
Deutsch-Chinesische Enzyklopädie, 德汉百科
 Italy
Italy

 Emilia-Romagna
Emilia-Romagna
 Bologna
Bologna
 FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 1990
FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 1990

 International cities
International cities
 *European Capital of Culture
*European Capital of Culture
 Italy
Italy
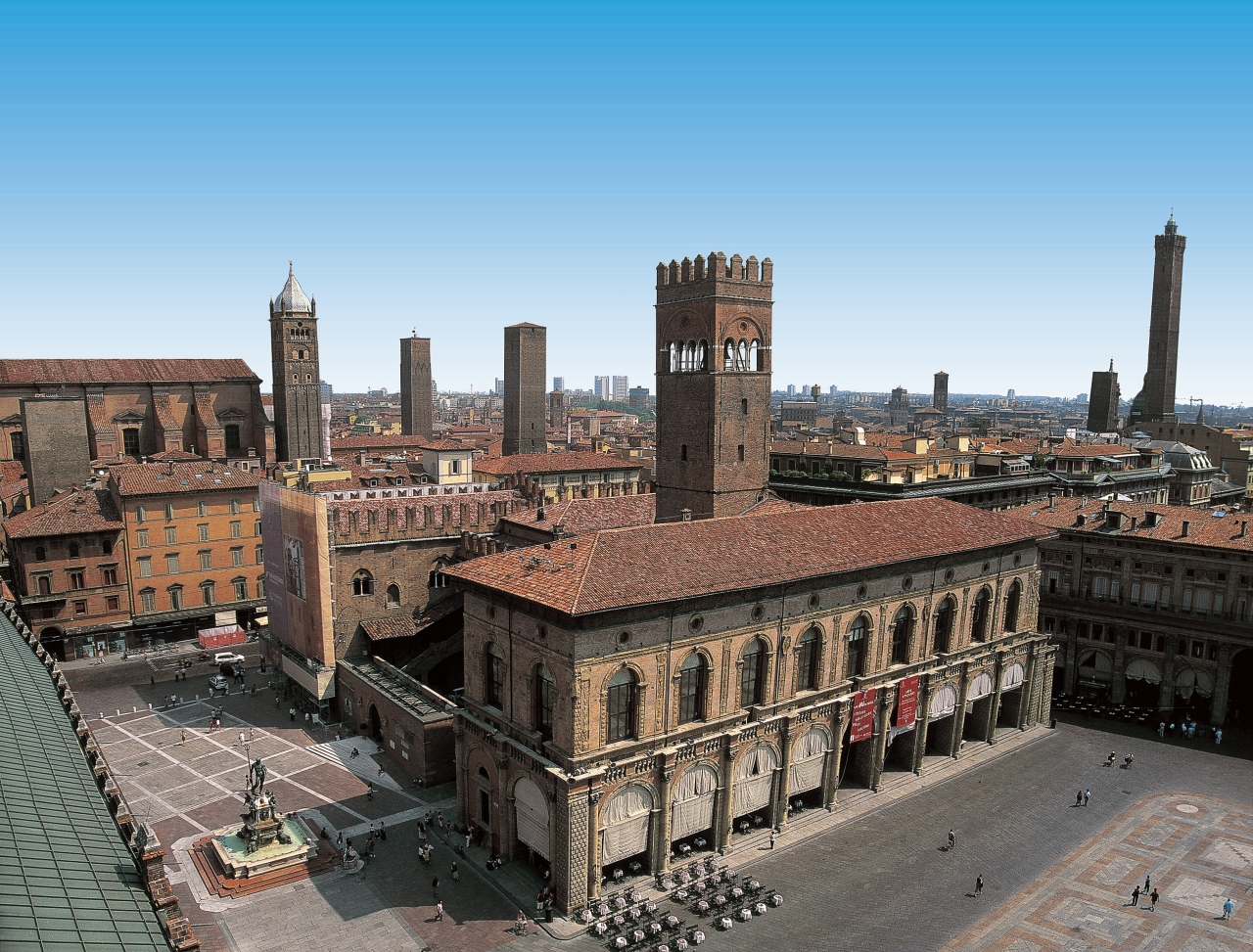

Bologna besitzt eine der schönsten und besterhaltenen Altstädte Europas mit vielen Türmen aus dem Mittelalter und ca. 40 km Arkadengängen, die die weitläufige Innenstadt mit ihren Fußgängerzonen, Plätzen, Kirchen und Palästen miteinander verbinden.
Weit ab vom Massentourismus, dafür mit gut erhaltener Bausubstanz und großartiger Kultur und Geschichte war Bologna im Jahr 2000 zur europäischen Kulturhauptstadt ernannt worden.
Für Motorsportfans ist Bologna und Umgebung ein Mekka, kann man hier die Museen und teilweise auch die Werke von Ducati, Maserati, Lamborghini sowie Ferrari bewundern.
博洛尼亚(意大利语:Bologna)是一座意大利城市,位于北部波河与亚平宁山脉之间,也是艾米利亚-罗马涅的首府。博洛尼亚也是意大利最发达的城市之一。
ボローニャ(イタリア語: Bologna (![]() 音声ファイル))は、イタリア共和国北部にある都市で、その周辺地域を含む人口約39万人の基礎自治体(コムーネ)。エミリア=ロマーニャ州の州都であり、ボローニャ県の県都でもある。
音声ファイル))は、イタリア共和国北部にある都市で、その周辺地域を含む人口約39万人の基礎自治体(コムーネ)。エミリア=ロマーニャ州の州都であり、ボローニャ県の県都でもある。
アペニン山脈とポー川の間にあるポー川谷に位置する。1088年創立と、西欧最古の大学ボローニャ大学(ラテン語名アルマ・マーテル・ストゥディオルム)がある。
Bologna (/bəˈloʊnjə/, also UK: /bəˈlɒnjə/; Italian: [boˈloɲːa] (![]() listen); Emilian: Bulåggna [buˈlʌɲːa]; Latin: Bononia) is the capital and largest city of the Emilia-Romagna Region in Northern Italy. It is the seventh most populous city in Italy, at the heart of a metropolitan area of about one million people.
listen); Emilian: Bulåggna [buˈlʌɲːa]; Latin: Bononia) is the capital and largest city of the Emilia-Romagna Region in Northern Italy. It is the seventh most populous city in Italy, at the heart of a metropolitan area of about one million people.
Of Etruscan origin, the city has been a major urban centre for centuries, first under the Etruscans, then under the Romans (Bononia), then again in the Middle Ages, as a free municipality and signoria, when it was among the largest European cities by population. Famous for its towers, churches and lengthy porticoes, Bologna has a well-preserved historical centre, thanks to a careful restoration and conservation policy which began at the end of the 1970s.[3] Home to the oldest university in the world,[4][5][6][7][8] the University of Bologna, established in AD 1088, the city has a large student population that gives it a cosmopolitan character. In 2000 it was declared European capital of culture[9] and in 2006, a UNESCO "city of music".
Bologna is an important agricultural, industrial, financial and transport hub, where many large mechanical, electronic and food companies have their headquarters as well as one of the largest permanent trade fairs in Europe. According to the most recent data gathered by the European Regional Economic Growth Index (E-REGI) of 2009, Bologna is the first Italian city and the 47th European city in terms of its economic growth rate.[10] As a consequence, Bologna is also one of the wealthiest cities in Italy, often ranking as one of the top cities in terms of quality of life in the country: in 2011 it ranked 1st out of 107 Italian cities.[11]
Bologne (en italien : Bologna, prononcé /boˈloɲa/) est une ville italienne située dans le nord-est du pays, entre le Pô et les Apennins. C'est le chef-lieu de la région d'Émilie-Romagne (plaine du Pô) et de la province de même nom et l'une des principales villes d'Italie. Bologne compte environ 390 000 habitants (les Bolonais2) et son aire urbaine regroupe 1 005 000 habitants.
Elle est considérée comme le siège de la plus ancienne université du monde occidental puisqu'elle a été fondée en 10883. Plus de 900 ans après sa fondation, l'université est encore aujourd'hui le cœur de la ville puisque ses 100 000 étudiants constituent un quart de sa population.
Ce rayonnement culturel et son université lui ont valu le surnom de la Dotta (la savante). La ville possède également d'autres surnoms comme la Rossa (la rouge), en référence à ses tuiles en terre cuite et aussi pour son âme politique de gauche communiste, et la Grassa (la grasse) pour son excellente cuisine.
La sauce bolognaise (ragù alla bolognese en italien) est une recette de la région.
Chaque année au printemps, Bologne accueille un salon du livre de jeunesse de renommée internationale, Foire du livre de jeunesse de Bologne (La Fiera del Libro per Ragazzi).
Bologna (pronuncia: [boˈloɲɲa][4] [5]; Bulåggna [buˈlʌɲɲa] in dialetto bolognese[6]) è un comune italiano di 390 198 abitanti,[2] capoluogo dell'omonima città metropolitana, a sua volta capoluogo della regione Emilia-Romagna[7]. Si tratta del settimo comune più popolato d'Italia (4º del Nord dopo Milano, Torino e Genova) ed è il cuore di un'area metropolitana di 1.011.608 abitanti[8]. Antichissima città universitaria, Bologna ospita numerosi studenti. Nota per le sue torri e i suoi lunghi portici, possiede un ben conservato centro storico, fra i più estesi d'Italia.
La città, i cui primi insediamenti risalirebbero almeno al I millennio a.C., fu un importante centro urbano dapprima sotto gli Etruschi e i Celti, poi sotto i Romani poi ancora, nel Medioevo, come libero comune. Capitale settentrionale dello Stato Pontificio a partire dal Cinquecento, ebbe un ruolo molto importante durante il Risorgimento e, durante la seconda guerra mondiale, fu un importante centro della Resistenza. Nel secondo dopoguerra, come buona parte dell'Emilia, è stata governata quasi ininterrottamente da amministrazioni di sinistra.
Bologna è un importante nodo di comunicazioni stradali e ferroviarie del nord Italia, in un'area in cui risiedono importanti industrie meccaniche, elettroniche e alimentari. È sede di prestigiose istituzioni culturali, economiche e politiche e di uno dei più avanzati quartieri fieristici d'Europa. Nel 2000 è stata "capitale europea della cultura", mentre dal 2006 è "città della musica" UNESCO[9].
Bolonia (![]() /boˈloɲa/ (?·i) en italiano, Bologna, en emiliano-romañol, Bulåggna, pronunciado /buˈlʌɲɲa/) es una ciudad de Italia, capital de la ciudad metropolitana homónima y de la región Emilia-Romaña (en el norte del país), situada entre el río Reno y el río Savena, cerca de los Apeninos. Es una de las ciudades históricas mejor conservadas y tiene el segundo casco antiguo medieval más grande de Europa, después del de Venecia.
/boˈloɲa/ (?·i) en italiano, Bologna, en emiliano-romañol, Bulåggna, pronunciado /buˈlʌɲɲa/) es una ciudad de Italia, capital de la ciudad metropolitana homónima y de la región Emilia-Romaña (en el norte del país), situada entre el río Reno y el río Savena, cerca de los Apeninos. Es una de las ciudades históricas mejor conservadas y tiene el segundo casco antiguo medieval más grande de Europa, después del de Venecia.










乔托钟楼位于意大利佛罗伦萨的主教座堂广场。在圣母百花大教堂旁,面对佛罗伦萨圣若望洗礼堂。 有文艺复兴开创者乔托设计。
这座钟楼的样式属于哥特式,平面为周长14.45米的正方形,四角为高84.7米的四个多边形扶壁[1],四条垂直线又被四条水平线所分割,整座建筑布满了丰富的雕刻,和多种色彩的大理石镶嵌,其壮观的建筑和巧妙的设计博得了许多艺术爱好者的赞美。
Giottos Campanile (/ˌkæmpəˈniːli, -leɪ/, auch US: /ˌkɑːm-/, italienisch: [kampaˈniːle]) ist ein freistehender Campanile (Glockenturm), der Teil des Gebäudekomplexes ist, aus dem die Kathedrale von Florenz auf der Piazza del Duomo in Florenz, Italien, besteht.
Der Turm steht neben der Basilika Santa Maria del Fiore und dem Baptisterium San Giovanni und ist mit seinem Entwurf von Giotto, seinem reichen Skulpturenschmuck und seinen polychromen Marmorverkrustungen eines der Prunkstücke der florentinischen Gotik.
Das schlanke Bauwerk hat einen quadratischen Grundriss mit einer Seitenlänge von 14,45 m. Er ist 84,7 m hoch und weist an jeder Ecke polygonale Strebepfeiler auf.[1] Der Turm ist horizontal in fünf Stufen unterteilt.
 Financial
Financial
 Lombardia
Lombardia
 Companies
Companies
 Life and Style
Life and Style
 Fashion world
Fashion world
 Geography
Geography

 IT-Times
IT-Times
 Veneto
Veneto
 Eat and Drink
Eat and Drink
 Toscana
Toscana
 Lazio
Lazio
 Piemonte
Piemonte
 Sardegna
Sardegna
 Architecture
Architecture
 History
History