
漢德百科全書 | 汉德百科全书
 Architecture
Architecture







Die Ciutat de les Arts i les Ciències (span. Ciudad de las Artes y las Ciencias, dt. Stadt der Künste und der Wissenschaften) ist ein kultureller und architektonischer Gebäude- und Parkkomplex in Valencia, Spanien. Das moderne Wahrzeichen der Stadt liegt im trockengelegten Flussbett des Turia.
艺术科学城(巴伦西亚语:Ciutat de les Arts i les Ciències、西班牙语:Ciudad de las Artes y las Ciencias)是西班牙巴伦西亚图里亚河(Turia)干河床上5个地区的总称。它是在巴伦西亚城市最重要的现代旅游目的地,和在西班牙最相关的现代旅游目的地之一。
艺术科学城是由巴伦西亚的设计师圣地亚哥·卡拉特拉瓦(Santiago Calatrava)所设计的,并且在1996年7月开始动工,与完成了的“城市”正式成立在1998年4月16日,以L'Hemisfèric天文馆开幕。旧河床变成了风景如画的下沉式公园。
芸術科学都市(バレンシア語:Ciutat de les Arts i les Ciències、スペイン語:Ciudad de las Artes y las Ciencias)は、スペインのバレンシアにある科学教育と芸術のための施設の複合体。1957年に大洪水を起こしたため付け替えられ1980年に公園となったトゥリア川の旧い川床に、5つの印象的な現代建築群が連なっている。
設計者はバレンシア生まれの建築家・構造技術者サンティアゴ・カラトラバ。1996年7月に建設が始まり、1998年4月16日にプラネタリウム・IMAXシアターの「レミスフェリック」(L'Hemisfèric)が開館した。2005年10月9日にソフィア王妃芸術宮殿(El Palau de les Arts Reina Sofía)が一般に公開されすべての施設が完成したが、ソフィア王妃芸術宮殿の公演開始は2006年秋にずれ込んでいる。
芸術科学都市は次の施設から成り立っている(カッコ内はバレンシア語名称)。バレンシア州が造ったこれらの施設はいずれもヨーロッパ最大級の規模を誇り、多くの観光客を集めている。
The City of Arts and Sciences (Valencian: Ciutat de les Arts i les Ciències [siwˈtad de les ˈaɾts i les siˈɛnsi.es]; Spanish: Ciudad de las Artes y las Ciencias [θjuˈðað de las ˈartes i las ˈθjenθjas]) is a cultural and architectural complex in the city of Valencia, Spain. It is the most important modern tourist destination in the city of Valencia and one of the 12 Treasures of Spain.
The City of Arts and Sciences is situated at the southeast end of the former riverbed of the river Turia, which was drained and rerouted after a catastrophic flood in 1957. The old riverbed was turned into a picturesque sunken park.
Designed by Santiago Calatrava and Félix Candela, the project began the first stages of construction in July 1996, and was inaugurated on 16 April 1998 with the opening of L'Hemisfèric. The last major component of the City of Arts and Sciences, Palau de les Arts Reina Sofía, was inaugurated on 9 October 2005, Valencian Community Day. The most recent building in the complex, L'Àgora, was opened in 2009.[1]
Originally budgeted at €300 million in 1991 for three structures, it has expanded about three times the initial expected cost.[2]
La Cité des arts et des sciences (Ciutat de les Arts i les Ciències en valencien, Ciudad de las Artes y las Ciencias en castillan) est un complexe culturel situé à Valence (Espagne). C'est une entreprise publique appartenant à la Généralité valencienne.
Le complexe, dessiné par l'architecte et ingénieur Santiago Calatrava, ainsi que par Félix Candela, fut inauguré le avec l'ouverture de l’Hemisfèric. Le palais des Arts Reine Sofía, fut présenté le , jour de la Communauté valencienne. Le pont de l’Assut de l'Or a été inauguré le . Le dernier élément de la Cité des arts et des sciences, l’Ágora, a été inauguré en novembre 2009.
Après la grande inondation de Valence de 1957, le lit de la rivière Turia traversant Valence a été dévié. Depuis les années 1980, la partie correspondant au centre-ville avait été transformée en jardins et lieux de promenade pour les citadins. L'embouchure de cet ancien lit offre le site de construction contemporain de la cité des sciences. Le complexe s'étend sur une surface de 350 000 m2.
Dans le film À la poursuite de demain, elle sert de décor pour une des scènes se passant dans le monde de Tomorrowland. Ce décor résolument futuriste est également utilisé dans la série de science-fiction Westworld (saison 3), censée se dérouler en 2052.
La Città delle Arti e delle Scienze sorge a Valencia, in Spagna, sul vecchio letto, ora spostato, del fiume Turia e copre una superficie di 350.000 m².
Progettato dagli architetti Santiago Calatrava e Félix Candela, ed iniziato nel luglio 1996, è un esempio di architettura organica, che grazie a qualità costruttive d'avanguardia riesce ad armonizzare gli elementi con i contenuti, lasciando però trasparire la tradizione mediterranea del mare e della luce attraverso un gioco di colori tra l'azzurro dei grandi stagni d'acqua a cielo aperto e il bianco del cemento.
La Ciudad de las Artes y las Ciencias (en valenciano y oficialmente Ciutat de les Arts i les Ciències) es un complejo arquitectónico, cultural y de entretenimiento de la ciudad de Valencia (España).12
El complejo fue diseñado por Santiago Calatrava y Félix Candela, junto con los ingenieros autores del diseño estructural de las cubiertas del L'Oceanografic Alberto Domingo y Carlos Lázaro.3 Fue inaugurado el 9 de junio de 1998 con la apertura de El Hemisférico. El último gran componente de la Ciudad es el Ágora, situado entre el puente de l'Assut de l'Or y l'Oceanogràfic.4
La Ciudad de las Artes y las Ciencias está situada al final del viejo cauce del río Turia (Jardín del Turia), cauce que se convirtió en jardín en los años 1980, tras el desvío del río por la gran riada de Valencia en 1957. En 2007, fue uno de los ganadores del concurso 12 Tesoros de España.5
Город искусств и наук (валенс. Ciutat de les Arts i les Ciències, исп. Ciudad de las Artes y las Ciencias) — архитектурный комплекс из пяти сооружений на осушенном дне реки Турия в городе Валенсия (Испания). Дизайн принадлежит валенсианскому архитектору Сантьяго Калатраве, работа над проектом началась в 1989 году. Комплекс является одним из выдающихся образцов современной архитектуры.
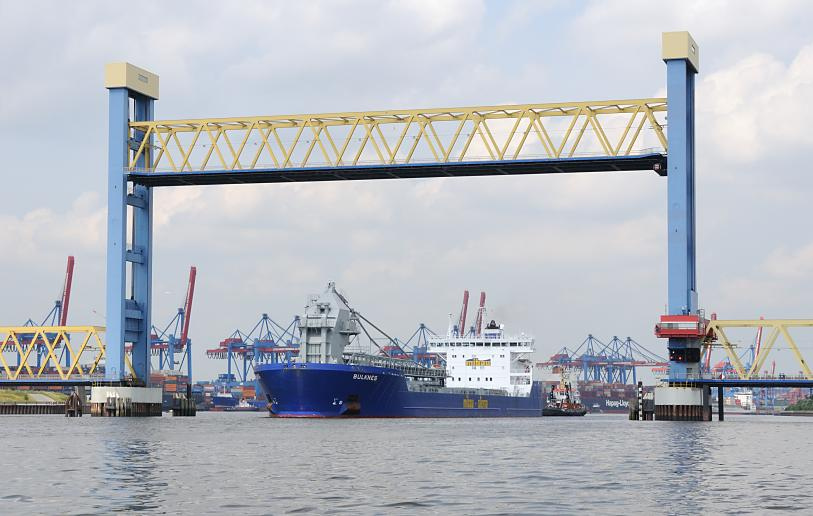





Die Elbphilharmonie (kurz auch „Elphi“ genannt)[1][2] ist ein im November 2016 fertiggestelltes Konzerthaus in Hamburg. Sie wurde mit dem Ziel geplant, ein neues Wahrzeichen der Stadt und ein „Kulturdenkmal für alle“ zu schaffen.[3][4][5] Das 110 Meter hohe Gebäude im Stadtteil HafenCity liegt am rechten Ufer der Norderelbe an der Spitze des Großen Grasbrooks zwischen den Mündungen der Hafenbecken Sandtorhafen und Grasbrookhafen. Es wurde unter Einbeziehung der Hülle des früheren Kaispeichers A (Baujahr 1963) errichtet. Auf diesen Sockel wurde ein moderner Aufbau mit einer Glasfassade gesetzt, die an Segel, Wasserwellen, Eisberge oder einen Quarzkristall erinnert. Die Lage am Kaiserhöft ist von der einstigen industriellen Hafennutzung und der neugotischen Backsteinarchitektur der Speicherstadt geprägt.
Das Konzept des Konzerthauses geht auf eine 2001 vorgestellte Idee des Hamburger Projektentwicklers Alexander Gérard zurück. Der Bau wurde dann 2007 durch die Bürgerschaft unter Bürgermeister Ole von Beust beschlossen. Entwurf und Planung der Philharmonie stammen im Wesentlichen vom Architekturbüro Herzog & de Meuron. Bauherr war die Elbphilharmonie Bau KG, deren Teilgesellschafter und Hauptfinanzier die Freie und Hansestadt Hamburg mit Steuermitteln ist. Das Gebäude wurde in ihrem Auftrag vom Baudienstleister Hochtief errichtet.
Die Fertigstellung des Gebäudes war nach einem mehrjährigen Vorlauf für das Jahr 2010 vorgesehen, verzögerte sich jedoch mehrfach, u. a. auch bedingt durch einen anderthalbjährigen Baustopp im öffentlichen Bereich. Erst nach einer umfangreichen Projektneuordnung zwischen den Architekten, dem Bauherren und der Baufirma kurz nach der Wahl des Bürgermeisters Olaf Scholz wurde nach dem Baustopp weitergebaut. Durch die Verzögerungen am Bau und die Überschreitung der ursprünglich veranschlagten Baukosten wurde die Elbphilharmonie bereits lange vor der Fertigstellung bundesweit bekannt: Die Baukosten betrugen am Ende mit rund 866 Millionen Euro etwas mehr als das 11,24-fache bzw. mehr als plus 1.124 % der mit ursprünglich 77 Millionen Euro geplanten Summe.[6] Der im neuen Vertrag vereinbarte Termin für die Bau- und Schlüsselübergabe am 31. Oktober 2016 wurde eingehalten.[7] Die Einweihung des Konzertbereichs wurde am 11. und 12. Januar 2017 mit dem Konzert „Zum Raum wird hier die Zeit“ des NDR Elbphilharmonie Orchesters gefeiert (Konzertprogramm).[8][9] Der Kleine Saal wurde am 12. Januar 2017 vom Ensemble Resonanz eingeweiht. Im ersten Jahr nach der Eröffnung besuchten rund 850.000 Menschen die über 600 Konzerte in der Elbphilharmonie, über 4,5 Millionen Besucher pilgerten auf die Plaza, mehr als 70.000 Menschen nahmen an Konzerthausführungen und über 60.000 am Musikvermittlungsprogramm des Hauses teil.[10]
汉堡易北爱乐音乐厅是德国北部音乐之都的新心脏,凭借其别具一格的建筑风格和精彩纷呈的各类活动,这座宏伟的音乐厅将卓越艺术和开放包容融为一体。易北爱乐音乐厅由赫尔佐格和德梅隆建筑事务所(Herzog & de Meuron)设计,矗立于城市与港口之间,并将从前的码头仓库与新颖的玻璃结构和弧形屋顶合为一体。建筑内除了设有三座音乐厅外,还拥有豪华酒店和公共观景平台,平台的开放式设计突显出汉堡这座德国新地标建筑作为“一个面向所有人的音乐厅”的特点。(Quelle:www.Baidu.com)
易北爱乐厅(Elbphilharmonie)是一座位于德国汉堡的音乐厅,是建设中的汉堡港城的一部分,位于仓库城的最西端,高达110米,是汉堡最高的居住建筑。音乐厅的一至七层使用了港口仓库A(Kaispeicher A)的37米高的基座[1]。港口仓库A曾经用于存贮可可、茶及烟草[2]。音乐厅除了面向音乐厅听众和酒店住户外,也向其他所有人开放[1]。
エルプフィルハーモニー・ハンブルク (独: Elbphilharmonie Hamburg、愛称: Elphi) は、2017年1月にオープンしたドイツ・ハンブルクのハーフェンシティ地区にあるコンサートホール。「エルプ」はハーフェンシティが面するエルベ川を意味する。
当該ホールの竣工により、NDRエルプフィルハーモニー管弦楽団(NDR Elbphilharmonie Orchestra, 旧称:北ドイツ放送交響楽団)の新たな本拠地となった。
古い倉庫「埠頭倉庫A(Kaispeicher A)」の上部にコンサートホールを新設する計画で、建築設計を担当するのはスイス・バーゼルのヘルツォーク&ド・ムーロン[2][3]、建設業者はホッホティーフ。また、日本からも永田音響設計が音響設計に携わっている[4]。完成すると高さが110mになり、人が居住する建物としてはハンブルクで最も高い建築物となる予定である。
巨額なコストの増加と建設の大幅な遅れから、スキャンダラスな事業であるとみられている。当事業の当初の推定予算は7700万ユーロで、ハンブルク市が負担するはずであったが、2007年には、市は建設コストを支えるために、1.14億ユーロとすることで決着した。その後も幾度かの交渉を経て、2012年12月にはゼネコンのホッホティーフに対して市側が(計画コストを含めて)最終的な建設コストの総計を手取りで5.75億ユーロとすることで合意した。2013年4月23日、ハンブルク市長のオーラフ・ショルツは、当事業にかかる費用の合計が7.89億ユーロになることを納税者(市民)に公表した[5]。建物の完成は、当初は2010年に計画されていたが、度々延期された。上棟式は、3年間の建設期間の後に、2010年5月に挙行された。建設作業は2016年10月に完了し、古い建物と新しい建物の間にある公共広場は2016年11月から一般公開された。
The Elbphilharmonie (![]() German pronunciation (help·info)) (Elbe Philharmonic) is a concert hall in the HafenCity quarter of Hamburg, Germany, on the Grasbrook peninsula of the Elbe River. It is one of the largest and acoustically most advanced concert halls in the world.[3] It is popularly nicknamed Elphi.[4][5]
German pronunciation (help·info)) (Elbe Philharmonic) is a concert hall in the HafenCity quarter of Hamburg, Germany, on the Grasbrook peninsula of the Elbe River. It is one of the largest and acoustically most advanced concert halls in the world.[3] It is popularly nicknamed Elphi.[4][5]
The new glassy construction resembles a hoisted sail, water wave, iceberg or quartz crystal; it sits on top of an old warehouse building (Kaispeicher A, built 1963) near the historical Speicherstadt and is designed by architecture firm Herzog & de Meuron.[6][7] It is the tallest inhabited building in Hamburg, with a final height of 108 metres (354 ft).[2]
The Elbphilharmonie was officially inaugurated with concerts of the NDR Elbphilharmonie Orchestra and a light show on 11 January 2017.[8][9][10]
La Philharmonie de l’Elbe (Elbphilharmonie, surnommée Elphi) est une salle de concert symphonique de Hambourg construite par les architectes Herzog & de Meuron.
La Elbphilharmonie (letteralmente "Filarmonica dell'Elba") è una sala da concerto della città di Amburgo, in Germania, situata nel quartiere di HafenCity (distretto di Hamburg-Mitte).
È una delle sale di concerto più grandi ed acusticamente avanzate a livello mondiale. È anche nota con il soprannome Elphi.
La costruzione in vetro assomiglia ad una vela issata, ad una onda o ad un cristallo di quarzo, ed è appoggiata sopra un vecchio magazzino (Kaispeicher A, costruito nel 1963), nelle vicinanze dello storico Speicherstadt. Costruita su progetto dello studio Herzog & de Meuron[1][2], include due sale da concerto, una da 2 000 posti e una da 550 circa, un hotel e 44 appartamenti.[3] È l'edificio abitabile più alto di Amburgo, con una altezza finale di 108 metri.[4]
È stata inaugurata l'11 gennaio 2017, con un concerto della NDR Elbphilharmonie Orchester diretto da Thomas Hengelbrock.[3]
La Filarmónica del Elba (en alemán, Elbphilharmonie), conocida también por su sobrenombre Elphi,12 es una sala de conciertos en la HafenCity de Hamburgo, Alemania.
Proyectada por el estudio de arquitectura suizo Herzog & de Meuron, esta construcción junto al río Elba incluye apartamentos en sus pisos superiores. La construcción fue finalizada el 31 de octubre 2016; no obstante, debido a los múltiples retrasos e incalculables incrementos de costo de obra, en torno al 1000%,3 la prensa estuvo castigando a este proyecto.4
La inauguración de la nueva sala de conciertos se produjo el 11 de enero de 2017, con un concierto de la NDR Elbphilharmonie Orchester5 (anteriormente conocida como Orquesta Sinfónica de la NDR), que se convertirá en la orquesta residente del auditorio.6
Эльбская филармония (нем. Elbphilharmonie) — концертный зал Гамбурга, расположенный на острове Грасброок на Эльбе.

 New York-NY
New York-NY
 Religion
Religion
 Vacation and Travel
Vacation and Travel
 World Heritage
World Heritage
 Music
Music
 Valencian Community
Valencian Community
 Saxony
Saxony
 Hamburg
Hamburg
 Performing Arts
Performing Arts