
Deutsch-Chinesische Enzyklopädie, 德汉百科
 Singapore
Singapore
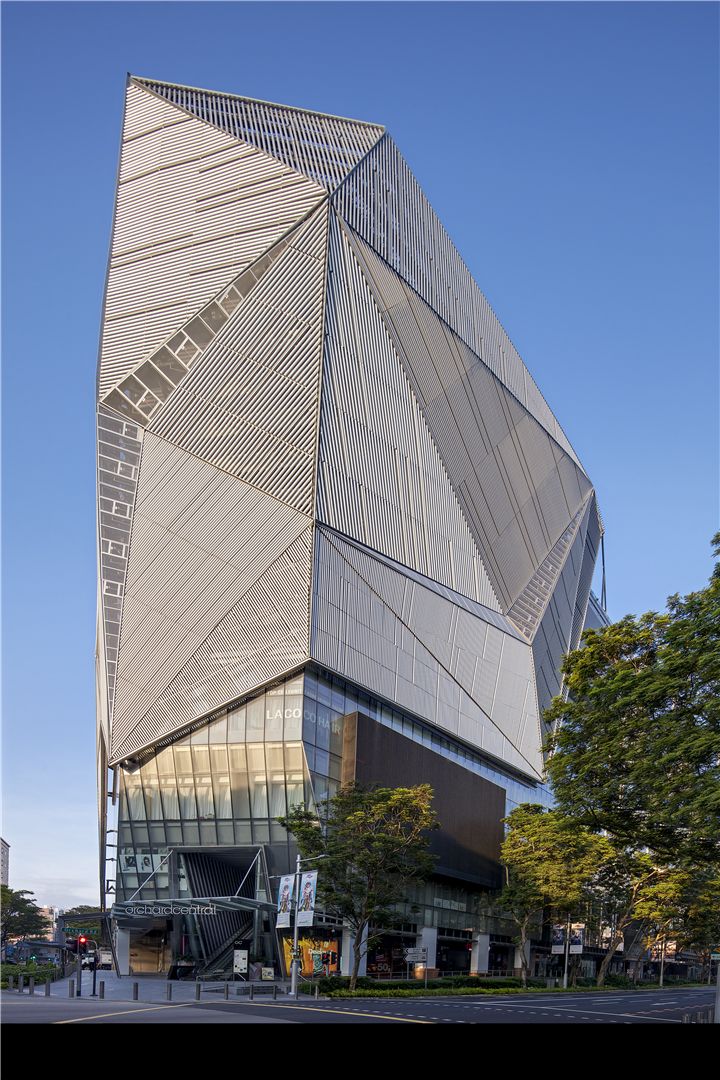
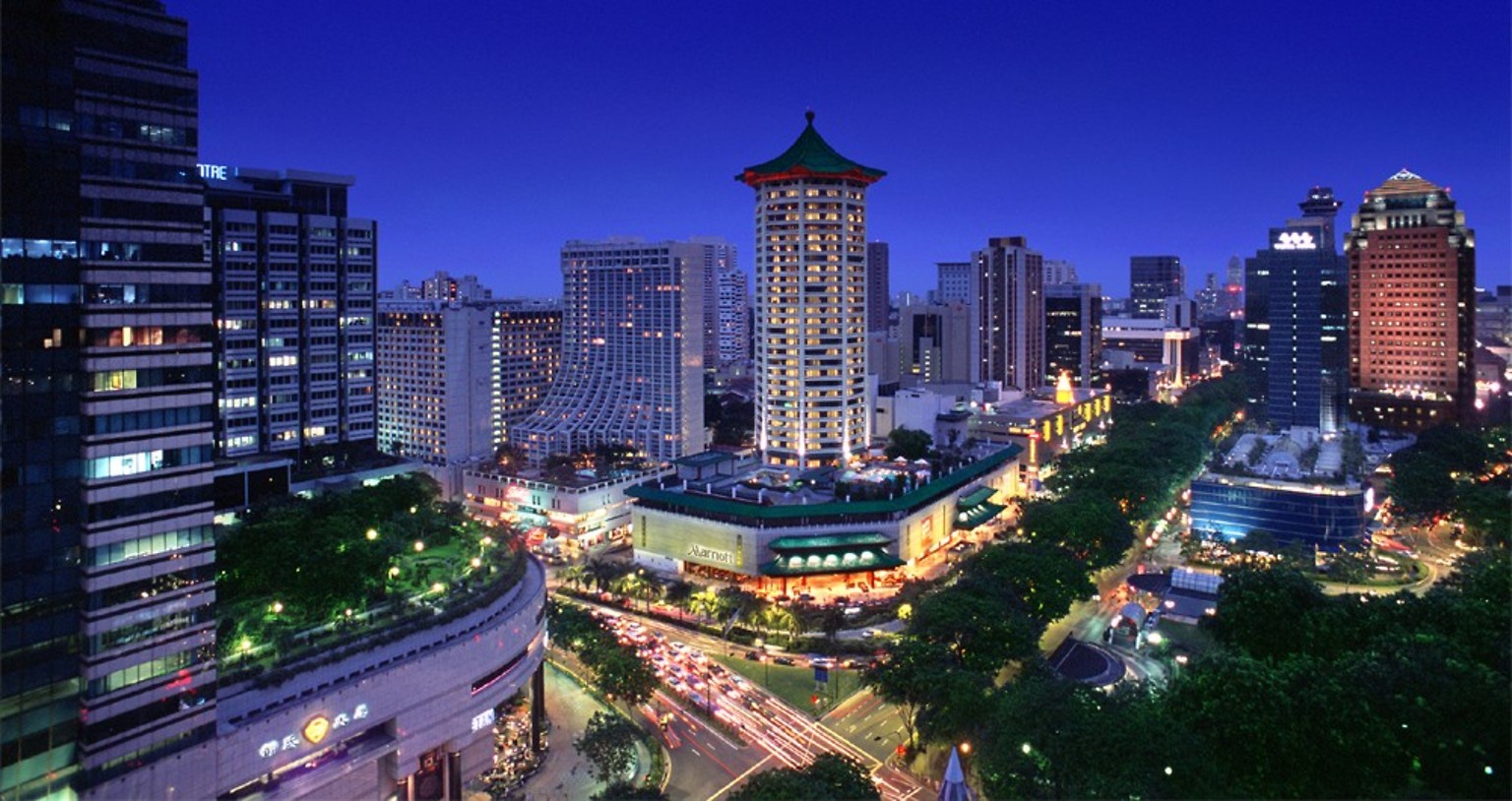
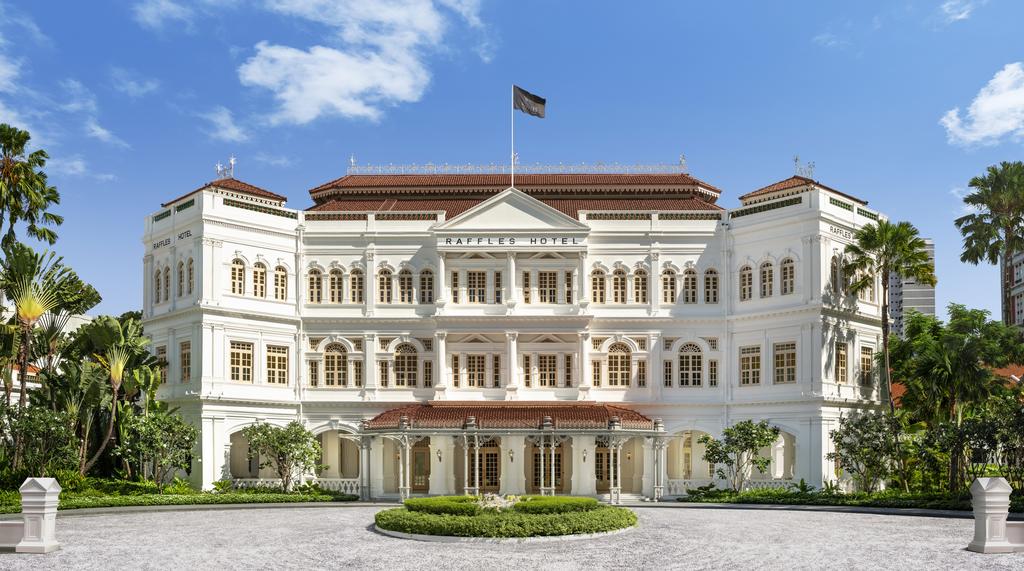




 Australia
Australia
 Brunei Darussalam
Brunei Darussalam
 China
China
 Indonesia
Indonesia
 Japan
Japan
 Cambodia
Cambodia
 Laos
Laos
 Malaysia
Malaysia
 Myanmar
Myanmar
 New Zealand
New Zealand
 Philippines
Philippines
 Republic of Korea
Republic of Korea
 Singapore
Singapore
 Thailand
Thailand
 Vietnam
Vietnam
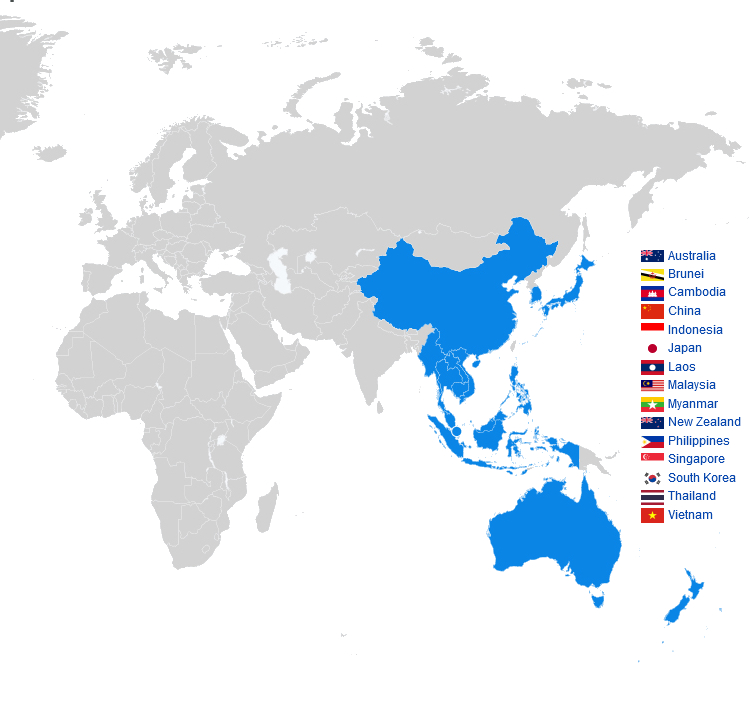
Die Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (kurz RCEP, deutsch Regionale, umfassende Wirtschaftspartnerschaft) ist ein seit 2020 bestehendes Freihandelsabkommen zwischen den zehn ASEAN-Mitgliedsstaaten und fünf weiteren Staaten in der Region Asien-Pazifik. Es ist die größte Freihandelszone der Welt.[1]
Das Projekt zur Gründung der RCEP entstand 2012, als die ASEAN-Staaten Verhandlungen mit der Volksrepublik China, Japan und Südkorea (ASEAN+3) sowie mit Indien, Australien und Neuseeland (ASEAN+6) aufgenommen hatten. Ursprünglich war die Einführung der Freihandelszone für 2017 geplant gewesen. Aufgrund von Bedenken verließ Indien 2019 die Verhandlungen. Am 15. November 2020, zum Abschluss des 37. ASEAN-Gipfeltreffens in der vietnamesischen Hauptstadt Hanoi, fand schließlich die Vertragsunterzeichnung statt.[2][3]
東アジア地域包括的経済連携(ひがしアジアちいきほうかつてきけいざいれんけい、英語: Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership; RCEP、アールセップ、域内包括的経済連携)とは、ASEAN加盟10カ国(ブルネイ、カンボジア、インドネシア、ラオス、マレーシア、ミャンマー、フィリピン、シンガポール、タイ、ベトナム)と、そのFTAパートナー5カ国(オーストラリア、中国、日本、ニュージーランド、韓国)の間で提案されている、アジア太平洋地域の自由貿易協定であり、世界の人口の3割、世界のGDPの3割を占める15カ国が交渉に参加している。交渉国15カ国は世界の人口の30%、GDPの30%弱を占めている[1]。
FTAパートナーであるインドは、交渉が開始された2011年からRCEP交渉に参加していたが、主に中国からの製造品やオーストラリアやニュージーランドからの農産物・乳製品のダンピング懸念を理由に、交渉の最終時点の2019年11月に交渉から離脱した[2]。2020年11月15日に第4回RCEP首脳会議の席上で協定は署名された[3]。
The Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP; /ˈɑːrsɛp/ AR-sep) is a free trade agreement between the Asia-Pacific nations of Australia, Brunei, Cambodia, China, Indonesia, Japan, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, New Zealand, the Philippines, Singapore, South Korea, Thailand, and Vietnam. The 15 member countries account for about 30% of the world's population (2.2 billion people) and 30% of global GDP ($26.2 trillion) as of 2020, making it the biggest trade bloc in history.[1] It was signed on 15 November 2020 at a virtual ASEAN Summit hosted by Vietnam, and will take effect within two years, after it has been ratified by the member countries.[2][3][4]
The trade pact, which includes a mix of high-income,[note 1] middle-income,[note 2] and low-income countries,[note 3] was conceived at the 2011 ASEAN Summit in Bali, Indonesia, while its negotiations were formally launched during the 2012 ASEAN Summit in Cambodia.[5][6][7] It was expected to eliminate about 90% of the tariffs on imports between its signatories within 20 years of coming into force, and establish common rules for e-commerce, trade, and intellectual property.[8]
The RCEP is the first free trade agreement between China, Japan, and South Korea, three of the four largest economies in Asia.[8] At the time it was signed, analysts predicted that it would help stimulate the economy amid the COVID-19 pandemic, as well as "pull the economic centre of gravity back towards Asia," and amplify the decline of the United States in economic and political affairs.[6][9][10]
Le partenariat régional économique global1, ou en anglais : Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP), est un projet d'accord de libre-échange entre quinze pays autour de l'océan Pacifique. C'est l'accord commercial le plus important du monde2.
Il inclut les dix pays membres de l'ASEAN, à savoir : la Birmanie, Brunei, le Cambodge, l'Indonésie, le Laos, la Malaisie, les Philippines, Singapour, la Thaïlande et le Vietnam ; ainsi que cinq autres pays qui possèdent déjà un accord de libre-échange bilatéral avec l'ASEAN, à savoir : l'Australie, la Chine, le Japon, la Corée du Sud et la Nouvelle-Zélande.
Il Partenariato Economico Globale Regionale (in lingua inglese Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership, RCEP) è un accordo di libero scambio nella regione dell'Asia Pacifica tra i dieci stati dell'ASEAN (cioè Brunei, Cambogia, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, Filippine, Singapore, Thailandia e Vietnam) e cinque dei loro partner di libero scambio: Australia, Cina, Giappone, Nuova Zelanda e Corea del Sud. I 15 paesi membri rappresentano circa il 30% della popolazione mondiale e del PIL, rendendolo il più grande blocco commerciale.[1] È stato firmato al vertice dell'ASEAN virtuale ospitato in Vietnam il 15 novembre 2020,[2][3] e dovrebbe entrare in vigore entro due anni, dopo che sarà stato ratificato dai paesi membri.[4]
Il patto commerciale, che comprende un mix di alto reddito, reddito medio, e paesi a basso reddito, è stato concepito al vertice dell'ASEAN del 2011 a Bali,[5] mentre i negoziati sono stati avviati ufficialmente nel corso del vertice dell'ASEAN del 2012 in Cambogia.[6]
L'RCEP è il primo accordo di libero scambio tra Cina, Giappone e Corea del Sud (tre delle quattro maggiori economie asiatiche) ed è il primo accordo multilaterale di libero scambio a includere la Cina.[7] Al momento della firma, gli analisti prevedevano che avrebbe aiutato a stimolare l'economia durante la pandemia di COVID-19, e "avrebbe attirato il centro di gravità economico verso l'Asia".
La Asociación Económica Integral Regional (abreviado RCEP por sus siglas en inglés) es un acuerdo de libre comercio (TLC) entre los diez estados miembros de la Asociación de Naciones del Sudeste Asiático (ASEAN) (Brunéi, Camboya, Indonesia, Laos, Malasia, Myanmar, Filipinas, Singapur, Tailandia , Vietnam) y cinco estados de Asia-Pacífico con los que la ASEAN tiene acuerdos de libre comercio existentes (Australia, China, Japón, Corea del Sur y Nueva Zelanda). El tratado fue firmado en la Cumbre de la ASEAN del 15 de noviembre de 202012 y se espera que entre en vigor en un plazo inferior a dos años, después de que sea ratificado por todos los estados miembros.
Incluye estados con PIBs muy diversos,3 conformando entre los 15 países en torno al 30% de la población mundial y el 30% del Producto Mundial Bruto.
Las negociaciones se iniciaron formalmente en noviembre de 2012 en la Cumbre de la ASEAN en Camboya.4 El RCEP se considera una alternativa al Acuerdo de Asociación Transpacífico (TPP, por sus siglas en inglés), un acuerdo comercial propuesto que incluye varias naciones de Asia y América, pero excluye a China y la India.5 Tras la salida de Estados Unidos durante la presidencia de Donald Trump del TPP se retomaron con más fuerza las negociaciones en el RCEP y se firmó el acuerdo en noviembre de 2020 por las naciones de la ASEAN, incluida China.6 El pacto entrará en vigor cuando los países que lo han firmado procedan a tramitar su ratificación a nivel nacional.7
El tratado RCEP es el primer tratado de libre comercio entre China, Japón y Corea del sur (tres de las cuatro grandes economías asiáticas), y es el primer tratado multilateral que incluye a China.8 En el momento de la firma, los analistas predijeron que ayudaría en la recuperación de la economía tras la pandemia de COVID-19, así como a empujar el centro de gravedad de la economía mundial hacia Asia.9
Всесторо́ннее региона́льное экономи́ческое партне́рство, сокращенно ВРЭП (англ. Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership, RCEP) — это соглашение о «зоне свободной торговли плюс» («ЗСТ +»), охватывающее 10 государств-членов Ассоциации государств Юго-Восточной Азии (АСЕАН) (Бруней, Вьетнам, Индонезия, Камбоджа, Лаос, Малайзия, Мьянма, Сингапур, Таиланд, Филиппины) и 6 государств, с которыми у АСЕАН уже подписаны соглашения о свободной торговле (Австралия, Индия, КНР, Новая Зеландия, Республика Корея и Япония). ВРЭП охватывает 4 развитые и 12 развивающихся государств. Начало переговоров было положено 20 ноября 2012 г. на саммите АСЕАН в Камбодже[1].
Соглашение о создании ВРЭП было подписано в Ханое 15 ноября 2020 года. Его вступление в силу создаст крупнейшую в мире зону свободной торговли с примерно 2,2 млрд потребителями и объемом ВВП в $28 трлн, что составляет более 32% от общего мирового объема ВВП.[2].
 Commonwealth of Nations
Commonwealth of Nations

 Geography
Geography

 Geography
Geography
 ***IMF Developed countries
***IMF Developed countries
 IMF Developed countries
IMF Developed countries
 IMF Developed countries
IMF Developed countries
 TOP4
TOP4
 Singapore
Singapore
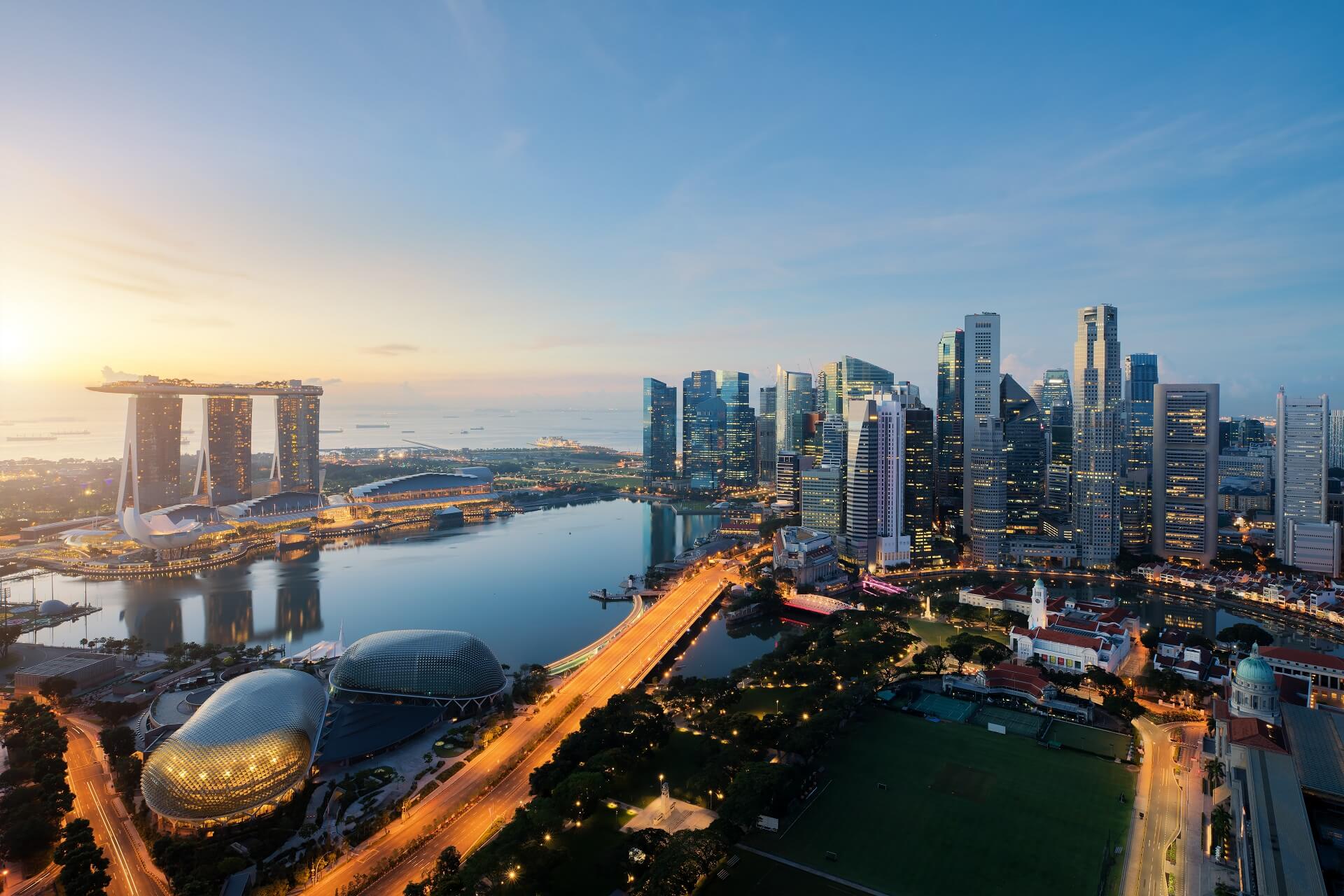

新加坡共和国(英语:Republic of Singapore;马来语:Singapura;泰米尔语:சிங்கப்பூர் குடியரச),通称新加坡,是东南亚中南半岛南端的一个城邦岛国、城市国家。该国位于马来半岛南端,扼守马六甲海峡最南端出口,其南面有新加坡海峡与印尼相隔,北面有柔佛海峡与西马来西亚相隔,并以新柔长堤与第二通道等这两座桥梁相连于新马两岸之间。新加坡的国土除了新加坡本岛之外,还包括周围所属岛屿,新加坡最大的外岛为德光岛。从新加坡独立以来,大规模的填海已经为新加坡增加了23%的面积,相等于增加了130平方公里。
1819年,任职于英国不列颠东印度公司的斯坦福·莱佛士与柔佛苏丹签订条约,获准在新加坡建立交易站和殖民地,经莱佛士的努力,逐渐发展成繁荣的转口港。由于地理位置特殊,新加坡在第二次世界大战以前一直是大英帝国在东南亚最重要的战略据点。1942年至1945年间,新加坡曾被日本占领三年半之久,其后回归英国管理,并从海峡殖民地独立出来,1959年成立自治邦,1963年加入马来西亚成为一个州,称为新加坡州(简称星州)。1965年8月9日,马来西亚国会以126票赞成、0票反对,同意将新加坡驱逐出联邦。新加坡共和国正式成立,李光耀为总理,尤索夫·伊萨为总统。新加坡被驱逐马来西亚后独立建国。
自1965年独立后,新加坡从穷困潦倒中,依靠着国际贸易和人力资本的操作,迅速转变成为富裕的亚洲四小龙之一,同时凭借着地理优势,新加坡也是亚洲重要的金融、服务和航运中心之一。教育素质良好的国民也是亚洲政治和科学文化的纽带,大多数的新加坡人都通晓至少两种语言,分别是英语以及自己的母语。新加坡是个多元文化种族的社会,也是全球最国际化的国家之一,所以主要由华人组成的新加坡并非为单一民族国家,而是和一部分马来人及印度人所组成的移民国家,其中华人文化以福建移民为大宗[6]。在国内居住的居民有38%为永久居民、持有工作签证的外籍劳工以及持有学生签证的学生,建筑业和服务业的外劳比例分别为80%和50%[7][8][9][10]。整个城市在绿化和环境卫生方面效果显著,故有花园城市之美称。
Singapur (amtlich Republik Singapur, englisch Republic of Singapore [ɹɪˈpʰʌb.lɪkʰ.əv.ˈsɪŋ.(g)ə.pʰɔː], malaiisch Republik Singapura, chinesisch 新加坡共和国, Pinyin Xīnjiāpō Gònghéguó, auch: 新加坡 [ɕin.tɕiɑ.pʰuɔ], Tamil சிங்கப்பூர் குடியரசு Ciṅkappūr Kudiyarasu) ist ein Insel- und Stadtstaat und der flächenmäßig kleinste Staat Südostasiens. Er ist Mitglied im Commonwealth of Nations.
Beim Index der menschlichen Entwicklung belegte Singapur 2018 den neunten Platz.[6] Singapur ist eines der reichsten Länder (und Städte) weltweit und gilt als eine der Städte mit den weltweit höchsten Lebenshaltungskosten.[7] Zudem zählt der Stadtstaat mit mehr als elf Millionen ausländischen Touristen im Jahr zu den zehn meistbesuchten Städten der Welt[8] und gilt neben Hongkong als wichtigster Finanzplatz Asiens. Singapur ist ein multiethnischer Staat, in dem Chinesen, Malaien und Inder die größten Bevölkerungsteile stellen.
シンガポール共和国(シンガポールきょうわこく、英語: Republic of Singapore、マレー語: Republik Singapura、簡体字: 新加坡共和国、繁体字: 新加坡共和國、タミル語: சிங்கப்பூர் குடியரசு)、通称シンガポールは、東南アジアに位置し、シンガポール島及び60以上の小規模な島々からなる共和制国家[4]。
同国は、北はジョホール海峡により半島マレーシアから、南はシンガポール海峡によりインドネシアのリアウ諸島州から各々切り離されている。同国は高度に都市化され、原初の現存植生はほとんどない。シンガポールの領土は、一貫して埋立てにより拡大してきた。
シンガポールは、教育・エンターテインメント・金融・ヘルスケア・人的資本・イノベーション・ロジスティクス・製造・技術・観光・貿易・輸送の世界的な中心である。多くの国際順位で格付けされており、最も「テクノロジー対応」国(WEF)、国際会議のトップ都市(UIA)、世界で最もスマートな都市である「投資の可能性が最も高い」都市(BERI)、世界で最も安全な国、世界で最も競争力のある経済、3番目に腐敗の少ない国、3番目に大きい外国為替市場、3番目に大きい金融センター、3番目に大きい石油精製貿易センター、5番目に革新的な国、2番目に混雑するコンテナ港湾。2013年以来、エコノミストはシンガポールを「最も住みやすい都市」として格付けしている[5][6][7][8]。
シンガポールは、すべての主要な格付け機関からAAAソブリン格付けを持つ、アジアで唯一の国であり、世界11か国のうちの1つである。シンガポール航空は2018年の「世界最高の航空会社」であり、世界的にはシンガポール港とチャンギ国際空港がそれぞれ「マリタイムキャピタル」と「ベスト空港」のタイトルを連続して獲得している[9][10]。
シンガポールは、1人当たりGDPが2番目に高く、国連人間開発指数で9位である、主権国にとってアジアで最高。これは、教育・医療・平均余命・生活の質・個人の安全・住宅などの主要な社会的指標に高く置かれており、人口の90%が家の所有者である。
Singapore (/ˈsɪŋ(ɡ)əpɔːr/ ( listen)), officially the Republic of Singapore, is a sovereign city-state and island country located in maritime Southeast Asia. Singapore lies about one degree of latitude (137 kilometres or 85 miles) north of the equator, and is situated off the southern tip of the Malay peninsula, and, by extension, the southernmost extremity of continental Eurasia. The island country is wedged between western Indonesia and peninsular Malaysia, sharing its southern maritime border with the Batam, Bintan, and Karimun archipelago of the former's Riau Islands province, and its northern, western, and eastern maritime borders with the latter's Johor state; it is additionally in the vicinity of Sumatra to its west and Borneo to its east. The island country is enveloped by the littoral waters of the Johore Strait to its north and the Singapore Strait to its south, and is geographically positioned within the confluence of the Indian and Pacific Oceans, being bounded by the Malacca Strait to its west and the South China Sea to its east. The country's territory, which is archipelagic, is composed of one main island, 63 satellite islands and islets, and one outlying islet, the combined area of which has increased by 25% since the country's independence as a result of extensive land reclamation projects.
listen)), officially the Republic of Singapore, is a sovereign city-state and island country located in maritime Southeast Asia. Singapore lies about one degree of latitude (137 kilometres or 85 miles) north of the equator, and is situated off the southern tip of the Malay peninsula, and, by extension, the southernmost extremity of continental Eurasia. The island country is wedged between western Indonesia and peninsular Malaysia, sharing its southern maritime border with the Batam, Bintan, and Karimun archipelago of the former's Riau Islands province, and its northern, western, and eastern maritime borders with the latter's Johor state; it is additionally in the vicinity of Sumatra to its west and Borneo to its east. The island country is enveloped by the littoral waters of the Johore Strait to its north and the Singapore Strait to its south, and is geographically positioned within the confluence of the Indian and Pacific Oceans, being bounded by the Malacca Strait to its west and the South China Sea to its east. The country's territory, which is archipelagic, is composed of one main island, 63 satellite islands and islets, and one outlying islet, the combined area of which has increased by 25% since the country's independence as a result of extensive land reclamation projects.
Throughout its millennia-long history, Singapore—historically known by the names Pulau Ujong, Temasek, and subsequently Singapura—was a maritime emporium that fell under the suzerainty of several successive Indianised and Islamicate Malay polities: initially a series of ancient to medieval Hindu-Buddhist thalassocratic empires, subsequently a medieval localised Hindu-Buddhist kingdom, and ultimately two medieval to early modern Islamic sultanates.[14][Note 8] The 1819 arrival of Stamford Raffles, a British colonial officer, and the subsequent establishment of a British East India Company trading post on the main island—then part of the Johor Sultanate—marked the genesis of modern Singapore. Five years later, the British and Dutch East India companies partitioned the Sultanate, with the British coercively wresting Singapore from the Sultan in the process, marking the cessation of indigenous rule over the island for the first time in its history. In 1826, Singapore was incorporated into the Straits Settlements, a pan-Malayan presidency of the Company with Penang as capital,[15][Note 9] and in 1830, the Settlements were annexed to British India as a residency, where they would be governed from the capital of Calcutta under two administrations—until 1858 under Company rule, and—following the Company's collapse in the wake of the 1857 Indian Rebellion—until 1867 under the successive British Raj. In 1867, the administration of the Settlements was transferred to London, bringing them under the direct control of the United Kingdom as a Malayan crown colony.[16][17][18]
From 1867 to the 1940s, Singapore, having taken over Penang as capital of the Settlements, grew into a thriving entrepôt and settler-colony under the auspices of the British Empire, attracting large numbers of non-indigenous settlers and sojourners from the region and beyond.[19] During the Second World War, Imperial Japan invaded and annexed Singapore, resulting in an interregnum of British colonial rule corresponding with a brief but bloody Japanese occupation from 1942 to 1945. Following Japan's surrender in 1945, Singapore was returned to British control; in 1946, the Straits Settlements were dissolved, and Singapore became a standalone crown colony. In 1959, following a protracted period of agitation against colonial rule, Singapore was granted limited autonomy; in 1963, it became fully emancipated from the British Empire upon its federation with the territories of the erstwhile British Malaya and British Borneo to form the new country of Malaysia.[Note 10] However, after two tumultuous years as a constituent state of the Malaysian Federation, marred by violent ethnoreligious strife and other intractable differences between indigenous and non-indigenous groups, Singapore was expelled in 1965, becoming the first country in modern history to gain independence against its will—although this narrative remains contentious.[Note 11] After early years of turbulence, the newly sovereign nation—viewed as a nonviable state by international observers due to its diminutiveness, geostrategic vulnerability, absence of natural resources, and lack of a hinterland—defied odds by rapidly developing and industrialising under the leadership of the inaugural People's Action Party to become a high-income economy and developed country within a single generation.
Singapore is a unitary parliamentary constitutional republic with a unicameral legislature that has been characterised by dominant-party rule since independence. It is considered a soft authoritarian technocratic state; the Economist Intelligence Unit rated Singapore a "flawed democracy" in 2019.[21] It is the only truly sovereign city-state in the world; it has its own currency and a well-funded military that is considered the most advanced in Southeast Asia.[22] The country is home to 5.6 million residents, 61% (3.4 million) of whom are Singaporeans; as a legacy of its historical nature as an entrepôt and settler-colony, modern Singapore is a pluralistic country with a racially, culturally, and religiously diverse citizenry,[23][24] with one indigenous ethnic group, the Malays, and two settler-descended ethnic groups, the Chinese and Indians, forming the historical and contemporary core of the citizen populace. As a reflection of this pluralism, multiracialism has been enshrined as a foundational principle of the state, and has shaped the country's politics and national policies. The country, which is Anglophone, has four official languages: English, Malay, Chinese, and Tamil; Malay, as the ancestral language of the country, is accorded protected status in the country's constitution as the national language, while English is the lingua franca, being spoken as a common tongue by the vast majority of Singaporeans.
Singapore is one of the five founding members of ASEAN, is the headquarters of the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC) Secretariat and Pacific Economic Cooperation Council (PECC) Secretariat,[25] is a member of the United Nations, World Trade Organization, East Asia Summit, Non-Aligned Movement, and the Commonwealth of Nations, and is a recurrent guest invitee to the annual G20 summit;[26] its outsized influence on global affairs, relative to its size, has lead to it being classified as a middle power.[27][28] The country is the most developed sovereign nation in Asia, being ranked 9th on the UN Human Development Index, and has the 7th highest GDP per capita in the world.[29][30] It is also considered by Transparency International to be the most incorruptible nation in Asia, and the fifth most incorruptible worldwide. Singapore is placed highly in key social indicators: education, healthcare, quality of life, personal safety and housing, with a home-ownership rate of 91%. Singaporeans enjoy one of the world's longest life expectancies and one of the lowest infant mortality rates in the world.[31] As a city, Singapore is classified as an Alpha+ global city, and is the only country in Asia with an AAA sovereign rating from all major rating agencies. It is a major financial and shipping hub, consistently ranked the most expensive city to live in since 2013, and has been identified as a tax haven.[32][33] Singapore is also a popular tourist destination, with well-known landmarks such as the Merlion, Marina Bay Sands, Gardens by the Bay, the Jewel, the Orchard Road shopping belt, the resort island of Sentosa, and the Singapore Botanic Gardens, the only tropical garden in the world to be honoured as a UNESCO World Heritage Site.[34][35]
Singapour, en forme longue la république de Singapour (en anglais : Singapore et Republic of Singapore, en chinois : 新加坡 (Xīnjiāpō) et 新加坡共和国 (Xīnjiāpō Gònghéguó), en malais : Singapura et Republik Singapura, en tamoul : சிங்கப்பூர் (Ciṅkappūr) et சிங்கப்பூர் குடியரசு) (Ciŋkappūr Kudiyarasu), est une cité-État d’Asie du Sud-Est. Sa superficie est de 719,1 km2. Elle comprend 63 îles, dont la principale est Pulau Ujong (584,8 km2). Cette île est très densément urbanisée, mais la végétation luxuriante – même en plein centre-ville – a valu à Singapour le surnom de « ville jardin ». Cette abondance de verdure découle en partie d'un climat équatorial, uniformément chaud et orageux tout au long de l'année. Sa densité de population est la plus élevée d'Asie et la deuxième sur le plan mondial.
L'État de Singapour est situé à l'extrême sud de la péninsule Malaise, dont il est séparé au nord par le détroit de Johor, et borde au sud le détroit de Singapour. Il est connu et souvent montré en exemple pour son extraordinaire réussite économique. Après l'indépendance de l'Empire britannique en 1958, le rattachement à la Malaisie en 1963, puis l'indépendance en 1965, Singapour a su devenir, avec très peu de ressources naturelles et des problèmes socio-économiques importants – émeutes raciales, chômage massif, difficultés de logement et d'accès à l'eau –, l'un des pays les plus développés et les plus prospères du monde, en termes d'économie, d'éducation, de santé, de sécurité et d'urbanisme. La ville, cité souveraine, est un réduit chinois au cœur même du monde malais : la population est majoritairement composée de Chinois (74,3 %). De cette confrontation ethnique sont nés en partie les troubles qui ont accéléré son retrait de la Malaisie, le 9 août 19656.
Dans les années 1980, le pays fait partie, avec Hong Kong, la Corée du Sud et Taïwan, des quatre dragons asiatiques, des États en transition et au développement économique effréné. En 2011, Singapour est le troisième pays au monde en termes de produit intérieur brut à parité de pouvoir d'achat (PPA) par habitant après le Qatar et le Luxembourg7. Plaque tournante commerciale et financière entre la zone Pacifique et l'Europe, la ville doit son essor à sa situation maritime exceptionnelle à l'extrémité Est du détroit de Malacca, qui lui vaut le surnom de : Cité marchande aux confins de l'Orient. Elle possède le deuxième port au monde (après Shanghai) en termes d'exportations et de trafic maritime. La population singapourienne dispose d'un très haut niveau de vie et la Cité-État est souvent surnommée La Suisse d'Asie8. En 2009, Singapour affichait ainsi la plus forte concentration de millionnaires rapportés à la population totale devançant Hong Kong (Chine), la Suisse, le Qatar et le Koweït9.
Présentant une stabilité politique remarquable, Singapour est considéré aujourd'hui comme une « démocratie autoritaire » ou « dictature bienveillante », avec la même famille au pouvoir depuis l'indépendance. La cité-État est donc considérée comme un pays pratiquant le libéralisme économique sans le libéralisme politique.
Le centre-ville est situé dans le sud de l'île de Pulau Ujong, à l'embouchure de la rivière Singapour (Singapore River). Il comprend un centre d'affaires qui a fait de la ville la quatrième place financière au monde, ainsi que différents quartiers ethniques (chinois, malais, et indien) et une grande zone commerciale autour d'Orchard Road.
Singapore (AFI: /sinɡaˈpore/[5]), ufficialmente Repubblica di Singapore (in malese Republik Singapura; in inglese Republic of Singapore; in cinese 新加坡共和国, Xīnjiāpō Gònghéguó; in tamil சிங்கப்பூர் குடியரசு, Ciŋkappūr Kudiyarasu), è una città-Stato del sud-est asiatico, situata sull'estrema punta meridionale della penisola malese, 152 km a nord dell'equatore. Si sviluppa su un arcipelago formato da 58 isole, la più grande e principale delle quali è l'isola di Singapore che ospita la metropoli. A nord Singapore è separata dalla Malaysia dallo Stretto di Johor, a sud è separata dalle indonesiane isole Riau dallo Stretto di Singapore.
La città-Stato è il quarto principale centro finanziario del mondo[6] ed è una delle principali città cosmopolite del globo, con un importante ruolo nel commercio internazionale e nella finanza. Il suo porto è tra i primi cinque per attività e traffico su scala mondiale.[7]
Singapore è un Paese con una lunga storia di immigrazione. Ha una popolazione variegata e gli oltre 5 milioni di abitanti sono composti prevalentemente da cinesi, malesi, indiani e altre discendenze di asiatici ed europei.[8]
Il 42% della popolazione è straniero, qui presente per lavoro o studio. I lavoratori stranieri costituiscono il 50% del settore dei servizi.[9][10]
Singapore è il secondo Paese più densamente popolato del mondo dopo il Principato di Monaco e nel 2009 ha raggiunto la più alta concentrazione di milionari in rapporto alla popolazione, davanti a Hong Kong, Svizzera, Qatar e Kuwait.[11]
Singapur, oficialmente República de Singapur (en inglés: Republic of Singapore; en chino: 新加坡共和国 [Xīnjīapō Gònghéguó]; en malayo: Republik Singapura; y en tamil: சிங்கப்பூர் குடியரசு [Siṅkappūr Kuṭiyarasu]), es un país soberano insular de Asia, formado por sesenta y tres islas, cuya forma de gobierno es la república parlamentaria.
Su territorio se divide en cinco consejos de desarrollo comunitario. Su capital es la ciudad de Singapur, por lo que Singapur se considera una ciudad-estado. Está situado al sur del Estado de Johor en la península de Malasia y al norte de las islas Riau de Indonesia, separada de estas por el estrecho de Singapur. Con 697 km²,1 es el país más pequeño del Sudeste Asiático. Su territorio ha crecido constantemente con tierras ganadas al mar.
Desde el siglo II d. C., cuando se establecieron allí los primeros humanos, la isla de Singapur ha formado parte de varios imperios regionales. El moderno Singapur fue fundado en 1819 por el británico Thomas Stamford Raffles como puesto comercial de la Compañía Británica de las Indias Orientales con el permiso del Sultanato de Johor. El Reino Unido obtuvo la soberanía sobre la isla en 1824 y esta pasó a ser una de las Colonias del Estrecho británicas en 1826. Ocupada por los japoneses durante la Segunda Guerra Mundial, Singapur declaró su independencia del Reino Unido en 1963 como un estado más de Malasia mediante un referéndum de incorporación, de la que se separó dos años después. Desde entonces la ciudad-estado ha prosperado rápidamente y se ha ganado la distinción de ser uno de los «cuatro tigres asiáticos».
Singapur es una de las principales ciudades globales y uno de los centros neurálgicos del comercio mundial, contando con el tercer mayor centro financiero y el segundo puerto que más mercancías mueve. Su economía globalizada y diversificada depende especialmente del comercio y del sector manufacturero. En términos de paridad de poder adquisitivo, Singapur es el tercer país con mayor renta per cápita del mundo, además de figurar entre los primeros países en las listas internacionales de educación, sanidad, transparencia política y competitividad económica.
Políticamente, Singapur es una república parlamentaria multipartidista con un gobierno parlamentario unicameral inspirado en el sistema Westminster británico. El Partido de Acción Popular ha ganado todas las elecciones desde que el país obtuvo la independencia. Sin embargo, las libertades civiles y de expresión están sumamente restringidas y se dan casos de censura por parte del Gobierno, por lo que está considerado como un país con rasgos tanto democráticos como autoritarios.4 La población, unos cinco millones de habitantes, es muy diversa: alrededor de dos millones son de origen extranjero y entre los nativos, el 75 % son chinos y el resto minorías de malayos, indios o euroasiáticos. Esta diversidad tiene su reflejo en los cuatro idiomas oficiales del país, que son el inglés, el chino, el malayo y el tamil, así como en las políticas gubernamentales que promueven el multiculturalismo.5
Singapur es uno de los miembros fundadores de la Asociación de Naciones del Sudeste Asiático y ha sido sede del secretariado del Foro de Cooperación Económica Asia-Pacífico, además de formar parte de la Cumbre de Asia Oriental, del Movimiento de Países No Alineados y de la Mancomunidad de Naciones. El rápido desarrollo del país lo ha llevado a tener una influencia importante en los asuntos internacionales y a que algunos analistas lo consideren una potencia intermedia.67
Республика Сингапу́р (англ. Republic of Singapore; малайск. Republik Singapura, ريڤوبليق سيڠاڤورا; кит. трад. 新加坡共和國, упр. 新加坡共和国, пиньинь: Xīnjiāpō Gònghéguó, палл.: Синьцзяпо Гунхэго; там. சிங்கப்பூர் குடியரசு Ciŋkappūr Kudiyarasu) — город-государство, расположенный на островах в Юго-Восточной Азии, отделённых от южной оконечности Малаккского полуострова узким Джохорским проливом. Граничит с султанатом Джохор, входящим в состав Малайзии, и с провинцией Острова Риау, входящей в состав Индонезии.
Площадь Сингапура составляет 725,7 км² (2019 год), она постепенно увеличивается благодаря программе намыва территории, действующей с 1960-х годов. В настоящее время государство Сингапур состоит из 63 островов. Самые крупные из них — Сингапур (главный остров), Убин, Теконг-Бесар, Брани, Сентоса, Семакау и Судонг. Высшая точка — холм Букит-Тимах (163,3 м).




 Architecture
Architecture
 Life and Style
Life and Style
 Party and government
Party and government
 Economy and trade
Economy and trade
 States of Asia
States of Asia


 Religion
Religion
 Transport and traffic
Transport and traffic
 Sport
Sport
 Companies
Companies
 Exhibition
Exhibition
 Ships and Nautics
Ships and Nautics