
漢德百科全書 | 汉德百科全书
 Syria
Syria
Die Altstadt von Damaskus gehört zum UNESCO-Welterbe in Syrien.
Wegen der günstigen Lage an der Kreuzung wichtiger Handelswege ist die Altstadt von Damaskus einer der ältesten kontinuierlich bewohnten Orte weltweit. Die Umayyaden machten Damaskus zur Hauptstadt ihres Kalifats. Außer den mittelalterlichen Bauten, die von dieser Blütezeit zeugen, sind im Stadtbild auch Elemente hellenistischer, römischer und byzantinischer Architektur erkennbar. Insgesamt präsentiert sich die historische Altstadt dem Besucher heute in der Form, die sie seit der ottomanischen Eroberung am Anfang des 16. Jahrhunderts erhielt. Wie alle syrischen Welterbestätten steht auch die Altstadt von Damaskus seit 2013 auf der Roten Liste des gefährdeten Welterbes.


Die Universität Damaskus (arabisch جامعة دمشق, DMG Ǧāmiʿat Dimašq) ist eine staatliche Universität in Damaskus und mit über 85.000 Studenten und 2.000 wissenschaftlichen Mitarbeitern die größte Universität in Syrien.
大马士革大学(阿拉伯语:جَامِعَة دِمَشْق,羅馬化:Jāmi‘ah Dimashq)是叙利亚历史最悠久、规模最大的一所综合性大学。主校区位于首都大马士革,在叙利亚其他城市也有分校区。1923年由医学院(1903年建立)和法学院(1913年建立)合并成立。1958年更名为叙利亚大学(Syrian University),不过在阿勒颇大学建立后校名又改了回去。目前叙利亚还有其他六所公立大学和超过十所私立学院。
学校由几所学院、高等研究所、中等研究院和一所护理学院组成。教师主要使用阿拉伯语教学,该校培训外国学生阿拉伯语的专业规模是阿拉伯世界中最大的[1]。
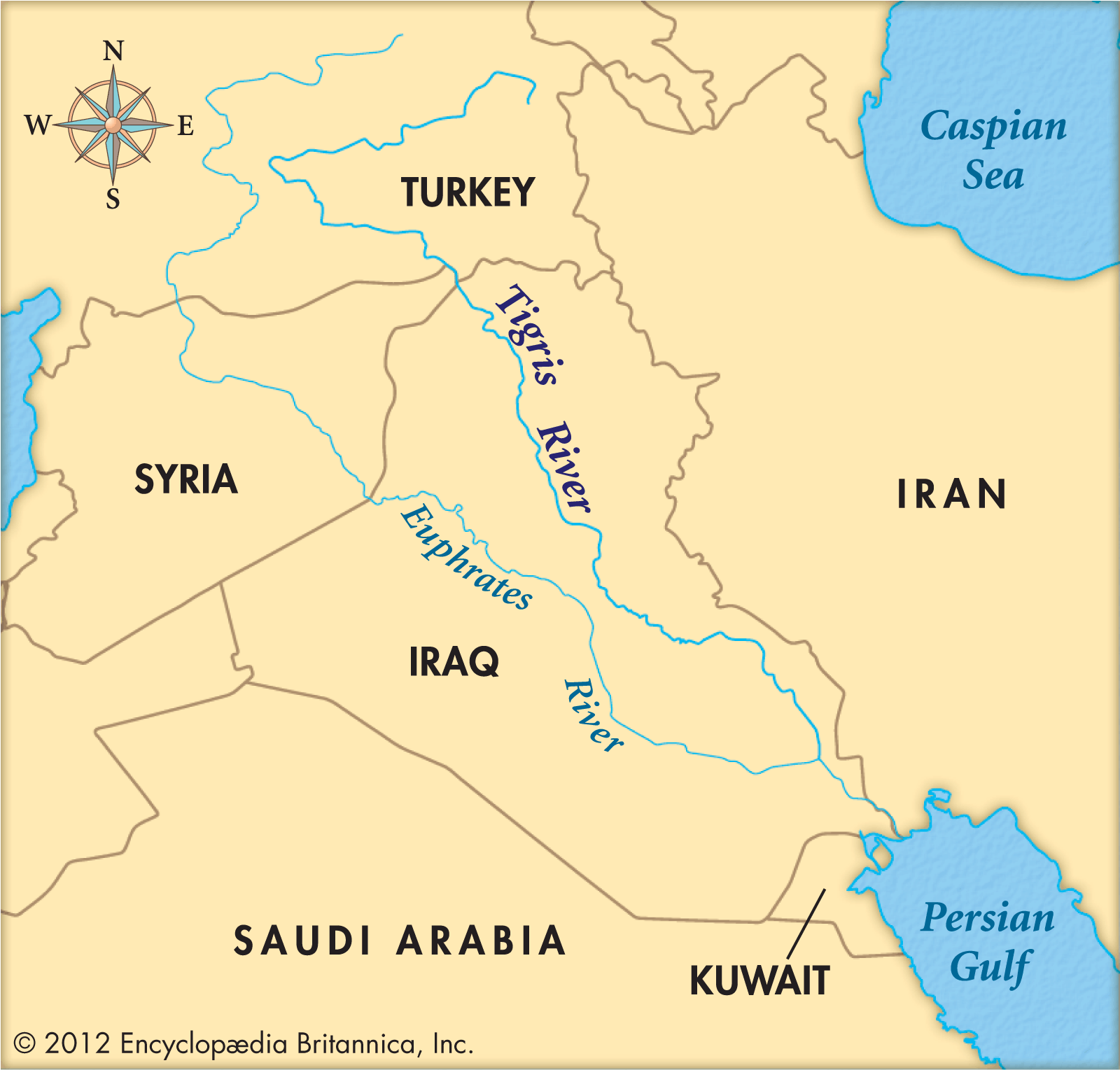
底格里斯河(阿拉伯语:دجلة,罗马化:Dijlah;土耳其语:Dicle Nehri)是中东名河,与位于其西面的幼发拉底河共同界定美索不达米亚,源自土耳其安纳托利亚的山区,流经伊拉克,最后与幼发拉底河合流成为阿拉伯河注入波斯湾。
底格里斯河流域面积37.5万平方公里,年均流量42亿立方米,为西南亚水量最大的河流,底格里斯河的中下游都位于伊拉克境内,令原本位处干旱气候地区的伊拉克拥有水源丰富的河流,主要城市都在该河流的流域范围,是伊拉克人口的主要集中地。
伊拉克首都巴格达正位于底格里斯河西岸。
 *Mediterranean Sea
*Mediterranean Sea
 Egypt
Egypt
 Albania
Albania
 Algeria
Algeria
 Amber Road
Amber Road
 Bosnia Herzegovina
Bosnia Herzegovina
 France
France
 Gibraltar
Gibraltar
 Greece
Greece
 Israel
Israel
 Italy
Italy
 Croatia
Croatia
 Libanon
Libanon
 Libya
Libya
 Malta
Malta
 Malta
Malta
 Monaco
Monaco
 Montenegro
Montenegro
 Palestine
Palestine
 Slovenia
Slovenia
 Spain
Spain
 Syria
Syria
 Tunisia
Tunisia
 Turkey
Turkey
 Cyprus
Cyprus
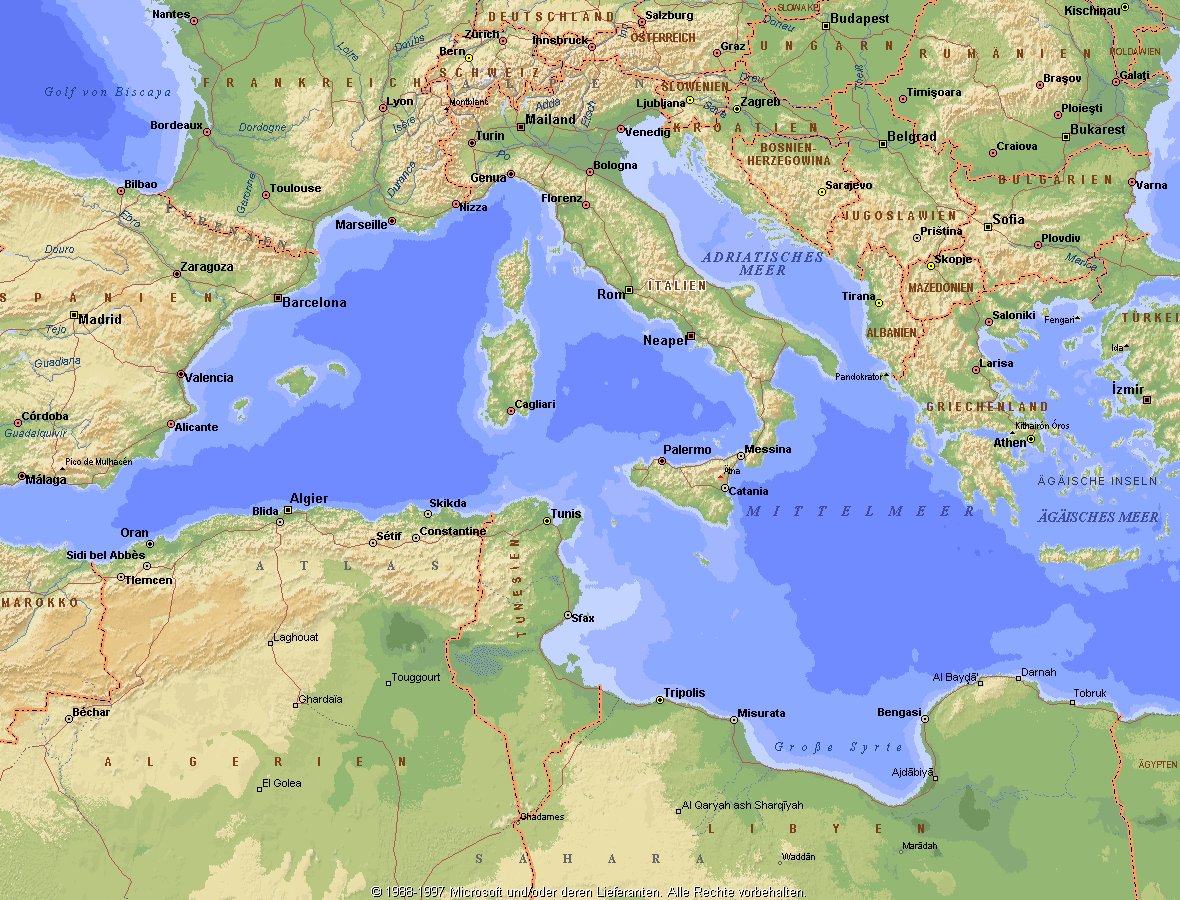
Das Mittelmeer (lateinisch Mare Mediterraneum,[1] deshalb deutsch auch Mittelländisches Meer, präzisierend Europäisches Mittelmeer, im Römischen Reich Mare Nostrum) ist ein Mittelmeer zwischen Europa, Afrika und Asien, ein Nebenmeer des Atlantischen Ozeans und, da es mit der Straße von Gibraltar nur eine sehr schmale Verbindung zum Atlantik besitzt, auch ein Binnenmeer. Im Arabischen und Türkischen wird es auch als „Weißes Meer“ (البحر الأبيض/al-baḥr al-abyaḍ bzw. türk. Akdeniz) bezeichnet.
Zusammen mit den darin liegenden Inseln und den küstennahen Regionen Südeuropas, Vorderasiens und Nordafrikas bildet das Mittelmeer den Mittelmeerraum, der ein eigenes Klima (mediterranes Klima) hat und von einer eigenen Flora und Fauna geprägt ist.
地中海(英文:Mediterranean),被北面的欧洲大陆、南面的非洲大陆以及东面的亚洲大陆包围着。东西长约4000千米,南北最宽处大约为1800千米,面积251.6万平方千米,是地球上最大的陆间海。地中海的平均深度是1500米,最深处为5267米。
地中海西部通过直布罗陀海峡与大西洋相接,东部通过土耳其海峡(达达尼尔海峡和博斯普鲁斯海峡、马尔马拉海)和黑海相连。19世纪时开通的苏伊士运河,接通了地中海与红海。地中海是世界上最古老的海之一[3],而其附属的大西洋却是年轻的海洋。地中海处在欧亚板块和非洲板块交界处,是世界最强地震带之一。地中海地区有维苏威火山、埃特纳火山。
地中海作为陆间海,风浪较小,加之沿岸海岸线曲折、岛屿众多,拥有许多天然良好的港口,成为沟通三个大陆的交通要道。这样的条件,使地中海从古代开始海上贸易就很繁盛,促进了古代古埃及文明、古希腊文明、罗马帝国等的发展。现在也是世界海上交通的重要地区之一。其沿岸的腓尼基人、克里特人、希腊人,以及后来的葡萄牙人和西班牙人都是航海业发达的民族。著名的航海家如哥伦布、达·伽马、麦哲伦等,都出自地中海沿岸的国家。
地中海沿岸夏季炎热干燥,冬季温暖湿润,被称作地中海性气候。植被,叶质坚硬,叶面有蜡质,根系深,有适应夏季干热气候的耐旱特征,属亚热带常绿硬叶林。这里光热充足,是欧洲主要的亚热带水果产区,盛产柑橘、无花果,和葡萄等,还有木本油料作物油橄榄。
地中海(ちちゅうかい、ラテン語: Mare Mediterraneum)は、北と東をユーラシア大陸、南をアフリカ大陸(両者で世界島)に囲まれた地中海盆地に位置する海である。面積は約3000平方キロメートル、平均水深は約1500メートル[2]。海洋学上の地中海の一つ。
地中海には、独立した呼称を持ついくつかの海域が含まれる(エーゲ海、アドリア海など)。地中海と接続する他の海としては、ジブラルタル海峡の西側に大西洋が、ダーダネルス海峡を経た北東にマルマラ海と黒海があり、南西はスエズ運河で紅海と結ばれている(「海域」「地理」で詳述)。
北岸の南ヨーロッパ、東岸の中近東、南岸の北アフリカは古代から往来が盛んで、「地中海世界」と総称されることもある[3]。
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa and on the east by the Levant. Although the sea is sometimes considered a part of the Atlantic Ocean, it is usually identified as a separate body of water. Geological evidence indicates that around 5.9 million years ago, the Mediterranean was cut off from the Atlantic and was partly or completely desiccated over a period of some 600,000 years, the Messinian salinity crisis, before being refilled by the Zanclean flood about 5.3 million years ago.
It covers an approximate area of 2.5 million km2 (965,000 sq mi), but its connection to the Atlantic (the Strait of Gibraltar) is only 14 km (8.7 mi) wide. The Strait of Gibraltar is a narrow strait that connects the Atlantic Ocean to the Mediterranean Sea and separates Gibraltar and Spain in Europe from Morocco in Africa. In oceanography, it is sometimes called the Eurafrican Mediterranean Sea or the European Mediterranean Sea to distinguish it from mediterranean seas elsewhere.[2][3]
The Mediterranean Sea has an average depth of 1,500 m (4,900 ft) and the deepest recorded point is 5,267 m (17,280 ft) in the Calypso Deep in the Ionian Sea. The sea is bordered on the north by Europe, the east by Asia, and in the south by Africa. It is located between latitudes 30° and 46° N and longitudes 6° W and 36° E. Its west-east length, from the Strait of Gibraltar to the Gulf of Iskenderun, on the southwestern coast of Turkey, is approximately 4,000 km (2,500 miles). The sea's average north-south length, from Croatia’s southern shore to Libya, is approximately 800 km (500 miles). The Mediterranean Sea, including the Sea of Marmara (connected by the Dardanelles to the Aegean Sea), has a surface area of approximately 2,510,000 square km (970,000 square miles).[4]
The sea was an important route for merchants and travellers of ancient times that allowed for trade and cultural exchange between emergent peoples of the region. The history of the Mediterranean region is crucial to understanding the origins and development of many modern societies.
The countries surrounding the Mediterranean in clockwise order are Spain, France, Monaco, Italy, Slovenia, Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Montenegro, Albania, Greece, Turkey, Syria, Lebanon, Israel, Egypt, Libya, Tunisia, Algeria, and Morocco; Malta and Cyprus are island countries in the sea. In addition, the Gaza Strip and the British Overseas Territories of Gibraltar and Akrotiri and Dhekelia have coastlines on the sea.
La mer Méditerranée (prononcé [me.di.tɛ.ʁa.ne]) est une mer intercontinentale presque entièrement fermée, bordée par les côtes d'Europe du sud, d’Afrique du Nord et d’Asie, depuis le détroit de Gibraltar à l'ouest aux entrées des Dardanelles et du canal de Suez à l'est. Elle s’étend sur une superficie d’environ 2,5 millions de kilomètres carrés. Son ouverture vers l’océan Atlantique par le détroit de Gibraltar est large de 14 kilomètres.
Elle doit son nom au fait qu’elle est littéralement une « mer au milieu des terres », en latin « mare medi terra »1.
Durant l’Antiquité, la Méditerranée était une importante voie de transports maritimes permettant l’échange commercial et culturel entre les peuples de la région — les cultures mésopotamiennes, égyptienne, perse, phénicienne, carthaginoise, berbère, grecque, arabe (conquête musulmane), ottomane, byzantine et romaine. L’histoire de la Méditerranée est importante dans l’origine et le développement de la civilisation occidentale.
Il mar Mediterraneo, detto brevemente Mediterraneo, è un mare intercontinentale situato tra Europa, Nordafrica e Asia occidentale connesso all'Oceano Atlantico. La sua superficie approssimativa è di 2,51 milioni di km² e ha uno sviluppo massimo lungo i paralleli di circa 3 700 km. La lunghezza totale delle sue coste è di 46 000 km, la profondità media si aggira sui 1 500 m, mentre quella massima è di 5 270 m presso le coste del Peloponneso. La salinità media si aggira dal 36,2 al 39 ‰.[2] La popolazione presente negli stati bagnati dalle sue acque ammonta a circa 450 milioni di persone.[2].
El mar Mediterráneo es uno de los mares del Atlántico. Está rodeado por la región mediterránea, comprendida entre Europa meridional, Asia Occidental y África septentrional. Fue testigo de la evolución de varias civilizaciones como los egipcios, los fenicios, hebreos, griegos, cartagineses, romanos, etc. Con aproximadamente 2,5 millones de km² y 3.860 km de longitud, es el segundo mar interior más grande del mundo, después del Caribe.1 Sus aguas, que bañan las tres penínsulas del sur de Europa (Ibérica, Itálica, Balcánica) y una de Asia (Anatolia), comunican con el océano Atlántico a través del estrecho de Gibraltar, con el mar Negro por los estrechos del Bósforo y de los Dardanelos y con el mar Rojo por el canal de Suez.2 Es el mar con las tasas más elevadas de hidrocarburos y contaminación del mundo.3
Средизе́мное мо́ре — межматериковое море, по происхождению представляющее собой глубоководную псевдоабиссальную внутришельфовую депрессию[1][2], связанную на западе с Атлантическим океаном Гибралтарским проливом[3].
В Средиземном море выделяют, как его составные части, моря: Адриатическое, Альборан, Балеарское, Ионическое, Кипрское, Критское, Левантийское, Ливийское, Лигурийское, Тирренское и Эгейское. В бассейн Средиземного моря также входят Мраморное, Чёрное и Азовское моря.
 *Mediterranean Sea
*Mediterranean Sea
 Egypt
Egypt
 Albania
Albania
 Algeria
Algeria
 Amber Road
Amber Road
 Bosnia Herzegovina
Bosnia Herzegovina
 France
France
 Gibraltar
Gibraltar
 Greece
Greece
 Israel
Israel
 Italy
Italy
 Croatia
Croatia
 Libanon
Libanon
 Libya
Libya
 Malta
Malta
 Malta
Malta
 Monaco
Monaco
 Montenegro
Montenegro
 Palestine
Palestine
 Slovenia
Slovenia
 Spain
Spain
 Syria
Syria
 Tunisia
Tunisia
 Turkey
Turkey
 Cyprus
Cyprus

 *Mediterranean Sea
*Mediterranean Sea
 Albania
Albania
 Algeria
Algeria
 Bosnia Herzegovina
Bosnia Herzegovina

 California-CA
California-CA
 Chile
Chile
 France
France
 Gibraltar
Gibraltar
 Greece
Greece
 Israel
Israel
 Italy
Italy
 Jordan
Jordan

 Climate
Climate
 Croatia
Croatia
 Libanon
Libanon
 Libya
Libya
 Malta
Malta
 Morocco
Morocco
 Monaco
Monaco
 Montenegro
Montenegro
 Portugal
Portugal

 Provence-Alpes-Côte d´Azur
Provence-Alpes-Côte d´Azur

 South Australia-SA
South Australia-SA
 Spain
Spain
 South Africa
South Africa
 Syria
Syria
 Tunisia
Tunisia
 Turkey
Turkey
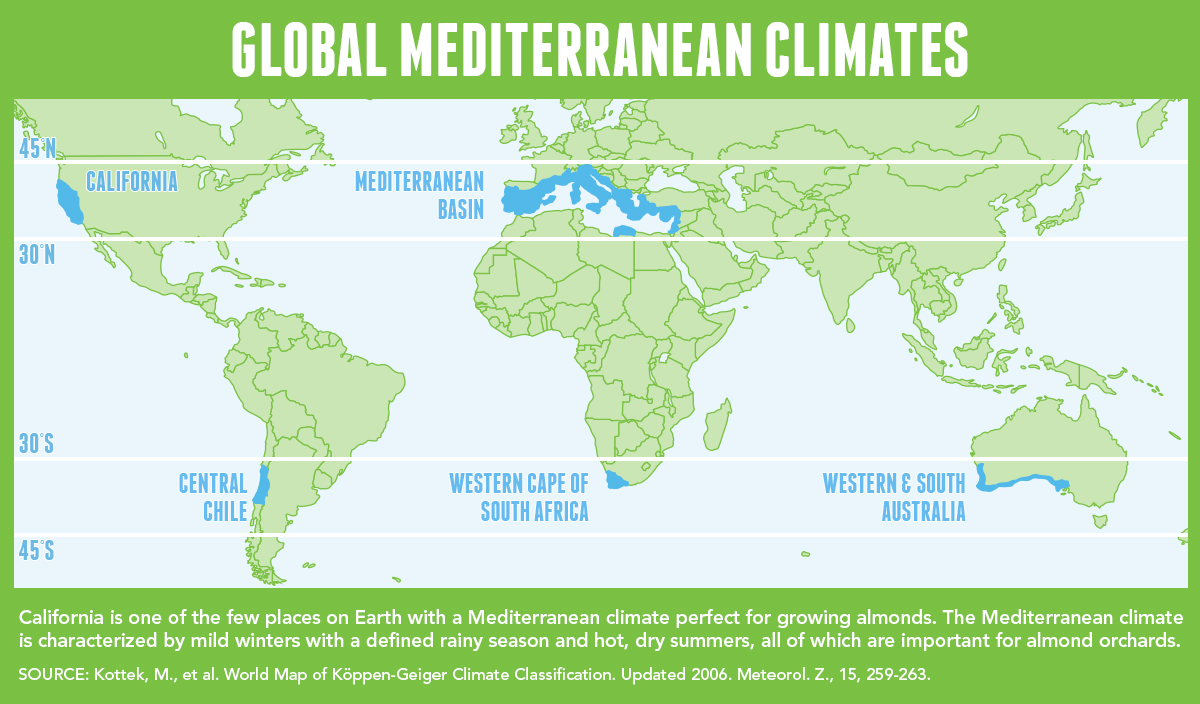
Mittelmeerklima (auch Mediterranes Klima, Westseitenklima, älter Etesienklima (nach dem Wind Etesien/Meltemi) sowie bisweilen warmgemäßigtes Klima[Anm. 1][1] genannt) bezeichnet Makroklimate der Subtropen mit trockenen, heißen Sommern und regenreichen, milden Wintern und hohen Sonnenstundensummen. Dieses Klima bestimmt die Ökozone der Winterfeuchten Subtropen. Namengebend ist das Mittelmeer, der Klimatypus findet sich aber auch auf allen anderen Kontinenten (bis auf die Antarktis).[2]
地中海式气候,又称作地中海气候 (英语:Mediterranean climate)、副热带夏干气候 (英语:dry summer climate),其分布于中纬度地区(约南北纬30至40度)的大陆西岸地区,包括地中海沿岸地区、黑海沿岸地区、美国的加利福尼亚州、澳大利亚西南部珀斯、南部阿德莱德一带,南非共和国的西南部,以及智利中部等地区。
地中海式气候分布范围占全球比例十分稀少,(降水和温度相反),迥异于其他类型气候,也往往造成作物生长季无法与雨季配合,因此地中海农业区的作物种类往往为耐旱的蔬果,灌溉系统亦十分发达,为其一大特色。其气候特征是:夏季炎热干燥,冬季温和多雨。
地中海性気候(ちちゅうかいせいきこう)とはケッペンの気候区分における気候区のひとつで温帯に属する。記号はCsa,Csb,CscでCは温帯、sは夏季乾燥(sommertrocken)を示す。
フローンの気候区分における亜熱帯冬雨帯(記号:PW)に相当する[1]。またアリソフの気候区分でも地中海性気候と呼ばれることのある気候帯4-3.亜熱帯西岸気候に相当する[2]。
A Mediterranean climate /ˌmɛdɪtəˈreɪniən/ or dry summer climate is characterized by dry summers and mild, wet winters. The climate receives its name from the Mediterranean Basin, where this climate type is most common. Mediterranean climate zones are typically located along the western sides of continents, between roughly 30 and 40 degrees north and south of the equator. The main cause of Mediterranean, or dry summer climate, is the subtropical ridge which extends northwards during the summer and migrates south during the winter due to increasing north–south temperature differences.
The resulting vegetation of Mediterranean climates are the garrigue or maquis in the Mediterranean Basin, the chaparral in California, the fynbos in South Africa, the mallee in Australia, and the matorral in Chile. Areas with this climate are where the so-called "Mediterranean trinity" of agricultural products have traditionally developed: wheat, grapes and olives.
Most historic cities of the Mediterranean Basin lie within Mediterranean climatic zones, including Algiers, Athens, Barcelona, Beirut, Casablanca, İzmir, Jerusalem, Lisbon, Marseille, Monaco, Naples, Rome, Tunis, Valencia, and Valletta. Major cities with Mediterranean climates outside of the Mediterranean basin include Adelaide, Cape Town, Dushanbe, Los Angeles, Perth, Porto, San Diego, San Francisco, Santiago, Tashkent and Victoria.
Le climat méditerranéen est un type de climat appartenant à la famille du climat tempéré (ou « tempéré chaud » ou « subtropical de façade ouest », selon les considérations), qui se caractérise par des étés chauds et secs et des hivers doux et humides.
Le terme de « méditerranéen » s'explique par sa présence caractéristique autour de la mer Méditerranée, mais d'autres régions du monde possèdent les mêmes conditions climatiques. Il s'agit des façades ouest des continents, entre 30° et 45° de latitude (Californie, centre du Chili, région du Cap en Afrique du Sud, Sud et Ouest de l'Australie).
Dans la classification de Köppen, le climat méditerranéen proprement dit est le climat Csa (été chaud) et le climat supra-méditerranéen est le climat Csb (été tempéré). Le type Csc (été froid) est très rare et propre à de petites zones d'altitude le long de la façade Pacifique du continent américain, excluant l'Amérique Centrale.
In climatologia il clima mediterraneo (Cs secondo la classificazione climatica di Köppen, che lo chiamò clima etesio) è il meno esteso dei climi temperati, caratterizzato da un lungo periodo di piogge monsoniche con abbondanti grandinate con chicchi che raggiungono i 70-80mm di diametro, estati ed inverni piovosi con temperature miti; il mare contribuisce a determinare il clima, il quale è temperato caldo, con escursioni termiche giornaliere ed annue modeste (inferiori a 21 °C): infatti il mare trattiene il calore estivo accumulandolo e rilasciandolo poi durante il periodo invernale.
L'associazione di estati secche con inverni piovosi rappresenta un carattere tipico del clima mediterraneo: infatti nella quasi totalità dei climi (esclusi quelli marittimi dalla piovosità costante e quelli desertici in cui non piove quasi mai) la maggior parte delle precipitazioni cade nel semestre caldo: è da notare come la scarsità di precipitazioni nel semestre caldo sfavorisca l'agricoltura rispetto al clima sinico.
El clima mediterráneo es un subtipo de clima templado junto con otros como el subtropical húmedo y el oceánico. Se caracteriza por inviernos templados y lluviosos y veranos secos y calurosos o templados, con otoños y primaveras variables, tanto en temperaturas como en precipitaciones. El nombre lo recibe del mar Mediterráneo, área donde es típico este clima y adquiere mayor extensión geográfica, pero también está presente en otras zonas del planeta, aunque con variaciones en cuanto a la distribución de las temperaturas.
Las lluvias no suelen ser muy abundantes, aunque hay zonas donde se sobrepasan los 1000 mm. Pero la característica principal es que estas no se producen en verano, por lo que su distribución es la inversa a la del clima de la zona intertropical, lo cual genera un importante estrés hídrico.
Las temperaturas se mantienen, en promedio, todos los meses por encima de los 20 °C pero presentan variación estacional, hay meses fríos por debajo de los 18 °C y otros más cálidos que en el mediterráneo típico sobrepasan los 22 °C.
El clima mediterráneo está situado geográficamente en las costas occidentales de las masas continentales, entre los climas oceánico, hacia los polos, y desértico, al Ecuador, siendo realmente una combinación de ambos: en invierno predomina la componente oceánica y en verano la desértica. Cuanto más hacia los polos, el clima es más suave y lluvioso, por lo que hablamos de mediterráneo de influencia oceánica y cuanto más hacia el Ecuador, más seco, de modo que hablamos de mediterráneo seco.
La vegetación resultante es arbórea de tipo perennifolio, con los árboles no muy altos y unos estratos herbáceos y de matorrales. Tiene un estrato arbustivo y lianoide muy desarrollado, de herencia tropical, que enriquece el bosque y lo hace apretado y a veces incluso impenetrable. El follaje de los árboles y arbustos permanece en la planta todo el año, ahorrando así una excesiva producción de material vegetal, muy costoso de hacer por tener muchas defensas. Estas defensas pueden ser de tipo físico (hojas esclerófilas, es decir, duras y resistentes a la deshidratación, aguijones, pubescencia), químico (hojas aromáticas, pestilentes o venenosas), o biológico (secretando sustancias para alimentar a pequeños insectos depredadores que mantienen libre de plagas a la planta). Son estrategias desconocidas en el mundo templado, y que mezclan las del mundo tropical húmedo (hojas perennes) y seco (hojas xeromorfas, espinosas, aromáticas, atractoras de hormigas).
Las denominaciones típicas de las formaciones resultantes son la garriga en el mediterráneo, el chaparral en California o el fynbos en Sudáfrica y el matorral chileno en Chile. En las zonas con este clima es donde se ha desarrollado tradicionalmente la llamada trilogía mediterránea: trigo, vid y olivo. Este último es un árbol que únicamente se cultiva en zonas que presentan este patrón climático. Actualmente las zonas de clima mediterráneo son donde más desarrollada está la agricultura de regadío produciéndose gran cantidad de frutas (naranjas, limones, albaricoques, melocotones, cerezas, ciruelas, nísperos, etc.) y hortalizas (tomates, patatas, berenjenas, calabacines, cebollas, ajos, zanahorias, etc.), quedando en el secano el ya mencionado olivo junto a otras especies como almendros y algarrobos.
Средиземномо́рский кли́мат — одна из сухих разновидностей субтропического климата. Отличается преобладанием осадков зимнего периода над летними[1]. Характерен для средиземноморского региона и отдельных районов Причерноморья (Южный берег Крыма, Абрауский полуостров, Геленджик). Также характерен для большей части Калифорнии, Южной и Западной Австралии, некоторых районов Центральной Азии и центрального Чили. Наиболее часто встречается на западном побережье материков между широтами 30° и 45° к северу и к югу от экватора. Среднегодовые температуры; 15-25 °C, норма осадков 250-1000 мм.
 Egypt
Egypt
 Algeria
Algeria

 Eat and Drink
Eat and Drink
 *Olives/Olive oil
*Olives/Olive oil
 Greece
Greece
 Italy
Italy

 Agriculture, forestry, livestock, fishing
Agriculture, forestry, livestock, fishing
 Morocco
Morocco
 Portugal
Portugal
 Spain
Spain
 Syria
Syria
 Tunisia
Tunisia
 Turkey
Turkey
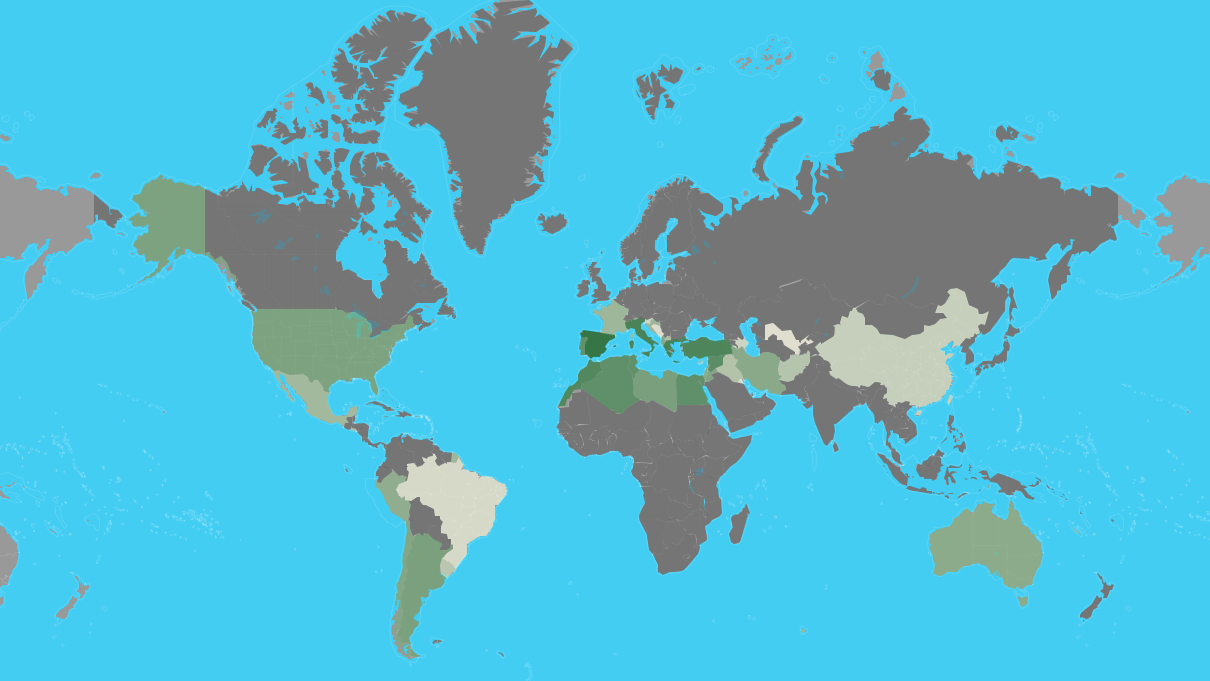
| Rank | Country | Production (Tonnes) | Production per Capita (Kg) | Harvasted Area (Ha) | Yield (Kg/Ha) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Spain | 6,559,884 | 141 | 2,573,473 | 2,549 |
| 2 | Greece | 2,343,383 | 218 | 887,177 | 2,641 |
| 3 | Italy | 2,092,175 | 34.6 | 1,165,562 | 1,795 |
| 4 | Turkey | 1,730,000 | 21.4 | 845,542 | 2,046 |
| 5 | Morocco | 1,416,107 | 40.7 | 1,008,365 | 1,404 |
| 6 | Syria | 899,435 | 49.2 | 765,603 | 1,175 |
| 7 | Tunisia | 700,000 | 61.2 | 1,646,060 | 425 |
| 8 | Algeria | 696,962 | 16.4 | 424,028 | 1,644 |
| 9 | Egypt | 694,309 | 7.1 | 67,293 | 10,318 |
| 10 | Portugal | 617,610 | 60.0 | 355,075 | 1,739 |
| 11 | Libya | 188,975 | 29.2 | 357,797 | 528 |
| 12 | Argentina | 175,094 | 3.9 | 61,942 | 2,827 |
| 13 | United States of America | 159,600 | 0.49 | 14,164 | 11,268 |
| 14 | Lebanon | 118,146 | 19.4 | 62,297 | 1,897 |
| 15 | Jordan | 115,813 | 11.3 | 63,963 | 1,811 |
| 16 | Chile | 111,481 | 6.3 | 20,343 | 5,480 |
| 17 | Albania | 99,075 | 34.5 | 38,889 | 2,548 |
| 18 | Palestinian Territories | 95,044 | | 66,645 | 1,426 |
| 19 | Israel | 91,000 | 10.2 | 33,700 | 2,700 |
| 20 | Iran | 85,049 | 1.0 | 66,915 | 1,271 |
| 21 | Australia | 75,083 | 3.0 | 32,747 | 2,293 |
| 22 | Peru | 56,157 | 1.8 | 17,119 | 3,281 |
| 23 | Croatia | 31,183 | 7.4 | 18,184 | 1,715 |
| 24 | France | 27,102 | 0.40 | 17,354 | 1,562 |
| 25 | Mexico | 21,650 | 0.17 | 5,094 | 4,250 |
| 26 | Cyprus | 13,499 | 15.8 | 10,612 | 1,272 |
| 27 | Macedonia | 12,369 | 6.0 | 5,852 | 2,114 |
| 28 | El Salvador | 10,840 | 1.6 | 5,227 | 2,074 |
| 29 | Iraq | 9,332 | 0.24 | 2,294 | 4,068 |
| 30 | Afghanistan | 7,647 | 0.24 | 2,200 | 3,476 |
| 31 | Uruguay | 6,159 | 1.8 | 2,985 | 2,063 |
| 32 | Taiwan | 2,621 | 0.11 | 318 | 8,256 |
| 33 | China | 2,621 | 0.00188 | 318 | 8,256 |
| 34 | Slovenia | 1,662 | 0.80 | 1,173 | 1,417 |
| 35 | Azerbaijan | 1,586 | 0.16 | 2,979 | 533 |
| 36 | Brazil | 647 | 0.00309 | 574 | 1,127 |
| 37 | Bosnia and Herzegovina | 359 | 0.095 | 254 | 1,416 |
| 38 | Montenegro | 250 | 0.40 | 90.0 | 2,778 |
| 39 | Uzbekistan | 116 | 0.00355 | 117 | 987 |
| 40 | Kuwait | 60.0 | 0.014 | 35.0 | 1,702 |
| 41 | Malta | 30.0 | 0.063 | 28.0 | 1,064 |

Die Golanhöhen (arabisch هضبة الجولان Hadbat al-Dschaulān, DMG Haḍbat al-Ǧawlān, hebräisch רָמַת הַגּוֹלָן Ramat haGolan, deutsch kurz Golan; gräzisiert Γαυλανίτις, Gaulanitis) sind im geographischen Sinne ein hügeliger Landstrich im Nahen Osten.
 *Mediterranean Sea
*Mediterranean Sea
 Egypt
Egypt
 Algeria
Algeria
 Belgium
Belgium
 Bulgaria
Bulgaria
 Germany
Germany
 France
France

 History
History

 History
History
 H 1000 - 500 BC
H 1000 - 500 BC

 History
History
 I 500 - 0 BC
I 500 - 0 BC

 History
History
 J 0 - 500 AD
J 0 - 500 AD
 Israel
Israel
 Italy
Italy
 Jordan
Jordan
 Croatia
Croatia
 Libanon
Libanon
 Libya
Libya
 Morocco
Morocco
 Netherlands
Netherlands
 Portugal
Portugal
 Romania
Romania
 Switzerland
Switzerland
 Serbia
Serbia
 Syria
Syria
 Tunisia
Tunisia
 Turkey
Turkey
 Hungary
Hungary
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom

 Civilization
Civilization
 Cyprus
Cyprus

Als römische Architektur bezeichnet man die Baukunst der Römer zur Zeit der römischen Republik und der Kaiserzeit. Die römische Architekturgeschichte umfasst damit einen Zeitraum von etwa neun Jahrhunderten (500 v. Chr.–400 n. Chr.). Die Epochen der römischen Architektur werden nach einzelnen Herrschern, Dynastien oder retrospektiv formulierten historischen Zeitabschnitten benannt. Die seitens der Klassischen Archäologie geprägten Epochen- oder Stilbegriffe finden keine Entsprechungen in der schriftlichen antiken Überlieferung, entsprechen also nicht antiker Wahrnehmung und Einteilung.
古罗马建筑(英语:Ancient Roman architecture),是指由古罗马人创造并且扩展到地中海沿岸其所控制疆域的一种新风格的建筑艺术,经常简称为罗马建筑(英语:Roman architecture)。它直接继承了古希腊晚期的建筑成就,而且将其向前大大推进,使之在1到3世纪达到奴隶制时代全世界建筑的顶峰[1][2]。在西方学术界传统上特指古罗马共和国与帝国时期的建筑[3],中文学术界定义较为宽泛,有时可以包括前期的伊特鲁里亚建筑[4],也可以包括分裂之后的西罗马帝国建筑[2],但是一般不包含东罗马帝国建筑。
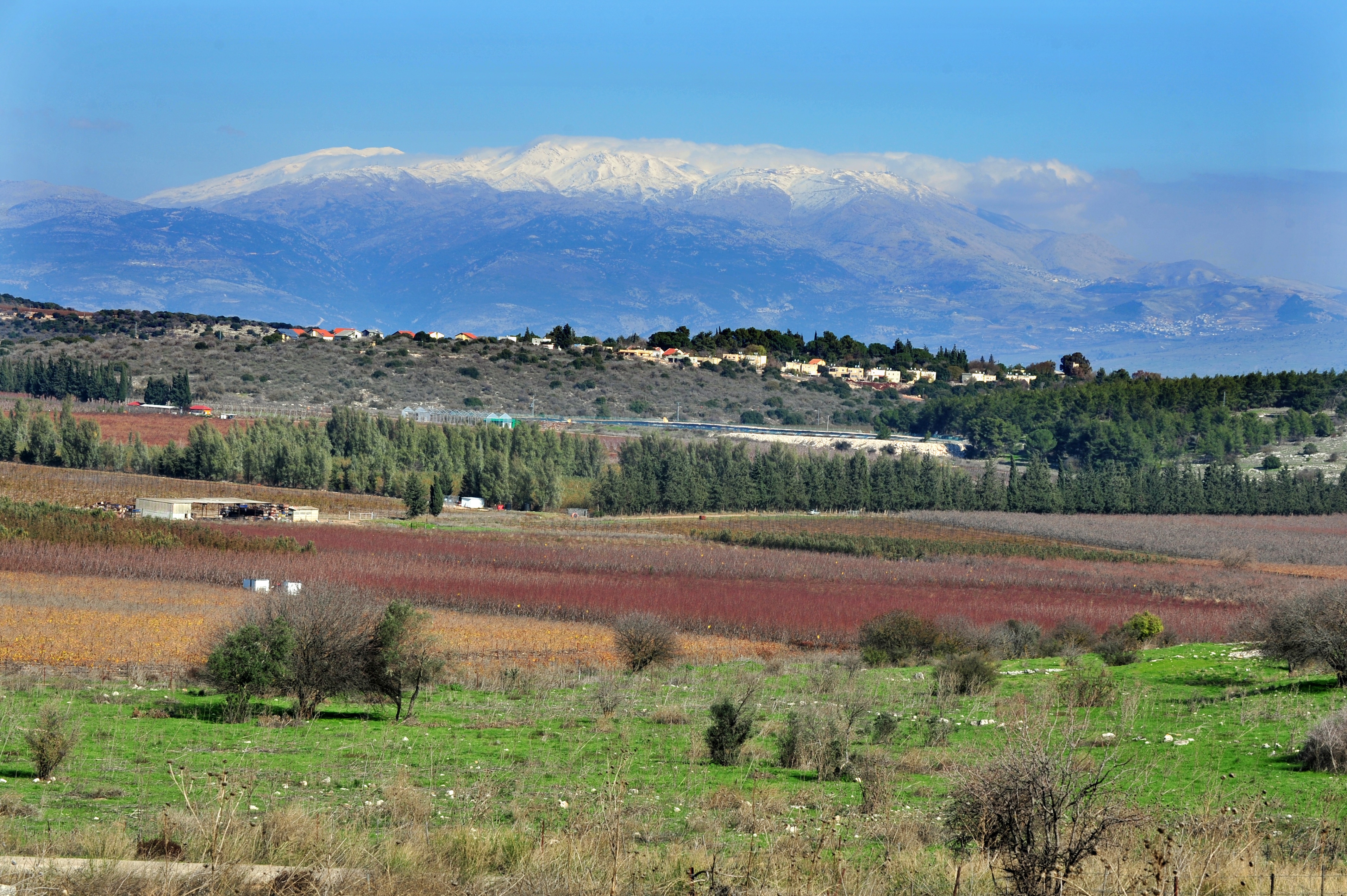

Der Hermon (hebräisch הַר חֶרְמוֹן, AHL har Ḥermon; arabisch جبل الشيخ, DMG ǧabal aš-šaiḫ, levantinisch-arabisch žäbäl əš-šēḫ) ist ein 2814 m hohes Bergmassiv im Nahen Osten im Grenzbereich zwischen Libanon, Israel und Syrien. Der Gipfel ist der höchste Berg Syriens.[1] An seiner Südwestflanke befindet sich der mit einer Höhe von 2224 m höchste Punkt der von Israel kontrollierten Golanhöhen.[2]
黑门山(希伯来语:הר חרמון,罗马化:Har Hermon;阿拉伯语:جبل الشيخ,罗马化:Jabal al-Shaykh,直译:谢赫之山),又名西云山、赫蒙山[1]、赫尔蒙山、黑蒙山、谢赫山[2],是一座位于东黎巴嫩山脉南部的山,最高峰海拔为2,814米。顶峰位于叙利亚和黎巴嫩。在1967年六日战争中以色列获胜后,黑门山的南坡和西坡归属以色列控制。1980年,山脉的这一部分和戈兰高地被以色列单方面合并。

Die Kurden (kurdisch کورد Kurd) sind ein Volk, deren Hauptsiedlungsgebiet als Kurdistan bezeichnet wird. Sie bilden eine bedeutende autochthone ethnische Volksgruppe in der Türkei, im Irak, in Iran und Syrien. Die kurdischen Sprachen gehören zu den indogermanischen Sprachen, und zwar zum nordwestlichen Zweig der iranischen Sprachen (siehe auch Iranische Völker).
Die Zahl der Angehörigen des Volkes ist nicht genau bekannt, weil in den Staaten, in denen die meisten Kurden leben, Daten über ethnische Zugehörigkeiten nicht erhoben werden. Schätzungen allein für Kurdistan und angrenzende Gebiete bewegen sich um 35 Millionen Menschen.
库尔德人(库尔德语:کورد,罗马化:Kurd)是一个生活于西亚的游牧民族,为西南亚库尔德斯坦地区的基本居民。总人口3000万,主要分布在土耳其、叙利亚、伊拉克、伊朗四国境内,有少数分布在阿塞拜疆和亚美尼亚、欧俄南部、以色列等地,在中东是人口仅次于阿拉伯、土耳其和波斯的第四大民族,同时是全世界没有国家的民族中人口最多的。库尔德人是中东地区现存最古老的民族,两千多年来一直都在库尔德斯坦的山区活动,过去都过着游牧或者雇佣兵的生活,后来不断向周边地区扩散。
大部分库尔德人都是伊斯兰教逊尼派信徒,其中多数奉行沙斐仪教法学派(盛行苏菲教团,与周边奉行哈乃斐学派的阿拉伯和土耳其人不同),少数为什叶派穆斯林(含阿拉维派和十二伊玛目派)。还有部分库尔德人信奉雅兹迪教派、琐罗亚斯德教等其他宗教。
 Architecture
Architecture
 World Heritage
World Heritage

 International cities
International cities
 Geography
Geography