
Deutsch-Chinesische Enzyklopädie, 德汉百科
 Shanghai Shi-SH
Shanghai Shi-SH
 Beijing Shi-BJ
Beijing Shi-BJ
 Chinese Super League 2020
Chinese Super League 2020
 Chongqing Shi-CQ
Chongqing Shi-CQ
 Guangdong Sheng-GD
Guangdong Sheng-GD
 Guangdong Sheng-GD
Guangdong Sheng-GD
 Hebei Sheng-HE
Hebei Sheng-HE
 Hebei Sheng-HE
Hebei Sheng-HE
 Henan Sheng-HA
Henan Sheng-HA
 Hubei Sheng-HB
Hubei Sheng-HB
 Jiangsu Sheng-JS
Jiangsu Sheng-JS
 Liaoning Sheng-LN
Liaoning Sheng-LN
 Shandong Sheng-SD
Shandong Sheng-SD
 Shandong Sheng-SD
Shandong Sheng-SD
 Shanghai Shi-SH
Shanghai Shi-SH
 Shanghai Shi-SH
Shanghai Shi-SH
 Tianjin Shi-TJ
Tianjin Shi-TJ
 Tianjin Shi-TJ
Tianjin Shi-TJ
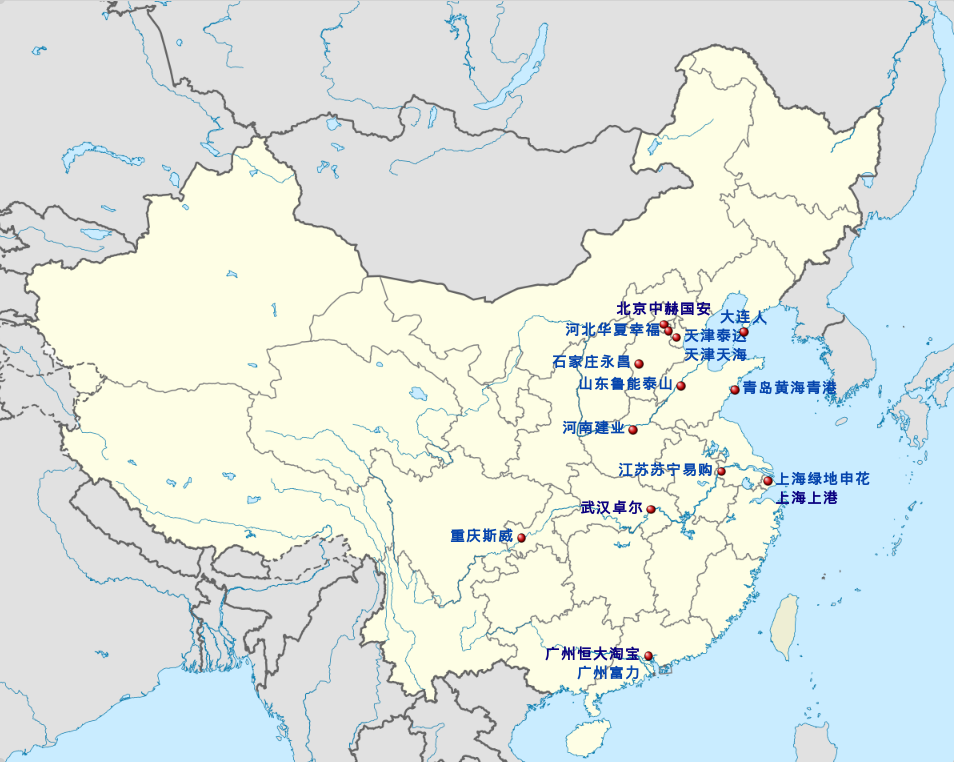
 Beijing Shi-BJ
Beijing Shi-BJ
 Chinese Super League 2021
Chinese Super League 2021
 Chongqing Shi-CQ
Chongqing Shi-CQ
 Guangdong Sheng-GD
Guangdong Sheng-GD
 Hebei Sheng-HE
Hebei Sheng-HE
 Henan Sheng-HA
Henan Sheng-HA
 Hubei Sheng-HB
Hubei Sheng-HB
 Jilin Sheng-JL
Jilin Sheng-JL
 Liaoning Sheng-LN
Liaoning Sheng-LN
 Shandong Sheng-SD
Shandong Sheng-SD
 Shanghai Shi-SH
Shanghai Shi-SH
 Tianjin Shi-TJ
Tianjin Shi-TJ
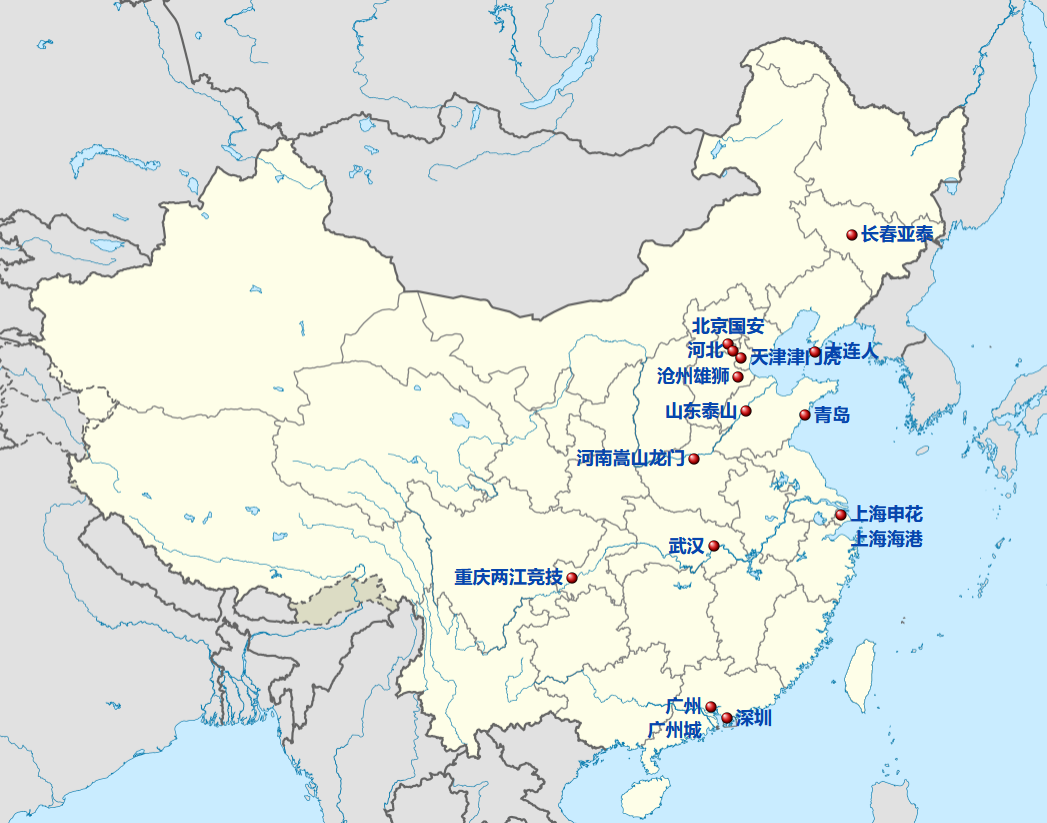
 Beijing Shi-BJ
Beijing Shi-BJ
 Chinese Super League 2022
Chinese Super League 2022
 Guangdong Sheng-GD
Guangdong Sheng-GD
 Hebei Sheng-HE
Hebei Sheng-HE
 Henan Sheng-HA
Henan Sheng-HA
 Hubei Sheng-HB
Hubei Sheng-HB
 Jilin Sheng-JL
Jilin Sheng-JL
 Liaoning Sheng-LN
Liaoning Sheng-LN
 Shandong Sheng-SD
Shandong Sheng-SD
 Shanghai Shi-SH
Shanghai Shi-SH
 Sichuan Sheng-SC
Sichuan Sheng-SC
 Tianjin Shi-TJ
Tianjin Shi-TJ
 Zhejiang Sheng-ZJ
Zhejiang Sheng-ZJ

 Beijing Shi-BJ
Beijing Shi-BJ
 Chinese Super League 2023
Chinese Super League 2023
 Guangdong Sheng-GD
Guangdong Sheng-GD
 Hebei Sheng-HE
Hebei Sheng-HE
 Henan Sheng-HA
Henan Sheng-HA
 Hubei Sheng-HB
Hubei Sheng-HB
 Jiangsu Sheng-JS
Jiangsu Sheng-JS
 Jilin Sheng-JL
Jilin Sheng-JL
 Liaoning Sheng-LN
Liaoning Sheng-LN
 Shandong Sheng-SD
Shandong Sheng-SD
 Shanghai Shi-SH
Shanghai Shi-SH
 Sichuan Sheng-SC
Sichuan Sheng-SC
 Tianjin Shi-TJ
Tianjin Shi-TJ
 Zhejiang Sheng-ZJ
Zhejiang Sheng-ZJ

 Beijing Shi-BJ
Beijing Shi-BJ
 Chinese Super League 2024
Chinese Super League 2024
 Guangdong Sheng-GD
Guangdong Sheng-GD
 Hebei Sheng-HE
Hebei Sheng-HE
 Henan Sheng-HA
Henan Sheng-HA
 Hubei Sheng-HB
Hubei Sheng-HB
 Jiangsu Sheng-JS
Jiangsu Sheng-JS
 Jilin Sheng-JL
Jilin Sheng-JL
 Shandong Sheng-SD
Shandong Sheng-SD
 Shanghai Shi-SH
Shanghai Shi-SH
 Sichuan Sheng-SC
Sichuan Sheng-SC
 Tianjin Shi-TJ
Tianjin Shi-TJ
 Zhejiang Sheng-ZJ
Zhejiang Sheng-ZJ


 *Chinese think tanks
*Chinese think tanks
 Anhui Sheng-AH
Anhui Sheng-AH
 Beijing Shi-BJ
Beijing Shi-BJ
 Breakthrough Prize
Breakthrough Prize
 Fundamental Physics Breakthrough Prize
Fundamental Physics Breakthrough Prize
 Chinese Academy of Science
Chinese Academy of Science
 Gansu Sheng-GS
Gansu Sheng-GS
 Guangdong Sheng-GD
Guangdong Sheng-GD
 Hubei Sheng-HB
Hubei Sheng-HB
 Jiangsu Sheng-JS
Jiangsu Sheng-JS
 Jilin Sheng-JL
Jilin Sheng-JL
 Liaoning Sheng-LN
Liaoning Sheng-LN
 National Key Laboratory of Plant Molecular Genetics
National Key Laboratory of Plant Molecular Genetics
 Shaanxi Sheng-SN
Shaanxi Sheng-SN
 Shanghai Shi-SH
Shanghai Shi-SH
 Sichuan Sheng-SC
Sichuan Sheng-SC
 State key laboratory
State key laboratory
 State Key Laboratory for Superlattices and Microstructures
State Key Laboratory for Superlattices and Microstructures
 State Key Laboratory of Applied Optics
State Key Laboratory of Applied Optics
 State Key Laboratory of Biomembrane and Membrane Biotechnology
State Key Laboratory of Biomembrane and Membrane Biotechnology
 State Key Laboratory of Bioorganic and Natural Products Chemistry
State Key Laboratory of Bioorganic and Natural Products Chemistry
 State Key Laboratory of Catalysis
State Key Laboratory of Catalysis
 State Key Laboratory of Cell Biology
State Key Laboratory of Cell Biology
 State Key Laboratory of Coal Conversion
State Key Laboratory of Coal Conversion
 State Key Laboratory of Computer Architecture
State Key Laboratory of Computer Architecture
 State Key Laboratory of Computer Science, Institute of Software
State Key Laboratory of Computer Science, Institute of Software
 State Key Laboratory of Desert and Oasis Ecology
State Key Laboratory of Desert and Oasis Ecology
 State Key Laboratory of Drug Research
State Key Laboratory of Drug Research
 State Key Laboratory of Electroanalytical Chemistry
State Key Laboratory of Electroanalytical Chemistry
 State Key Laboratory of Fire Science
State Key Laboratory of Fire Science
 State Key Laboratory of Functional Mmaterials for Informatics
State Key Laboratory of Functional Mmaterials for Informatics
 State Key Laboratory of Genetic Resources and Evolution
State Key Laboratory of Genetic Resources and Evolution
 State Key Laboratory of High Field Laser Physics
State Key Laboratory of High Field Laser Physics
 State Key Laboratory of High Performance Ceramics and Superfine Microstructure
State Key Laboratory of High Performance Ceramics and Superfine Microstructure
 State Key Laboratory of Information Security
State Key Laboratory of Information Security
 State Key Laboratory of Infrared Physics
State Key Laboratory of Infrared Physics
 State Key Laboratory of Isotope Geochemistry
State Key Laboratory of Isotope Geochemistry
 State Key Laboratory of Microfabrication Optical Technology
State Key Laboratory of Microfabrication Optical Technology
 State Key Laboratory of Molecular Biology
State Key Laboratory of Molecular Biology
 State Key Laboratory of Molecular Reaction Dynamics
State Key Laboratory of Molecular Reaction Dynamics
 State Key Laboratory of Multiphase Complex Systems
State Key Laboratory of Multiphase Complex Systems
 State Key Laboratory of Neuroscience
State Key Laboratory of Neuroscience
 State Key Laboratory of Nuclear Detection and Nuclear Electronics
State Key Laboratory of Nuclear Detection and Nuclear Electronics
 State Key Laboratory of Organometallic Chemistry
State Key Laboratory of Organometallic Chemistry
 State Key Laboratory of Phytochemistry and Plant Resources in Western China
State Key Laboratory of Phytochemistry and Plant Resources in Western China
 State Key Laboratory of Plant Genomics Institute of Genetics and Developmental Biology Institute of
State Key Laboratory of Plant Genomics Institute of Genetics and Developmental Biology Institute of
 State Key Laboratory of Polymer Physics and Chemistry
State Key Laboratory of Polymer Physics and Chemistry
 State Key Laboratory of Rare Earth Resource Utilization
State Key Laboratory of Rare Earth Resource Utilization
 State Key Laboratory of Remote Sensing Science
State Key Laboratory of Remote Sensing Science
 State Key Laboratory of Robotics
State Key Laboratory of Robotics
 State Key Laboratory of Soil and Sustainable Agriculture
State Key Laboratory of Soil and Sustainable Agriculture
 State Key Laboratory of Structural Chemistry
State Key Laboratory of Structural Chemistry
 State Key Laboratory of Transducer Technology
State Key Laboratory of Transducer Technology
 State Key Laboratory of Tropical Oceanography
State Key Laboratory of Tropical Oceanography
 State Key Laboratory on Integrated Optoelectronics
State Key Laboratory on Integrated Optoelectronics

 Science and technology
Science and technology
 *World famous research institutions
*World famous research institutions

 Science and technology
Science and technology
 Asian city
Asian city
 Xinjiang Uygur Zizhiqu-XJ
Xinjiang Uygur Zizhiqu-XJ
 Yunnan Sheng-YN
Yunnan Sheng-YN

Die Chinesische Akademie der Wissenschaften, früher auch bekannt als Academia Sinica (chin. 中國科學院 / 中国科学院, Zhōngguó Kēxuéyuàn, engl. Chinese Academy of Sciences (Abk. CAS)), ist die nationale Akademie für Naturwissenschaften der Volksrepublik China. Sie ist dem Staatsrat der Volksrepublik China unterstellt. Sie wurde im November 1949 gegründet und hat ihren Sitz in Peking mit zahlreichen Instituten in ganz China.
Die Chinesische Akademie der Wissenschaften hat fünf Abteilungen:
- I. Mathematik,
- II. Physik,
- III. Chemie,
- IV. Geowissenschaften und
- V. Technologie.
Weiter gliedert sich die Akademie in zwölf Zweigstellen in Shenyang, Changchun, Shanghai, Nanking, Wuhan, Guangzhou, Chengdu, Kunming, Xi'an, Lanzhou und in Xinjiang. Die Chinesische Akademie der Wissenschaften hat 84 Institute, eine Universität (die Chinesische Universität der Wissenschaften und Technik in Hefei, Anhui), zwei Colleges, vier Dokumentations- und Informationszentren, drei Zentren für technologischen Support und zwei Editionseinheiten. Diese Zweigstellen und Büros der Chinesischen Akademie der Wissenschaften befinden sich in zwanzig Provinzen und regierungsunabhängigen Städten Chinas. Die Chinesische Akademie der Wissenschaften hat in acht Industriezweigen über 430 Hochtechnologie-Unternehmen ausgestattet oder geschaffen. Acht dieser Gesellschaften sind börsennotiert.
中国科学院[注 1],又简称中科院、科学院[4],是中华人民共和国科学技术方面的最高学术机构,全国自然科学与高新技术综合研究发展中心,为正部级国务院直属事业单位[5],于1949年11月在北京成立。1977年5月,哲学社会科学学部独立为中国社会科学院,1994年,在技术科学部的基础上及国家科委的支持下,成立中国工程院。
中国科学院与中国工程院并称“两院”。发展至今,中科院下设6个学部(数学物理学部、化学部、生命科学和医学学部、地学部、信息技术科学部、技术科学部),以及12个分院(北京、沈阳、长春、上海、南京、武汉、广州、成都、昆明、西安、兰州、新疆)、84个研究院所、2所大学、2所学院、4个文献情报中心、3个技术支撑机构和2个新闻出版单位,分布在全国20多个省(市)。此外,还投资兴办了430余家科技型企业(含转制单位),涉及11个行业,其中包括8家上市公司。此外,中国科学院还拥有(含与其他单位共建)4个国家实验室、85个国家重点实验室和153个中国科学院重点实验室。
管理有承担中科院各分院、研究所及大学的网络互联的中国科技网互联网骨干网。

崇明岛是中国国家地质公园,公园范围涵盖整个崇明岛,东西长约76公里,南北宽约13~18公里,面积约1200平方公里。崇明岛有“长江门户、东海瀛洲”之称。全岛三面环江,一面临海,东濒东海,南与上海浦东新区、宝山区及江苏省太仓隔水相望,西、北以长江与江苏省海门、启东一衣带水。全岛面积1225平方公里,东西长80公里,南北宽13至18公里,为中国大陆地区实际管辖之第二大岛,面积次于海南岛。岛上地势平坦,无山岗丘陵,西北部和中部稍高,西南部和东部略低
Chongming Dao (chinesisch 崇明島 / 崇明岛, Pinyin Chóngmíng Dǎo) ist mit 1.267 km² nach Hainan die zweitgrößte Insel der Volksrepublik China. Chongming Dao liegt an der Mündung des Jangtsekiangs in das Ostchinesische Meer.
Chongming Dao befindet sich zum überwiegenden Teil innerhalb der Regierungsunmittelbaren Stadt Shanghai und ist Namensgeber für den Stadtbezirk Chongming, zu dem sie selbst auch gehört. Ein Teil der Nordküste der Insel, der bis zur Verbindung mit Chongming Dao die separate Insel Yonglongsha bildete, ist Teil des Stadtgebiets Nantongs in der Provinz Jiangsu.
崇明島(すうめいとう、チョンミンダオ、拼音: )は、中華人民共和国の長江河口にあり、上海市崇明区及び江蘇省海門市、啓東市に属す島である。東経121°09′30〃から121°54′00〃,北経31°27′00〃から31°51′15〃に位置する。北亜熱帯に属す気候は温和で湿潤。年平均気温は15.2℃で、四季がある。 崇明島の面積は約1225平方kmあり、東西約80km、南北約15kmあり、中国の台湾島 海南島に次ぐ3番目に大きい島である。また、世界一大きい沖積島でもあり、長江の門戸、東海瀛洲とも称される。 島の東に東シナ海、南には長江をはさみ上海浦東新区、宝山区、江蘇省太倉市、西、北には長江、江蘇省海門市、啓東市がある。崇明島の大部分は上海市に属すが、ごく一部が江蘇省海門市海永郷と啓東市啓隆郷に属する。 島は全体的に平らで、山も丘もなく、約90%が標高3m〜4mの間で、西部が東部よりも少し高い。南にある長興島、横沙島とともに崇明区を構成している。
Chongming, formerly known as Chungming, is an alluvial island at the mouth of the Yangtze River in eastern China covering 1,267 square kilometers (489 sq mi) as of 2010. Together with the islands Changxing and Hengsha, it forms Chongming County, the northernmost area of the provincial-level municipality of Shanghai. At the time of the 2010 Chinese census, its population was 660 000.
A 20-kilometer-long (12 mi) stretch of the north shore of the island is not part of Chongming County or Shanghai but are instead two pene-exclaves of Jiangsu, formed by the connection of Chongming to the formerly-separate island of Yonglongsha.
Chongming (en chino, 崇明; pinyin, Chóngmíng; Wu: Dzonmin) es una isla china localizada en la desembocadura del río Yangtsé en el océano Pacífico. Junto a las dos islas menores de Changxing y Hengsha conforma el condado de Chongming. Con un área de 1041,38 km², es la tercera isla más grande de China, después de Hainan y Taiwán. En 2001 tenía una población de 694.600 habitantes.
Fue una de las áreas más rurales de Shanghái, pero actualmente es sujeto de un plan maestro urbano y agrícola, patrocinado por el gobierno chino. Se constrirá un túnel para conectar la isla con Shanghái, y se quiere incrementar la población mediante la construcción de una ecociudad al este de Chongming, Dongtan, incorporando agricultura specializada y desarrollo sustentable.
La historia de Chongming: Au moins dans la première année de Shen long ( Chinese: 神龍元年)( A.D. 705 ) , il y avait des habitants installés dans l'île de Chong-Ming.
Чунминдао (кит. упр. 崇明岛, пиньинь Chóngmíng Dǎo) — остров в устье Янцзы, третий по величине остров Китая (после Тайваня и Хайнаня).


 Anhui Sheng-AH
Anhui Sheng-AH
 Chongqing Shi-CQ
Chongqing Shi-CQ

 History
History
 H 1000 - 500 BC
H 1000 - 500 BC

 History
History
 I 500 - 0 BC
I 500 - 0 BC
 Guizhou Sheng-GZ
Guizhou Sheng-GZ
 Henan Sheng-HA
Henan Sheng-HA
 Hubei Sheng-HB
Hubei Sheng-HB
 Hunan Sheng-HN
Hunan Sheng-HN
 Jiangsu Sheng-JS
Jiangsu Sheng-JS
 Jiangxi Sheng-JX
Jiangxi Sheng-JX
 Shandong Sheng-SD
Shandong Sheng-SD
 Shanghai Shi-SH
Shanghai Shi-SH
 Sichuan Sheng-SC
Sichuan Sheng-SC
 Zhejiang Sheng-ZJ
Zhejiang Sheng-ZJ
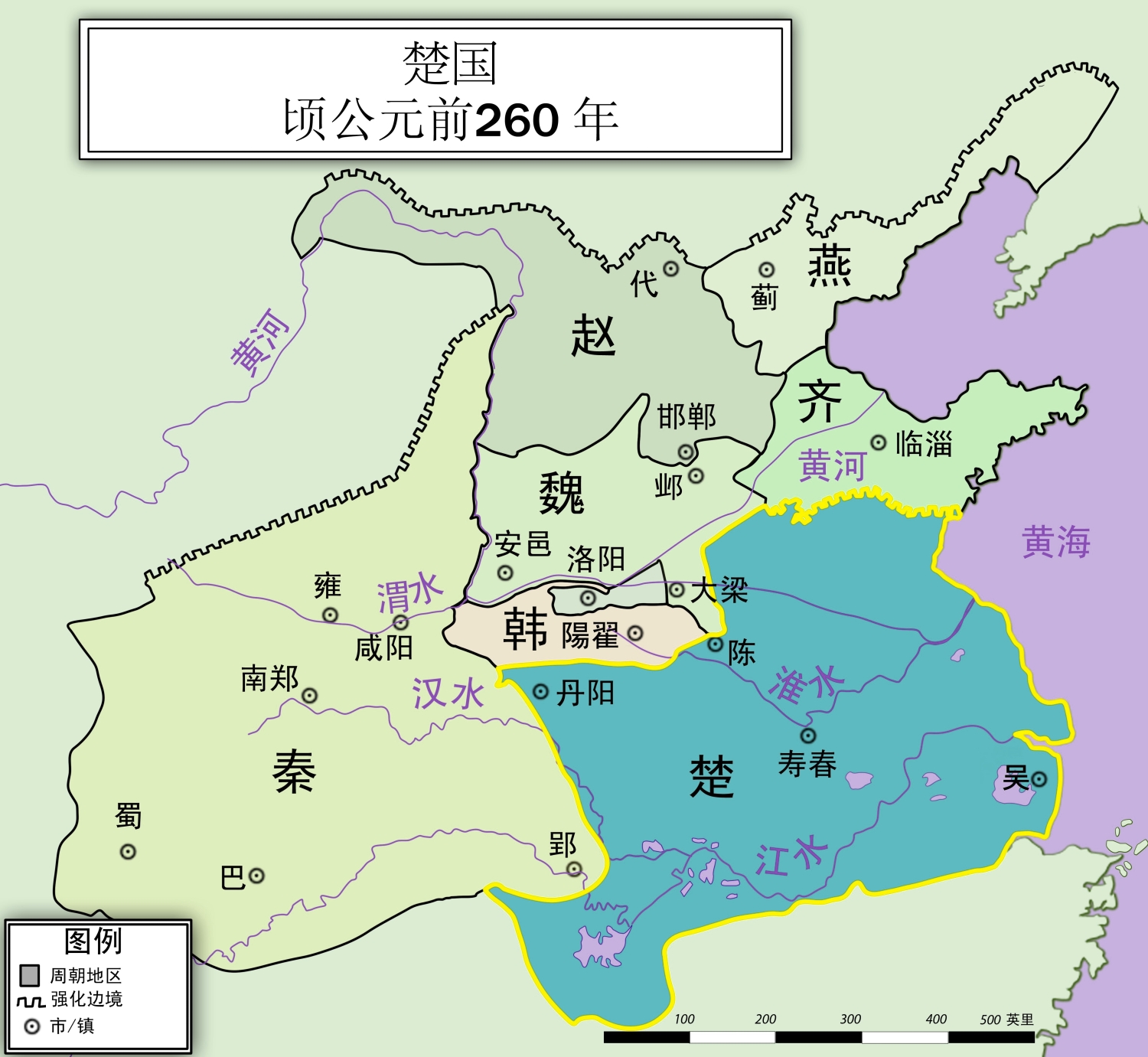
Chu (chinesisch 楚, Pinyin Chǔ, W.-G. Ch'u) war ein Königreich im Gebiet des heutigen Süd-China während der Westlichen Zhou-Dynastie (1046 bis 771 v. Chr.), der Zeit der Frühlings- und Herbstannalen (722 bis 481 v. Chr.) und der Zeit der Streitenden Reiche (475 bis 221 v. Chr.).
Ursprünglich war das Land als Jing (荆) und nachfolgend als Jingchu (荆楚) bekannt. Die größte Ausdehnung umfasste ein umfangreiches Gebiet, einschließlich das der heutigen Provinzen Hunan, Hubei, Chongqing, Henan, und Teile von Jiangsu. Die Hauptstadt von Chu war Ying.
Chu war zu seiner Zeit einer der mächtigsten Staaten und unterwarf zum Beispiel auch den kleineren Staat Lu im heutigen Shandong.
Größere Bedeutung erlangte Chu erstmals unter der Herrschaft von König Zhuang.
Chu (Chinese: 楚, Old Chinese: *s-r̥aʔ[2]) was a hegemonic, Zhou dynasty era state. From King Wu of Chu in the early 8th century BCE, the rulers of Chu declared themselves kings on an equal footing with the Zhou kings. Though initially inconsequential, removed to the south of the Zhou heartland and practising differing customs, Chu began a series of administrative reforms, becoming a successful expansionist state during the Spring and Autumn period. With its continued expansion Chu became a great Warring States period power, until it was overthrown by the Qin in 223 BCE.
Also known as Jing (荆) and Jingchu (荆楚), Chu included most of the present-day provinces of Hubei and Hunan, along with parts of Chongqing, Guizhou, Henan, Anhui, Jiangxi, Jiangsu, Zhejiang, and Shanghai. For more than 400 years, the Chu capital Danyang was located at the junction of the Dan and Xi Rivers[3][4] near present-day Xichuan County, Henan, but later moved to Ying. The ruling house of Chu originally bore the clan name Nai (嬭) and lineage name Yan (酓), but they are later written as Mi (芈) and Xiong (熊), respectively.[5]
Chu ou l'état de Chu (chinois simplifié : 楚国 ; chinois traditionnel : 楚國 ; pinyin : ; littéralement : « pays Chǔ ») était un État des périodes des Printemps et Automnes et des Royaumes combattants, établi sur le fleuve Yangzi. Chu a été annexé par Qin en 223 av. J.-C. La maison royale de Chu à l'origine portait le nom ancestral Nai (嬭) et le nom de clan Yan (酓) mais ceux-ci sont devenus plus tard Mi (芈) et Xiong (熊)1.
Chǔ (楚) fu un regno situato nell'attuale Cina centro meridionale, durante il Periodo delle primavere e degli autunni, (722-481 a.C. e il Periodo dei regni combattenti (481-221 a.C.). La famiglia dominante possedeva il cognome "mi" (芈), nome del clan "xiong" 熊, e il titolo nobiliare di "zi", corrispondente approssimativamente al nostro visconte.
Il primo nome dello Stato era Jing (荆) e successivamente Jingchu (荆楚). Al massimo della sua espansione il regno di Chu occupava una vasta area di territorio, comprendente le attuali province dello Hunan, Hubei, Chongqing, Henan, Shanghai, e parte dello Jiangsu. La capitale del regno era Ying (郢), localizzata approssimativamente nei pressi dell'attuale Jingzhou, nella provincia dell'Hubei.
Chǔ (楚, Wade-Giles: Ch'u3, pinyin: Chǔ) fue un reino situado en lo que hoy es China central y meridional durante el período de Primaveras y Otoños (722-481 a. C.) y el período de Reinos Combatientes (481-212 a. C.).
Fue originalmente conocido como Jing (荆) y luego como Jingchǔ (荆楚). Con el peso de su poder, el reino Chǔ ocupó vastas tierras, incluyendo las provincias actuales de Hunan, Hubei, Chongqing, Henan, Shanghái, y partes de Jiangsu. La capital de Chu era Ying (郢) y estaba ubicada en lo que hoy es la provincia de Hubei.
Чу (кит. 楚) — царство в южном Китае во время эпохи Чуньцю (722—481 гг. до н. э.) и Чжаньго («Воюющие царства» 481—221 до н. э.).
Первоначально царство было известно под названием Цзин (荆), затем Цзинчу (荆楚). На пике могущества под властью Чу находилась территория современных провинций Хунань, Хубэй, Чжэцзян, частично Цзянсу, Цзянси, Аньхой и Фуцзянь, а также города Шанхай. Ранней столицей Чу был Даньян 丹陽, в правление Сюн Туна (8-7 вв. до н. э.) столица была перенесена в Ин 郢 (совр. Цзинчжоу).
 Sport
Sport
 Exhibition
Exhibition
 Ships and Nautics
Ships and Nautics

 Geography
Geography
 Architecture
Architecture