
漢德百科全書 | 汉德百科全书
 States of Europe
States of Europe


 *Mediterranean Sea
*Mediterranean Sea
 Commonwealth of Nations
Commonwealth of Nations

 Geography
Geography

 Geography
Geography
 ***IMF Developed countries
***IMF Developed countries
 IMF Developed countries
IMF Developed countries
 IMF Developed countries
IMF Developed countries
 TOP6
TOP6

 States of Asia
States of Asia

 States of Europe
States of Europe
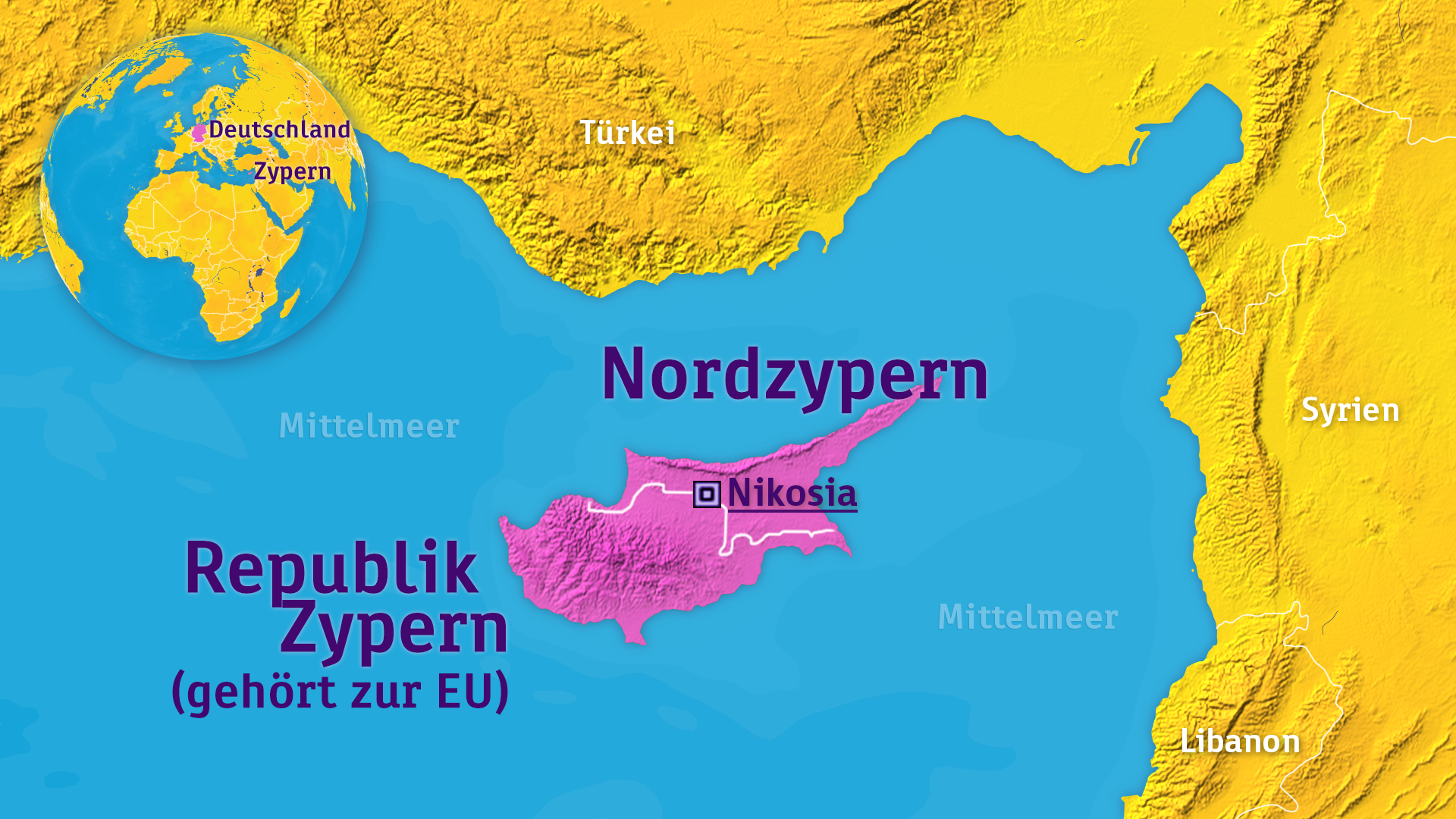
 Cyprus
Cyprus
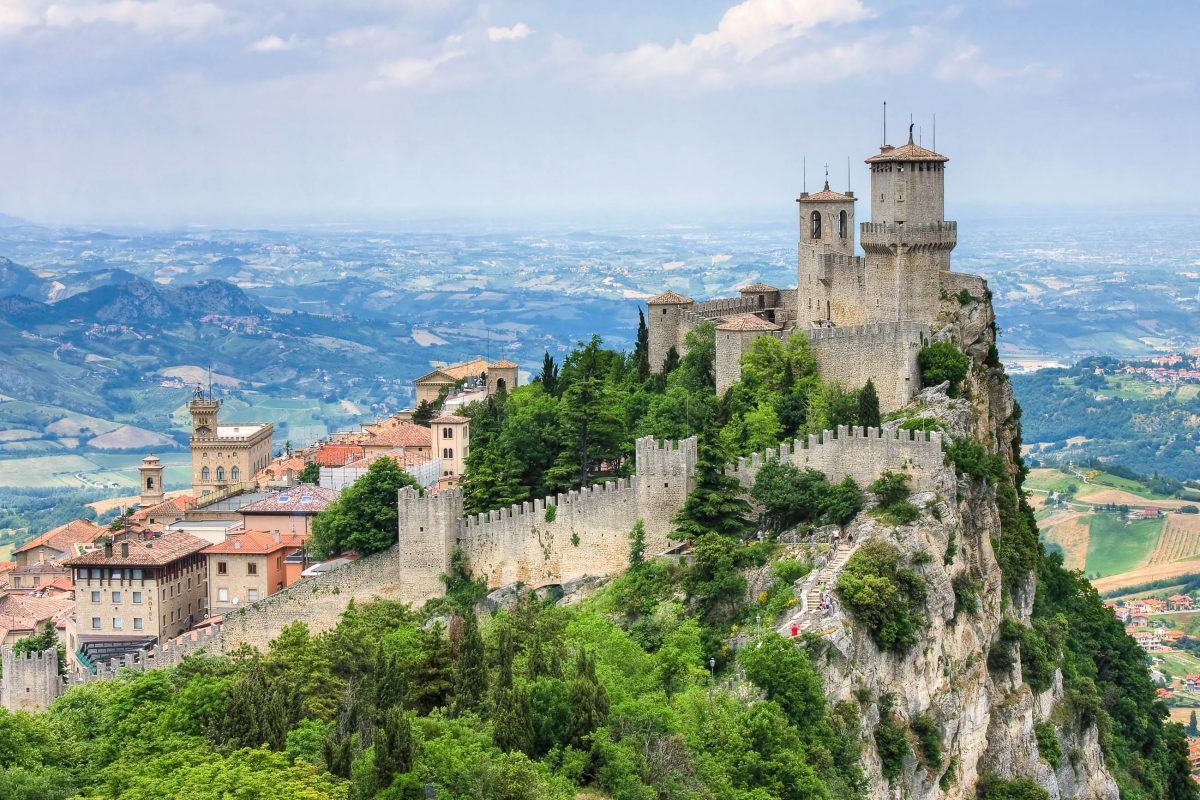




San Marino (amtlich Republik San Marino, italienisch Repubblica di San Marino, Beiname La Serenissima ‚die Allerdurchlauchteste‘) ist die vermutlich älteste bestehende Republik der Welt mit einer Geschichte, die der Überlieferung nach bis auf das Jahr 301 mit der Gründung durch den heiligen Marinus zurückgeht. Sie ist als Enklave vollständig von Italien umgeben und liegt zwischen den Regionen Emilia-Romagna (Provinz Rimini) und Marken (Provinz Pesaro und Urbino), nahe der adriatischen Küste bei Rimini. San Marino ist mit einer Fläche von etwa 60 Quadratkilometern der fünftkleinste Staat der Welt und gehört zu den sechs europäischen Zwergstaaten und nach Einwohnerzahl mit einer Bevölkerung von rund 30.000 Einwohnern zu den kleinsten Staaten der Erde. Hauptstadt ist die gleichnamige Stadt, Amtssprache ist Italienisch.
Den Felskamm des zum UNESCO-Welterbe gehörenden Monte Titano krönen die drei Festungen Guaita, Cesta und Montale. Der Staat ist Mitglied der Vereinten Nationen (UNO), des Europarats und der Lateinischen Union, nicht jedoch der Europäischen Union, nutzt aber dennoch den Euro als Währung. San Marino gehört gemessen am nominalen BIP pro Kopf zu den reichsten Ländern der Welt, hat keine Staatsschulden und eine der niedrigsten Arbeitslosenquoten der Welt.
圣马力诺共和国[1](義大利語:Repubblica di San Marino),[2][3] 通稱圣马力诺 (![]() i/sæn məˈriːnoʊ/;義大利語:[san maˈriːno]),又称“最庄严尊贵的圣马力诺共和国”(義大利語:Serenissima Repubblica di San Marino),[3] 位于意大利半岛的亚平宁山脉东北侧,处于被意大利包围的国中国状态。圣马力诺国土面积61.2平方公里(23.6平方英里),人口33,344人。 其国家首都是圣马力诺市,最大的城市是位于塞拉瓦莱的多加钠。圣马力诺是欧洲委员会所有国家中人口最少的国家。
i/sæn məˈriːnoʊ/;義大利語:[san maˈriːno]),又称“最庄严尊贵的圣马力诺共和国”(義大利語:Serenissima Repubblica di San Marino),[3] 位于意大利半岛的亚平宁山脉东北侧,处于被意大利包围的国中国状态。圣马力诺国土面积61.2平方公里(23.6平方英里),人口33,344人。 其国家首都是圣马力诺市,最大的城市是位于塞拉瓦莱的多加钠。圣马力诺是欧洲委员会所有国家中人口最少的国家。
圣马力诺之名,来源于公元3世紀一個叫圣玛利诺(圣马利诺斯)的石匠,他来自當時罗马帝国的殖民地拉布岛(位于现在的克罗地亚),公元257年,圣玛利诺参与了里米尼的城墙重建工作,该城市的城墙曾因为遭受利布尔尼亚海盗的袭击而被破坏。公元301年,圣玛利诺在蒂塔诺山修建了一个独立的修道院社区。因此圣玛利诺号称是现存最古老的主权国家和历史最悠久的立宪制共和国。[4]
圣马力诺由《圣马力诺宪法》管理,该宪法成书于16世纪,由拉丁文书写完成的一套六本的文件,其中规定了该国的政治制度。圣马力诺认为这是最古老的迄今仍然有效的政府文件或宪法。[5]
圣马力诺的国家经济主要依靠金融业、工业、服务业和旅游业。就以购买力平价计算的人均国内生产总值来说,圣马力诺是全球最富裕的国家之一,与欧洲发达地区水准持平。圣马力诺被认为是国家经济高度稳定和欧洲失业率最低的国家之一,该国既没有国家债务也没有预算盈余。[2] 圣马力诺也是全球唯一一个车比人多的国家。在外交上,圣马力诺追随意大利领导,且是团结谋共识集团的核心成员。[6]
サンマリノ共和国(サンマリノきょうわこく、伊: Repubblica di San Marino)、通称サンマリノは、イタリア半島の中東部に位置する共和制国家。首都はサンマリノ市。国土の周囲は全てイタリアで、国土の面積は十和田湖とほぼ同じ。世界で5番目に小さなミニ国家である。また、現存する世界最古の共和国として知られる。
San Marino (/ˌsæn məˈriːnoʊ/ (![]() listen), Italian: [sam maˈriːno]), officially the Republic of San Marino[1][2] (Italian: Repubblica di San Marino; Romagnol: Ripóbblica d' San Marein), also known as the Most Serene Republic of San Marino[2] (Italian: Serenissima Repubblica di San Marino), is a microstate in Southern Europe completely enclosed by Italy.[7][8]
listen), Italian: [sam maˈriːno]), officially the Republic of San Marino[1][2] (Italian: Repubblica di San Marino; Romagnol: Ripóbblica d' San Marein), also known as the Most Serene Republic of San Marino[2] (Italian: Serenissima Repubblica di San Marino), is a microstate in Southern Europe completely enclosed by Italy.[7][8]
Located on the northeastern side of the Apennine Mountains, San Marino covers a land area of just over 61 km2 (24 sq mi), and has a population of 33,562.[9] Its capital is the City of San Marino and its largest settlement is Dogana. The capital is set at the highest point of the country on a steep mountain. San Marino's official language is Italian, although Romagnol is the historical language and still in existence in a non-official capacity.
The country derives its name from Saint Marinus, a stonemason from the then Roman island of Rab, in modern-day Croatia. Born in AD 275, Marinus participated in the reconstruction of Rimini's city walls after their destruction by Liburnian pirates. Marinus then went on to found an independent monastic community on Monte Titano in AD 301; thus, San Marino lays claim to being the oldest extant sovereign state, as well as the oldest constitutional republic.[10]
San Marino's politics are ruled by its constitution, which dictates that every six months San Marino's parliament must elect two Captains Regent. The Captains Regent have equal powers, and are free to exercise them within the limits of the constitution and parliamentary legislation until their term expires.
The country's economy is mainly based on finance, industry, services and tourism. It is one of the wealthiest countries in the world in terms of GDP per capita, with a figure comparable to the most developed European regions. San Marino is considered to have a highly stable economy, with one of the lowest unemployment rates in Europe, no national debt and a budget surplus.[1]
Saint-Marin, en forme longue la sérénissime république de Saint-Marin ou république de Saint-Marin (en italien : San Marino ou Serenissima Repubblica di San Marino ou Repubblica di San Marino), est un micro-État européen enclavé à l'intérieur de l'Italie. Il est le troisième plus petit État d'Europe après le Vatican et Monaco, et le cinquième au monde après ces deux mêmes États, Nauru et Tuvalu. C’est aussi la plus ancienne république au monde existante de manière continue jusqu'à aujourd'hui, avec un système constitutionnel qui remonte au XVIe siècle2.
Enclavé à l’intérieur de l’Italie entre l'Émilie-Romagne et les Marches, en février 2015 le pays comptait 32 793 habitants dont 5 042 étrangers1. Il y a 12 973 Saint-Marinais résidant à l'étranger3. La République fait partie intégrante de la région historique du Montefeltro.
San Marino (in dialetto sammarinese: San Marèin o San Maroin), ufficialmente Serenissima Repubblica di San Marino, spesso abbreviato in Repubblica di San Marino, è uno Stato senza sbocco al mare dell'Europa meridionale situato nel centro-nord della penisola italiana, al confine tra le regioni italiane dell'Emilia-Romagna (provincia di Rimini) e delle Marche (provincia di Pesaro e Urbino).
Con un'estensione territoriale di 61,19 km², popolata da 33 909 abitanti[7], è uno dei meno popolosi fra gli Stati membri del Consiglio d'Europa e delle Nazioni Unite. La capitale è Città di San Marino, la lingua ufficiale è l'italiano e gli abitanti sono chiamati sammarinesi. A partire dal 2008 il centro storico della Città di San Marino e il monte Titano sono stati inseriti dall'UNESCO tra i patrimoni dell'umanità[8] in quanto "testimonianza della continuità di una repubblica libera fin dal XIII secolo".[9]
San Marino, oficialmente la Serenísima República de San Marino (en italiano: Serenissima Repubblica di San Marino), es una república parlamentaria y el Estado soberano más antiguo del mundo. Es un enclave1 rodeado de territorio italiano, entre las regiones de Emilia-Romaña y las Marcas. Contiene al Monte Titano, de 739 metros, y se encuentra a 10 kilómetros del mar Adriático, por lo que, dada su ubicación, el país no tiene salida a dicho mar. Junto a la Ciudad del Vaticano y el estado africano de Lesoto es el único país independiente del mundo cuyo territorio está completamente rodeado por un solo país. Es uno de los microestados europeos.
Сан-Мари́но (итал. San Marino), официально — Респу́блика Сан-Мари́но[4] (итал. Serenissima Repubblica di San Marino, дословно Светле́йшая Респу́блика Сан-Мари́но) — одно из самых маленьких государств в мире. Находится в Южной Европе, со всех сторон окружено территорией Италии. В своих нынешних границах Сан-Марино — самое старое государство Европы.Сан-Марино не входит ни в НАТО, ни в ЕС. Сан-Марино использует евро, и ей разрешено чеканить собственные монеты.

 Geography
Geography

 Geography
Geography
 ***IMF Developed countries
***IMF Developed countries
 IMF Developed countries
IMF Developed countries
 IMF Developed countries
IMF Developed countries
 TOP5
TOP5

 Mitglieder der NATO
Mitglieder der NATO
 Slovakia
Slovakia

 States of Europe
States of Europe
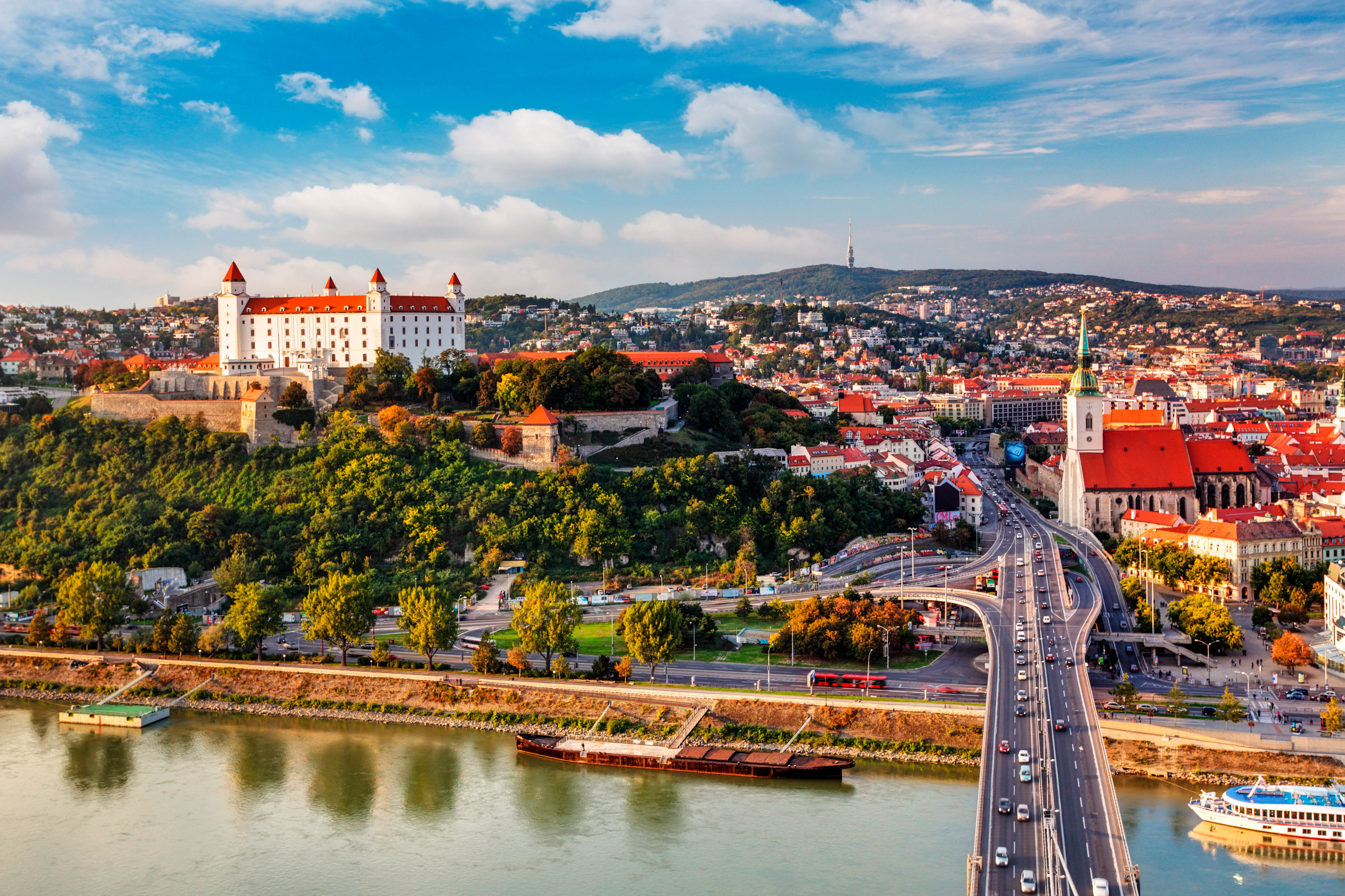

Die Slowakei (slowakisch , amtlich Slowakische Republik, slowakisch ) ist ein Binnenstaat in Mitteleuropa, der an Österreich, Tschechien, Polen, die Ukraine und Ungarn grenzt. Die Hauptstadt und gleichzeitig größte Stadt des Landes ist Bratislava (deutsch Pressburg), weitere wichtige Städte sind Košice (Kaschau), Prešov (Eperies), Žilina (Sillein), Banská Bystrica (Neusohl) und Nitra (Neutra).
Das Land ist zu zwei Dritteln gebirgig und hat einen beträchtlichen Anteil am Karpatenbogen. Im Westen reicht es bis zum nördlich der Donau liegenden Teil des Wiener Beckens, während der Süden und Südosten bis zur Donau und einem kleinen Teil der Theiß durch Ausläufer der Pannonischen Tiefebene geprägt sind. Die Slowakei liegt in der kontinental-gemäßigten Klimazone mit Unterschieden zwischen dem tiefer gelegenen Süden und dem gebirgigen Norden des Landes.
Das Gebiet der heutigen Slowakei wurde am Wendepunkt des 5. und 6. Jahrhunderts von den Slawen besiedelt. Deren erstes politisches Gebilde war das Reich des Samo (7. Jahrhundert), später befand sich in der Slowakei eines der Zentren des frühmittelalterlichen Mährerreiches. Im 11. Jahrhundert wurde die Slowakei in das Königreich Ungarn eingegliedert, das ab 1526 Teil der Habsburgermonarchie und ab 1867 Teil Österreich-Ungarns war. Nach der Auflösung der Doppelmonarchie 1918 wurde die Slowakei Teil der neu gegründeten Tschechoslowakei. Mit deren Zerschlagung durch das Deutsche Reich entstand 1939 der kurzlebige Slowakische Staat. Nach dem Ende des Zweiten Weltkrieges wurde die tschechoslowakische Republik 1945 wiederhergestellt. Am 1. Januar 1993 entstand nach friedlicher Aufteilung der Tschechoslowakei die unabhängige Slowakische Republik als Nationalstaat der Slowaken.
Seit 2004 ist die Slowakei Mitglied der Europäischen Union und der NATO. Im Jahr 2007 wurden gemäß dem Schengen-Abkommen die Grenzkontrollen zu EU-Staaten aufgehoben, 2009 trat die Slowakei der Eurozone bei. Das Land ist eine demokratisch verfasste parlamentarische Republik. Mit Polen, Tschechien und Ungarn bildet die Slowakei die Visegrád-Gruppe.
Das Entwicklungsprogramm der Vereinten Nationen zählt die Slowakei zu den Ländern mit sehr hoher menschlicher Entwicklung.[3]
斯洛伐克共和国(斯洛伐克语:Slovenská republika[1][2]![]() i/sloʊˈvækiə, -ˈvɑːk-/;[3][4] ;通称斯洛伐克,斯洛伐克语:Slovensko [ˈslɔʋenskɔ] (
i/sloʊˈvækiə, -ˈvɑːk-/;[3][4] ;通称斯洛伐克,斯洛伐克语:Slovensko [ˈslɔʋenskɔ] (![]() 聆听)),是位于中欧的议会制国家。斯洛伐克的官方语言为斯洛伐克语。其前身为捷克斯洛伐克,于1993年和平分离成捷克与斯洛伐克两个国家。面积约4.9万平方公里,居民约546万。西北邻捷克,北邻波兰,东邻乌克兰,南邻匈牙利,西南邻奥地利,首都和最大城市为布拉迪斯拉发。
聆听)),是位于中欧的议会制国家。斯洛伐克的官方语言为斯洛伐克语。其前身为捷克斯洛伐克,于1993年和平分离成捷克与斯洛伐克两个国家。面积约4.9万平方公里,居民约546万。西北邻捷克,北邻波兰,东邻乌克兰,南邻匈牙利,西南邻奥地利,首都和最大城市为布拉迪斯拉发。
斯洛伐克人系斯拉夫人的一支,祖先于六世纪左右定居斯洛伐克。公元7世纪,同其他部落共组萨摩帝国。公元9世纪,斯洛伐克人建立尼特拉公国,后被摩拉维亚公国征服,并为大摩拉维亚王国的一部分。10世纪,即大摩拉维亚王国解体后,斯洛伐克并入匈牙利公国,并于公元1000年成为匈牙利的构成地域。[5]经1241年和1242年的蒙古西征,该地因征战曾被焚毁殆尽,但随后在匈牙利王贝拉四世的领导下逐渐恢复,他同时也引入日耳曼德意志移民,使德裔民族成为除斯洛伐克人外的主要民族,尤其在中部和东部。[6]
奥匈帝国经一战解体,成立捷克斯洛伐克共和国。在第二次世界大战期间,斯洛伐克成为纳粹德国附庸国。二战结束后,捷克斯洛伐克重获独立。1948年共产党人发动二月政变,使捷克斯洛伐克成为共产主义国家,并接受苏联领导,成为其东方集团成员。随后的二十年里,捷克斯洛伐克民族主义及反共情绪逐渐高涨,这一热潮在布拉格之春达到巅峰;在该年八月份,因苏联武装入侵捷克斯洛伐克平息此运动。1989年,以公民论坛为主导的社会团体发起天鹅绒革命,结束了共产主义统治。1993年1月1日,捷克斯洛伐克议决天鹅绒分离,使斯洛伐克正式成为一个主权独立的国家。
スロバキア共和国(スロバキアきょうわこく、スロバキア語: Slovenská republika)、通称スロバキアは、中央ヨーロッパの共和制国家。首都はブラチスラヴァで、北西にチェコ、北にポーランド、東にウクライナ、南にハンガリー、南西にオーストリアと隣接する。
国体が常に激しく変化して来た歴史を持つ国家の一つである。古代にはサモ王国[注釈 1](623年 - 658年)・モラヴィア王国として独立を保った期間もあったが、この地のスラブ人は1000年間少数民族としてハンガリー王国の支配下に置かれていた。ハンガリーにとっても歴史的に重要な地域であり、多くのハンガリー人の出身地、ハンガリー貴族の発祥地でもある(元来スラブ系で、ハンガリー文化に同化した者も多い)。第一次世界大戦後、オーストリア・ハンガリー帝国からチェコと合併するかたちで独立し、1989年のビロード革命による共産党政権崩壊を経て、1993年1月1日にチェコスロバキアから分離独立し現在に至る。
Slovakia (/sloʊˈvækiə, -ˈvɑːk-/ (![]() listen);[7][8] Slovak: Slovensko [ˈslɔʋenskɔ] (
listen);[7][8] Slovak: Slovensko [ˈslɔʋenskɔ] (![]() listen)), officially the Slovak Republic (Slovak: Slovenská republika [ˈslɔʋenskaː ˈrepublika] (
listen)), officially the Slovak Republic (Slovak: Slovenská republika [ˈslɔʋenskaː ˈrepublika] (![]() listen)), is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Poland to the north, Ukraine to the east, Hungary to the south, Austria to the southwest, and the Czech Republic to the northwest. Slovakia's mostly mountainous territory spans about 49,000 square kilometres (19,000 sq mi), with a population of over 5.4 million. The capital and largest city is Bratislava, while the second largest city is Košice.
listen)), is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Poland to the north, Ukraine to the east, Hungary to the south, Austria to the southwest, and the Czech Republic to the northwest. Slovakia's mostly mountainous territory spans about 49,000 square kilometres (19,000 sq mi), with a population of over 5.4 million. The capital and largest city is Bratislava, while the second largest city is Košice.
The Slavs arrived in the territory of present-day Slovakia in the 5th and 6th centuries. In the 7th century, they played a significant role in the creation of Samo's Empire. In the 9th century, they established the Principality of Nitra, which was later conquered by the Principality of Moravia to establish Great Moravia. In the 10th century, after the dissolution of Great Moravia, the territory was integrated into the Principality of Hungary, which would then become the Kingdom of Hungary in 1000.[9] In 1241 and 1242, after the Mongol invasion of Europe, much of the territory was destroyed. The area was recovered largely thanks to Béla IV of Hungary, who also settled Germans, leading them to become an important ethnic group in the area, especially in what are today parts of central and eastern Slovakia.[10]
After World War I and the dissolution of Austria-Hungary, the state of Czechoslovakia was established. It was the only country in central and eastern Europe to remain a democracy during the interwar period. Nevertheless, local fascist parties gradually came to power in the Slovak lands, and the first Slovak Republic existed during World War II as a partially-recognized client state of Nazi Germany. At the end of World War II, Czechoslovakia was re-established as an independent country. After a coup in 1948, Czechoslovakia came under communist administration, and became a part of the Soviet-led Eastern Bloc. Attempts to liberalize communism in Czechoslovakia culminated in the Prague Spring, which was crushed by the Warsaw Pact invasion of Czechoslovakia in August 1968. In 1989, the Velvet Revolution peacefully ended the Communist rule in Czechoslovakia. Slovakia became an independent state on 1 January 1993 after the peaceful dissolution of Czechoslovakia, sometimes known as the Velvet Divorce.
La Slovaquie, en forme longue la République slovaque (en slovaque : Slovensko et Slovenská republika), est un pays situé en Europe centrale, au cœur de l'Europe continentale et à l'est de l'Union européenne, dont elle est membre depuis 200417. Ses pays frontaliers sont la Pologne au nord, l'Ukraine à l'est, la Hongrie au sud, l'Autriche à l'ouest et la Tchéquie à l'ouest-nord-ouest17. Coeur de la Grande-Moravie, la Slovaquie fit partie du Royaume de Hongrie à partir du XIè siècle. Du 28 octobre 1918 au 21 mars 1939, puis du 4 avril 1945 au 31 décembre 1992, elle a, avec la Tchéquie, fait partie de la Tchécoslovaquie8,18. De 1939 à 1945 fut constituée, à partir des décombres de la Tchécoslovaquie, une République slovaque - en partie démembrée au profit de la Hongrie - soumise au Troisième Reich.
La Slovaquie est membre de nombreuses organisations internationales, telles que l'ONU19, l'OTAN19, l'OMC20, l'OCDE19 ou encore le V421, et fait partie de la zone euro15.
La Slovacchia (Slovàcchia), ufficialmente Repubblica Slovacca (in slovacco Slovensko o Slovenská republika)[7] è uno Stato senza sbocco al mare costituito come repubblica parlamentare, situato nell'Europa centro-orientale. Ha una popolazione di più di 5 milioni di abitanti e un'area di circa 49.000 chilometri quadrati. La città più grande è anche la capitale, Bratislava, e la seconda città più grande è Košice. Confina con la Repubblica Ceca a nord-ovest, con la Polonia a nord, con l'Ucraina a est, con l'Ungheria a sud e con l'Austria a sud-ovest. È uno Stato membro dell'Unione europea, della NATO, delle Nazioni Unite, dell'OCSE e dell'OMC. La lingua ufficiale è lo slovacco, lingua appartenente al ceppo delle lingue slave.
Gli slavi arrivarono in quello che oggi è il territorio slovacco tra il V e il VI secolo durante le invasioni barbariche. Nel corso della storia, diverse parti del territorio attuale appartennero al Regno di Samo (il primo ente politico conosciuto degli Slavi), al Principato di Nitra, alla Grande Moravia, al Regno d'Ungheria, all'Impero austro-ungarico e alla Cecoslovacchia. Il 30 ottobre 1918 venne approvata la Dichiarazione di Martin o Dichiarazione del popolo slovacco. Uno Stato slovacco indipendente è esistito brevemente durante la seconda guerra mondiale, quale Stato fantoccio della Germania nazista dal 1939 al 1944. Dal 1945 la Slovacchia tornò a far parte nuovamente della Cecoslovacchia. La Repubblica Slovacca e la Repubblica Ceca sono nate il 1º gennaio 1993 dalla divisione, sancita dal parlamento della Cecoslovacchia, che già dal 1990 aveva assunto il nome di Repubblica Federale Ceca e Slovacca.
La Slovacchia rientra nel gruppo degli Stati avanzati. Nel 2004 è entrata a fare parte dell'Unione europea e nel 2009 ha adottato l'euro. La Slovacchia, la Slovenia, l'Estonia, la Lettonia e la Lituania sono gli unici Stati del passato blocco orientale a far parte allo stesso tempo dell'Unione europea, dell'eurozona, della zona Schengen e della NATO.
Eslovaquia (en eslovaco: ![]() Slovensko (?·i)), oficialmente denominada República Eslovaca (en eslovaco:
Slovensko (?·i)), oficialmente denominada República Eslovaca (en eslovaco: ![]() Slovenská republika (?·i)), es uno de los veintisiete Estados soberanos que forman la Unión Europea. Situado en Europa Central, limita al norte con Polonia, al este con Ucrania, al sur con Hungría, al oeste con Austria y al noroeste con República Checa. Tiene una población de 5 389 180 habitantes y su capital es Bratislava, con 425 155 habitantes. Los montes Cárpatos ocupan toda la zona septentrional del país.
Slovenská republika (?·i)), es uno de los veintisiete Estados soberanos que forman la Unión Europea. Situado en Europa Central, limita al norte con Polonia, al este con Ucrania, al sur con Hungría, al oeste con Austria y al noroeste con República Checa. Tiene una población de 5 389 180 habitantes y su capital es Bratislava, con 425 155 habitantes. Los montes Cárpatos ocupan toda la zona septentrional del país.
Слова́кия (словацк. Slovensko [ˈslɔʋɛnskɔ]), официальное название — Слова́цкая Респу́блика (словацк. Slovenská republika) — государство в Центральной Европе. Население составляет 5 443 120 человек (декабрь 2017)[7], территория — 48 845 км². Занимает 112-е место в мире по численности населения и 127-е по территории.
Столица — Братислава. Государственный язык — словацкий.
Унитарное государство, парламентская республика. По состоянию на апрель 2021 года пост президента занимает Зузана Чапутова, премьер-министра — Эдуард Хегер. Подразделяется на 8 краёв.
Расположена в центре Европы. Континентальное государство, не имеющее выхода к морю. Имеет сухопутную границу с Чехией, Австрией, Польшей, Венгрией, Украиной.
Большая часть верующих (около 70 % населения) исповедует католицизм.
Словакия — член НАТО и ЕС. Индустриальная страна с динамично развивающейся экономикой. Объём ВВП за 2011 год составил 127,111 млрд долларов США (около 23 384 долларов на душу населения). Денежная единица — евро.
Независимость страны провозглашена 1 января 1993 года. На протяжении истории территория страны входила в состав многих держав и государственных образований, начиная от Государства Само в VII веке вплоть до Чехословакии в XX веке. В годы Второй мировой войны существовало зависимое от нацистской Германии словацкое государство, которое в 1945 году вновь стало частью Чехословакии.




Slowenien (slowenisch Slovenija, amtlich Republik Slowenien, slowenisch Republika Slovenija) ist ein demokratischer Staat in Europa mit rund 2 Millionen Einwohnern, der an Italien, Österreich, Ungarn und Kroatien grenzt. Hauptstadt und zugleich größte Stadt des Landes ist das zentral gelegene Ljubljana (deutsch Laibach). Weitere wichtige Städte sind Maribor, Celje, Kranj, Koper und Velenje. Im Jahr 2004 trat Slowenien der EU und der NATO bei, 2007 auch der Eurozone. Das Land ist eine demokratisch verfasste parlamentarische Republik.
Das Gebiet des heutigen Sloweniens wurde Anfang des 6. Jahrhunderts von den Slawen besiedelt, die das Fürstentum Karantanien gründeten. Im Jahr 788 eroberten die Franken das Gebiet und die Bistümer Aquileia und Salzburg missionierten es. Im 11. Jahrhundert wurde das Land in das Heilige Römische Reich eingegliedert und 1364 zum Herzogtum Krain erhoben. In den folgenden Jahrhunderten geriet das Territorium an die Habsburgermonarchie. Nach der Auflösung Österreich-Ungarns 1918 ging das vormalige Kronland im neu gegründeten Königreich Jugoslawien auf. Nach dem Ende des Zweiten Weltkrieges existierte Slowenien als Teilrepublik im sozialistischen Jugoslawien. Nach der Unabhängigkeitserklärung am 25. Juni 1991 und dem 10-Tage-Krieg wurde Slowenien ein eigenständiger Nationalstaat und am 22. Mai 1992 eigenständiges Mitglied der UNO.
Slowenien ist heute das wohlhabendste Land des ehemaligen Jugoslawiens. Es verzeichnet sowohl im Bezug auf die politische als auch die wirtschaftliche Transformation überdurchschnittlich hohe Erfolge.[4] Im Index der menschlichen Entwicklung belegte Slowenien 2019 Rang 24 von 189 Ländern weltweit.[5]
斯洛文尼亚共和国(斯洛文尼亚语:Republika Slovenija),通称斯洛文尼亚(斯洛文尼亚语:Slovenija),是一个位于中欧的,毗邻阿尔卑斯山的小国。西邻意大利,西南通往亚得里亚海,东部和南部被克罗地亚包围,东北有匈牙利,北接奥地利。斯洛文尼亚国土面积为20,273平方公里,全国人口约205万人[2],半数以上居民信仰罗马天主教,卢布尔雅那为首都及最大城市[8]。该国虽然是中欧国家,但是在历史和文化上深受南欧的意大利和东南欧的克罗地亚和塞尔维亚影响,斯洛文尼亚在1991年之前为前南斯拉夫社会主义联邦共和国的一个加盟共和国(斯洛文尼亚社会主义共和国)。1991年6月25日独立。
スロベニア共和国(スロベニアきょうわこく、スロベニア語: Slovenija: ![]() [sloˈveːnija])、通称スロベニア、スロヴェニアは、中央ヨーロッパに位置する国で[1]、主要なヨーロッパの文化や交易の交差路である[2][3]。
[sloˈveːnija])、通称スロベニア、スロヴェニアは、中央ヨーロッパに位置する国で[1]、主要なヨーロッパの文化や交易の交差路である[2][3]。
スロベニアは西はイタリア、北はオーストリア、南や南東はクロアチア、北東でハンガリーとそれぞれ国境を接している。[4]国土面積は20,273km2 (7,827 sq mi)で、人口は205万人を擁する。[5]議会制共和国で、欧州連合や北大西洋条約機構の加盟国である。[6]スロベニアではアルプス山脈とディナル・アルプス山脈、地中海のアドリア海に沿った少ない海岸部分のヨーロッパの4つの大きな地理的な部分が接している。[7][8] スロベニアの国土はモザイク状の構造で多様性に富んだ景観や[8]、生物多様性があり[9][10]、この多様性は自然の特質と長期の人間の存在による。[11]主に丘陵地の気候[7]であるが、スロベニアの国土は大陸性気候の影響を受け、プリモルスカ地方は亜地中海性気候に恵まれており、スロベニア北西部では高山気候が見られる。[12] スロベニアはヨーロッパの国の中でも水が豊かな国の一つで[13]、密度が高い河川や豊かな帯水層、かなりのカルスト地形(クラス地方はカルストの語源)の地下水流がある[14]。スロベニアの国土の半分以上は森林に覆われている[15]。スロベニアの集落は分散しており、一様ではない[16]。
スラヴ語派やゲルマン語派、ロマンス諸語、フィン・ウゴル語派などの言語や文化のグループはスロベニアで接し領域は均質でないが[17][18][19] 、人口数ではスロベニア人が優勢である。[20]スロベニア語はスロベニアの唯一の公用語であるが、イタリア語やハンガリー語などは地域の少数言語となっている。スロベニアの大部分は宗教と分離しているが[21]、文化やアイデンティティの面ではカトリック教会やルーテル教会の大きな影響を受けている。[22] スロベニアの経済は小規模で、輸出志向型工業化の経済[23] でありその後の国際的な経済情勢に大きく影響を受けている。[24]スロベニアの経済は2000年代後半に始まった欧州経済危機により厳しい痛手を負っている。[25] 経済の主要な分野は第三次産業で、工業や建設がそれに続く。[26]
多くのスロベニア人がスポーツ界で成功しており、特にウィンタースポーツ、ウォータースポーツ、登山、耐久性が要求されるエンデュランススポーツで顕著である。[27]
Slovenia (/sloʊˈviːniə, slə-/ (![]() listen)[10][11] sloh-VEE-nee-ə; Slovene: Slovenija [slɔˈʋèːnija]),[12] officially the Republic of Slovenia (Slovene:
listen)[10][11] sloh-VEE-nee-ə; Slovene: Slovenija [slɔˈʋèːnija]),[12] officially the Republic of Slovenia (Slovene: ![]() Republika Slovenija (help·info),[13] abbr.: RS[14]), is a country located in Central Europe at the crossroads of main European cultural and trade routes.[15][16] It is bordered by Italy to the west, Austria to the north, Hungary to the northeast, Croatia to the southeast, and the Adriatic Sea to the southwest.[17] Slovenia covers 20,271 square kilometers (7,827 sq mi) and has a population of 2.095 million.[18] One of the successor states of the former Yugoslavia, Slovenia is now a parliamentary republic[19] and member nation of the European Union, United Nations, and NATO.[20] The capital and largest city is Ljubljana.[21]
Republika Slovenija (help·info),[13] abbr.: RS[14]), is a country located in Central Europe at the crossroads of main European cultural and trade routes.[15][16] It is bordered by Italy to the west, Austria to the north, Hungary to the northeast, Croatia to the southeast, and the Adriatic Sea to the southwest.[17] Slovenia covers 20,271 square kilometers (7,827 sq mi) and has a population of 2.095 million.[18] One of the successor states of the former Yugoslavia, Slovenia is now a parliamentary republic[19] and member nation of the European Union, United Nations, and NATO.[20] The capital and largest city is Ljubljana.[21]
Slovenia has a mostly mountainous terrain[22] with a mainly continental climate,[23] with the exception of the Slovene Littoral, which has a sub-Mediterranean climate, and of the Julian Alps in the northwest, which have an Alpine climate.[24] Additionally, the Dinaric Alps and the Pannonian Plain meet on the territory of Slovenia. The country, marked by significant biological diversity,[25][26] is one of the most water-rich in Europe,[27] with a dense river network, a rich aquifer system, and significant karst underground watercourses.[28] Over half of the territory is covered by forest.[29] The human settlement of Slovenia is dispersed and uneven.[30]
Slovenia has historically been the crossroads of Slavic, Germanic, and Romance languages and cultures.[31][32][33] Ethnic Slovenes make up more than 80% of the population.[34] The South Slavic language Slovene is the official language throughout the country. Slovenia is a largely secularized country,[35] but Catholicism and Lutheranism have significantly influenced its culture and identity.[36] The economy of Slovenia is small, open and export-oriented[citation needed] and is thus strongly influenced by the conditions of its exporting partners' economies. This is especially true with Germany, Slovenia's biggest trade partner.[37] Like most of the developed world, Slovenia was severely hurt by the Eurozone crisis beginning in 2009, but started to recover in 2014.[38][39] The main economic driver for the country is the services industry, followed by manufacturing and construction.[40]
Historically, the territory of Slovenia has formed part of many different states, such as: the Roman Empire, Byzantine Empire, Carolingian Empire, the Holy Roman Empire, the Kingdom of Hungary, the Republic of Venice, the Illyrian Provinces of the First French Empire, the Austrian Empire and Austro-Hungarian Empire. In October 1918, the Slovenes exercised self-determination for the first time by co-founding the State of Slovenes, Croats and Serbs. In December 1918 they merged with the Kingdom of Serbia into the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes (renamed the Kingdom of Yugoslavia in 1929).
During World War II (1939–1945) Germany, Italy, and Hungary occupied and annexed the territories included in today's Slovenia (1941–1945), with a tiny area transferred to the Independent State of Croatia, a Nazi puppet state.[41] In 1945 Slovenia became a founding member of the Federal People's Republic of Yugoslavia, renamed in 1963 as the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia. In the first years after World War II this state was initially allied with the Eastern Bloc, but because of the Tito-Stalin split in 1948 it never subscribed to the Warsaw Pact and in 1961 became one of the founders of the Non-Aligned Movement.[citation needed]
In June 1991, after the introduction of multi-party representative democracy, Slovenia became the first republic that split from Yugoslavia and became an independent sovereign state.[4] In 2004, it entered NATO and the European Union; in 2007 became the first formerly communist country to join the Eurozone;[42] and in 2010 it joined the OECD, a global association of high-income developed countries.[43] Slovenia is a developed country with an advanced, high-income economy[44][45] and a very high Human Development Index.[46] It ranks 12th in the inequality-adjusted human development index.
La Slovénie, en forme longue la république de Slovénie, en slovène : Slovenija et Republika Slovenija, est un pays d’Europe centrale au carrefour des principales cultures européennes. Sa capitale est Ljubljana. Le pays partage ses frontières avec l'Italie à l'ouest, l’Autriche au nord, la Hongrie à l'est-nord-est et la Croatie au sud-est. La Slovénie est également bordée par la mer Adriatique au sud-ouest. Comptant environ 2 millions d'habitants, la Slovénie est un État membre de l'Union européenne.
Historiquement, le territoire de la Slovénie a intégré de nombreux États différents : l'Empire romain, l'Empire byzantin, l'Empire carolingien, le Saint-Empire romain germanique, le Royaume de Hongrie, la République de Venise, le territoire des Provinces Ilyriennes du Premier Empire français, l'Empire d'Autriche, l'Empire austro-hongrois et enfin la Yougoslavie.
C'est en octobre 1918 que les Slovènes ont cofondé l'État des Slovènes, des Croates et des Serbes. Cette monarchie sera appelée royaume de Yougoslavie à partir de 1929. Pendant la seconde guerre mondiale, la Slovénie est démembrée et annexée par l'Allemagne, l'Italie et la Hongrie. Une toute petite part est donnée à la Croatie, État fantoche nazi. En 1945, la Slovénie devient un membre fondateur de la République fédérative socialiste de Yougoslavie. Dans les premières années de son existence, cet État était allié au bloc de l'Est, dominé par l'Union soviétique, bien que n'ayant pas intégré le Pacte de Varsovie. En 1961, la Yougoslavie devient un des fondateurs du mouvement des non-alignés.
En 1991, après l'introduction du multipartisme et de la démocratie, la Slovénie est devenue la première république à faire sécession de la Yougoslavie en devenant un État souverain indépendant. La République de Slovénie entre dans l'Union européenne et l'OTAN en 2004. En 2007, le pays devient le premier ancien pays communiste à intégrer la zone euro.
La Slovénie est aujourd'hui un pays développé à revenu élevé, avec un indice de développement humain élevé, se classant 13e dans l'indice de développement humain ajusté aux inégalités.
La Slovenia, ufficialmente Repubblica di Slovenia (in sloveno Republika Slovenija, in ungherese Szlovén Köztársaság), è uno Stato sovrano dell'Europa centrale, confinante a ovest con l'Italia (Friuli-Venezia Giulia), a nord con l'Austria, a est con l'Ungheria e la Croazia a sud, affacciandosi a sud-ovest sul mare Adriatico (golfo di Trieste). La sua capitale è Lubiana.
Dal 1º maggio 2004 la Slovenia è membro dell'Unione europea e la valuta nazionale, dal 1º gennaio 2007, è l'euro, che ha sostituito il tallero sloveno, adottato nel 1991 dopo l'indipendenza; in precedenza la moneta era il dinaro iugoslavo. Nella regione istriana del Paese vive una comunità autoctona italiana, mentre nella zona di confine orientale si trova quella ungherese; crescente è l'immigrazione serba e bosniaco-erzegovina. La Festa nazionale slovena, così come quella croata, ricorre il 25 giugno, anniversario della dichiarazione d'indipendenza del 1991 dalla Repubblica Socialista Federale di Iugoslavia.
Eslovenia, oficialmente República de Eslovenia (en esloveno: ![]() Republika Slovenija (?·i) antigua Carantania) es uno de los veintisiete estados soberanos que forman la Unión Europea. Limita con Italia al oeste; con el mar Adriático, al suroeste; con Croacia al sur y al este; con Hungría, al noreste; y con Austria, al norte. Tiene una población de 2 080 908 habitantes a fecha del 1 de enero de 2019.5 La capital y ciudad más poblada es Liubliana.
Republika Slovenija (?·i) antigua Carantania) es uno de los veintisiete estados soberanos que forman la Unión Europea. Limita con Italia al oeste; con el mar Adriático, al suroeste; con Croacia al sur y al este; con Hungría, al noreste; y con Austria, al norte. Tiene una población de 2 080 908 habitantes a fecha del 1 de enero de 2019.5 La capital y ciudad más poblada es Liubliana.
La actual Eslovenia se formó el 25 de junio de 1991 al independizarse de Yugoslavia, tras un conflicto armado relativamente corto denominado Guerra de los diez días (que fue la primera guerra de la disolución de Yugoslavia), en la que se opuso al ejército de la antigua federación yugoslava. Por aquel entonces, ya era el país más desarrollado de aquella federación.
Cultural e históricamente, Eslovenia gravita hacia Italia, Austria y Alemania (cultura católica y protestante). A lo largo de la historia, Eslovenia siempre fue parte de los imperios, reinos, etc. de Europa central y nunca ha sido parte de los cuerpos políticos que gobernaron la mayoría de los Balcanes, por ejemplo del Imperio Romano de Oriente (iglesia ortodoxa) y el Sultanato de Turquía (islam).
En 2004 se adhirió a la Unión Europea.6 Eslovenia se integró en el euro el 1 de enero de 2007, y en el área de Schengen, en 2004. Ya en 1993 se había adherido al Consejo de Europa y desde julio de 2010 forma parte de la OCDE.
Слове́ния (словен. Slovenija), официальное название — Респу́блика Слове́ния (словен. Republika Slovenija) — государство в Южной Европе. Территория — 20 236 км², население — 2 089 310 человек (июль 2019 год)[8]. Занимает 144-е место в мире по численности населения и 150-е по территории.
Столица — Любляна. Государственный язык — словенский.
Унитарная, парламентская республика. В марте 2020 года пост премьер-министра занял Янез Янша[9].
Административное деление: 210 общин, в том числе 11 городов.
Расположена в предальпийской части Балканского полуострова. Омывается водами Адриатического моря с юго-запада. На западе граничит с Италией, на севере — с Австрией, на северо-востоке — с Венгрией, на востоке и юге — с Хорватией.
Индустриальная страна с динамично развивающейся экономикой. Объём ВВП за 2011 год составил 58,979 миллиарда долларов США (около 29 179 долларов США на душу населения). Денежная единица — евро.

 European Union
European Union
 International cities
International cities
 Medieval cities in Europe
Medieval cities in Europe
 World Heritage
World Heritage