
漢德百科全書 | 汉德百科全书
 Portugal
Portugal
 *Mediterranean Sea
*Mediterranean Sea
 Egypt
Egypt
 Algeria
Algeria
 Belgium
Belgium
 Bulgaria
Bulgaria
 Germany
Germany
 France
France

 History
History

 History
History
 H 1000 - 500 BC
H 1000 - 500 BC

 History
History
 I 500 - 0 BC
I 500 - 0 BC

 History
History
 J 0 - 500 AD
J 0 - 500 AD
 Israel
Israel
 Italy
Italy
 Jordan
Jordan
 Croatia
Croatia
 Libanon
Libanon
 Libya
Libya
 Morocco
Morocco
 Netherlands
Netherlands
 Portugal
Portugal
 Romania
Romania
 Switzerland
Switzerland
 Serbia
Serbia
 Syria
Syria
 Tunisia
Tunisia
 Turkey
Turkey
 Hungary
Hungary
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom

 Civilization
Civilization
 Cyprus
Cyprus

Als römische Architektur bezeichnet man die Baukunst der Römer zur Zeit der römischen Republik und der Kaiserzeit. Die römische Architekturgeschichte umfasst damit einen Zeitraum von etwa neun Jahrhunderten (500 v. Chr.–400 n. Chr.). Die Epochen der römischen Architektur werden nach einzelnen Herrschern, Dynastien oder retrospektiv formulierten historischen Zeitabschnitten benannt. Die seitens der Klassischen Archäologie geprägten Epochen- oder Stilbegriffe finden keine Entsprechungen in der schriftlichen antiken Überlieferung, entsprechen also nicht antiker Wahrnehmung und Einteilung.
古罗马建筑(英语:Ancient Roman architecture),是指由古罗马人创造并且扩展到地中海沿岸其所控制疆域的一种新风格的建筑艺术,经常简称为罗马建筑(英语:Roman architecture)。它直接继承了古希腊晚期的建筑成就,而且将其向前大大推进,使之在1到3世纪达到奴隶制时代全世界建筑的顶峰[1][2]。在西方学术界传统上特指古罗马共和国与帝国时期的建筑[3],中文学术界定义较为宽泛,有时可以包括前期的伊特鲁里亚建筑[4],也可以包括分裂之后的西罗马帝国建筑[2],但是一般不包含东罗马帝国建筑。
 Egypt
Egypt
 Australia
Australia
 Belgium
Belgium
 Brazil
Brazil
 China
China
 Denmark
Denmark
 Germany
Germany
 Finland
Finland
 France
France
 Greece
Greece

 Hand in Hand
Hand in Hand

 Hand in Hand
Hand in Hand
 Driver's license
Driver's license
 India
India
 Indonesia
Indonesia
 Italy
Italy
 Japan
Japan
 Canada
Canada
 Kasachstan
Kasachstan
 Croatia
Croatia
 Malaysia
Malaysia

 Mongolei
Mongolei
 New Zealand
New Zealand
 Netherlands
Netherlands
 Useful info
Useful info
 Austria
Austria
 Portugal
Portugal
 Republic of Korea
Republic of Korea
 Russia
Russia
 Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia
 Sweden
Sweden
 Switzerland
Switzerland
 Singapore
Singapore
 Spain
Spain
 South Africa
South Africa
 Thailand
Thailand
 Czech Republic
Czech Republic
 Turkey
Turkey
 Hungary
Hungary

 Vacation and Travel
Vacation and Travel
 United Arab Emirates
United Arab Emirates
 United States
United States
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
国际驾驶执照(International Driving Permit)依照1949年日内瓦国际道路交通公约及1968年维也纳国际道路交通公约,由公约签署国政府签发,方便本国驾驶员在其他签约国驾驶私人车辆。国际驾驶执照为附加在一国驾驶执照之上的一本附加多国语言的说明,标注了驾驶人的基本信息以及允许驾驶的对应车辆种类等,解决驾驶员与其他国家的交通管理部门之间的沟通障碍。国际驾照不能独立存在,当驾驶员同时持有一国驾照与该国政府签发的国际驾照时,此国际驾照才视作有效。[1]
国际驾驶执照之内容及格式依照维也纳道路交通会议制订,但并非各国均批准该公约。
Ein Internationaler Führerschein ist ein Dokument, das von den Straßenverkehrsbehörden oder Automobilclubs[1] eines Landes aufgrund zwischenstaatlicher Verträge ausgestellt wird. Er soll vor allem der Polizei eines anderen Landes die Feststellung ermöglichen, ob ein ausländischer Kraftfahrer die Fahrerlaubnis hat, die für sein aktuelles Fahrzeug erforderlich ist.
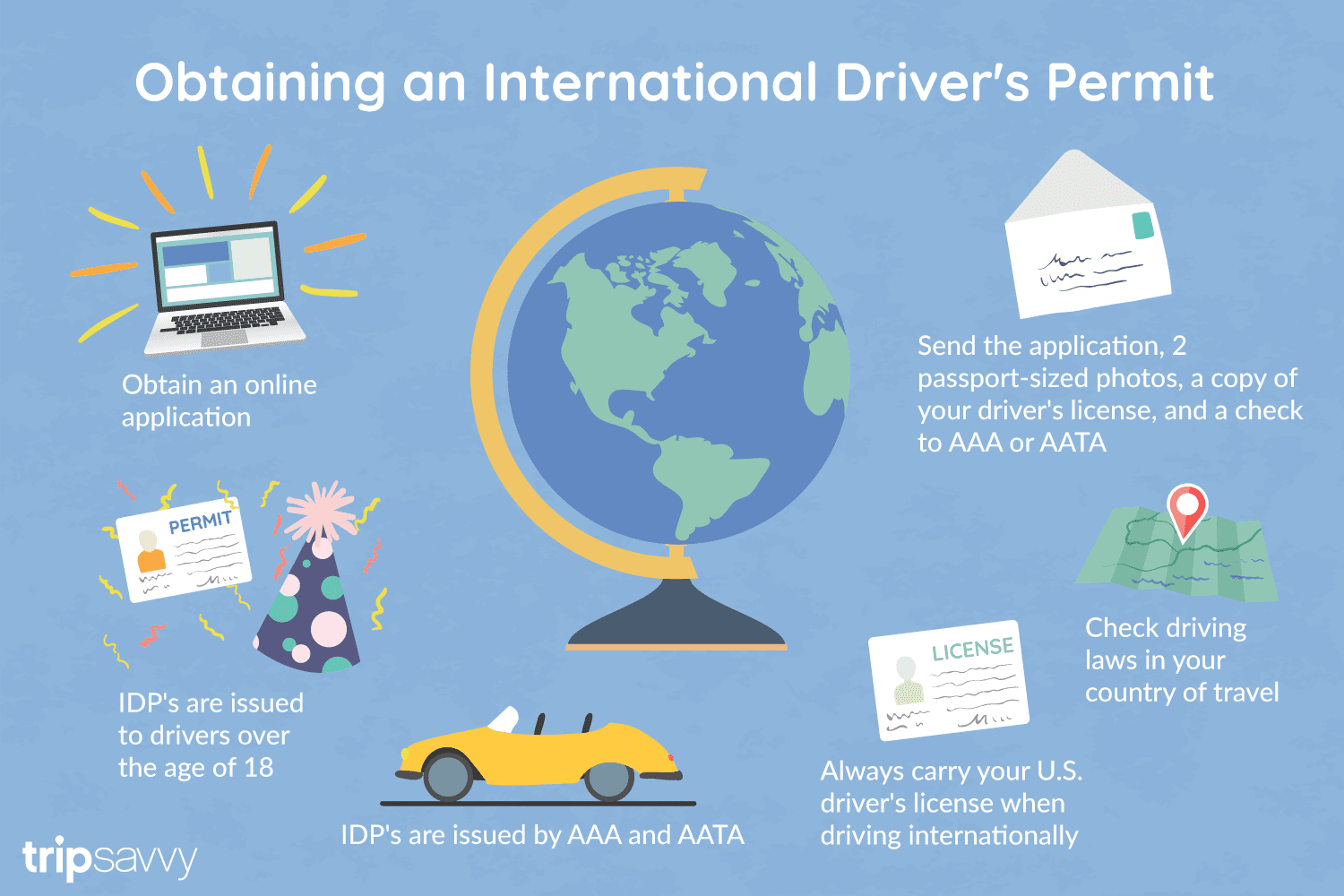
An International Driver's Permit (IDP) allows you to drive a vehicle in another country, as long as you also have a valid driver's license issued by your state. It is also recognized as a proper form of identification in over 175 countries and by many major car rental companies internationally.
Getting an International Driver's Permit (sometimes incorrectly called an international driver's license) can take anywhere from a day to a few weeks, depending on whether you're going through walk-in processing or applying via mail, so make sure to plan ahead if you're planning to drive on your international trip. There are only two locations in the United States that issue these documents: The American Automobile Association (AAA) and the American Automobile Touring Alliance (AATA).
In the United States, International Driver Permits (IDPs) are only issued by the American Automobile Association and the American Automobile Touring Alliance, and the State Department recommends against purchasing an IDP from other outlets as they are all entirely illegal to buy, carry, or sell.
IDPs can be issued to anyone over 18 who has had a valid driver's license for six months or longer. They typically remain valid for one year or the expiration of your existing state driving license. It's essential to investigate an IDP before your trip and make sure you know the requirements.
Both AAA and AATA are excellent sources for these documents, so once you've selected a provider, go to either the AAA's or NAATA's website, print out the International Driving Permit Application, complete all applicable fields, and submit it.
Once you have the application completed, you can send it in via the mail or visit a local office of an organization like AAA; you'll also need two original passport-sized photos and a signed copy of your valid U.S. driver's license as well as an enclosed check for the fee.
Tips to Getting and Using Your Permit
AAA offices can process IDPs during your visit, but processing generally takes 10 to 15 business days if you send the application in. However, expedited services may be available to get your license within one or two business days for an additional fee.
When applying, you'll need a computer and printer, a completed application, a copy of your valid U.S. driver's license, two passport photos, and a check, money order, or credit card to complete the process. Remember to bring these with you if you're applying in person.
Always make sure to carry your valid United States driver's license when driving internationally, as your IDP is invalid without this accompanying proof of eligibility to drive. IDPs only translate domestically-accepted licenses and do not allow those without government-issued driver's licenses to drive abroad.
You'll also want to make sure to enclose the proper fees (the fee for the IDP, as well as any shipping and handling fees), photos, and photocopies of your license when submitting your application to AAA or AATA as omitting any of these required documents will result in your application being rejected.
You should also check the driving requirements and laws for the countries you will be driving in on your vacation, so you'll know what will be required in the event you get stopped by local authorities. (Quelle:https://www.tripsavvy.com/)
 Australia
Australia
 China
China
 Germany
Germany
 France
France
 ITU World Championship Series
ITU World Championship Series
 Japan
Japan
 Canada
Canada
 Kasachstan
Kasachstan
 Mexico
Mexico
 New Zealand
New Zealand
 Netherlands
Netherlands
 Austria
Austria
 Portugal
Portugal
 Republic of Korea
Republic of Korea
 Sweden
Sweden
 Switzerland
Switzerland
 Spain
Spain
 South Africa
South Africa
 Hungary
Hungary
 United Arab Emirates
United Arab Emirates
 United States
United States
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 Bermuda
Bermuda





Veranstaltungen Spiele des FC Porto Fußball-Europameisterschaft 2004 Südeuropa-Regional-Finale des Race of Champions 2009 Final Four der UEFA Nations League 2018/19 Endspiel der UEFA Champions League 2020/21 Konzerte



 Argentina
Argentina
 Brazil
Brazil
 Bulgaria
Bulgaria
 Chile
Chile
 Columbia
Columbia
 Germany
Germany
 FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 2014
FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 2014
 FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 2018
FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 2018
 FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 2022
FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 2022

 FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 2026
FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 2026
 FIFA WM Goldener Schuh
FIFA WM Goldener Schuh
 France
France
 Italy
Italy
 Croatia
Croatia
 Poland
Poland
 Portugal
Portugal
 Russia
Russia
 Czech Republic
Czech Republic
 Hungary
Hungary
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom

| Top goalscorer[45][46] | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| World Cup | Top goalscorer | Goals | Runners-up | Goals | Third place | Goals |
| 1930 Uruguay | 8 | 5 | 4 | |||
| 1934 Italy | 5[a] | 4 | None |
— |
||
| 1938 France | 7[b] | 5 | None |
— |
||
| 1950 Brazil | 9[c] | 5 | 4 | |||
| 1954 Switzerland | 11 | 6 | None |
— |
||
| 1958 Sweden | 13 | 6 | None |
— |
||
| 1962 Chile | 4 | None |
— |
None |
— |
|
| 1966 England | 9 | 6 | 4 | |||
| 1970 Mexico | 10 | 7 | 5 | |||
| 1974 West Germany | 7 | 5 | None |
— |
||
| 1978 Argentina[50] | 6 | 5 | 5 | |||
| Golden Shoe[44] | ||||||
| World Cup | Golden Shoe | Goals | Silver Shoe | Goals | Bronze Shoe | Goals |
| 1982 Spain | 6 | 5 | 4 | |||
| 1986 Mexico | 6 | 5 | None[51] | |||
| 1990 Italy | 6 | 5 | 4 | |||
| 1994 United States | 6 | None |
— |
5[f] | ||
| 1998 France[54] | 6 | 5 | None[g] | |||
| 2002 South Korea/Japan[55] | 8[h] | 5 | ||||
| 2006 Germany[57] | 5 | 3[i] | 3[i] | |||
| Golden Boot[44] | ||||||
| World Cup | Golden Boot | Goals | Silver Boot | Goals | Bronze Boot | Goals |
| 2010 South Africa | 5[j] | 5[j] | 5[j] | |||
| 2014 Brazil | 6 | 5 | 4[k] | |||
| 2018 Russia | 6 | 4[l] | 4[l] | |||
| 2022 Qatar | 8 | 7 | 4[m] | |||
| Notes | ||||||
|
||||||
 Australia
Australia
 Belgium
Belgium
 Chile
Chile
 Denmark
Denmark
 Germany
Germany
 Estonia
Estonia
 Finland
Finland
 France
France
 Greece
Greece
 Ireland
Ireland
 Iceland
Iceland
 Israel
Israel
 Italy
Italy
 Japan
Japan
 Canada
Canada
 Luxembourg
Luxembourg
 Mexico
Mexico
 New Zealand
New Zealand
 Netherlands
Netherlands
 Norwegen
Norwegen
 OECD
OECD
 Emiel van Lennep
Emiel van Lennep
 OECD
OECD
 Don Johnston
Don Johnston
 OECD
OECD
 Jean-Claude Paye
Jean-Claude Paye
 OECD
OECD
 José Ángel Gurría
José Ángel Gurría
 OECD
OECD
 Staffan Sohlman
Staffan Sohlman
 OECD
OECD
 Thorkil Kristensen
Thorkil Kristensen
 Austria
Austria
 Poland
Poland
 Portugal
Portugal
 Republic of Korea
Republic of Korea
 Sweden
Sweden
 Switzerland
Switzerland
 Slovakia
Slovakia
 Slovenia
Slovenia
 Spain
Spain
 Czech Republic
Czech Republic
 Turkey
Turkey
 Hungary
Hungary
 United States
United States
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom

 Important International Organizations
Important International Organizations

経済協力開発機構(けいざいきょうりょくかいはつきこう)は、国際経済全般について協議することを目的とした国際機関。公用語の正式名称は、英語では"Organisation[1] for Economic Co-operation and Development"(イギリス英語表記)、フランス語では"Organisation de Coopération et de Développement Economiques"。略称は英語ではOECD、フランス語ではOCDE。
本部事務局はパリ16区の旧ラ・ミュエット宮殿に置かれている。事務総長はアンヘル・グリア。
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD; French: Organisation de Coopération et de Développement Économiques, OCDE) is an intergovernmental economic organisation with 37 member countries,[1] founded in 1961 to stimulate economic progress and world trade. It is a forum of countries describing themselves as committed to democracy and the market economy, providing a platform to compare policy experiences, seek answers to common problems, identify good practices and coordinate domestic and international policies of its members. Generally, OECD members are high-income economies with a very high Human Development Index (HDI) and are regarded as developed countries. As of 2017, the OECD member countries collectively comprised 62.2% of global nominal GDP (US$49.6 trillion)[3] and 42.8% of global GDP (Int$54.2 trillion) at purchasing power parity.[4] The OECD is an official United Nations observer.[5]
In 1948, the OECD originated as the Organisation for European Economic Co-operation (OEEC),[6] led by Robert Marjolin of France, to help administer the Marshall Plan (which was rejected by the Soviet Union and its satellite states).[7] This would be achieved by allocating United States financial aid and implementing economic programs for the reconstruction of Europe after World War II. (Similar reconstruction aid was sent to the war-torn Republic of China and post-war Korea, but not under the name "Marshall Plan".)[8]
In 1961, the OEEC was reformed into the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development by the Convention on the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development and membership was extended to non-European states.[9][10] The OECD's headquarters are at the Château de la Muette in Paris, France.[11] The OECD is funded by contributions from member countries at varying rates and had a total budget of €386 million in 2019.[2]
Although OECD does not have a power to enforce its decisions, which further require unanimous vote from its members, it is recognized as highly influential publisher of mostly economic data through publications as well as annual evaluations and rankings of members countries.[12]
L'Organisation de coopération et de développement économiques (OCDE) est une organisation internationale d'études économiques, dont les pays membres — des pays développés pour la plupart — ont en commun un système de gouvernement démocratique et une économie de marché. Elle joue essentiellement un rôle d'assemblée consultative1.
L'OCDE a succédé à l'Organisation européenne de coopération économique (OECE) issue du plan Marshall et de la Conférence des Seize (Conférence de coopération économique européenne) qui a existé de 1948 à 1960. Son but était l'établissement d'une organisation permanente chargée en premier lieu d'assurer la mise en œuvre du programme de relèvement commun (le plan Marshall), et, en particulier, d'en superviser la répartition2.
En 2020, l'OCDE compte 37 pays membres et regroupe plusieurs centaines d'experts. Elle publie fréquemment des études économiques et sociales — analyses, prévisions et recommandations de politique économique — et des statistiques, principalement concernant ses pays membres.
Le siège de l'OCDE se situe à Paris (16e), au château de la Muette. L'organisation possède également des bureaux dans plusieurs autres métropoles, notamment à Berlin, Mexico, Tokyo et Washington.
L'Organizzazione per la cooperazione e lo sviluppo economico (OCSE) – in inglese Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), e in francese Organisation de coopération et de développement économiques (OCDE) – è un'organizzazione internazionale di studi economici per i paesi membri, paesi sviluppati aventi in comune un'economia di mercato.
L'organizzazione svolge prevalentemente un ruolo di assemblea consultiva che consente un'occasione di confronto delle esperienze politiche, per la risoluzione dei problemi comuni, l'identificazione di pratiche commerciali e il coordinamento delle politiche locali e internazionali dei paesi membri[1]. Ha sede a Parigi nello Château de la Muette[2].
Gli ultimi paesi ad aver aderito all'OCSE sono la Colombia (28 aprile 2020),la Lettonia (1º luglio 2016) e la Lituania (5 luglio 2018), per un totale di 36 paesi membri.
La Organización para la Cooperación y el Desarrollo Económico1 (OCDE) es un organismo de cooperación internacional, compuesto por 37 estados,34 cuyo objetivo es coordinar sus políticas económicas y sociales. La OCDE fue fundada en 1961 y su sede central se encuentra en el Château de la Muette en París (Francia). Los idiomas oficiales de la entidad son el francés y el inglés.2
En la OCDE, los representantes de los países miembros se reúnen para intercambiar información y armonizar políticas con el objetivo de maximizar su crecimiento económico y colaborar a su desarrollo y al de los países no miembros.
Conocida como «club de los países ricos»,56 a partir de 2017, sus países miembros comprendieron colectivamente el 62,2 % del PIB nominal global (US$49,6 billones) y el 42,8 % del PIB global (Int US$54,2 billones).7
Организа́ция экономи́ческого сотру́дничества и разви́тия (сокр. ОЭСР, англ. Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development, OECD) — международная экономическая организация развитых стран, признающих принципы представительной демократии и свободной рыночной экономики.
Создана в 1948 году под названием Организа́ция европе́йского экономи́ческого сотру́дничества (англ. Organisation for European Economic Co-operation, OEEC) для координации проектов экономической реконструкции Европы в рамках плана Маршалла.
Штаб-квартира организации располагается в Шато де ла Мюетт, в Париже. Генеральный секретарь (с 2006 года) — Хосе Анхель Гурриа Тревиньо (Мексика). Руководящим органом ОЭСР является совет представителей стран — членов организации. Все решения в нём принимаются на основе консенсуса.
По данным на 2011 год, в странах ОЭСР проживало 18 % населения мира[2].
 Architecture
Architecture
 Driving school
Driving school
 Sport
Sport
 Agriculture, forestry, livestock, fishing
Agriculture, forestry, livestock, fishing
 Dances
Dances
 Performing Arts
Performing Arts
 International cities
International cities
 World Heritage
World Heritage
 CESAER
CESAER
 Colleges and Universities in Europe
Colleges and Universities in Europe
 Economy and trade
Economy and trade