
漢德百科全書 | 汉德百科全书
 Canada
Canada



 Connecticut-CT
Connecticut-CT

 Georgia-GA
Georgia-GA
 Canada
Canada

 Kentucky-KY
Kentucky-KY

 Maine-ME
Maine-ME

 Maryland-MD
Maryland-MD

 Massachusetts-MA
Massachusetts-MA

 New Brunswick-NB
New Brunswick-NB

 New hampshire-NH
New hampshire-NH

 New jersey-NJ
New jersey-NJ

 New jersey-NJ
New jersey-NJ

 New York-NY
New York-NY

 Newfoundland and Labrador-NL
Newfoundland and Labrador-NL

 North Carolina-NC
North Carolina-NC

 Nova Scotia-NS
Nova Scotia-NS

 Ohio-OH
Ohio-OH

 Pennsylvania-PA
Pennsylvania-PA

 Quebec-QC
Quebec-QC
 South Carolina-SC
South Carolina-SC

 Tennessee-TN
Tennessee-TN

 Tennessee-TN
Tennessee-TN
 United States
United States

 Vermont-VT
Vermont-VT

 Virginia-VA
Virginia-VA

 West Virginia-WV
West Virginia-WV
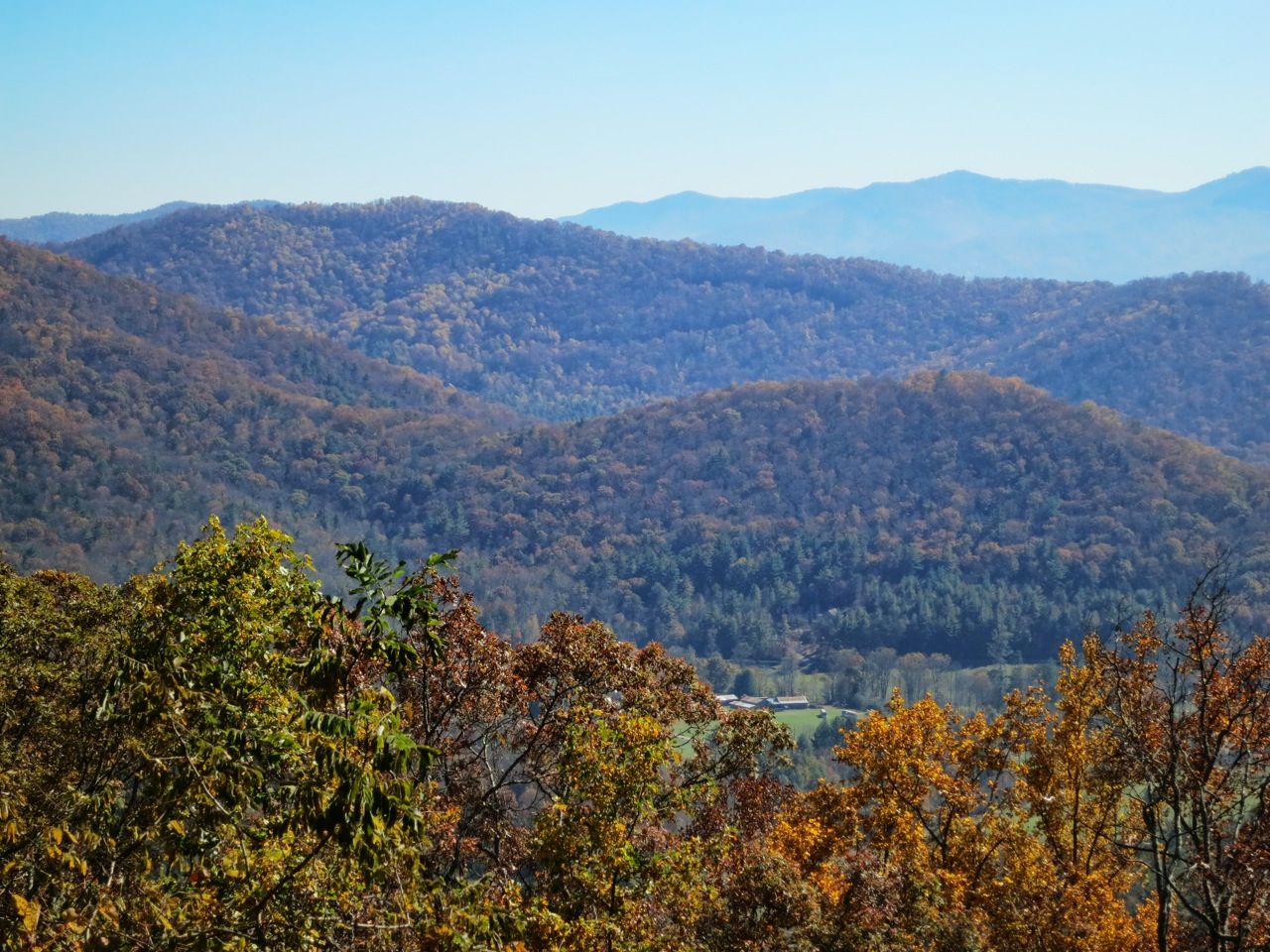

Die Appalachen (englisch Appalachian Mountains) sind ein bewaldetes Gebirgssystem im Osten Nordamerikas, das sich über eine Länge von 2400 Kilometer von den Long Range Mountains an der Westküste der kanadischen Insel Neufundland bis in den Norden des US-Bundesstaates Alabama erstreckt. Obwohl ihr höchster Gipfel mehr als 2000 Meter hoch ist, haben die Appalachen sowohl hinsichtlich ihrer Höhe als auch ihrer Morphologie einen Mittelgebirgscharakter. Nur wenige Berge erheben sich über mehr als 1200 m Höhe, und viele Bergkuppen bleiben deutlich unter 800 m.
Benannt sind die Appalachen nach dem indigenen Stamm der Apalachee. Für die Appalachenregion als Kultur- und Wirtschaftsraum wird auch die Bezeichnung Appalachia verwendet.[1]
阿巴拉契亚山脉(英语:Appalachian Mountains),又译阿帕拉契山脉,是北美洲东部的一座山系。南起美国的阿拉巴马州,北至加拿大的纽芬兰和拉布拉多省。最北部余脉则延伸到魁北克的加斯佩地区。最高峰在北卡罗莱纳州的米切尔峰(2037米)。
构成阿巴拉契亚山脉的有纽芬兰省的长岭山、魁北克的圣母山、缅因州的朗费罗山、新罕布夏州的怀特山、佛蒙特州的格林山脉、塔库尼克山;马萨诸塞州的勃克夏山;跨宾夕法尼亚州、马里兰州和西佛吉尼亚州三州的阿勒格尼山脉;跨宾夕法尼亚州、马里兰州、西佛吉尼亚州以及佛吉尼亚州四州的阿巴拉契亚岭谷。还有从宾夕法尼亚州南部到佐治亚州北部的蓝岭山脉。
实际上阿巴拉契高地 严格的边界范围存有争议,阿第伦达克山脉一般被认为是属于加拿大地盾,而非阿巴拉契亚高地。
アパラチア山脈(Appalachian Mountains)は、カナダ及びアメリカ合衆国東北部に位置し、北東から南西方向に全長約2,600kmにわたって延びる丘陵・山脈。狭義では、そのうちのウエストバージニア州、バージニア州、ケンタッキー州、テネシー州、ノースカロライナ州等の南側の部分のみを指すこともある。
複雑に褶曲した山脈で、侵食が進んだ丘陵性の古い山脈である。北端はカナダニューファンドランド島で、そこから北アメリカ大陸東部を南西方向に縦断し、南端はアラバマ州の中央に至る。また、その裾野はミシシッピ州北西部にまで及んでいる。個々の山の標高は平均して1,000m前後で、最高峰はノースカロライナ州にあるミッチェル山(標高2,037m)。
山脈の西部では石油・石炭が盛んに採掘されているなど地下資源が豊富。山脈の東側には都市が発達している。国立公園が多く、グレート・スモーキー山脈国立公園やシェナンドー国立公園が有名である。
The Appalachian Mountains,[a] often called the Appalachians, are a system of mountains in eastern North America. The Appalachians first formed roughly 480 million years ago during the Ordovician Period. They once reached elevations similar to those of the Alps and the Rocky Mountains before experiencing natural erosion.[4][5] The Appalachian chain is a barrier to east–west travel, as it forms a series of alternating ridgelines and valleys oriented in opposition to most highways and railroads running east–west.
Definitions vary on the precise boundaries of the Appalachians. The United States Geological Survey (USGS) defines the Appalachian Highlands physiographic division as consisting of thirteen provinces: the Atlantic Coast Uplands, Eastern Newfoundland Atlantic, Maritime Acadian Highlands, Maritime Plain, Notre Dame and Mégantic Mountains, Western Newfoundland Mountains, Piedmont, Blue Ridge, Valley and Ridge, Saint Lawrence Valley, Appalachian Plateaus, New England province, and the Adirondack areas.[6][7] A common variant definition does not include the Adirondack Mountains, which geologically belong to the Grenville Orogeny and have a different geological history from the rest of the Appalachians.[8][9][10]
Les Appalaches sont une chaîne de montagnes située dans l'Est de l'Amérique du Nord et s'étendant de Terre-Neuve (Canada), au nord, jusqu'au centre de l'État de l'Alabama, au sud (États-Unis). Elle culmine au mont Mitchell (2 037 mètres) en Caroline du Nord.
Les Appalaches séparent la plaine côtière atlantique (à l'est) du bassin du fleuve Mississippi et des Grands Lacs (à l'ouest). Elles s'étirent sur près de 2 000 km de longueur.
L'exploitation du charbon, qui fournit la moitié de l'électricité américaine, y a fortement périclité, et l'industrie métallurgique est en grande difficulté.
Les Appalaches ont donné leur nom à un type de relief, le relief appalachien, qui désigne les vestiges d'une ancienne montagne fortement arasée. De longs couloirs s'étendent parallèlement à des échines rectilignes. Les cluses appalachiennes forment des passages étroits à travers les chaînons de la montagne.
Le Sentier des Appalaches (AT) parcourt les sommets de la chaîne depuis le Maine jusqu'à la Géorgie et le Sentier international des Appalaches (SIA - IAT) passe par les sommets du nord du Maine jusqu'au cap Gaspé, en Gaspésie. Leur point d'intersection est le sommet du mont Katahdin.
Gli Appalachi (AFI: /appaˈlaki/) o Appalaci (/appaˈlaʧi/[1]; in inglese Appalachian Mountains, in francese Appalaches) sono una catena montuosa situata nella parte orientale dell'America del Nord.
Si sviluppa, quasi parallelamente alla costa orientale atlantica, dal golfo del fiume San Lorenzo fino all'Alabama, per almeno 2500 km con picchi non molto elevati (i più alti sono con 2037 m il monte Mitchell e con 1917 m il monte Washington). Gli Appalachi riguardano anche l'isola di Terranova (Canada) e l'isola francese di Miquelon parte della collettività territoriale di Saint-Pierre e Miquelon[2][3]. La porzione sud degli Appalachi viene chiamata monti Unakas.
Per via dell'età geologica, gli Appalachi sono la catena montuosa più vecchia delle Americhe. Gli Appalachi statunitensi sono una delle zone economicamente più depresse degli Stati Uniti.
Apalaches o montes Apalaches (en inglés: Appalachian Mountains o Appalachians; en francés: Appalaches1) es una importante cordillera ubicada en el este de Norteamérica. Se extiende desde la Isla de Terranova en Canadá, pasado por la colectividad de ultramar francés de San Pedro y Miquelón, hasta Alabama en los Estados Unidos, aunque su parte más septentrional termina en la península de Gaspé, en Quebec. Constituye el elemento morfológico más sobresaliente de la parte oriental de América del Norte.
Se originó en antiguas montañas formadas en el periodo Paleozoico con relieves suavizados por la prolongada acción de los agentes exógenos. El sistema está dividido en una serie de cordilleras, en las que la medida de altura de los picos es de unos 1000 m s. n. m. (metros sobre el nivel del mar). La cima más elevada es el monte Mitchell, en Carolina del Norte, mide 2037 m s. n. m. y es el punto más alto de los Estados Unidos al este del río Misisipi y de todo el este de Norteamérica.
Аппала́чи[2] (англ. Appalachian Mountains) — горная система на востоке Северной Америки, в США и Канаде. Длина — 2600 км.
Северные Аппалачи (к северу от рек Мохок и Гудзон) — холмистое плоскогорье с отдельными массивами высотой до 1916 м (гора Вашингтон), имеют следы древнего оледенения. Южные Аппалачи в осевой зоне состоят из параллельных хребтов и массивов, разделённых широкими долинами; к осевой зоне прилегают с востока плато Пидмонт, с запада — Аппалачское плато. Высота — до 2037 м (гора Митчелл). В горах имеются месторождения каменного угля, нефти и газа, железных руд, титана; широколиственные, хвойные и смешанные леса.
Горы образовались в пермский период в результате столкновения двух материков (возникновение Пангеи).

 Alberta-AB
Alberta-AB
 Nobel prize
Nobel prize
 Nobel Prize in Physics
Nobel Prize in Physics
 Nobel prize
Nobel prize
 Nobel Prize in Literature
Nobel Prize in Literature
 Nobel prize
Nobel prize
 University/Institute
University/Institute
 Universities in Canada
Universities in Canada
 Nobel prize
Nobel prize
 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine
Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine
 Nobel prize
Nobel prize
 University/Institute
University/Institute

 Nova Scotia-NS
Nova Scotia-NS
 Universities in Canada
Universities in Canada




Edmonton [ˈedməntən] ist die Hauptstadt der kanadischen Provinz Alberta. Sie hat 932.546 Einwohner, hingegen hat die Metropolregion (CMA) 1.411.945 Einwohner (2017).[2] Damit ist Edmonton nach Calgary die zweitgrößte Stadt der Provinz und die fünftgrößte in Kanada. Mit 683 km² Gesamtfläche ist sie eine der flächengrößten Städte Nordamerikas, hat damit aber auch eine der niedrigsten Bevölkerungsdichten.
Indianische Siedlungen reichen mindestens 11.000 Jahre zurück, doch führt sich die Stadt auf ein Fort, das 1795 errichtet wurde, zurück. 1905 wurde Edmonton Hauptstadt der Provinz, die etwa bis zum Zweiten Weltkrieg stark von der Landwirtschaft abhing. Kriegsproduktion und Bodenschätze brachten der Stadt trotz des unwirtlichen Klimas einen lange anhaltenden industriellen Boom. Den bedeutendsten Wirtschaftszweig stellen heute die Dienstleistungsgewerbe dar, deren größter Arbeitgeber neben der Regierung die University of Alberta ist.
埃德蒙顿(英语:Edmonton,香港作爱民顿,台湾作艾德蒙顿,台山话作点问顿)是加拿大阿尔伯塔省的首府,该省的第二大城市(仅次于卡尔加里),城市人口为 899,447人(2016年数据),而大埃德蒙顿地区(CMA)人口为1,363,300(2015年数据)。埃德蒙顿是加拿大人口第二多的省会城市(排在多伦多之后)。埃德蒙顿是阿尔伯塔省的文化、政府和教育中心,城市拥有轻轨运输,一年有许多节日,大多集中在夏季,并有北美最大的室内购物中心——西部埃德蒙顿购物中心和加拿大最大的历史公园——埃德蒙顿炮台公园(Fort Edmonton Park)。2004年,埃德蒙顿庆祝其建市100周年(1904年)。
エドモントン(英: Edmonton[2])は、カナダのアルバータ州にある都市。同州の州都であり、州内ではカルガリーに次ぐ第2の都市である(国内5位)。また、カナダの州都としてはトロントに次ぐ第2位の人口規模を持つ。肥沃な農業地帯が広がるプレーリーに位置し、ノースサスカチュワン川が周辺地域の中心を流れている。
市内人口はおよそ81万人、広域圏人口はおよそ116万人で、北米の100万人都市としては最北端に位置する。州北部で盛んなオイルサンド産業と、ノースウエスト準州で運営されている大規模なダイヤモンド鉱への玄関口となっている。文化や行政、教育が盛んな地域でもある。「ザ・フェスティバル・シティ」[3]と呼ばれるほど年間を通してイベント行事が開催され、市内には北米最大のショッピングモール「ウェスト・エドモントン・モール」と最大の歴史公園「フォート・エドモントン(Fort Edmonton)」がある。
Edmonton (/ˈɛdməntən/ (![]() listen); Cree: ᐊᒥᐢᑲᐧᒋᐊᐧᐢᑲᐦᐃᑲᐣ;[13] Blackfoot: Omahkoyis[14]) is the capital city of the Canadian province of Alberta. Edmonton is on the North Saskatchewan River and is the centre of the Edmonton Metropolitan Region, which is surrounded by Alberta's central region. The city anchors the north end of what Statistics Canada defines as the "Calgary–Edmonton Corridor".[15]
listen); Cree: ᐊᒥᐢᑲᐧᒋᐊᐧᐢᑲᐦᐃᑲᐣ;[13] Blackfoot: Omahkoyis[14]) is the capital city of the Canadian province of Alberta. Edmonton is on the North Saskatchewan River and is the centre of the Edmonton Metropolitan Region, which is surrounded by Alberta's central region. The city anchors the north end of what Statistics Canada defines as the "Calgary–Edmonton Corridor".[15]
The city had a population of 932,546 in 2016, making it Alberta's second-largest city and Canada's fifth-largest municipality.[5] Also in 2016, Edmonton had a metropolitan population of 1,321,426, making it the sixth-largest census metropolitan area (CMA) in Canada.[7] Edmonton is North America's northernmost metropolitan area with a population over one million. A resident of Edmonton is known as an Edmontonian.[16]
Edmonton's historic growth has been facilitated through the absorption of five adjacent urban municipalities (Strathcona, North Edmonton, West Edmonton, Beverly and Jasper Place)[17] in addition to a series of annexations through 1982,[18] and the annexation of 8,260 ha (82.6 km2) of land from Leduc County and the city of Beaumont on January 1, 2019.[8] Known as the "Gateway to the North",[19] the city is a staging point for large-scale oil sands projects occurring in northern Alberta and large-scale diamond mining operations in the Northwest Territories.[20]
Edmonton is a cultural, governmental and educational centre. It hosts a year-round slate of festivals, reflected in the nickname "Canada's Festival City".[1] It is home to North America's largest mall, West Edmonton Mall (the world's largest mall from 1981 until 2004),[21] and Fort Edmonton Park, Canada's largest living history museum.[22]
Edmonton (![]() /ˈɛdməntən/ (?·i)) es la capital de la provincia canadiense de Alberta, así como sede de sus poderes y su administración. Está ubicada en la parte central de la provincia, una de las zonas más fértiles de las llanuras canadienses, en torno al río Saskatchewan Norte. 812 201 personas viven en Edmonton,1 lo que la convierte en la segunda ciudad más populosa de la provincia, detrás de Calgary, la segunda capital de provincia con más habitantes tras Toronto y la quinta de Canadá. Además, su área metropolitana es la sexta más poblada del país, con una población de 1 034 945 habitantes.2
/ˈɛdməntən/ (?·i)) es la capital de la provincia canadiense de Alberta, así como sede de sus poderes y su administración. Está ubicada en la parte central de la provincia, una de las zonas más fértiles de las llanuras canadienses, en torno al río Saskatchewan Norte. 812 201 personas viven en Edmonton,1 lo que la convierte en la segunda ciudad más populosa de la provincia, detrás de Calgary, la segunda capital de provincia con más habitantes tras Toronto y la quinta de Canadá. Además, su área metropolitana es la sexta más poblada del país, con una población de 1 034 945 habitantes.2
La ciudad abarca 683 km², una superficie mayor que la de Chicago, Filadelfia, Toronto o Montreal. Sin embargo, tiene una de las densidades de población más bajas de América del Norte, alrededor del 9,4 % de la de Nueva York. El residente de Edmonton es conocido como edmontoniano.
Edmonton sirve como enlace a la zona norte del «Corredor Calgary-Edmonton», una de las cuatro regiones que en conjunto comprenden el 50 % de la población de Canadá. Desde ella se organizan proyectos a gran escala de arenas de alquitrán que se desarrollan en el norte de Alberta, así como para proyectos de minería de diamantes en los Territorios del Noroeste.
Es el centro cultural, gubernamental y educativo de Alberta. Es sede de varios festivales de talla mundial, lo que le ha valido para ganarse el título de «La ciudad festival» (The Festival City).3 En Edmonton está el centro comercial más grande de Norteamérica, el West Edmonton Mall (que fue el más grande del mundo desde 1981 hasta 2004), y el museo de historia viva más grande de Canadá, el Fort Edmonton Park. En 2004, la ciudad celebró el centenario de su fundación como ciudad.
Edmonton è il capoluogo della provincia canadese dell'Alberta. Si trova nella parte centro settentrionale della provincia, un'area che conta alcune delle più fertili terre agricole delle praterie canadesi. Dopo Calgary, è la seconda città dell'Alberta, con 932.546 abitanti. La sua area metropolitana, con una popolazione stimata nel 2016 in 1.392.600 abitanti,[2] è la quinta del Canada. Tra le città delle Americhe con più di un milione di abitanti è quella situata più a nord.
Edmonton (![]() /ˈɛdməntən/ (?·i)) es la capital de la provincia canadiense de Alberta, así como sede de sus poderes y su administración. Está ubicada en la parte central de la provincia, una de las zonas más fértiles de las llanuras canadienses, en torno al río Saskatchewan Norte. 812 201 personas viven en Edmonton,1 lo que la convierte en la segunda ciudad más populosa de la provincia, detrás de Calgary, la segunda capital de provincia con más habitantes tras Toronto y la quinta de Canadá. Además, su área metropolitana es la sexta más poblada del país, con una población de 1 034 945 habitantes.2
/ˈɛdməntən/ (?·i)) es la capital de la provincia canadiense de Alberta, así como sede de sus poderes y su administración. Está ubicada en la parte central de la provincia, una de las zonas más fértiles de las llanuras canadienses, en torno al río Saskatchewan Norte. 812 201 personas viven en Edmonton,1 lo que la convierte en la segunda ciudad más populosa de la provincia, detrás de Calgary, la segunda capital de provincia con más habitantes tras Toronto y la quinta de Canadá. Además, su área metropolitana es la sexta más poblada del país, con una población de 1 034 945 habitantes.2
La ciudad abarca 683 km², una superficie mayor que la de Chicago, Filadelfia, Toronto o Montreal. Sin embargo, tiene una de las densidades de población más bajas de América del Norte, alrededor del 9,4 % de la de Nueva York. El residente de Edmonton es conocido como edmontoniano.
Edmonton sirve como enlace a la zona norte del «Corredor Calgary-Edmonton», una de las cuatro regiones que en conjunto comprenden el 50 % de la población de Canadá. Desde ella se organizan proyectos a gran escala de arenas de alquitrán que se desarrollan en el norte de Alberta, así como para proyectos de minería de diamantes en los Territorios del Noroeste.
Es el centro cultural, gubernamental y educativo de Alberta. Es sede de varios festivales de talla mundial, lo que le ha valido para ganarse el título de «La ciudad festival» (The Festival City).3 En Edmonton está el centro comercial más grande de Norteamérica, el West Edmonton Mall (que fue el más grande del mundo desde 1981 hasta 2004), y el museo de historia viva más grande de Canadá, el Fort Edmonton Park. En 2004, la ciudad celebró el centenario de su fundación como ciudad.
Эдмонтон (англ. Edmonton [ˈɛdməntən]) — административный центр канадской провинции Альберта.




爱德华王子岛省(英语:Prince Edward Island;法语:Île-du-Prince-Édouard;苏格兰盖尔语:Eilean a' Phrionnsa或Eilean Eòin;米克马克语:Apekweit或Epikwetk),简称爱省,也常被简称为皮伊爱(英语常简称为:PEI;法语常简称为:Î.-P.-É.) ,是加拿大东部海洋三省之一。爱德华王子岛省全境包含了与省同名的岛屿及其周遭的离岛;此滨海省分的人口(154,331人,2021年统计)和面积(5,683.91平方公里,2006年统计)虽然都是全国最少,人口密度却是全国最高,达到每平方公里约 27 人 (24.47/km2)。除此之外,该岛也是全球面积排名第104位(全加拿大第23位)的岛屿。首府为夏洛特敦(Charlottetown)。
爱德华王子岛的命名源自于爱德华·奥古斯都王子,肯特与斯特拉森公爵(Prince Edward Augustus, Duke of Kent and Strathearn,英国维多利亚女王的父亲)。
知名加拿大女作家露西·莫德·蒙哥马利(Lucy M. Montgomery)是出身于爱德华王子岛的名人之一,名著《绿山墙的安妮》(Anne of The Green Gables)就是以她自己的故乡爱德华王子岛作为故事背景。Prince Edward Island [ˌpɹɪns‿ˌɛdwɚd‿ˈaɪ̯lɨnd] (französisch Île-du-Prince-Édouard, Mi’kmaq Epekwitk oder Abegweit,[2] kurz PEI oder P.E.I., deutsch Prinz-Eduard-Insel) ist eine Insel im Atlantik und eine Provinz im Osten Kanadas. Die Nachbarprovinzen der Insel sind New Brunswick im Westen und Nova Scotia im Süden und Osten. Prince Edward Island ist flächenmäßig die kleinste Provinz des Landes. Benannt ist sie nach Edward Augustus, Duke of Kent and Strathearn, dem Vater von Königin Victoria.


 Architecture
Architecture
 Ontario-ON
Ontario-ON
 Companies
Companies

 IT-Times
IT-Times
 Geography
Geography
 Energy resource
Energy resource
 Economy and trade
Economy and trade
 International cities
International cities
 Sport
Sport
 Agriculture, forestry, livestock, fishing
Agriculture, forestry, livestock, fishing
 Prince Edward Island-PEI
Prince Edward Island-PEI
 Animal world
Animal world
 British Columbia-BC
British Columbia-BC