
Deutsch-Chinesische Enzyklopädie, 德汉百科
 Finland
Finland
 Amber Road
Amber Road
 Denmark
Denmark
 Germany
Germany
 Estonia
Estonia
 Finland
Finland

 Geography
Geography
 Latvia
Latvia
 Lithuania
Lithuania

 Mecklenburg-Vorpommern
Mecklenburg-Vorpommern
 Kiel Canal
Kiel Canal
 Poland
Poland
 Russia
Russia

 Schleswig-Holstein
Schleswig-Holstein
 Sweden
Sweden

波罗的海是中欧和北欧之间的陆间海,海域横贯北纬53度至北纬66度,东经10度至东经30度,介于斯堪的纳维亚半岛的瑞典部分、欧洲大陆和丹麦诸岛之间。
波罗的海由厄勒海峡、大贝尔特海峡和小贝尔特海峡注入卡特加特海峡,而后者则通过斯卡格拉克海峡注入北海,最后进入大西洋;此外它还通过白海运河同白海相连,通过基尔运河同北海相连。
波罗的海在北端与波的尼亚湾相邻,在东北端与芬兰湾相邻,在东端与里加湾相邻。这些海湾同样可以被看作是波罗的海的一部分。
Die Ostsee (auch Baltisches Meer, von lat. Mare Balticum, oder auch Baltische See genannt) ist ein 412.500 km²[2] großes und bis zu 459 m tiefes Binnenmeer in Europa und gilt als das größte Brackwassermeer der Erde, auch wenn in der westlichen Ostsee aufgrund des Wasseraustausches mit der Nordsee zumeist ein höherer Salz- und Sauerstoffgehalt beobachtet werden kann. Der Rauminhalt des Meeres beträgt rund 20.000 km³. Im Ostseeraum leben, je nachdem, wie weit man diese Region eingrenzt, zwischen 50 und 85 Millionen Menschen.[3]
バルト海(バルトかい、Baltic Sea)は、北ヨーロッパに位置する地中海。ヨーロッパ大陸とスカンディナビア半島に囲まれた海域である。ユーラシア大陸に囲まれた海域と説明されることもある[1]。
西岸にスウェーデン、東岸は、北から順にフィンランド、ロシア、エストニア、ラトビア、リトアニア、南岸は、東から西にポーランド、ドイツ、デンマークが位置する。
The Baltic Sea is a marginal sea of the Atlantic Ocean, enclosed by Finland, Sweden, Denmark, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Russia, Poland, Germany and the North and Central European Plain.
The sea stretches from 53°N to 66°N latitude and from 10°E to 30°E longitude. A mediterranean sea of the Atlantic, with limited water exchange between the two bodies, the Baltic Sea drains through the Danish islands into the Kattegat by way of the straits of Øresund, the Great Belt, and the Little Belt. It includes the Gulf of Bothnia, the Bay of Bothnia, the Gulf of Finland, the Gulf of Riga, and the Bay of Gdańsk.
The Baltic Proper is bordered on its northern edge, at the latitude 60°N, by the Åland islands and the Gulf of Bothnia, on its northeastern edge by the Gulf of Finland, on its eastern edge by the Gulf of Riga, and in the west by the Swedish part of the southern Scandinavian Peninsula.
The Baltic Sea is connected by artificial waterways to the White Sea via the White Sea Canal and to the German Bight of the North Sea via the Kiel Canal.
La mer Baltique est une mer intracontinentale et intérieure de 364 800 km2 située dans le Nord de l'Europe et reliée à l'océan Atlantique par la mer du Nord. Elle communique au sud-ouest avec la mer du Nord par le Cattégat et le Skagerrak. Trois golfes principaux intègrent cet espace : le golfe de Botnie au nord, le golfe de Finlande à l'est et le golfe de Riga au sud-est.
Les pays riverains sont :
- la Suède à l'ouest et au nord ;
- la Finlande au nord-est ;
- la Russie (par le golfe de Finlande) et l'Estonie à l'est ;
- la Lettonie au sud-est ;
- la Lituanie, la Russie (à Kaliningrad) et la Pologne au sud;
- l'Allemagne et le Danemark au sud-ouest.
Ces pays riverains, ainsi que la mer proprement dite, font l'objet, depuis 2009, d'une « stratégie de la Commission européenne en faveur du développement de la région de la mer Baltique »1, incluant un effort de dépollution de la Baltique et un système commun de surveillance maritime.
Il mar Baltico è un mare interno dell'oceano Atlantico settentrionale e si trova nell'Europa nord-orientale, circondato dalla Penisola scandinàva (meno correttamente scandìnava)[1], dalla terraferma dell'Europa centrale e orientale e dalle Isole danesi. Sfocia nel Kattegat e nel mare del Nord passando attraverso le isole danesi in tre stretti, l'Øresund, il Piccolo Belt e il Grande Belt.
Sfociano nel mar Baltico cinque grandi fiumi: l'Oder, la Vistola, il Njemen, la Daugava (o Dvina Occidentale) e la Neva. Le coste del Baltico tendono a ghiacciare d'inverno specie in occasione di eventi meteorologici particolarmente freddi.
Viene indicato come "mare dell'Est" in diverse lingue dell'Europa continentale, precisamente in danese (Østersøen), tedesco (Ostsee), finlandese (Itämeri), olandese (Oostzee), norvegese (Østersjøen), e svedese (Östersjön). In estone viene invece chiamato "mare Occidentale" (Läänemeri). Oltre all'italiano, viene chiamato mar Baltico in francese (mer Baltique), inglese (Baltic Sea), polacco (Morze Bałtyckie), russo (Baltijskoe more, Балтийское море), lituano (Baltijos Jūra), lettone (Baltijas Jūra) e greco (Baltiké thálassa, Βαλτική Θάλασσα).
El mar Báltico (del latín: Mare Balticum) es un mar interior de agua salobre del norte de Europa abierto al mar del Norte y, finalmente, al océano Atlántico a través de los estrechos de Kattegat y Skagerrak. Los países que lo rodean son (empezando por la península Escandinava y siguiendo en sentido horario): Suecia, Finlandia, Rusia (óblast de Leningrado y Kaliningrado), Estonia, Letonia, Lituania, Polonia, Alemania y Dinamarca.
Su superficie es de 432 800 km² e incluye dos grandes golfos: el golfo de Finlandia, entre el sur de este país y Estonia, y el golfo de Botnia, entre la costa oriental de Suecia y el occidental de Finlandia. Geológicamente es muy joven: sólo existe desde el VI milenio a.C. Es muy poco profundo (la media es de 57 m; la profundidad máxima es de 459 m al norte de la isla sueca de Gotland), lo que, unida a la poca apertura al océano, hace la renovación de las aguas muy lenta y favorece los problemas de contaminación. Las mareas son de muy pequeña amplitud.
El mar Báltico es también, el mayor depósito de ámbar del mundo y, además, su calidad es de las mejores: de los veinte depósitos del mundo que hay de ámbar, se dice que el del mar báltico sólo es superado por los de México y la República Dominicana, siendo el que más ámbar de conífera produce y el de mejor calidad. De él se extraen de 500 a 800 millones de toneladas de ámbar.
La cuenca que drena al mar Báltico abarca la totalidad de algunos países ribereños como las repúblicas bálticas, Polonia y la región rusa de Kaliningrado. Además, estos ríos nacen en, o atraviesan territorios pertenecientes a otros países que, a pesar de no poseer costas, se comunican al mar por vía fluvial. Tal es el caso de la República Checa, Eslovaquia, Ucrania y Bielorrusia, quienes acaban aportando agua (indirectamente) al mar Báltico.
Балти́йское мо́ре (Варяжское[1], польск. Morze Bałtyckie, нем. Ostsee, н.-нем. Oostsee, швед. Östersjön, дат. Østersøen, фин. Itämeri, эст. Läänemeri, латыш. Baltijas jūra, лит. Baltijos jūra) — внутриматериковое море Евразии, расположенное в Северной Европе (частично омывает также берега Западной и Восточной Европы). Относится к бассейну Атлантического океана.
Крайняя северная точка Балтийского моря находится вблизи Северного полярного круга (65°40' с. ш.), крайняя южная — около города Висмара (53°45' с. ш.).
Крайняя западная точка расположена в районе Фленсбурга (9°10' в. д.), крайняя восточная — в районе Санкт-Петербурга (30°15' в. д.)
Площадь поверхности моря (без островов) — 415 тыс. км². Объём воды — 21,5 тыс. км³. Из-за огромного стока рек вода имеет низкую солёность и потому море является солоноватоводным. Является крупнейшим в мире морем с такой особенностью[2].
Участок континентальной коры, на котором лежит современное Балтийское море, является частью устойчивой Русской тектонической плиты (Фенносарматия). Как единый массив он сложился около 1,8 миллиарда лет назад и с тех пор пребывал в относительной стабильности. Бо́льшая часть территории, соответствующей дну современной Балтики, бо́льшую часть времени находилась выше уровня моря, хотя южная и восточная части этого пространства продолжительное время были покрыты мелководными шельфовыми морями, о чём свидетельствует мощный слой донных осадков в этих областях. Балтийский кратон образовался в южном полушарии, дрейфовал на запад, находясь в эдиакарии в районе Южного Полярного круга, а далее на север, пересёк экватор около 375 млн л. н., и около 30 миллионов лет назад уже приблизился к современному положению. В разное время он был составной частью различных материков (Нуна, Нена, Родиния, Протолавразия, Паннотия, Лавруссия, Пангея, Лавразия, Евразия), а некоторое время также отдельным материком Балтикой.
Примерно 40 миллионов лет назад, когда контуры северной, центральной и восточной Европы уже сложились на близких к современным широтах, на месте будущего Балтийского моря возникла долина реки Эридан, протекавшей в юго-западном направлении параллельно Скандинавским горам — то есть приблизительно так же, как будет расположено Балтийское море: исток брала в Лапландии, а сильно ветвистая дельта в районе современных Нидерландов впадала в древнее Северное море, и в области нынешнего Финского залива располагался крупный приток. С наступлением четвертичного оледенения, примерно 700 тыс. л. н. Эридан прекратил существование, поскольку его долина, как и вся северная Европа, скрылась под ледниковым щитом. По берегам Эридана росла тайга. После образования ледника смола хвойных деревьев превратилась в янтарь.
ности и другие параметры Литоринового моря стали близки к современным — начинается около 4 тысяч лет назад. Примерно в это же время возникает и Нева.

Der Ostseerat (englisch Council of the Baltic Sea States, CBSS) ist eine am 6. März 1992 in Kopenhagen (Dänemark) gegründete Internationale Organisation mit dem Ziel der wirtschaftlichen, politischen, kulturellen und umweltpolitischen Kooperation der Anrainerstaaten der Ostsee sowie Norwegens und Islands. Als Initiatoren gelten die damaligen Außenminister Deutschlands Hans-Dietrich Genscher und Dänemarks Uffe Ellemann-Jensen. Der Rat unterhält ein internationales Sekretariat in Nyborg, (Dänemark).
波罗的海国家理事会(英语:Council of the Baltic Sea States,缩写:CBSS)是由北欧波罗的海国家政府所组成的合作组织,于苏联解体后成立。理事会特别针对经济发展、能源、教育与文化、公共安全与人类发展,包括人口贩运的五个优先范畴的进行全面的协商。

 Australia
Australia
 Belgium
Belgium
 Brazil
Brazil
 Denmark
Denmark
 Germany
Germany
 Finland
Finland
 France
France
 Ireland
Ireland
 Israel
Israel
 Italy
Italy
 Japan
Japan
 Canada
Canada
 Netherlands
Netherlands
 Norwegen
Norwegen
 Austria
Austria
 Republic of Korea
Republic of Korea
 Russia
Russia
 Sweden
Sweden
 Switzerland
Switzerland
 Spain
Spain
 United States
United States
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom


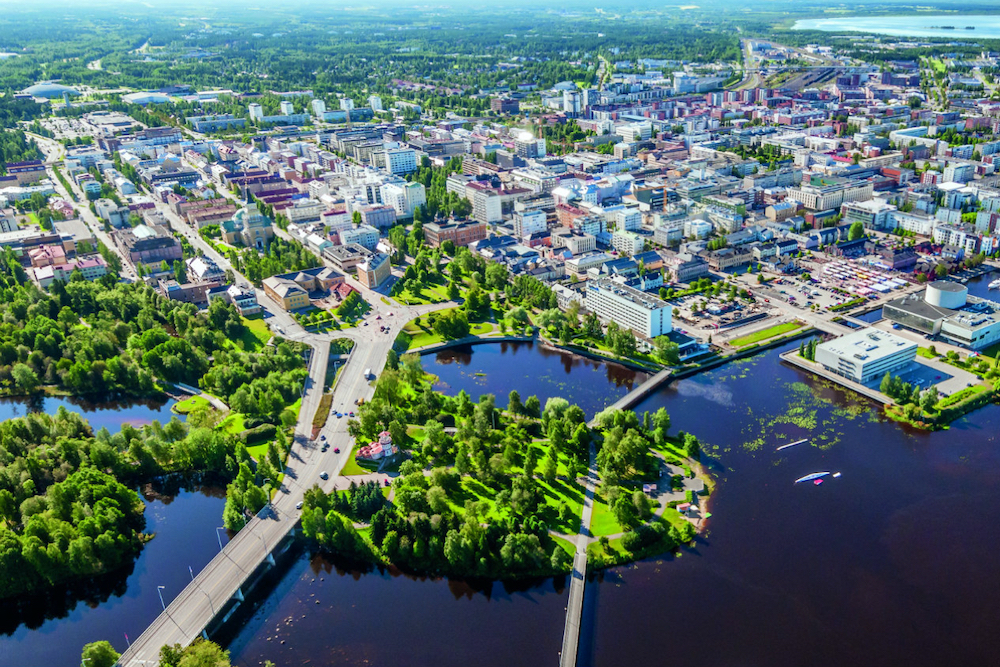
 Finland
Finland

 Medical, Pharmaceutical, Rehabilitation
Medical, Pharmaceutical, Rehabilitation
 Medical Equipment
Medical Equipment

 Medical equipment
Medical equipment
 Dental Equipment
Dental Equipment

 Alaska-AK
Alaska-AK
 Denmark
Denmark
 Finland
Finland
 Iceland
Iceland
 Canada
Canada

 Northwest Territories-NT
Northwest Territories-NT
 Norwegen
Norwegen
 Nunavut-NU
Nunavut-NU
 Russia
Russia
 Sweden
Sweden
 United States
United States

 Yukon-YT
Yukon-YT

北极圈是指纬度数值为北纬66°34′(90°-23°26′) 的一个假想圈,是北寒带与北温带的分界线,与黄赤交角(南回归线、北回归线所在的纬度数值)余角。北极圈以北的地区被称为“北极圈内”。通常,北极圈内的地区被叫做北极地区,由北冰洋以及周边陆地组成,其陆地部分包括了格陵兰、北欧三国、冰岛格里姆赛岛、俄罗斯北部、美国阿拉斯加北部以及加拿大北部。北极圈内岛屿很多,最大的是格陵兰岛。由于严寒,北极圈以内的生物种类很少。植物以地衣、苔藓为主,动物有北极熊、海豹、鲸等。
北极圈也是极昼和极夜现象开始出现的界线,北极圈以北的地区在夏天会出现极昼,而在冬天会出现极夜。
Polarkreise nennt man die Besonderen Breitenkreise der Erde auf 66° 33′ 55″ (66,565°) nördlicher und südlicher Breite, auf denen die Sonne an den beiden Tagen der Sonnenwende gerade nicht mehr auf- bzw. untergeht. Ihr Radius entspricht dem axialen Abstand der Wendekreise vom Äquator.
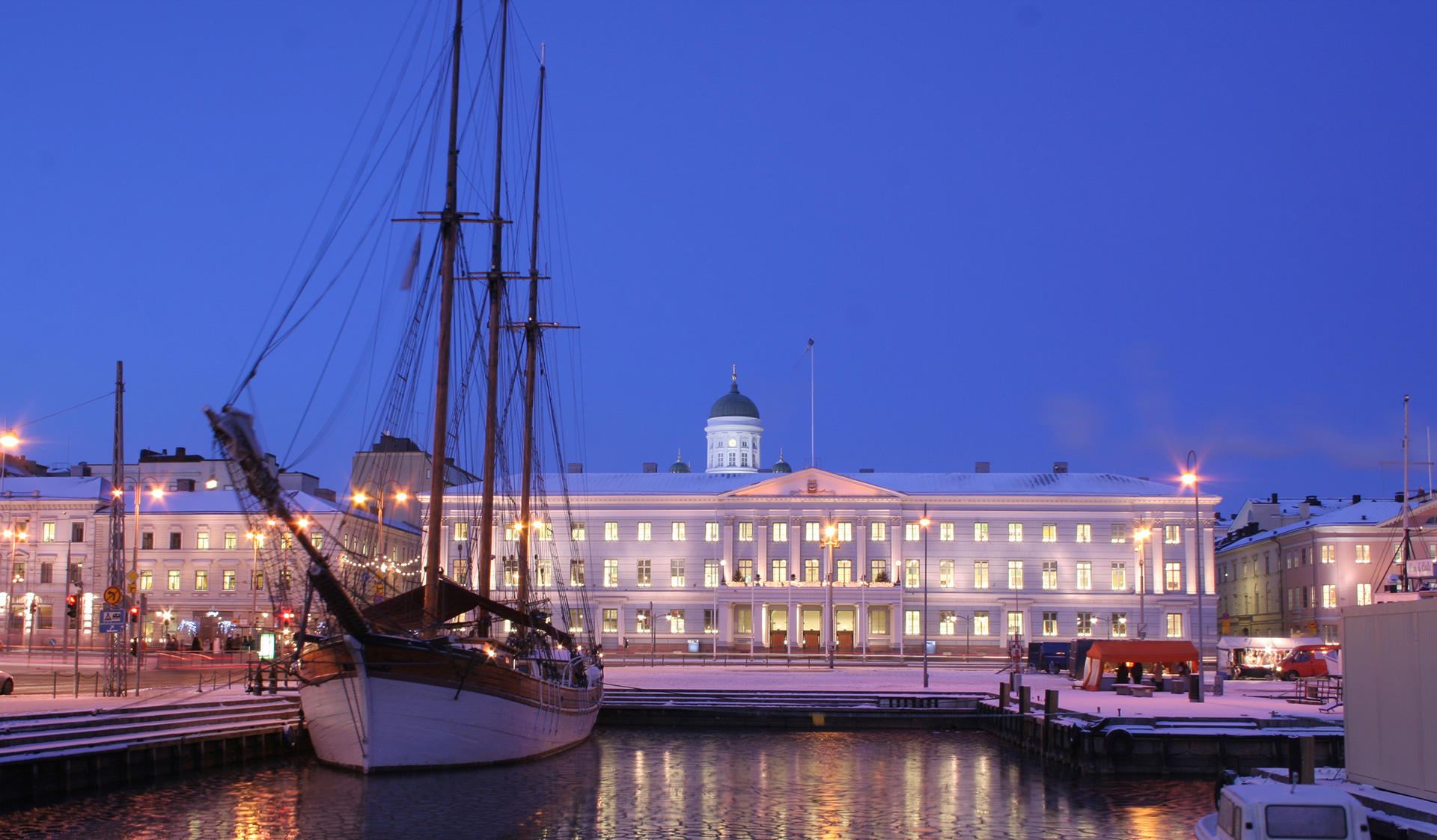
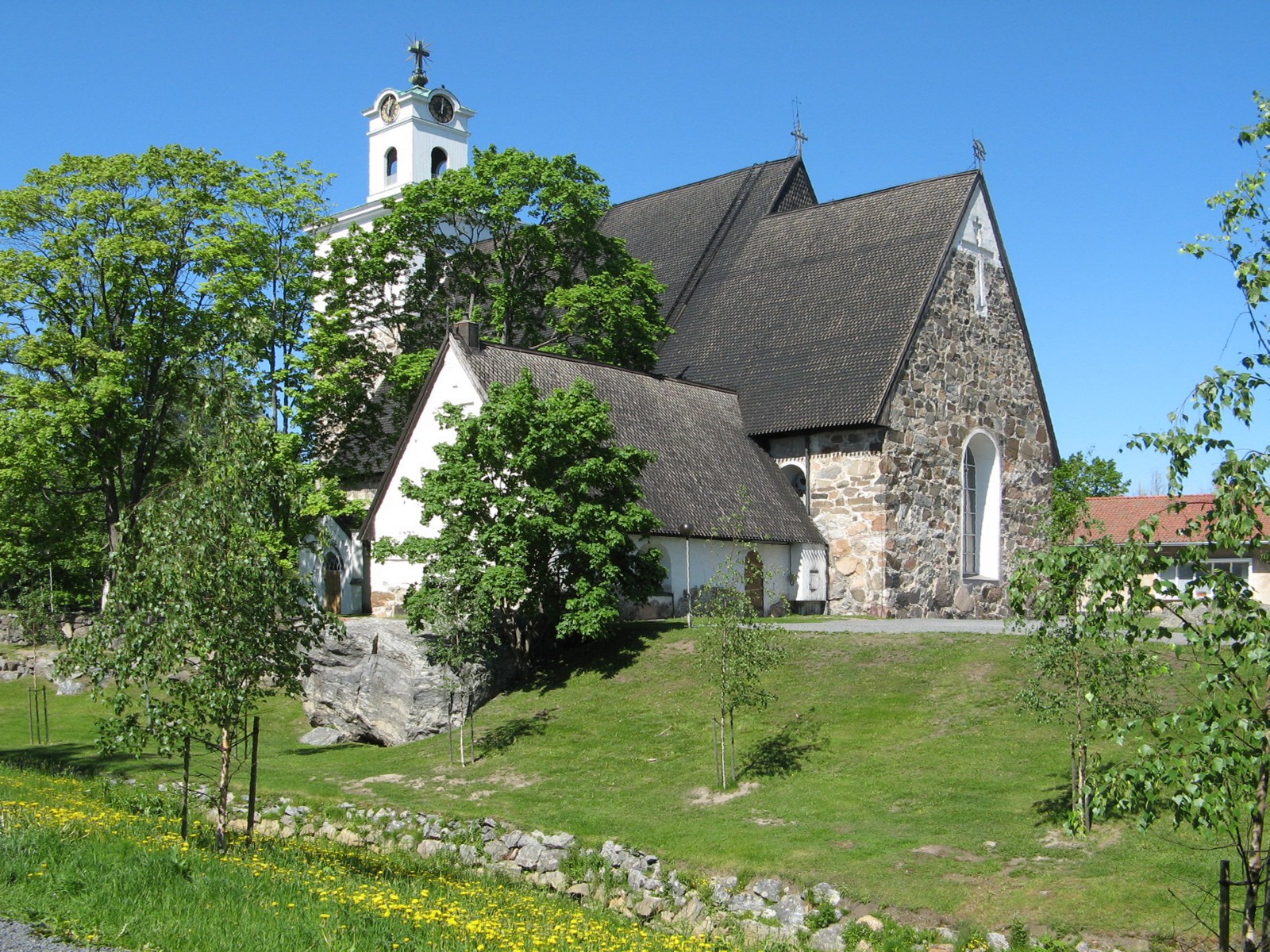





 Vacation and Travel
Vacation and Travel
 Hand in Hand
Hand in Hand
 European Union
European Union
 International cities
International cities
 Financial
Financial
 Party and government
Party and government

 IT-Times
IT-Times
 Ships and Nautics
Ships and Nautics
 Architecture
Architecture
 World Heritage
World Heritage