
Deutsch-Chinesische Enzyklopädie, 德汉百科
 Jiangxi Sheng-JX
Jiangxi Sheng-JX
 Chinesisches Nationalmuseum
Chinesisches Nationalmuseum
 Jiangxi Sheng-JX
Jiangxi Sheng-JX

 Art
Art
 CK - Chinese Art 1368 - 1644 AD
CK - Chinese Art 1368 - 1644 AD
 Nationales Palastmuseum Taipeh
Nationales Palastmuseum Taipeh
 Palastmuseum
Palastmuseum

 2019–20 Chinese Basketball Association season
2019–20 Chinese Basketball Association season
 Beijing Shi-BJ
Beijing Shi-BJ
 Fujian Sheng-FJ
Fujian Sheng-FJ
 Guangdong Sheng-GD
Guangdong Sheng-GD
 Jiangsu Sheng-JS
Jiangsu Sheng-JS
 Jiangxi Sheng-JX
Jiangxi Sheng-JX
 Jilin Sheng-JL
Jilin Sheng-JL
 Liaoning Sheng-LN
Liaoning Sheng-LN
 Shandong Sheng-SD
Shandong Sheng-SD
 Shanghai Shi-SH
Shanghai Shi-SH
 Shanxi Sheng-SX
Shanxi Sheng-SX
 Sichuan Sheng-SC
Sichuan Sheng-SC
 Tianjin Shi-TJ
Tianjin Shi-TJ
 Xinjiang Uygur Zizhiqu-XJ
Xinjiang Uygur Zizhiqu-XJ
 Zhejiang Sheng-ZJ
Zhejiang Sheng-ZJ


 Anhui Sheng-AH
Anhui Sheng-AH
 Chongqing Shi-CQ
Chongqing Shi-CQ

 History
History
 H 1000 - 500 BC
H 1000 - 500 BC

 History
History
 I 500 - 0 BC
I 500 - 0 BC
 Guizhou Sheng-GZ
Guizhou Sheng-GZ
 Henan Sheng-HA
Henan Sheng-HA
 Hubei Sheng-HB
Hubei Sheng-HB
 Hunan Sheng-HN
Hunan Sheng-HN
 Jiangsu Sheng-JS
Jiangsu Sheng-JS
 Jiangxi Sheng-JX
Jiangxi Sheng-JX
 Shandong Sheng-SD
Shandong Sheng-SD
 Shanghai Shi-SH
Shanghai Shi-SH
 Sichuan Sheng-SC
Sichuan Sheng-SC
 Zhejiang Sheng-ZJ
Zhejiang Sheng-ZJ
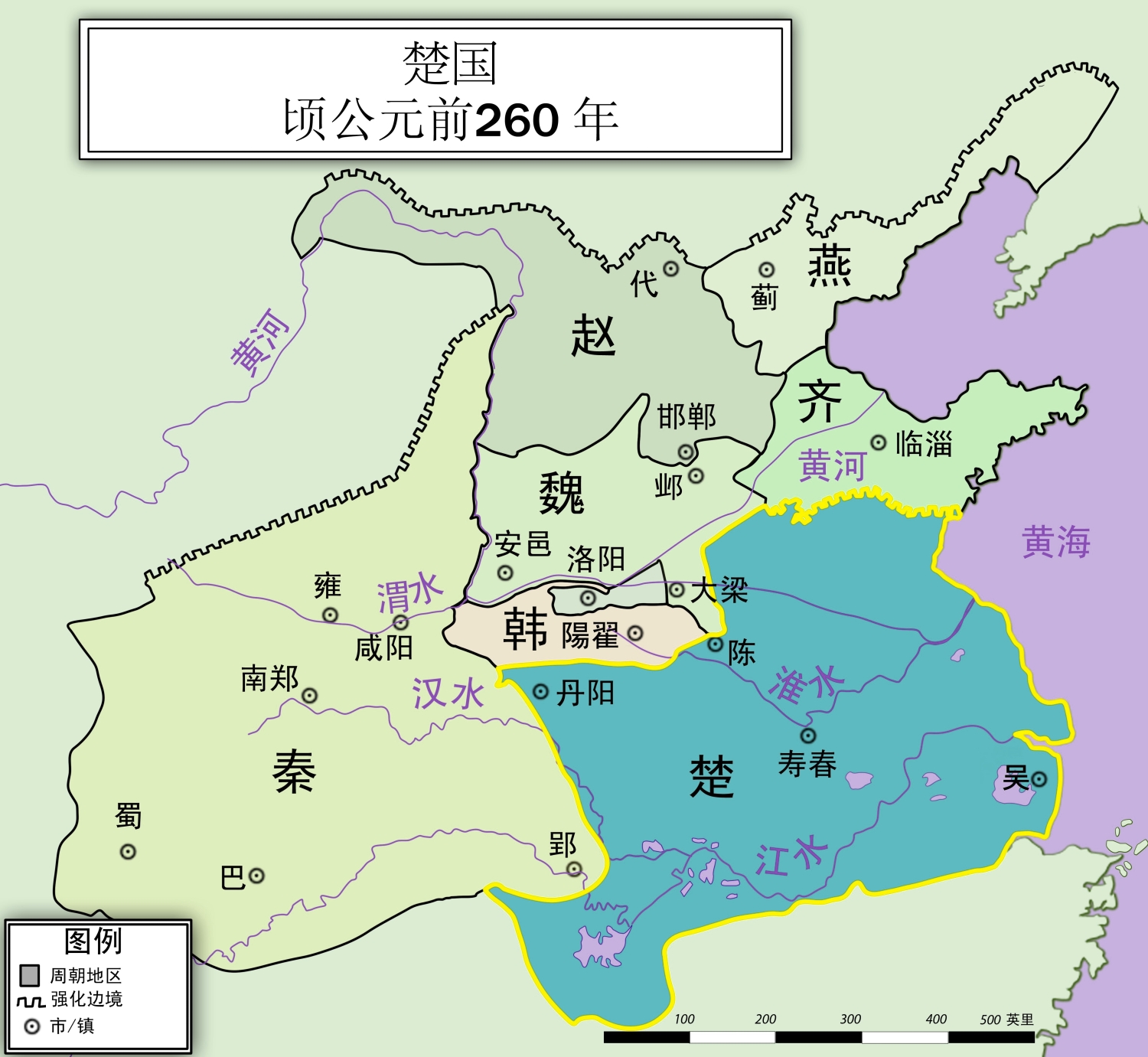
Chu (chinesisch 楚, Pinyin Chǔ, W.-G. Ch'u) war ein Königreich im Gebiet des heutigen Süd-China während der Westlichen Zhou-Dynastie (1046 bis 771 v. Chr.), der Zeit der Frühlings- und Herbstannalen (722 bis 481 v. Chr.) und der Zeit der Streitenden Reiche (475 bis 221 v. Chr.).
Ursprünglich war das Land als Jing (荆) und nachfolgend als Jingchu (荆楚) bekannt. Die größte Ausdehnung umfasste ein umfangreiches Gebiet, einschließlich das der heutigen Provinzen Hunan, Hubei, Chongqing, Henan, und Teile von Jiangsu. Die Hauptstadt von Chu war Ying.
Chu war zu seiner Zeit einer der mächtigsten Staaten und unterwarf zum Beispiel auch den kleineren Staat Lu im heutigen Shandong.
Größere Bedeutung erlangte Chu erstmals unter der Herrschaft von König Zhuang.
Chu (Chinese: 楚, Old Chinese: *s-r̥aʔ[2]) was a hegemonic, Zhou dynasty era state. From King Wu of Chu in the early 8th century BCE, the rulers of Chu declared themselves kings on an equal footing with the Zhou kings. Though initially inconsequential, removed to the south of the Zhou heartland and practising differing customs, Chu began a series of administrative reforms, becoming a successful expansionist state during the Spring and Autumn period. With its continued expansion Chu became a great Warring States period power, until it was overthrown by the Qin in 223 BCE.
Also known as Jing (荆) and Jingchu (荆楚), Chu included most of the present-day provinces of Hubei and Hunan, along with parts of Chongqing, Guizhou, Henan, Anhui, Jiangxi, Jiangsu, Zhejiang, and Shanghai. For more than 400 years, the Chu capital Danyang was located at the junction of the Dan and Xi Rivers[3][4] near present-day Xichuan County, Henan, but later moved to Ying. The ruling house of Chu originally bore the clan name Nai (嬭) and lineage name Yan (酓), but they are later written as Mi (芈) and Xiong (熊), respectively.[5]
Chu ou l'état de Chu (chinois simplifié : 楚国 ; chinois traditionnel : 楚國 ; pinyin : ; littéralement : « pays Chǔ ») était un État des périodes des Printemps et Automnes et des Royaumes combattants, établi sur le fleuve Yangzi. Chu a été annexé par Qin en 223 av. J.-C. La maison royale de Chu à l'origine portait le nom ancestral Nai (嬭) et le nom de clan Yan (酓) mais ceux-ci sont devenus plus tard Mi (芈) et Xiong (熊)1.
Chǔ (楚) fu un regno situato nell'attuale Cina centro meridionale, durante il Periodo delle primavere e degli autunni, (722-481 a.C. e il Periodo dei regni combattenti (481-221 a.C.). La famiglia dominante possedeva il cognome "mi" (芈), nome del clan "xiong" 熊, e il titolo nobiliare di "zi", corrispondente approssimativamente al nostro visconte.
Il primo nome dello Stato era Jing (荆) e successivamente Jingchu (荆楚). Al massimo della sua espansione il regno di Chu occupava una vasta area di territorio, comprendente le attuali province dello Hunan, Hubei, Chongqing, Henan, Shanghai, e parte dello Jiangsu. La capitale del regno era Ying (郢), localizzata approssimativamente nei pressi dell'attuale Jingzhou, nella provincia dell'Hubei.
Chǔ (楚, Wade-Giles: Ch'u3, pinyin: Chǔ) fue un reino situado en lo que hoy es China central y meridional durante el período de Primaveras y Otoños (722-481 a. C.) y el período de Reinos Combatientes (481-212 a. C.).
Fue originalmente conocido como Jing (荆) y luego como Jingchǔ (荆楚). Con el peso de su poder, el reino Chǔ ocupó vastas tierras, incluyendo las provincias actuales de Hunan, Hubei, Chongqing, Henan, Shanghái, y partes de Jiangsu. La capital de Chu era Ying (郢) y estaba ubicada en lo que hoy es la provincia de Hubei.
Чу (кит. 楚) — царство в южном Китае во время эпохи Чуньцю (722—481 гг. до н. э.) и Чжаньго («Воюющие царства» 481—221 до н. э.).
Первоначально царство было известно под названием Цзин (荆), затем Цзинчу (荆楚). На пике могущества под властью Чу находилась территория современных провинций Хунань, Хубэй, Чжэцзян, частично Цзянсу, Цзянси, Аньхой и Фуцзянь, а также города Шанхай. Ранней столицей Чу был Даньян 丹陽, в правление Сюн Туна (8-7 вв. до н. э.) столица была перенесена в Ин 郢 (совр. Цзинчжоу).
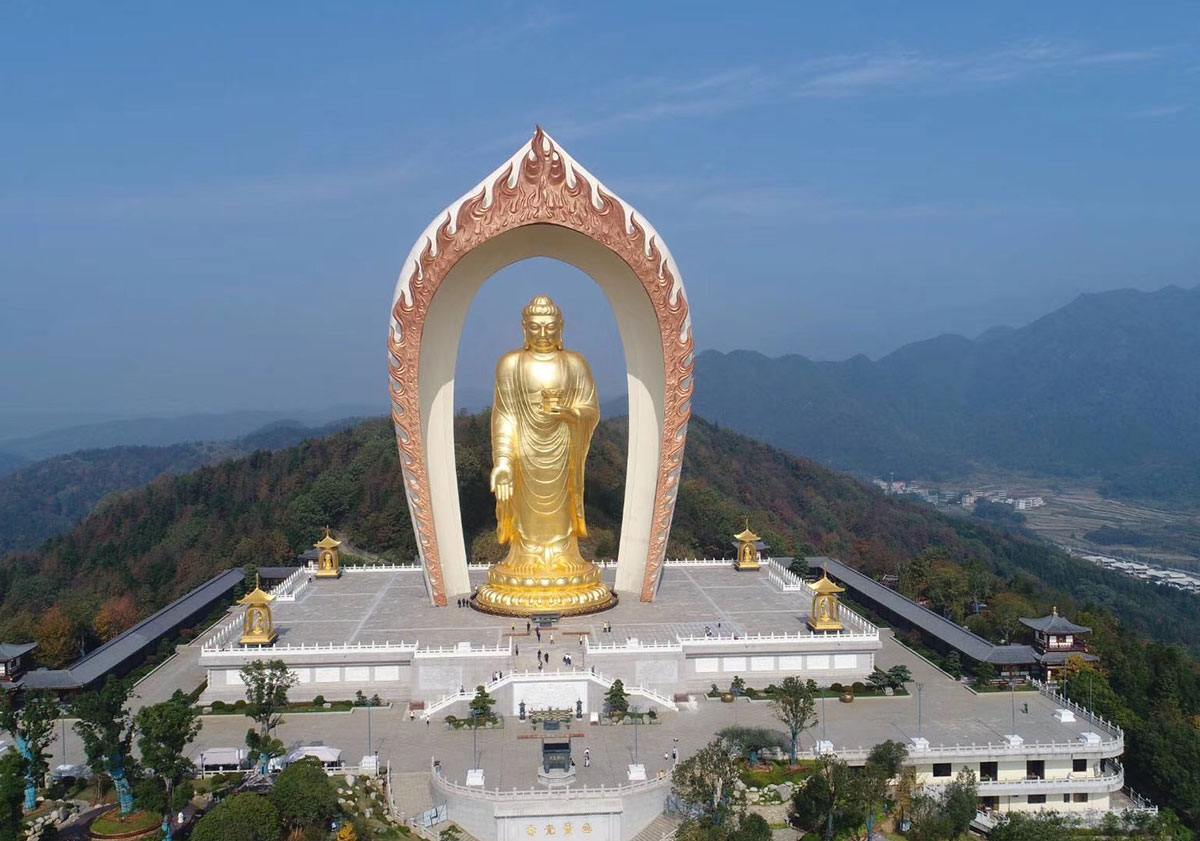

东林寺位于长江南岸,庐山西北麓,南面正对庐山香炉、天地诸峰,北倚分水岭及上方塔,西北有香谷,东南有乌龙潭,地势雄伟。寺前明堂开阔,香炉峰呈趋拜之势,千年紫烟不断,虎溪具眷恋之情,万载常流。唐大书法家柳公权曾写下流泉匝寺四字,盛赞此寺之妙。原寺内建筑恢弘,兼之布局合理,避阴抱阳,松竹密植,石径苔合。徜徉其中,莫不神清气爽,心旷而情怡,透出世外桃源,人间净土之神韵。东林寺建成于东晋太元十一年(386年),为中国佛教净土宗发祥地,南方佛教中心,隋朝以后为全国佛教八大道场之一。历史上,与东林寺结缘的名流高士不乏其人,如佛陀跋陀罗尊者、智者大师、鉴真大师、李世民、刘遗民、谢灵运、陶渊明、孟浩然、韩愈、白居易、柳公权、王安石、苏东坡、李白、陆游、杜甫、杜 牧、杜荀鹤、刘长卿、王昌龄、李邕、王阳明、黄庭坚、周敦颐、岳飞、范成大、朱熹、康有为等等。寺内文物甚多,从东晋远公与西域经师译经驻锡的译经台,到 清末康有为题刻的《柳公权残碑记》,时间跨度千余年,每一处古迹都寄寓着一段历史典故,其丰厚的文化底蕴,对中国传统文化也产生了至为深远的影响。东林寺自建造以来,迄今已有1600多年历史,沧桑历尽,屡废屡兴。
这里是中国净土宗的发祥地,是净土宗初祖祖庭之所在。寺当庐山之阴,南面香炉峰,北倚灵竹山。山不甚高,为庐山之外廓,寺前临溪,入门为虎溪桥。古木葱茏,梵音缭绕,人间净境,秀挹庐山。
東林寺(とうりんじ、donglinsi)は、中国の世界遺産である廬山にあり、江西省九江市に位置している。九江市の中心部から16キロのところにあり、廬山にあることから廬山東林寺とよく呼ばれている。建立は東晋時代の大元九年(384年)であり、廬山にある寺院の有名な一つになる[1]。東林寺はなんといっても浄土宗発祥の地とされ、日本の浄土宗や浄土真宗からも師が居た場所とされている。1983年に国務院に仏教全国重点寺院に指定された[2]。
東林寺の始まりは慧遠大師である。彼は南下して仏法を広めようとしていたその途中で、廬山に立ち寄った。それがいつの間にか三年にも及び、慕うものも増えた。江州の刺史であった桓伊が、この地に寺を建立するように提案し、それがきっかけとなり朝廷の許可と百姓の支援もあり、慧遠を中心にして寺院が建立された[3]。
慧遠は常に東林にいたとされ、大元十五年(390年)に中国でも初めてとなる仏教結社「白蓮社」を立ち上げた。浄土業を修行の中心にし、「阿弥陀仏の浄土法門」を唱えた。隋の時代、天台大師もこの地を訪れ、足を休めた。日本でも有名な鑑真大師は六度目の日本への渡航に挑戦する前に、この地を訪れ、日本の浄土宗への伝承の大きな役割を果たした。中国で有名な南宋時代の将軍、岳飛も母親のために、この地を訪れたことがある[4]。日中国交正常化20周年の際、日本の浄土宗団体が二度この地を訪れ,蓮と蓮の実を贈った。日本の浄土宗総長であった成田有恒氏と果公上人が手を携えて蓮の池に入り、友好と平和を象徴する青蓮華を共同で植えた[5]。
Donglin Monastery is the birthplace of the Pure Land School of Chinese Buddhism. It is located behind Mount Lu, facing Xianglu Peak to the South, at the foot of Donglin Hill, which is one of the outer ring hills of Mount Lu. The Tiger stream (Huxi) runs in front of the Monastery, and the bridge over the Tiger leads the way to the monastery gate. The area is clothed with old trees and luxuriant vegetation and with Buddhist chanting fills the air. It is the most graceful place in Mount Lu, the pure land in our Saha world.
Donglin Temple (simplified Chinese: 东林寺; traditional Chinese: 東林寺; pinyin: Dōnglín sì; lit. 'Eastern Forest Temple') is a Buddhist monastery approximately 20 kilometres (12 mi) from Jiujiang, in the north of Jiangxi province, China. Built in 386 CE at the foot of Lushan by Huiyuan, founder of the Pure Land Sect of Buddhism, it is well known for how long it has stood without collapsing.[1][2]
In the Tang dynasty, Jianzhen made several trips to Japan for the mission of preaching Buddhism. As a result, Huiyuan and the doctrine of Donglin Temple began to spread in Japan. Donglin Temple made contributions to improve cultural exchanges and friendly visits between China and Nepal, India, Japan.[3]
The monastery reached its peak of influence during the Tang Dynasty (618–907 CE), but was severely damaged during the Taiping Rebellion and was almost destroyed during the Republican period (1912–1949) of Chinese history.[2]
 China
China
 Fujian Sheng-FJ
Fujian Sheng-FJ
 Guangdong Sheng-GD
Guangdong Sheng-GD
 Guizhou Sheng-GZ
Guizhou Sheng-GZ
 Hongkong Tebiexingzhengqu-HK
Hongkong Tebiexingzhengqu-HK
 Hubei Sheng-HB
Hubei Sheng-HB
 Hunan Sheng-HN
Hunan Sheng-HN
 Jiangsu Sheng-JS
Jiangsu Sheng-JS
 Jiangxi Sheng-JX
Jiangxi Sheng-JX
 Sichuan Sheng-SC
Sichuan Sheng-SC
 Taiwan Sheng-TW
Taiwan Sheng-TW
 Zhejiang Sheng-ZJ
Zhejiang Sheng-ZJ


 Anhui Sheng-AH
Anhui Sheng-AH
 Gansu Sheng-GS
Gansu Sheng-GS
 Guangdong Sheng-GD
Guangdong Sheng-GD
 Guangxi Zhuangzu Zizhiqu-GX
Guangxi Zhuangzu Zizhiqu-GX
 Henan Sheng-HA
Henan Sheng-HA
 Hubei Sheng-HB
Hubei Sheng-HB
 Hunan Sheng-HN
Hunan Sheng-HN
 Jiangxi Sheng-JX
Jiangxi Sheng-JX
 Liaoning Sheng-LN
Liaoning Sheng-LN
 Shandong Sheng-SD
Shandong Sheng-SD
 Shanxi Sheng-SX
Shanxi Sheng-SX
 Sichuan Sheng-SC
Sichuan Sheng-SC
 Tianjin Shi-TJ
Tianjin Shi-TJ
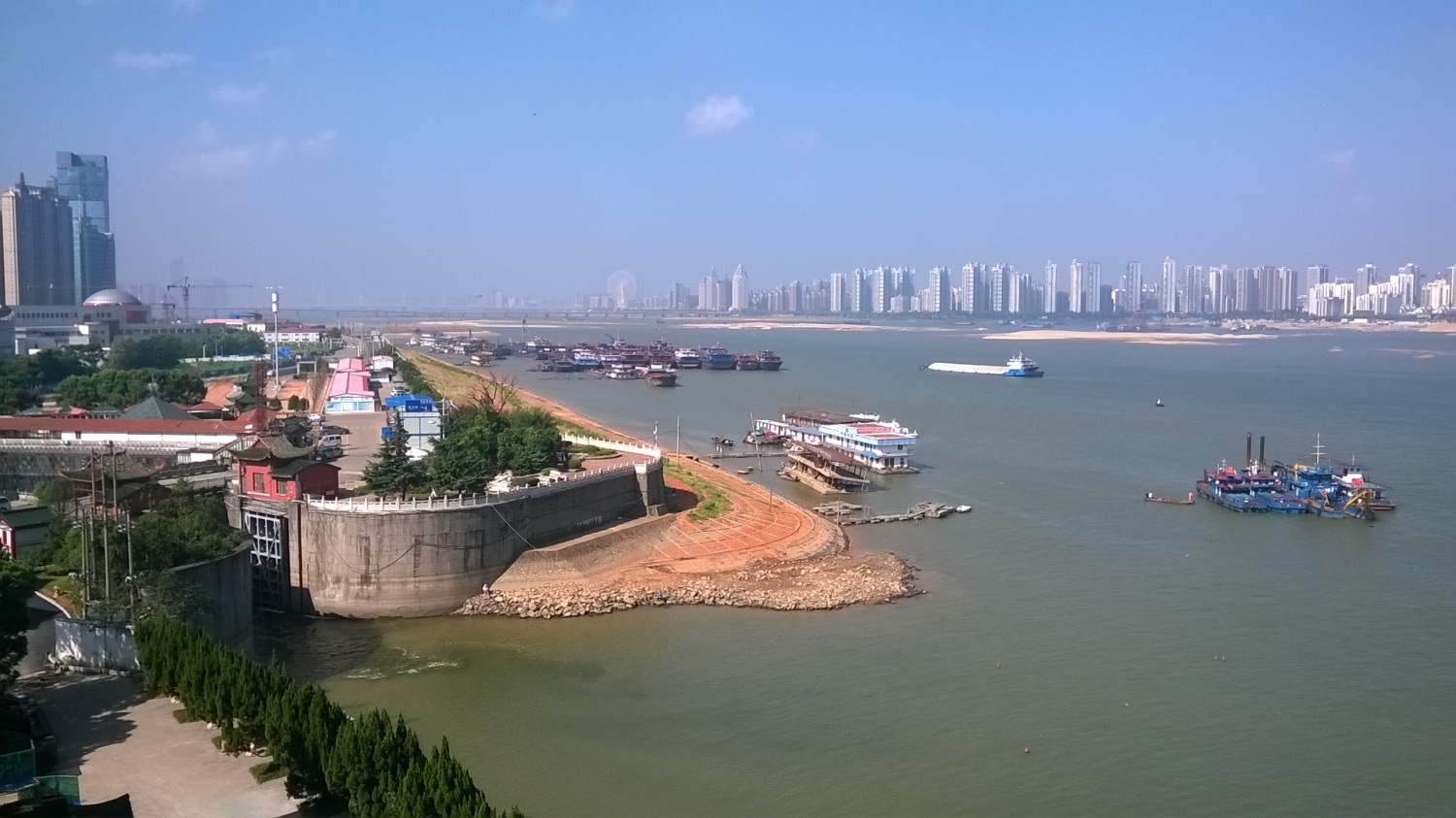




Der Gan Jiang („Gan-Fluss“; chinesisch 赣江, Pinyin Gàn Jiāng) ist der größte Fluss in der chinesischen Provinz Jiangxi.
Er fließt durch den See Poyang Hu und dann in den Jangtsekiang. Er hat eine Länge von 758 km und ein Einzugsgebiet von 81.600 km².[1] Es ist Hauptarterie Nanchangs.
 Architecture
Architecture
 Sport
Sport
 Religion
Religion
 Theme park
Theme park
 Geography
Geography