
漢德百科全書 | 汉德百科全书
 Malaysia
Malaysia

Die Putra-Moschee (malaiisch Masjid Putra, auch Rote Moschee) ist die Hauptmoschee von Putrajaya, Malaysia. Sie ist nach Almarhum Tunku Abdul Rahman Putra Al Haj benannt, dem ersten Premierminister Malaysias.[1]
Die Moschee befindet sich am Putraplatz und grenzt an den künstlich angelegten Putrajayasee, unweit der Residenz des Premierministers von Malaysia.
Die Putra-Moschee mit ihrer pinkfarbenen Kuppel ist aus rosafarbenem Granit gebaut und besteht aus drei Hauptfunktionsbereichen: der Gebetshalle, dem Sahn und verschiedenen Lern- und Funktionsräumen. Die Moschee bietet Platz für 15.000 Gläubige. Der Bau der Moschee begann 1997 und wurde im September 1999 abgeschlossen. Die Baukosten beliefen sich auf 250.000.000 Malaysische Ringgit; das entspricht etwa 50.000.000 Euro. Das 116 m hohe Minarett besteht aus fünf Stockwerken, die die fünf Säulen des Islam verkörpern. Die größte der neun Kuppeln ist 50 m hoch und hat einen Durchmesser von 36 m. Sie wird von zwölf Säulen getragen.
Die Putra-Moschee erfüllt nicht nur spirituelle Bedürfnisse, sondern bietet auch Dienstleistungen für die Community an. Öffentliche Räume stehen für Konferenzen, Seminare, Symposien, Tagungen und Ausstellungen zur Verfügung.

 Brunei Darussalam
Brunei Darussalam
 China
China
 Indonesia
Indonesia
 Japan
Japan
 Cambodia
Cambodia
 Laos
Laos
 Malaysia
Malaysia
 Myanmar
Myanmar
 Philippines
Philippines
 Republic of Korea
Republic of Korea
 Singapore
Singapore
 Thailand
Thailand
 Vietnam
Vietnam

 Important International Organizations
Important International Organizations

 Australia
Australia
 Brunei Darussalam
Brunei Darussalam
 China
China

 Hand in Hand
Hand in Hand
 India
India
 Indonesia
Indonesia
 Japan
Japan
 Cambodia
Cambodia
 Laos
Laos
 Malaysia
Malaysia
 Myanmar
Myanmar
 New Zealand
New Zealand
 Philippines
Philippines
 Republic of Korea
Republic of Korea
 Russia
Russia
 Singapore
Singapore
 Thailand
Thailand
 United States
United States
 Vietnam
Vietnam

Der Ostasiengipfel (EAS) ist ein regionales Forum, das jährlich von den Staats- und Regierungschefs von zunächst 16 Ländern der Regionen Ostasien, Südostasien, Südasien und Ozeanien auf der Grundlage des ASEAN-plus-Six-Mechanismus abgehalten wird. Auf der sechsten EAS-Konferenz im Jahr 2011 wurde die Mitgliedschaft auf 18 Länder erweitert, darunter Russland und die Vereinigten Staaten. Seit seiner Gründung hat die ASEAN die zentrale Rolle und Führung in dem Forum inne. Die EAS-Treffen finden im Anschluss an die jährlichen Treffen der ASEAN-Staats- und Regierungschefs statt und spielen eine wichtige Rolle in der regionalen Architektur des asiatisch-pazifischen Raums. Der erste Gipfel fand am 14. Dezember 2005 in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, statt.
东亚峰会(英语:East Asia Summit, EAS),是每年一次由泛东亚地区16个国家领导人参加的国际会议,东南亚国家联盟(东盟)是该会议的领导者。俄罗斯也于2005年申请加入,并以观察员身份参加。第一届峰会于2005年12月14日在马来西亚首都吉隆坡举行,此后的峰会都于每年东盟领导人会议之后举行。并同时在东盟十加三会议后举行。

 ASEAN University Network
ASEAN University Network
 Brunei Darussalam
Brunei Darussalam
 Indonesia
Indonesia
 Cambodia
Cambodia
 Laos
Laos
 Malaysia
Malaysia
 Myanmar
Myanmar
 Philippines
Philippines
 Singapore
Singapore
 Thailand
Thailand
 Vietnam
Vietnam

 Brunei Darussalam
Brunei Darussalam

 Hand in Hand
Hand in Hand
 Indonesia
Indonesia
 Cambodia
Cambodia
 Laos
Laos
 Malaysia
Malaysia
 Myanmar
Myanmar
 Philippines
Philippines
 Singapore
Singapore
 Thailand
Thailand
 Vietnam
Vietnam
 ASEAN Summit
ASEAN Summit
 Association of Southeast Asian Nations,ASEAN
Association of Southeast Asian Nations,ASEAN
 Hassanal Bolkiah
Hassanal Bolkiah
 Association of Southeast Asian Nations,ASEAN
Association of Southeast Asian Nations,ASEAN
 Htin Kyaw
Htin Kyaw
 Association of Southeast Asian Nations,ASEAN
Association of Southeast Asian Nations,ASEAN
 Hun Sen
Hun Sen
 Association of Southeast Asian Nations,ASEAN
Association of Southeast Asian Nations,ASEAN
 Joko Widodo
Joko Widodo
 Association of Southeast Asian Nations,ASEAN
Association of Southeast Asian Nations,ASEAN
 Lee Hsien Loong
Lee Hsien Loong
 Association of Southeast Asian Nations,ASEAN
Association of Southeast Asian Nations,ASEAN
 Najib Razak
Najib Razak
 Association of Southeast Asian Nations,ASEAN
Association of Southeast Asian Nations,ASEAN
 Nguyễn Xuân Phúc
Nguyễn Xuân Phúc
 Association of Southeast Asian Nations,ASEAN
Association of Southeast Asian Nations,ASEAN
 Prayut Chan-o-cha
Prayut Chan-o-cha
 Association of Southeast Asian Nations,ASEAN
Association of Southeast Asian Nations,ASEAN
 Rodrigo Duterte
Rodrigo Duterte
 Association of Southeast Asian Nations,ASEAN
Association of Southeast Asian Nations,ASEAN
 Thongloun Sisoulith
Thongloun Sisoulith
 Brunei Darussalam
Brunei Darussalam
 Indonesia
Indonesia
 Cambodia
Cambodia
 Laos
Laos
 Malaysia
Malaysia
 Myanmar
Myanmar

 Party and government
Party and government

 Party and government
Party and government
 Association of Southeast Asian Nations,ASEAN
Association of Southeast Asian Nations,ASEAN
 Philippines
Philippines
 Singapore
Singapore
 Thailand
Thailand
 Vietnam
Vietnam

 Important International Organizations
Important International Organizations

Der Verband Südostasiatischer Nationen, kurz ASEAN (deutsche Aussprache: [ˈaːzean]; englische Aussprache [ˈæzɪən],[4] von englisch Association of Southeast Asian Nations), ist eine internationale Organisation südostasiatischer Staaten mit Sitz in Jakarta (Indonesien). Jedes Jahr findet ein Gipfeltreffen der ASEAN-Staaten statt.
Das ursprüngliche Ziel war die Verbesserung der wirtschaftlichen, politischen und sozialen Zusammenarbeit. Später erweiterte sich das Betätigungsfeld um Sicherheits-, Kultur- und Umweltfragen. Im September 2009 beschlossen die Staats- und Regierungschefs der ASEAN-Mitglieder, einen gemeinsamen Wirtschaftsraum nach dem Vorbild der EU zu schaffen.[5]
Im Laufe der Jahre wurden weitere Organisationen gegründet: das ASEAN-Regionalforum (ARF) für Sicherheitsfragen, die ASEAN-Freihandelszone (AFTA) zur Förderung des Handels, die ASEAN Investment Area (AIA) zur Förderung gegenseitiger Direktinvestitionen und andere mehr.
Vorläufer der Organisationsgemeinschaft war der Verband Südostasiens, ASA (1961–1967). Diese erlebte nach einer Stagnationsphase und dem Sturz Sukarnos im September 1965 zwar eine Wiedererweckung, ging aber auf indonesische Initiative hin sowie unter Beibehaltung der Strukturen und des Sicherheitskonzepts schließlich in das intensivere Bündnis der ASEAN über.
东南亚国家联盟(英语:Association of Southeast Asian Nations,英文简称ASEAN),中文简称东盟、亚细安、东南亚国协或东协,是集合东南亚区域国家的一个政府性国际组织。[6]
东盟成立初期,基于冷战背景立场反共,主要任务之一为防止区域内共产主义势力扩张,合作侧重在军事安全与政治中立。冷战结束后东南亚各国政经情势趋稳,并接纳越南社会主义共和国和老挝人民民主共和国加入。
東南アジア諸国連合(とうなんアジアしょこく れんごう、英語: Association of South‐East Asian Nations、ASEAN [ˈɑːsi.ɑːn] AH-see-ahn)は、東南アジア10か国の経済、社会、政治、安全保障、文化に関する地域協力機構。本部所在地はインドネシアの首都ジャカルタ。
The Association of Southeast Asian Nations[9] (ASEAN; /ˈɑːsiɑːn/ AH-see-ahn,[10] /ˈɑːziɑːn/ AH-zee-ahn)[11][12] is a regional intergovernmental organization comprising ten countries in Southeast Asia, which promotes intergovernmental cooperation and facilitates economic, political, security, military, educational, and sociocultural integration among its members and other countries in Asia.
ASEAN also regularly engages other countries in the Asia-Pacific region and beyond. A major partner of Shanghai Cooperation Organisation, ASEAN maintains a global network of alliances and dialogue partners and is considered by many as a global powerhouse,[13][14] the central union for cooperation in Asia-Pacific, and a prominent and influential organization. It is involved in numerous international affairs, and hosts diplomatic missions throughout the world.[15][16][17][18]
L’Association des nations de l'Asie du Sud-Est (ANASE ou ASEANa) est une organisation politique, économique et culturelle regroupant dix pays d'Asie du Sud-Est. Elle a été fondée en 1967 à Bangkok (Thaïlande) par cinq pays dans le contexte de la guerre froide pour faire barrage aux mouvements communistes, développer la croissance et le développement et assurer la stabilité dans la région. Aujourd'hui, l'association a pour but de renforcer la coopération et l'assistance mutuelle entre ses membres, d'offrir un espace pour régler les problèmes régionaux et peser en commun dans les négociations internationales. Un sommet est organisé chaque année au mois de novembre. Son secrétariat général est installé à Jakarta (Indonésie).
L'ASEAN (IPA: ˈɑːsiɑːn; in inglese: Association of South-East Asian Nations; in italiano: Associazione delle Nazioni del Sud-est asiatico[6]), è un'organizzazione politica, economica e culturale di nazioni situate nel Sud-est asiatico. È stata fondata nel 1967 con lo scopo principale di promuovere la cooperazione e l'assistenza reciproca fra gli stati membri per accelerare il progresso economico e aumentare la stabilità della regione. Inoltre, l'organizzazione coinvolge regolarmente altri paesi nella regione Asia-Pacifico e oltre. L'ASEAN mantiene una rete globale di alleanze e partner di dialogo ed è considerata da alcuni come una potenza globale e un'organizzazione di spicco e influente.[7][8] È coinvolta in numerosi affari internazionali e ospita missioni diplomatiche in tutto il mondo.[9][10][11][12] È uno dei principali partner dell'Organizzazione per la Cooperazione di Shanghai, con il quale sviluppa un modello di cooperazione per la pace, la stabilità, lo sviluppo e la sostenibilità dell'Asia.[13][14][15][16] Serve anche come modello di riferimento internazionale nella ricerca di armonia e forza tra diversità e differenze, nonché una figura di spicco nell'economia globale, commercio, diplomazia e politica.[17][18][19][20][21][22][23]
La Asociación de Naciones del Sureste Asiático (ASEAN por sus siglas en inglés: Association of Southeast Asian Nations) es una organización intergubernamental de estados del sudeste asiático creada el 8 de agosto de 1967 por cinco países: Tailandia, Indonesia, Malasia, Singapur y Filipinas. En la actualidad está integrada por 10 países de la región del sudeste asiático: Malasia, Indonesia, Brunéi, Vietnam, Camboya, Laos, Myanmar, Singapur, Tailandia y Filipinas.
De acuerdo con el diario digital Expansión (Datos Macro), la habitan unos 646 millones de personas y su PIB anual es de 2,45 billones de euros,2 aunque otras fuentes apuntan a un PIB de 5,7 billones de dólares.3
Los principales objetivos de la ASEAN son: acelerar el crecimiento económico y fomentar la paz y la estabilidad regional. La ASEAN ha establecido un foro conjunto con Japón, sostiene un acuerdo de cooperación con la Unión Europea (UE), y ha iniciado conversaciones para la cooperación comercial oficial con Unión Económica Euroasiática (UEE).4 Su sede principal se encuentra en Yakarta.
Ассоциация государств Юго-Восточной Азии (АSEАN) (англ. Association of South East Asian Nations) — политическая, экономическая и культурная региональная межправительственная организация 10 стран, расположенных в Юго-Восточной Азии. АСЕАН образована 8 августа 1967 года в Бангкоке вместе с подписанием «Декларации АСЕАН», более известной как «Бангкокская декларация». Договорное оформление АСЕАН произошло лишь в 1976 году в подписанных на острове Бали Договоре о дружбе и сотрудничестве в Юго-Восточной Азии и Декларации согласия АСЕАН.
 Brunei Darussalam
Brunei Darussalam
 Demokratische Republik Timor-Leste
Demokratische Republik Timor-Leste
 Indonesia
Indonesia
 Cambodia
Cambodia
 Laos
Laos
 Malaysia
Malaysia
 Myanmar
Myanmar
 Philippines
Philippines
 Singapore
Singapore
 Thailand
Thailand
 Vietnam
Vietnam


 Egypt
Egypt
 Australia
Australia
 Belgium
Belgium
 Brazil
Brazil
 China
China
 Denmark
Denmark
 Germany
Germany
 Finland
Finland
 France
France
 Greece
Greece

 Hand in Hand
Hand in Hand

 Hand in Hand
Hand in Hand
 Driver's license
Driver's license
 India
India
 Indonesia
Indonesia
 Italy
Italy
 Japan
Japan
 Canada
Canada
 Kasachstan
Kasachstan
 Croatia
Croatia
 Malaysia
Malaysia

 Mongolei
Mongolei
 New Zealand
New Zealand
 Netherlands
Netherlands
 Useful info
Useful info
 Austria
Austria
 Portugal
Portugal
 Republic of Korea
Republic of Korea
 Russia
Russia
 Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia
 Sweden
Sweden
 Switzerland
Switzerland
 Singapore
Singapore
 Spain
Spain
 South Africa
South Africa
 Thailand
Thailand
 Czech Republic
Czech Republic
 Turkey
Turkey
 Hungary
Hungary

 Vacation and Travel
Vacation and Travel
 United Arab Emirates
United Arab Emirates
 United States
United States
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
国际驾驶执照(International Driving Permit)依照1949年日内瓦国际道路交通公约及1968年维也纳国际道路交通公约,由公约签署国政府签发,方便本国驾驶员在其他签约国驾驶私人车辆。国际驾驶执照为附加在一国驾驶执照之上的一本附加多国语言的说明,标注了驾驶人的基本信息以及允许驾驶的对应车辆种类等,解决驾驶员与其他国家的交通管理部门之间的沟通障碍。国际驾照不能独立存在,当驾驶员同时持有一国驾照与该国政府签发的国际驾照时,此国际驾照才视作有效。[1]
国际驾驶执照之内容及格式依照维也纳道路交通会议制订,但并非各国均批准该公约。
Ein Internationaler Führerschein ist ein Dokument, das von den Straßenverkehrsbehörden oder Automobilclubs[1] eines Landes aufgrund zwischenstaatlicher Verträge ausgestellt wird. Er soll vor allem der Polizei eines anderen Landes die Feststellung ermöglichen, ob ein ausländischer Kraftfahrer die Fahrerlaubnis hat, die für sein aktuelles Fahrzeug erforderlich ist.
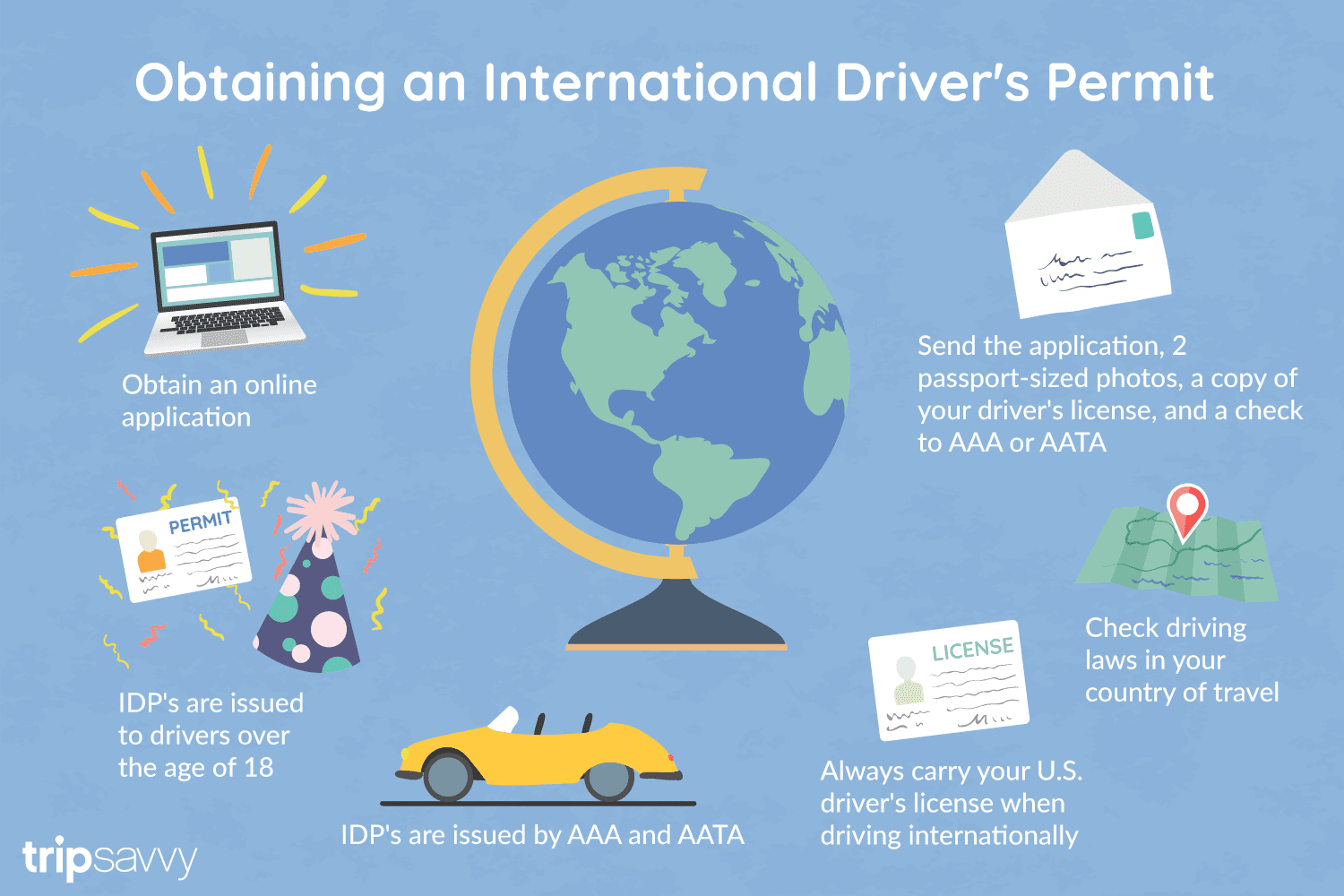
An International Driver's Permit (IDP) allows you to drive a vehicle in another country, as long as you also have a valid driver's license issued by your state. It is also recognized as a proper form of identification in over 175 countries and by many major car rental companies internationally.
Getting an International Driver's Permit (sometimes incorrectly called an international driver's license) can take anywhere from a day to a few weeks, depending on whether you're going through walk-in processing or applying via mail, so make sure to plan ahead if you're planning to drive on your international trip. There are only two locations in the United States that issue these documents: The American Automobile Association (AAA) and the American Automobile Touring Alliance (AATA).
In the United States, International Driver Permits (IDPs) are only issued by the American Automobile Association and the American Automobile Touring Alliance, and the State Department recommends against purchasing an IDP from other outlets as they are all entirely illegal to buy, carry, or sell.
IDPs can be issued to anyone over 18 who has had a valid driver's license for six months or longer. They typically remain valid for one year or the expiration of your existing state driving license. It's essential to investigate an IDP before your trip and make sure you know the requirements.
Both AAA and AATA are excellent sources for these documents, so once you've selected a provider, go to either the AAA's or NAATA's website, print out the International Driving Permit Application, complete all applicable fields, and submit it.
Once you have the application completed, you can send it in via the mail or visit a local office of an organization like AAA; you'll also need two original passport-sized photos and a signed copy of your valid U.S. driver's license as well as an enclosed check for the fee.
Tips to Getting and Using Your Permit
AAA offices can process IDPs during your visit, but processing generally takes 10 to 15 business days if you send the application in. However, expedited services may be available to get your license within one or two business days for an additional fee.
When applying, you'll need a computer and printer, a completed application, a copy of your valid U.S. driver's license, two passport photos, and a check, money order, or credit card to complete the process. Remember to bring these with you if you're applying in person.
Always make sure to carry your valid United States driver's license when driving internationally, as your IDP is invalid without this accompanying proof of eligibility to drive. IDPs only translate domestically-accepted licenses and do not allow those without government-issued driver's licenses to drive abroad.
You'll also want to make sure to enclose the proper fees (the fee for the IDP, as well as any shipping and handling fees), photos, and photocopies of your license when submitting your application to AAA or AATA as omitting any of these required documents will result in your application being rejected.
You should also check the driving requirements and laws for the countries you will be driving in on your vacation, so you'll know what will be required in the event you get stopped by local authorities. (Quelle:https://www.tripsavvy.com/)

Der Istana Negara („Nationalpalast“), auch Istana Negara Jalan Istana, in Kuala Lumpur war von 1957 bis 2011 die offizielle Residenz des Yang di-Pertuan Agong (Königs) von Malaysia.[1] Sei 2013 beherbergt er das Königliche Museum und ist als Alter Istana Negara bekannt.
国家皇宫(马来语:Istana Negara Lama),原是马来西亚最高元首的宫邸,坐落于赛布特拉路与皇宫路交汇的八打灵山上,占地面积为28英亩(约11.34公顷),在这里可以俯视到巴生河的一角。2011年11月15日,元首宫邸搬迁至位于大使路(马来语:Jalan Duta,现名端古·阿卜杜勒哈利姆路)的新国家王宫,原建筑改建为皇家博物馆(马来语:Muzium Diraja),于2013年2月1日起对公众开放。
 Architecture
Architecture
 Religion
Religion
 Life and Style
Life and Style
 Economy and trade
Economy and trade
 Education and Research
Education and Research
 Sport
Sport
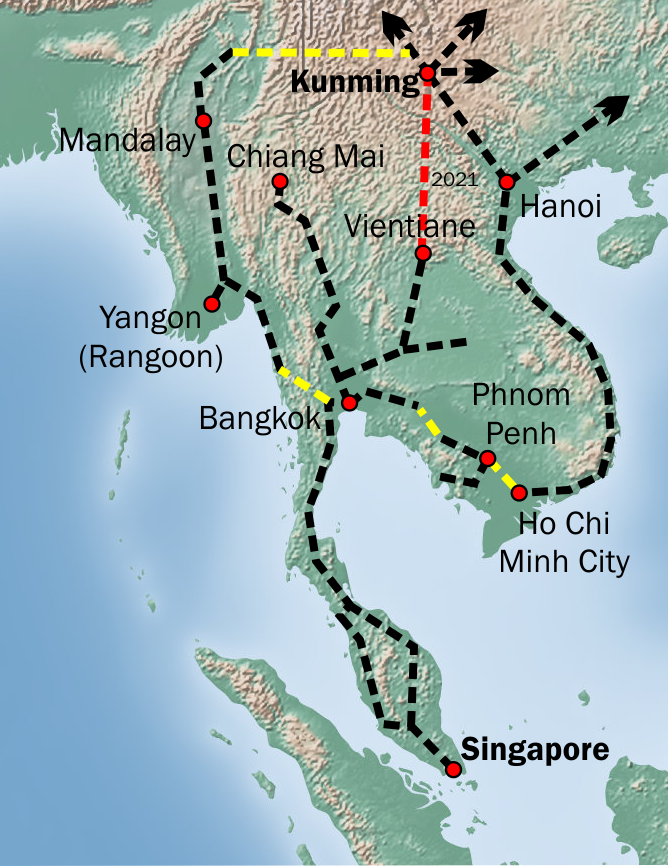
 Transport and traffic
Transport and traffic
 Driving school
Driving school