里亚王后”、“水之都”、“面具之城”、“桥梁之城”、“漂浮之都”、“运河之城”。
威尼斯共和国是中世纪和文艺复兴时期的主要金融和海运力量,是十字军东征和勒班陀战役的集结地,也是从13世纪直到17世纪末的一个非常重要的商业(特别是丝绸,粮食和香料)和艺术中心。[7] 威尼斯市被认为是第一个真正的国际金融中心,9世纪逐渐形成,14世纪达到了顶峰。这使威尼斯在其大部分历史中成为一座极为富裕的城市。[8]后来因为土耳其人对地中海东边的控制促使欧洲国家寻找其他航线的欲望,威尼斯因此失去了大部分的重要性与影响力。
它同样因为几次特别是文艺复兴时期的重要的艺术运动而众所周知的。在拿破仑战争和维也纳会议之后,共和国被奥地利帝国所吞并,直到1866年,由于第三次意大利独立战争而举行的全民公投,威尼斯成为意大利王国的一部分。威尼斯在交响乐和歌剧音乐史上也起着重要的作用,它是安东尼奥·维瓦尔第的诞生地。[9]2016年,威尼斯被评为世界上最美丽的城市。[10]
Venedig (italienisch Venezia [veˈnɛʦːi̯a], venezianisch Venesia[2] [veˈnɛzi̯a] oder [veˈnɛzja]) ist eine Stadt im Nordosten Italiens. Sie ist die Hauptstadt der Region Venetien, Metropolitanstadt Venedig und trägt den Beinamen La Serenissima („Die Durchlauchtigste“).[3] Ihr historisches Zentrum (centro storico) liegt auf einigen größeren Inseln in der Lagune von Venedig.
Die Gesamtfläche Venedigs beträgt 414,6 km², davon entfallen 257,7 km² auf Wasserflächen.[4] Am 31. Dezember 2016 zählte die Stadt 261.905 Einwohner, davon 181.883 in den Stadtteilen auf dem Festland, 58.901 im historischen Zentrum und 29.674 innerhalb der Lagune.[5] In der Lagune befinden sich 118 Inseln.[6] Sie erstreckt sich über etwa 50 km zwischen den Mündungen der Flüsse Adige (Etsch) im Süden und Piave im Norden in die Adria.
Venedig war bis 1797 Hauptstadt der Republik Venedig und mit über 180.000 Einwohnern eine der größten europäischen Städte. Bis ins 16. Jahrhundert war sie eine der größten Handelsstädte, über die der Handel zwischen Westeuropa und dem östlichen Mittelmeer abgewickelt wurde. Venedig unterhielt die meisten Handels- und Kriegsschiffe. Ihr Adel profitierte vom Handel mit Luxuswaren, Gewürzen, Salz und Weizen. Venedig entwickelte sich zum größten Finanzzentrum und dominierte ein Kolonialreich, das von Oberitalien bis Kreta und zeitweise bis nach Zypern reichte.[7] Nach französischer und österreichischer Herrschaft zwischen 1798 und 1866 wurde Venedig ein Teil Italiens. 1929 wurde der Industriekomplex Mestre-Marghera in die Comune di Venezia eingemeindet. Der jüdische Anteil der Bevölkerung wurde während des Zweiten Weltkriegs vernichtet. In den Jahren 1965 bis 1970 erreichte die Stadt mit knapp 370.000 Einwohnern die höchste Bevölkerungszahl, die seitdem wieder um etwa 100.000 Einwohner zurückgegangen ist.
Venedig und seine Lagune stehen seit 1987 auf der UNESCO-Liste des Weltkulturerbes.[8] Sie inspirierten besonders die Künstler und Venedig wurde zu einer der von Touristen meistbesuchten Städte. Seit einem Jahrhundert ist die wirtschaftliche Struktur der Altstadt einseitig auf den Tourismus ausgerichtet, während sich die industrielle Tätigkeit vor allem um Mestre und Marghera auf dem westlichen Festland konzentriert.
ヴェネツィア(イタリア語: Venezia (![]() 音声ファイル)[5])は、イタリア共和国北東部に位置する都市で、その周辺地域を含む人口約26万人の基礎自治体(コムーネ)。ヴェネト州の州都、ヴェネツィア県の県都である。ヴの表記によりベネチアと表記されることもある。
音声ファイル)[5])は、イタリア共和国北東部に位置する都市で、その周辺地域を含む人口約26万人の基礎自治体(コムーネ)。ヴェネト州の州都、ヴェネツィア県の県都である。ヴの表記によりベネチアと表記されることもある。
中世にはヴェネツィア共和国の首都として栄えた都市で、「アドリア海の女王」・「水の都」・「アドリア海の真珠」[要出典]などの別名をもつ。英語では「Venice」と呼ばれ、これに由来して日本語でもヴェニス、ベニスと呼ばれることもある。
古来はラテン語でウェネティ人の土地を意味し、ウェネティ人が住んでいたアドリア海の奥に拡がる土地をウェネティア (Venetia) と呼んだことから来ている。この綴りをそのままイタリアでのラテン語の読み方に従うと、ヴェネツィア(ヴェネツャ)となる。英語でヴェニス (Venice)、フランス語でヴニーズ (Venise)、ドイツ語でヴェネーディヒ (Venedig) と呼ばれる。ヴェネツィア方言では、古語は Venexia、現代語では Venessia(まれに Venezsia)と表記され、ヴェネーシアとヴェネースィアの中間に近い音で発音される。
日本語の表記では、イタリア語から来たものでもヴェネーツィアを始めとして、ヴェネチア、ベネチア、ベネツィアなどもある。英語由来の日本語表記では、ヴェニス、ベニスなどと書かれることもある。
英語での形容詞形"Venetian"はヴィニーシャンとヴェニーシャンの中間に近い発音だが、これの日本語表記は「ヴェネチアン」または「ベネチアン」となることが多く、また、綴りは異なるがイタリア語の影響から「ヴェネツィアン」と表記されることもしばしば。
Venice (/ˈvɛnɪs/, VEN-iss; Italian: Venezia [veˈnɛttsja] (![]() listen); Venetian: Venesia, Venexia [veˈnɛsja]) is a city in northeastern Italy and the capital of the Veneto region. It is situated across a group of 118 small islands[1] that are separated by canals and linked by 400 bridges.[2][3] The islands are located in the shallow Venetian Lagoon, an enclosed bay that lies between the mouths of the Po and the Piave rivers (more exactly between the Brenta and the Sile). Parts of Venice are renowned for the beauty of their settings, their architecture, and artwork.[2] The lagoon and a part of the city are listed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site.[2]
listen); Venetian: Venesia, Venexia [veˈnɛsja]) is a city in northeastern Italy and the capital of the Veneto region. It is situated across a group of 118 small islands[1] that are separated by canals and linked by 400 bridges.[2][3] The islands are located in the shallow Venetian Lagoon, an enclosed bay that lies between the mouths of the Po and the Piave rivers (more exactly between the Brenta and the Sile). Parts of Venice are renowned for the beauty of their settings, their architecture, and artwork.[2] The lagoon and a part of the city are listed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site.[2]
In 2014, 264,579 people resided in Comune di Venezia, of whom around 55,000 live in the historic city of Venice (Centro storico). Together with Padua and Treviso, the city is included in the Padua-Treviso-Venice Metropolitan Area (PATREVE), with a total population of 2.6 million. PATREVE is only a statistical metropolitan area.[4]
The name is derived from the ancient Veneti people who inhabited the region by the 10th century BCE.[5][6] The city was historically the capital of the Republic of Venice. Venice has been known as the "La Dominante", "Serenissima", "Queen of the Adriatic", "City of Water", "City of Masks", "City of Bridges", "The Floating City", and "City of Canals."
The Republic of Venice was a major financial and maritime power during the Middle Ages and Renaissance, and a staging area for the Crusades and the Battle of Lepanto, as well as a very important center of commerce (especially silk, grain, and spice) and art in the 13th century up to the end of the 17th century. The city-state of Venice is considered to have been the first real international financial center which gradually emerged from the 9th century to its peak in the 14th century.[7] This made Venice a wealthy city throughout most of its history.[8]
It is also known for its several important artistic movements, especially the Renaissance period. After the Napoleonic Wars and the Congress of Vienna, the Republic was annexed by the Austrian Empire, until it became part of the Kingdom of Italy in 1866, following a referendum held as a result of the Third Italian War of Independence. Venice has played an important role in the history of symphonic and operatic music, and it is the birthplace of Antonio Vivaldi.[9] Venice has been ranked the most beautiful city in the world as of 2016.[10] The city is facing some major challenges, however, including financial difficulties, erosion, pollution, subsidence, an excessive number of tourists in peak periods and problems caused by oversized cruise ships sailing close to the banks of the historical city.[11][12][13]
Venise (italien : Venezia /veˈnɛtʦja/, vénitien : Venexia /veˈnɛˑsja/) est une ville portuaire du nord-est de l'Italie, sur les rives de la mer Adriatique. Elle s'étend sur un ensemble de 118 petites îles séparées par un réseau de canaux et reliées par des ponts. Située au large de la lagune vénète, entre les estuaires du Pô et du Piave, Venise est renommée pour cette particularité, ainsi que pour son architecture et son patrimoine culturel — elle et sa lagune sont inscrites au patrimoine mondial de l'UNESCO.
Venise est la capitale de la région de la Vénétie. En 2012, la commune compte 269 810 habitants, dont 58 666 intra-muros (Centro storico)1. 176 000 résident sur les rives (Terraferma), pour la plupart dans les frazioni de Mestre et Marghera, et les 31 000 habitants restants résident dans d'autres îles de la lagune. Avec Padoue et Trévise, Venise constitue l'aire métropolitaine Padoue-Trévise-Venise (PATREVE), une entité statistique de 1 600 000 habitants.
Fondée peu après 528, elle fut la capitale pendant onze siècles (697-1797) de la République de Venise. Durant le Moyen Âge et la Renaissance, la ville fut une grande puissance maritime, à l'origine de la Quatrième croisade et victorieuse lors de la bataille de Lépante en 1571 contre l'Empire ottoman. Grâce à ses liens avec l'Asie et le Proche-Orient, dont le marchand et explorateur Marco Polo fut l'initiateur, elle devint également l'une des principales places commerciales d'Europe, notamment de la soie, des céréales et des épices. Enfin, elle est un centre culturel majeur, du XIIIe à la fin du XVIIe siècle, dont les peintres de l’École vénitienne (dont Titien, Véronèse et Le Tintoret), Carlo Goldoni et Antonio Vivaldi sont les principaux représentants.
Son nom provient du peuple qui habitait la région avant le Xe siècle, les Veneti. Dénommée Venetiae en latin, elle est parfois surnommée la « Cité des Doges », la « Sérénissime », la « Reine de l'Adriatique », la « Cité des Eaux », la « Cité des Masques », la « Cité des Ponts » ou encore la « Cité flottante ». La ville est aujourd'hui célèbre pour ses canaux — notamment le Grand Canal — et ses gondoles, ses nombreuses églises, la place Saint-Marc, le palais des Doges, le Pont des Soupirs, sa Biennale ainsi que son carnaval.
Venezia (AFI: /veˈnɛʦja/[5], ; [veˈnɛːsja][Nota 3]) è un comune italiano di 260 923 abitanti, il cui centro storico (limitato ai sestieri della città lagunare) ne conta invece 53 976[6] [7], capoluogo dell'omonima città metropolitana e della regione Veneto. È il primo comune della regione per popolazione, undicesimo in Italia[8] e primo in Veneto per superficie[9]. Il comune di Venezia comprende sia territori insulari sia di terraferma ed è articolato attorno ai due principali centri di Venezia (al centro dell'omonima laguna) e di Mestre (nella terraferma).
La città di Venezia è stata per più di un millennio capitale della repubblica di Venezia ed è conosciuta a questo riguardo come la Serenissima, la Dominante e la Regina dell'Adriatico. Per le peculiarità urbanistiche e per il suo patrimonio artistico, Venezia è universalmente considerata una tra le più belle città del mondo ed è annoverata, assieme alla sua laguna, tra i siti italiani patrimonio dell'umanità dall'UNESCO[10]: questo fattore ha contribuito a farne la terza città italiana (dopo Roma e Milano) con il più alto flusso turistico[11], in gran parte proveniente da fuori Italia.
Venecia (en italiano: Venezia [veˈnɛʦːi̯a] y en véneto: Venessia o Venesia [veˈnɛsi̯a]) es una ciudad ubicada en el noreste de Italia. Es también la capital de la región véneta y de la provincia de Venecia. Su centro histórico, declarado Patrimonio de la Humanidad por la Unesco,2 está situado en un conjunto de islas en la laguna de Venecia, en el norte del mar Adriático.
La ciudad está construida sobre un archipiélago de 118 pequeñas islas unidas entre sí por 455 puentes, si incluimos las islas de Murano y Burano. Se llega a Venecia desde tierra firme por el Puente de la Libertad, que desde la vecina ciudad de Mestre accede al Piazzale Roma. En el interior de la ciudad no hay tráfico rodado, siendo, a excepción de la navegación por los canales que separan a las islas, una ciudad totalmente peatonal. El transporte colectivo se realiza mediante embarcaciones transbordadoras conocidas como vaporettos. Están a cargo de la empresa municipal ACTV.3
Sus canales componen un gran entramado a modo de calles que parten del Gran Canal, gran vía por donde discurren multitud de embarcaciones, grandes y pequeñas, las más conocidas de las cuales son las llamadas góndolas.
Вене́ция (итал. Venezia [veˈnɛttsia] ![]() слушать, вен. Venesia) — город на северо-востоке Италии. Административный центр области Венеция и провинции Венеция. Образует коммуну, разделённую на 6 самоуправляемых районов. Покровителем города считается апостол Марк, евангелист, чьи мощи хранятся здесь же в Соборе Св. Марка, в связи с чем в город всегда приезжало много паломников-христиан со всего мира.
слушать, вен. Venesia) — город на северо-востоке Италии. Административный центр области Венеция и провинции Венеция. Образует коммуну, разделённую на 6 самоуправляемых районов. Покровителем города считается апостол Марк, евангелист, чьи мощи хранятся здесь же в Соборе Св. Марка, в связи с чем в город всегда приезжало много паломников-христиан со всего мира.
Население — 261 905 человек (31 декабря 2016 года)[1]. Расположена на материке (после объединения с городом Местре в 1926 году) и 118 островах Венецианской лагуны Адриатического моря. Подвержена осенним наводнениям от нагонной волны со стороны моря.
Крупный туристический и научно-образовательный центр. В материковой части — морской порт и международный аэропорт Марко Поло, нефтеперерабатывающий и другие заводы. Место проведения Венецианского карнавала и Венецианского кинофестиваля.
Архитектурный облик города сформировался в период расцвета Венецианской республики в XIV—XVI веках. Вместе с Венецианской лагуной внесён в список Всемирного наследия ЮНЕСКО.
Во времена античности район Венеции населяли венеты (отсюда название города). Островной город с IX века. В Средние века — центр Венецианской республики с многочисленными колониями в Средиземном море. Рост Османской империи привёл к упадку Венеции в XVII—XVIII веках; во время Наполеоновских войн попала под власть Австрии. В 1866 году вошла в состав Италии.

 Architecture
Architecture

 Financial
Financial

 Financial
Financial
 *Brazil economic data
*Brazil economic data

 Financial
Financial
 *China economic data
*China economic data

 Financial
Financial
 *Germany economic data
*Germany economic data

 Financial
Financial
 *European Union economic data
*European Union economic data

 Financial
Financial
 *France economic data
*France economic data

 Financial
Financial
 *India economic data
*India economic data

 Financial
Financial
 *Indonesia economic data
*Indonesia economic data

 Financial
Financial
 *Italy economic data
*Italy economic data

 Financial
Financial
 *Japan economic data
*Japan economic data

 Financial
Financial
 *Canada economic data
*Canada economic data

 Financial
Financial
 *Russia economic data
*Russia economic data

 Financial
Financial
 *United States economic data
*United States economic data

 Financial
Financial
 *United Kingdom economic data
*United Kingdom economic data

 Important port
Important port

 Ontario-ON
Ontario-ON

 Medieval cities in Europe
Medieval cities in Europe
 Veneto
Veneto
 Transport and traffic
Transport and traffic