
漢德百科全書 | 汉德百科全书
 Aerospace
Aerospace



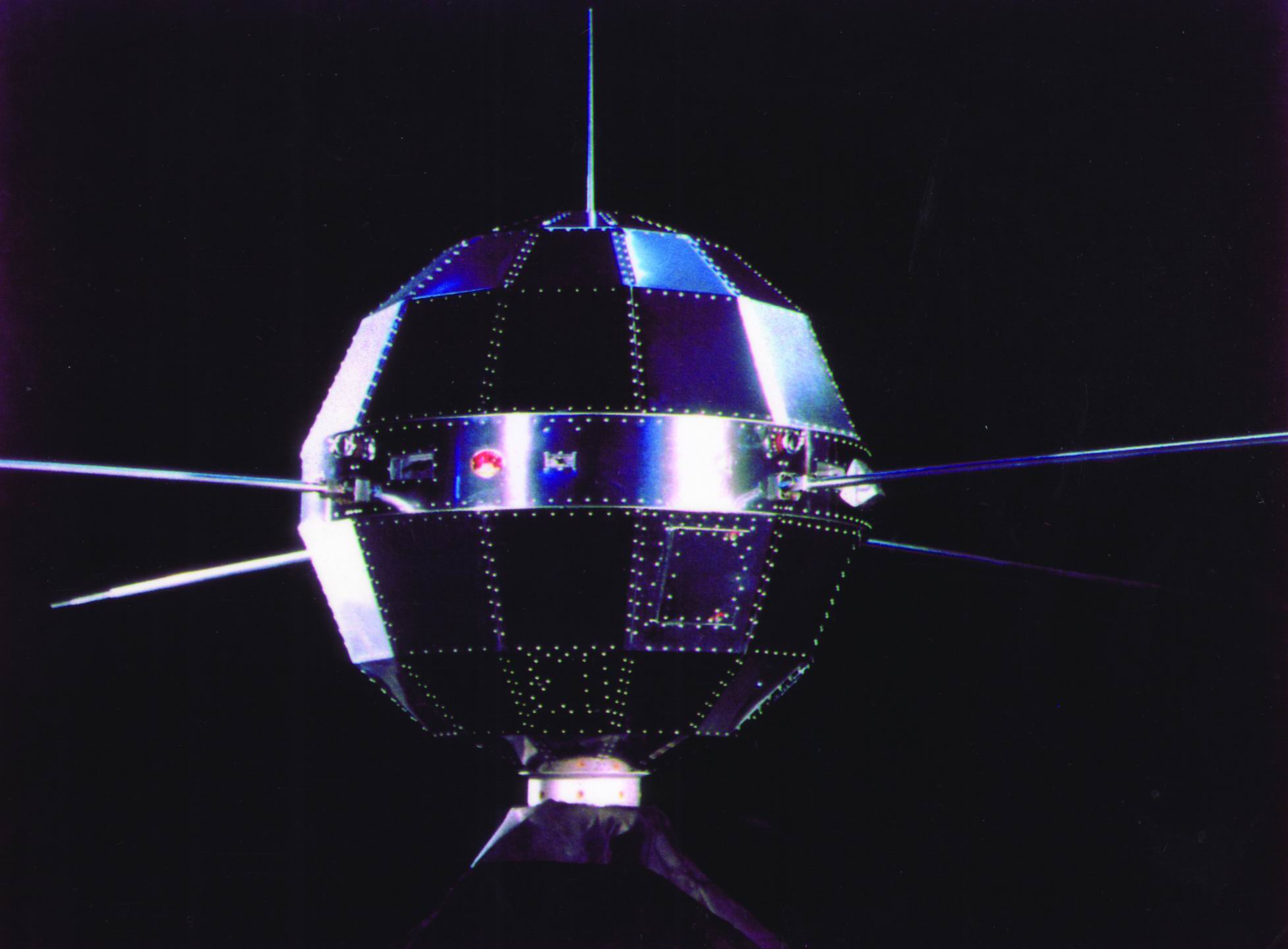
“东方红一号”(国际卫星标识符: 1970-034A)是中华人民共和国于1970年4月24日在酒泉卫星发射中心由长征一号运载火箭发射升空的一颗人造地球卫星[1][2],同时也是东方红人造卫星系列的首颗卫星[3][4]。该人造卫星与中国1964年的第一颗原子弹(596原子弹)、1966年的第一颗装载核弹头导弹、1967年的第一颗氢弹并称为“两弹一星”[5][6],是中国在1960-1970年代在国防科技领域的取得的一项重大成就[6][7]。
中国大陆于1958年提出研发人造卫星,同年酒泉发射中心亦开始筹建,1960年前获得了苏联方面一定的援助[1][8][9]。但由于技术困难等原因,卫星的研制于1965年才正式立项,此后还遭遇了文化大革命、中苏军事对峙及冲突等重大事件的冲击[1][10][11][12][13]。1970年东方红一号卫星最终研制成功,并在酒泉发射成功,标志着中华人民共和国成为世界上继苏联、美国、法国和日本之后第五个能够独立发射人造卫星的国家[14][15][16]。该卫星的重量大于前四个国家首颗卫星重量的总和[15][16],至今仍在轨道上运行[3][17]。
Dong Fang Hong I (chinesisch 東方紅一號 / 东方红一号, Pinyin Dōngfāng Hóng Yīhào), auch bekannt als „China 1“, war der erste chinesische Erdsatellit. Er wurde am 24. April 1970 um 13:35 Uhr UTC mit einer Trägerrakete des Typs Langer Marsch 1 gestartet[2] und war Teil des Dong-Fang-Hong-Satellitenprogramms, damals nach dem Beginn im Januar 1965 noch „Projekt 651“ genannt.







Die russische Raumfahrtbehörde Roskosmos (russ. Роскосмос, frühere Namen: RKA (Rossijskoje Kosmitscheskoje Agenstwo), RAKA (Rossiiskoje Awiazionno-Koswitscheskoje Agenstwo), Rosaviakosmos) hat ihren Sitz nahe Moskau im Sternenstädtchen. Die Agentur wurde 1992 nach der Auflösung der Sowjetunion und Gründung der russischen Föderation gegründet und hat die wesentlichen Ressourcen der sowjetischen Raumfahrt übernommen. Sie ist für das zivile Raumfahrtprogramm des Landes zuständig. Zum Leiter von Roskosmos wurde im März 2004 General Anatoli Nikolajewitsch Perminow ernannt.
Roskosmos benutzt aktuell zwei Raumfahrtbahnhöfe: Plessezk bei Archangelsk in Russland, das langfristig zur Hauptbasis ausgebaut werden soll, sowie Baikonur in Kasachstan, die bisherige Hauptbasis. Die Nutzung von Baikonur muss aktuell auf Basis eines Pachtvertrages bezahlt werden. Als mögliche Alternative wurde Swobodny im fernen Osten Russlands in Betracht gezogen. Eine Vielzahl von Raketenstarts erfolgte auch vom Startkomplex Kapustin Jar an der Wolga.
Lange Zeit unterhielt die russische Raumfahrtbehörde die Raumstation Mir, die sich trotz Finanzierungsschwierigkeiten sogar acht Jahre länger als vorgesehen im Dienst befand. Sie wurde schließlich am 23. März 2001 aufgegeben, da man sich auf die Internationale Raumstation (ISS) konzentrieren wollte.
Russland beteiligt sich jetzt maßgeblich an der ISS, zu deren Versorgung, insbesondere nach der Verzögerung des Space-Shuttle-Programms, die Sojus-Rakete mit dem Sojus-Raumschiff und dem Progress-Raumtransporter eingesetzt werden.
Roskosmos ist Vollmitglied des Consultative Committee for Space Data Systems (CCSDS).(Quelle:wikipedia.org)



 Aerospace
Aerospace




 Military, defense and equipment
Military, defense and equipment
 Aircraft propulsion
Aircraft propulsion




 Military, defense and equipment
Military, defense and equipment
 Military aircraft
Military aircraft
 Militärflugzeuge
Militärflugzeuge
 MiG-21
MiG-21
 Militärflugzeuge
Militärflugzeuge
 MiG-23
MiG-23
 Militärflugzeuge
Militärflugzeuge
 MiG-25
MiG-25
 Militärflugzeuge
Militärflugzeuge
 MiG-27
MiG-27
 Militärflugzeuge
Militärflugzeuge
 MiG-29
MiG-29
 Militärflugzeuge
Militärflugzeuge
 MiG-31
MiG-31
 Militärflugzeuge
Militärflugzeuge
 MiG-35
MiG-35
 Russia
Russia



 Astronomy
Astronomy
 History
History
 Review
Review
 Science and technology
Science and technology
 Transport and traffic
Transport and traffic
 Architecture
Architecture
 Companies
Companies