
Deutsch-Chinesische Enzyklopädie, 德汉百科
 South Africa
South Africa

 Egypt
Egypt
 Australia
Australia
 Belgium
Belgium
 Brazil
Brazil
 Denmark
Denmark
 Germany
Germany
 Finland
Finland
 France
France
 Greece
Greece

 Hand in Hand
Hand in Hand

 Hand in Hand
Hand in Hand
 Driver's license
Driver's license
 India
India
 Indonesia
Indonesia
 Italy
Italy
 Japan
Japan
 Canada
Canada
 Kasachstan
Kasachstan
 Croatia
Croatia
 Malaysia
Malaysia
 Mexico
Mexico

 Mongolei
Mongolei
 New Zealand
New Zealand
 Netherlands
Netherlands
 Useful info
Useful info
 Austria
Austria
 Portugal
Portugal
 Republic of Korea
Republic of Korea
 Russia
Russia
 Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia
 Sweden
Sweden
 Switzerland
Switzerland
 Singapore
Singapore
 Spain
Spain
 South Africa
South Africa
 Thailand
Thailand
 Czech Republic
Czech Republic
 Turkey
Turkey
 Hungary
Hungary

 Vacation and Travel
Vacation and Travel
 United Arab Emirates
United Arab Emirates
 United States
United States
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
国际驾驶执照(International Driving Permit)依照1949年日内瓦国际道路交通公约及1968年维也纳国际道路交通公约,由公约签署国政府签发,方便本国驾驶员在其他签约国驾驶私人车辆。国际驾驶执照为附加在一国驾驶执照之上的一本附加多国语言的说明,标注了驾驶人的基本信息以及允许驾驶的对应车辆种类等,解决驾驶员与其他国家的交通管理部门之间的沟通障碍。国际驾照不能独立存在,当驾驶员同时持有一国驾照与该国政府签发的国际驾照时,此国际驾照才视作有效。[1]
国际驾驶执照之内容及格式依照维也纳道路交通会议制订,但并非各国均批准该公约。
Ein Internationaler Führerschein ist ein Dokument, das von den Straßenverkehrsbehörden oder Automobilclubs[1] eines Landes aufgrund zwischenstaatlicher Verträge ausgestellt wird. Er soll vor allem der Polizei eines anderen Landes die Feststellung ermöglichen, ob ein ausländischer Kraftfahrer die Fahrerlaubnis hat, die für sein aktuelles Fahrzeug erforderlich ist.
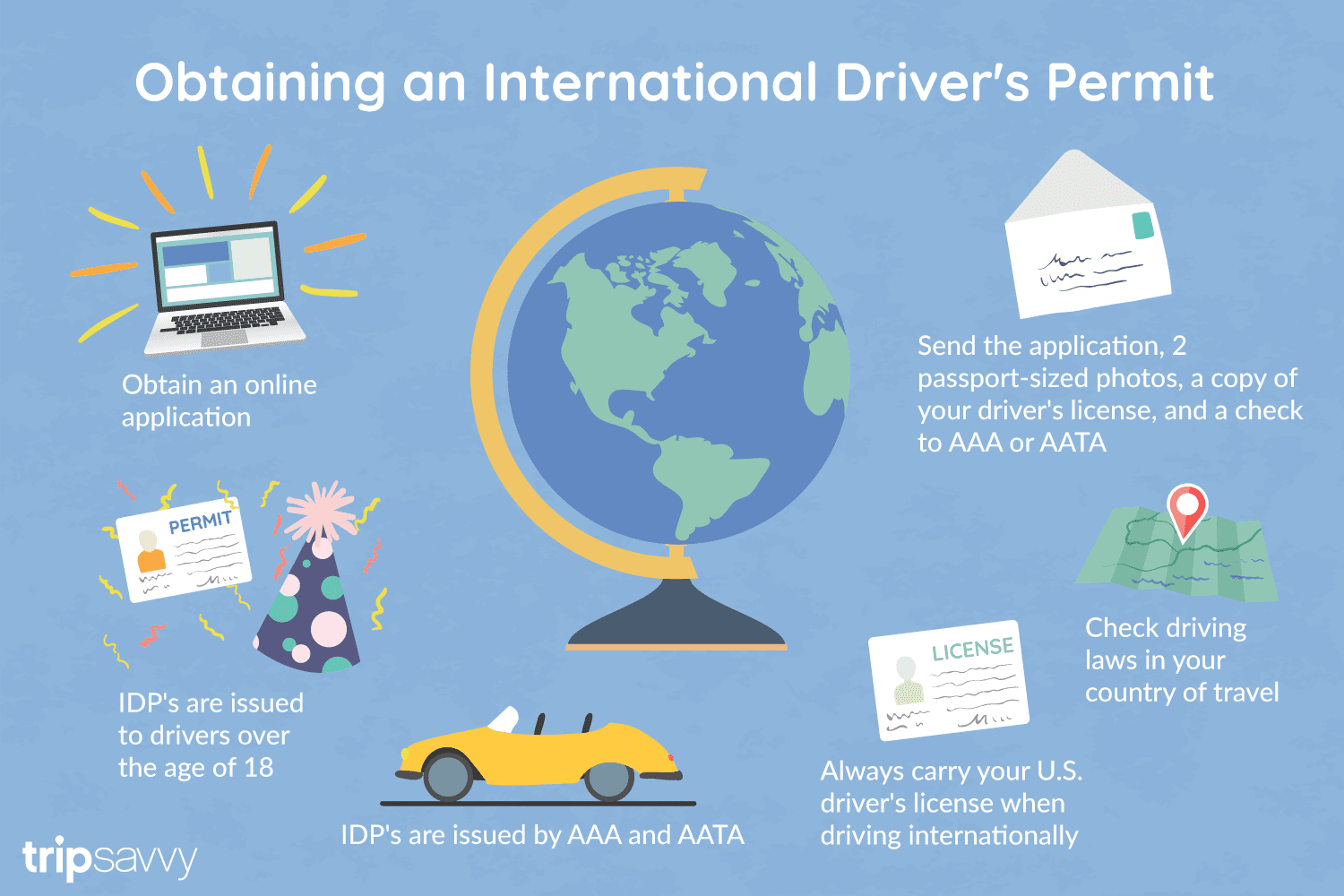
An International Driver's Permit (IDP) allows you to drive a vehicle in another country, as long as you also have a valid driver's license issued by your state. It is also recognized as a proper form of identification in over 175 countries and by many major car rental companies internationally.
Getting an International Driver's Permit (sometimes incorrectly called an international driver's license) can take anywhere from a day to a few weeks, depending on whether you're going through walk-in processing or applying via mail, so make sure to plan ahead if you're planning to drive on your international trip. There are only two locations in the United States that issue these documents: The American Automobile Association (AAA) and the American Automobile Touring Alliance (AATA).
In the United States, International Driver Permits (IDPs) are only issued by the American Automobile Association and the American Automobile Touring Alliance, and the State Department recommends against purchasing an IDP from other outlets as they are all entirely illegal to buy, carry, or sell.
IDPs can be issued to anyone over 18 who has had a valid driver's license for six months or longer. They typically remain valid for one year or the expiration of your existing state driving license. It's essential to investigate an IDP before your trip and make sure you know the requirements.
Both AAA and AATA are excellent sources for these documents, so once you've selected a provider, go to either the AAA's or NAATA's website, print out the International Driving Permit Application, complete all applicable fields, and submit it.
Once you have the application completed, you can send it in via the mail or visit a local office of an organization like AAA; you'll also need two original passport-sized photos and a signed copy of your valid U.S. driver's license as well as an enclosed check for the fee.
Tips to Getting and Using Your Permit
AAA offices can process IDPs during your visit, but processing generally takes 10 to 15 business days if you send the application in. However, expedited services may be available to get your license within one or two business days for an additional fee.
When applying, you'll need a computer and printer, a completed application, a copy of your valid U.S. driver's license, two passport photos, and a check, money order, or credit card to complete the process. Remember to bring these with you if you're applying in person.
Always make sure to carry your valid United States driver's license when driving internationally, as your IDP is invalid without this accompanying proof of eligibility to drive. IDPs only translate domestically-accepted licenses and do not allow those without government-issued driver's licenses to drive abroad.
You'll also want to make sure to enclose the proper fees (the fee for the IDP, as well as any shipping and handling fees), photos, and photocopies of your license when submitting your application to AAA or AATA as omitting any of these required documents will result in your application being rejected.
You should also check the driving requirements and laws for the countries you will be driving in on your vacation, so you'll know what will be required in the event you get stopped by local authorities. (Quelle:https://www.tripsavvy.com/)
 Argentina
Argentina
 Australia
Australia
 Belgium
Belgium
 Brazil
Brazil
 China
China
 Denmark
Denmark
 Germany
Germany

 Financial
Financial
 International Bank for Cooperation
International Bank for Cooperation
 France
France
 India
India
 Indonesia
Indonesia
 Internationaler Währungsfonds
Internationaler Währungsfonds
 Camille Gutt
Camille Gutt
 Internationaler Währungsfonds
Internationaler Währungsfonds
 Christine Lagarde
Christine Lagarde
 Internationaler Währungsfonds
Internationaler Währungsfonds
 Dominique Strauss-Kahn
Dominique Strauss-Kahn
 Internationaler Währungsfonds
Internationaler Währungsfonds
 Horst Köhler
Horst Köhler
 Internationaler Währungsfonds
Internationaler Währungsfonds
 Ivar Rooth
Ivar Rooth
 Internationaler Währungsfonds
Internationaler Währungsfonds
 Jacques de Larosière
Jacques de Larosière
 Internationaler Währungsfonds
Internationaler Währungsfonds
 Johan Witteveen
Johan Witteveen
 Internationaler Währungsfonds
Internationaler Währungsfonds
 Michel Camdessus
Michel Camdessus
 Internationaler Währungsfonds
Internationaler Währungsfonds
 Per Jacobsson
Per Jacobsson
 Internationaler Währungsfonds
Internationaler Währungsfonds
 Pierre-Paul Schweitzer
Pierre-Paul Schweitzer
 Internationaler Währungsfonds
Internationaler Währungsfonds
 Rodrigo Rato
Rodrigo Rato
 Internationaler Währungsfonds
Internationaler Währungsfonds
 Kristalina Georgiewa
Kristalina Georgiewa
 Italy
Italy
 Japan
Japan
 Canada
Canada
 Malaysia
Malaysia
 Mexico
Mexico
 Netherlands
Netherlands
 Nigeria
Nigeria
 Norwegen
Norwegen
 Austria
Austria
 Poland
Poland
 Republic of Korea
Republic of Korea
 Russia
Russia
 Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia
 Sweden
Sweden
 Switzerland
Switzerland
 Spain
Spain
 South Africa
South Africa
 Venezuela
Venezuela
 United States
United States
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom

 Washington, D.C.
Washington, D.C.

 Important International Organizations
Important International Organizations

 Economy and trade
Economy and trade
 Economic and political research
Economic and political research

国际货币基金组织(法语:Fonds Monétaire International,缩写:FMI;英语:International Monetary Fund,缩写:IMF)于1945年12月27日成立,与世界银行同为世界两大金融机构,由189个国家组成,致力于促进全球货币合作,确保金融稳定,促进国际贸易。职责是监察货币汇率和各国贸易情况、提供技术和资金协助[3][4][5],确保全球金融制度运作正常;其总部设置于美国华盛顿特区。
Der Internationale Währungsfonds (IWF; englisch International Monetary Fund, IMF; auch bekannt als Weltwährungsfonds) ist eine rechtlich, organisatorisch und finanziell selbständige Sonderorganisation der Vereinten Nationen mit Sitz in Washington, D.C., USA.
Hauptaufgabe des IWF ist die Vergabe von Krediten an Länder ohne ausreichende Währungsreserven, die in Zahlungsbilanzschwierigkeiten geraten sind. Weitere Tätigkeitsfelder sind die Förderung der internationalen Zusammenarbeit in der Währungspolitik, Ausweitung des Welthandels, Stabilisierung von Wechselkursen, Überwachung der Geldpolitik und technische Hilfe.
Der IWF und seine Schwesterorganisation Weltbank haben ihren Ursprung im 1944 geschaffenen Bretton-Woods-System fester Wechselkurse, das auf der damals mit Gold gedeckten Leitwährung US-Dollar beruhte. Sie waren als internationale Steuerungsinstrumente geplant, mit denen eine Wiederholung der Währungsturbulenzen der Zwischenkriegszeit und der Fehler des Goldstandards aus den 1920er Jahren verhindert werden sollte. Beide Organisationen werden daher als Bretton-Woods-Institution bezeichnet. Die Kreditvergabe des IWF ist an wirtschaftspolitische Auflagen geknüpft, die die Rückzahlung der Kredite sichern sollen. Anders als der IWF vergibt die Weltbank auch Kredite für spezielle Projekte.
Der IWF hat zurzeit (Stand April 2020) 189 Mitgliedstaaten, deren Stimmrecht sich an ihrem Kapitalanteil orientiert. Die Mitgliedstaaten mit den größten Stimmanteilen sind: USA 16,51 %, Japan 6,15 %, China 6,08 %, Deutschland 5,32 %, Frankreich 4,03 %, Vereinigtes Königreich 4,03 % und Italien 3,02 %. Von den deutschsprachigen Ländern haben außerdem Luxemburg 0,29 %, Österreich 0,81 % und die Schweiz 1,18 % Stimmenanteile.[4]
Beschlüsse müssen im IWF mit einer Mehrheit von 85 % getroffen werden. Dadurch verfügen jeweils die USA allein und die EU-Staaten gemeinsam de facto über eine Sperrminorität.[5]
国際通貨基金(こくさいつうかききん、英語: International Monetary Fund, IMF)は、国際金融、並びに、為替相場の安定化を目的として設立された国際連合(国連)の専門機関である。本部は、アメリカ合衆国の首都ワシントンD.C.にある。2018年現在、加盟国は189か国である[2]。
加盟国の経常収支が著しく悪化した場合などに融資などを実施することで、国際貿易の促進、加盟国の高水準の雇用と国民所得の増大、為替の安定、などに寄与する事を目的としている。 また、為替相場の安定のために、経常収支が悪化した国への融資や、為替相場と各国の為替政策の監視などを行っている。各国の中央銀行の取りまとめ役のような役割を負う。世界銀行と共に、国際金融秩序の根幹を成す。
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) is an international organization headquartered in Washington, D.C., consisting of 189 countries working to foster global monetary cooperation, secure financial stability, facilitate international trade, promote high employment and sustainable economic growth, and reduce poverty around the world while periodically depending on the World Bank for its resources.[1] Formed in 1944 at the Bretton Woods Conference primarily by the ideas of Harry Dexter White and John Maynard Keynes,[6] it came into formal existence in 1945 with 29 member countries and the goal of reconstructing the international payment system. It now plays a central role in the management of balance of payments difficulties and international financial crises.[7] Countries contribute funds to a pool through a quota system from which countries experiencing balance of payments problems can borrow money. As of 2016, the fund had XDR 477 billion (about US$ 667 billion).[8]
Through the fund and other activities such as the gathering of statistics and analysis, surveillance of its members' economies, and the demand for particular policies,[9] the IMF works to improve the economies of its member countries.[10] The organization's objectives stated in the Articles of Agreement are:[11] to promote international monetary co-operation, international trade, high employment, exchange-rate stability, sustainable economic growth, and making resources available to member countries in financial difficulty.[12] IMF funds come from two major sources: quotas and loans. Quotas, which are pooled funds of member nations, generate most IMF funds. The size of a member's quota depends on its economic and financial importance in the world. Nations with larger economic importance have larger quotas. The quotas are increased periodically as a means of boosting the IMF's resources in the form of special drawing rights.[13]
The current Managing Director (MD) and Chairwoman of the IMF is Bulgarian Economist Kristalina Georgieva, who has held the post since October 1, 2019.[14]
Gita Gopinath was appointed as Chief Economist of IMF from 1 October 2018. She received her PhD in economics from Princeton University. Prior to her IMF appointment she was economic adviser to the Chief Minister of Kerala, India.[15]
Le Fonds monétaire international (FMI) est une institution internationale regroupant 189 pays, dont le but est de promouvoir la coopération monétaire internationale, garantir la stabilité financière, faciliter les échanges internationaux, contribuer à un niveau élevé d’emploi, à la stabilité économique et faire reculer la pauvreté2.
Le FMI a ainsi pour fonction d'assurer la stabilité du système monétaire international (SMI) et la gestion des crises monétaires et financières. Pour cela, il fournit des crédits aux pays qui connaissent des difficultés financières mettant en péril l'organisation gouvernementale du pays, la stabilité de son système financier (banques, marchés financiers) ou les flux d'échanges de commerce international avec les autres pays.
Lors d'une crise financière, pour éviter qu’un pays ne fasse « défaut » (c’est-à-dire que ce pays ne puisse plus rembourser ses créanciers, voire ne plus payer ses dépenses courantes), le FMI lui prête de l’argent le temps que la confiance des agents économiques revienne. Le FMI conditionne l’obtention de prêts à la mise en place de certaines réformes économiques visant en principe à réguler la gestion des finances publiques (ingérence financière) et à établir une croissance économique équilibrée à long terme.
L'institution a été créée le 27 décembre 1945 et devait à l'origine garantir la stabilité du système monétaire international, dont l'écroulement après le krach de 1929 avait eu des effets catastrophiques sur l'économie mondiale. Après 1976 et la disparition d’un système de change fixe, le FMI perd l'essentiel de sa raison d'être et hérite d'un nouveau rôle face aux problèmes d'endettement des pays en développement et à certaines crises financières.
Il Fondo Monetario Internazionale (in sigla FMI; in inglese International Monetary Fund, IMF) è un'organizzazione internazionale pubblica[1] a carattere universale composta dai governi nazionali di 189 Paesi e insieme al gruppo della Banca Mondiale fa parte delle organizzazioni internazionali dette di Bretton Woods, dal nome della località in cui si tenne la famosa conferenza che ne sancì la creazione. L'FMI è stato formalmente istituito il 27 dicembre 1945, quando i primi 44 stati firmarono l'accordo istitutivo e l'organizzazione nacque nel maggio del 1946. Attualmente gli Stati membri sono 189.
El Fondo Monetario Internacional o FMI (en inglés: International Monetary Fund, IMF) es una organización financiera internacional con sede en Washington D. C., Estados Unidos. Nace como idea el 22 de julio de 1944 en los acuerdos de Bretton Woods, una reunión de 730 delegados de 44 países aliados de la Segunda Guerra Mundial, entrando en vigor oficialmente el 27 de diciembre de 1945. Después de 1976 y de la desaparición del sistema de cambio fijo, el FMI toma un papel preponderante ante países en desarrollo y crisis financieras internacionales. En 2010, durante la 14ª revisión general de cuotas los fondos financieros disponibles del FMI se situaban en 755 700 millones de U.S.dólares.1
A través del fondo y otras actividades como la recolección de estadísticas y datos, monitoreo de las actividades económicas de los países miembros, y la demanda de políticas concretas,2 el FMI trabaja para mejorar la economía de sus países miembros.3 Los objetivos proclamados por la organización son:4 promover la cooperación monetaria internacional, comercio internacional, reducir la desocupación, conseguir tasas de cambio sustentables, lograr crecimiento económico, y otorgar razonablemente recursos a países miembros en dificultades económicas.5 El FMI se financia con dos grandes herramientas: cuotas y préstamo. Las cuotas son aportes realizados por los países miembros al fondo común de la organización. Las mayores economías hacen aportes proporcionales mayores que las economías más pequeñas. Además, las obligaciones de cuotas aumentan periódicamente como forma de aumentar los recursos de los que puede disponer el FMI en forma de derechos especiales de giro.6
Esta organización ha sido fuertemente criticada en las últimas décadas. Las principales críticas se centran en el papel dominante que tienen los países desarrollados dentro del organismo, lo que causa que el FMI oriente sus políticas globales al fomento de un capitalismo que suele denominarse neoliberal,7 a causa de haber impuesto a los países en vías de desarrollo —y más recientemente a algunos países europeos— sus programas económicos basados en el Consenso de Washington que consisten en la reducción del déficit y del gasto público y consecuentemente de servicios y prestaciones sociales, con fundamento en las políticas y teorías monetaristas y en el principio de libre mercado,8 que deben llevarse a cabo como condiciones de los préstamos realizados y que según sus críticos ha provocado un aumento de la brecha entre ricos y pobres y un empeoramiento de los servicios públicos, como la sanidad.9 También está acusada por haber apoyado y financiado a las dictaduras militares en Latinoamérica y Africa,10 y se le han criticado puntualmente sus políticas sobre medio ambiente11 y alimentación.12
Международный валютный фонд, (МВФ) (англ. International Monetary Fund, IMF) — специализированное учреждение (валютный фонд) Организации объединённых наций (ООН) с главным офисом в городе Вашингтон, США.
189 стран являются членами МВФ, в его структурах работают 2500 человек из 133 государств мира. МВФ предоставляет кратко- и среднесрочные кредиты при дефиците платёжного баланса государства. Предоставление кредитов обычно сопровождается набором определённых условий и рекомендаций. Политика и рекомендации МВФ в отношении развивающихся стран неоднократно подвергались критике, суть которой состоит в том, что выполнение рекомендаций и условий, в итоге, направлено не на повышение самостоятельности, стабильности и развитие национальной экономики государства, а лишь на привязывание её к международным финансовым потокам.
В отличие от Всемирного банка, деятельность МВФ сосредоточена на относительно кратковременных макроэкономических кризисах. Всемирный банк предоставляет кредиты только бедным странам, МВФ может давать кредиты любой из своих стран-членов, которая испытывает нехватку иностранной валюты для покрытия краткосрочных финансовых обязательств.

 *U.S. foreign territories
*U.S. foreign territories
 Australia
Australia
 China
China
 Germany
Germany
 France
France
 ITU World Championship Series
ITU World Championship Series
 Japan
Japan
 Canada
Canada
 Kasachstan
Kasachstan
 Mexico
Mexico
 New Zealand
New Zealand
 Netherlands
Netherlands
 Austria
Austria
 Portugal
Portugal
 Republic of Korea
Republic of Korea
 Sweden
Sweden
 Switzerland
Switzerland
 Spain
Spain
 South Africa
South Africa
 Hungary
Hungary
 United Arab Emirates
United Arab Emirates
 United States
United States
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 Bermuda
Bermuda



约翰内斯堡(南非语、英语:Johannesburg;科萨语:eGoli;祖鲁语:iGoli),简称约堡(英语:Jo'burg)[1],是南非最大的城市与经济、文化中心,同时也是为世界上最大的50个城市之一[6]。约翰内斯堡为豪登省首府和最大城市,也是该省最富裕的地区[7]。虽然约翰内斯堡不是南非三个首都城市之一,但它是宪法法院的所在地。这城市位于富含矿物的维瓦特斯兰山脉中,是世界上最大规模黄金和钻石贸易的中心。
这座大都市是全球化与世界城市研究网络列出的全球城市之一。2011年,约翰内斯堡市的人口为4,434,827,成为南非人口最多的城市[8]。同年,大约翰内斯堡都会区人口为7,860,781[9]。但都会区的面积达1,645平方公里(635平方英里),较其他主要城市大,所以人口密度为较适中的2,364/平方公里(6,120平方英里)。
这城市成立于1886年,当时在农场发现了黄金。由于威特沃特斯兰德发现了极大规模的金矿,这座城市通常被形容为现代的黄金国[10]。该名称源于参与建立城市的三名男子中的一人或全部。在十年来,人口增长达到10万。
从20世纪70年代末到1994年,索韦托是一个独立的城市,现在则为约翰内斯堡的一部分。索韦托最初是“South-Western Townships”的首字母缩写,其起源于约翰内斯堡郊区的一系列定居点,主要由来自黄金采矿业的非洲本地工人居住。索韦托虽然最终被并入约翰内斯堡,但已经被分开作为黑人的住宅区,他们不被允许居住在约翰内斯堡。兰萨尼亚主要由讲英语的印度裔南非人居住。根据南非白人政府的种族隔离政策,这些地区被指定为非白人地区。
Johannesburg, auch iGoli/eGoli (isiZulu für ‚Ort des Goldes‘) oder iRhawutini (isiXhosa), umgangssprachlich oft Joburg oder Jozi, ist die Hauptstadt der Provinz Gauteng in Südafrika.
Mit 957.441 Einwohnern (Volkszählung 2011) ist Johannesburg die größte Stadt und der gesamte Großraum City of Johannesburg Metropolitan Municipality mit etwa 4,43 Millionen Einwohnern die größte Metropolregion im südlichen Afrika. Hauptstadt Südafrikas ist allerdings das rund 50 Kilometer nördlich gelegene Pretoria. Bürgermeister der Stadt ist seit 2016 Herman Mashaba (Democratic Alliance).
ヨハネスブルグ(Johannesburg、アフリカーンス語: [juˈɦɑnəsbœrx, juɦɑnəsˈbœrx]、英語: [dʒoʊˈhænɪsbɜrɡ]、南アフリカ英語: [ʤəˈhænəsbøːg]、ズールー語: IGoli)[1]は、南アフリカ共和国ハウテン州にある都市(都市圏)、同州の州都である。同国最大の都市であり、人口は2011年で約443万人[2]。2011年の近郊を含む都市圏人口は755万人であり、同国第1位、アフリカでは第4位である[3]。
アフリカを代表する世界都市の一つであり、アメリカのシンクタンクが2017年に発表した総合的な世界都市ランキングにおいて、世界53位の都市と評価された[4]。アフリカの都市では首位である。また、2016年に発表された「世界の都市総合力ランキング」では、世界42位と評価された[5]。都市のGDPは1100億ドルで、南部アフリカ第1位である[6]。アフリカ最大の証券取引所であるJSEの所在地でもあり、アフリカ最高の金融センターと評価されている[7]。ヨハネスバーグとも表記される[8]。
Johannesburg (/dʒoʊˈhænɪsbɜːrɡ/; Afrikaans: [jʊəˈɦanəsbœrχ]; also known as Jozi, Jo'burg, and eGoli)[1] is the largest city in South Africa and one of the 50 largest urban areas in the world.[10] It is the provincial capital and largest city of Gauteng, which is the wealthiest province in South Africa.[11] While Johannesburg is not one of South Africa's three capital cities, it is the seat of the Constitutional Court. The city is located in the mineral-rich Witwatersrand range of hills and is the centre of large-scale gold and diamond trade.
The metropolis is an alpha global city as listed by the Globalization and World Cities Research Network. In 2011, the population of the city of Johannesburg was 4,434,827, making it the most populous city in South Africa.[12] In the same year, the population of Johannesburg's urban agglomeration was put at 7,860,781.[5] The land area of the municipal city (1,645 km2 (635 sq mi)) is large in comparison with those of other major cities, resulting in a moderate population density of 2,364/km2 (6,120/sq mi).
The city was established in 1886 following the discovery of gold on what had been a farm. The city is commonly interpreted as the modern day El Dorado[by whom?] due to the extremely large gold deposit found along the Witwatersrand.[13] In ten years, the population grew to 100,000 inhabitants.
A separate city from the late 1970s until 1994, Soweto is now part of Johannesburg. Originally an acronym for "South-Western Townships", Soweto originated as a collection of settlements on the outskirts of Johannesburg, populated mostly by native African workers from the gold mining industry. Soweto, although eventually incorporated into Johannesburg, had been separated as a residential area for Blacks, who were not permitted to live in Johannesburg proper. Lenasia is predominantly populated by English-speaking South Africans of Indian descent. These areas were designated as non-white areas in accordance with the segregationist policies of the South African government known as Apartheid.
Johannesbourg (Johannesburg en afrikaans et en anglais) est une métropole d'Afrique du Sud, fondée en 1886 au Transvaal. Elle est l'actuelle capitale de la province de Gauteng, la plus riche du pays. L'agglomération de Johannesbourg-Pretoria se classe parmi les trente plus grandes régions métropolitaines du monde, avec plus de 12 millions d'habitants, et est l'une des six villes mondiales d'Afrique.
Située sur le gisement aurifère du Witwatersrand, Johannesbourg est considérée comme la capitale économique du pays ; elle abrite ainsi la bourse d'Afrique du Sud. La ville est également hôte de la Cour Constitutionnelle, qui y a son siège dans le quartier de Braamfontein.
Elle accueille environ, en 2000, 710 000 habitants (4 434 827 habitants dans la municipalité1), ce qui en fait, de loin, la ville la plus peuplée du pays. Avec son agglomération, elle est la troisième ville la plus peuplée d'Afrique. La ville a été hôte du Sommet de la Terre 2002, le second sommet de la Terre dit « sommet de Johannesbourg » pour les associations et ONG qui y tenaient un sommet parallèle à celui des États, dix ans après le « sommet de Rio » de 1990.
Johannesburg è una città del Sudafrica, capoluogo della provincia di Gauteng.
È la città più popolosa del Sudafrica e la terza più popolosa dell'Africa subsahariana dopo Lagos (Nigeria) e Kinshasa (Repubblica Democratica del Congo). Viene anche informalmente chiamata Joburg, Jozi e eGoli; quest'ultimo nome, che significa "luogo d'oro" in zulu, può essere riferita all'attività mineraria nella zona o alla ricchezza economica della città. Johannesburg non è la capitale del Sudafrica; le capitali dello stato sono tre: Pretoria (amministrativa), Città del Capo (legislativa) e Bloemfontein (giudiziaria).
Johannesburgo (en afrikáans e inglés: Johannesburg, en zulú: Igoli, 'lugar de oro'2) es la ciudad más grande y poblada de Sudáfrica. Es la capital de la provincia de Gauteng, la más rica de dicho país y la cuarta economía más grande del África austral. Coloquialmente los sudafricanos le llaman Joburg, Jozi,3 o JHB. Así mismo es considerada el principal centro económico y financiero del país.
Esta ciudad es una de las 40 áreas metropolitanas más grandes del mundo4 y una de las únicas tres de África oficialmente denominadas "ciudad global" (clasificada como una ciudad de clase mundial); las otras dos son El Cairo y Ciudad del Cabo.5
Erróneamente, se le confunde con la capital de Sudáfrica (este país posee tres ciudades capitales oficiales, de las cuales Johannesburgo no forma parte). Sin embargo, allí se ubica la Corte Constitucional, la corte de mayor rango de todo Sudáfrica.
En Johannesburgo existe comercio a gran escala de oro y diamantes, debido a su ubicación privilegiada en el área de las colinas de Witwatersrand muy ricas en minerales.
Johannesburgo recibe visitantes por medio del Aeropuerto Internacional O.R. Tambo, el más grande y con mayor circulación en África y puerta aérea al resto del sur de África.
Es una de las pocas grandes ciudades del mundo que ni están en la costa, ni poseen un río importante o canal que la comunique con el mar (como Madrid o Berlín). Los cambios en las fronteras municipales llevadas al efecto en el año 2000, han hecho que la población alcanzara los 3 millones (5.61 millones en 2013).
La población del área metropolitana (que incluye los otros municipios del Gauteng excepto Pretoria) se estima actualmente en unos 9 millones de habitantes.
Eso la convierte en la tercera ciudad más poblada de África tras El Cairo y Lagos.
Johannesburgo es una ciudad con un contraste muy fuerte entre la minoría de blanca (17%) que vive con parámetros de país desarrollado y una población de negra (73%) con unos niveles de vida tercermundistas.
La ciudad se halla en la línea divisoria de aguas entre los océanos Atlántico e Índico.
Йоха́ннесбург (англ. Johannesburg [dʒoʊˈhænɪsbɜrɡ], африк. Johannesburg [joˈhɑnəsbʏrx], зулу iGoli, коса iRhawutini) — самый крупный по численности жителей город в ЮАР. Местные жители называют его «Йобург», «Йози» и «Еголи». Йоханнесбург — центр провинции Гаутенг, самой богатой провинции в ЮАР. В 2010 году в Йоханнесбурге проводились матчи Чемпионата Мира по футболу.
Население муниципалитета на конец 2011 года составляло 4 434 827 жителей[4], а всей агломерации — 7 860 781 человек. Однако если считать с окрестностями метрополии, население превышает восемь миллионов жителей.
Территория, подчинённая городу, достаточно большая. К Йоханнесбургу на юго-западе непосредственно примыкает город Соуэто, в котором сосредоточено большое количество мигрантов и сезонных рабочих.
В 2000 году из города Йоханнесбург и окружающих его территорий была сформирована новая административная единица — городской округ Йоханнесбург.
В Йоханнесбурге расположен Конституционный Суд ЮАР.
В 2002 году в городе состоялась встреча на высшем уровне по вопросам устойчивого развития. Йоханнесбург — центр широкомасштабной торговли золотом и алмазами, которые добывают в окрестных горах.

 FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 2010
FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 2010

 International cities
International cities
 *World Design Capital
*World Design Capital
 Silk road
Silk road

 Sport
Sport
 The Ocean Race
The Ocean Race
 South Africa
South Africa

 Important port
Important port

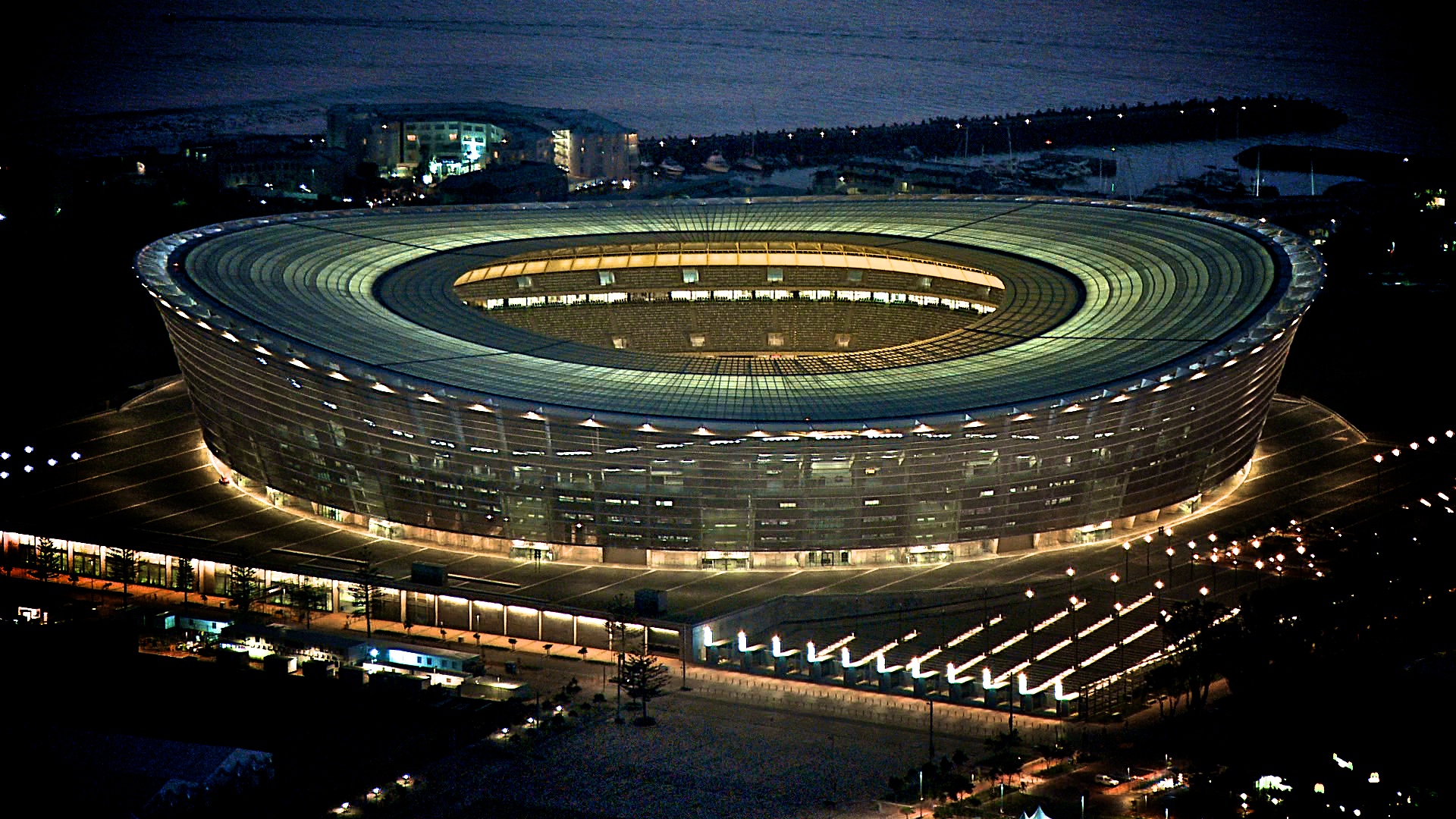
开普敦是南非第二大城市和重要港口,立法机关所在地,开普敦省首府。开普敦位于南非西南端,临大西洋桌湾,南距好望角52公里,处于重要国际航线的交汇点。开普敦始建于1652年,是西欧殖民者在南部非洲最早建立的据点,曾长期是荷兰、英国殖 民者向非洲内陆扩张的基地。城市背山面海,风光绮丽,文物众多,旅游业兴盛,工商业发达。城市有大型纺织、酿酒、烟叶、炼油等工业,还有化工、皮革、造纸 等企业。港口优良,可同时停泊近百艘海轮,有世界著名的现代化大船坞,并建有国际航空港,主要出口皮革、水果、纺织品等。城市有著名的开普敦大学、南非博 物馆等。
1652年荷兰东印度公司为了在非洲建立一个补给站,以供应往来欧亚间的船只,于是选择了南非开普敦省的桌湾做为据地。在当年,开普敦尚是一块不毛之地,然历经300多年的演变,今日的开普敦却成了南非最古老且最富特色的城市了。
从1652年建城开始,似乎即注定了开普敦多舛的命运。她曾是葡萄牙人、荷兰人、法国人与英国人争相拥有的海上客栈。
在1870年正值英国人在此兴建直达约翰内斯堡铁路时,赫然发现了钻石矿,立即引来了大批的掘宝客及挖矿的奴隶,其中,以印度人、马来人及中国人居多。
100多年前,开普敦周围仍是独立小城林立。开普敦真正具有国际港口规模,是在1913年南非联邦成立后,由于地位的确定及组织的完善,造就了开普敦在80多年后的今天,成为一座缤纷多彩的美丽城市,备受世人欣赏与惊叹。(Quelle:http://www.aiutrip.com)
开普敦(英语:Cape Town;南非荷兰语:Kaapstad /ˈkɑːpstɑt/;科萨语:iKapa),是南非人口排名第二大城市,也是开普敦都会城区组成部分、西开普省省会,开普敦为南非立法首都,因此国会及很多政府部门亦座落于该市。开普敦以其美丽的自然景观及码头闻名,知名的地标有被誉为“上帝之餐桌”的桌山,以及印度洋和大西洋的交汇点好望角。因其美丽的自然及地理环境,开普敦被称为世界最美丽的城市之一,亦成为南非其中一处旅游胜地。
开普敦最初环绕码头发展,因为由荷兰开往东非、印度和亚洲的商船都会路经此地作补给,久而久之便成为欧洲人在撒哈拉以南非洲地区的第一个长期聚居点。其后欧洲人亦建立了他们的第一所军事基地好望堡,亦即good hope castle,在约翰内斯堡的建立及在德兰士瓦发现大量的黄金和钻石之前,开普敦是非洲南部最大的城市。开普敦拥有南非第二繁忙的机场开普敦国际机场,是世界旅客到南非的主要渠道之一。
Kapstadt wird von den Südafrikanern gern als “Moederstad” (Mutterstadt) bezeichnet, da es zur Kolonialzeit eine der ersten gegründeten Städte war. Sein Name leitet sich vom nahe gelegenen Kap der guten Hoffnung ab, welches man durchfahren musste um nach Indien zu gelangen. Berühmt ist Kapstadt für seine einzigartige Skyline, aus welcher vor allem der Table Mountain (Tafelberg), der Lion`s Head (Löwenkopf, oder auch als Löwenberg zu finden), sowie der Devil`s Peak (Teufelspitze) herausstechen.
Gegründet wurde Kapstadt 1652, von dem niederländischen Schiffsarzt Jan Anthoniszoon van Riebeeck, als Versorgungsstation für die niederländische Handelsflotte, wenn diese auf ihrem Weg nach Indien unterwegs war. 1814 übernahmen die Briten die Herrschaft über Kapstadt. 1860 lies Prinz Alfred, der zweite Sohn von Königin Victoria, den Grundstein für eine neue, größere Hafenanlage legen. In den folgenden Jahren, unter dem Einfluss der etwa zu selben Zeit entdeckten Goldvorkommen im Landesinneren, wuchs der nun zu klein gewordene Hafen noch einmal an.
Die aus dieser Zeit erhaltenen und in den 90er Jahren aufwendig restaurierten Gebäude machen den Hafen zu einem Victorianischen Kleinod, welches seines gleichen sucht. Ebenso findet sich hier im Hafen das “Robben Island Embarkation Building”. Von hier starten die 3 stündigen geführten Touren auf die Insel.(Quelle:http://www.mytraveltips.de/afrika/kapstadt-eine-reise-in-die-geschichte/)
Kapstadt (englisch Cape Town, afrikaans Kaapstad, isiXhosa iKapa) ist eine der größten Städte Südafrikas. Seit 2004 bildet sie den ausschließlichen Sitz des südafrikanischen Parlaments. Kapstadt ist die Hauptstadt der Provinz Westkap und ist der Kernort der City of Cape Town Metropolitan Municipality, die Metropolgemeinde um Kapstadt. Als von der Statistik erfasster Ort (Main Place) hatte Kapstadt 433.688 Einwohner im Jahr 2011.[1]
Den Namen erhielt Kapstadt nach dem Kap der Guten Hoffnung, das etwa 45 Kilometer südlicher liegt und eine Hauptgefahr auf dem Seeweg nach Indien darstellte. Da Kapstadt die erste Stadtgründung der südafrikanischen Kolonialzeit war, wird es gelegentlich als „Mutterstadt“ (afrikaans: Moederstad, englisch: Mother City) bezeichnet.
ケープタウン(英語: Cape Town、アフリカーンス語: Kaapstad、コサ語: IKapa)は、南アフリカ共和国西ケープ州に位置する都市(都市圏)である。立法府所在地で、同州の州都。アフリカ有数の世界都市である。
テーブル湾に面する同市はその港が有名であるとともに、世界的に有名なテーブルマウンテンや喜望峰などを含んだケープ草原(en:Cape floral kingdom)のなかにある。
ケープタウンはもともと東アフリカ・インド・東アジア貿易に携わるオランダ船の食料基地として建設されており、それはスエズ運河が1869年に建設される200年以上も前のことであった。ヤン・ファン・リーベックが1652年4月6日に到着して南アフリカで初めてのヨーロッパ植民地を設立するのであるが、ケープタウンは急速に成長してヨーロッパ初の前哨基地(キャッスル・オブ・グッドホープ)という元々の目的を超えてしまった。ヨハネスブルグやダーバンが成長するまでは南アフリカ最大の都市であったのである。南アフリカに始めて白人が入植した土地であり、のちの内陸部へのすべての開拓の起点ともなった。そのため、南アフリカの白人からは「マザー・シティー」(母なる都市)との愛称で呼ばれる。
2001年の南アフリカの国勢調査によれば、ケープタウン大都市圏は295万人の人口を持ち、[1] 面積は2499平方キロメートルで南アフリカの他の都市よりも大きい。この結果、人口密度は比較的低くなり1平方キロメートルあたり1158人である。ケープタウンはフランスのニースやイスラエルのハイファと姉妹都市となっている。
Cape Town (Afrikaans: Kaapstad [ˈkɑːpstat]; Xhosa: iKapa; Dutch: Kaapstad; South Sotho: Motse Kapa) is the oldest city in South Africa, colloquially named the Mother City. It is the legislative capital of South Africa and primate city of the Western Cape province.[7] It forms part of the City of Cape Town metropolitan municipality.
The Parliament of South Africa sits in Cape Town.[8] The other two capitals are located in Pretoria (the administrative capital where the Presidency is based) and Bloemfontein (the judicial capital where the Supreme Court of Appeal is located).[9] The city is known for its harbour, for its natural setting in the Cape Floristic Region, and for landmarks such as Table Mountain and Cape Point. Cape Town is home to 64% of the Western Cape's population.[10] It is one of the most multicultural cities in the world, reflecting its role as a major destination for immigrants and expatriates to South Africa.[11] The city was named the World Design Capital for 2014 by the International Council of Societies of Industrial Design.[12] In 2014, Cape Town was named the best place in the world to visit by both The New York Times[13] and The Daily Telegraph.[14]
Located on the shore of Table Bay, Cape Town, as the oldest urban area in South Africa, was developed by the Dutch East India Company (VOC) as a supply station for Dutch ships sailing to East Africa, India, and the Far East. Jan van Riebeeck's arrival on 6 April 1652 established Dutch Cape Colony, the first permanent European settlement in South Africa. Cape Town outgrew its original purpose as the first European outpost at the Castle of Good Hope, becoming the economic and cultural hub of the Cape Colony. Until the Witwatersrand Gold Rush and the development of Johannesburg, Cape Town was the largest city in South Africa.
Le Cap (Kaapstad en afrikaans, Cape Town en anglais, iKapa en xhosa) est une ville d'Afrique du Sud, capitale de la colonie du Cap (1652-1910) puis de la province du Cap (1910-1994). Elle est actuellement la capitale provinciale du Cap-Occidental.
Depuis 1910, Le Cap est également la capitale parlementaire du pays aux côtés de Pretoria (capitale administrative) et de Bloemfontein (capitale judiciaire).
La ville du Cap, fondée en 1652, est considérée comme la cité-mère d'Afrique du Sud. Ville la plus australe du continent africain, elle est établie sur les rives de la baie de la Table et est surmontée par la Montagne de la Table coiffée de deux pics nommés Lion's Head et Devil's Peak. La ville a été baptisée en référence au Cap de Bonne-Espérance situé à plus de 47 km au sud de son centre historique.
Città del Capo (in afrikaans Kaapstad, in xhosa iKapa, in inglese Cape Town, 3 497 097 abitanti nel 2007) è la capitale legislativa del Sudafrica[1] e la terza città più popolosa del Paese. Amministrativamente facente parte della provincia del Capo Occidentale, della quale è capoluogo, il suo centro si trova all'estremità settentrionale della penisola del Capo, a circa 47 km a nord del capo di Buona Speranza.
Fondata nel 1652, Città del Capo fu il primo insediamento europeo del Sudafrica; di qui il suo soprannome di città madre. Capitale della colonia del Capo prima (1652-1910) e capoluogo della provincia del Capo dopo (1910-1994), tutta la storia del Sudafrica moderno, dallo storico sbarco dei primi coloni olandesi al primo discorso di Nelson Mandela dell'era post-apartheid ha qui lasciato indelebili tracce culturali e architettoniche. Antichi edifici in stile coloniale olandese del Capo e di epoca vittoriana coesistono con moderni grattacieli e lussureggianti giardini botanici.
Città del Capo è dotata di un aeroporto internazionale e può considerarsi la capitale del turismo del Sudafrica. I numerosi visitatori sono attratti sia dalla città in sé che dalle bellezze naturalistiche della Penisola del Capo; molti tour del Paese partono da qui, imboccando poi le celebri Wine Route e Garden Route, dirigendosi verso il Karoo, il Boland o la costa meridionale.
Ciudad del Cabo (en afrikáans, Kaapstad /ˈkɑːpstɑt/; en inglés, Cape Town; en xhosa, iKapa) es la segunda ciudad más poblada de Sudáfrica, después de Johannesburgo. Forma parte del municipio metropolitano de la Ciudad del Cabo. Es la capital de la Provincia Occidental del Cabo, así como la capital legislativa de Sudáfrica, donde se ubican tanto el Parlamento Nacional como muchas otras sedes gubernamentales. Ciudad del Cabo es famosa por su puerto, así como por su conjunción natural de flora, la Montaña de la Mesa y Punta del Cabo. Es también el destino turístico más popular de África.4
Situada en la Bahía de la Mesa, se desarrolló originalmente como estación de abastecimiento para los barcos de la Compañía Neerlandesa de las Indias Orientales, que viajaban a África Oriental, India y Asia, más de doscientos años antes de la apertura del Canal de Suez en 1869. La llegada del navegante holandés Jan van Riebeeck el 6 de abril de 1652 significó el establecimiento del primer asentamiento europeo en el África subsahariana. Rápidamente superó su propósito original como el primer puesto de avanzada en el Castillo de Buena Esperanza, convirtiéndose en el centro económico y cultural de la Colonia del Cabo. Hasta la fiebre del oro de Witwatersrand y el desarrollo de Johannesburgo y Durban, Ciudad del Cabo era la ciudad más grande de Sudáfrica.
Desde 2007 la ciudad tiene una población estimada de 3,5 millones de habitantes.5 Su superficie de 2.499 kilómetros cuadrados la convierte en una de las ciudades más extensas del país, con una densidad demográfica comparativamente baja de 1.425 habitantes por kilómetro cuadrado.
En Robben Island (lit. ‘isla de las focas’), una isla muy cercana a Ciudad del Cabo, estuvo preso durante 27 años el líder del movimiento anti-apartheid y Premio Nobel de la Paz, Nelson Mandela.
Desde el fin del Apartheid, Ciudad del Cabo se mantiene como la plaza fuerte de la oposición política al ANC, siendo la única gran ciudad gobernada por la oposición. Ciudad del Cabo ocupa el 85º puesto entre 215 ciudades del mundo por su nivel y calidad de vida, siendo la 1.ª ciudad de Sudáfrica y de África (según este ranquin realizado por el Mercer Human Resources Consulting) y su alcaldesa Helen Zille fue nombrada mejor alcalde de 2008 (en sus tres años de gobierno el PIB de la ciudad creció en un 12 %, la delincuencia descendió en un 90 % y el desempleo cayó del 21 al 18 %).
Ciudad del Cabo es una de las ciudades más multiculturales del mundo, reflejando su rol como mayor destino para inmigrantes y expatriados de Sudáfrica. La ciudad fue nombrada Capital Mundial del Diseño en 2014 por el 'International Council of Societies of Industrial Design'. En 2014, Ciudad del Cabo fue nombrado como el mejor lugar del mundo para ser visitado por el 'American New York Times' y el 'British Daily Telegraph'.
Кейпта́ун (англ. Cape Town, африк. Kaapstad, коса iKapa,сесото Motse Kapa) — второй по численности населения (после Йоханнесбурга) город Южно-Африканской Республики. Расположен на юго-западе страны на побережье Атлантического океана, недалеко от Мыса Доброй Надежды. Столица Западно-Капской провинции, законодательная столица ЮАР. Входит в городской округ Кейптаун.
В Кейптауне расположены парламент ЮАР и многие правительственные учреждения. Город знаменит своей гаванью и известными на весь мир достопримечательностями, такими как Столовая гора (Южная Африка), мыс Доброй Надежды, Кейп-Пойнт. Кейптаун часто называют одним из красивейших городов мира, который является самым посещаемым туристами городом Южной Африки.
Кейптаун развивался как перевалочный пункт для голландских кораблей по пути из Европы в Восточную Африку, Индию и другие части Азии и играл ведущую роль в этом качестве более 200 лет, до открытия Суэцкого канала в 1869 году. Кейптаун, основанный 6 апреля 1652 года колонистами под руководством Яна ван Рибека, долгое время оставался столицей и крупнейшим городом Капской колонии.



绿植葱茏的康斯坦亚山谷是Klein Constantia(克莱坦亚酒园)的所在地是好望角地区历史最悠久的葡萄园汇集地, 在1689年就开始酿造葡萄酒。康斯坦亚山谷在18世纪酿制出的 '康斯坦亚' 葡萄酒,曾被当时包括拿破仑在内的全欧洲诸多统治者及贵族大加赞赏,克莱坦亚酒园已凭藉此款著名甜酒的重新复兴。由家族拥有并经营的克莱坦亚酒园,其酿酒 理念建立在品质至上,而非数量。
Klein Constantia的葡萄园紧靠南太平洋,海洋和山脉形成的特殊气候环境为酿造高品质的葡萄酒创造了良好的条件。Klein Constantia距离开普敦市中心20公里。从酒庄望去,Constantia山谷和False湾的景色尽收眼底,是世界上最美的葡萄园之一。
Klein Constantia是开普敦地区唯一一个赢得南非农业局功勋奖章的酒厂。
Klein Constantia系列中最受欢迎的葡萄酒非Vin de Constance莫属。它是由18-19世纪著名的Constantia葡萄酒复制出来的,酒庄甚至复制了原始的500毫升的酒瓶用来装酒。这种酒呈天 然金黄色,不经过任何强化处理,在法国橡木桶中陈酿2年,再经过瓶储3年后才是它的最佳饮用期。(Quelle:http://www.vinehoo.com)

库玛拉是英国市场最畅销的南非葡萄酒品牌,其成功的秘诀就在于高水准且高稳定性的品质。拥有酿造与种植学位的年轻酿酒师本•乔丹(Ben Jordan),将美国、澳洲等地的新式酿酒风格融入库玛拉的酿制中,酿制出了出最富表现力的南非葡萄酒。
库玛拉酒庄出产多种类型的葡萄酒,除以酒庄命名的干红、干白、桃红葡萄酒外,还包括巅峰桃红葡萄酒(Zenith Rose)、巅峰白诗南-霞多丽干 白葡萄酒(Zenith Chenin/Chardonnay Blend)、巅峰梅洛-赤霞珠-西拉干红葡萄酒(Zenith Merlot/Cabernet/Shiraz Blend)、西开普西拉干红葡萄酒(Western Cape Shiraz)、西开普霞多丽干白葡萄酒(Western Cape Chardonnay)、半甜红葡萄酒(Medium Sweet Red Wine)、皮诺塔吉•西拉干红葡萄酒(Pinotage Shiraz)以及鸽笼白-霞多丽干白葡萄酒(Colombard Chardonnay)。 (Quelle:http://www.wine-world.com/)
 Party and government
Party and government
 Driving school
Driving school
 United Nations
United Nations
 Animal world
Animal world
 Geography
Geography
 Architecture
Architecture
 Eat and Drink
Eat and Drink