Deutsch-Chinesische Enzyklopädie, 德汉百科
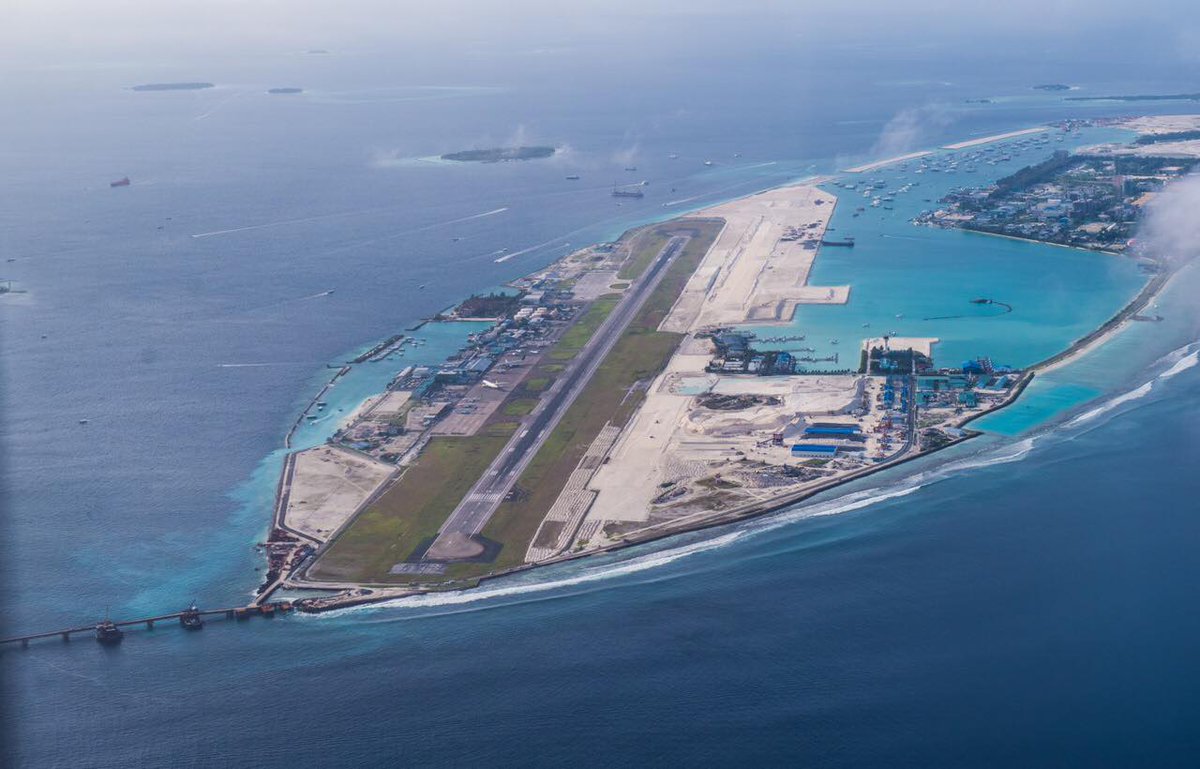
 马尔代夫
马尔代夫

Das Arabische Meer (arabisch بحر العرب, DMG Baḥr al-ʿArab, persisch دریای عرب, Urdu بحیرہ عرب, Hindi अरब सागर) ist ein Randmeer des Indischen Ozeans zwischen der Arabischen Halbinsel und Indien. Es hat eine Flächenausdehnung von 3,9 Millionen km². Seine größte Tiefe von 4481 Metern liegt im Süden.[1]
Im Nordwesten grenzt es an den Golf von Oman, der wiederum mit dem Persischen Golf verbunden ist. Im Südwesten verbindet der Golf von Aden das Arabische Meer mit dem Roten Meer. Im Südosten grenzt das Arabische Meer an die Lakkadivensee. Die meisten Ozeanographen betrachten die Lakkadivensee als Teil des Arabischen Meeres. Weiter im Osten grenzt diese, bzw. das Arabische Meer im erweiterten Sinn, an den Golf von Bengalen.[2]
Länder mit Küstenabschnitten am Arabischen Meer sind die Malediven, Indien, Pakistan, Oman, Jemen und Somalia.
Städte an der Küste sind unter anderem Mumbai (Bombay) und Karachi.
Der Indus ist der bedeutendste Strom zum Arabischen Meer. Weitere Flüsse sind Narmada und Tapti, die beide in den Golf von Khambhat münden.
Im Westen des Arabischen Meeres verläuft die Owen-Bruchzone.
阿拉伯海(阿拉伯语:بحر العرب)为印度洋的一部分。位于亚洲南部的阿拉伯半岛同印度半岛之间。北部为波斯湾和阿曼湾,西部经亚丁湾通红海。面积为386万平方公里。为世界性交通要道。
アラビア海(アラビアかい)は、インド洋の北西部、アラビア半島とインドとの間の海域。
面積約3,862,000 km2[1]、最大幅約2,400 km、最大水深4,652mである。インダス川が最大の流入河川。北側にオマーン湾があり、ホルムズ海峡を通じてペルシャ湾に繋がっている。西側にはアデン湾があり、紅海に通じる。アラビア海に面する国はインド、パキスタン、オマーン、イエメン、ソマリア、モルディブである。代表的な島にソコトラ島(イエメン)やマシーラ島(オマーン)がある。
紀元前数世紀から大航海時代にかけて重要な交易ルートであった。現在も、中東原油を運ぶタンカーや欧州との間の船舶が頻繁に往来し、ソマリア海賊を取り締まる海域でもある。
The Arabian Sea is a region of the northern Indian Ocean bounded on the north by Pakistan and Iran, on the west by the Gulf of Aden, Guardafui Channel and the Arabian Peninsula, on the southeast by the Laccadive Sea,[1] on the southwest by the Somali Sea,[2] and on the east by India. Its total area is 3,862,000 km2 (1,491,000 sq mi) and its maximum depth is 4,652 metres (15,262 ft). The Gulf of Aden in the west, connects the Arabian Sea to the Red Sea through the strait of Bab-el-Mandeb, and the Gulf of Oman is in the northwest, connecting it to the Persian Gulf.
The Arabian Sea has been crossed by important marine trade routes since the third or second millennium BCE. Major seaports include Kandla Port, Okha Port, Mumbai Port, Nhava Sheva Port (Navi Mumbai), Mormugão Port (Goa), New Mangalore Port and Kochi Port in India, the Port of Karachi, Port Qasim, and the Gwadar Port in Pakistan, Chabahar Port in Iran and the Port of Salalah in Oman. The largest islands in the Arabian Sea include Socotra (Yemen), Masirah Island (Oman), Lakshadweep (India) and Astola Island (Pakistan).
La mer d’Arabie ou mer d'Oman, parfois appelée mer arabique (en arabe بحر العرب translittéré en Baḥr al-'Arab, en sanskrit सिन्धु सागर, translittéré en Sindhu Sagar), est une partie de l'océan Indien située entre la péninsule Arabique à l'ouest, le Pakistan au nord, le subcontinent indien au nord-est et à l'est, les îles Laquedives à l'est-sud-est et l'archipel des Maldives au sud-est. Elle est limitée au nord-ouest par le golfe d'Oman et à l'ouest par le golfe d'Aden. Sa surface est d'environ 3,6 millions de km², et sa profondeur maximale est de 5 800 mètres.
La mer est une voie de passage très fréquentée, en particulier pour le transport de pétrole venant du golfe Persique. Elle est également une zone de pêche pour les pays côtiers (sardine, maquereau, thon).
Il Mar Arabico (arabo: بحر العرب; translitterato: Bahr al-'Arab, latino: Mare Erythraeum) è la sezione nord-occidentale dell'oceano Indiano, stretto tra la penisola arabica a ovest, il corno d'Africa a sud-ovest, il sub-continente indiano ad est e la costa asiatica a nord.
Il mar Arabico copre approssimativamente una superficie di 3.686.000 km² ed ha una profondità massima di 5800 metri. Corrisponde alla porzione nord-occidentale dell'oceano Indiano, ed è delimitato ad oriente dalla costa occidentale della penisola indiana, a nord dalla costa pakistana e in parte da quella persiana, ad ovest dalla penisola arabica e a sud da una linea ideale che va dal capo Guardafui, la punta nord-est della Somalia, all'isola di Socotra e fino al Capo Comorin, punta meridionale della penisola del Deccan.
Il mar Arabico comunica tramite il golfo di Oman e lo stretto di Hormuz con il golfo Persico e tramite il golfo di Aden e lo stretto di Bab al Mandab con il mar Rosso. Altri golfi importanti che fanno parte del mar Arabico sono quelli di Cambay e di Kutch in prossimità della costa nord-occidentale indiana. Le isole principali che vi affiorano sono Socotra, prolungamento della costa africana, le isole Laccadive poste in prossimità alla costa sud-orientale dell'India e le isole di Masirah e Kuria Muria poste in prossimità della costa dell'Oman.
I fiumi principali che vi sfociano sono l'Indo, il Narmada, il Tapti ed il Mahi. Le principali città che si affacciano sul mar Arabico sono Aden in Yemen; Mascate in Oman; Gwadar e Karachi in Pakistan; Mumbai, Mangalore, Calicut e Kochi (Cochin) in India. Le coste sono per la maggior parte rocciose ed accidentate, ma non mancano buoni approdi naturali che hanno favorito la nascita di importanti porti (Aden, Mascate, Bandar-e Abbas, Karachi, Bombay, Cochin, Colombo ecc.). Il clima è tropicale; la regione è interessata dai venti monsonici che la investono in maniera decrescente da est verso ovest.
El mar arábigo (también llamado mar de Arabia o mar de Omán) es un mar que forma parte del océano Índico y que está localizado en la costa suroccidental de Asia, entre la península arábiga y la península del Indostán.
Tienen costa al mar arábigo, desde oeste a este, Somalia, Yemen, Omán, Pakistán, India y las islas Maldivas. Los Emiratos Árabes Unidos no tienen costa a este mar, sino a uno de sus entrantes, el golfo de Omán, en el noroeste, que luego se estrecha hasta conectar con el golfo Pérsico o Arábico en el estrecho de Ormuz.
La máxima anchura del mar arábigo es de aproximadamente 2400 km, y su máxima profundidad es de 4652 m, cerca de la península arábiga, aproximadamente a la misma latitud que el extremo sur de India. El Indo es el único río de gran envergadura que fluye hacia este mar.
Entre sus principales ciudades costeras se encuentran Bombay en India y Karachi en Pakistán.
Арави́йское мо́ре (араб. بحر العرب, перс. دریای عرب, урду بحیرہ عرب, хинди अरब सागर, сомал. Bada Carbeed, англ. Arabian Sea) — окраинное море в северной части Индийского океана. Ограничено Аравийским полуостровом на западе и полуостровом Индостан на востоке.
Общая площадь моря — 3 862 000 км²[1]. Максимальная ширина — 2400 км. Максимальная глубина — 5803 м.[2] Крупнейшая река, впадающая в море — Инд.
Крупнейшими заливами являются: на западе Аденский залив, соединяющийся с Красным морем через Баб-эль-Мандебский пролив и на северо-западе Оманский залив, соединяющийся с Персидским заливом. На побережье Индии крупными являются Камбейский залив и залив Кач.
На берегах Аравийского моря расположены Сомали, Джибути, Йемен, Оман, Иран, Пакистан, Индия и Мальдивские острова. Крупнейшие города — Карачи, Аден, Маскат, Мумбаи, Коччи и др.

 阿富汗
阿富汗
 埃及
埃及
 亚美尼亚
亚美尼亚
 阿塞拜疆
阿塞拜疆
 埃塞俄比亚
埃塞俄比亚
 澳大利亚
澳大利亚
 孟加拉国
孟加拉国
 北京市-京
北京市-京
 文莱
文莱
 中国
中国
 丹麦
丹麦
 东帝汶民主共和国
东帝汶民主共和国
 联邦德国
联邦德国
 斐济
斐济

 财政金融
财政金融
 国际银行合作
国际银行合作
 芬兰
芬兰
 法国
法国
 格鲁吉亚
格鲁吉亚
 香港特别行政区-港
香港特别行政区-港
 印度
印度
 印度尼西亚
印度尼西亚
 伊朗
伊朗
 爱尔兰
爱尔兰
 冰岛
冰岛
 以色列
以色列
 意大利
意大利
 约旦
约旦
 柬埔寨
柬埔寨
 哈萨克斯坦
哈萨克斯坦
 卡塔尔
卡塔尔
 吉尔吉斯斯坦
吉尔吉斯斯坦
 老挝
老挝
 卢森堡
卢森堡
 马来西亚
马来西亚
 马尔代夫
马尔代夫
 马耳他
马耳他

 蒙古
蒙古
 缅甸
缅甸
 尼泊尔
尼泊尔
 新西兰
新西兰
 荷兰
荷兰
 挪威
挪威
 阿曼
阿曼
 奥地利
奥地利
 巴基斯坦
巴基斯坦
 菲律宾
菲律宾
 波兰
波兰
 葡萄牙
葡萄牙
 韩国
韩国
 俄罗斯
俄罗斯
 萨摩亚
萨摩亚
 沙特阿拉伯
沙特阿拉伯
 瑞典
瑞典
 瑞士
瑞士
 新加坡
新加坡
 西班牙
西班牙
 斯里兰卡
斯里兰卡
 南非
南非
 塔吉克斯坦
塔吉克斯坦
 泰国
泰国
 土耳其
土耳其
 匈牙利
匈牙利
 乌兹别克斯坦
乌兹别克斯坦
 阿拉伯联合酋长国
阿拉伯联合酋长国
 英国
英国
 越南
越南

 重要的国际组织
重要的国际组织

 经济和贸易
经济和贸易
 经济与政治研究
经济与政治研究
 塞浦路斯
塞浦路斯

亚洲基础设施投资银行(英语:Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank,縮寫:AIIB),简称亚投行,是一个愿意向亚洲国家和地區的基础设施建设提供资金支持的政府间性质的亚洲区域多边开发机构,成立的目的是促进亚洲区域的互联互通建设和经济一体化的进程,並且加大中國與其他亚洲國家和地区的合作力度。总部设在中国北京,法定资本为1,000亿美元。[2]
中华人民共和国主席习近平于2013年10月2日在雅加达同印度尼西亚总统苏西洛举行会谈时首次倡议筹建亚投行。[3]2014年10月24日,中国、印度、新加坡等21国在北京正式签署《筹建亚投行备忘录》。[2]2014年11月25日,印度尼西亚签署备忘录,成为亚投行第22个意向创始成员国。[4]
2015年3月12日,英国正式申请作为意向创始成员国加入亚投行,[5]成为正式申请加入亚投行的首个欧洲国家、主要西方国家。[6]随后法国、意大利、德国等西方国家纷纷以意向创始成员国身份申请加入亚投行。[7]接收新意向创始成员国申请截止日期3月31日临近,韩国[8]、俄罗斯[9]、巴西[10]等域内国家和重要新兴经济体也抓紧申请成为亚投行意向创始成员国。
各方商定将于2015年年中完成亚投行章程谈判并签署,年底前完成章程生效程序,正式成立亚投行。[11]
Die Asiatische Infrastrukturinvestmentbank (亞洲基礎設施投資銀行 / 亚洲基础设施投资银行, kurz: 亞投行 / 亚投行, englisch Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank, AIIB) ist eine multilaterale Entwicklungsbank, die 2014 von verschiedenen Staaten gegründet wurde und im Wettbewerb zur Weltbank, zum Internationalen Währungsfonds und zur Asiatischen Entwicklungsbank steht.
Anlass zur Initiative der Gründung war insbesondere die Unzufriedenheit Chinas über eine Dominanz der US-Amerikaner im Internationalen Währungsfonds, der keine faire Verteilung der globalen Machtverhältnisse aus Sicht Chinas widerspiegelte.[2] Da sich die US-Amerikaner strikt weigerten, eine Änderung der Stimmverhältnisse zu implementieren, begann China 2013 mit der Gründung der Initiative. Neben den 21 Gründungsmitgliedern haben im Jahr 2015 auch unter anderem Deutschland, Italien, Frankreich und das Vereinigte Königreich ihr Interesse bekundet, als nicht-regionale Mitglieder die neue Entwicklungsbank zu unterstützen.[3]
Die Gründungsurkunde der AIIB wurde am 29. Juni 2015 von Vertretern aus 57 Ländern in Peking unterzeichnet.[4] Die Bank nahm im Januar 2016 ihre Arbeit ohne Beteiligung der USA und Japan auf.[5]
Joachim von Amsberg ist der "Vizepräsident für Politik und Strategie".
アジアインフラ投資銀行(アジアインフラとうしぎんこう、英: Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank, AIIB、中: 亚洲基础设施投资银行,亞洲基礎設施投資銀行)は、国際開発金融機関のひとつである。
中華人民共和国が2013年秋に提唱し主導する形で発足した[1]。「合計の出資比率が50%以上となる10以上の国が国内手続きを終える」としていた設立協定が発効条件を満たし、2015年12月25日に発足し[2][3]、2016年1月16日に開業式典を行った[1][4]。
57か国を創設メンバーとして発足し[1][5]、2017年3月23日に加盟国は70カ国・地域となってアジア開発銀行の67カ国・地域を超え[6][7]、一方で日本、アメリカ合衆国などは2017年の現時点で参加を見送っている[8]。 創設時の資本金は1000億ドルである[9]。
The Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank (AIIB) is a multilateral development bank that aims to support the building of infrastructure in the Asia-Pacific region. The bank currently has 93 members from around the world [7]. The bank started operation after the agreement entered into force on 25 December 2015, after ratifications were received from 10 member states holding a total number of 50% of the initial subscriptions of the Authorized Capital Stock.[8]
The United Nations has addressed the launch of AIIB as having potential for "scaling up financing for sustainable development"[9] and to improve the global economic governance.[10] The starting capital of the bank was $100 billion, equivalent to 2⁄3 of the capital of the Asian Development Bank and about half that of the World Bank.[11]
The bank was proposed by China in 2013[12] and the initiative was launched at a ceremony in Beijing in October 2014.[13] It received the highest credit ratings from the three biggest rating agencies in the world, and is seen as a potential rival to the World Bank and IMF.[14][15]
La Banque asiatique d'investissement dans les infrastructures (BAII ou AIIB), est une banque d'investissement proposée par la République populaire de Chine dans le but de concurrencer le Fonds monétaire international, la Banque mondiale et la Banque asiatique de développement1 pour répondre au besoin croissant d'infrastructures en Asie du Sud-Est et en Asie centrale. Cette banque s'inscrit dans la stratégie de la nouvelle route de la soie, développée par la Chine.
La Banca Asiatica d'Investimento per le infrastrutture (AIIB), fondata a Pechino nell'ottobre 2014, è un'istituzione finanziaria internazionale proposta dalla Repubblica Popolare Cinese. Si contrappone al Fondo Monetario Internazionale, alla Banca Mondiale e all'Asian Development Bank[1], le quali si trovano sotto il controllo del capitale e delle scelte strategiche dei paesi sviluppati come gli Stati Uniti d'America.[2] Scopo della Banca è fornire e sviluppare progetti di infrastrutture nella regione Asia-Pacifico attraverso la promozione dello sviluppo economico-sociale della regione e contribuendo alla crescita mondiale.
El Banco Asiático de Inversión en Infraestructura (Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank o AIIB) es una institución financiera internacional propuesta por el gobierno de China. El propósito de este banco de desarrollo multilateral es proporcionar la financiación para proyectos de infraestructura en la región de Asia basado en un sistema financiero de préstamo1 y el fomento del sistema de libre mercado en los países asiáticos.
El AIIB está considerado por algunos como una versión continental del FMI y del Banco Mundial, y busca ser un rival por la influencia en la región del Banco de Desarrollo asiático (ADB), el cual esta alineado a los intereses de potencias, tanto regionales (Japón), como globales (Estados Unidos, la Unión Europea).2
El banco fue propuesto por Xi Jinping en 2013 e inaugurado con una ceremonia en Pekín en octubre de 2014. La ONU se a mostrado entusiasta con la propuesta china, a la que a descrito como el FMI del futuro y a señalado como "una gran propuesta para financiar el desarrollo sostenible" y "mejorar la gobernanza económica mundial". La entidad constó inicialmente con 100 mil millones de dolares, es decir, la mitad del dinero de que posee el Banco Mundial.
La entidad a recibido inversión por parte de corporaciones financieras estadounidenses como la Standard & Poor's, Moody's o Fitch Group34. Actualmente la entidad consta de 87 miembros, incluyendo los 57 miembros fundadores. Bélgica, Canadá, y Ucrania están barajando unirse al AIIB. Estados Unidos, Japón y Colombia no tienen intención de participar. China a prohibido a Corea del Norte unirse, instigando además una política de aislamiento contra esta por parte del AIIB.
Азиатский банк инфраструктурных инвестиций (АБИИ) (англ. Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank, AIIB) — международная финансовая организация, создание которой было предложено Китаем. Основные цели, которые преследует АБИИ, — стимулирование финансового сотрудничества в Азиатско-Тихоокеанском регионе, финансирование инфраструктурных проектов в Азии от строительства дорог и аэропортов до антенн связи и жилья экономкласса[1].
По заявлениям вице-премьера России Игоря Шувалова, AБИИ не рассматривается как потенциальный конкурент МВФ, Всемирного банка и Азиатского банка развития (АБР). Однако эксперты рассматривают AIIB как потенциального конкурента базирующихся в США Международного валютного фонда (МВФ) и Всемирного банка. После сообщений об успехах AIIB американский министр финансов США Джейкоб Лью предупредил, что международным финансовым организациям в США, таким как ВБ и МВФ, грозит потеря доверия [2][3].
Китай, Индия и Россия возглавили организацию, оказавшись в тройке крупнейших владельцев голосов. При этом на важнейшие решения КНР имеет фактическое право вето[4].
 澳大利亚
澳大利亚
 孟加拉国
孟加拉国
 文莱
文莱
 中国
中国
 海南省-琼
海南省-琼
 印度
印度
 印度尼西亚
印度尼西亚
 伊朗
伊朗
 以色列
以色列
 日本
日本
 柬埔寨
柬埔寨
 哈萨克斯坦
哈萨克斯坦
 吉尔吉斯斯坦
吉尔吉斯斯坦
 老挝
老挝
 马来西亚
马来西亚
 马尔代夫
马尔代夫

 蒙古
蒙古
 缅甸
缅甸
 尼泊尔
尼泊尔
 新西兰
新西兰
 巴基斯坦
巴基斯坦
 菲律宾
菲律宾
 韩国
韩国
 新加坡
新加坡
 斯里兰卡
斯里兰卡
 塔吉克斯坦
塔吉克斯坦
 泰国
泰国
 土库曼斯坦
土库曼斯坦
 乌兹别克斯坦
乌兹别克斯坦
 越南
越南

ボアオ・アジア・フォーラム(博鰲アジアフォーラム、Boao Forum for Asia、略称BFA、中国語:博鳌亚洲论坛、ピンイン:Bóáo Yàzhōu Lùntán)は、中華人民共和国に本拠を置く国際非営利組織。
スイスのダボスで開催されている世界の政治家・財界人・知識人が集まる国際会議(ダボス会議)を主催する世界経済フォーラムにならい、そのアジア版を目指して、中国政府の全面的支援を受けて構想された。2001年2月27日の設立にはアジアの25カ国とオーストラリアの計26カ国が参加している。
ボアオ・アジア・フォーラム主催の最初の国際会議は2002年4月12日・4月13日に開催され、日本からは小泉純一郎内閣総理大臣が出席して演説を行った[1]。国際会議の会場は、2001年の発足会議以来、中国・海南省の海浜リゾート地・ボアオ(博鰲、海南島東海岸の瓊海市)に固定されている。会議は毎年行われ、各国首脳や大企業経営者、学者、NGO代表など政府・民間のハイレベルの人材が集い、アジアや世界の経済動向、金融政策、経済統合、経済投資、国際協力、社会問題、環境問題などに関する討議が行われる。また多くの経済人や政治家、社会運動家らが直接話し合い、国家間協力や企業提携などのトップ会談が持たれる。 過去の議題には中国の世界貿易機関(WTO)への加入問題、90年代後半のアジア金融危機問題などが取り上げられ、2004年には中国の地政学的な「和平崛起」(平和的台頭)戦略の可否が議題となった。
The Boao Forum for Asia (BFA; Chinese: 博鳌亚洲论坛; pinyin: Bó'áo Yàzhōu Lùntán) is a non-profit organisation that hosts high-level forums for leaders from government, business and academia in Asia and other continents to share their vision on the most pressing issues in this dynamic region and the world at large. BFA is modelled on the World Economic Forum held annually in Davos, Switzerland. Its fixed address is in Bo'ao, Hainan province, China, although the Secretariat is based in Beijing. The forum, sometimes known as the “Asian Davos”, takes its name from the town of Boao, located in China’s southern Hainan province, which has been the permanent venue for its annual conference since 2002.[1]
The Forum is committed to promoting regional economic integration and bringing Asian countries even closer to their development goals. Initiated in 1998 by Fidel V. Ramos, former President of the Philippines, Bob Hawke, former Prime Minister of Australia, and Morihiro Hosokawa, former Prime Minister of Japan, the Boao Forum for Asia was formally inaugurated in February 2001. The founding of the BFA was driven by the People's Republic of China and founded by 26 Asian and Australasian states on 27 February 2001. The organisation held its first meeting from 12–13 April 2002.
Discussions at the BFA focus on economics, integration, cooperation, society and the environment. In the past the forum also addressed China's entry into the World Trade Organization, as well as Southeast Asia's economic crisis during the 1990s. The geopolitical strategy 'China's peaceful rise' was a topic of discussion for the forum in 2004. In addition to its annual meeting, the BFA also sponsors other forums and meetings related to Asian issues.
El Foro de Boao para Asia (en chino: 博鳌亚洲论坛, pinyin: Bó'áo Yàzhōu Lùntán), conocida también por sus siglas en inglés BFA, es una organización no lucrativa que organiza foros de alto nivel para líderes del gobierno, los negocios y la academia en Asia y otros continentes para compartir su visión sobre los asuntos más apremiantes en esta región y en el mundo entero. El Foro Boao es el modelo del Foro Económico Mundial que se celebra anualmente en Davos, Suiza. Tiene su sede en Bo'ao, Hainan, China, aunque la Secretaría se encuentra en Pekín.
El Foro tiene como objetivos promover la integración económica regional y acercar a los países asiáticos hacia sus metas de desarrollo.1 Fue creado en 1998 por Fidel V. Ramos, expresidente de Filipinas, Bob Hawke, ex primer ministro de Autralia y Morihiro Hosokawa, ex primer ministro de Japón.2 El Foro de Boao para Asia fue formalmente inaugurado en febrero de 2001. La creación del foro fue liderado por la República Popular de China y fundada por 26 países de Asia y Australasia el 27 de febrero de 2001. La organización tuvo su primera reunión el 12 y 13 de abril de 2002.
Las discusiones del Foro Boao se centran en economía, cooperación, sociedad y medio ambiente. En e pasado el foro también abordaba el ingreso de China en la Organización Mundial del Comercio, así como la crisis financiera asiática de los años noventa. Además de su reunión anual, el foro también patrocina otros foros y reuniones relacionados con temas asiáticos.
Боаоский Азиатский Форум, БАФ (кит: 博鳌亚洲论坛; пиньинь: Bó'áo Yàzhōu Lùntán, англ: Boao Forum for Asia, аббр: BFA), также известен как «Восточный Давос» — неправительственная и некоммерческая международная организация, имеющая своей целью поддержку и развитие экономического обмена, взаимодействия и сотрудничества как в Азии, так и за её пределами путём проведения ежегодных встреч высокого уровня с участием представителей правительственных, деловых, промышленных и научных кругов и обсуждения актуальных экономических, социальных, экологических и др. проблем.
Учреждён в 2001 году. Ежегодные конференции в Боао проводятся с 2002 года.
Главный офис организации находится в г. Боао, пров. Хайнань, КНР.
В 2018 году Боаоский азиатский форум /БАФ/ пройдет 8-11 апреля. Главными темами мероприятия станут реформы, открытость, инновации и "Пояс и путь"[1].
 *英国政治
*英国政治
 安提瓜和巴布达
安提瓜和巴布达
 澳大利亚
澳大利亚
 巴哈马
巴哈马
 孟加拉国
孟加拉国
 巴巴多斯
巴巴多斯
 伯利兹
伯利兹
 博茨瓦纳
博茨瓦纳
 文莱
文莱
 英联邦国家
英联邦国家
 多米尼克
多米尼克
 加纳
加纳
 格林纳达
格林纳达
 圭亚那
圭亚那
 印度
印度
 牙买加
牙买加
 喀麦隆
喀麦隆
 加拿大
加拿大
 肯尼亚
肯尼亚
 基里巴斯
基里巴斯
 莱索托
莱索托
 马拉维
马拉维
 马来西亚
马来西亚
 马尔代夫
马尔代夫
 马耳他
马耳他
 莫桑比克
莫桑比克
 纳米比亚
纳米比亚
 瑙鲁
瑙鲁
 新西兰
新西兰
 尼日利亚
尼日利亚
 巴基斯坦
巴基斯坦
 巴布亚新几内亚
巴布亚新几内亚
 所罗门群岛
所罗门群岛
 赞比亚
赞比亚
 萨摩亚
萨摩亚
 塞舌尔
塞舌尔
 塞拉利昂
塞拉利昂
 新加坡
新加坡
 斯里兰卡
斯里兰卡
 圣基茨和尼维斯
圣基茨和尼维斯
 圣文森特和格林纳丁斯
圣文森特和格林纳丁斯
 南非
南非
 斯威士兰
斯威士兰
 坦桑尼亚
坦桑尼亚
 汤加
汤加
 特立尼达和多巴哥
特立尼达和多巴哥
 图瓦卢
图瓦卢
 乌干达
乌干达
 瓦努阿图
瓦努阿图
 英国
英国

 重要的国际组织
重要的国际组织
 塞浦路斯
塞浦路斯

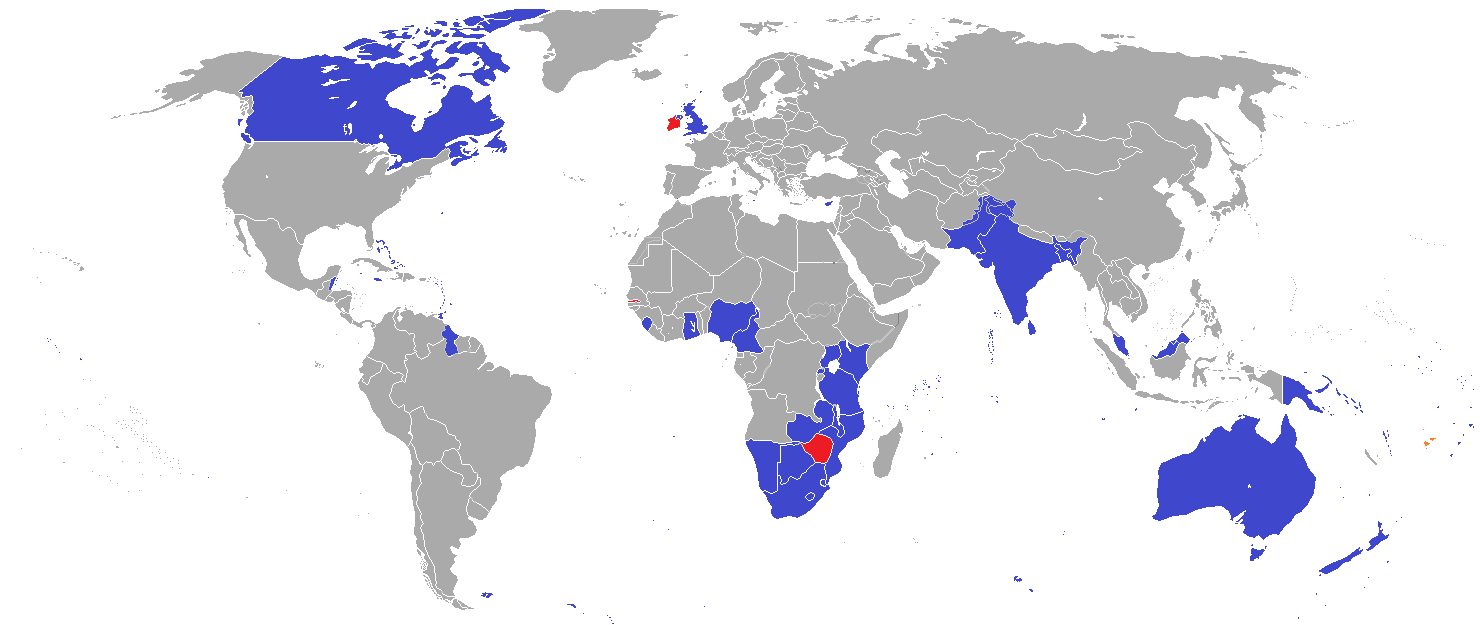
英联邦(英语:Commonwealth of Nations,新马作共和联邦,台湾作大英国协),是一个现代的国际组织,由56个英语系的主权国家联合而成。
英联邦不是一个统一的联邦国家,而是一个国际组织,英联邦也无权约束旗下任何成员国内政。英联邦元首通常由英国君主兼任,其首任元首是乔治六世,现任是查尔斯三世,但元首并无实权,秘书长才是英联邦实际上的掌权者[4][5]。该组织的成员国基本由英国及其旧殖民地组成,也以英式英语为共通语言,但英国的地位并没有凌驾于他国之上,所有成员国一律平等。目前英联邦有56个成员国,其中15个属于英联邦王国,英联邦王国的国家元首、英联邦元首均和英国的一致,即现在的查尔斯三世;另外5个属于独立君主国,它们不以英国君主为自己的元首,而是自立君主,这五国是文莱、斯威士兰、莱索托、马来西亚、汤加;其余的36个均属于共和国,没有君主。
The Commonwealth of Nations, generally known simply as the Commonwealth,[3] is a political association of 53 member states, nearly all of them former territories of the British Empire.[4] The chief institutions of the organisation are the Commonwealth Secretariat, which focuses on intergovernmental aspects, and the Commonwealth Foundation, which focuses on non-governmental relations between member states.[5]
The Commonwealth dates back to the first half of the 20th century with the decolonisation of the British Empire through increased self-governance of its territories. It was originally created as the British Commonwealth of Nations[6] through the Balfour Declaration at the 1926 Imperial Conference, and formalised by the United Kingdom through the Statute of Westminster in 1931. The current Commonwealth of Nations was formally constituted by the London Declaration in 1949, which modernised the community and established the member states as "free and equal".[7]
The human symbol of this free association is the Head of the Commonwealth, currently Queen Elizabeth II, and the 2018 Commonwealth Heads of Government Meeting appointed Charles, Prince of Wales to be her designated successor, although the position is not technically hereditary. The Queen is the head of state of 16 member states, known as the Commonwealth realms, while 32 other members are republics and five others have different monarchs.
Member states have no legal obligations to one another, but are connected through their use of the English language and historical ties. Their stated shared values of democracy, human rights and the rule of law are enshrined in the Commonwealth Charter[8] and promoted by the quadrennial Commonwealth Games.
The countries of the Commonwealth cover more than 29,958,050 km2 (11,566,870 sq mi), equivalent to 20% of the world's land area, and span all six inhabited continents.
Le Commonwealth ou Commonwealth of Nations (littéralement, la « Communauté des Nations ») est une organisation intergouvernementale composée de 53 États membres qui sont presque tous d'anciens territoires de l'Empire britannique.
Le Commonwealth a émergé au milieu du XXe siècle pendant le processus de décolonisation. Il est formellement constitué par la Déclaration de Londres de 1949 qui fait des États membres des partenaires « libres et égaux ». Le symbole de cette libre association est la reine Élisabeth II qui est chef du Commonwealth. La reine est également le chef d'État monarchique des 16 royaumes du Commonwealth. Les autres États membres sont 32 républiques et cinq monarchies dont le monarque est différent.
Les États membres n'ont aucune obligation les uns envers les autres. Ils sont réunis par la langue, l'histoire et la culture et des valeurs décrites dans la Charte du Commonwealth telles que la démocratie, les droits humains et l'état de droit.
Les États du Commonwealth couvrent 29 958 050 km2 de territoire sur les cinq continents habités. Sa population est estimée à 2,328 milliards d'habitants.
Il Commonwealth delle Nazioni o Commonwealth (acronimo CN) è un'organizzazione intergovernativa di 53 Stati membri indipendenti, tutti accomunati, eccetto il Mozambico e il Ruanda, da un passato storico di appartenenza all'Impero britannico, del quale il Commonwealth è una sorta di sviluppo su base volontaria. La popolazione complessiva degli stati che vi aderiscono è di oltre due miliardi di persone. La parola Commonwealth deriva dall'unione di common (comune) e wealth (benessere), cioè benessere comune.
In passato fu noto anche come Commonwealth britannico, benché tale definizione esistette formalmente solo dalla fondazione nel 1926 fino al 1948.
La Mancomunidad de Naciones (en inglés: Commonwealth of Nations)?, antiguamente Mancomunidad Británica de Naciones (British Commonwealth of Nations), es una organización compuesta por 53 países soberanos independientes y semi independientes que, con la excepción de Mozambique y Ruanda,1 comparten lazos históricos con el Reino Unido. Su principal objetivo es la cooperación internacional en el ámbito político y económico, y desde 1950 la pertenencia a ella no implica sumisión alguna a la Corona británica, aunque se respeta la figura de la reina del Reino Unido. Con el ingreso de Mozambique, la organización ha favorecido el término Mancomunidad de Naciones para subrayar su carácter internacionalista. Sin embargo, el adjetivo británico se sigue utilizando con frecuencia para diferenciarla de otras mancomunidades existentes a nivel internacional.
La reina Isabel II del Reino Unido es la cabeza de la organización, según los principios de la Mancomunidad, «símbolo de la libre asociación de sus miembros».
Содру́жество на́ций (англ. Commonwealth of Nations, до 1946 года — Британское Содружество наций — англ. British Commonwealth of Nations), кратко именуемое просто Содружество (англ. The Commonwealth) — добровольное объединение суверенных государств, в которое входят Великобритания и почти все её бывшие доминионы, колонии и протектораты. Членами Содружества также являются Мозамбик, Руанда, Намибия и Камерун[2].

 阿富汗
阿富汗
 埃及
埃及
 阿尔巴尼亚
阿尔巴尼亚
 阿尔及利亚
阿尔及利亚
 阿塞拜疆
阿塞拜疆
 巴林
巴林
 孟加拉国
孟加拉国
 贝宁
贝宁
 文莱
文莱
 布基纳法索
布基纳法索
 科特迪瓦
科特迪瓦
 吉布提
吉布提
 加蓬
加蓬
 冈比亚
冈比亚
 几内亚
几内亚
 几内亚比绍
几内亚比绍
 圭亚那
圭亚那
 印度尼西亚
印度尼西亚
 伊拉克
伊拉克
 伊朗
伊朗
 也门
也门
 约旦
约旦
 喀麦隆
喀麦隆
 哈萨克斯坦
哈萨克斯坦
 卡塔尔
卡塔尔
 吉尔吉斯斯坦
吉尔吉斯斯坦
 科摩罗
科摩罗
 科威特
科威特
 黎巴嫩
黎巴嫩
 利比亚
利比亚
 马来西亚
马来西亚
 马尔代夫
马尔代夫
 马里
马里
 摩洛哥
摩洛哥
 毛里塔尼亚
毛里塔尼亚
 莫桑比克
莫桑比克
 尼日尔
尼日尔
 尼日利亚
尼日利亚
 阿曼
阿曼
 巴基斯坦
巴基斯坦
 巴勒斯坦
巴勒斯坦
 苏丹共和国
苏丹共和国
 沙特阿拉伯
沙特阿拉伯
 塞内加尔
塞内加尔
 塞拉利昂
塞拉利昂
 索马里
索马里
 苏里南
苏里南
 叙利亚
叙利亚
 塔吉克斯坦
塔吉克斯坦
 多哥
多哥
 乍得
乍得
 突尼斯
突尼斯
 土耳其
土耳其
 土库曼斯坦
土库曼斯坦
 乌干达
乌干达
 乌兹别克斯坦
乌兹别克斯坦
 阿拉伯联合酋长国
阿拉伯联合酋长国

 重要的国际组织
重要的国际组织

伊斯兰合作组织(阿拉伯语:منظمة التعاون الإسلامي;英语:Organisation of Islamic Cooperation;法语:Organisation de la coopération islamique)原名伊斯兰会议组织,是一个伊斯兰世界的政府间国际组织,为联合国大会观察员;该组织由遍及西亚(中东)、中亚、西非、北非、印度次大陆和东南亚的57个国家组成,覆盖的人口约为16亿。秘书处设在沙特阿拉伯王国的吉达市;现任秘书长是原沙特社会事务大臣Yousef Al-Othaimeen(从2016年开始)。
组织的宗旨是促进各成员国之间在经济、社会、文化和科学等方面的合作;努力消除种族隔离和种族歧视,反对一切形式的殖民主义;支持巴勒斯坦人民恢复民族权利和重返家园的斗争;支持穆斯林保障其尊严、独立和民族权利的斗争。
但要注意的是并非每个成员国是伊斯兰国家,如圭亚那、苏里南、莫桑比克、喀麦隆、乌干达和加蓬等国,伊斯兰反而是极少数人的信仰,阿尔巴尼亚则是唯一加入该组织的欧洲大陆的主权国家和联合国会员国,2011年脱离苏丹独立的南苏丹也在独立后脱离该组织的势力范围。
Die Organisation für Islamische Zusammenarbeit (arabisch منظمة التعاون الإسلامي, DMG Munaẓẓamat at-Taʿāwun al-islāmī; englisch Organization of Islamic Cooperation, OIC; französisch L’Organisation de Coopération Islamique, OCI; früher Organisation der Islamischen Konferenz) ist eine zwischenstaatliche internationale Organisation von derzeit 56 Staaten,[2] in denen der Islam Staatsreligion, Religion der Bevölkerungsmehrheit oder Religion einer nennenswerten Minderheit ist. Die Organisation nimmt für sich in Anspruch, den Islam zu repräsentieren. Mehrere größere Mitgliedsstaaten (Saudi-Arabien, Ägypten, die Türkei und der Iran) erheben hinter den Kulissen Führungsansprüche; die jeweils anderen Staaten bestreiten deren Recht dazu. Infolge dieser Rivalitäten ist die OIC seit 2017 kaum handlungsfähig.[3]
イスラム協力機構(イスラムきょうりょくきこう、アラビア語: منظمة التعاون الاسلامي、略称OIC; 英語: Organisation of Islamic Cooperation、略称OCI; フランス語: Organisation de la coopération Islamique)は、イスラム諸国をメンバーとして構成され、国際連合に対する常任代表を有する国際機構。公用語はアラビア語、英語、フランス語。かつてはイスラム諸国会議機構(منظمة المؤتمر الإسلامي、英語: Organisation of the Islamic Conference、フランス語: Organisation de la Conférence Islamique)という名称であったが、2011年6月にカザフスタンのアスタナでの会議で「イスラム協力機構」への変更と紋章が決定された[1]。
イスラム諸国の政治的協力、連帯を強化すること、イスラム諸国に対する抑圧に反対し、解放運動を支援することを目的とする。
加盟国はムスリム(イスラム教徒)が国民の多数を占める西アジア、北アフリカ、西アフリカ、東アフリカ、中央アジア、南アジア、東南アジアなどの57か国、オブザーバーが5ヵ国・8組織(国連など)からなり、世界13億人のムスリムの大部分を代表する。
加盟条件としては、国内でムスリムが大多数を占めることを必ずしも条件としているわけではなく、南アメリカのいくつかの国のようにマイノリティとしてある程度のムスリム人口を抱えているだけであっても、外相会議における審査で承認されればイスラム諸国のひとつとして機構に加盟することができる。イスラム教徒が多数派を占める国はほとんど参加しているが、イスラム教徒比率の高い国のうちエチオピア(30~50%)とタンザニア(約30%)が加盟していない。イスラム教徒人口の多い国で言えばインド(約1億5000万人)や中国(約2000万人)も加盟していない。逆にイスラム教徒比率の低い国ではガボン、ウガンダ、スリナム、ガイアナなどが加盟している(それぞれ10%未満)。
The Organisation of Islamic Cooperation (OIC; Arabic: منظمة التعاون الإسلامي; French: Organisation de la coopération islamique), formerly the Organisation of the Islamic Conference, is an international organization founded in 1969, consisting of 57 member states, with a collective population of over 1.8 billion as of 2015 with 53 countries being Muslim-majority countries. The organisation states that it is "the collective voice of the Muslim world" and works to "safeguard and protect the interests of the Muslim world in the spirit of promoting international peace and harmony".[1]
The OIC has permanent delegations to the United Nations and the European Union. The official languages of the OIC are Arabic, English, and French.
L’Organisation de la coopération islamique (OCI), en arabe : منظمة التعاون الإسلامي (Munaẓẓamat at-Taʿāwun al-islāmī), en anglais : Organisation of Islamic Cooperation (OIC), appelée jusqu'en 2011 Organisation de la conférence islamique (en arabe : منظمة المؤتمر الإسلامي, en anglais : Organisation of the Islamic Conference), est une organisation intergouvernementale créée le 25 septembre 1969. Son siège se situe à Djeddah en Arabie saoudite et elle possède une délégation permanente aux Nations unies.
Regroupant 57 États membres, sa vocation est de promouvoir la coopération dans les domaines économiques, sociaux, culturels et scientifiques (grâce notamment à la Banque islamique de développement), mais aussi la sauvegarde des lieux saints de l'islam ou encore le soutien au peuple palestinien. À l'échelle mondiale, il n'existe pas d'autre organisation confessionnelle dont les membres signataires soient des États.
Ses trois langues officielles sont l'arabe, l'anglais et le français2.
L'Organizzazione della cooperazione islamica (in arabo: منظمة التعاون الإسلامي, Munaẓẓamat al-taʿāwun al-islāmī; in inglese: Organization of the Islamic Cooperation, OIC; in francese: Organisation de la coopération islamique, OCI) è un'organizzazione internazionale con una delegazione permanente presso le Nazioni Unite. Rappresenta 56 Stati dell'Europa, Vicino Oriente, Medio Oriente, America meridionale, Africa, Asia centrale e del Subcontinente indiano.[1]
L'organizzazione, fondata a Rabat, in Marocco, il 25 settembre 1969 con il nome Organisation of the Islamic Conference, in arabo: منظمة المؤتمر الإسلامي, Munaẓẓamat al-muʾtamar al-islāmī; (FR) Organisation de la conférence islamique, mutato nell'attuale nel 2011.[2]
Ha come finalità la salvaguardia degli interessi e lo sviluppo delle popolazioni musulmane nel mondo.
Il 10 ottobre 1975 le è stato riconosciuto lo status di osservatore dell'Assemblea generale delle Nazioni Unite.
La Organización para la Cooperación Islámica (Árabe:منظمة التعاون الاسلامي); (Francés: Organisation de la Coopération Islamique); (Inglés: Organisation of Islamic Cooperation) es un organismo internacional que agrupa a los estados de confesión musulmana, creado en 1969 durante la Conferencia de Rabat y formalizada dos años después.
Su sede está en Yidda, ciudad costera de Arabia Saudí a orillas del Mar Rojo. Sus miembros son países con mayoría de población musulmana o con una comunidad significativa en ellos, con Estados miembros y observadores de África, Asia, Europa y América del Sur. El 28 de junio de 2011 se oficializó el cambio de nombre,1 anteriormente se llamó: Organización de la Conferencia Islámica (Árabe:منظمة المؤتمر الإسلامي); (Francés: Organisation de la Conférence Islamique); (Inglés:Organization of the Islamic Conference).
Sus acciones se circunscriben a la actividad colaborativa entre sus miembros, sobre todo en la lucha contra el imperialismo, el neocolonialismo y por la emancipación de Palestina. Históricamente se celebraron diversos congresos que contribuyeron con su desarrollo: Lahore (1974), La Meca (1981), Casablanca (1984), Kuwait (1987), Dakar (1991). Sus repercusiones son menores que las de la Liga Árabe.
Организация исламского сотрудничества (англ. Organisation of Islamic Cooperation (OIC), араб. منظمة التعاون الاسلامي) — международная организация исламских стран (до 2011 года называлась Организация Исламская конференция (ОИК).

南亚区域合作联盟(英语:South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation)是1985年12月8日成立的旨在推动南亚人民间友谊、信任与理解的平台,由孟加拉国、不丹、印度、马尔代夫、尼泊尔、巴基斯坦和斯里兰卡七国政府发起成立。2005年11月13日,接受阿富汗为成员。缅甸、模里西斯、澳大利亚、中华人民共和国、日本、大韩民国、欧盟、美国和伊朗成为观察员。
Die Südasiatische Vereinigung für regionale Kooperation (auch Südasiatische Wirtschaftsgemeinschaft) (von englisch South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation) (SAARC) wurde am 8. Dezember 1985 in Dhaka (Bangladesch) gegründet und hat ihren Sitz in der nepalesischen Hauptstadt Kathmandu. Gründungsmitglieder sind Indien, Pakistan, Bangladesch, Nepal, Sri Lanka, Bhutan und die Malediven. Im April 2007 trat Afghanistan auf dem Gipfeltreffen in Neu-Delhi der Organisation bei. Die Volksrepublik China, Japan, die Europäische Union, Südkorea, die Vereinigten Staaten und der Iran besitzen Beobachterstatus.

 阿富汗
阿富汗
 埃及
埃及
 阿尔及利亚
阿尔及利亚

 历史
历史

 历史
历史
 公元 500 - 1000
公元 500 - 1000
 伊拉克
伊拉克
 伊朗
伊朗
 也门
也门
 约旦
约旦
 卡塔尔
卡塔尔
 科摩罗
科摩罗
 黎巴嫩
黎巴嫩
 利比亚
利比亚
 马尔代夫
马尔代夫
 摩洛哥
摩洛哥
 巴基斯坦
巴基斯坦

 宗教
宗教
 伊斯兰教
伊斯兰教
 苏丹共和国
苏丹共和国
 沙特阿拉伯
沙特阿拉伯
 索马里
索马里
 叙利亚
叙利亚
 塔吉克斯坦
塔吉克斯坦
 突尼斯
突尼斯
 土耳其
土耳其
 乌兹别克斯坦
乌兹别克斯坦

Verteilung muslimischer Glaubensrichtungen: Grün: sunnitische Gebiete; Rot: schiitische Gebiete; Blau: Ibaditen (Oman)
Die Sunniten bilden die größte Glaubensgruppe im Islam. Ihre Glaubensrichtung selbst wird als Sunnitentum oder Sunnismus bezeichnet. Die Bezeichnung ist von dem arabischen Wort Sunna (‚Brauch, Handlungsweise, überlieferte Norm, Tradition‘) abgeleitet. Diejenigen, die der sunnat an-nabī, der „Sunna des Propheten“ (sc. Mohammed), folgen, werden im Arabischen als ahl as-sunna („Leute der Sunna“) und im Türkischen als Ehl-i Sünnet bezeichnet, was im Deutschen üblicherweise als „Sunniten“ wiedergegeben wird. Neben ahl as-sunna wird im Arabischen auch der erweiterte Ausdruck ahl as-sunna wal-dschamāʿa (arabisch أهل السنة والجماعة, DMG ahl as-sunna wal-ǧamāʿa ‚Leute der Sunna und der Gemeinschaft‘) verwendet. Die Glaubenslehren der Sunniten werden in verschiedenen Glaubensbekenntnissen dargestellt, die sich je nach dogmatischer Ausrichtung der Autoren unterscheiden.
Heute gelten die Schiiten als die wichtigste Gegengruppe zu den Sunniten, allerdings hat sich das sunnitische Selbstbewusstsein im Mittelalter nicht nur in Absetzung zu den Schiiten, sondern auch zu den Charidschiten, Qadariten und Murdschi'iten herausgebildet. Über die Frage, welche dogmatischen Lehrrichtungen dem Sunnitentum angehören, besteht unter den muslimischen Gelehrten keine Einigkeit. Eine der wenigen internationalen Initiativen zur Klärung der sunnitischen Identität war die Sunnitenkonferenz von Grosny im August 2016. Auf ihr wurden die Takfīrī-Salafisten und andere extremistische Gruppen wie der Islamische Staat aus dem sunnitischen Islam ausgeschlossen.[1]
逊尼派(阿拉伯语:أهل السنة والجماعة,ʾAhl ūs-Sunnah wa āl-Ǧamāʿah,简称أهل السنة ʾAhl ūs-Sunnah),又译素尼派,原意为遵循圣训者,为伊斯兰教中的最大派别,自称“正统派”,与什叶派对立。一般认为,全世界大约有85~91%穆斯林隶属此派别[1][2][3]。
スンナ派(アラビア語:(أهل السنة (والجماعة 、ラテン文字転写:Ahl as-Sunnah (wa’l-Jamā‘ah))、あるいはスンニ派(日本では報道などでこちらが一般的に知られる)は、イスラム教(イスラーム)の二大宗派のひとつとされる。他のひとつはシーア派である。イスラームの各宗派間では、最大の勢力、多数派を形成する。
Sunni Islam (/ˈsuːni, ˈsʊni/) is the largest denomination of Islam, followed by 87–90% of the world's Muslims, characterized by a greater emphasis upon the prophet, the sahabah (in particular the Rashidun), and customs deduced thereof.[1][2] Its name comes from the word sunnah, referring to the behaviour of the Islamic prophet Muhammad.[3] The differences between Sunni and Shia Muslims arose from a disagreement over the succession to Muhammad and subsequently acquired broader political significance, as well as theological and juridical dimensions.[4]
According to Sunni traditions, Muhammad did not clearly designate a successor and the Muslim community acted according to his sunnah in electing his father-in-law Abu Bakr as the first caliph.[4] This contrasts with the Shia view, which holds that Muhammad announced his son-in-law and cousin Ali ibn Abi Talib as his successor, most notably at Ghadir Khumm.[5][6][7][8][9] Political tensions between Sunnis and Shias continued with varying intensity throughout Islamic history and have been exacerbated in recent times by ethnic conflicts and the rise of Wahhabism.[4]
The adherents of Sunni Islam are referred to in Arabic as ahl as-sunnah wa l-jamāʻah ("the people of the sunnah and the community") or ahl as-sunnah for short.[10][11] In English, its doctrines and practices are sometimes called Sunnism,[12] while adherents are known as Sunni Muslims, Sunnis, Sunnites and Ahlus Sunnah. Sunni Islam is sometimes referred to as "orthodox Islam",[13][14][15] though some scholars view this translation as inappropriate.[16]
The Quran, together with hadith (especially those collected in Kutub al-Sittah) and binding juristic consensus, form the basis of all traditional jurisprudence within Sunni Islam. Sharia rulings are derived from these basic sources, in conjunction with analogical reasoning, consideration of public welfare and juristic discretion, using the principles of jurisprudence developed by the traditional legal schools. In matters of creed, the Sunni tradition upholds the six pillars of iman (faith) and comprises the Ash'ari and Maturidi schools of rationalistic theology as well as the textualist school known as traditionalist theology. Sunni Islam is not a coherent line of tradition, but a consolidation of doctrines and positions worked out over time in discussions and writings.[17]
Le sunnisme1 est le principal courant religieux de l'islam représentant 90 % des musulmans du monde2. Constituant l'un des trois grands courants de l'islam avec le chiisme et le kharidjisme, le sunnisme se distingue des autres courants de l'islam par son interprétation de la religion. Les sunnites sont désignés en arabe comme les gens de la « sunna » et de la majorité religieuse (ahl al-sunna wa'l-djama‘a). Par opposition aux chiites et aux kharidjites, on les appelle parfois « musulmans orthodoxes »3.
Il sunnismo (in arabo: أهل السنة والجماعة, ahl al-sunna wa l-jamāʿa[1], "il popolo della Sunna e della Comunità") è la corrente maggioritaria dell'Islam, comprendendo circa l'85% dell'intero mondo islamico[2]. Essa riconosce la validità della Sunna (consuetudine[3], identificata coi Sei libri) e si ritiene erede della giusta interpretazione del Corano[1], articolata giuridicamente in 4 scuole o madhhab. Queste si dividono in Hanafismo, Malikismo, Sciafeismo, Hanbalismo. Mentre il cristianesimo è la maggiore religione del mondo (con 2,1 miliardi di aderenti) e l'Islam la seconda (con 1,8 miliardi), come confessioni il sunnismo (1,6 miliardi) supera il cattolicesimo (1,2 miliardi). Nell'islam, oltre al sunnismo, le principali confessioni sono rappresentate dallo Sciismo e dal Kharigismo. Sono presenti inoltre numerose forme minori (vedi denominazioni islamiche).
Nel sunnismo, così come nelle altre confessioni islamiche, ci sono divisioni interne tra i credenti sufi e coloro che rifiutano l'approccio sufico.
Los suníes1(en idioma árabe, سنّة) ʾAhlu-s-Sunnati wa-l-Jamāʿah (en árabe, أهل السنة والجماعة) son el grupo musulmán mayoritario en la comunidad islámica mundial. Su nombre procede del hecho de que, además del Corán, son devotos de la Sunna, colección de dichos y hechos atribuidos al profeta Mahoma. Aunque el Islam sunita se compone de una variedad de escuelas teológicas y legales que se desarrollaron a través de entornos históricos, localidades y culturas, los sunitas de todo el mundo comparten algunas creencias comunes: la aceptación de la legitimidad de los primeros cuatro sucesores del profeta Mahoma (Abu Bakr, Omar , Uthman y Ali), y la creencia de que otras sectas islámicas han introducido innovaciones (bidah), partiendo de la creencia mayoritaria.
Sunni Islam se desarrolló a partir de las luchas en el Islam temprano sobre el liderazgo. Las posiciones políticas y religiosas surgieron de las disputas sobre la definición de la creencia "verdadera", la libertad y el determinismo. Los sunitas tienden a rechazar el racionalismo excesivo o el intelectualismo en cuestiones de credo, centrándose en el espíritu y la intención de las fuentes primarias y utilizando argumentos racionales, cuando sea necesario, para defender la ortodoxia y refutar la herejía.23
Сунни́ты, ахль ас-су́нна ва-ль-джама‘а (от араб. أهل السنة والجماعة — «люди сунны и согласия общины») — последователи основного и наиболее многочисленного направления в исламе.
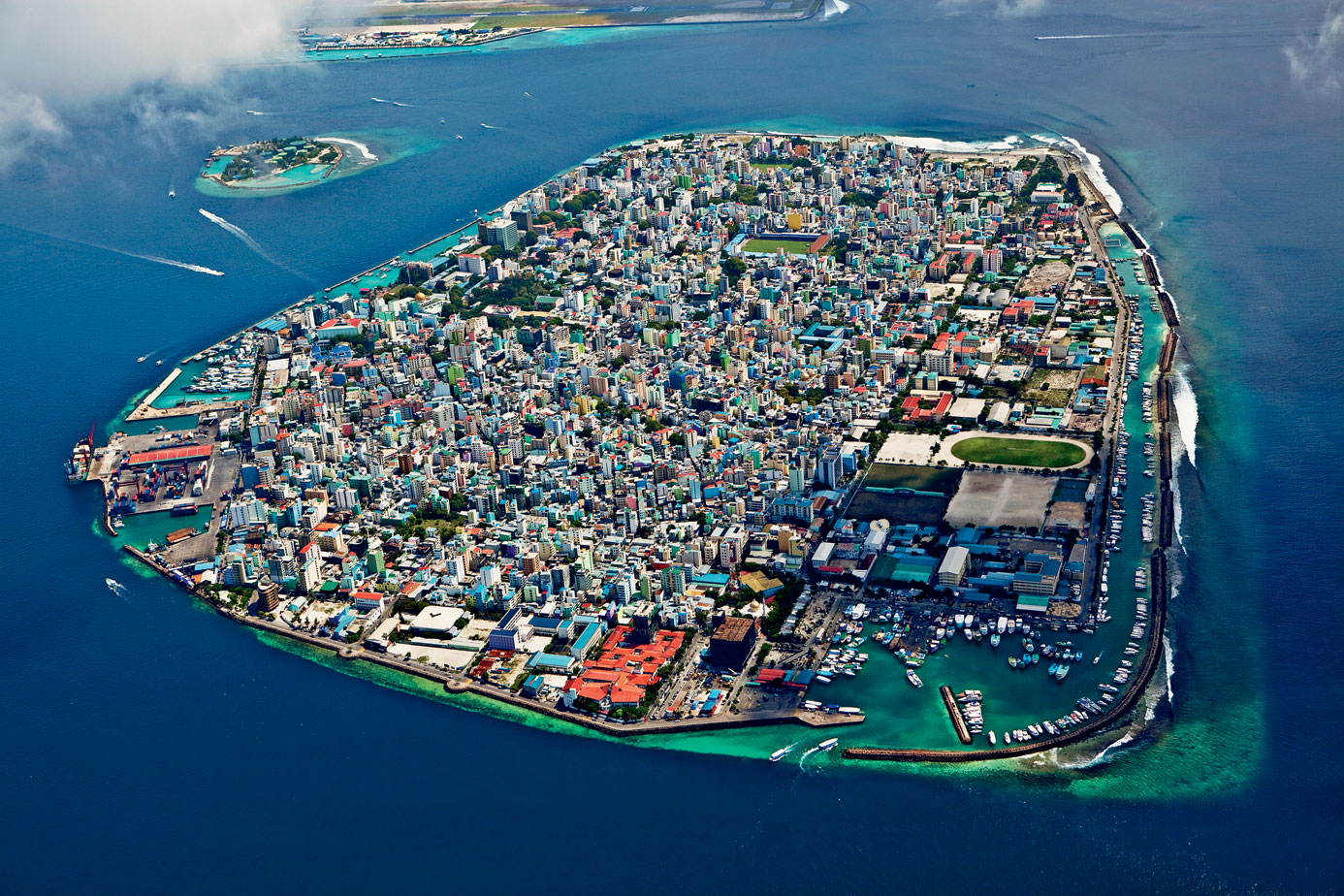
 地理
地理
 国际城市
国际城市

 体育
体育

 手拉手
手拉手
 亚洲国家
亚洲国家


 建筑艺术
建筑艺术
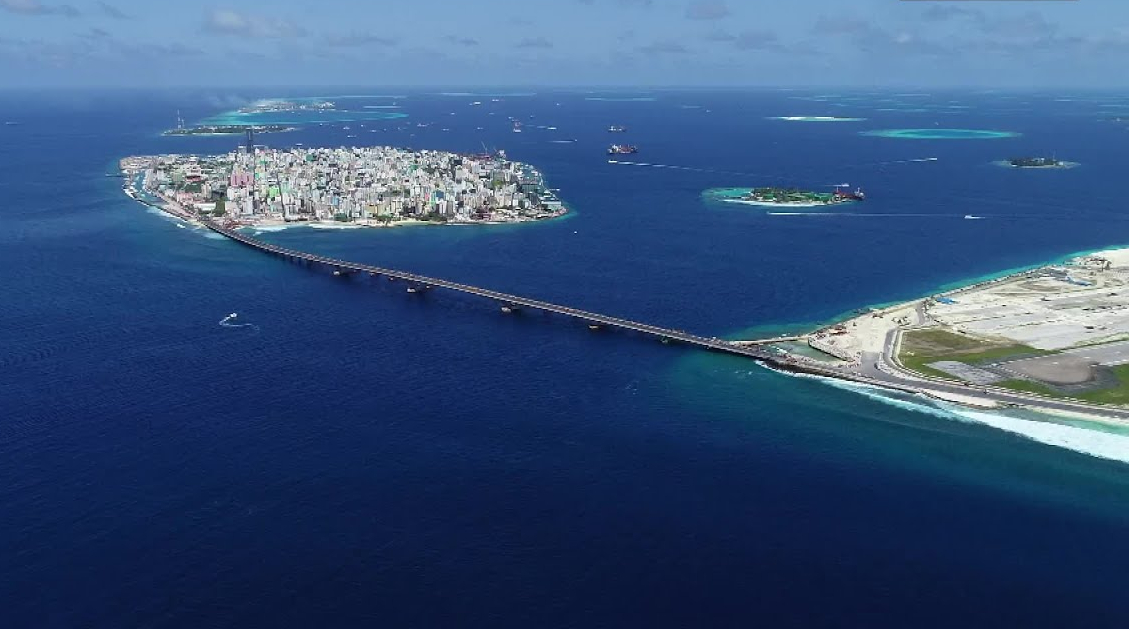

 运输和交通
运输和交通
