
Deutsch-Chinesische Enzyklopädie, 德汉百科
 美国
美国

美国国家图书奖(又译美国国家书卷奖;英语:American National Book Award)是美国文学界的最高荣誉之一,始于1950年,每年11月在纽约颁奖,设有小说、非小说、诗歌、少年图书4个大奖,颁发给前一年出版的文学作品,并向做出卓越贡献的作家颁发终身成就奖。评奖宗旨是扩大美国文学的影响、吸引读者以及提高作品的文化价值。
Der National Book Award (NBA) ist neben dem Pulitzer-Preis der renommierteste Literaturpreis der USA. Er wurde 1936 von der American Booksellers Association ins Leben gerufen und wird nach einer Unterbrechung durch den Zweiten Weltkrieg seit 1950 jährlich vergeben. Seit dem Jahr 1989 wird die Auszeichnung von der eigens zu diesem Zweck gegründeten Non-Profit-Organisation National Book Foundation ausgelobt.


Amerikanisch-Samoa (englisch American Samoa, samoanisch Sāmoa Amelika) ist als Teil von Amerikanisch-Ozeanien ein Außengebiet der Vereinigten Staaten im südlichen Pazifik. Amerikanisch-Samoa ist Teil der Samoainseln und schließt südöstlich an den unabhängigen Staat Samoa an. Die flächengrößte und bevölkerungsreichste Insel Amerikanisch-Samoas ist Tutuila mit dem Hauptort Pago Pago.
Ein besonderes kulturelles Merkmal der gesamten Inselgruppe ist das Nebeneinander von modernem amerikanischem Lebensstil und samoanischen Traditionen.
Während des Zweiten Weltkriegs erlangte Amerikanisch-Samoa in den Jahren 1942 bis 1945 vorübergehend größere strategische Bedeutung für die Vereinigten Staaten, da der Bau einer Marinebasis und eines Flughafens (Pago Pago International Airport) beschlossen wurde.
美属萨摩亚(萨摩亚语:Amelika Sāmoa;英语:American Samoa),又称东萨摩亚,是美国在南太平洋的属地,在美国法律中定位为“未通过组织法的未合并属地”[2][3]。自公元前1000年就有人定居,欧洲探险家在18世纪到达萨摩亚。首府帕果帕果,是太平洋上天然良港之一。主要的岛是图图伊拉岛(最大和人口最多),其余岛屿为马努阿群岛、罗斯环礁和斯温斯岛。19世纪后半叶,德国、英国和美国为争夺萨摩亚群岛发生了严重的国际对抗。最后,根据1899年条约规定,德国和美国分割萨摩亚群岛。次年美国正式占领群岛东半部,由五个火山岛与两个珊瑚礁组成。西萨摩亚现在是萨摩亚独立国。美国通过1929年2月20日一项国会法案,正式接受将这些岛屿割让给美国的契约。该法案规定,当地居民享有美国国民地位。该法案规定设立一个美属萨摩亚政府,其一切民政、司法和军事方面的权力属于美国总统指定的人。由于美国在该地区的利益主要是军事利益,该领土由美国海军管辖。1951年一项行政命令把对该领土的权力移交给内政部。


Die Amerikanischen Jungferninseln (englisch United States Virgin Islands, Virgin Islands of the United States oder kurz USVI, so u. a. auf den Autokennzeichen) sind ein nicht inkorporiertes Außengebiet der Vereinigten Staaten östlich von Puerto Rico. Geographisch sind sie ein Teil der in der Karibik gelegenen Inselgruppe der Jungferninseln. Sie bestehen aus den drei Hauptinseln Saint Croix, Saint John und Saint Thomas. 1996 übergab die Bundesregierung der Vereinigten Staaten Water Island an das Außengebiet. Daneben gibt es noch zahlreiche kleinere Inseln.
美属维尔京群岛(英语:Virgin Islands of the United States,常写作United States Virgin Islands,缩写为USVI)[注 1]是美国在加勒比海的一个已通过组织法的非合并属地,位于波多黎各以东,处于小安的列斯群岛背风群岛的最北端。该群岛原名为丹属西印度群岛,后于1916年被美国买下并改为现名。在地理方面,美属维尔京群岛属于维尔京群岛的一部分。由于维尔京群岛中的另外一部分岛屿的主权现在为英国所有,故该群岛的英国属地部分通常称为“英属维尔京群岛”,而美国属地部分则称为“美属维尔京群岛”。
美属维尔京群岛由50多个大小岛和珊瑚礁组成,面积达344平方千米,岛屿中最大的有圣克罗伊岛、圣约翰岛和圣托马斯岛以及面积上比较小,但是拥有特殊历史意义的海岛。属热带气候。根据美国2000年人口普查数据美属维尔京群岛共有居民108,612人[3],主要是黑人和混血种人,大多数为非裔加勒比海后裔。通用英语。多信奉基督教新教和天主教。旅游、建筑、食品、捕鱼、水果种植为主要行业。首府夏洛特阿马利亚。美属维尔京群岛是美国唯一道路交通靠路左侧行驶的地区。美属维尔京群岛的主要经济领域为旅游业,此外也有重要的生产部门。
美国的葡萄酒起源于17世纪之前,当时法兰西斯克、瑞比尔传教团首先在加勒比海沿岸种植欧洲系葡萄。到了18世纪,从墨西哥通往美国的近海公路旁已 遍布葡萄园,而且迅速扩展。19世纪,大批移民开始在加州定居,并且以洛杉矶为中心,大量种植葡萄。到了1860年,能收获的葡萄树已达6万株。在加州所 产的,从旧金山到洛杉矶间,或者以旧金山为中心的邻近地带最为著名。
美国葡萄酒的真正发展是在1933年,“禁酒令”废除后,在加州地区得到了迅速的发展,美国葡萄酒业重获生机。一些有心人为发展美国的葡萄酒业,遍游欧 洲,与当地酿酒师切磋酿技术,并积极寻觅,引进适宜在美国生长的优良酿酒葡萄品种。因此,如今在美国种植的酿酒葡萄品种繁多,包括法国、意大利、德国等国 家的知名品系。
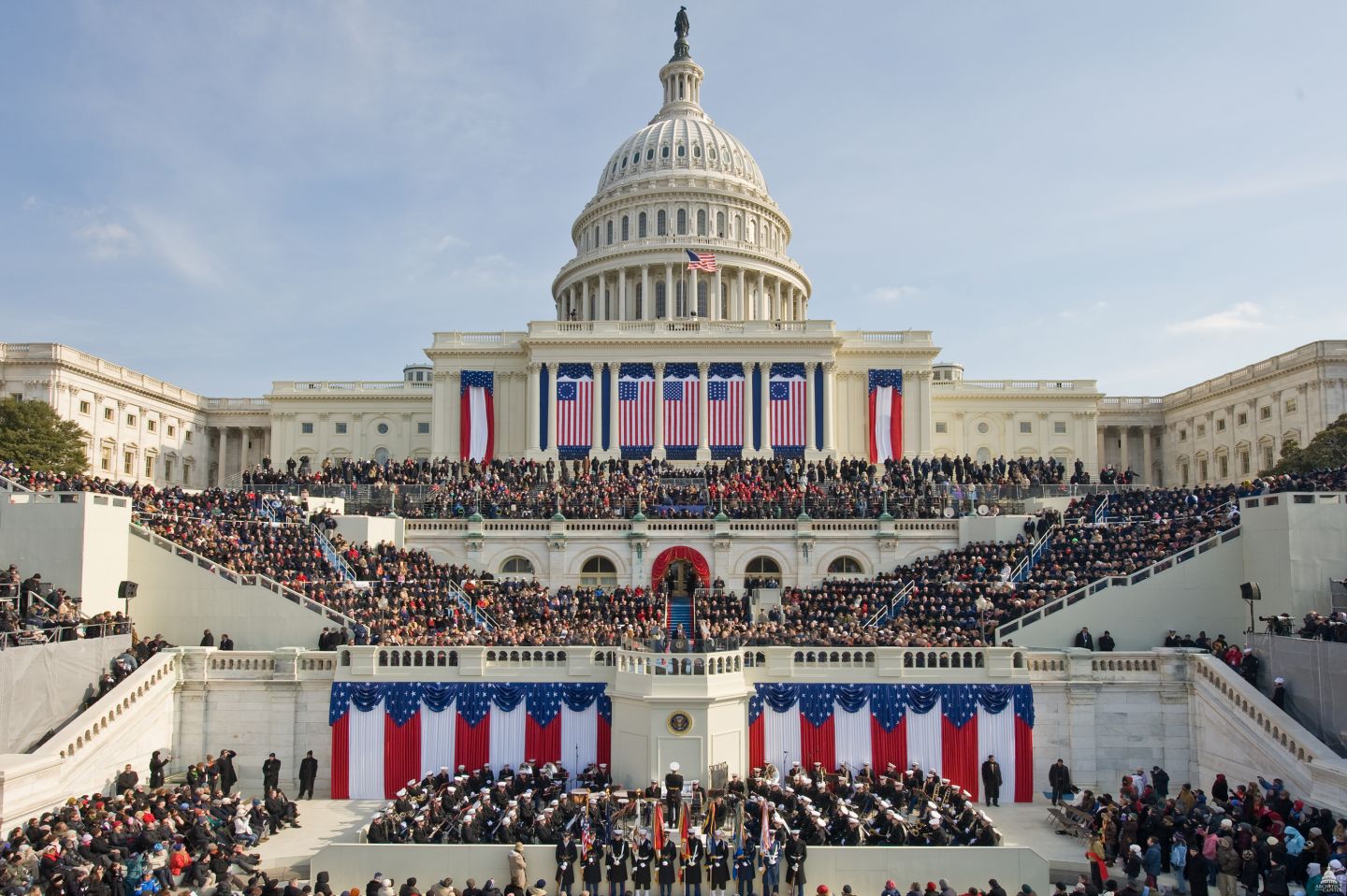

美国总统就职典礼的举行,标志着新一届美国总统任期的开始。实际上,美国宪法中对就职典礼所规定的唯一一项,就是在总统进入总统办公室执政前,必须进行宣誓。然而随着历史的推移,就职典礼的传统项目也逐渐扩大,已从最初一个简单的就职宣誓仪式,发展成为如今一个包括游行、演讲和舞会的为期一天的活动。
宣誓当天,被称为就职典礼日(Inauguration Day),是美国联邦的公共假期。从1793年至1933年为3月4日,从1937年之后,就职日为1月20日(1933年批准的美國憲法第二十修正案改变任期的开始日期)。从安德鲁·杰克逊总统至吉米·卡特总统,就职典礼主要在美国国会的东门廊(East Portico)举行[1]。
Die Amtseinführung des Präsidenten der Vereinigten Staaten (englisch United States presidential inauguration) ist der von Feierlichkeiten begleitete Beginn der Amtszeit eines US-Präsidenten. Die Verfassung der Vereinigten Staaten legt diesen Zeitpunkt seit 1933 auf den 20. Januar nach der Präsidentschaftswahl um 12 Uhr fest (in Kraft ab 1937).
アメリカ合衆国大統領就任式(アメリカがっしゅうこくだいとうりょうしゅうにんしき、United States presidential inauguration)は、次期大統領 (President-elect) によるアメリカ合衆国大統領職への就任宣誓を中心とする式典。
The inauguration of the president of the United States is a ceremony to mark the commencement of a new four-year term of the president of the United States. This ceremony takes place for each new presidential term, even if the president is continuing in office for a second term. Since 1937, it has taken place at noon EST on January 20, the first day of the new term, some 72 to 78 days after the presidential election, except for three occasions when January 20 fell on a Sunday. In those years, the presidential oath of office was administered on that day privately and then again in a public ceremony the next day, on Monday, January 21. The most recent presidential inauguration ceremony was held on January 20, 2017, when Donald Trump officially assumed office. The next inauguration will take place on Wednesday, January 20, 2021.
Recitation of the presidential oath of office is the only component in this ceremony mandated by the United States Constitution (in Article II, Section One, Clause 8). Though it is not a constitutional requirement, the chief justice typically administers the presidential oath of office. Since 1789, the oath has been administered at 58 scheduled public inaugurations, by 15 chief justices, one associate justice, and one New York state judge. Others, in addition to the chief justice, have administered the oath of office to several of the nine vice presidents who have succeeded to the presidency upon their predecessor's death or resignation intra-term.
Since the 1981 inauguration of Ronald Reagan, the ceremony has been held at the west front of the United States Capitol facing the National Mall with its iconic Washington Monument and distant Lincoln Memorial. Other swearing-in ceremonies have taken place on a platform over the steps at the Capitol's east portico on a regular basis for 180 years, and occasionally inside the Old Senate Chamber on the old north side, the chamber of the House of Representatives in the south wing, and the central Rotunda under the dome.[1] The last regularly scheduled inauguration not to take place at the Capitol was Franklin D. Roosevelt's fourth inauguration in 1945, which was held at the White House.
Over the years, various traditions have arisen that have expanded the inauguration from a simple oath-taking ceremony to a day-long event, including parades and multiple social gatherings. The ceremony itself is carried live via the major U.S. commercial television and cable news networks; various ones also stream it live on their websites.
When a president has assumed office intra-term the inauguration ceremony has been conducted without pomp or fanfare. To facilitate a quick presidential transition under extraordinary circumstances, the new president takes the oath of office in a simple ceremony and usually addresses the nation afterward.
L'Inauguration Day (en français, Jour d'investiture) est le jour aux États-Unis où le président élu prête serment et prend ses fonctions comme président des États-Unis, au mois de janvier. Le vice-président élu prête également serment et entre en fonction le même jour.
Le dernier Inauguration Day s'est déroulé le 20 janvier 2017 avec l'investiture de Donald Trump comme 45e président des États-Unis.
Le mandat d'un président américain débutant constitutionnellement le 20 janvier à midi, heure de Washington (17h00 TU/UTC), il est de tradition si ce jour tombe un dimanche, que la prestation de serment se tienne en comité restreint à la Maison-Blanche et de reporter les manifestations publiques, avec une seconde prestation de serment, au lendemain.
L'insediamento del presidente degli Stati Uniti è la cerimonia tenuta all'inizio del mandato presidenziale. La costituzione statunitense impone in realtà un unico adempimento: che il presidente presti un giuramento o comunque una dichiarazione solenne prima di entrare in carica. Tuttavia, nel corso degli anni sono sorte numerose prassi che hanno esteso l'insediamento da spartana cerimonia sacramentale a vera e propria giornata di sfilate, discorsi e danze.
Questa giornata, nota oggi come Inauguration Day, cadde il 4 marzo dal 1798 al 1933. Nel 1933 la ratifica del 20º emendamento, modificando la data di inizio mandato, la fissò al 20 gennaio. Dalla presidenza di Martin Van Buren a quella di Jimmy Carter la cerimonia principale dell'Inauguration Day si tenne nel portico est del Campidoglio. Dal 1981, con l'insediamento di Ronald Reagan, si è invece svolta sul lato ovest. Gli insediamenti di William Howard Taft nel 1909 e dello stesso Reagan nel 1985 si tennero dentro il Campidoglio a causa del freddo.
Da quando Oliver Ellsworth amministrò l'insediamento di John Adams, nessun altro presidente della Corte Suprema ha mai mancato a questo ufficio in una cerimonia d'insediamento regolarmente programmata. Allorché l'Inauguration Day è caduto di domenica, il giudice ha assistito al giuramento o il giorno stesso o altrimenti due volte: il sabato in privato e il lunedì in pubblico. La guerra del 1812 e la seconda guerra mondiale imposero di spostare la cerimonia da Washington.
La investidura presidencial de Estados Unidos se produce a partir de la apertura de un nuevo plazo de un presidente de los Estados Unidos.
Инаугурация президента США — торжественная церемония присяги и вступления в должность президента и вице-президента США. По традиции проводится публично перед Капитолием в Вашингтоне, привлекает большое число зрителей, сопровождается программной речью президента, по её случаю устраиваются торжественный парад и бал. До 1933 года включительно инаугурация проходила 4 марта, а после внесения Двадцатой поправки к Конституции — 20 января. В случае, если президентом становится вице-президент после досрочного окончания полномочий его предшественника, он приносит присягу, но публичной церемонии не проводится.
 文学
文学
 纽约州
纽约州
 建筑艺术
建筑艺术

 华盛顿哥伦比亚特区
华盛顿哥伦比亚特区

 能源
能源
 路易斯安那州
路易斯安那州

 体育
体育



 美食家
美食家
 加利福尼亚州
加利福尼亚州
 农业、林业、畜牧业、渔业
农业、林业、畜牧业、渔业
 俄勒冈州
俄勒冈州
 宾夕法尼亚州
宾夕法尼亚州
 华盛顿州
华盛顿州
 企业
企业
 医疗、制药、 康复
医疗、制药、 康复

 赛车,艇运动
赛车,艇运动

 得克萨斯州
得克萨斯州
 经济和贸易
经济和贸易
