
漢德百科全書 | 汉德百科全书
 Sweden
Sweden


 Astronomy
Astronomy



 Automobile
Automobile
 *Self-driving car
*Self-driving car
 Belgium
Belgium
 Denmark
Denmark
 Germany
Germany

 European Union
European Union
 Finland
Finland
 France
France
 Greece
Greece
 Ireland
Ireland


 IT-Times
IT-Times
 Italy
Italy

 Agriculture, forestry, livestock, fishing
Agriculture, forestry, livestock, fishing



 Aerospace
Aerospace
 *ASI
*ASI



 Aerospace
Aerospace
 *CNES
*CNES



 Aerospace
Aerospace
 *DLR
*DLR



 Aerospace
Aerospace
 *ESA
*ESA
 Luxembourg
Luxembourg




 Military, defense and equipment
Military, defense and equipment
 Navigation Satellite System
Navigation Satellite System
 Netherlands
Netherlands
 Norwegen
Norwegen
 Austria
Austria
 Portugal
Portugal
 Romania
Romania

 Ships and Nautics
Ships and Nautics
 Sweden
Sweden
 Spain
Spain

 Transport and traffic
Transport and traffic
 Czech Republic
Czech Republic
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom

 Science and technology
Science and technology
Die genaue Bestimmung des Standorts und der Zeit - Informationen, die in Zukunft immer häufiger mit hoher Zuverlässigkeit zu zur Verfügung stehen müssen. In wenigen Jahren wird dies mit dem Satellitennavigationssystem GALILEO, einer gemeinsamen Initiative der Europäischen Union und der Europäischen Weltraumorganisation (ESA), möglich sein. Dieses weltweite System wird zugleich komplementär zum derzeitigen GPS-System sein.
Die Satellitennavigation ist eine Spitzentechnologie. Dabei werden von mehreren Satelliten im Weltraum höchst genaue Zeitsignale ausgestrahlt, anhand derer jedermann mit einem kleinen und preisgünstigen Empfangsgerät seinen Standort oder den eines bewegten oder unbewegten Objekts (Fahrzeug, Schiff, Viehherde usw.) auf den Meter genau bestimmen kann.
GALILEO basiert auf einer Konstellation von 30 Satelliten und Bodenstationen, die Nutzer aus den verschiedensten Bereichen mit Ortungsinformationen versorgen können. Zu diesen Sektoren gehören das Verkehrswesen (Ortung und Ermittlung der Geschwindigkeit von Fahrzeugen, Wegplanung, Navigationssysteme usw.), soziale Einrichtungen (z.B. Hilfe für Behinderte oder Senioren), die Justiz und der Zoll (Feststellung des Aufenthaltsortes von Verdächtigen, Grenzkontrollen), das Bauwesen (geografische Informationssysteme), Not- und Rettungsdienste oder der Freizeitsektor (Orientierung auf dem Meer und in den Bergen usw.).(Quelle: http://ec.europa.eu/dgs/energy_transport/galileo/index_de.htm)
Galileo ist ein im Aufbau befindliches, teilweise bereits operationelles, europäisches globales Satellitennavigations- und Zeitgebungssystem unter ziviler Kontrolle (europäisches GNSS).[1]
Es liefert weltweit Daten zur genauen Positionsbestimmung und ähnelt dem US-amerikanischen NAVSTAR-GPS, dem russischen GLONASS-System und dem chinesischen Beidou-System. Die Systeme unterscheiden sich hauptsächlich durch die Frequenznutzungs-/Modulationskonzepte, die Art und Anzahl der angebotenen Dienste und die Art der Kontrolle (GLONASS, Beidou und GPS sind militärisch kontrolliert).
Auftraggeber von Galileo ist die Europäische Union. Der Sitz der Agentur für das Europäische GNSS (Galileo-Agentur, GSA) befindet sich seit 2014 in der tschechischen Hauptstadt Prag.[2]
Mit Stand Ende 2017 sind 22 der vorgesehenen 30 Satelliten in ihrem Orbit.[3] Bis Ende 2019 sollen alle Satelliten in ihre Umlaufbahn gebracht werden. Das Satellitennavigationssystem ist für die Allgemeinheit seit dem 15. Dezember 2016 zugänglich.[4][5]
伽利略定位系统(意大利语:Galileo),是一个正在建造中的卫星定位系统,该系统由欧盟通过欧洲空间局和欧洲导航卫星系统管理局建造[3],总部设在捷克共和国的布拉格。该系统有两个地面操控站,分别位于德国慕尼黑附近的奥伯法芬霍芬和意大利的富齐诺。这个造价五十亿欧元[4]的项目是以意大利天文学家伽利略的名字命名的。伽利略系统的目的之一是为欧盟国家提供一个自主的高精度定位系统,该系统独立于俄罗斯的格洛纳斯系统和美国的全球定位系统(GPS),在这些系统被关闭时,欧盟就可以使用伽利略系统。该系统的基本服务(低精度)是提供给所有用户免费使用的,高精度定位服务仅提供给付费用户使用。伽利略系统的目标是在水平和垂直方向提供精度1米以内的定位服务,并且在高纬度地区提供比其他系统更好的定位服务。[5]
伽利略系统是中地球轨道搜救卫星系统的一部分,可提供一种新的全球搜救方式。伽利略系统的卫星安装有转发器,可以把求救信号从事故地点发送到救援协调中心,救援协调中心就会开始组织救援。同时,该系统还会发射一个返回信号到事故地点处,通知求救人员他们的信号已被收到,相应的救援也正在展开。现有的全球卫星搜救系统是不具备反馈信号功能的,所以伽利略系统这个发消息功能被认为是对全球卫星搜救系统的一个重要升级。[6]2014年,研究人员对伽利略系统的搜救功能进行了测试,该系统是作为当时的全球卫星搜救系统的一部分工作的,测试结果显示,该系统对77%的模拟求救位置定位精度在2千米以内,95%的求救位置定位精度在5千米以内。[7]
伽利略系统的第一颗试验卫星GIOVE-A于2005年12月28日发射,第一颗正式卫星于2011年8月21日发射。该系统计划发射30颗卫星,截止2016年5月,已有14颗卫星发射入轨。伽利略系统于2016年12月15日在布鲁塞尔举行激活仪式,提供早期服务。于2017年到2018年提供初步工作服务,最终于2019年具备完全工作能力。[8] 该系统的30颗卫星预计将于2020年前发射完成,其中包含24颗工作卫星和6颗备用卫星。[9]
ガリレオ(Galileo)は、EUが構築した全地球航法衛星システム。
ガリレオはEUによる全地球航法衛星システムである。高度約24000kmの上空に30機の航法衛星を運用することを予定している。民間主体としては初の衛星航法システムであり、EUはアメリカ国防総省が運営するGPSのように、軍事上の理由によるサービスの劣化及び中断を避けられる利点があるとコメントしている。さらに、測位にかかる時間が短縮され、GPSの数メートルに比べて1メートルまで精度を向上できる。
試験衛星は2005年12月28日に1機目のGIOVE-A衛星が打ち上げられ、2006年1月12日から試験電波が発射されており、2007年5月2日に英Surrey Satellite Technologyによって作成された航法メッセージがギルドフォード地球局からGIOVE-A衛星にアップロードされ放送された。2006年中に打ち上げ予定だった2機目の試験衛星GOOV-Bは、打上げが2008年4月まで遅れた。本格利用開始は2010年頃とされていたが、2013年へと先送りされ、2010年末段階計画では2014年末に18機による初期運用とし2016年末に規定の機数による本格運用に入る計画で進められている。年間の運用コストはEGNOSと合わせて8億ユーロになると見積もられている。
無料で利用できるGPSに対して、莫大な費用を投資し有料での活用を予定しているガリレオの採算性を疑問視する意見も多い。当初の事業費は36億ユーロないし38億ユーロと見込まれており、うち民間企業が24億ユーロを負担する予定だったが、2007年に共同事業体が解散し計画の中止が検討された。2007年5月にEUは公的資金で全額を肩代わりすることを決定し、11月に承認された。2010年には、Wikileaksによって漏出したアメリカ外交当局の資料に、ガリレオに用いる14機の衛星製造を請け負っているドイツの契約企業の担当役員が、ガリレオ計画を「フランスの国益に基づく馬鹿げたアイデア」だとコメントしたことが明らかとなり、問題の役員が解任される騒ぎがあった[1]。
Galileo is the global navigation satellite system (GNSS) that went live in 2016,[4] created by the European Union (EU) through the European GNSS Agency (GSA),[5] headquartered in Prague in the Czech Republic,[6] with two ground operations centres, Oberpfaffenhofen near Munich in Germany and Fucino in Italy. The €10 billion project[3][7] is named after the Italian astronomer Galileo Galilei. One of the aims of Galileo is to provide an independent high-precision positioning system so European nations do not have to rely on the U.S. GPS, or the Russian GLONASS systems, which could be disabled or degraded by their operators at any time.[8] The use of basic (lower-precision) Galileo services will be free and open to everyone. The higher-precision capabilities will be available for paying commercial users. Galileo is intended to provide horizontal and vertical position measurements within 1-metre precision, and better positioning services at higher latitudes than other positioning systems. Galileo is also to provide a new global search and rescue (SAR) function as part of the MEOSAR system.
The first Galileo test satellite, the GIOVE-A, was launched 28 December 2005, while the first satellite to be part of the operational system was launched on 21 October 2011. As of July 2018, 26 of the planned 30 active satellites are in orbit.[9][10] Galileo started offering Early Operational Capability (EOC) on 15 December 2016,[1] providing initial services with a weak signal, and is expected to reach Full Operational Capability (FOC) in 2019.[11] The complete 30-satellite Galileo system (24 operational and 6 active spares) is expected by 2020.[12]
Le programme Galileo est un système de positionnement par satellites (radionavigation) développé par l'Union européenne et incluant un segment spatial dont le déploiement doit s'achever vers 2020. Comme les systèmes américain GPS, russe GLONASS et chinois Beidou, il permet à un utilisateur muni d'un terminal de réception d'obtenir sa position. La précision attendue pour le service de base, gratuit, est de 4 mètres horizontalement et de 8 mètres en altitude[réf. nécessaire]. Un niveau de qualité supérieur sera fourni dans le cadre de services payants proposés aux professionnels.
Le segment spatial de Galileo sera constitué à terme de 30 satellites dont 6 de rechange. Chaque satellite, d'une masse d'environ 700 kg, circule sur une orbite moyenne (23 222 kilomètres) dans trois plans orbitaux distincts ayant une inclinaison de 56°. Ces satellites émettent un signal qui leur est propre et retransmettent un signal de navigation fourni par le segment de contrôle de Galileo. Ce dernier est constitué par deux stations chargées également de surveiller l'orbite et l'état des satellites.
Le projet Galileo, après une phase de définition technique qui débute en 1999, est lancé le 26 mai 2003 avec la signature d'un accord entre l'Union européenne et l'Agence spatiale européenne chargée du segment spatial. Une des motivations principales du projet est de mettre fin à la dépendance de l'Europe vis-à-vis du système américain, le GPS. Contrairement à ce dernier, Galileo est uniquement civil. Le projet parvient à surmonter l'opposition de certains membres de l'UE et d'une partie des décideurs américains ainsi que les difficultés de financement (le coût final est évalué à 5 milliards d'euros). Les tests de Galileo débutent fin 2005 grâce aux lancements des satellites précurseurs Giove-A et Giove-B en décembre 2005 et avril 2008. Les premiers satellites en configuration opérationnelle (FOC) sont lancés en août 2014. Au 15 août 2018, vingt-six satellites ont été lancés, dont 18 sont opérationnels et 4 en cours de mise en service1. Les premiers services de Galileo sont opérationnels depuis le 15 décembre 20162,3. La précision maximale ne sera pas atteinte avant 2020, lorsque 24 des 30 satellites seront opérationnels3,4. En janvier 2018, Galileo compte déjà près de 100 millions d'utilisateurs5, et 200 millions en septembre6.
Il sistema di posizionamento Galileo è un sistema di posizionamento e navigazione satellitare civile (in inglese GNSS - Global Navigation Satellite System), sviluppato in Europa come alternativa al Global Positioning System (NAVSTAR GPS), controllato invece dal Dipartimento della Difesa degli Stati Uniti d'America.
La sua entrata in servizio prevista per la fine del 2019[1] è stata anticipata al 15 dicembre 2016[2]. Il sistema una volta completato potrà contare su 26 satelliti artificiali orbitanti (24 operativi più 2 di scorta)[3] su 3 piani inclinati rispetto al piano equatoriale terrestre di circa 56° e ad una quota di circa 23.925 km[3]. Le orbite che saranno seguite dai satelliti sono quelle MEO (Medium earth orbit). A luglio 2018 si trovano in orbita 26 satelliti ma non tutti sono completamente operativi.
Galileo es el programa europeo de radionavegación y posicionamiento por satélite desarrollado por la Unión Europea (UE) conjuntamente con la Agencia Espacial Europea. Este programa dota a la Unión Europea de una tecnología independiente del GPS estadounidense y el GLONASS ruso.1 Al contrario de estos dos, será de uso civil.2 El sistema se pudo poner en marcha el 15 de diciembre del 20163 con alrededor de media constelación y será completado para 2020.4
«Галиле́о» (Galileo) — совместный проект спутниковой системы навигации Европейского союза и Европейского космического агентства, является частью транспортного проекта Трансевропейские сети (англ. Trans-European Networks). Система предназначена для решения геодезических и навигационных задач. В последнее время всё больше производителей ГССН-оборудования интегрируют в свои спутниковые приёмники и антенны возможность принимать и обрабатывать сигналы со спутников «Галилео», этому способствует достигнутая договорённость о совместимости и взаимодополнении с системой NAVSTAR GPS третьего поколения. Финансирование проекта будет осуществляться в том числе за счёт продажи лицензий производителям приёмников.
Помимо стран Европейского Союза, в проекте участвуют: Китай, Израиль, Южная Корея, Украина. Кроме того, ведутся переговоры с представителями Аргентины, Австралии, Бразилии, Чили, Индии, Малайзии. Ожидалось, что «Галилео» войдёт в строй в 2014—2016 годах, когда на орбиту будут выведены все 30 запланированных спутников (24 операционных и 6 резервных[1]). Но на 2018 год спутниковая группировка «Галилео» так и не достигла необходимого количества аппаратов. Компания Arianespace заключила договор на 10 ракет-носителей «Союз» для запуска спутников, начиная с 2010 года[2]. Космический сегмент будет обслуживаться наземной инфраструктурой, включающей в себя три центра управления и глобальную сеть передающих и принимающих станций.
В отличие от американской GPS и российской ГЛОНАСС, система «Галилео» не контролируется национальными военными ведомствами, однако в 2008 году парламент ЕС принял резолюцию «Значение космоса для безопасности Европы», согласно которой допускается использование спутниковых сигналов для военных операций, проводимых в рамках европейской политики безопасности. Разработку системы осуществляет Европейское космическое агентство. Общие затраты оцениваются в 4,9 млрд евро.
Спутники «Галилео» выводятся на круговые геоцентрические орбиты высотой 23 222 км (или 29 600 км от центра Земли), проходят один виток за 14 ч 4 мин 42 с и обращаются в трёх плоскостях, наклонённых под углом 56° к экватору. Долгота восходящего узла каждой из трёх орбит отстоит на 120° от двух других. На каждой из орбит при полном развёртывании системы будет находиться 8 действующих и 2 резервных спутника. Эта конфигурация спутниковой группировки обеспечит одновременную видимость из любой точки земного шара по крайней мере четырёх аппаратов. Временна́я погрешность атомных часов, установленных на спутниках, составляет одну миллиардную долю секунды, что обеспечит точность определения места приёмника около 30 см на низких широтах. За счёт более высокой, чем у спутников GPS, орбиты, на широте Полярного круга будет обеспечена точность до одного метра.
Каждый аппарат «Галилео» весит около 675 кг, его габариты со сложенными солнечными батареями составляют 3,02×1,58×1,59 м, а с развёрнутыми — 2,74×14,5×1,59 м, энергообеспечение равно 1420 Вт на солнце и 1355 Вт в тени. Расчётный срок эксплуатации спутника превышает 12 лет.
Gotland ist eine schwedische Insel und historische Provinz. Die nach Seeland (Dänemark) und vor Fünen (Dänemark) sowie Saaremaa (Estland) zweitgrößte Insel der Ostsee liegt nordöstlich von Öland. Ihren Namen hat sie vom Germanenstamm der Goten, die die Insel laut der Gutasaga um die Zeitenwende zumindest teilweise verließen, um auf dem Kontinent, später als Ost- und Westgoten, große Reiche im mediterranen Raum zu errichten.
Die Insel Gotland bildet zusammen mit einigen benachbarten kleineren Inseln die Provinz Gotlands län, die historische Provinz Gotland sowie die Gemeinde Gotland.

 Göteborg?/i (schwedisch [ˌʝøtəˈbɔrj]; deutsch veraltet Gotenburg oder Gothenburg; lateinisch Gothoburgum, englisch Gothenburg, dänisch Gøteborg) ist eine Großstadt in den schwedischen Provinzen Västra Götalands län, deren Residenzstadt sie ist, und Hallands län sowie den historischen Provinzen Västergötland, Bohuslän und Halland.
Göteborg?/i (schwedisch [ˌʝøtəˈbɔrj]; deutsch veraltet Gotenburg oder Gothenburg; lateinisch Gothoburgum, englisch Gothenburg, dänisch Gøteborg) ist eine Großstadt in den schwedischen Provinzen Västra Götalands län, deren Residenzstadt sie ist, und Hallands län sowie den historischen Provinzen Västergötland, Bohuslän und Halland.
Göteborg ist nach Stockholm und vor Malmö die zweitgrößte Stadt Schwedens; denselben Rang nimmt auch die Storgöteborg („Groß-Göteborg“) genannte, 13 Gemeinden umfassende Metropolregion mit 993.453 Einwohnern (Stand 30. September 2016) ein.[2] Die Stadt gliedert sich in zehn Stadtbezirke.
Göteborg——哥德堡的瑞典名字,瑞典第二大城市,经历了从工业海港到现代文化中心和国际运动赛场的转变。随着1994年哥德堡歌剧院的修建和部分城市博物馆的修复,哥德堡的文化景观也在进行着日新月异的提升。哥德堡最令人吃惊的变化当属餐厅和饭馆。这座城市凭借烹饪北大西洋的鱼类和贝类等当地特产,享有国际创新烹饪艺术城市的美誉。许多家餐馆都荣登过米其林指南,这令哥德堡引以为傲,当您旅行至此时,千万不要错过品尝当地美食。哥德堡是西部群岛的门户,拥有无与伦比的岛屿和姿态万千的碎礁,从市区乘船很容易到达各个岛屿。 (Quelle:http://www.sweden.cn)
哥德堡(瑞典语:Göteborg, 发音:[jœtɛˈbɔrj] ![]() 聆听)是瑞典的第二大城市,仅次于首都斯德哥尔摩。哥德堡近邻挪威,也是瑞典经济最发达的城市之一。哥德堡是瑞典享誉全球的汽车制造厂沃尔沃汽车之创厂地,而瑞典超级足球联赛中的哥登堡足球会则是一支以哥德堡为主场的球队。同时它也拥有在斯堪的纳维亚地区最多学生的哥德堡大学(Göteborgs universitet)。
聆听)是瑞典的第二大城市,仅次于首都斯德哥尔摩。哥德堡近邻挪威,也是瑞典经济最发达的城市之一。哥德堡是瑞典享誉全球的汽车制造厂沃尔沃汽车之创厂地,而瑞典超级足球联赛中的哥登堡足球会则是一支以哥德堡为主场的球队。同时它也拥有在斯堪的纳维亚地区最多学生的哥德堡大学(Göteborgs universitet)。
约塔河在哥德堡流入卡特加特海湾,将城市分成了两个部分。约塔河的入海口很适合作为港口,因此哥德堡也是北欧国家里最大的港口城市之一。
ヨーテボリ(スウェーデン語: Göteborg[ヘルプ/ファイル]、 スウェーデン語発音: [jœtɛˈbɔrj])は、ヴェストラ・イェータランド県に属するスウェーデンの港湾都市で、県庁所在地である。人口は約52万人。スウェーデンではストックホルムに次ぎ、北欧では5番目に大きい都市である。町の名前は「ゴートの都市」を意味する。日本語ではイェーテボリ、イエテボリ、エーテボリなどとも呼ばれる。
Göteborg[ヘルプ/ファイル]、 スウェーデン語発音: [jœtɛˈbɔrj])は、ヴェストラ・イェータランド県に属するスウェーデンの港湾都市で、県庁所在地である。人口は約52万人。スウェーデンではストックホルムに次ぎ、北欧では5番目に大きい都市である。町の名前は「ゴートの都市」を意味する。日本語ではイェーテボリ、イエテボリ、エーテボリなどとも呼ばれる。
Gothenburg (/ˈɡɒθənbɜːrɡ/ ( listen);[5] abbreviated Gbg;[6][7] Swedish: Göteborg [jœtɛˈbɔrj] (
listen);[5] abbreviated Gbg;[6][7] Swedish: Göteborg [jœtɛˈbɔrj] ( listen)) is the second-largest city in Sweden and the fifth-largest in the Nordic countries, and part of Västra Götaland County. It is situated by Kattegat, on the west coast of Sweden, and has a population of approximately 570,000 in the city center and about 1 million inhabitants in the metropolitan area.[1]
listen)) is the second-largest city in Sweden and the fifth-largest in the Nordic countries, and part of Västra Götaland County. It is situated by Kattegat, on the west coast of Sweden, and has a population of approximately 570,000 in the city center and about 1 million inhabitants in the metropolitan area.[1]
Gothenburg was founded as a heavily fortified, primarily Dutch, trading colony, by royal charter in 1621 by King Gustavus Adolphus. In addition to the generous privileges (e.g. tax relaxation) given to his Dutch allies from the then-ongoing Thirty Years' War, the king also attracted significant numbers of his German and Scottish allies to populate his only town on the western coast. At a key strategic location at the mouth of the Göta älv, where Scandinavia's largest drainage basin enters the sea, the Port of Gothenburg is now the largest port in the Nordic countries.[8]
Gothenburg is home to many students, as the city includes the University of Gothenburg and Chalmers University of Technology. Volvo was founded in Gothenburg in 1927.[9] The original parent Volvo Group and the now separate Volvo Car Corporation are still headquartered on the island of Hisingen in the city. Other key companies are SKF and Astra Zeneca.
Gothenburg is served by Göteborg Landvetter Airport 30 km (19 mi) southeast of the city center. The smaller Göteborg City Airport, 15 km (9.3 mi) from the city center, was closed to regular airline traffic in 2015.
The city hosts some of the largest annual events in Scandinavia. The Gothenburg Film Festival, held in January since 1979, is the leading Scandinavian film festival with over 155,000 visitors each year.[10] In summer, a wide variety of music festivals are held in the city, such as Way Out West and Metaltown.
Göteborg (pronuncia svedese [jœtəˈbɔrj][2] ascolta[?·info]), in italiano Gotemburgo[3], è una città della Svezia meridionale, situata nella contea di Västra Götaland e collocata nella provincia storica del Västergötland, sebbene alcuni sobborghi cittadini si estendano nella provincia di Bohuslän. Fu fondata nel 1621 dal re Gustavo II Adolfo.
Göteborg ha circa mezzo milione di abitanti, è la seconda città più popolosa della Svezia dopo Stoccolma e la quinta del Nord Europa. Se si considera l'intera area metropolitana, gli abitanti diventano più di 940.000.
Gotemburgo1 (en sueco, Göteborg  [jœteˈbɔrj] (?·i)) es la segunda ciudad en importancia y tamaño de Suecia, después de la capital, Estocolmo. Ubicada en la provincia de Västra Götaland en la costa oeste del país, en la desembocadura del río Göta älv en el estrecho de Kattegat. Es la sede administrativa y arzobispal de la provincia.
[jœteˈbɔrj] (?·i)) es la segunda ciudad en importancia y tamaño de Suecia, después de la capital, Estocolmo. Ubicada en la provincia de Västra Götaland en la costa oeste del país, en la desembocadura del río Göta älv en el estrecho de Kattegat. Es la sede administrativa y arzobispal de la provincia.
Su puerto es el más grande entre los países nórdicos ya que tiene sus aguas descongeladas durante todo el año. Es el lugar de tránsito de la mayor parte de las exportaciones e importaciones de Suecia.
Grandes industrias como SKF y AB Volvo tienen sus oficinas principales en esta ciudad. Sede de dos establecimientos universitarios, tiene la población universitaria más numerosa de Escandinavia. En las últimas décadas se ha desarrollado el turismo y los eventos culturales.
Fue fundada y fortificada en 1621 por el rey Gustavo II Adolfo, después de varios intentos fallidos de fundación debido a los ataques de daneses y noruegos.
Гётеборг, Йётеборг[2] (швед. Göteborg, (Göteborg (инф.), /jœte'bɔrj/)) — город на юго-западе Швеции в лене Вестра-Гёталанд. Является вторым по величине городом Швеции после Стокгольма. Площадь города примерно — 450 км².
Расположен на берегу пролива Каттегат в устье реки Гёта-Эльв[3].




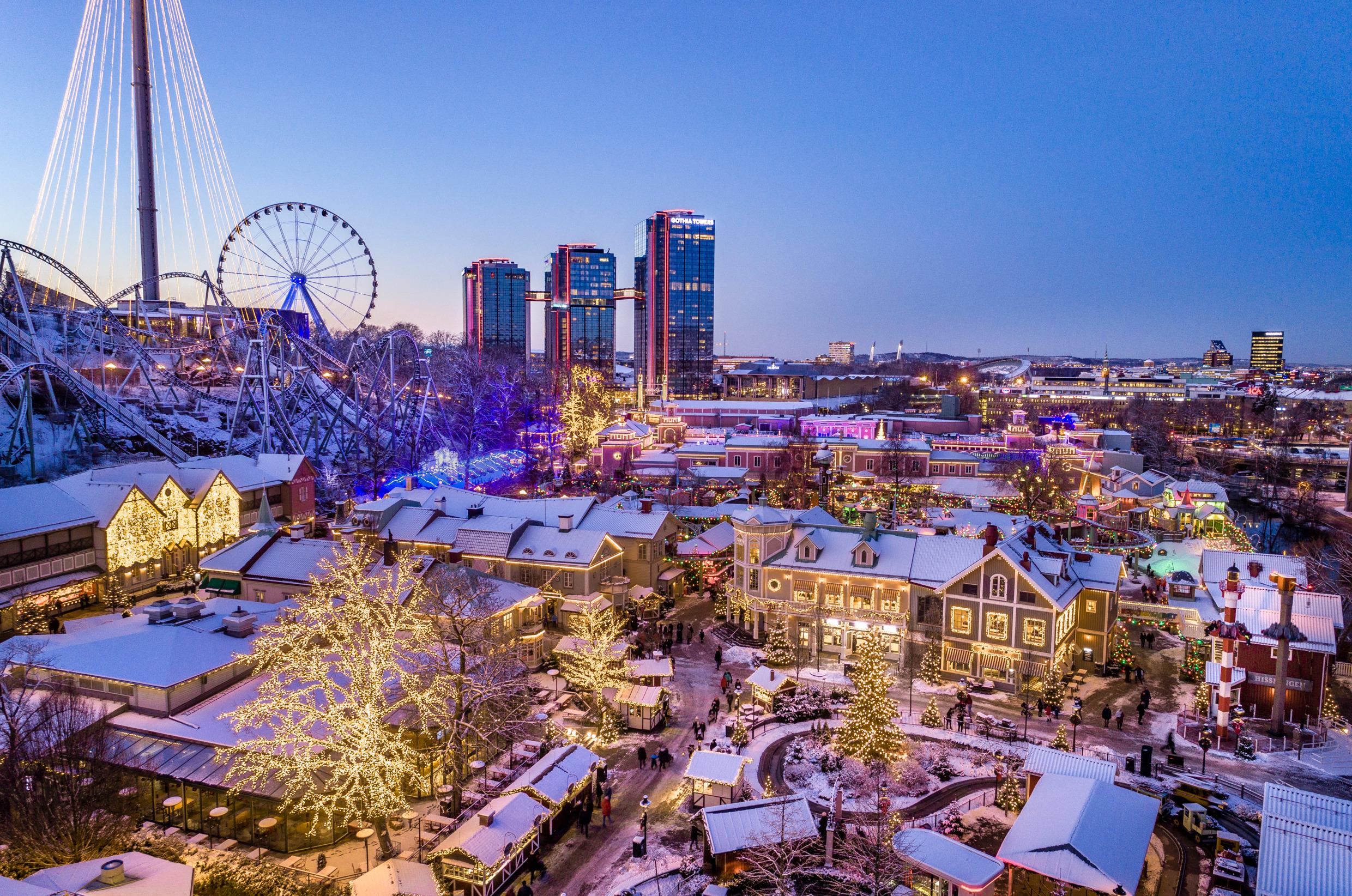
Zur Weihnachtszeit verwandelt sich der Freizeitpark Liseberg in ein funkelndes Weihnachtsmärchen mit Millionen von Weihnachtslichtern, Karussells, Glögg und zahlreichen Buden mit Süßigkeiten und Köstlichkeiten. Natürlich wird alles begleitet von Weihnachtsmusik. Hier kannst du Eislaufen, das Weihnachtsmanndorf besuchen und spannende Abenteuer hinter jeder Tür finden. Wenn du einmal das typisch schwedische Weihnachtsessen probieren möchtest, kannst du in Liseberg ein Julbord, ein Buffet mit vielen warmen und kalten Speisen genießen.





 Belarus
Belarus

 Berlin
Berlin

 Brandenburg
Brandenburg

 Bremen
Bremen
 Denmark
Denmark
 Germany
Germany
 Estonia
Estonia
 Finland
Finland
 France
France

 Hamburg
Hamburg
 Italy
Italy
 Latvia
Latvia
 Lithuania
Lithuania

 Mecklenburg-Vorpommern
Mecklenburg-Vorpommern
 Netherlands
Netherlands

 Lower Saxony
Lower Saxony

 North Rhine-Westphalia
North Rhine-Westphalia
 Poland
Poland
 Russia
Russia

 Saxony
Saxony

 Saxony-Anhalt
Saxony-Anhalt

 Schleswig-Holstein
Schleswig-Holstein
 Sweden
Sweden
 Switzerland
Switzerland
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom

 World Heritage
World Heritage

Die Backsteingotik (englisch Brick Gothic, polnisch Gotyk ceglany) umfasst gotische Bauwerke, die aus oder mit sichtbarem Backstein errichtet wurden. Sie ist vor allem in Norddeutschland, dem Ostseeraum und den Niederlanden[1] verbreitet. Ihr Verbreitungsgebiet erstreckt sich im Westen bis an die Straße von Dover und im Südosten bis nach Galizien. Der auch oft verwendete Begriff Norddeutsche Backsteingotik erfasst daher nur einen Teil der gesamten Backsteingotik. Gotische Backsteinarchitektur in Italien und Südfrankreich wird in der Regel allein den dortigen Regionalstilen zugerechnet.
Die mittelalterliche Verwendung von Backstein als Baustoff setzte nördlich der Alpen im 12. Jahrhundert ein. Die ältesten Bauten gehören deshalb noch der so genannten Backsteinromanik an. Im 16. Jahrhundert ging die Backsteingotik in die Backsteinrenaissance über. Die geografische Verbreitung des Bauens aus Backstein und mit sichtbarem Backstein unterlag vom Beginn des Hochmittelalters bis in die frühe Neuzeit aber durchaus Veränderungen. So gab es in Teilen des Münsterlandes zwischen Pionierbauten der Romanik und dem starken Backsteineinsatz in Renaissance und Barock eine zeitliche Lücke.
Viele von der Backsteingotik geprägte Altstädte und Einzelbauten wurden in die Liste des UNESCO-Welterbes aufgenommen.
一种特别在德国北海和波罗的海海岸常见的哥特式建筑是用烤砖建造起来的建筑结构.这个十二世纪开始使用那红色的烤砖作为建 筑材料的独特建筑风格之所以在北部德国低地如此普及是因为这块地区缺少天然石而且运输也非常困难,由于那片地区和汉萨盟的一 致性,因此它就成为了汉萨同盟的象征.有些历史悠久的建筑也就成了联合国教科文组织世界文化遗产项目之一。
Brick Gothic (German: Backsteingotik, Polish: Gotyk ceglany, Dutch: Baksteengotiek) is a specific style of Gothic architecture common in Northwest and Central Europe especially in the regions in and around the Baltic Sea, which do not have resources of standing rock, but in many places a lot of glacial boulders. The buildings are essentially built using bricks. Buildings classified as Brick Gothic (using a strict definition of the architectural style based on the geographic location) are found in Belgium (and the very north of France), Netherlands, Germany, Poland, Lithuania, Latvia, Estonia, Kaliningrad (former East Prussia), Sweden and Finland.
As the use of baked red brick arrived in Northwestern and Central Europe in the 12th century, the oldest such buildings are classified as the Brick Romanesque. In the 16th century, Brick Gothic was superseded by Brick Renaissance architecture.
Brick Gothic is characterised by the lack of figural architectural sculpture, widespread in other styles of Gothic architecture. Typical for the Baltic Sea region is the creative subdivision and structuring of walls, using built ornaments and the colour contrast between red bricks, glazed bricks and white lime plaster. Nevertheless, these characteristics are neither omnipresent nor exclusive. Many of the old town centres dominated by Brick Gothic, as well as some individual structures, have been listed as UNESCO World Heritage sites.
The real extent and the real variety of this brick architecture has to be distinguished from the view of late 19th and early 20th century, especially the years around the end of World War I, when it was instrumentalized, politically.
Indeed, about a quarter of medieval Gothic brick architecture is standing in the Netherlands, in Flanders and in French Flanders. Some dominant buildings combinations of brick and stone. But the criterion "no stone at all" looks like a trick to exclude them.[according to whom?] The towers of St Mary church in Lübeck, the very top Brick Gothic church of the Baltic Sea region, have corners of granite ashley. And many village churches in northern Germany and Poland have Brick Gothic design, but most of their walls are formed by boulders.
L'architettura gotica dei paesi baltici è una varietà regionale dell'architettura gotica, in particolare del gotico tedesco. Le aree coinvolte in questa forma di architettura medievale si affacciano sul mar Baltico e sul Mare del Nord e, da un punto di vista politico, comprendevano gli stati settentrionali del Sacro Romano Impero, le città della Lega Anseatica, i possedimenti dell'Ordine Teutonico. Il periodo interessato va dal XIII secolo al XV secolo.
Le caratteristiche distintive sono che si tratta di un'architettura prevalentemente in laterizio e di una rielaborazione originale e per certi aspetti molto distante dall'iniziale gotico francese. I paesi europei attuali che hanno testimonianze di questa architettura sono Germania, Polonia, Lituania, Lettonia, Estonia, e nell'area della storica Prussia Orientale, (Oblast di Kaliningrad Russia); alcune testimonianze sono anche presenti in Scandinavia.
Le gothique de brique (allemand : Backsteingotik) est un style d´architecture gothique du Nord de l´Europe, et plus particulièrement du Nord de l'Allemagne et des régions autour de la mer Baltique. Il s'est surtout répandu dans les villes culturellement allemandes de l'ancienne Ligue Hanséatique à partir du XIIIe siècle, puis bien au-delà par influence (Scandinavie, Flandres, toute la Pologne, Allemagne du Sud). Les bâtiments sont essentiellement constitués de briques et le style de la décoration s'est adapté aux possibilités et aux limites de ce matériaux, conférant à cette architecture une identité bien particulière.
Il existe d'autres styles d'architecture gothique en brique en Europe, plus ou moins indépendants, comme en Italie et dans la région Toulousaine en France. Le style gothique baltique ne comprend pas tout le gothique en brique d'Europe.
El gótico báltico (en alemán, Norddeutsche Backsteingotik), forma la parte mayor del gótico de ladrillos (en alemán: Backsteingotik). Es una variante de la arquitectura gótica y neogótica que apareció en la Europa septentrional. Sin la especificación "Baltico" es estendido del estrecho de Calais a la Galicia de los Cárpatos. Con la especificación "Baltico" esta concentrada en el norte de Alemania y las zonas aledañas al mar Báltico. En todas estas regiones mancan recursos naturales para construir edificios de piedra. Se extendió principalmente en las ciudades culturalmente alemanas de la antigua Liga Hanseática desde el siglo XIII, y luego por influencia (Escandinavia, toda Polonia, el sur de Alemania). Los edificios son esencialmente de ladrillo y el estilo de decoración se ha adaptado a las posibilidades y límites de este material, dando a esta arquitectura una identidad muy particular.
Кирпичная, ганзейская или северогерманская готика — разновидность готического стиля архитектуры, распространённая в Северной Германии, Польше, Белоруссии и Прибалтике в XIII—XVI веках. Красный керамический кирпич как строительный материал стал использоваться в Северной Европе в XII веке, поэтому самые древние кирпичные образцы относятся ещё к так называемой «кирпичной романике». В XVI в. кирпичную готику сменил «кирпичный ренессанс».
Для кирпичной готики характерны, с одной стороны, отсутствие скульптурных украшений, которые невозможно выполнить из кирпича, и, с другой стороны, богатство орнаментальных деталей кладки и структуризация плоскостей за счёт чередования красного либо глазурованного кирпича и известковой побелки стен.
Многие города, внешний облик которых украшают готические сооружения из красного кирпича, являются объектами Всемирного культурного наследия ЮНЕСКО.
 Energy resource
Energy resource

 Geography
Geography
 International cities
International cities
 Sport
Sport
 Important port
Important port
 Colleges and Universities in Europe
Colleges and Universities in Europe
 Architecture
Architecture
 Music
Music


 Christmas Market
Christmas Market