
Deutsch-Chinesische Enzyklopädie, 德汉百科
 Vietnam
Vietnam


越南社会主义共和国(越南语:Cộng hòa xã hội chủ nghĩa Việt Nam/共和社會主義越南 ![]() 聆听 帮助·信息),通称越南(越南语:Việt Nam/越南),是位于东南亚的中南半岛东端的社会主义国家,北邻中国,西接柬埔寨和老挝,拥有超过9,600万人口,位居世界第15名。越南的首都是河内市,最大城市是胡志明市。执政党越南共产党是目前越南境内唯一的合法政党。越南为东亚文化圈之一,是东南亚国家联盟[4][5]、世界贸易组织、亚洲太平洋经济合作组织及法语圈国际组织成员,未来11国之一。
聆听 帮助·信息),通称越南(越南语:Việt Nam/越南),是位于东南亚的中南半岛东端的社会主义国家,北邻中国,西接柬埔寨和老挝,拥有超过9,600万人口,位居世界第15名。越南的首都是河内市,最大城市是胡志明市。执政党越南共产党是目前越南境内唯一的合法政党。越南为东亚文化圈之一,是东南亚国家联盟[4][5]、世界贸易组织、亚洲太平洋经济合作组织及法语圈国际组织成员,未来11国之一。
Vietnam ([vi̯ɛtˈna[ː]m], vietnamesisch Việt Nam [in Hanoi viɜʔt̚˧ˀ˨ʔ naːm˧˧], Bedeutung „Viet des Südens“, amtlich Sozialistische Republik Vietnam, vietnamesisch Cộng hòa Xã hội chủ nghĩa Việt Nam, Chữ Nôm 共和社會主義越南 [in Hanoi kɜwŋ͡m˧ˀ˨ʔ hwaː˨˩ s̪aː˦ˀ˥ hoj˧ˀ˨ʔ ṯɕu˧˩ ŋiɜ˦ˀ˥ viɜʔt̚˧ˀ˨ʔ naːm˧˧]) ist ein langgestreckter Küstenstaat in Südostasien. Er grenzt an China, Laos, Kambodscha, den Golf von Thailand und das Südchinesische Meer.
Das erste historisch belegte Königreich auf dem Gebiet des heutigen Vietnams entstand im 1. Jahrtausend v. Chr. Danach entwickelte sich ein friedliches Zusammenleben zwischen den Yues und den Han während der Trieu-Dynastie. 111 v. Chr. kam die Dynastie unter die Kontrolle der Han-Chinesen als Provinz der Han-Dynastie und blieb dies – unterbrochen von kurzen Zeiträumen der Unabhängigkeit – bis 938 n. Chr., als sie nach der Schlacht am Bạch Đằng-Fluss die Unabhängigkeit errang. Danach folgte eine Blütezeit der Kultur, Gesellschaft, Wirtschaft und Politik. In den folgenden Jahrhunderten expandierte Vietnam nach Süden. Im 19. Jahrhundert kam das Gebiet nach und nach als Teil von Französisch-Indochina unter französische Kolonialherrschaft.
Im Zweiten Weltkrieg besetzte Japan die Region. Von 1946 bis 1954 versuchte Frankreich im Ersten Indochinakrieg ohne Erfolg, seine Kolonialherrschaft wiederherzustellen. Als Folge der französischen Niederlage wurde 1954 aus Tonkin und dem nördlichen Teil Annams das sozialistische Nordvietnam mit der Hauptstadt Hanoi und aus Cochinchina und dem südlichen Teil Annams das von den Westmächten unterstützte Südvietnam mit der Hauptstadt Saigon. Von 1964 bis 1973 scheiterten die Vereinigten Staaten von Amerika im Vietnamkrieg, Nordvietnam und die mit ihm verbündete Nationale Front für die Befreiung Südvietnams zu besiegen. Stattdessen wurden die beiden vietnamesischen Staaten 1976 unter kommunistischer Führung wiedervereinigt. Seit 1986 laufen im Rahmen des Đổi mới marktwirtschaftliche Reformen, die aber bislang nur in Ansätzen zu einer politischen Liberalisierung führten. Hanoi wurde 1976 Hauptstadt des wiedervereinigten Vietnams, größte Stadt nach Einwohnern ist Ho-Chi-Minh-Stadt (Saigon); Haiphong, Cần Thơ und Đà Nẵng sind ebenfalls bedeutende Metropolen des Landes.
ベトナム社会主義共和国(ベトナムしゃかいしゅぎきょうわこく、ベトナム語:Cộng Hoà Xã Hội Chủ Nghĩa Việt Nam/ 共和社會主義越南)、通称ベトナム(越南、えつなん、ベトナム語:Việt Nam/ 越南、ヴィエットナム) は、東南アジアのインドシナ半島東部に位置する社会主義共和制国家。ベトナム共産党による一党独裁体制下にある。首都はハノイ。東南アジア諸国連合(ASEAN)加盟国。人口約9,936万人(2021年)。通貨はドン。
インドシナ半島の東海岸をしめるベトナムの国土は南北に長く、北は中華人民共和国、西はラオス、南西はカンボジアと国境を接する。東と南は南シナ海に面し、フィリピン、ボルネオ島(マレーシア連邦やブルネイ、インドネシア)そしてマレー半島(マレーシア連邦およびタイ王国南部)と相対する。
Vietnam (Vietnamese: Việt Nam, [vîət nāːm] (![]() listen)), officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam,[a] is a country in Southeast Asia. It is located at the eastern edge of the Indochinese Peninsula, and is divided into 58 provinces and five municipalities, covering 331,699 square kilometres, with a population of over 96 million inhabitants, making it the world's sixteenth-most populous country. Vietnam shares borders with China to the north, Laos and Cambodia to the west; whilst maintaining maritime borders with Thailand through the Gulf of Thailand, and the Philippines, Indonesia and Malaysia through the South China Sea.[n 5] Its capital is Hanoi and its largest city is Ho Chi Minh City (Saigon).
listen)), officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam,[a] is a country in Southeast Asia. It is located at the eastern edge of the Indochinese Peninsula, and is divided into 58 provinces and five municipalities, covering 331,699 square kilometres, with a population of over 96 million inhabitants, making it the world's sixteenth-most populous country. Vietnam shares borders with China to the north, Laos and Cambodia to the west; whilst maintaining maritime borders with Thailand through the Gulf of Thailand, and the Philippines, Indonesia and Malaysia through the South China Sea.[n 5] Its capital is Hanoi and its largest city is Ho Chi Minh City (Saigon).
Archaeological excavations indicate that Vietnam was inhabited as early as the Paleolithic age. The ancient Vietnamese nation, which was centered on the Red River valley and nearby coastal areas, was annexed by the Han dynasty in the 2nd century BC, which subsequently made Vietnam a division of Imperial China for over a millennium. The first independent monarchy emerged in the 10th century AD. This paved the way for successive imperial dynasties as the nation expanded southward until the Indochina Peninsula was colonised by the French in the late 19th century. Modern Vietnam was born upon the Proclamation of Independence from France in 1945 following Japanese occupation. Following Vietnamese victory against the French in the First Indochina War, which ended in 1954, the nation was divided into two rival states: communist North and anti-communist South. Conflicts intensified in the Vietnam War, which saw extensive American intervention in support of South Vietnam, while the Soviets and the PRC supported the North, which ended with North Vietnamese victory in 1975.
After North and South Vietnam were reunified as a communist state under a unitary socialist government in 1976, the country became economically and politically isolated until 1986, when the Communist Party initiated a series of economic and political reforms that facilitated Vietnamese integration into world politics and the global economy. As a result of the successful reforms, Vietnam has enjoyed high economic growth rate, consistently ranked amongst the fastest growing economies of the world.
Vietnam is a regional power,[10] and is considered a middle power in global affairs.[11][12] Vietnam is a part of several major international and intergovernmental institutions or groupings including the United Nations, the ASEAN, the APEC, the CPTPP, the Non-Aligned Movement, the OIF, the RCEP, and the World Trade Organization, and has also assumed a seat on the United Nations Security Council twice. Vietnam was listed as a developing country by the UN until 2019, and by the US until 2020.[13]
Le Viêt Nam, Viet Nam, Vietnam ou Viêtnam, en forme longue la république socialiste du Viêt Nam (en vietnamien : Việt Nam Écouter et Cộng hoà Xã hội Chủ nghĩa Việt Nam Écouter est un pays d'Asie du Sud-Est situé à l'est de la péninsule indochinoise.
Il partage ses frontières avec la Chine au nord, le Laos au nord-ouest et le Cambodge au sud-ouest. Sa capitale est Hanoï. La langue officielle est le vietnamien et la monnaie le dong. C'est un État communiste à parti unique, dirigé par le Parti communiste vietnamien depuis 1975.
Le pays est classé 66e pays par ordre de superficie (330 967 km2) et le 16e pays le plus peuplé du monde avec environ 102,8 millions d'habitants en 2021. Constitué d'une longue côte maritime qui s'étend sur près de 3 260 kilomètres, il est bordé du golfe de Thaïlande à l'ouest et de la mer de Chine méridionale à l'est. Environ 85 % de la population est d'ethnie viet que l'on trouve à proximité des rizières, le reste étant composé des 54 groupes minoritaires reconnus par le gouvernement vietnamien et essentiellement répartis dans les reliefs montagneux du nord, du nord-ouest et du centre.
Fruit d’une histoire longue et mouvementée, marquée par des occupations étrangères et des guerres de résistance successives, le Viêt Nam est, en 2019, avec une économie dynamique affichant l’un des taux de croissance les plus élevés de la région, un des nouveaux pays industrialisés, comptant parmi les Tigres asiatiques. Son économie repose notamment sur les services, l'agriculture et les exportations avec la Chine, les États-Unis, Singapour, la Corée du Sud et le Japon comme principaux partenaires commerciaux.
Le Viêt Nam est membre de l’Organisation des Nations unies (ONU), de l’Association des nations de l'Asie du Sud-Est (ASEAN), de la Coopération économique pour l’Asie-Pacifique (APEC) et de l’Organisation mondiale du commerce (OMC).
Il Vietnam (AFI: /vjetˈnam/[5][6]; in vietnamita Việt Nam), ufficialmente Repubblica Socialista del Vietnam (Cộng hòa xã hội chủ nghĩa Việt Nam), è uno Stato del sud-est asiatico. Confina a nord con la Cina, a ovest con il Laos e la Cambogia, mentre a est e a sud si affaccia sul Mar Cinese Meridionale, che tra l'isola cinese di Hainan e il nord del Vietnam forma il golfo del Tonchino. A sud, per un breve tratto, il Vietnam si affaccia sul golfo del Siam.
Il Vietnam è una repubblica di tipo socialista; l'attuale capo dello Stato è Nguyễn Phú Trọng che allo stesso tempo è anche Segretario generale del Partito Comunista del Vietnam, mentre capo del governo è Nguyễn Xuân Phúc. La lingua ufficiale è il vietnamita.
Nel 1986, il governo ha avviato una serie di riforme economiche e politiche chiamate Đổi mới, riforme che hanno aperto il Vietnam al libero mercato e all'integrazione nell'economia mondiale. Nel 2000 la nazione ha riallacciato le relazioni diplomatiche con il resto del mondo e da allora sta registrando una rapida crescita economica e sociale, crescita che per quasi due decenni si è assestata a livelli tra il 7% e l’8% del PIL su base annua, abbattendo la povertà e favorendo l'aumento dei salari.Vietnam7 (en vietnamita: Việt Nam, [vîət nāːm] ![]() escuchar), oficialmente la República Socialista de Viet Nam (en vietnamita: Cộng hòa Xã hội chủ nghĩa Việt Nam),8 es un país soberano del Sudeste Asiático, el más oriental de la península Indochina. Con una población estimada de 98 millones, es el decimosexto país más poblado del mundo y el octavo de Asia. El nombre del país se traduce como «Viet del sur», un sinónimo del antiguo nombre del Reino de Nanyue (Nam Việt) establecido en el siglo III a. C., y que fue adoptado oficialmente por primera vez en 1802 por el emperador Gia Long. En 1945 volvió a fijarse de manera oficial el topónimo con la fundación de la República Democrática de Vietnam presidida por Hồ Chí Minh. El país tiene frontera por el norte con China, con Laos por el noroeste y con Camboya por el suroeste, mientras que hacia el este tiene una extensa costa bañada por el mar de la China Meridional. Su capital es Hanói desde la reunificación de Vietnam del Norte y Vietnam del Sur en 1976.
escuchar), oficialmente la República Socialista de Viet Nam (en vietnamita: Cộng hòa Xã hội chủ nghĩa Việt Nam),8 es un país soberano del Sudeste Asiático, el más oriental de la península Indochina. Con una población estimada de 98 millones, es el decimosexto país más poblado del mundo y el octavo de Asia. El nombre del país se traduce como «Viet del sur», un sinónimo del antiguo nombre del Reino de Nanyue (Nam Việt) establecido en el siglo III a. C., y que fue adoptado oficialmente por primera vez en 1802 por el emperador Gia Long. En 1945 volvió a fijarse de manera oficial el topónimo con la fundación de la República Democrática de Vietnam presidida por Hồ Chí Minh. El país tiene frontera por el norte con China, con Laos por el noroeste y con Camboya por el suroeste, mientras que hacia el este tiene una extensa costa bañada por el mar de la China Meridional. Su capital es Hanói desde la reunificación de Vietnam del Norte y Vietnam del Sur en 1976.
Los vietnamitas se independizaron de la China Imperial en el año 938 tras la batalla del río Bach Dang, la cual marcó el fin de 1100 años de dominación extranjera. En los siglos siguientes florecieron diversas dinastías reales vietnamitas al tiempo que el reino expandía sus fronteras geográficas y políticas por el Sudeste Asiático. En el siglo XIX la península Indochina fue colonizada por los franceses. Tras un período de ocupación japonesa durante la Segunda Guerra Mundial, los vietnamitas iniciaron la Guerra de Indochina contra Francia, que acabó con la derrota y expulsión de las tropas galas en 1954. Sin embargo, el país quedó dividido políticamente en dos estados rivales, el Norte y el Sur, que iniciaron un conflicto de creciente intensidad que acabó en la conocida como Guerra de Vietnam, en la que se enfrentaron el Norte y las guerrillas comunistas conocidas como Viet Cong, contra las tropas del Sur y las fuerzas armadas de los Estados Unidos. La guerra finalizó en 1975 con la victoria del Norte y al año siguiente el país se unificó bajo un régimen de orientación socialista.

 Brunei Darussalam
Brunei Darussalam
 Demokratische Republik Timor-Leste
Demokratische Republik Timor-Leste
 Indonesia
Indonesia
 Cambodia
Cambodia
 Laos
Laos
 Malaysia
Malaysia
 Myanmar
Myanmar
 Philippines
Philippines
 Singapore
Singapore
 Thailand
Thailand
 Vietnam
Vietnam



 Argentina
Argentina
 China
China

 Eat and Drink
Eat and Drink
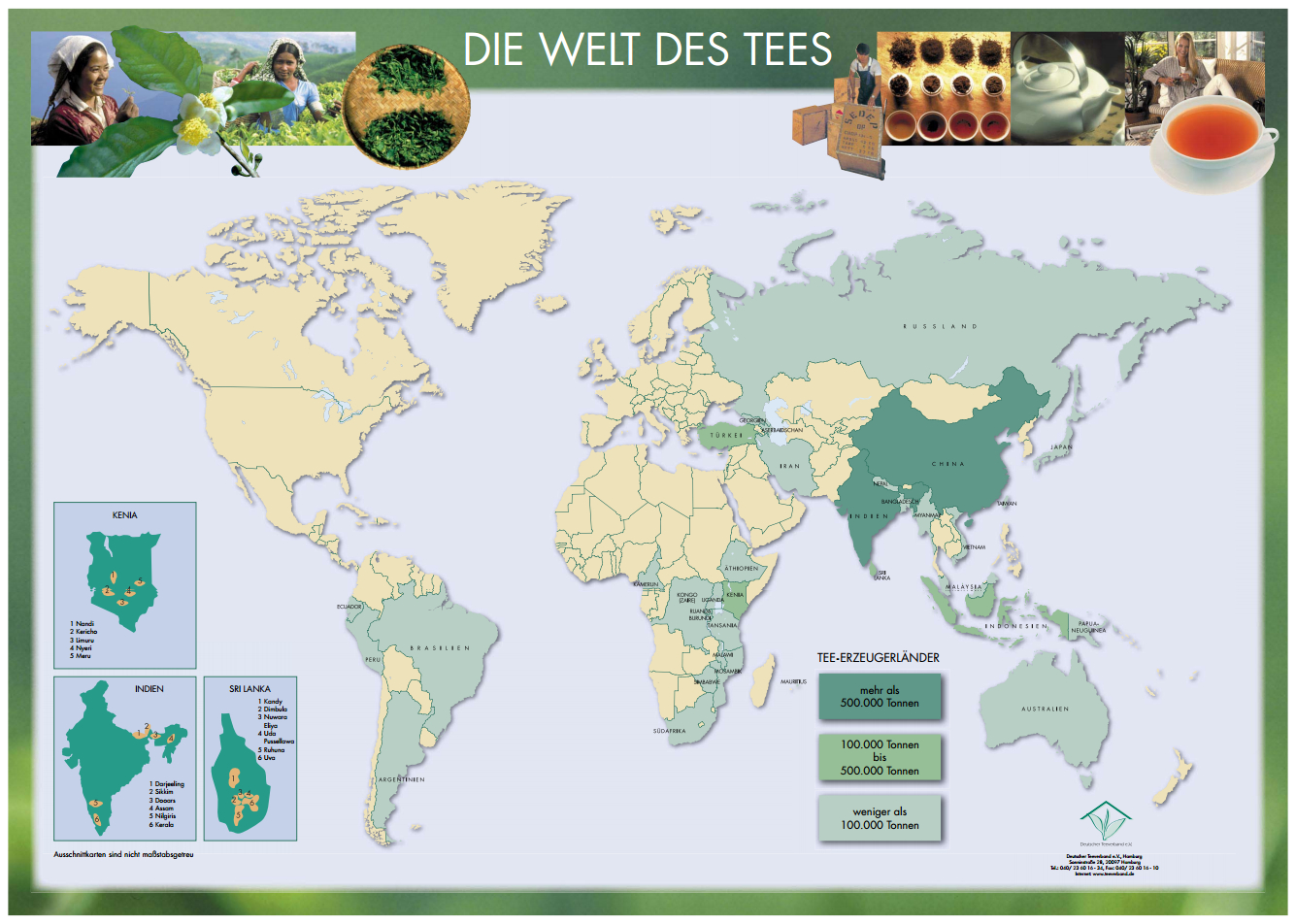
 *Types of tea, Tea growing areas, Tea ceremony, Tea culture
*Types of tea, Tea growing areas, Tea ceremony, Tea culture
 India
India
 Indonesia
Indonesia
 Iran
Iran
 Japan
Japan
 Kenya
Kenya
 Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka
 Turkey
Turkey
 Vietnam
Vietnam
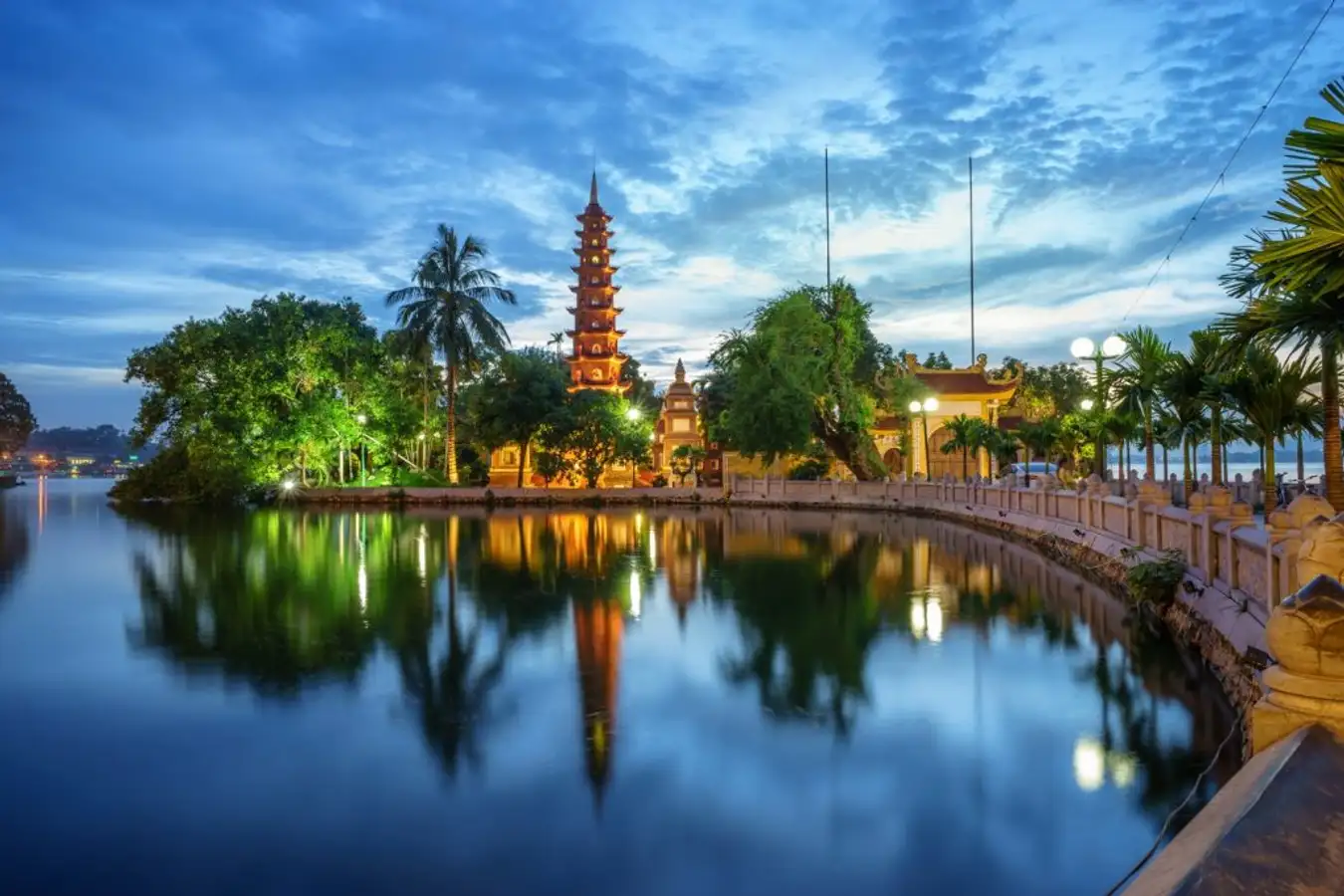
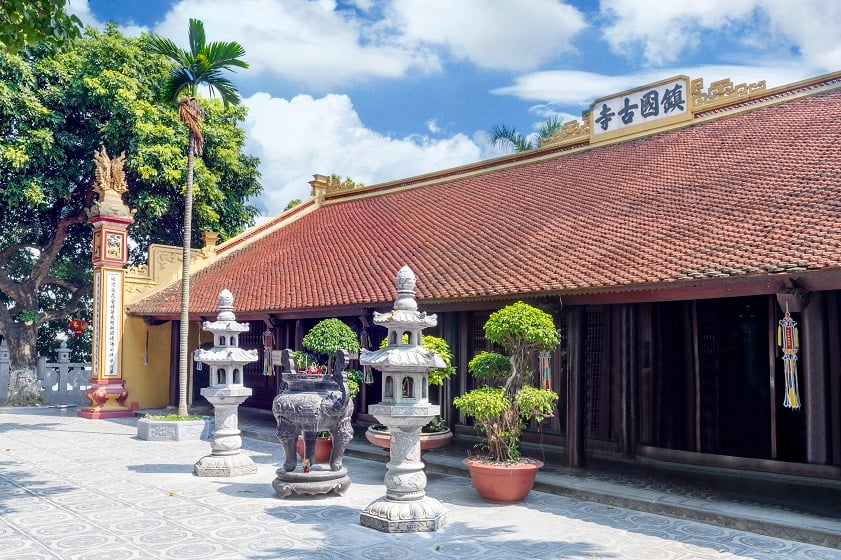
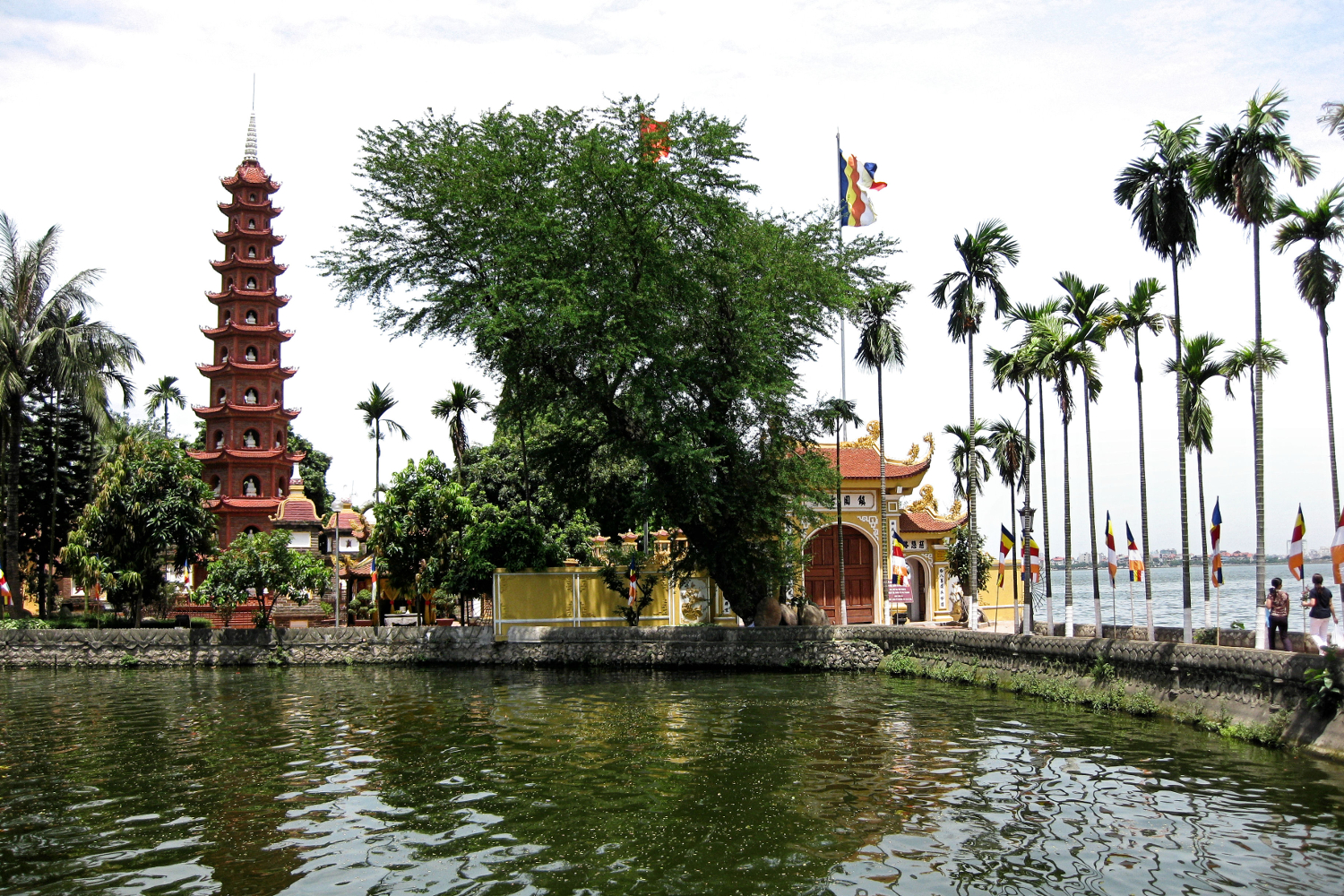




Trấn Quốc Pagode (Vietnamesisch: chùa Trấn Quốc, chữ Nôm: ?鎭國; Vietnamesisch: Trấn Quốc tự, chữ Hán: 鎮國寺), der älteste buddhistische Tempel in Hanoi, befindet sich auf einer kleinen Insel in der Nähe des südöstlichen Ufers des Westsees in Hanoi, Vietnam.
镇国寺(越南语:Chùa Trấn Quốc/?鎮國)是越南河内的一座佛寺,坐落于靠近西湖东南岸的一个小岛上。镇国寺是河内最古老的佛寺,最初建于公元六世纪李南帝统治时期,名为开国寺,选址在红河岸边。由于河流的侵蚀,该寺在1615年搬迁到西湖中的金鱼岛,即今天的所在地。一条小堤道连接着陆地。多年来,镇国寺曾命名为安国寺以及镇北寺。 镇国寺位于西湖以东的一座小岛上,是河内市最古老的寺庙。这座寺年纪1500岁多并最近被评选为世界上最美的寺庙之一”。该网站还提供镇国寺的水湖和这座寺庙的亮点——菩提树。这是源自25个世纪前印度菩提伽耶释迦牟尼悟道的菩提树衍生出来的。
 Australia
Australia
 Brunei Darussalam
Brunei Darussalam
 Chile
Chile

 Hand in Hand
Hand in Hand
 Japan
Japan
 Canada
Canada
 Malaysia
Malaysia
 Mexico
Mexico
 New Zealand
New Zealand
 Peru
Peru
 Singapore
Singapore
 Vietnam
Vietnam
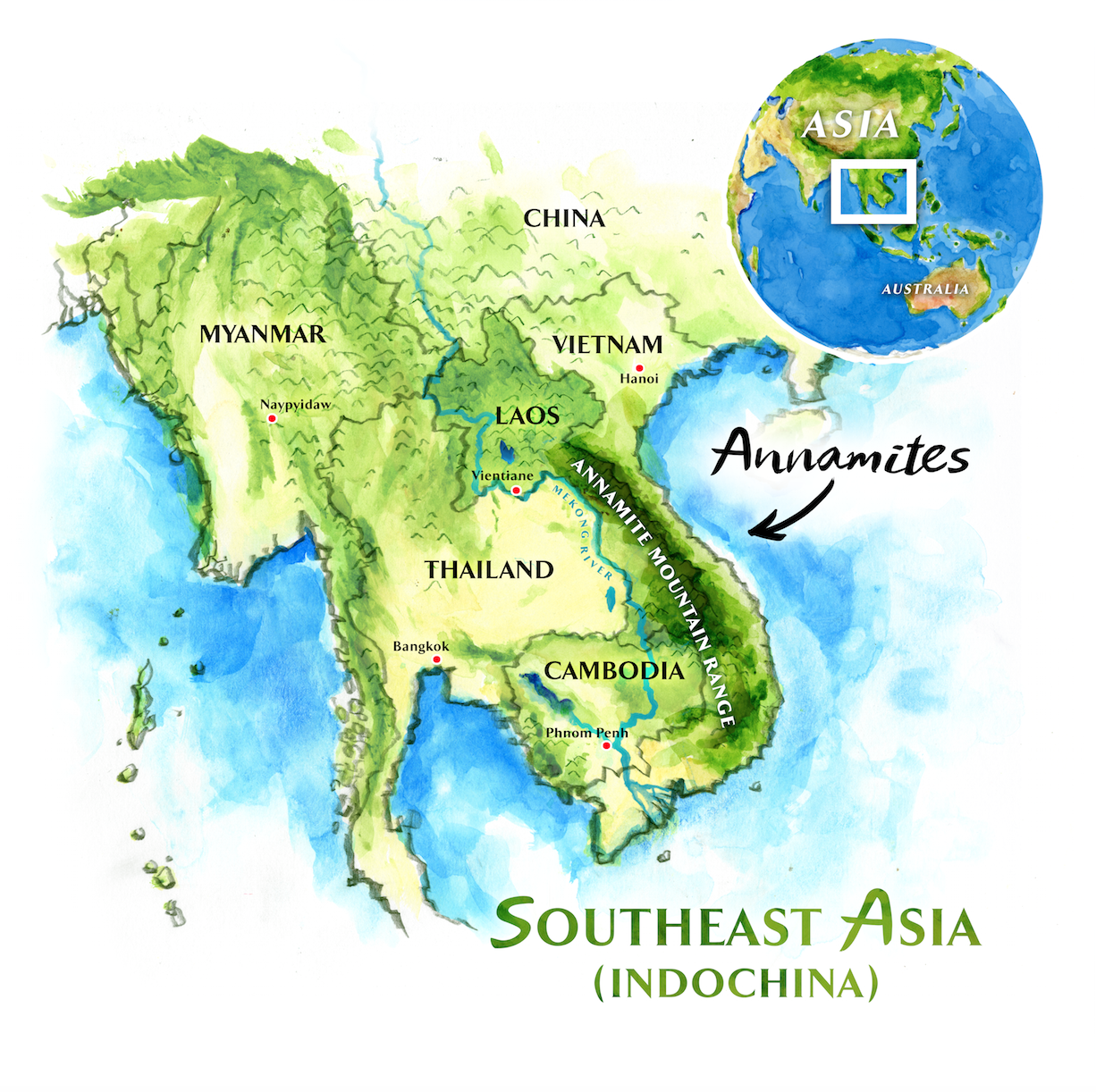
安南山脉,亦称为长山山脉(越南语:Dãy núi Trường Sơn),是中南半岛的主要山脉,约长1,100公里,呈西北至东南走向。安南山脉既为南海水系与湄公河之分水岭,也是越南中部与老挝的分界山岭。该处是全球仅余的湿常绿林之一,因此有“绿廊”之称。
Das Truong-Son-Gebirge, auch Annamitische Kordillere genannt, ist eine etwa 1100 Kilometer lange Gebirgskette im östlichen Indochina auf den Staatsgebieten von Vietnam, Laos und zum kleinen Teil Kambodscha. Der Name lautet im Vietnamesischen Dãy (núi) Trường Sơn, im Laotischen Phou Luang (ພູ ຫລວງ) und im Französischen Chaîne Annamitique.
Die Gebirgskette verläuft parallel zur Küste des Südchinesischen Meeres und trennt die Ebene des Mekong von dem schmalen Küstenstreifen Mittelvietnams. Die Ostseite der Annamitischen Kordillere steigt steil an. Zahlreiche kurze Flüsse führen von hier zum Südchinesischen Meer.
Der höchste Berg ist mit 2819 Metern der Phu Bia in Laos. Der höchste Gipfel im vietnamesischen Teil ist mit 2711 Metern der Phu Xai Lai Leng. Er liegt im nördlichen Teil der Gebirgskette. Der höchste Gipfel im Süden des Truong Son ist der 2589 Meter hohe Ngọc Linh.
Laos liegt größtenteils auf der westlichen Seite des Gebirges. Ausnahmen sind die Houaphan- und die Xieng Khouang-Provinz. Vietnam erstreckt sich östlich des Hauptkamms mit Ausnahme der Tây-Nguyên-Region.
Das Truong-Son-Gebirge ist Heimat einiger seltener Tierarten wie dem Annamitischen Streifenkaninchen, dem Vietnamesischen Waldrind und dem Annam-Muntjak. Auch zahlreiche Reptilien und Amphibien kommen hier teilweise endemisch vor, von denen einige erst in jüngerer Zeit entdeckt und wissenschaftlich beschrieben wurden. Hierzu zählen u. a. der Phong Nha-Ke Bang-Bogenfingergecko und die Dreihorn-Grubenotter.

 Sport
Sport
 States of Asia
States of Asia
 Geography
Geography


 Architecture
Architecture
 Religion
Religion
 Financial
Financial
 Companies
Companies
 History
History
 Economy and trade
Economy and trade
 ASEAN University Network
ASEAN University Network