
Deutsch-Chinesische Enzyklopädie, 德汉百科
 新西兰
新西兰

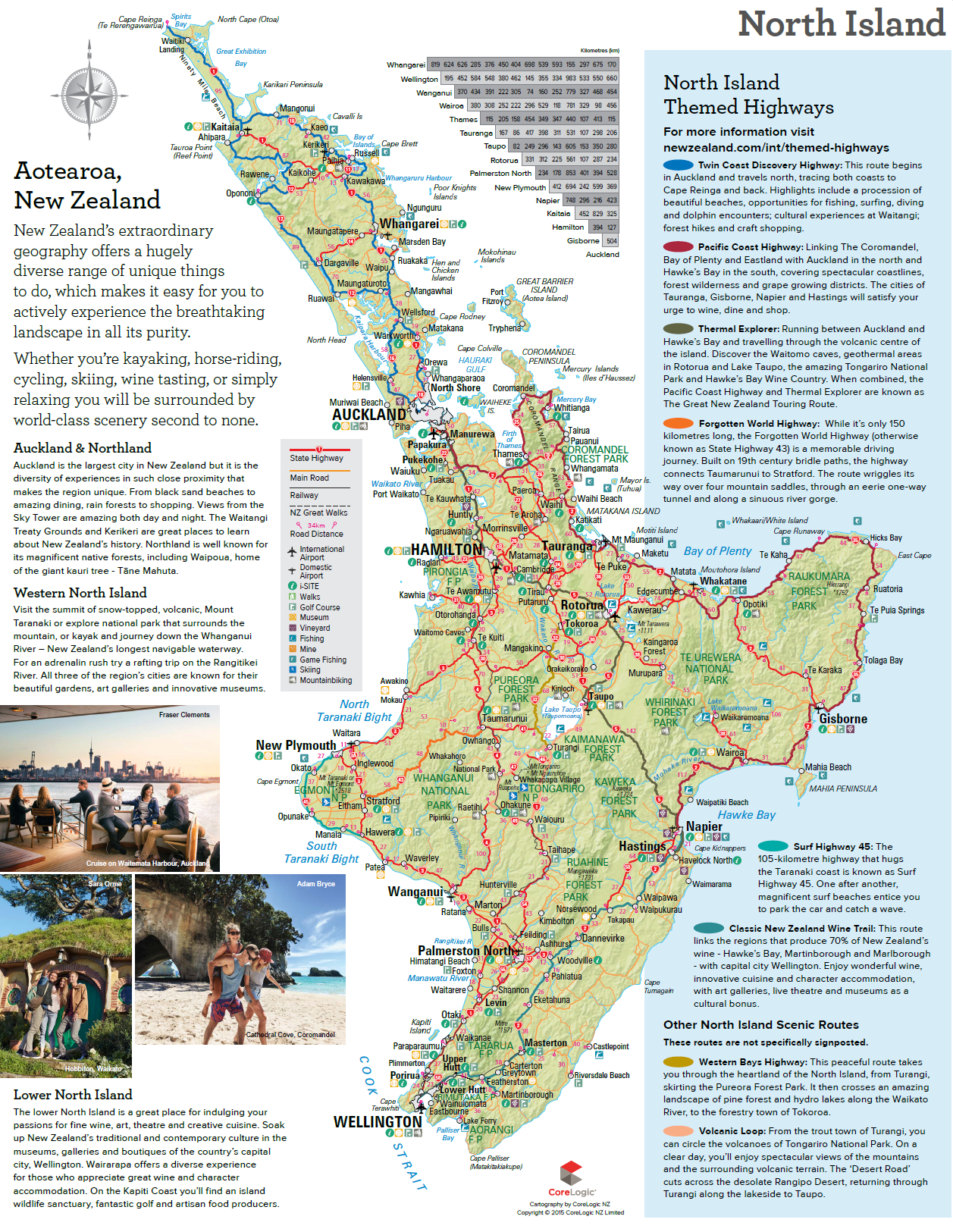
新西兰分为南岛与北岛两大岛屿,南岛寒冷,北岛较为炎热,温差再春夏季则约有十度以上,两岛葡萄采收期大约从每年的二月一直延续到六月才能全部完成。过度充沛的雨水,是葡萄生长期最常遇到的主要问题之一,雨水稀释葡萄内含糖份,多少影响到葡萄含糖量与成熟度。
重要的产区有霍克斯湾(Hawkes)、奥克兰(Auckland)、吉斯伯恩(Gisborne)、万宝龙(Marlborough)四大产区。虽 然新西兰出产的红葡萄酒品质不差,但白葡萄酒还是占了全国产量的90%,在南岛万宝龙区出产白沙威浓葡萄酒(Sauvignon Blanc)更以香味丰富浓郁、雅致清新闻名世界。
新西兰拥有500余家葡萄酒厂,分布在十大葡萄酒主要产区,即北地、奥克兰、怀卡托/丰盛湾、吉斯本、霍克斯湾、怀拉拉帕、马尔堡、尼尔森、坎特伯雷和中奥塔哥。新西兰的葡萄生产区域达24,000公顷。
葡萄酒是新西兰出口额增长最快的行业之一。澳大利亚、英国、美国、加拿大、荷兰、中国大陆、中国香港、爱尔兰、新加坡和瑞典是新西兰葡萄酒的十大出口市场。中国也是是亚洲地区新西兰葡萄酒最大的出口场。(Quelle:http://www.wines-info.com) 澳大利亚
澳大利亚
 比利时
比利时
 智利
智利
 丹麦
丹麦
 联邦德国
联邦德国
 爱沙尼亚
爱沙尼亚
 芬兰
芬兰
 法国
法国
 希腊
希腊
 爱尔兰
爱尔兰
 冰岛
冰岛
 以色列
以色列
 意大利
意大利
 日本
日本
 加拿大
加拿大
 卢森堡
卢森堡
 墨西哥
墨西哥
 新西兰
新西兰
 荷兰
荷兰
 挪威
挪威
 经济合作与发展组织
经济合作与发展组织
 埃米尔·范伦内普
埃米尔·范伦内普
 经济合作与发展组织
经济合作与发展组织
 唐纳德·约翰顿
唐纳德·约翰顿
 经济合作与发展组织
经济合作与发展组织
 让·克劳德·帕耶
让·克劳德·帕耶
 经济合作与发展组织
经济合作与发展组织
 何塞·安赫尔·古里亚
何塞·安赫尔·古里亚
 经济合作与发展组织
经济合作与发展组织
 斯塔凡·索尔曼
斯塔凡·索尔曼
 经济合作与发展组织
经济合作与发展组织
 托尔基·克里斯藤森
托尔基·克里斯藤森
 奥地利
奥地利
 波兰
波兰
 葡萄牙
葡萄牙
 韩国
韩国
 瑞典
瑞典
 瑞士
瑞士
 斯洛伐克
斯洛伐克
 斯洛文尼亚
斯洛文尼亚
 西班牙
西班牙
 捷克
捷克
 土耳其
土耳其
 匈牙利
匈牙利
 美国
美国
 英国
英国

 重要的国际组织
重要的国际组织

経済協力開発機構(けいざいきょうりょくかいはつきこう)は、国際経済全般について協議することを目的とした国際機関。公用語の正式名称は、英語では"Organisation[1] for Economic Co-operation and Development"(イギリス英語表記)、フランス語では"Organisation de Coopération et de Développement Economiques"。略称は英語ではOECD、フランス語ではOCDE。
本部事務局はパリ16区の旧ラ・ミュエット宮殿に置かれている。事務総長はアンヘル・グリア。
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD; French: Organisation de Coopération et de Développement Économiques, OCDE) is an intergovernmental economic organisation with 37 member countries,[1] founded in 1961 to stimulate economic progress and world trade. It is a forum of countries describing themselves as committed to democracy and the market economy, providing a platform to compare policy experiences, seek answers to common problems, identify good practices and coordinate domestic and international policies of its members. Generally, OECD members are high-income economies with a very high Human Development Index (HDI) and are regarded as developed countries. As of 2017, the OECD member countries collectively comprised 62.2% of global nominal GDP (US$49.6 trillion)[3] and 42.8% of global GDP (Int$54.2 trillion) at purchasing power parity.[4] The OECD is an official United Nations observer.[5]
In 1948, the OECD originated as the Organisation for European Economic Co-operation (OEEC),[6] led by Robert Marjolin of France, to help administer the Marshall Plan (which was rejected by the Soviet Union and its satellite states).[7] This would be achieved by allocating United States financial aid and implementing economic programs for the reconstruction of Europe after World War II. (Similar reconstruction aid was sent to the war-torn Republic of China and post-war Korea, but not under the name "Marshall Plan".)[8]
In 1961, the OEEC was reformed into the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development by the Convention on the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development and membership was extended to non-European states.[9][10] The OECD's headquarters are at the Château de la Muette in Paris, France.[11] The OECD is funded by contributions from member countries at varying rates and had a total budget of €386 million in 2019.[2]
Although OECD does not have a power to enforce its decisions, which further require unanimous vote from its members, it is recognized as highly influential publisher of mostly economic data through publications as well as annual evaluations and rankings of members countries.[12]
L'Organisation de coopération et de développement économiques (OCDE) est une organisation internationale d'études économiques, dont les pays membres — des pays développés pour la plupart — ont en commun un système de gouvernement démocratique et une économie de marché. Elle joue essentiellement un rôle d'assemblée consultative1.
L'OCDE a succédé à l'Organisation européenne de coopération économique (OECE) issue du plan Marshall et de la Conférence des Seize (Conférence de coopération économique européenne) qui a existé de 1948 à 1960. Son but était l'établissement d'une organisation permanente chargée en premier lieu d'assurer la mise en œuvre du programme de relèvement commun (le plan Marshall), et, en particulier, d'en superviser la répartition2.
En 2020, l'OCDE compte 37 pays membres et regroupe plusieurs centaines d'experts. Elle publie fréquemment des études économiques et sociales — analyses, prévisions et recommandations de politique économique — et des statistiques, principalement concernant ses pays membres.
Le siège de l'OCDE se situe à Paris (16e), au château de la Muette. L'organisation possède également des bureaux dans plusieurs autres métropoles, notamment à Berlin, Mexico, Tokyo et Washington.
L'Organizzazione per la cooperazione e lo sviluppo economico (OCSE) – in inglese Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), e in francese Organisation de coopération et de développement économiques (OCDE) – è un'organizzazione internazionale di studi economici per i paesi membri, paesi sviluppati aventi in comune un'economia di mercato.
L'organizzazione svolge prevalentemente un ruolo di assemblea consultiva che consente un'occasione di confronto delle esperienze politiche, per la risoluzione dei problemi comuni, l'identificazione di pratiche commerciali e il coordinamento delle politiche locali e internazionali dei paesi membri[1]. Ha sede a Parigi nello Château de la Muette[2].
Gli ultimi paesi ad aver aderito all'OCSE sono la Colombia (28 aprile 2020),la Lettonia (1º luglio 2016) e la Lituania (5 luglio 2018), per un totale di 36 paesi membri.
La Organización para la Cooperación y el Desarrollo Económico1 (OCDE) es un organismo de cooperación internacional, compuesto por 37 estados,34 cuyo objetivo es coordinar sus políticas económicas y sociales. La OCDE fue fundada en 1961 y su sede central se encuentra en el Château de la Muette en París (Francia). Los idiomas oficiales de la entidad son el francés y el inglés.2
En la OCDE, los representantes de los países miembros se reúnen para intercambiar información y armonizar políticas con el objetivo de maximizar su crecimiento económico y colaborar a su desarrollo y al de los países no miembros.
Conocida como «club de los países ricos»,56 a partir de 2017, sus países miembros comprendieron colectivamente el 62,2 % del PIB nominal global (US$49,6 billones) y el 42,8 % del PIB global (Int US$54,2 billones).7
Организа́ция экономи́ческого сотру́дничества и разви́тия (сокр. ОЭСР, англ. Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development, OECD) — международная экономическая организация развитых стран, признающих принципы представительной демократии и свободной рыночной экономики.
Создана в 1948 году под названием Организа́ция европе́йского экономи́ческого сотру́дничества (англ. Organisation for European Economic Co-operation, OEEC) для координации проектов экономической реконструкции Европы в рамках плана Маршалла.
Штаб-квартира организации располагается в Шато де ла Мюетт, в Париже. Генеральный секретарь (с 2006 года) — Хосе Анхель Гурриа Тревиньо (Мексика). Руководящим органом ОЭСР является совет представителей стран — членов организации. Все решения в нём принимаются на основе консенсуса.
По данным на 2011 год, в странах ОЭСР проживало 18 % населения мира[2].

The Professional Bull Riders, Inc. (PBR) is an international professional bull riding organization based in Pueblo, Colorado, United States. In the U.S., PBR events have been televised on CBS and CBS Sports Network since 2012. In 2013, the PBR and CBS signed a contract that extended CBS Sport's partnership with PBR, making them the primary sports broadcaster for PBR.[1][2] In 2018, the PBR launched RidePass; its own subscription-based video on demand service that live-streams PBR events, as well as PBR-produced events for other western sport organizations. On July 20, 2021, RidePass switched from a subscription-based streaming service to a free, ad-supported streaming channel on Pluto TV.[3][4] More than 500 cowboys from the United States, Canada, Mexico, Brazil, Australia and other countries hold PBR memberships.
职业骑牛大赛(英语:Professional Bull Riders)是一项由职业骑牛大赛公司所组织的国际化体育赛事。此项赛事起源于1992年,比赛的主要内容是让骑手骑在一头暴躁的公牛身上尽可能长的时间,评委会综合时间及技巧进行打分。
 美食家
美食家
 农业、林业、畜牧业、渔业
农业、林业、畜牧业、渔业
 建筑艺术
建筑艺术

 体育
体育

 政党和政府组织
政党和政府组织


 地理
地理


 经济和贸易
经济和贸易
 手拉手
手拉手

 生活时尚
生活时尚
