
漢德百科全書 | 汉德百科全书
 Valle d´Aosta
Valle d´Aosta





 Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes
Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes

 Baden-Wuerttemberg
Baden-Wuerttemberg

 Bavaria
Bavaria
 Germany
Germany
 France
France

 Friuli-Venezia Giulia
Friuli-Venezia Giulia
 Italy
Italy
 Liechtenstein
Liechtenstein

 Lombardia
Lombardia
 Monaco
Monaco
 Austria
Austria

 Piemonte
Piemonte

 Provence-Alpes-Côte d´Azur
Provence-Alpes-Côte d´Azur
 Switzerland
Switzerland
 Slovenia
Slovenia

 Tyrol
Tyrol

 Trentino-Alto Adige
Trentino-Alto Adige

 Valle d´Aosta
Valle d´Aosta
 Veneto
Veneto

 Vorarlberg
Vorarlberg
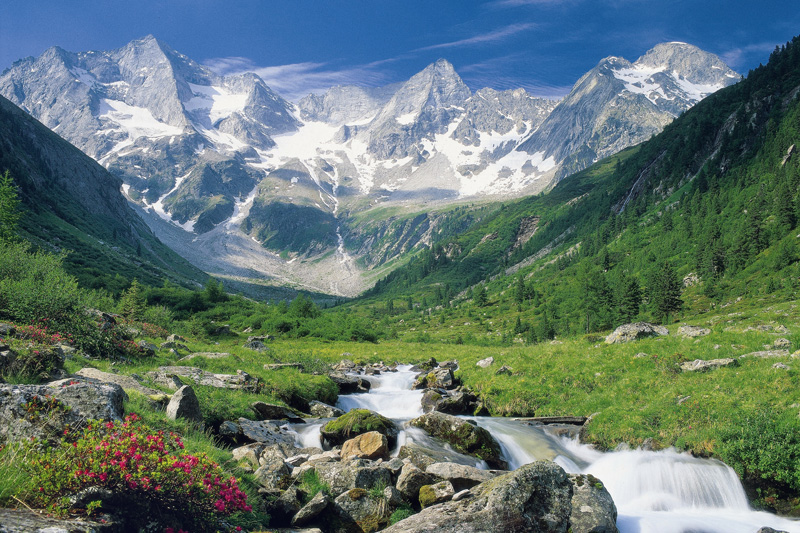

Die Alpen sind das höchste Gebirge im Inneren Europas. Es erstreckt sich in einem 1200 Kilometer langen und zwischen 150 und 250 Kilometer[1] breiten Bogen vom Ligurischen Meer bis zum Pannonischen Becken.
Die gesamte Alpenregion nimmt eine Fläche von etwa 200.000 Quadratkilometern ein.[2] Sie dehnt sich etwa 750 km von West nach Ost und ca. 400 km von Süd nach Nord aus und wird vom Rhonetal, dem Schweizer Mittelland, dem Oberlauf der Donau, der Kleinen Ungarischen Tiefebene, der Po-Ebene und dem Golf von Genua umgrenzt.
Der Alpenbogen schließt im Südwesten am Golf von Genua an den Apennin an, umfasst die Po-Ebene, verzweigt sich zum Französischen und Schweizer Jura und endet fächerförmig im Osten vor dem westpannonischen Berg- und Hügelland. Im Nordosten an der Donau bei Wien sind die Alpen durch das Wiener Becken von den geologisch verwandten Karpaten getrennt, im Südosten gehen sie in das stark verkarstete Dinarische Gebirge über. Im Norden fallen die Alpen allmählich zum österreichischen und deutschen Alpenvorland ab. Im Süden ist der Abfall zur Po-Ebene steiler. Der Gebirgszug, zu dem die Alpen gehören, erstreckt sich vom afrikanischen Atlas bis nach Südostasien.[3]
Die Gipfelhöhen in den westlichen Gebirgsstöcken liegen meist zwischen 3000 und 4300 Meter über dem Meeresspiegel, in den Ostalpen sind die Berge etwas niedriger. Der höchste Gipfel der Alpen ist der Mont Blanc mit 4810 Metern. 128 Berge der Alpen sind Viertausender, etliche Berge mehr oder weniger vergletschert. Die Alpen sind in zahlreiche Gebirgsgruppen und -ketten gegliedert.
Die Alpen bilden im „Herzen Europas“[4] eine wichtige Klima- und Wasserscheide. Sie trennen den zentralen Mittelmeerraum mit dem Etesienklima vom atlantisch beeinflussten nördlichen Mitteleuropa und stehen am Ostrand unter kontinentalem Einfluss. Auch die Entwässerung folgt diesen Großrichtungen zu Mittelmeer, Nordsee und Schwarzem Meer.
Der Alpenraum umfasst Gebiete der acht Alpenstaaten Frankreich, Monaco, Italien, Schweiz, Liechtenstein, Deutschland, Österreich und Slowenien. Er bildet den Lebensraum von 13 Millionen Menschen und genießt europäische Bedeutung als Erholungsraum.[4] Ungarn hat Anteile an Mittelgebirgen, die zu den Alpen gezählt werden, beispielsweise an Günser und Ödenburger Gebirge, wird in der Regel jedoch nicht zum Alpenraum gezählt. Seit der Frühgeschichte stellen Alpentäler und -pässe auch wichtige transeuropäische Verkehrsverbindungen dar.
欧洲南部高大的山脉。西起法国尼斯附近地中海海岸,呈弧形向北、东延伸,经意大利北部、瑞士南部、列支敦士登、德国西南部,东止奥地利的维也纳盆 地。总面积约22万平方千米。长约1200千米,宽130~260千米,东宽西窄。平均海拔3000米左右。 山脉主干向西南方向延伸为比利牛斯山脉,向南延伸为亚平宁山脉,向东南方向延伸为迪纳拉山脉,向东延伸为喀尔巴阡山脉。阿尔卑斯山脉可分为3段。西段西阿 尔卑斯山从地中海岸,经法国东南部和意大利的西北部,到瑞士边境的大圣伯纳德山口附近,为山系最窄部分,也是高峰最集中的山段。勃朗峰(4810米)是整 个山脉的最高点,位于法国和意大利边界。中段中阿尔卑斯山,介于大圣伯纳德山口和博登湖之间,宽度最大。有马特峰(4479米)和蒙特罗莎峰( 4634米)。东段东阿尔卑斯山在博登湖以东,海拔低于西、中两段阿尔卑斯山。
阿尔卑斯山(德语:Alpen;法语:Alpes;意大利语:Alpi;斯洛文尼亚语:Alpe)是一座位于欧洲中心的山脉,它覆盖了意大利北部边界、法国东南部、瑞士、列支敦士登、奥地利、德国南部及斯洛文尼亚。它可以被细分为三个部分,从地中海到勃朗峰的西阿尔卑斯山,从瓦莱达奥斯塔到布伦纳山口(奥地利和意大利交界处)的中阿尔卑斯山,从布伦纳山口到斯洛文尼亚的东阿尔卑斯山。欧洲许多大河都发源于此,水力资源丰富,为旅游、度假、疗养胜地。
阿尔卑斯山共有128座海拔超过4000米的山峰,其中最高峰勃朗峰海拔4810.45米[1],位于法国和意大利的交界处。山脉呈弧形,长1200千米,宽130~260千米,平均海拔约3000米,总面积约22万平方千米[2]。阿尔卑斯山北边是水汽较多的气候,而南边则较为干燥,雨量很少。
アルプス山脈(アルプスさんみゃく、羅: Alpes アルペース、仏: Alpes、伊: Alpi、独: Alpen、英: Alps)は、アルプス・ヒマラヤ造山帯に属し、ヨーロッパ中央部を東西に横切る「山脈」である。オーストリア、スロベニアを東端とし、イタリア、ドイツ、リヒテンシュタイン、スイス各国にまたがり、フランスを南西端とする多国にまたがっている。アルプ(スイスの高山山腹の夏季放牧場;英語: alp,フランス語: alpe,ドイツ語: Alpe)がいっぱいであるからアルプスであると考える説と、ケルト語の alp「岩山」を語源とし、ラテン語を経由したと考える説がある。最高峰のモンブランは標高4,810.9m(2007年)で、フランスとイタリアの国境をなし、ヨーロッパの最高峰[1]でもある。
アルプス山脈はヨーロッパの多数の河川の水源地となっており、ここからドナウ川、ライン川、ローヌ川、ポー川、といった大河川が流れ出て、それぞれ黒海、北海、地中海、アドリア海へと注ぐ。
The Alps (/ælps/; French: Alpes [alp]; German: Alpen [ˈalpn̩]; Italian: Alpi [ˈalpi]; Romansh: Alps; Slovene: Alpe [ˈáːlpɛ]) are the highest and most extensive mountain range system that lies entirely in Europe,[2][note 1] stretching approximately 1,200 kilometres (750 mi) across eight Alpine countries (from west to east): France, Switzerland, Italy, Monaco, Liechtenstein, Austria, Germany, and Slovenia.[3] The mountains were formed over tens of millions of years as the African and Eurasian tectonic plates collided. Extreme shortening caused by the event resulted in marine sedimentary rocks rising by thrusting and folding into high mountain peaks such as Mont Blanc and the Matterhorn. Mont Blanc spans the French–Italian border, and at 4,810 m (15,781 ft) is the highest mountain in the Alps. The Alpine region area contains about a hundred peaks higher than 4,000 metres (13,000 ft).
The altitude and size of the range affects the climate in Europe; in the mountains precipitation levels vary greatly and climatic conditions consist of distinct zones. Wildlife such as ibex live in the higher peaks to elevations of 3,400 m (11,155 ft), and plants such as Edelweiss grow in rocky areas in lower elevations as well as in higher elevations. Evidence of human habitation in the Alps goes back to the Palaeolithic era. A mummified man, determined to be 5,000 years old, was discovered on a glacier at the Austrian–Italian border in 1991.
By the 6th century BC, the Celtic La Tène culture was well established. Hannibal famously crossed the Alps with a herd of elephants, and the Romans had settlements in the region. In 1800, Napoleon crossed one of the mountain passes with an army of 40,000. The 18th and 19th centuries saw an influx of naturalists, writers, and artists, in particular, the Romantics, followed by the golden age of alpinism as mountaineers began to ascend the peaks.
The Alpine region has a strong cultural identity. The traditional culture of farming, cheesemaking, and woodworking still exists in Alpine villages, although the tourist industry began to grow early in the 20th century and expanded greatly after World War II to become the dominant industry by the end of the century. The Winter Olympic Games have been hosted in the Swiss, French, Italian, Austrian and German Alps. At present, the region is home to 14 million people and has 120 million annual visitors.[4]
Les Alpes (prononcé [alp]) sont une chaîne de montagnes qui s'étend en Europe, recouvrant la frontière nord de l'Italie, le Sud-Est de la France, Monaco, la Suisse, le Liechtenstein, l'Autriche, le Sud de l'Allemagne et la Slovénie.
Les Alpes culminent à 4 809 mètres, au sommet du mont Blanc. On recense 82 sommets majeurs de plus de 4 000 m d'altitude (Suisse : 48, Italie : 38, France : 24). Les cols de montagne reliant les vallées ou les pays dépassent souvent les 2 000 m d'altitude. Les Alpes forment une barrière de 1 200 km entre la Méditerranée et le Danube.
Le Alpi sono la catena montuosa più importante d'Europa, situate nell'Europa centrale a cavallo dei confini di Italia, Francia, Svizzera, Liechtenstein, Germania, Austria, Slovenia e Ungheria, separando l'Europa settentrionale da quella meridionale con lo stivale italiano. Suddivise in varie sezioni e svariati sottogruppi racchiudono in sé le vette più alte del continente centrale europeo, rivestendo anche un'importanza storica, naturalistica, idrografica e turistico-economica per i rispettivi paesi.
Los Alpes son una importante cadena de montañas situada en la Europa Central. Su cumbre más alta es el Mont Blanc, con 4.810 metros de altitud. Alrededor de los Alpes, favorecidos por ríos importantes de caudal uniforme y ricas tierras de cultivo, se ubicaron desde la prehistoria diversos pueblos, principalmente celtas, como los borgoñones, leucos, lombardos, helvecios, y posteriormente germánicos en el noreste y pueblos itálicos después de la conquista de la Galia Cisalpina por Julio César. Actualmente viven unos 14 millones de personas en la región de los Alpes.
А́льпы (фр. Alpes, нем. Alpen, итал. Alpi, романш. Alps, словен. Alpe) — самый высокий и протяжённый горный хребет среди систем, целиком лежащих в Европе. При этом Кавказские горы выше, а Уральские — протяжённей, но они лежат также и на территории Азии (в зависимости от выбранного определения границы между Европой и Азией).
Альпы представляют собой сложную систему хребтов и массивов, протянувшуюся выпуклой к северо-западу дугой от Лигурийского моря до Среднедунайской низменности. Альпы располагаются на территории 8 стран: Франции, Монако, Италии, Швейцарии, Германии, Австрии, Лихтенштейна и Словении. Общая длина альпийской дуги составляет около 1200 км (по внутреннему краю дуги — около 750 км), ширина — до 260 км. Самой высокой вершиной Альп является гора Монблан высотой 4810 метров над уровнем моря, расположенная на границе Франции и Италии[1]. Всего в Альпах сосредоточено около 100 вершин-четырёхтысячников[2].
Альпы являются международным центром альпинизма, горнолыжного спорта и туризма. Туризм в Альпах начал активно развиваться в XX веке и получил большой толчок после окончания Второй мировой войны, став одним из главных направлений в конце столетия. Пять стран из восьми (Швейцария, Франция, Италия, Австрия и Германия) были хозяйками Зимних Олимпийских игр, которые проводились в альпийских объектах[3]. Несмотря на активное развитие туризма, в альпийском регионе по-прежнему существует самобытная традиционная культура, включая сельское хозяйство, деревообработку и сыроварение.
Благодаря расположению в центре Западной Европы, Альпы являются одной из наиболее изученных горных систем. Многие понятия названы по имени Альп, в частности, альпийский климатический пояс, период альпийской складчатости, альпийский тип рельефа, альпийские луга, альпинизм.


Aosta (französisch amtlich Aoste, frankoprovenzalisch Aoûta, walserdeutsch Augschtal, deutsch auch Osten) ist die Hauptstadt der Region Aostatal in den italienischen Alpen. Aosta liegt etwa 583 Meter über dem Meeresspiegel und erstreckt sich auf 21 Quadratkilometern. Die Stadt hat 34.361 Einwohner (Stand 31. Dezember 2016).
Der Ort wird vom Monte Emilius überragt.
奥斯塔(意大利语:Aosta;法语:Aoste)是意大利双语政区瓦莱达奥斯塔的主要城市,位于阿尔卑斯山上近白山隧道入口处,距都灵约110千米。
奥斯塔2005年人口约为3万5千。
Aosta (Italian: [aˈɔsta] (![]() listen); French: Aoste [ɔst];[2][3] Arpitan: Aoûta; Latin: Augusta Praetoria Salassorum; Walser: Augschtal; Piemontese: Osta) is the principal city of Aosta Valley, a bilingual region in the Italian Alps, 110 km (68 mi) north-northwest of Turin. It is situated near the Italian entrance of the Mont Blanc Tunnel, at the confluence of the Buthier and the Dora Baltea, and at the junction of the Great and Little St. Bernard routes. Aosta is not the capital of the province, because Aosta Valley is the only Italian region not divided into provinces. Provincial administrative functions are instead shared by the region and the communes.
listen); French: Aoste [ɔst];[2][3] Arpitan: Aoûta; Latin: Augusta Praetoria Salassorum; Walser: Augschtal; Piemontese: Osta) is the principal city of Aosta Valley, a bilingual region in the Italian Alps, 110 km (68 mi) north-northwest of Turin. It is situated near the Italian entrance of the Mont Blanc Tunnel, at the confluence of the Buthier and the Dora Baltea, and at the junction of the Great and Little St. Bernard routes. Aosta is not the capital of the province, because Aosta Valley is the only Italian region not divided into provinces. Provincial administrative functions are instead shared by the region and the communes.
Aoste ([ɔst] dans l'usage local ainsi qu'en Suisse romande et en Savoie, [a'ɔst] par hypercorrection dans l'usage de France, Aosta en italien), appelée Aouste en ancien français, est une ville italienne d'environ 35 000 habitants, chef-lieu de la région autonome et bilingue de la Vallée d'Aoste, au nord-ouest de l'Italie.
Aosta (pronuncia Aòsta, /a'ɔsta/[3]; Aoste in francese[4][5]; Aoûta in arpitano sopradialettale; Oûta, o Veulla in patois valdostano standard, Ohta nella variante della bassa valle[5]; Augschtal in walser[6]; Osta o Aosta in piemontese[7]) è un comune italiano di 33 960 abitanti[1], capoluogo della regione autonoma Valle d'Aosta.
Aosta (en francés, Aoste, en arpitano: Aoûta) es la principal ciudad del Valle de Aosta en los Alpes italianos. Se encuentra en el lado italiano del túnel del Mont Blanc.

 Architecture
Architecture
 Renaissance architecture
Renaissance architecture

 Architecture
Architecture
 Neoclassic architecture *
Neoclassic architecture *

 History
History
 L 1000 - 1500 AD
L 1000 - 1500 AD

 Religion
Religion

 Valle d´Aosta
Valle d´Aosta
 Aosta
Aosta
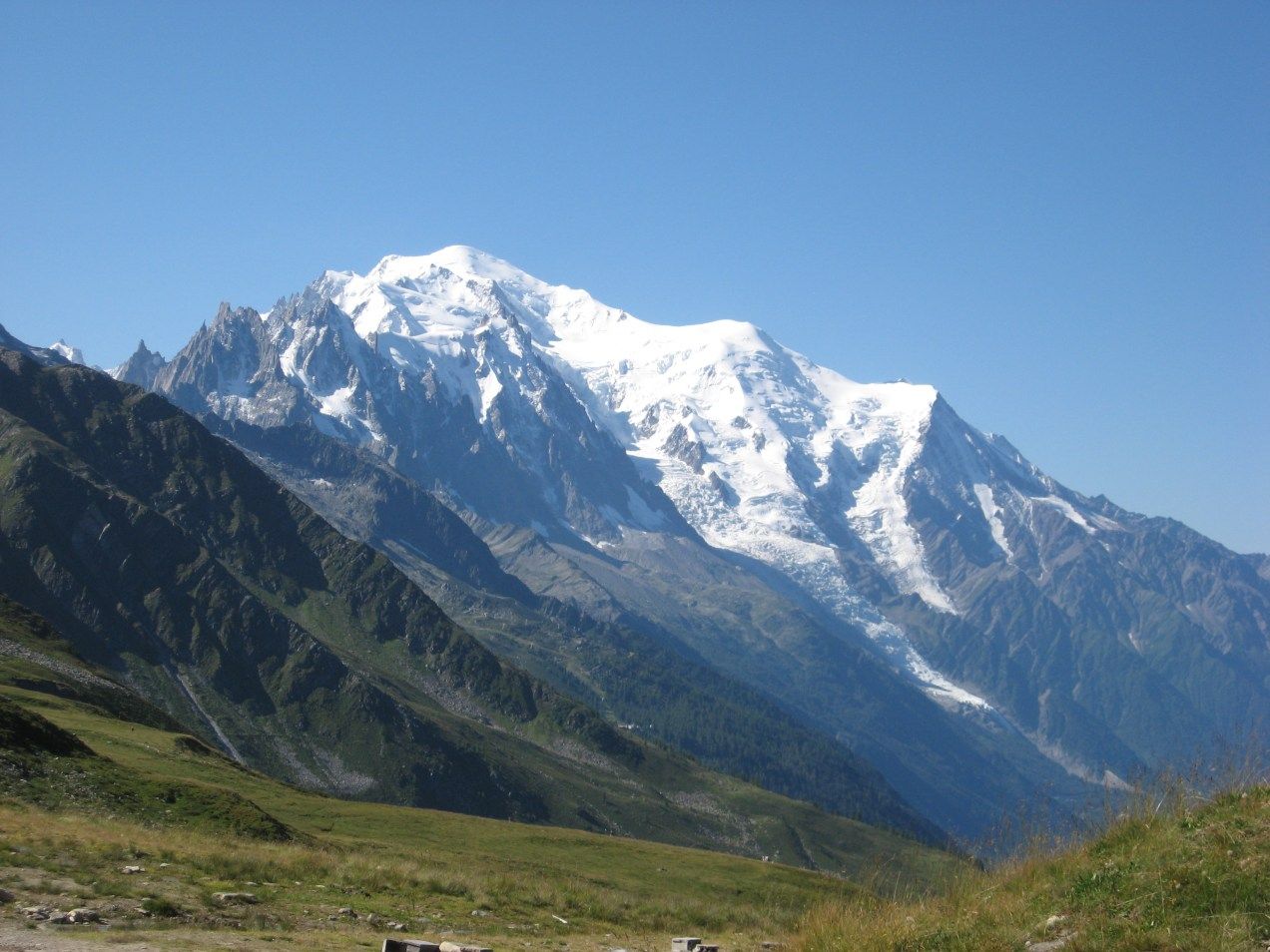



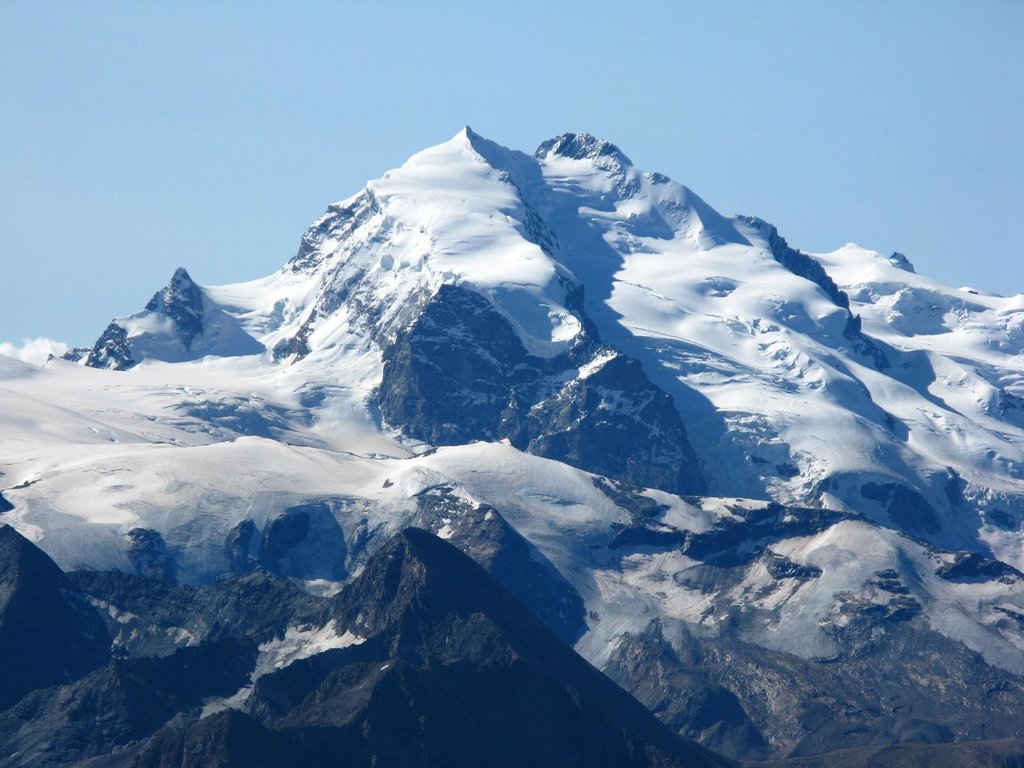
勃朗峰(法语:Mont Blanc,意大利语:Monte Bianco,意为“白色山峰”[1]),是阿尔卑斯山的最高峰,位于法国的上萨瓦省和意大利的瓦莱达奥斯塔大区的交界处。勃朗峰是西欧与欧盟境内的最高峰[2],海拔为4,808.73米[3][4]。勃朗峰于1786年8月8日首次被人类征服。勃朗峰有时也被称为“白色少女”(法语:La Dame blanche)或“白色山峰”(意大利语:Il Bianco)。
勃朗峰附近最有名的两个城镇是意大利瓦莱达奥斯塔大区的库马约尔与法国罗讷-阿尔卑斯大区上萨瓦省的霞慕尼(Chamonix),这里也是第一届冬季奥运会的举办地区。游客可以搭乘缆车上山,路线会经过库尔马耶乌尔与霞慕尼。
白山隧道于1957年开始建造,于1965年完成,连接着法国的霞慕尼及意大利的库马约尔,全长11.6公里,是穿越阿尔卑斯山主要的交通路线。
モンブラン(仏: Mont Blanc 伊: Monte Bianco)は、フランスとイタリアの国境に位置する、ヨーロッパアルプスの最高峰。標高4810.9m。ヨーロッパではロシアのエルブルス山に次ぎ高い山であり、西ヨーロッパでは最高峰である。
Mont Blanc (French: [mɔ̃ blɑ̃]; Italian: Monte Bianco [ˈmonte ˈbjaŋko]; meaning "White Mountain") is the second-highest mountain in Europe after Mount Elbrus. It is the highest mountain in the Alps, rising 4,808 m (15,774 ft) above sea level. It is the eleventh-most prominent peak in the world.[3] The mountain stands in a range called the Graian Alps, between the regions of Aosta Valley, Italy, and Savoie and Haute-Savoie, France. The location of the summit is on the watershed line between the valleys of Ferret and Veny in Italy and the valleys of Montjoie, and Arve in France, on the border between the two countries.
The Mont Blanc massif is popular for outdoor activities like hiking, climbing, trail running and winter sports like skiing, and snowboarding. The most popular route is the Goûter Route, which typically takes two days.
The three towns and their communes which surround Mont Blanc are Courmayeur in Aosta Valley, Italy; and Saint-Gervais-les-Bains and Chamonix in Haute-Savoie, France. The latter town was the site of the first Winter Olympics. A cable car ascends and crosses the mountain range from Courmayeur to Chamonix, through the Col du Géant. The 11.6 km (7 1⁄4-mile) Mont Blanc Tunnel, constructed between 1957 and 1965, runs beneath the mountain and is a major trans-Alpine transport route.
Le mont Blanc (en italien : Monte Bianco), dans le massif du Mont-Blanc, est le point culminant de la chaîne des Alpes. Avec une altitude de 4 809 mètres, il est le plus haut sommet d'Europe occidentale et le sixième sur le plan continental en prenant en compte les montagnes du Caucase, dont l'Elbrouz (5 642 mètres) est le plus haut sommet. Il se situe sur la frontière franco-italienne, entre le département de la Haute-Savoie (en France) et la Vallée d'Aoste (en Italie) ; cette frontière est l'objet d'un litige entre les deux pays.
Le sommet, objet de fascination dans de nombreuses œuvres culturelles, a depuis plusieurs siècles représenté un objectif pour toutes sortes d'aventuriers, depuis sa première ascension en 1786. De nombreux itinéraires fréquentés permettent désormais de le gravir avec une préparation sérieuse. Afin de déterminer son altitude précise et quantifier l'évolution de celle-ci, des géomètres experts font l'ascension périodiquement. La dernière mesure connue (2017) est de 4 808,72 mètres.
Il Monte Bianco (Mont Blanc in francese e in arpitano) è la montagna più alta delle Alpi, d'Italia, di Francia, con i suoi 4.808,72 m di altitudine (ultima misura ufficiale il 13 settembre 2017)[1], e secondo alcune convenzioni, dell'Europa[2][3], da cui il soprannome, a volte usato, di Re delle Alpi[4], condividendo assieme al monte Elbrus nel Caucaso un posto tra le cosiddette Sette Vette del Pianeta.
Posta nel settore delle Alpi Nord-occidentali, lungo la sezione alpina delle Alpi Graie, sulla linea spartiacque tra la Valle d'Aosta (val Veny e val Ferret in Italia) e l'Alta Savoia (valle dell'Arve in Francia), nei territori comunali di Courmayeur[5] e Chamonix, dà il nome all'omonimo massiccio, appartenente alla sottosezione delle Alpi del Monte Bianco. Prevalentemente di natura granitica, irta di guglie e di creste, intagliata da profondi valloni nei quali scorrono numerosi ghiacciai, è considerata una montagna di grande richiamo per l'alpinismo internazionale[6] e, dal punto di vista della storiografia alpinistica, la nascita dell'alpinismo stesso coincide con la data della sua prima ascensione: l'8 agosto 1786[7].
El Mont Blanc o Monte Bianco —orónimo en francés e italiano, respectivamente; traducido al español como ‘Monte Blanco’— es la montaña granítica culminante de los Alpes, con una altitud oficial de 4810 m s. n. m. (metros sobre el nivel del mar) según la última medición de septiembre de 2013.1 Es el punto más elevado de la Unión Europea y uno de los más altos del resto de Europa, superado solo por varias montañas de Rusia y Georgia como el Elbrús (5642 m s. n. m.).3
Rodeado de valles con numerosos glaciares, el Mont Blanc forma parte del macizo homónimo que se extiende entre las demarcaciones del valle de Aosta, en Italia, y de Alta Saboya, en Francia. Las ciudades más pobladas cercanas al Mont Blanc son Chamonix-Mont-Blanc y Saint-Gervais-les-Bains, situadas en Francia, y Courmayeur en Italia.45
La situación de la cima es compartida entre Italia y Francia por un tratado internacional de 1860, aunque desde entonces se mantiene cierta controversia y diferentes fuentes cartográficas atribuyen enteramente la ubicación a uno de los dos países. Así, los mapas del Instituto Geográfico Nacional de Francia incluyen toda la cumbre dentro de las propias fronteras, lo que contrasta con el mapa geográfico del Archivo de Estado de Turín, según el cual la cima es íntegramente italiana.6
Numerosos glaciares se encuentran a su alrededor: al sur los glaciares de Freney, de La Brenva, de Miage, del Mont Blanc y de Brouillard, y al norte, los glaciares de Bossons y de Taconnaz. En 1957 se inició la construcción del túnel de Mont Blanc (se terminó en 1965), que tiene 11,6 km de largo y es una de las mayores rutas de transporte transalpino, ya que une a Italia y Francia.7 El macizo del Mont Blanc es la cuna del alpinismo, cuyas expediciones empezaron hacia el siglo xviii, siendo un destino de referencia en Europa para la práctica del senderismo, el esquí y el snowboarding.
Монбла́н (фр. Mont Blanc, итал. Monte Bianco, букв. «белая гора») — кристаллический массив, высота которого достигает 4810 м (самая высокая точка Европы при условии проведения границы Европы и Азии по северной границе Кавказа). Расположен в Западных Альпах, входящих в горную систему Альпы. Находится на границе Франции и Италии в районах Верхняя Савойя и Курмайор. Высшая точка Альп и Европы, без учёта кавказских пиков. Протяжённость — около 50 км. Площадь оледенения свыше 200 км², крупный ледник Мер-де-Глас. Центр альпинизма, а также горного туризма — вокруг Монблана проходит популярный в Европе пеший туристический маршрут Tour du Mont Blanc.
Под Монбланом проложен автомобильный тоннель длиной в 11,6 км, соединяющий Францию и Италию. Проезд через тоннель платный. Стоимость проезда зависит от стороны въезда, типа транспортного средства и количества поездок.
У западного подножья Монблана, на французской стороне расположен известный горнолыжный курорт Шамони. У южного, на итальянской стороне — Курмайор.



 Sport
Sport
 Eat and Drink
Eat and Drink
 Geography
Geography
 International cities
International cities
 Animal world
Animal world