
Deutsch-Chinesische Enzyklopädie, 德汉百科
 Louisiana-LA
Louisiana-LA


Das Air Force Global Strike Command (AFGSC; deutsch Luftwaffenkommando für weltweite Luftangriffsoperationen, im Rahmen teilstreitkräfteübergreifender Operationen als Air Forces Strategic – Air, kurz AFSTRAT, bezeichnet) ist ein Hauptkommando der United States Air Force (USAF), mit Hauptquartier auf der Barksdale Air Force Base, Louisiana, USA. Es ist für den im Rahmen der United Air Force organisierten Teil der US-Atomstreitkräfte zuständig und führt zudem über die Eight Air Force die strategische Bomberflotte und über die Twentieth Air Force die Interkontinentalraketen der Vereinigten Staaten. In der Zielstruktur beträgt der Personalbestand 23.000 Personen.
空军全球打击司令部(Air Force Global Strike Command,AFGSC)[1] , 是美国空军的一个一级司令部,负责空军的战略武器,包括核武、战略导弹、战略轰炸机等,在2009年8月本司令部成立之前,这些战略武器分属于美国空军太空司令部和美国空军空战司令部,分别于2009年12月和2010年2月移交到本司令部[2]。 成立空军全球打击司令部是2007年美国空军核武事件调查中列出的建议之一[3]。2015年,全球打击司令部正式升格为四星上将担任司令的司令部,而相应,空军教育训练司令部降格为由三星中将担任司令。



Heimspielbetrieb New Orleans Saints (NFL, seit 1975) Tulane Green Wave (NCAA-College-Football, seit 1975) New Orleans Jazz (NBA, 1975–1979) New Orleans Breakers (USFL, 1984) Veranstaltungen Sugar Bowl (NCAA, seit 1975) Super Bowl XII (1978) Super Bowl XV (1981) Super Bowl XX (1986) Super Bowl XXIV (1990) Super Bowl XXXI (1997) Super Bowl XXXVI (2002) Super Bowl XLVII (2013) WrestleMania XXX (2014) WrestleMania 34 (2018) Final Four der NCAA Division I Basketball Championship 1982, 1987, 1993, 2002, 2012 Konzerte Ausstellungen Messen





 Alabama-AL
Alabama-AL
 Cuba
Cuba

 Florida-FL
Florida-FL

 Louisiana-LA
Louisiana-LA
 Mexico
Mexico
 Mississippi River
Mississippi River

 Mississippi-MS
Mississippi-MS

 Texas-TX
Texas-TX
 United States
United States
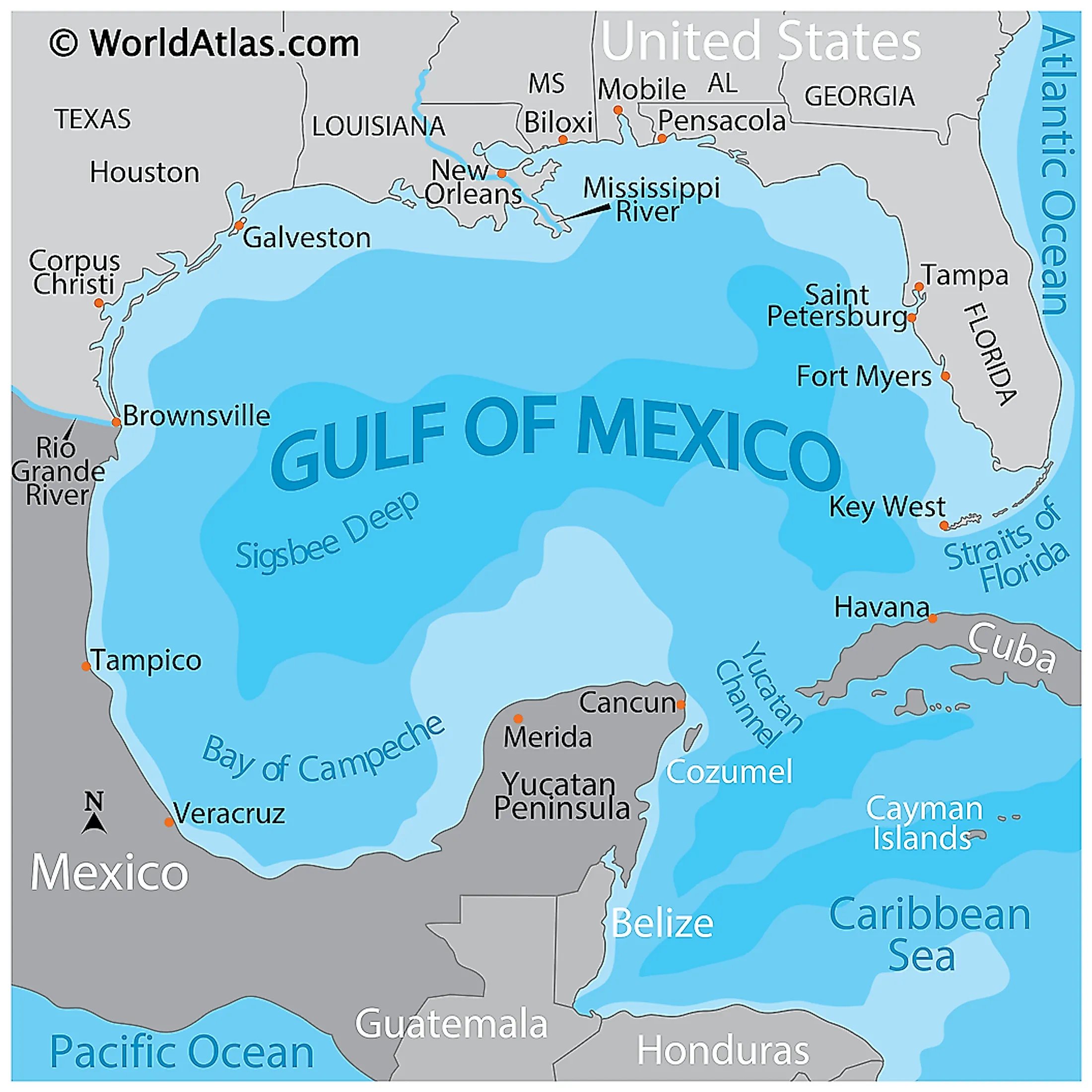
墨西哥湾是北美洲南部大西洋的一海湾,以佛罗里达半岛-古巴-犹加敦半岛一线与外海分割。北为美国,南、西为墨西哥,东南为古巴,东经佛罗里达海峡与大西洋相连,经尤卡坦海峡与加勒比海相接,是著名的墨西哥湾暖流的起点。墨西哥湾形成于3亿年前的地球板块运动。[1]
Der Golf von Mexiko (englisch Gulf of Mexico, spanisch Golfo de México; veraltet: Meerbusen von Mexiko[1]) ist eine nahezu vollständig von Nordamerika eingeschlossene Meeresbucht. Der Golf ist ein Randmeer des Atlantischen Ozeans und der nordwestliche Teil des Amerikanischen Mittelmeers.
湾の東部、北部、および北西部の海岸線はアメリカ合衆国(フロリダ州、アラバマ州、ミシシッピ州、ルイジアナ州、テキサス州)に接し、南西部と南部の海岸線はメキシコ(タマウリパス州、ベラクルス州、タバスコ州、カンペーチェ州、ユカタン州およびキンタナ・ロー州)に接している。また南東部はキューバとの海岸線をもつ。
アメリカとキューバの間にあるフロリダ海峡を経て大西洋に通じており、メキシコとキューバの間にあるユカタン海峡を経てカリブ海へと通じている。支湾として北東部にアパラチー湾、南西部にカンペチェ湾などがある。
メキシコ湾は東西の幅が約1,500km、総面積は約160万 km²で、南の3分の1は熱帯に入る。最大水深はSigsbee Deepでの4,384m。二大海流として黒潮と共に知られるメキシコ湾流はここを起源とし、巨大ハリケーンが頻繁に訪れることでも有名である。
The Gulf of Mexico (Spanish: Golfo de México) is an ocean basin and a marginal sea of the Atlantic Ocean,[1] largely surrounded by the North American continent.[2] It is bounded on the northeast, north and northwest by the Gulf Coast of the United States, on the southwest and south by the Mexican states of Tamaulipas, Veracruz, Tabasco, Campeche, Yucatan, and Quintana Roo, and on the southeast by Cuba. The US states of Texas, Louisiana, Mississippi, Alabama, and Florida border the Gulf on the north, which are often referred to as the "Third Coast", in comparison with the U.S. Atlantic and Pacific coasts.
The Gulf of Mexico formed approximately 300 million years ago as a result of plate tectonics.[3] The Gulf of Mexico basin is roughly oval and is approximately 810 nautical miles (1,500 km; 930 mi) wide and floored by sedimentary rocks and recent sediments. It is connected to part of the Atlantic Ocean through the Florida Straits between the U.S. and Cuba, and with the Caribbean Sea via the Yucatán Channel between Mexico and Cuba. With the narrow connection to the Atlantic, the Gulf experiences very small tidal ranges. The size of the Gulf basin is approximately 1.6 million km2 (615,000 sq mi). Almost half of the basin is shallow continental shelf waters. The basin contains a volume of roughly 2,500 quadrillion liters (550 quadrillion Imperial gallons, 660 quadrillion US gallons, 2.5 million km3 or 600,000 cu mi).[4] The Gulf of Mexico is one of the most important offshore petroleum production regions in the world, comprising one-sixth of the United States' total production.[5]
Le golfe du Mexique est un golfe de l'océan Atlantique, situé au sud-sud-est de l'Amérique du Nord. Il s'étend sur une superficie de 1 550 000 km2. Il baigne la péninsule de Floride, la Louisiane , le Sud-Est du Texas, la côte orientale du Mexique et une partie du littoral nord de Cuba.
Il golfo del Messico è uno dei golfi più grandi del mondo[1], situato nell'Oceano Atlantico, tra la costa dell'America settentrionale e centrale ad ovest e il mar dei Caraibi ad est.
Situato a Sud degli Stati Uniti e a Nord del Messico, e delimitato da due grandi penisole, lo Yucatán e la Florida, rispettivamente in Messico e negli Stati Uniti, comprende i litorali di undici stati: Florida, Alabama, Mississippi, Louisiana e Texas (per gli Stati Uniti) e Tamaulipas, Veracruz, Tabasco, Campeche, Yucatán e Quintana Roo (per gli Stati del Messico). Sul golfo si affaccia anche lo Stato di Cuba ed è collegato ad est al Mar dei Caraibi.
L'ampia sezione del golfo compresa tra la penisola dello Yucatán e la costa messicana assume la denominazione di baia di Campeche, mentre insieme al Mar dei Caraibi, forma il Mediterraneo Americano, espressione non riportata normalmente nelle carte, ma usata in oceanografia, geologia e biologia marina[2]. In esso viene generata la famosa Corrente del Golfo che rende abitabili la maggior parte delle coste atlantiche dell'Europa ed è inoltre luogo di formazione e transito di cicloni tropicali che qui prendono il nome di uragani a partire da tempeste tropicali che impattano poi sovente sulla costa messicana e statunitense o sulle isole caraibiche.
El golfo de México es una cuenca oceánica contenida entre los litorales de México, Estados Unidos y Cuba. Los estados mexicanos que tienen costa en este golfo son: Tamaulipas, Veracruz, Tabasco, Campeche, Yucatán; los estadounidenses son: Florida, Alabama, Misisipi, Luisiana y Texas. La península de Florida y la isla de Cuba ocupan la parte oriental del golfo, donde se encuentra la salida de este hacia el océano Atlántico, en tanto que la península de Yucatán, también al oriente, separa al golfo del mar Caribe.1
Мексика́нский зали́в (исп. Golfo de México, англ. Gulf of Mexico, фр. Golfe de Mexique) — внутреннее море западной части Атлантического океана. Ограничен с северо-запада, севера и востока побережьем США (штаты Флорида, Алабама, Миссисипи, Луизиана и Техас), на юге и юго-западе — побережьем Мексики (штаты Тамаулипас, Веракрус, Табаско, Кампече, Юкатан), а также островом Кубой[1]. Внешне напоминает овал. Площадь залива — 1543 тыс. км², объём воды — около 2332 тыс. км³[2]. Энергия вод, которые сильно нагреваются в летний период, служит основой для формирования сильных тропических штормов и мощных ураганов, крупнейшие из которых (Катрина, Густав, Иван и др.) практически ежегодно приводят к разрушительным последствиям в прибрежных регионах залива. Имеет важное хозяйственное значение для государств, омываемых им. Является одним из самых тёплых водоёмов в мире[3].
Мексиканский залив образовался примерно 300 миллионов лет назад в результате тектоники литосферных плит[4]. Поверхность залива по форме напоминает овал шириной около 1,5 тысяч километров. Дно залива составлено из осадочных пород и недавних отложений. Сообщается с Атлантическим океаном через Флоридский пролив между США и Кубой, и с Карибским морем через Юкатанский пролив между Кубой и Мексикой. Мексиканский залив и Карибское море иногда объединяют под названием Американское Средиземное море. Из-за слабой связи с Атлантическим океаном, залив испытывает лишь небольшие приливы и отливы. Площадь залива составляет 1,5—1,6 млн км², около половины составляют континентальные шельфовые воды. Объём воды в заливе оценивается в 2.5 миллиона кубических километров[3].

 Alabama-AL
Alabama-AL
 Alaska-AK
Alaska-AK
 Arizona-AZ
Arizona-AZ

 Arkansas-AR
Arkansas-AR

 Education and Research
Education and Research
 Universities and colleges in the United States of America
Universities and colleges in the United States of America

 California-CA
California-CA

 Colorado-CO
Colorado-CO

 Connecticut-CT
Connecticut-CT

 Delaware-DE
Delaware-DE

 Florida-FL
Florida-FL

 Georgia-GA
Georgia-GA

 Hawaii-HI
Hawaii-HI

 Idaho-ID
Idaho-ID

 Illinois-IL
Illinois-IL

 Indiana-IN
Indiana-IN

 Iowa-IA
Iowa-IA

 Kansas-KS
Kansas-KS

 Kentucky-KY
Kentucky-KY

 Louisiana-LA
Louisiana-LA

 Maine-ME
Maine-ME

 Maryland-MD
Maryland-MD

 Massachusetts-MA
Massachusetts-MA

 Michigan-MI
Michigan-MI

 Minnesota-MN
Minnesota-MN

 Mississippi-MS
Mississippi-MS

 Missouri-MO
Missouri-MO

 Montana-MT
Montana-MT

 Nebraska-NE
Nebraska-NE

 Nevada-NV
Nevada-NV

 New hampshire-NH
New hampshire-NH

 New jersey-NJ
New jersey-NJ
 New mexico-NM
New mexico-NM

 New York-NY
New York-NY

 North Carolina-NC
North Carolina-NC

 North Dakota-ND
North Dakota-ND

 Ohio-OH
Ohio-OH

 Oklahoma-OK
Oklahoma-OK

 Oregon-OR
Oregon-OR

 Pennsylvania-PA
Pennsylvania-PA

 Rhode Island-RI
Rhode Island-RI
 South Carolina-SC
South Carolina-SC

 South Dakota-SD
South Dakota-SD

 Tennessee-TN
Tennessee-TN

 Texas-TX
Texas-TX

 Universities in the USA
Universities in the USA

 Utah-UT
Utah-UT
 United States
United States

 Vermont-VT
Vermont-VT

 Virginia-VA
Virginia-VA

 Washington-WA
Washington-WA

 Washington, D.C.
Washington, D.C.

 West Virginia-WV
West Virginia-WV

 Wisconsin-WI
Wisconsin-WI

 Wyoming-WY
Wyoming-WY






 Military, defense and equipment
Military, defense and equipment
 Energy resource
Energy resource
 International cities
International cities
 Architecture
Architecture
 Sport
Sport
 Companies
Companies
 Exhibition
Exhibition
 Geography
Geography