
Deutsch-Chinesische Enzyklopädie, 德汉百科
 Turkey
Turkey

 Afghanistan
Afghanistan
 Egypt
Egypt
 Armenia
Armenia
 Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan
 Ethiopia
Ethiopia
 Australia
Australia
 Bangladesh
Bangladesh
 Beijing Shi-BJ
Beijing Shi-BJ
 Brunei Darussalam
Brunei Darussalam
 China
China
 Denmark
Denmark
 Demokratische Republik Timor-Leste
Demokratische Republik Timor-Leste
 Germany
Germany
 Fidschi
Fidschi

 Financial
Financial
 International Bank for Cooperation
International Bank for Cooperation
 Finland
Finland
 France
France
 Georgia
Georgia
 Hongkong Tebiexingzhengqu-HK
Hongkong Tebiexingzhengqu-HK
 India
India
 Indonesia
Indonesia
 Iran
Iran
 Ireland
Ireland
 Iceland
Iceland
 Israel
Israel
 Italy
Italy
 Jordan
Jordan
 Cambodia
Cambodia
 Kasachstan
Kasachstan
 Katar
Katar
 Kyrgyzstan
Kyrgyzstan
 Laos
Laos
 Luxembourg
Luxembourg
 Malaysia
Malaysia
 Malediven
Malediven
 Malta
Malta

 Mongolei
Mongolei
 Myanmar
Myanmar
 Nepal
Nepal
 New Zealand
New Zealand
 Netherlands
Netherlands
 Norwegen
Norwegen
 Oman
Oman
 Austria
Austria
 Pakistan
Pakistan
 Philippines
Philippines
 Poland
Poland
 Portugal
Portugal
 Republic of Korea
Republic of Korea
 Russia
Russia
 Samoa
Samoa
 Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia
 Sweden
Sweden
 Switzerland
Switzerland
 Singapore
Singapore
 Spain
Spain
 Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka
 South Africa
South Africa
 Tajikistan
Tajikistan
 Thailand
Thailand
 Turkey
Turkey
 Hungary
Hungary
 Uzbekistan
Uzbekistan
 United Arab Emirates
United Arab Emirates
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 Vietnam
Vietnam

 Important International Organizations
Important International Organizations

 Economy and trade
Economy and trade
 Economic and political research
Economic and political research
 Cyprus
Cyprus

亚洲基础设施投资银行(英语:Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank,縮寫:AIIB),简称亚投行,是一个愿意向亚洲国家和地區的基础设施建设提供资金支持的政府间性质的亚洲区域多边开发机构,成立的目的是促进亚洲区域的互联互通建设和经济一体化的进程,並且加大中國與其他亚洲國家和地区的合作力度。总部设在中国北京,法定资本为1,000亿美元。[2]
中华人民共和国主席习近平于2013年10月2日在雅加达同印度尼西亚总统苏西洛举行会谈时首次倡议筹建亚投行。[3]2014年10月24日,中国、印度、新加坡等21国在北京正式签署《筹建亚投行备忘录》。[2]2014年11月25日,印度尼西亚签署备忘录,成为亚投行第22个意向创始成员国。[4]
2015年3月12日,英国正式申请作为意向创始成员国加入亚投行,[5]成为正式申请加入亚投行的首个欧洲国家、主要西方国家。[6]随后法国、意大利、德国等西方国家纷纷以意向创始成员国身份申请加入亚投行。[7]接收新意向创始成员国申请截止日期3月31日临近,韩国[8]、俄罗斯[9]、巴西[10]等域内国家和重要新兴经济体也抓紧申请成为亚投行意向创始成员国。
各方商定将于2015年年中完成亚投行章程谈判并签署,年底前完成章程生效程序,正式成立亚投行。[11]
Die Asiatische Infrastrukturinvestmentbank (亞洲基礎設施投資銀行 / 亚洲基础设施投资银行, kurz: 亞投行 / 亚投行, englisch Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank, AIIB) ist eine multilaterale Entwicklungsbank, die 2014 von verschiedenen Staaten gegründet wurde und im Wettbewerb zur Weltbank, zum Internationalen Währungsfonds und zur Asiatischen Entwicklungsbank steht.
Anlass zur Initiative der Gründung war insbesondere die Unzufriedenheit Chinas über eine Dominanz der US-Amerikaner im Internationalen Währungsfonds, der keine faire Verteilung der globalen Machtverhältnisse aus Sicht Chinas widerspiegelte.[2] Da sich die US-Amerikaner strikt weigerten, eine Änderung der Stimmverhältnisse zu implementieren, begann China 2013 mit der Gründung der Initiative. Neben den 21 Gründungsmitgliedern haben im Jahr 2015 auch unter anderem Deutschland, Italien, Frankreich und das Vereinigte Königreich ihr Interesse bekundet, als nicht-regionale Mitglieder die neue Entwicklungsbank zu unterstützen.[3]
Die Gründungsurkunde der AIIB wurde am 29. Juni 2015 von Vertretern aus 57 Ländern in Peking unterzeichnet.[4] Die Bank nahm im Januar 2016 ihre Arbeit ohne Beteiligung der USA und Japan auf.[5]
Joachim von Amsberg ist der "Vizepräsident für Politik und Strategie".
アジアインフラ投資銀行(アジアインフラとうしぎんこう、英: Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank, AIIB、中: 亚洲基础设施投资银行,亞洲基礎設施投資銀行)は、国際開発金融機関のひとつである。
中華人民共和国が2013年秋に提唱し主導する形で発足した[1]。「合計の出資比率が50%以上となる10以上の国が国内手続きを終える」としていた設立協定が発効条件を満たし、2015年12月25日に発足し[2][3]、2016年1月16日に開業式典を行った[1][4]。
57か国を創設メンバーとして発足し[1][5]、2017年3月23日に加盟国は70カ国・地域となってアジア開発銀行の67カ国・地域を超え[6][7]、一方で日本、アメリカ合衆国などは2017年の現時点で参加を見送っている[8]。 創設時の資本金は1000億ドルである[9]。
The Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank (AIIB) is a multilateral development bank that aims to support the building of infrastructure in the Asia-Pacific region. The bank currently has 93 members from around the world [7]. The bank started operation after the agreement entered into force on 25 December 2015, after ratifications were received from 10 member states holding a total number of 50% of the initial subscriptions of the Authorized Capital Stock.[8]
The United Nations has addressed the launch of AIIB as having potential for "scaling up financing for sustainable development"[9] and to improve the global economic governance.[10] The starting capital of the bank was $100 billion, equivalent to 2⁄3 of the capital of the Asian Development Bank and about half that of the World Bank.[11]
The bank was proposed by China in 2013[12] and the initiative was launched at a ceremony in Beijing in October 2014.[13] It received the highest credit ratings from the three biggest rating agencies in the world, and is seen as a potential rival to the World Bank and IMF.[14][15]
La Banque asiatique d'investissement dans les infrastructures (BAII ou AIIB), est une banque d'investissement proposée par la République populaire de Chine dans le but de concurrencer le Fonds monétaire international, la Banque mondiale et la Banque asiatique de développement1 pour répondre au besoin croissant d'infrastructures en Asie du Sud-Est et en Asie centrale. Cette banque s'inscrit dans la stratégie de la nouvelle route de la soie, développée par la Chine.
La Banca Asiatica d'Investimento per le infrastrutture (AIIB), fondata a Pechino nell'ottobre 2014, è un'istituzione finanziaria internazionale proposta dalla Repubblica Popolare Cinese. Si contrappone al Fondo Monetario Internazionale, alla Banca Mondiale e all'Asian Development Bank[1], le quali si trovano sotto il controllo del capitale e delle scelte strategiche dei paesi sviluppati come gli Stati Uniti d'America.[2] Scopo della Banca è fornire e sviluppare progetti di infrastrutture nella regione Asia-Pacifico attraverso la promozione dello sviluppo economico-sociale della regione e contribuendo alla crescita mondiale.
El Banco Asiático de Inversión en Infraestructura (Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank o AIIB) es una institución financiera internacional propuesta por el gobierno de China. El propósito de este banco de desarrollo multilateral es proporcionar la financiación para proyectos de infraestructura en la región de Asia basado en un sistema financiero de préstamo1 y el fomento del sistema de libre mercado en los países asiáticos.
El AIIB está considerado por algunos como una versión continental del FMI y del Banco Mundial, y busca ser un rival por la influencia en la región del Banco de Desarrollo asiático (ADB), el cual esta alineado a los intereses de potencias, tanto regionales (Japón), como globales (Estados Unidos, la Unión Europea).2
El banco fue propuesto por Xi Jinping en 2013 e inaugurado con una ceremonia en Pekín en octubre de 2014. La ONU se a mostrado entusiasta con la propuesta china, a la que a descrito como el FMI del futuro y a señalado como "una gran propuesta para financiar el desarrollo sostenible" y "mejorar la gobernanza económica mundial". La entidad constó inicialmente con 100 mil millones de dolares, es decir, la mitad del dinero de que posee el Banco Mundial.
La entidad a recibido inversión por parte de corporaciones financieras estadounidenses como la Standard & Poor's, Moody's o Fitch Group34. Actualmente la entidad consta de 87 miembros, incluyendo los 57 miembros fundadores. Bélgica, Canadá, y Ucrania están barajando unirse al AIIB. Estados Unidos, Japón y Colombia no tienen intención de participar. China a prohibido a Corea del Norte unirse, instigando además una política de aislamiento contra esta por parte del AIIB.
Азиатский банк инфраструктурных инвестиций (АБИИ) (англ. Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank, AIIB) — международная финансовая организация, создание которой было предложено Китаем. Основные цели, которые преследует АБИИ, — стимулирование финансового сотрудничества в Азиатско-Тихоокеанском регионе, финансирование инфраструктурных проектов в Азии от строительства дорог и аэропортов до антенн связи и жилья экономкласса[1].
По заявлениям вице-премьера России Игоря Шувалова, AБИИ не рассматривается как потенциальный конкурент МВФ, Всемирного банка и Азиатского банка развития (АБР). Однако эксперты рассматривают AIIB как потенциального конкурента базирующихся в США Международного валютного фонда (МВФ) и Всемирного банка. После сообщений об успехах AIIB американский министр финансов США Джейкоб Лью предупредил, что международным финансовым организациям в США, таким как ВБ и МВФ, грозит потеря доверия [2][3].
Китай, Индия и Россия возглавили организацию, оказавшись в тройке крупнейших владельцев голосов. При этом на важнейшие решения КНР имеет фактическое право вето[4].
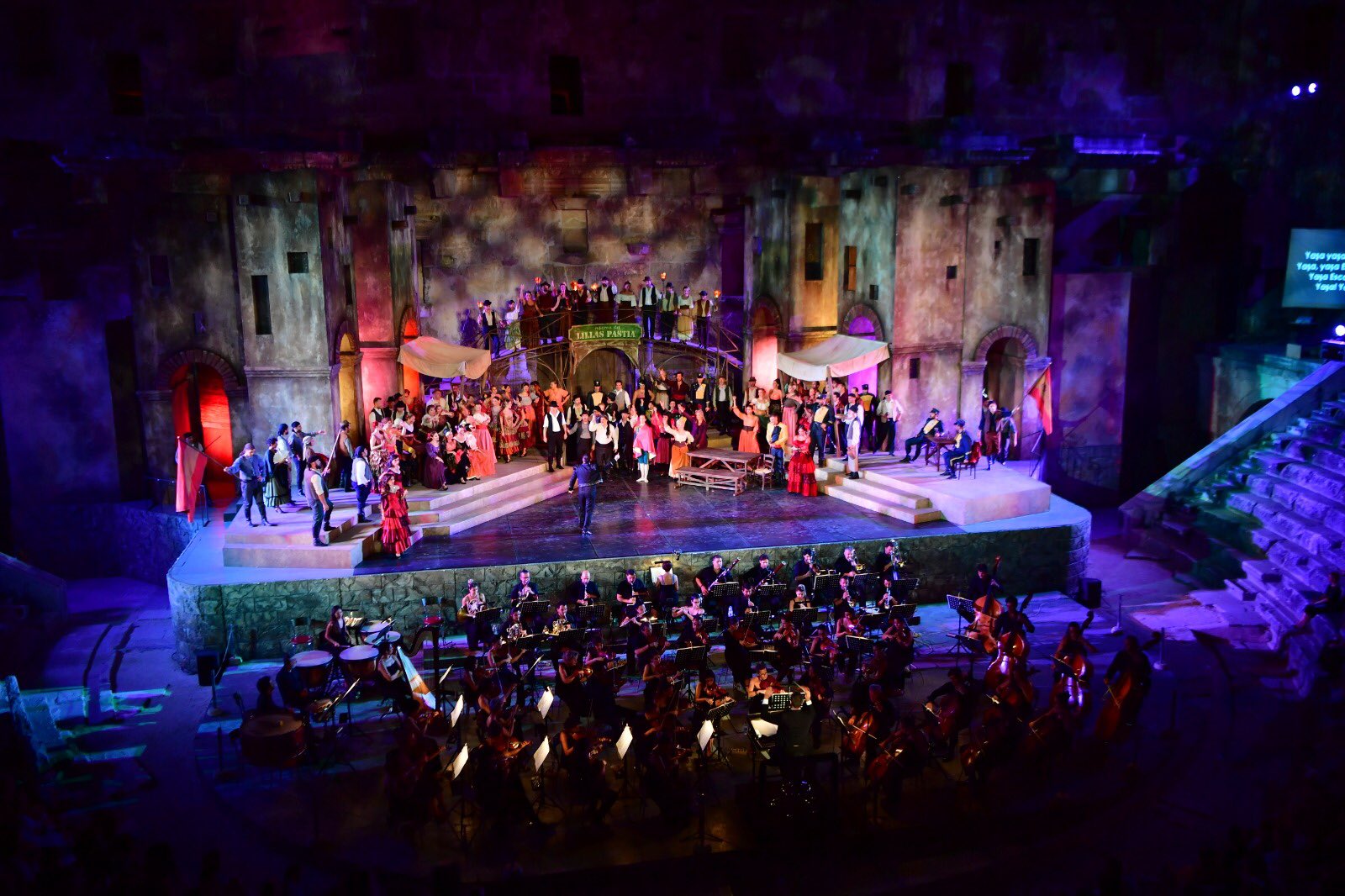

阿斯潘多斯国际戏剧芭蕾舞节(土耳其语:Aspendos Uluslararası Opera ve Bale Festivali)自 1994 年起由土耳其国家歌剧院和芭蕾舞团在土耳其安塔利亚附近的阿斯本多斯举办,来自多个国家的国际歌剧和芭蕾舞团参加了该活动。歌剧节每年 6 月和 7 月在拥有两千年历史的罗马剧院举行。该剧院是世界上保存最完好的古剧院之一,建筑的许多原始特征都保存完好。
Das Internationale Opern- und Ballettfestival Aspendos (türkisch: Aspendos Uluslararası Opera ve Bale Festivali) wird seit 1994 in Aspendos in der Nähe von Antalya (Türkei) von der türkischen Staatsoper und dem türkischen Staatsballett mit internationaler Beteiligung von Opern- und Ballettkompanien aus mehreren Ländern veranstaltet. Das Festival findet jährlich im Juni und Juli in dem zweitausend Jahre alten römischen Theater statt. Das Theater gilt als eines der am besten erhaltenen antiken Theater der Welt, in dem noch viele Originalmerkmale des Gebäudes erhalten sind.


Veranstaltungen Endspiel der Türkiye Kupası 2003/04 Endspiel der UEFA Champions League 2004/05 Endspiel der Türkiye Kupası 2004/05 Türkischer Fußball-Supercup: 2009, 2010 Spiele von Galatasaray Istanbul (2003–2004) Spiele von Istanbul BB (2007–2014) Spiele von Beşiktaş Istanbul (2013–2016) Endspiel der Türkiye Kupası 2019/20 Spiele des Fatih Karagümrük SK (seit 2020) Endspiel der UEFA Champions League 2022/23
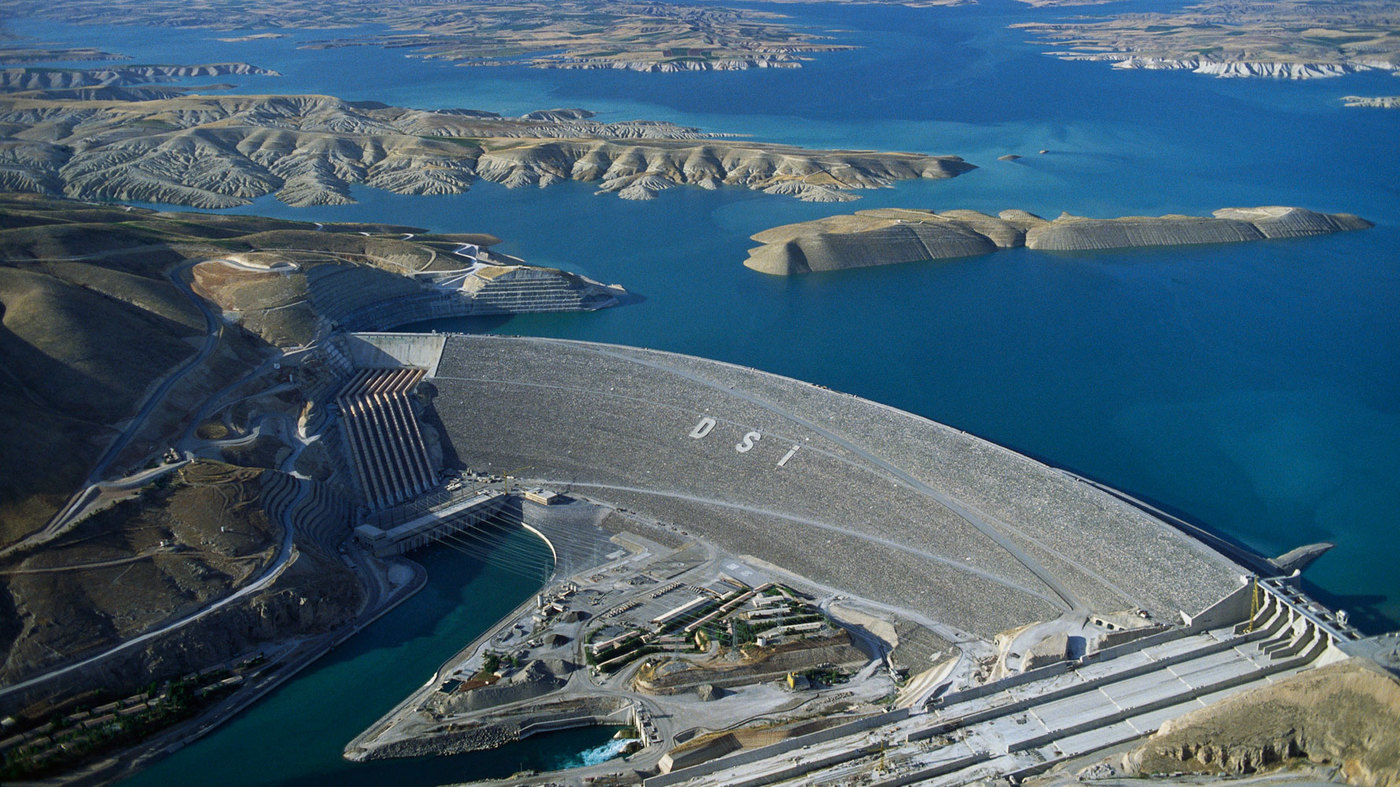



海达尔帕夏车站(土耳其语:Haydarpaşa Garı)是土耳其最大城市伊斯坦布尔的两个主要火车站之一,位于博斯普鲁斯海峡以东。始建于1872年,目前建筑1909年启用。
是伊斯坦布尔-安卡拉干线的西部终点站,也是巴格达铁路和希贾兹铁路的终点站。有火车渡轮横跨海峡到达欧洲一方的锡尔凯吉车站。
Der Bahnhof Haydarpaşa oder Bahnhof Haydarpascha, auch kurz Haydarpaşa genannt, ist der Hauptbahnhof Istanbuls für die asiatischen, östlichen Strecken.Der ehemalige Kopfbahnhof liegt auf der asiatischen Seite des Bosporus, innerhalb des Hafengeländes Haydarpaşa. Nördlich des Personenbahnhofes befindet sich der kombinierte Güter- und Hafenbahnhof. Der Bahnhof Haydarpaşa war eine Zwischenstation der Bosporusfähren Eminönü–Kadıköy und Karaköy-Kadıköy.
 Albania
Albania
 Bosnia Herzegovina
Bosnia Herzegovina
 Bulgaria
Bulgaria
 Greece
Greece
 Kosovo
Kosovo
 Croatia
Croatia
 Montenegro
Montenegro
 Nordmazedonien
Nordmazedonien
 Romania
Romania
 Serbia
Serbia
 Slovenia
Slovenia
 Turkey
Turkey
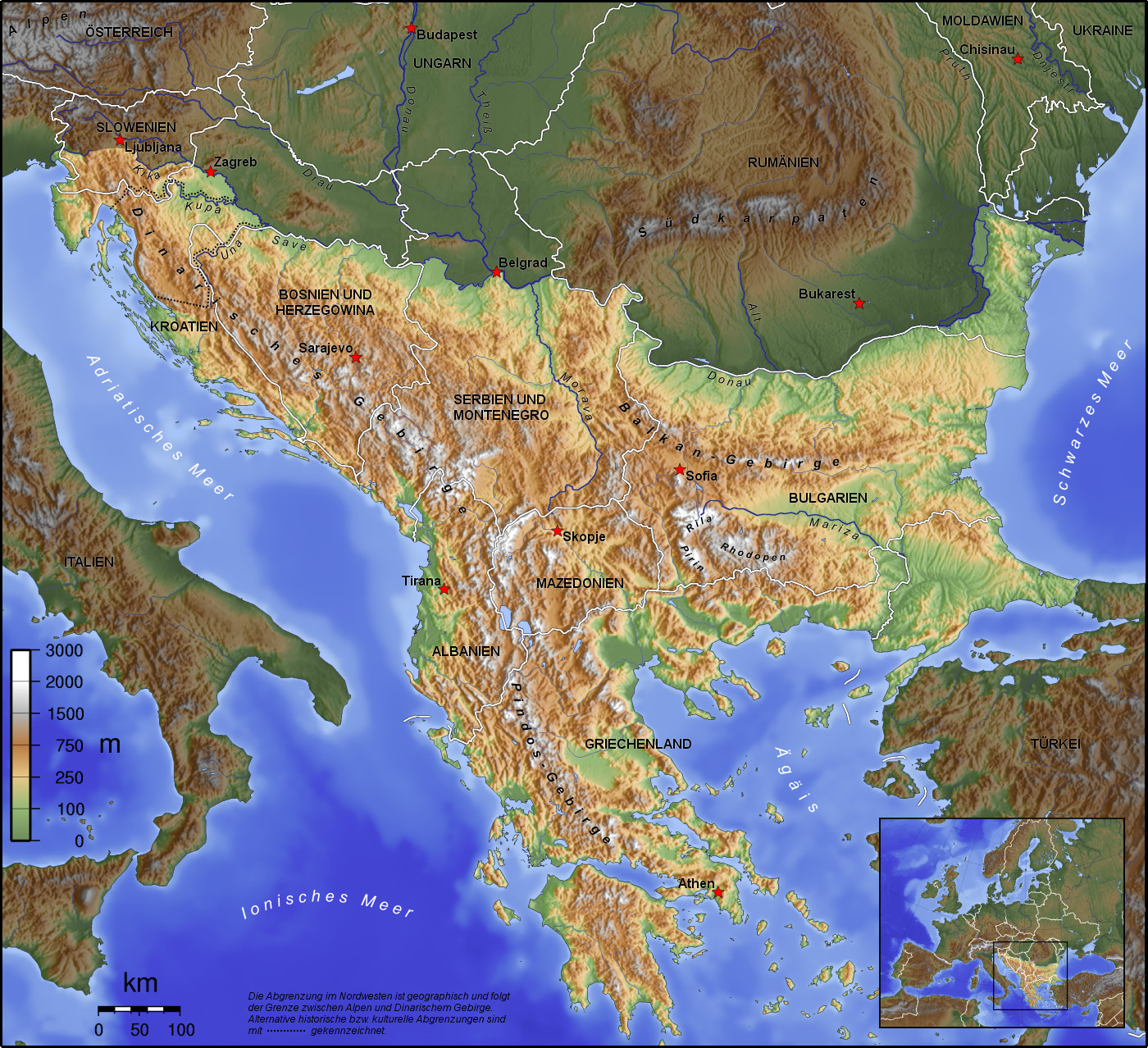
巴尔干半岛(Balkans),是一个地理名词,用以描述欧洲的东南隅位于亚得里亚海和黑海之间的陆地,详细的范围依照定义不同有许多种说法。该地约有55万平方公里和近5500万人口。在古希腊时代,巴尔干半岛被称为哈伊莫司半岛。该地区的名称来自于一条通过保加利亚中心到东塞尔维亚的巴尔干山脉。[1]
巴尔干地区向来存在诸多矛盾,其中既有宗教矛盾,也有领土争端。由于半岛的地缘政治重要性,由此而来的列强干涉致使这一地区的矛盾频繁被放大为战争,因此又有欧洲火药库之称。不过近年巴尔干半岛(南斯拉夫内战后至今)已实现停火与和平,只是偶然间在领土主权上有些纠纷,例如科索沃主权问题。第一次世界大战的触发点之——萨拉热窝事件亦是发生在巴尔干半岛上。
目前,巴尔干半岛共有11个国家,共有面积是47.6万平方公里,人口1.3亿。
南欧相邻地中海的三大半岛,从东向西分别为巴尔干半岛、意大利半岛(亚平宁半岛)、伊比利亚半岛。
半岛地处欧、亚、非三大陆之间,是欧、亚联系的陆桥,南临地中海重要航线,东有博斯普鲁斯海峡和达达尼尔海峡扼黑海的咽喉,地理位置极为重要。地形以山地为主,喀尔巴阡山以南多为山丘及石灰岩地形,以北多以为平原为主。半岛西部有迪纳拉-品都斯山脉,中东部有喀尔巴阡-老山(巴尔干)山脉。老山山脉是阿尔卑斯、喀尔巴阡山的延伸,经南斯拉夫东部,横贯保加利亚中部,直临黑海。东西两列山脉之间是古老的罗多彼山脉和马其顿山丛,最高峰穆萨拉峰,海拔2925米。半岛上平原分布零散,仅萨瓦河、多瑙河、马里查河谷较宽广。 巴尔干半岛位于欧洲东南部,三面被水环绕:西邻亚德里亚海、南面是地中海(包括爱奥尼亚海和爱琴海)和马尔马拉海、东边是黑海。其北部边界通常被定为多瑙河、萨瓦河和库帕河。[2] [3]巴尔干半岛包括49万平方公里土地。
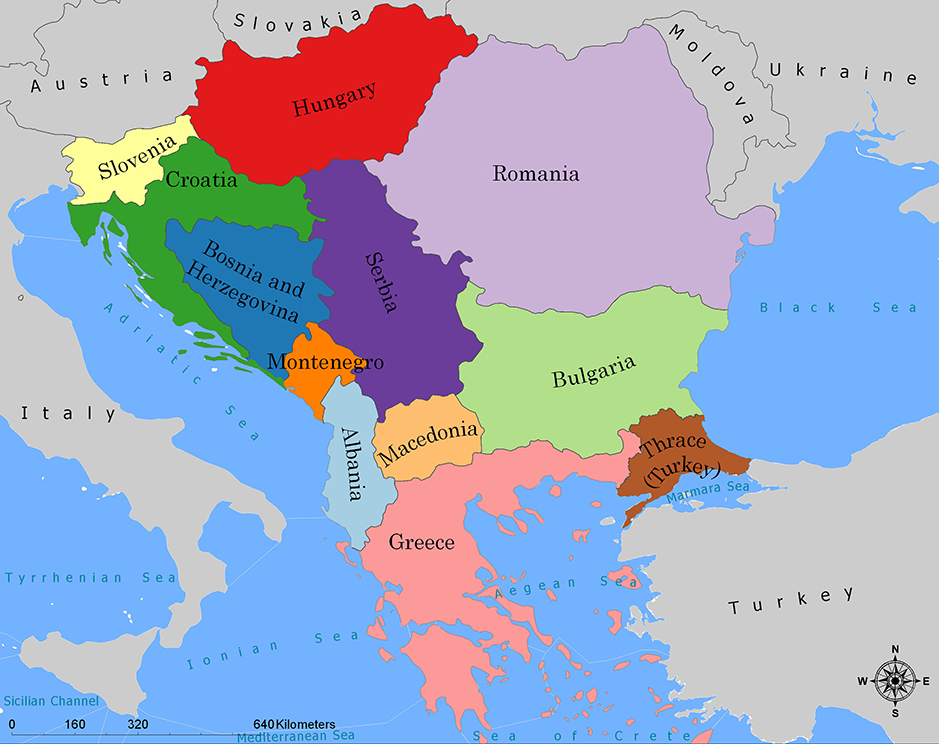
Die Balkanhalbinsel (auch kurz Balkan, oft synonym mit Südosteuropa verwendet) ist eine geographisch nicht eindeutig definierte Halbinsel im Südosten Europas. Sie ragt in das Mittelmeer und ist nach dem Balkangebirge benannt. Der größte Staat auf der Halbinsel ist Griechenland, gefolgt von Bulgarien (in dem sich der Großteil des Balkangebirges befindet), Serbien, Bosnien und Herzegowina, Albanien, Nordmazedonien, Montenegro und dem Kosovo. Die Staatsgebiete von Serbien, Kroatien, Rumänien, Slowenien und der Türkei, die durch ihre thrakischen Provinzen Anteil am Balkan hat, reichen über die Grenzen der Balkanhalbinsel hinaus.
Ungeachtet der Herleitung des geographischen Namens sind das dominierende Gebirge des Balkans die Dinariden im westlichen Teil der Halbinsel; ihr höchster Gipfel Jezerca (2694 m) liegt in Albanien. Die höchste Erhebung des Balkans ist der Gipfel Musala (2925 m) im Rila-Gebirge. Das Balkangebirge erreicht 2376 m maximale Gipfelhöhe.
バルカン半島(バルカンはんとう、Balkan Peninsula)、またはバルカン(Balkans)は東南ヨーロッパにある地理的領域であり、地理的・歴史的に様々な意味合いと定義付け[1][2]の下で使用される概念である[3]。名称はバルカン山脈からきている。この山脈はセルビアとブルガリアの国境から黒海沿岸まで、ブルガリア全土を横断している。バルカン半島は北西をアドリア海に、南西をイオニア海に、南と南東をエーゲ海に、そして東と北東を黒海によって区切られている[4]。北側の境界は論者と文脈によって様々に定義されていて不定である。バルカン半島の最高地点はリラ山地にあるムサラ山(2925メートル)である。
バルカン半島という概念はドイツの地理学者アウグスト・ツォイネによって1808年に創り出された[5][6]。彼はバルカン山脈がディナル・アルプス山脈と共にアドリア海から黒海まで東南ヨーロッパを区分していると誤認していた[5]。この地域はかつてオスマン帝国の属領であり、バルカン半島という用語は19世紀にはヨーロッパ・トルコ(European Turkey)の同義語であった[7]。バルカン半島という言葉は地理学的というよりもむしろ地政学的定義を持っており、この傾向は20世紀初頭にユーゴスラヴィア王国が成立するとさらに増した。バルカン半島を定義する自然境界が「半島」の学術的定義と一致していないため、現代の地理学者は「バルカン半島」という考え方を拒絶しており、通常はバルカンを「地域」として議論を行っている。この言葉には徐々に、特に1990年代以降、バルカニゼーション(バルカン化)のプロセスと関連して汚名と侮蔑的意味合いが与えられており[4][8]、それ故に東南ヨーロッパ(南東ヨーロッパ)という別の用語が使用されている。
The Balkans (/ˈbɔːlkənz/ BAWL-kənz), also known as the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographic area in Southeast Europe with various geographical and historical definitions.[2][3][4] The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throughout the whole of Bulgaria. The Balkan Peninsula is bordered by the Adriatic Sea in the northwest, the Ionian Sea in the southwest, the Aegean Sea in the south, the Turkish Straits in the east, and the Black Sea in the northeast. The northern border of the peninsula is variously defined.[5] The highest point of the Balkans is Mount Musala, 2,925 metres (9,596 ft), in the Rila mountain range, Bulgaria.
The concept of the Balkan Peninsula was created by the German geographer August Zeune in 1808,[6] who mistakenly considered the Balkan Mountains the dominant mountain system of Southeast Europe spanning from the Adriatic Sea to the Black Sea. The term Balkan Peninsula was a synonym for Rumelia in the 19th century, the European provinces of the Ottoman Empire. It had a geopolitical rather than a geographical definition, which was further promoted during the creation of the Kingdom of Yugoslavia in the early 20th century. The definition of the Balkan Peninsula's natural borders do not coincide with the technical definition of a peninsula; hence modern geographers reject the idea of a Balkan peninsula, while historical scholars usually discuss the Balkans as a region. The term has acquired a stigmatized and pejorative meaning related to the process of Balkanization,[5][7] and hence the preferred alternative term used for the region is Southeast Europe.
Les Balkans sont une des trois « péninsules » de l'Europe du Sud, mais cette appellation traditionnelle est parfois contestée en l'absence d'un isthme : les géographes préfèrent le terme de « région ». Elle est bordée par des mers sur trois côtés : la mer Adriatique et la mer Ionienne à l'ouest, la mer Égée au sud et la mer de Marmara et la mer Noire à l'est. Au nord, on la délimite généralement par les cours du Danube, de la Save et de la Kupa. Cette région couvre une aire totale de plus de 550 000 km2 et regroupe une population de près de 53 millions d’habitants.
La penisola balcanica, nota anche come Balcani (dalla forma abbreviata di Monti Balcani, sistema montuoso tra Bulgaria e Serbia; dal turco balkan ‘monteʼ[2]), è una penisola dell'Europa orientale; è delimitata a ovest dal mare Adriatico, a sud-ovest dal mar Ionio, a est dal mar Nero, a sud-est dal mar di Marmara, e a sud dal mar Egeo.
Come spesso accade per le penisole, incerta è la definizione del suo confine sulla terraferma, aggravato dal fatto che si tratta di uno dei suoi confini più estesi. Non aiuta inoltre la definizione di questa linea di demarcazione il fatto che il territorio presenta al suo interno grandi differenze e frammentazioni per storia, nazionalità, lingua, cultura e religione delle popolazioni che vi abitano.
Solitamente se ne stabilisce il confine sul Danubio e sul suo affluente Sava. In questo modo si include in tale area anche parte della Slovenia e della Romania (paese di lingua romanza orientale), che però storicamente hanno avuto a che fare con i Balcani solo dopo la dissoluzione dell'Impero asburgico. Secondo il geografo Vittorio Vialli, la delimitazione a nord è rappresentata dalla linea geografica Istria-Odessa. Esclude dalla regione la Slovenia l'interpretazione del confine che include il fiume Kupa, facendolo partire dalla città di Fiume e raggiungendo le foci del Danubio.[3] In tal modo confina a ovest con la cosiddetta regione geografica italiana,[4][5] che include anche territori non facenti parte della Repubblica Italiana. La definizione politica di Balcani venne in uso nel XIX secolo per designare i paesi europei interessati dall'espansione e dalla successiva dissoluzione dell'Impero ottomano.[6]
Del resto le caratteristiche del territorio, solcato da catene montuose parallele che ostacolarono il movimento in direzione nord-sud e una colonizzazione uniforme già ai tempi dell'espansione greco-romana, e la sua stessa collocazione geografica contribuiscono a spiegare le tormentate vicende storiche che hanno caratterizzato la penisola.[7]
Fino al 1975 la penisola era attraversata dal Balkan Express, un treno con partenza da Vienna e arrivo a Istanbul. Il clima è continentale nel nord e nell’est del territorio (con estati calde e inverni molto rigidi), mentre l’area occidentale e la Grecia hanno un clima mediterraneo.
La península balcánica o península de los Balcanes es una de las tres grandes penínsulas del sur de Europa, continente al que está unida por los montes Balcanes al este (cordilleras que han dado nombre a la península) y los Alpes Dináricos, al oeste.
Балка́нский полуо́стров (хорв. Balkanski poluotok, словен. Balkanski polotok, серб. Балканско полуострво, рум. Peninsula Balcanică, болг. и макед. Балкански полуостров, алб. Gadishulli Ballkanik, греч. Βαλκανική χερσόνησος, тур. Balkan Yarımadası, босн. Balkansko poluostrvo, черног. Balkansko poluostrvo) расположен на юго-востоке Европы. Площадь — около 467 тыс. км².
С юга, юго-запада и юго-востока омывается: Адриатическим, Ионическим, Мраморным, Критским, Эгейским и Чёрным морями.
Северной границей полуострова считается условная линия, проведённая от устья Дуная, по рекам Дунай, Сава и Купа (Колпа), а от истока последней в Горском Котаре (Хорватия) — до залива Кварнер с портом Риека (Хорватия).
Рельеф преимущественно гористый (Стара-Планина, Родопы, Динарское нагорье, Пинд). По размерам в Европе уступает только Скандинавскому и Пиренейскому полуостровам.
 Albania
Albania
 Bosnia Herzegovina
Bosnia Herzegovina
 Bulgaria
Bulgaria
 Greece
Greece
 Kosovo
Kosovo
 Croatia
Croatia
 Montenegro
Montenegro
 Nordmazedonien
Nordmazedonien
 Romania
Romania
 Serbia
Serbia
 Slovenia
Slovenia
 Turkey
Turkey


 Sport
Sport
 (F)UEFA Champions League
(F)UEFA Champions League
 Turkey
Turkey
 UEFA Champions League 2016/17
UEFA Champions League 2016/17
 Group B
Group B
 UEFA Champions League 2017/18
UEFA Champions League 2017/18
 Group G
Group G
 UEFA Europa League 2018/19
UEFA Europa League 2018/19
 Group I
Group I
 UEFA Europa League 2019/20
UEFA Europa League 2019/20
 Group K
Group K
 Vicente del Bosque
Vicente del Bosque

 Performing Arts
Performing Arts
 Music
Music
 Party and government
Party and government
 Architecture
Architecture
 Energy resource
Energy resource


 Automobile
Automobile
 Exhibition
Exhibition
 Geography
Geography
 Agriculture, forestry, livestock, fishing
Agriculture, forestry, livestock, fishing
 Companies
Companies