
漢德百科全書 | 汉德百科全书
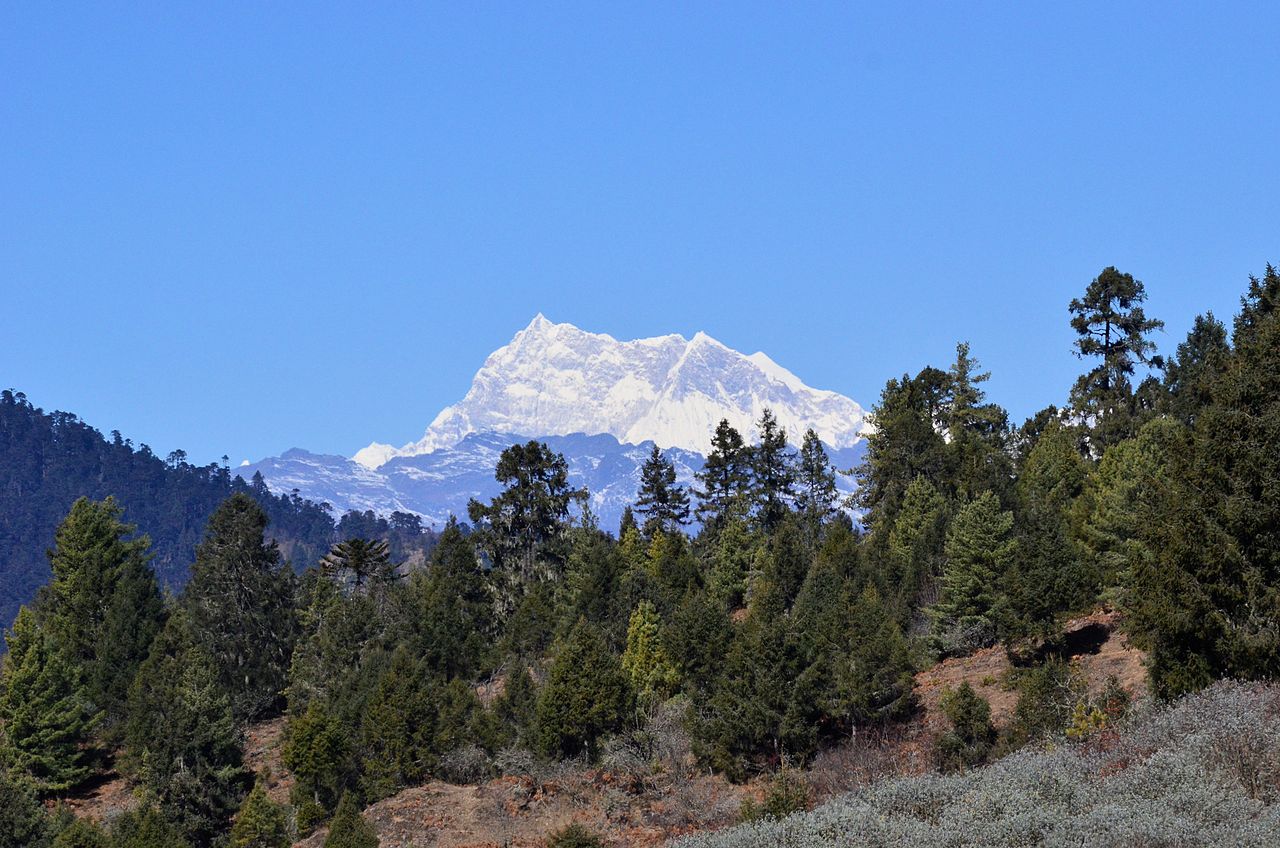
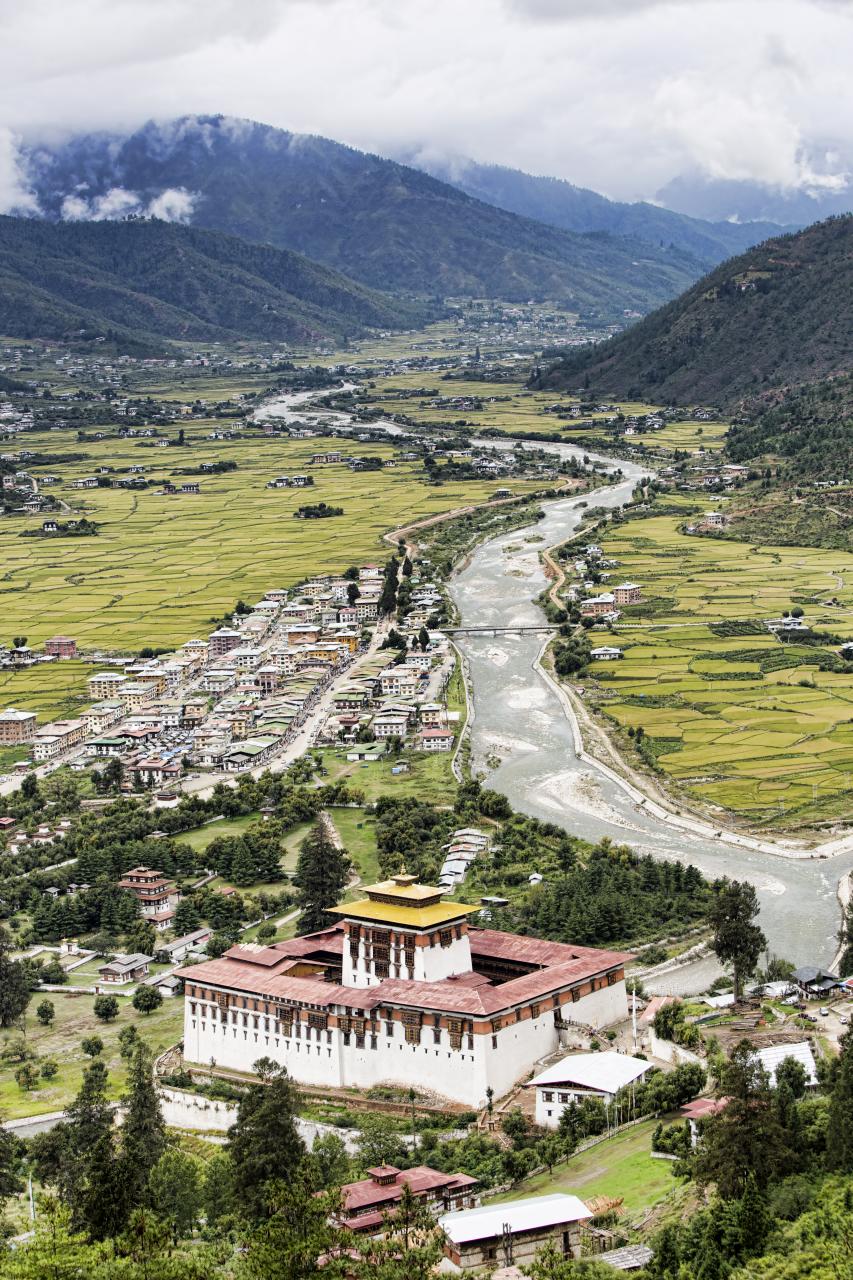
 Bhutan
Bhutan



 Architecture
Architecture
 Bhutan
Bhutan

 History
History
 K 500 - 1000 AD
K 500 - 1000 AD
 Himachal Pradesh
Himachal Pradesh

 Art
Art

 Mongolei
Mongolei
 Nei Mongol Zizhiqu-NM
Nei Mongol Zizhiqu-NM
 Nepal
Nepal
 Qinghai Sheng-QH
Qinghai Sheng-QH

 World Heritage
World Heritage
 Xizang Zizhiqu-XZ
Xizang Zizhiqu-XZ
 Yunnan Sheng-YN
Yunnan Sheng-YN




Die Südasiatische Vereinigung für regionale Kooperation (auch Südasiatische Wirtschaftsgemeinschaft) (von englisch South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation) (SAARC) wurde am 8. Dezember 1985 in Dhaka (Bangladesch) gegründet und hat ihren Sitz in der nepalesischen Hauptstadt Kathmandu. Gründungsmitglieder sind Indien, Pakistan, Bangladesch, Nepal, Sri Lanka, Bhutan und die Malediven. Im April 2007 trat Afghanistan auf dem Gipfeltreffen in Neu-Delhi der Organisation bei. Die Volksrepublik China, Japan, die Europäische Union, Südkorea, die Vereinigten Staaten und der Iran besitzen Beobachterstatus.
南亚区域合作联盟(英语:South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation)是1985年12月8日成立的旨在推动南亚人民间友谊、信任与理解的平台,由孟加拉国、不丹、印度、马尔代夫、尼泊尔、巴基斯坦和斯里兰卡七国政府发起成立。2005年11月13日,接受阿富汗为成员。缅甸、模里西斯、澳大利亚、中华人民共和国、日本、大韩民国、欧盟、美国和伊朗成为观察员。


 *Changjiang|Yangtze River
*Changjiang|Yangtze River
 *Changjiang|Yangtze River
*Changjiang|Yangtze River
 *Yellow river
*Yellow river
 *Yellow river
*Yellow river

 Afghanistan
Afghanistan
 Bhutan
Bhutan
 China
China
 Gansu Sheng-GS
Gansu Sheng-GS
 India
India
 Kyrgyzstan
Kyrgyzstan
 Nepal
Nepal
 Pakistan
Pakistan
 Qinghai Sheng-QH
Qinghai Sheng-QH
 Sichuan Sheng-SC
Sichuan Sheng-SC
 Tajikistan
Tajikistan
 Xinjiang Uygur Zizhiqu-XJ
Xinjiang Uygur Zizhiqu-XJ
 Xizang Zizhiqu-XZ
Xizang Zizhiqu-XZ
 Yunnan Sheng-YN
Yunnan Sheng-YN
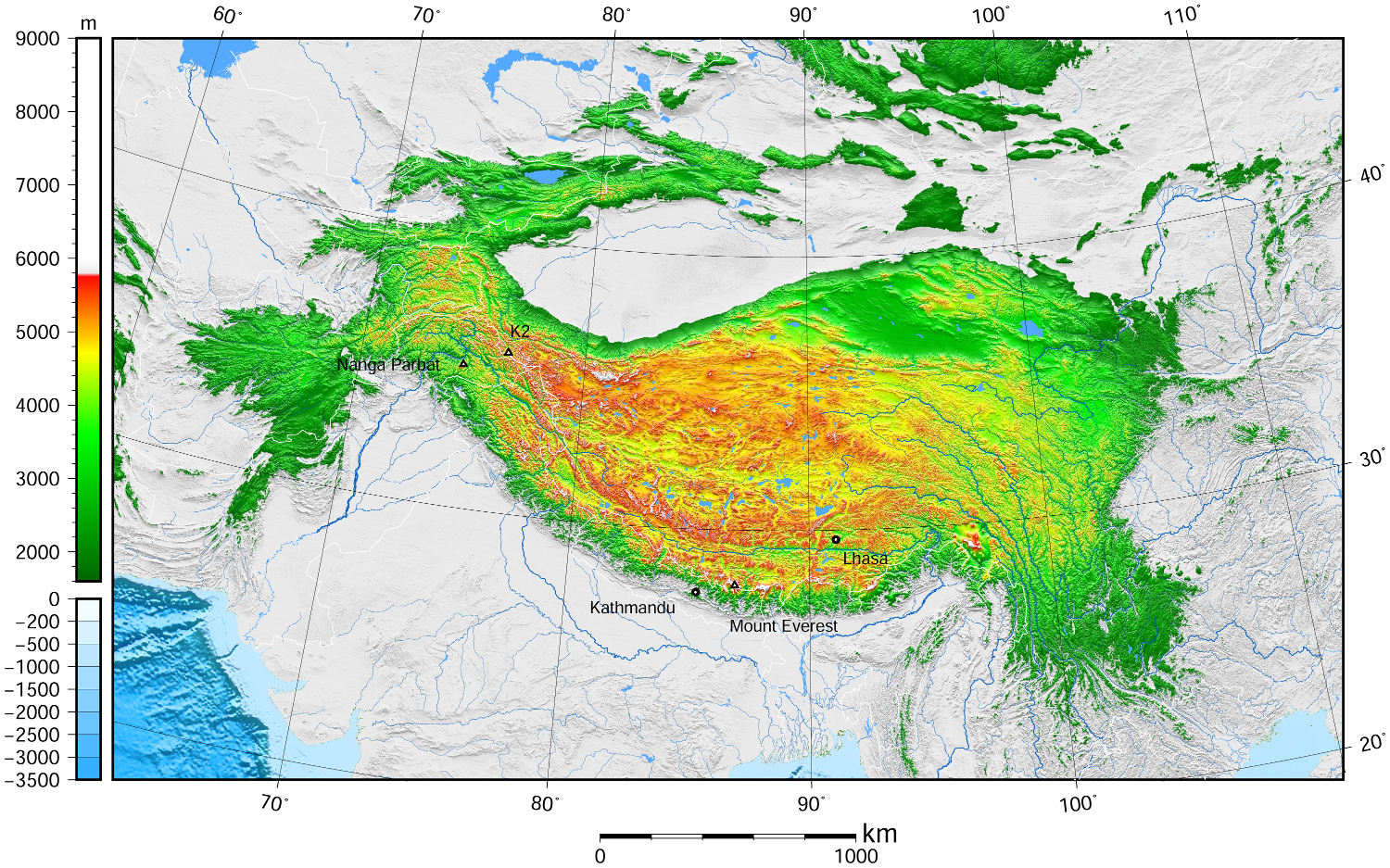
Das geographisch definierte Hochland von Tibet bzw. offiziell Qinghai-Tibet-Hochebene (chinesisch 青藏高原, Pinyin Qīng-Zàng gāoyuán), auch Hochasien, umfasst nicht nur den gesamten Lebensraum tibetisch-sprachiger Völkerschaften, das noch kleinere historische Tibet oder das heutige Autonome Gebiet Tibet (AGT) der Volksrepublik China, sondern auch die es eingrenzenden Hochgebirge Himalaya, Kunlun Shan, Qilian Shan usw.
Nachdem die Hochebene im frühen Miozän entstand, erreichte es die heutige Höhe vor etwa acht Millionen Jahren. Mit der Zeit schürften Erosion und Wetter Täler und bildeten Steilwände und Klippen.
Das Hochland, das etwa 4000 bis 5500 Meter Höhe über dem Meeresspiegel liegt und rund 2 Millionen km² groß ist, wird im Norden von den Wüsten des Tarimbeckens und Qaidam-Beckens begrenzt, im Süden und Westen von den Gebirgen Himalaya, Karakorum und Pamir. Obwohl der höchste Gipfel nur 7010 Meter hoch ist, ist die Ebene das höchste Plateau der Welt. Hier finden sich zahlreiche Salzseen in den Schluchten wie den Tilicho Lake, der auf 4920 Metern liegt und damit einer der höchstgelegenen Seen der Welt ist, des Weiteren weite Steppen, dichte Wälder und Wüsten. Diese Naturräume bieten vielen Tieren – darunter auch gefährdeten – Schutz, so etwa Yaks, Saigaantilopen, Asiatischen Schwarzbären, Schafen und Kiangs.
Zum Hochland von Tibet zählen demgemäß auch die Gebiete Ladakh, Zanskar, Lahaul und Spiti, Nord-Sikkim und weite Teile von Arunachal Pradesh in Nordindien, wie auch große Teile Bhutans und der Norden Nepals. Innerhalb der Volksrepublik China sind neben dem Autonomen Gebiet Tibet auch die gesamte Provinz Qinghai, der Südwesten von Gansu sowie Randbereiche des Nordwestens dieser Provinz, der Westen Sichuans und der Nordwesten Yunnans Teil des Hochlands, während das Aksai Chin im fernen Westen des Plateaus im Autonomen Gebiet Xinjiang in den Pamir überleitet.
青藏高原,是东亚一个高原地区,它是世界上最高的高原,平均海拔高度5900米(5800~6000米),面积250万平方公里,有“世界屋脊”,“雪域高原”,和“第三极”之称。它是在中亚[1][2][3][4]和西亚[5][6][7][8]的一个巨大的高原,大部分在中国西部的西藏自治区和青海省,以及在印度查谟-克什米尔邦拉达克的一部分。 它从南向北延伸约1,000千米(620英里),从东到西延伸约2,500千米(1,600英里)。中国境内之青藏高原,占全中国23%面积,位于北纬25°-40°和东经74°-104°之间。
高原边界,东为横断山脉,南、西为喜马拉雅山脉,北为昆仑山脉。涵盖国境有中国西藏自治区、青海省全境、新疆维吾尔自治区、甘肃省、四川省、云南省部分,以及不丹、尼泊尔、印度的拉达克等地。
チベット高原(チベットこうげん、中国語: 青藏高原、雪域高原)はユーラシア大陸の中央部に広がる世界最大級の高原。チベットの領域とほぼ等しい。 東西約2,000キロメートル、南北約1,200キロメートル、面積約250万平方キロメートル(日本の国土面積の約6倍)。高度は3,500から5,500メートル、平均4,500メートル。
南境にはヒマラヤ山脈、西境にはカラコルム山脈、北境には崑崙山脈・阿爾金山脈・祁連山脈、東境には横断山脈(邛崍山脈)が走り、7,000から8,000メートル級の高峰が連なる。東北部には面積20万平方キロメートルのツァイダム盆地やティショルギャルモ湖(青海湖)がある。
20世紀後半からこの高原の大部分を領有している中華人民共和国は西蔵・青海などの諸地方に区分して、両地方の略称「青」「藏」をあわせた青藏高原(拼音: せいぞうこうげん)としている。この高原は現在の中国領土の約23パーセントの面積を占めている。
また、チベット亡命政府が領有を主張している地域ともほぼ一致する。
The Tibetan Plateau (Tibetan: བོད་ས་མཐོ།, Wylie: bod sa mtho), also known in China as the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau[1] or the Qing–Zang Plateau[2] (Chinese: 青藏高原; pinyin: Qīng–Zàng Gāoyuán) or Himalayan Plateau, is a vast elevated plateau in Central Asia[3][4][5][6] and East Asia,[7][8][9][10] covering most of the Tibet Autonomous Region and Qinghai in western China, as well as Ladakh (Jammu and Kashmir) and Lahaul & Spiti (Himachal Pradesh) in India. It stretches approximately 1,000 kilometres (620 mi) north to south and 2,500 kilometres (1,600 mi) east to west. With an average elevation exceeding 4,500 metres (14,800 ft), the Tibetan Plateau is sometimes called "the Roof of the World" because it stands over 3 miles (4.8 km) above sea level and is surrounded by imposing mountain ranges that harbor the world's two highest summits, Mount Everest and K2, and is the world's highest and largest plateau, with an area of 2,500,000 square kilometres (970,000 sq mi) (about five times the size of Metropolitan France).[11] Sometimes termed the Third Pole, the Tibetan Plateau contains the headwaters of the drainage basins of most of the streams in surrounding regions. Its tens of thousands of glaciers and other geographical and ecological features serve as a "water tower" storing water and maintaining flow. The impact of global warming on the Tibetan Plateau is of intense scientific interest.[12][13][14][15]
Le plateau tibétain est un vaste ensemble de plateaux situé en Asie centrale, au nord de l'Himalaya, dont la majeure partie est située en République populaire de Chine et quelques parties le sont en Birmanie, au Bhoutan, au Népal et en Inde. Il a été créé par la collision des plaques indienne et eurasienne qui ont pris en étau les plaques de Qiantang et de Lhassa au cours du Cénozoïque. Constituant une des plus grandes structures topographiques de la Terre, il a d'importants effets climatiques régionaux (aridité du plateau lui-même, mousson) et mondiaux (circulation atmosphérique mondiale). Le nord-ouest du plateau, le Changtang, en est la région la plus élevée. D'une altitude dépassant souvent 5 000 m, il est pratiquement inhabité.
L'altopiano del Tibet (བོད་ས་མཐོ་) è un vasto ed elevato altopiano dell'Asia centrale che copre la maggior parte della regione autonoma del Tibet e della provincia del Qinghai in Cina e parte del Ladakh, nel Kashmir indiano.[1][2][3][4]
Occupa una superficie che si estende per 2.500 km di lunghezza e per 1.000 di larghezza, ad un'altitudine media di oltre 4.500 m s.l.m.[5][6][7] Talvolta chiamato il tetto del mondo, è l'altopiano più alto e più vasto del mondo, con una superficie di 1,2 milioni di chilometri quadrati (circa due volte la dimensione del Texas o della Francia, più di quattro volte l'Italia).[8]
L'altopiano tibetano è circondato da alte catene montuose: è delimitato a nord-ovest dai monti Kunlun che lo separano dal bacino del Tarim, e a nord-est dalla catena dei Qilian Shan che lo separa dal Corridoio di Hexi e dal deserto del Gobi. I suoi confini meridionali sono disegnati dalla valle del fiume Brahmaputra (Yǎlǔ Zàngbù Jiāng) che corre lungo la base dell'Himalaya. A occidente l'altopiano è abbracciato dalla robusta catena del Karakoram nel Kashmir settentrionale. A est e sud-est l'altopiano cede il passo alle gole boscose dei fiumi Salween, Mekong, Fiume Azzurro, alle regioni occidentali del Sichuan e sud-occidentali del Qinghai.
La meseta del Tíbet, también conocida como la meseta Tibetana-Qinghai, es una extensa y elevada meseta de Asia oriental que ocupa gran parte de la Región Autónoma del Tíbet y de la provincia de Qinghai, en la República Popular China, y de la región india de Ladakh, en Cachemira. Ocupa un área rectangular aproximada de 1.000 km de ancho por 2.500 km de largo, y tiene una elevación media de 4.500 metros. Es llamada "el techo del mundo", pues es la meseta más alta y grande del mundo, con un área de 2,5 millones de kilómetros cuadrados de extensión (cerca del tamaño de la República Argentina y cuatro veces el tamaño de Texas o Francia)
La meseta tibetana está rodeada por cadenas de montañas elevadas.1 Limita al noroeste con la cordillera Kunlun, que la separa de la cuenca del Tarim, y al noreste con las montañas Qilian, que separa la meseta del desierto de Gobi. La meseta limita al sur con el valle del río Yarlung Tsangpo, que fluye a lo largo del pie del Himalaya, y por la extensa Llanura indogangética. Al este y sureste, la meseta da paso a la geografía arbolada y abrupta de montaña de los nacimientos de los ríos Saluin, Mekong y Yangtsé, en la zona occidental de Sichuan. En el oeste está rodeada por la curva de la abrupta cordillera de Karakoram del norte de Cachemira.
Тибе́тское наго́рье — самое большое по площади и высочайшее нагорье мира[1],имеющее площадь около 2,5 млн кв. км, среднюю высоту 4877 м. Протяжённость с запада на восток 2500 км, с юга на север 1000 км[2]. Очень разнообразно по рельефу, растительности и животному миру. Посещаемости туристов способствует известность Тибета как обители буддийских монахов, святых (махатм).
Территория богата полезными ископаемыми, включая золото, что по некоторым сведениям и спровоцировало захват Тибета Китайской Народной Республикой в 1951 году, и последущее разграбление богатств страны[3] (Китай также получил контроль над источниками почти всех больших рек Азии).
Нагорье с севера ограничено хребтом Куньлунь, с северо-востока — системой хребтов Циляньшань, отделяющим его от пустыни Гоби. В Тибетском нагорье начинаются крупнейшие реки Инд, Брахмапутра, Салуин, Меконг, Янцзы, Хуанхэ. На западе нагорье граничит с хребтами Памира, на востоке с Сино-Тибетскими горами[4].

 Sport
Sport
 States of Asia
States of Asia
 Geography
Geography


 Party and government
Party and government
 Religion
Religion
 Hand in Hand
Hand in Hand
 Economy and trade
Economy and trade
 International cities
International cities