
漢德百科全書 | 汉德百科全书
 Latvia
Latvia



 Albania
Albania
 Aleksandar Vučić
Aleksandar Vučić
 Alexander De Croo
Alexander De Croo
 Alexander Stubb
Alexander Stubb
 Andorra
Andorra
 Andrej Plenković
Andrej Plenković
 Armenia
Armenia
 Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan
 Belgium
Belgium
 Bjarni Benediktsson
Bjarni Benediktsson
 Bosnia Herzegovina
Bosnia Herzegovina
 Bulgaria
Bulgaria
 Charles Michel
Charles Michel
 Denmark
Denmark
 Denis Bećirović
Denis Bećirović
 Germany
Germany
 Dick Schoof
Dick Schoof
 Donald Tusk
Donald Tusk
 Edi Rama
Edi Rama
 Emmanuel Macron
Emmanuel Macron
 England
England
 Estonia
Estonia

 European Union
European Union
 Evika Siliņa
Evika Siliņa
 Finland
Finland
 France
France
 Georgia
Georgia
 Giorgia Meloni
Giorgia Meloni
 Gitanas Nausėda
Gitanas Nausėda
 Greece
Greece
 Hristijan Mickoski
Hristijan Mickoski
 Ilham Aliyev
Ilham Aliyev
 Ireland
Ireland
 Iceland
Iceland
 Italy
Italy
 Jakov Milatović
Jakov Milatović
 Jens Stoltenberg
Jens Stoltenberg
 Jonas Gahr Støre
Jonas Gahr Støre
 Kaja Kallas
Kaja Kallas
 Keir Starmer
Keir Starmer
 Klaus Johannis
Klaus Johannis
 Kosovo
Kosovo
 Croatia
Croatia
 Kyriakos Mitsotakis
Kyriakos Mitsotakis
 Latvia
Latvia
 Liechtenstein
Liechtenstein
 Lithuania
Lithuania
 Luc Frieden
Luc Frieden
 Luxembourg
Luxembourg
 Maia Sandu
Maia Sandu
 Malta
Malta
 Mette Frederiksen
Mette Frederiksen
 Moldawien
Moldawien
 Monaco
Monaco
 Montenegro
Montenegro
 Netherlands
Netherlands
 Nikol Pashinyan
Nikol Pashinyan
 Nordmazedonien
Nordmazedonien
 Norwegen
Norwegen
 Olaf Scholz
Olaf Scholz
 Austria
Austria

 Party and government
Party and government

 Party and government
Party and government
 European Political Community Summit
European Political Community Summit
 Pedro Sánchez
Pedro Sánchez
 Petr Fiala
Petr Fiala
 Poland
Poland
 Portugal
Portugal
 Robert Abela
Robert Abela
 Robert Golob
Robert Golob
 Romania
Romania
 Rumen Radew
Rumen Radew
 San Marino
San Marino
 Sweden
Sweden
 Switzerland
Switzerland
 Serbia
Serbia
 Simon Harris
Simon Harris
 Slovakia
Slovakia
 Slovenia
Slovenia
 Spain
Spain
 Czech Republic
Czech Republic
 Turkey
Turkey
 Ukraine
Ukraine
 Hungary
Hungary
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 Viktor Orbán
Viktor Orbán
 Viola Amherd
Viola Amherd
 Wolodymyr Selenskyj
Wolodymyr Selenskyj
 Cyprus
Cyprus



 *United States Political System
*United States Political System
 *UK political system
*UK political system
 *French political system
*French political system
 Albania
Albania
 Belgium
Belgium
 Bulgaria
Bulgaria
 Denmark
Denmark
 Germany
Germany
 Estonia
Estonia
 Finland
Finland
 France
France
 Generalsekretäre der Nordatlantikpakt-Organisation
Generalsekretäre der Nordatlantikpakt-Organisation
 Anders Fogh Rasmussen
Anders Fogh Rasmussen
 Generalsekretäre der Nordatlantikpakt-Organisation
Generalsekretäre der Nordatlantikpakt-Organisation
 Dirk Stikker
Dirk Stikker
 Generalsekretäre der Nordatlantikpakt-Organisation
Generalsekretäre der Nordatlantikpakt-Organisation
 George Robertson
George Robertson
 Generalsekretäre der Nordatlantikpakt-Organisation
Generalsekretäre der Nordatlantikpakt-Organisation
 Hastings Ismay, 1. Baron Ismay
Hastings Ismay, 1. Baron Ismay
 Generalsekretäre der Nordatlantikpakt-Organisation
Generalsekretäre der Nordatlantikpakt-Organisation
 Jaap de Hoop Scheffer
Jaap de Hoop Scheffer
 Generalsekretäre der Nordatlantikpakt-Organisation
Generalsekretäre der Nordatlantikpakt-Organisation
 Javier Solana
Javier Solana
 Generalsekretäre der Nordatlantikpakt-Organisation
Generalsekretäre der Nordatlantikpakt-Organisation
 Jens Stoltenberg
Jens Stoltenberg
 Generalsekretäre der Nordatlantikpakt-Organisation
Generalsekretäre der Nordatlantikpakt-Organisation
 Joseph Luns
Joseph Luns
 Generalsekretäre der Nordatlantikpakt-Organisation
Generalsekretäre der Nordatlantikpakt-Organisation
 Manfred Wörner
Manfred Wörner
 Generalsekretäre der Nordatlantikpakt-Organisation
Generalsekretäre der Nordatlantikpakt-Organisation
 Manlio Giovanni Brosio
Manlio Giovanni Brosio
 Generalsekretäre der Nordatlantikpakt-Organisation
Generalsekretäre der Nordatlantikpakt-Organisation
 Paul-Henri Spaak
Paul-Henri Spaak
 Generalsekretäre der Nordatlantikpakt-Organisation
Generalsekretäre der Nordatlantikpakt-Organisation
 Peter Carington, 6. Baron Carrington
Peter Carington, 6. Baron Carrington
 Generalsekretäre der Nordatlantikpakt-Organisation
Generalsekretäre der Nordatlantikpakt-Organisation
 Sergio Balanzino
Sergio Balanzino
 Generalsekretäre der Nordatlantikpakt-Organisation
Generalsekretäre der Nordatlantikpakt-Organisation
 Willy Claes
Willy Claes

 History
History
 Greece
Greece
 Iceland
Iceland
 Italy
Italy
 Canada
Canada
 Croatia
Croatia
 Latvia
Latvia
 Lithuania
Lithuania
 Luxembourg
Luxembourg




 Military, defense and equipment
Military, defense and equipment

 Mitglieder der NATO
Mitglieder der NATO
 Montenegro
Montenegro

 NATO summit
NATO summit
 Netherlands
Netherlands
 Nordmazedonien
Nordmazedonien
 Norwegen
Norwegen
 Poland
Poland
 Portugal
Portugal
 Romania
Romania
 Sweden
Sweden
 Slovakia
Slovakia
 Slovenia
Slovenia
 Spain
Spain
 Czech Republic
Czech Republic
 Turkey
Turkey
 Hungary
Hungary
 United States
United States
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom

 Important International Organizations
Important International Organizations
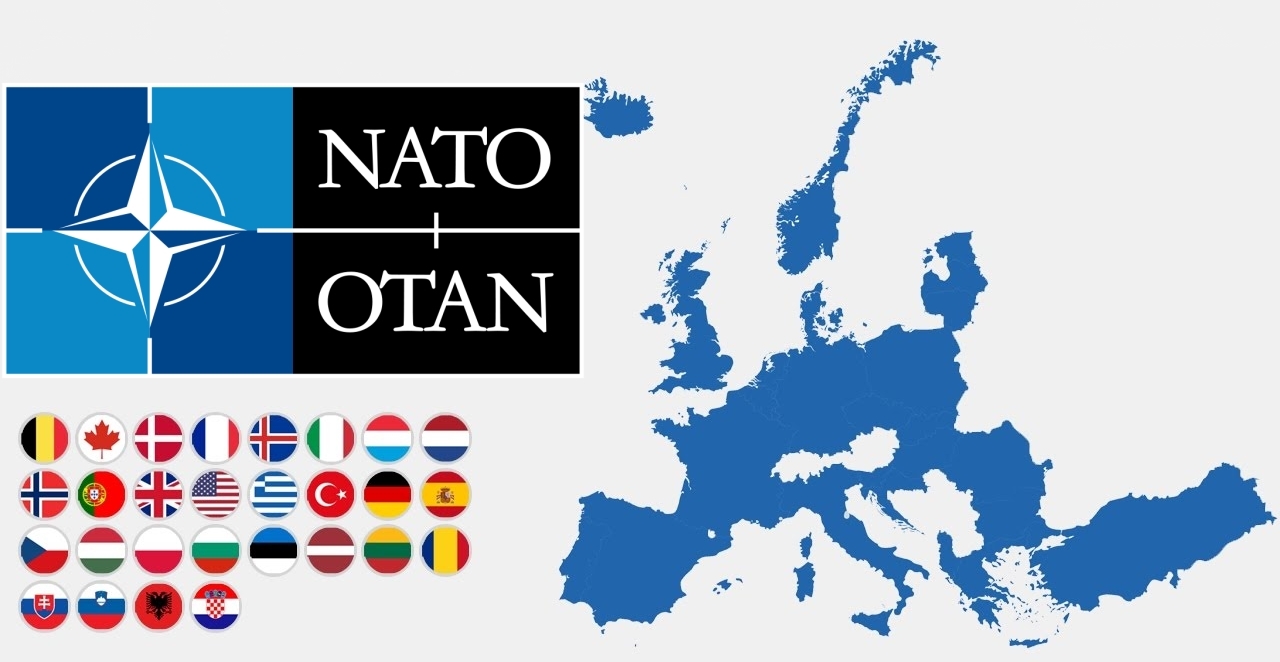
Die NATO (englisch North Atlantic Treaty Organization „Organisation des Nordatlantikvertrags“ bzw. Nordatlantikpakt-Organisation), im Deutschen häufig als Atlantisches Bündnis oder als Nordatlantikpakt bezeichnet (französisch OTAN – Organisation du Traité de l’Atlantique Nord), ist eine Internationale Organisation ohne Hoheitsrechte. Ihre Mitgliedstaaten behalten ihre volle Souveränität und Unabhängigkeit. Basis der NATO ist der Nordatlantikvertrag nach Artikel 51 der UN-Charta. Ihre Organisation versteht sich nicht nur als Verteidigungsbündnis, sondern auch als militärisch-politische Organisation von 29 europäischen und nordamerikanischen Mitgliedstaaten mit dem Ziel eigener Sicherheit und weltweiter Stabilität.
Das NATO-Hauptquartier beherbergt den Nordatlantikrat (das Hauptorgan der NATO) und seine unmittelbar nachgeordneten Einrichtungen, den International Staff (IS) und den International Military Staff (IMS); diese Institution hat seit 1967 ihren Sitz in Brüssel. Nach der Unterzeichnung des Nordatlantikpakts am 4. April 1949 – vorerst auf 20 Jahre – war das Hauptquartier zunächst in London ansässig und anschließend von 16. April 1952 bis 1967 in Paris angesiedelt worden.
Die beiden wichtigsten militärischen Hauptquartiere sind das ACO (aus historischen und juristischen Gründen auch als Supreme Headquarters Allied Powers Europe / SHAPE bezeichnet) im belgischen Casteau bei Mons und das Allied Command Transformation (ACT) in der US-Stadt Norfolk (Virginia).
北大西洋公约组织(英语:North Atlantic Treaty Organization,缩写为NATO;法语:Organisation du Traité de l'Atlantique Nord,缩写为OTAN),简称北约组织或北约,是欧洲及北美洲国家为实现防卫合作而建立的国际组织。1949年3月18日,美国、英国及法国公开建立北大西洋公约组织,于同年4月4日在美国华盛顿签署《北大西洋公约》后正式成立。为与以前苏联为首的东欧集团国成员相抗衡。及至苏联解体,华沙条约组织宣告解散,北约就成为一个地区性防卫协作组织。北约的最高决策机构是北约理事会。理事会由成员国国家元首及政府高层、外长、国防部长组成。总部设在比利时的布鲁塞尔。最新成员黑山于2017年6月5日加入,至此北约总共有跨域欧洲和北美的29个国家组成。北约军事开支占世界国防开支的70%[4],成员国国防开支占该国GDP的2%左右[5]。
公约第5条规定成员国受到的攻击一旦被确认,其他成员国将作出即时反应。该条款被理解为各国部队将自动参战,并不再次需要各国政府的参战授权。但这一条条款在九一一事件之前,一直都未有动用过[6] 。北约曾协助反海盗行动(counter-piracy operations),在联合国要求下打击亚丁湾、非洲之角和印度洋的海盗[7],并在2011年根据联合国安理会1973号决议将利比亚上空设为禁飞区。
北大西洋条約機構(きたたいせいようじょうやくきこう)は、北大西洋条約に基づき、アメリカ合衆国を中心とした北アメリカ(=アメリカとカナダ)およびヨーロッパ諸国によって結成された軍事同盟である。29カ国が加盟し、日本など非加盟国とも協力関係にある[1]。前身はブリュッセル条約 (1948年)。ベルギー首都ブリュッセルに本部を置く[2]。
略称は頭字語が用いられ、英語圏では、North Atlantic Treaty Organization を略した NATO(ネイトー)と呼ばれ、日本やドイツ語圏では NATO(ナトー)、フランス語圏・スペイン語圏・ポルトガル語圏等では OTAN(オタン)と呼ばれる。
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO /ˈneɪtoʊ/; French: Organisation du Traité de l'Atlantique Nord; OTAN), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 29 North American and European countries. The organization implements the North Atlantic Treaty that was signed on 4 April 1949.[3][4] NATO constitutes a system of collective defence whereby its independent member states agree to mutual defence in response to an attack by any external party. NATO’s Headquarters are located in Haren, Brussels, Belgium, while the headquarters of Allied Command Operations is near Mons, Belgium.
Since its founding, the admission of new member states has increased the alliance from the original 12 countries to 29. The most recent member state to be added to NATO is Montenegro on 5 June 2017. NATO currently recognizes Bosnia and Herzegovina, Georgia, Macedonia and Ukraine as aspiring members.[5] An additional 21 countries participate in NATO's Partnership for Peace program, with 15 other countries involved in institutionalized dialogue programs. The combined military spending of all NATO members constitutes over 70% of the global total.[6] Members have committed to reach or maintain defense spending of at least 2% of GDP by 2024.[7][8]
L’Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique norda (en anglais : North Atlantic Treaty Organization) est l'organisation politico-militaire mise en place par les pays signataires du traité de l'Atlantique nord afin de pouvoir remplir leurs obligations de sécurité et de défense collectives. Elle est le plus souvent désignée par son acronyme OTAN (en anglais NATO) mais aussi fréquemment nommée l’Alliance atlantique, plus rarement l’Alliance euro-atlantique ou l’Alliance transatlantique5, ou parfois, encore plus brièvement, simplement l’Alliance.
Le texte de ce traité, signé le 4 avril 1949, établit le Conseil de l'Atlantique nord (CAN), et lui donne mission de mettre en place l'organisation nécessaire à son application. Le choc provoqué par le déclenchement de la guerre de Corée conduit le CAN à décider fin 1950 la création d'une organisation militaire intégrée permanente, qui constitue encore actuellement la marque distinctive de l'OTAN et lui assure des capacités militaires qu'aucune autre alliance de défense ne possède. Sous le vocable OTAN, l'usage a prévalu d'englober l'alliance juridiquement conclue par les pays signataires du traité de l'Atlantique nord, et l'organisation civile et militaire mise en place pour en rendre opérants les objectifs. La France toutefois a fait exception en décidant en 1966, tout en restant membre de l'Alliance atlantique, de quitter l'organisation militaire intégrée, dont elle est redevenue membre à part entière en 2009.
L'Alliance voit le jour dans le contexte général des débuts de la guerre froide et plus spécifiquement pendant le blocus de Berlin exercé par les Soviétiques. Elle a pour vocation initiale d'assurer la sécurité de l'Europe occidentale en instaurant un couplage fort avec les États-Unis, seul moyen aux yeux des Européens après la Seconde Guerre mondiale de se prémunir contre toute tentative expansionniste de l'Union soviétique. Selon le mot de son premier secrétaire général, Lord Ismay, le rôle de l'OTAN consiste à « garder les Russes à l'extérieur, les Américains à l'intérieur et les Allemands sous tutelle »b. L'OTAN constitue le noyau dur du bloc de l'Ouest. Entre 1955 et 1991, l'adversaire désigné de l'OTAN est le pacte de Varsovie formé par les Soviétiques à la suite de l'adhésion de la RFA à l'Alliance atlantique et à son réarmement. L'OTAN s'organise donc pour faire face à cette menace par la définition de concepts stratégiques touchant notamment les questions relatives aux armes nucléaires, par la planification coordonnée entre tous ses membres de leurs moyens militaires, et par des commandements intégrés par zone géographique, dont le SHAPE est de loin le plus important.
Depuis la dissolution de l'URSS et la fin de la guerre froide en 1991, l'Alliance atlantique a perduré malgré la disparition de sa principale raison d'être initiale. Elle a procédé à son élargissement à d'anciens pays du bloc de l'Est et d'anciennes républiques de l'Union soviétique. Elle a pris en compte de nouvelles crises et menaces comme les conflits nationalistes dans l'ex-Yougoslavie, l'essor du terrorisme international ou la prolifération des armes de destruction massive, en conséquence de quoi l'OTAN a revu en profondeur son concept stratégique et son organisation civile et militaire à plusieurs reprises. Elle a développé une politique systématique de partenariats en Europe et dans le monde, au titre de laquelle les pays de l'Alliance ont établi depuis 1994 un partenariat pour la paix (PPP) avec la Russie, les pays de sa zone d'influence et avec les pays neutres d'Europe occidentale. L'OTAN a aussi mis en place en 2002 avec l'UE une relation privilégiée, l'Identité européenne de sécurité et de défense (IESD), qui permet à cette dernière de bénéficier de moyens de l'OTAN pour certaines opérations entrant dans le cadre de sa politique de sécurité et de défense commune.
Le siège de l'OTAN, initialement situé à Londres puis à Paris (dans les locaux désormais occupés par l'université Paris-Dauphine - PSL) se trouve depuis 1966 à Haren (Bruxelles), et son principal commandement militaire, le SHAPE, initialement installé à Rocquencourt (France), se trouve aujourd'hui à Maisières (Mons), également en Belgique.
L'Organizzazione del Trattato dell'Atlantico del Nord (in inglese North Atlantic Treaty Organization, in sigla NATO,[3] in francese: Organisation du Traité de l'Atlantique Nord, in sigla OTAN) è un'organizzazione internazionale per la collaborazione nel settore della difesa.
Il trattato istitutivo della NATO, il Patto Atlantico, fu firmato a Washington il 4 aprile 1949, ovvero nell'immediato secondo dopoguerra, ed entrò in vigore il 24 agosto dello stesso anno. Attualmente, fanno parte della NATO 29 stati del mondo.
La Organización del Tratado del Atlántico Norte u OTAN (en inglés: North Atlantic Treaty Organization o NATO; en francés: Organisation du Traité de l'Atlantique Nord u OTAN), también denominada Alianza del Atlántico, Alianza del Atlántico Norte o Alianza Atlántica, es una alianza militar intergubernamental basada en el Tratado del Atlántico Norte o Tratado de Washington firmado el 4 de abril de 1949. La organización constituye un sistema de defensa colectiva, en la cual los Estados miembros acuerdan defender a cualquiera de sus miembros si son atacados por una potencia externa.3
La sede de la OTAN se encuentra en Bruselas, Bélgica, uno de los veintinueve Estados miembros de la organización que se extiende por Norteamérica y Europa. La última incorporación fue Montenegro, en junio de 2017. Además, veintiún países colaboran con la OTAN dentro del programa Asociación para la Paz, con otros quince involucrados en programas de diálogo y nueve como socios globales. En 2017, el gasto militar combinado de los veintinueve países fue el 52 % del gasto militar mundial.45
En sus primeros años, la OTAN no era mucho más que una asociación política. Sin embargo, la guerra de Corea hizo que se planteara una coalición permanente. Entonces se creó una estructura militar bajo la dirección de los comandantes de Estados Unidos. La Guerra Fría llevó a las naciones rivales a crear el Pacto de Varsovia en 1955.
Siempre se han manifestado dudas sobre la alianza europeo-norteamericana ante una invasión soviética, desacuerdos que se plasmaron con la creación por parte de Francia de la fuerza de choque nuclear y con su retirada de la estructura militar de la alianza entre 1966 y 2009.
Después de la caída del Muro de Berlín en 1989, la organización intervino dentro de la guerra de Yugoslavia, lo que se convirtió en la primera intervención conjunta de la OTAN. En lo político la organización ha mejorado sus relaciones con los antiguos miembros del bloque del Este, dando como resultado la incorporación a la OTAN de varios miembros del Pacto de Varsovia.
La única ocasión en que un país miembro invocó el artículo 5 del tratado reivindicando la ayuda en su defensa, fue Estados Unidos en 2001.6 Desde entonces, los miembros colaboraron con los Estados Unidos en la guerra de Afganistán. El artículo 4 del tratado prevé llamar a consulta a los miembros y ha sido convocado cuatro veces, tres de ellas por Turquía, la primera por la guerra de Irak y las dos restantes por ataques recibidos durante la guerra civil siria,7 la cuarta ha sido invocada por Polonia durante la crisis de Crimea de 2014, debido a la movilización de tropas rusas en la frontera polaca con Kaliningrado y las maniobras rusas en el mar Báltico.
НА́ТО, Организа́ция Североатланти́ческого догово́ра, Североатлантический Альянс (англ. North Atlantic Treaty Organization, NATO; фр. Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique Nord, OTAN) — военно-политический блок, объединяющий большинство стран Европы, США и Канаду. Основан 4 апреля 1949 года в США, с целью защиты Европы от советского влияния[~ 1][~ 2][~ 3][~ 4][~ 5]. Тогда государствами — членами НАТО стали 12 стран: США, Канада, Исландия, Великобритания, Франция, Бельгия, Нидерланды, Люксембург, Норвегия, Дания, Италия и Португалия. Это «трансатлантический форум» для проведения странами-союзниками консультаций по любым вопросам, затрагивающим жизненно важные интересы его членов, включая события, способные поставить под угрозу их безопасность. Одной из декларированных целей НАТО является обеспечение сдерживания любой формы агрессии в отношении территории любого государства — члена НАТО или защиты от неё.
В настоящее время членами НАТО являются 29 стран. Военные расходы всех членов НАТО в совокупности составляют более 70 процентов от общемирового объёма[1].

Die Nordic Investment Bank (NIB) ist ein internationales Finanzinstitut, das 1975 von den fünf nordischen Staaten (Dänemark, Finnland, Island, Norwegen und Schweden) gegründet wurde. 2005 wurden auch die drei baltischen Staaten (Estland, Lettland und Litauen) Mitglieder der NIB. Ihr Hauptsitz ist in Helsinki (Finnland).
Die NIB vergibt Kredite und Garantien an private und öffentliche Gesellschaften, Regierungen, Gemeinden und Finanzinstitute. Die wichtigsten Kreditbereiche sind:
- Energie & Wasser
- Infrastruktur, Verkehr & Telekommunikation
- Branchen & Dienstleistungen
- Finanzinstitute & kleine und mittlere Unternehmen
Die NIB hat ein großes Kreditportfolio außerhalb ihrer Mitgliedsländer (einschließlich der Ostseeregion und Barents-Region) für Umweltprojekte. Die NIB nimmt Kredite auf den internationalen Kapitalmärkten auf und vergibt mit dem Geld Kredite. Die Bonität der Anleihen der NIB wurde (Stand Mitte 2021) von den Ratingagenturen Standard & Poor’s und Moody’s mit dem Rating AAA/Aaa eingestuft.
Ziel der NIB ist es, Projekte zu finanzieren, die die Produktivität verbessern und der Umwelt in den nordischen und baltischen Ländern zugutekommen.
北欧投资银行 (英语:Nordic Investment Bank, NIB)是北欧五国成立的一家国际金融机构,总部位于芬兰赫尔辛基。波罗的海三国于2005年加入北欧投资银行。

Der Ostseerat (englisch Council of the Baltic Sea States, CBSS) ist eine am 6. März 1992 in Kopenhagen (Dänemark) gegründete Internationale Organisation mit dem Ziel der wirtschaftlichen, politischen, kulturellen und umweltpolitischen Kooperation der Anrainerstaaten der Ostsee sowie Norwegens und Islands. Als Initiatoren gelten die damaligen Außenminister Deutschlands Hans-Dietrich Genscher und Dänemarks Uffe Ellemann-Jensen. Der Rat unterhält ein internationales Sekretariat in Nyborg, (Dänemark).
波罗的海国家理事会(英语:Council of the Baltic Sea States,缩写:CBSS)是由北欧波罗的海国家政府所组成的合作组织,于苏联解体后成立。理事会特别针对经济发展、能源、教育与文化、公共安全与人类发展,包括人口贩运的五个优先范畴的进行全面的协商。

 Amber Road
Amber Road
 Denmark
Denmark
 Germany
Germany
 Estonia
Estonia
 Finland
Finland
 Latvia
Latvia
 Lithuania
Lithuania

 Mecklenburg-Vorpommern
Mecklenburg-Vorpommern
 Kiel Canal
Kiel Canal
 Poland
Poland
 Russia
Russia

 Schleswig-Holstein
Schleswig-Holstein
 Sweden
Sweden

Die Ostsee (auch Baltisches Meer, von lat. Mare Balticum, oder auch Baltische See genannt) ist ein 412.500 km²[2] großes und bis zu 459 m tiefes Binnenmeer in Europa und gilt als das größte Brackwassermeer der Erde, auch wenn in der westlichen Ostsee (Beltsee) aufgrund des Wasseraustausches mit der Nordsee zumeist ein höherer Salz- und Sauerstoffgehalt beobachtet werden kann. Der Rauminhalt des Meeres beträgt rund 20.000 km³. Im Ostseeraum leben, je nachdem, wie weit man diese Region eingrenzt, zwischen 50 und 85 Millionen Menschen.
波罗的海是中欧和北欧之间的陆间海,海域横贯北纬53度至北纬66度,东经10度至东经30度,介于斯堪的纳维亚半岛的瑞典部分、欧洲大陆和丹麦诸岛之间。
波罗的海由厄勒海峡、大贝尔特海峡和小贝尔特海峡注入卡特加特海峡,而后者则通过斯卡格拉克海峡注入北海,最后进入大西洋;此外它还通过白海运河同白海相连,通过基尔运河同北海相连。
波罗的海在北端与波的尼亚湾相邻,在东北端与芬兰湾相邻,在东端与里加湾相邻。这些海湾同样可以被看作是波罗的海的一部分。
バルト海(バルトかい、Baltic Sea)は、北ヨーロッパに位置する地中海。ヨーロッパ大陸とスカンディナビア半島に囲まれた海域である。ユーラシア大陸に囲まれた海域と説明されることもある[1]。
西岸にスウェーデン、東岸は、北から順にフィンランド、ロシア、エストニア、ラトビア、リトアニア、南岸は、東から西にポーランド、ドイツ、デンマークが位置する。
The Baltic Sea is a marginal sea of the Atlantic Ocean, enclosed by Finland, Sweden, Denmark, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Russia, Poland, Germany and the North and Central European Plain.
The sea stretches from 53°N to 66°N latitude and from 10°E to 30°E longitude. A mediterranean sea of the Atlantic, with limited water exchange between the two bodies, the Baltic Sea drains through the Danish islands into the Kattegat by way of the straits of Øresund, the Great Belt, and the Little Belt. It includes the Gulf of Bothnia, the Bay of Bothnia, the Gulf of Finland, the Gulf of Riga, and the Bay of Gdańsk.
The Baltic Proper is bordered on its northern edge, at the latitude 60°N, by the Åland islands and the Gulf of Bothnia, on its northeastern edge by the Gulf of Finland, on its eastern edge by the Gulf of Riga, and in the west by the Swedish part of the southern Scandinavian Peninsula.
The Baltic Sea is connected by artificial waterways to the White Sea via the White Sea Canal and to the German Bight of the North Sea via the Kiel Canal.
La mer Baltique est une mer intracontinentale et intérieure de 364 800 km2 située dans le Nord de l'Europe et reliée à l'océan Atlantique par la mer du Nord. Elle communique au sud-ouest avec la mer du Nord par le Cattégat et le Skagerrak. Trois golfes principaux intègrent cet espace : le golfe de Botnie au nord, le golfe de Finlande à l'est et le golfe de Riga au sud-est.
Les pays riverains sont :
- la Suède à l'ouest et au nord ;
- la Finlande au nord-est ;
- la Russie (par le golfe de Finlande) et l'Estonie à l'est ;
- la Lettonie au sud-est ;
- la Lituanie, la Russie (à Kaliningrad) et la Pologne au sud;
- l'Allemagne et le Danemark au sud-ouest.
Ces pays riverains, ainsi que la mer proprement dite, font l'objet, depuis 2009, d'une « stratégie de la Commission européenne en faveur du développement de la région de la mer Baltique »1, incluant un effort de dépollution de la Baltique et un système commun de surveillance maritime.
Il mar Baltico è un mare interno dell'oceano Atlantico settentrionale e si trova nell'Europa nord-orientale, circondato dalla Penisola scandinàva (meno correttamente scandìnava)[1], dalla terraferma dell'Europa centrale e orientale e dalle Isole danesi. Sfocia nel Kattegat e nel mare del Nord passando attraverso le isole danesi in tre stretti, l'Øresund, il Piccolo Belt e il Grande Belt.
Sfociano nel mar Baltico cinque grandi fiumi: l'Oder, la Vistola, il Njemen, la Daugava (o Dvina Occidentale) e la Neva. Le coste del Baltico tendono a ghiacciare d'inverno specie in occasione di eventi meteorologici particolarmente freddi.
Viene indicato come "mare dell'Est" in diverse lingue dell'Europa continentale, precisamente in danese (Østersøen), tedesco (Ostsee), finlandese (Itämeri), olandese (Oostzee), norvegese (Østersjøen), e svedese (Östersjön). In estone viene invece chiamato "mare Occidentale" (Läänemeri). Oltre all'italiano, viene chiamato mar Baltico in francese (mer Baltique), inglese (Baltic Sea), polacco (Morze Bałtyckie), russo (Baltijskoe more, Балтийское море), lituano (Baltijos Jūra), lettone (Baltijas Jūra) e greco (Baltiké thálassa, Βαλτική Θάλασσα).
El mar Báltico (del latín: Mare Balticum) es un mar interior de agua salobre del norte de Europa abierto al mar del Norte y, finalmente, al océano Atlántico a través de los estrechos de Kattegat y Skagerrak. Los países que lo rodean son (empezando por la península Escandinava y siguiendo en sentido horario): Suecia, Finlandia, Rusia (óblast de Leningrado y Kaliningrado), Estonia, Letonia, Lituania, Polonia, Alemania y Dinamarca.
Su superficie es de 432 800 km² e incluye dos grandes golfos: el golfo de Finlandia, entre el sur de este país y Estonia, y el golfo de Botnia, entre la costa oriental de Suecia y el occidental de Finlandia. Geológicamente es muy joven: sólo existe desde el VI milenio a.C. Es muy poco profundo (la media es de 57 m; la profundidad máxima es de 459 m al norte de la isla sueca de Gotland), lo que, unida a la poca apertura al océano, hace la renovación de las aguas muy lenta y favorece los problemas de contaminación. Las mareas son de muy pequeña amplitud.
El mar Báltico es también, el mayor depósito de ámbar del mundo y, además, su calidad es de las mejores: de los veinte depósitos del mundo que hay de ámbar, se dice que el del mar báltico sólo es superado por los de México y la República Dominicana, siendo el que más ámbar de conífera produce y el de mejor calidad. De él se extraen de 500 a 800 millones de toneladas de ámbar.
La cuenca que drena al mar Báltico abarca la totalidad de algunos países ribereños como las repúblicas bálticas, Polonia y la región rusa de Kaliningrado. Además, estos ríos nacen en, o atraviesan territorios pertenecientes a otros países que, a pesar de no poseer costas, se comunican al mar por vía fluvial. Tal es el caso de la República Checa, Eslovaquia, Ucrania y Bielorrusia, quienes acaban aportando agua (indirectamente) al mar Báltico.
Балти́йское мо́ре (Варяжское[1], польск. Morze Bałtyckie, нем. Ostsee, н.-нем. Oostsee, швед. Östersjön, дат. Østersøen, фин. Itämeri, эст. Läänemeri, латыш. Baltijas jūra, лит. Baltijos jūra) — внутриматериковое море Евразии, расположенное в Северной Европе (частично омывает также берега Западной и Восточной Европы). Относится к бассейну Атлантического океана.
Крайняя северная точка Балтийского моря находится вблизи Северного полярного круга (65°40' с. ш.), крайняя южная — около города Висмара (53°45' с. ш.).
Крайняя западная точка расположена в районе Фленсбурга (9°10' в. д.), крайняя восточная — в районе Санкт-Петербурга (30°15' в. д.)
Площадь поверхности моря (без островов) — 415 тыс. км². Объём воды — 21,5 тыс. км³. Из-за огромного стока рек вода имеет низкую солёность и потому море является солоноватоводным. Является крупнейшим в мире морем с такой особенностью[2].
Участок континентальной коры, на котором лежит современное Балтийское море, является частью устойчивой Русской тектонической плиты (Фенносарматия). Как единый массив он сложился около 1,8 миллиарда лет назад и с тех пор пребывал в относительной стабильности. Бо́льшая часть территории, соответствующей дну современной Балтики, бо́льшую часть времени находилась выше уровня моря, хотя южная и восточная части этого пространства продолжительное время были покрыты мелководными шельфовыми морями, о чём свидетельствует мощный слой донных осадков в этих областях. Балтийский кратон образовался в южном полушарии, дрейфовал на запад, находясь в эдиакарии в районе Южного Полярного круга, а далее на север, пересёк экватор около 375 млн л. н., и около 30 миллионов лет назад уже приблизился к современному положению. В разное время он был составной частью различных материков (Нуна, Нена, Родиния, Протолавразия, Паннотия, Лавруссия, Пангея, Лавразия, Евразия), а некоторое время также отдельным материком Балтикой.
Примерно 40 миллионов лет назад, когда контуры северной, центральной и восточной Европы уже сложились на близких к современным широтах, на месте будущего Балтийского моря возникла долина реки Эридан, протекавшей в юго-западном направлении параллельно Скандинавским горам — то есть приблизительно так же, как будет расположено Балтийское море: исток брала в Лапландии, а сильно ветвистая дельта в районе современных Нидерландов впадала в древнее Северное море, и в области нынешнего Финского залива располагался крупный приток. С наступлением четвертичного оледенения, примерно 700 тыс. л. н. Эридан прекратил существование, поскольку его долина, как и вся северная Европа, скрылась под ледниковым щитом. По берегам Эридана росла тайга. После образования ледника смола хвойных деревьев превратилась в янтарь.
ности и другие параметры Литоринового моря стали близки к современным — начинается около 4 тысяч лет назад. Примерно в это же время возникает и Нева.

Die Osteuropäische Ebene umfasst als sehr weit ausgedehnte Großlandschaft, welche die größte einheitlich gegliederte Landschaftsform Europas darstellt, die Gebiete westlich des Urals in Osteuropa. Früher wurde sie oft auch als Osteuropäisches Flachland oder Osteuropäisches Tiefland bezeichnet.
Sie ist eine der russischen Großlandschaften, gliedert sich aber nach Höhenlage und Geologie in verschiedenste Formationen. Die Tiefländer und Niederungen, die von zahlreichen großen Flüssen durchströmt werden, weisen Höhen zwischen wenigen Metern und etwa 150 m über dem Meeresspiegel auf, während die sie unterbrechenden Höhenzüge und Hügelländer Meereshöhen zwischen 300 und 472 Meter erreichen. Die höchste Erhebung ist der Berg Kamula im Podolischen Hochland.
Geologisch ist vor allem zwischen den großen Tafeln mit „jungen“ (phanerozoischen), flachgeschichteten Sedimentgesteinen und den „alten“ (präkambrischen) Schilden des europäischen Urkontinents mit intensiv verfalteten metamorphen Gesteinen und Granitoiden zu unterscheiden. Unter den Tafelländern ist die Russische Tafel die bei weitem größte. Sie erstreckt sich in etwa über die Hälfte des Osteuropäischen Tieflandes. Ihre Begrenzungen im Süd- und Nordwesten sind der Ukrainische Schild und der Baltische Schild, die als präkambrische Rumpfgebirge eine Art stabilen Rahmen bilden. Im Osten wird das riesige Tafelland vom Ural, einem variszisch gefalteten und im Tertiär erneut angehobenen Gebirge begrenzt.
Die Gesteine des Baltischen und Ukrainischen Schildes setzen sich über hunderte Kilometer im Untergrund der Russischen Tafel fort und bilden ihr Grundgebirge. Die Ebenen und Tafelländer südwestlich des Ukrainischen Schildes bleiben in ihrer Ausdehnung deutlich hinter der Russischen Tafel zurück. Der Übergang zum Nordteil der Kaspischen Senke im Südosten des Osteuropäischen Tieflandes ist durch die sehr markante Höhenstufe der Wolgahöhen gekennzeichnet.
东欧平原位于欧洲东部,范围北起北冰洋,南至黑海、里海之滨;东起乌拉尔山,西至波罗的海,面积近400万平方公里,平均海拔170米。东欧平原大部分在俄罗斯境内,因此又称为俄罗斯平原、欧俄平原。它是欧亚草原,尤其是钦察荒原的延伸。俄罗斯乌拉尔山以西部分、爱沙尼亚、拉脱维亚、立陶宛、白俄罗斯、乌克兰等国都在这片波状平原上。
东欧平原有海拔300-400米的瓦尔代丘陵、中俄罗斯高地、伏尔加河沿岸丘陵等,并有低于洋面的里海低地。自北向南有苔原、森林、森林草原和草原带。里海北岸为半荒漠和沙漠。平原南部地形较平坦。以流水侵蚀作用为主,冲沟、平谷地貌比较发育。平原上有伏尔加河、顿河和第聂伯河等著名大河。
由于地形波浪起伏,面积广大,各地的气候并不相同,动植物分布的差异也很大。从北向南,依次是严寒的苔原带、比较寒冷的森林带、气候适中的森林草原带、最南边的草原带。其中森林带占了平原面积一半以上。
东欧平原上煤、铁、石油、锰等资源丰富,如世界著名的顿巴次煤田、库尔斯克和克里沃罗格铁矿区、尼科波尔锰矿区、第二巴库油田。人口稠密,工农业和水陆交通发达,以莫斯科为中心,分布许多重要工矿区,为俄罗斯心脏地带。
 Belarus
Belarus

 Berlin
Berlin

 Brandenburg
Brandenburg

 Bremen
Bremen
 Denmark
Denmark
 Germany
Germany
 Estonia
Estonia
 Finland
Finland
 France
France

 Hamburg
Hamburg
 Italy
Italy
 Latvia
Latvia
 Lithuania
Lithuania

 Mecklenburg-Vorpommern
Mecklenburg-Vorpommern
 Netherlands
Netherlands

 Lower Saxony
Lower Saxony

 North Rhine-Westphalia
North Rhine-Westphalia
 Poland
Poland
 Russia
Russia

 Saxony
Saxony

 Saxony-Anhalt
Saxony-Anhalt

 Schleswig-Holstein
Schleswig-Holstein
 Sweden
Sweden
 Switzerland
Switzerland
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom

 World Heritage
World Heritage

Die Backsteingotik (englisch Brick Gothic, polnisch Gotyk ceglany) umfasst gotische Bauwerke, die aus oder mit sichtbarem Backstein errichtet wurden. Sie ist vor allem in Norddeutschland, dem Ostseeraum und den Niederlanden[1] verbreitet. Ihr Verbreitungsgebiet erstreckt sich im Westen bis an die Straße von Dover und im Südosten bis nach Galizien. Der auch oft verwendete Begriff Norddeutsche Backsteingotik erfasst daher nur einen Teil der gesamten Backsteingotik. Gotische Backsteinarchitektur in Italien und Südfrankreich wird in der Regel allein den dortigen Regionalstilen zugerechnet.
Die mittelalterliche Verwendung von Backstein als Baustoff setzte nördlich der Alpen im 12. Jahrhundert ein. Die ältesten Bauten gehören deshalb noch der so genannten Backsteinromanik an. Im 16. Jahrhundert ging die Backsteingotik in die Backsteinrenaissance über. Die geografische Verbreitung des Bauens aus Backstein und mit sichtbarem Backstein unterlag vom Beginn des Hochmittelalters bis in die frühe Neuzeit aber durchaus Veränderungen. So gab es in Teilen des Münsterlandes zwischen Pionierbauten der Romanik und dem starken Backsteineinsatz in Renaissance und Barock eine zeitliche Lücke.
Viele von der Backsteingotik geprägte Altstädte und Einzelbauten wurden in die Liste des UNESCO-Welterbes aufgenommen.
一种特别在德国北海和波罗的海海岸常见的哥特式建筑是用烤砖建造起来的建筑结构.这个十二世纪开始使用那红色的烤砖作为建 筑材料的独特建筑风格之所以在北部德国低地如此普及是因为这块地区缺少天然石而且运输也非常困难,由于那片地区和汉萨盟的一 致性,因此它就成为了汉萨同盟的象征.有些历史悠久的建筑也就成了联合国教科文组织世界文化遗产项目之一。
Brick Gothic (German: Backsteingotik, Polish: Gotyk ceglany, Dutch: Baksteengotiek) is a specific style of Gothic architecture common in Northwest and Central Europe especially in the regions in and around the Baltic Sea, which do not have resources of standing rock, but in many places a lot of glacial boulders. The buildings are essentially built using bricks. Buildings classified as Brick Gothic (using a strict definition of the architectural style based on the geographic location) are found in Belgium (and the very north of France), Netherlands, Germany, Poland, Lithuania, Latvia, Estonia, Kaliningrad (former East Prussia), Sweden and Finland.
As the use of baked red brick arrived in Northwestern and Central Europe in the 12th century, the oldest such buildings are classified as the Brick Romanesque. In the 16th century, Brick Gothic was superseded by Brick Renaissance architecture.
Brick Gothic is characterised by the lack of figural architectural sculpture, widespread in other styles of Gothic architecture. Typical for the Baltic Sea region is the creative subdivision and structuring of walls, using built ornaments and the colour contrast between red bricks, glazed bricks and white lime plaster. Nevertheless, these characteristics are neither omnipresent nor exclusive. Many of the old town centres dominated by Brick Gothic, as well as some individual structures, have been listed as UNESCO World Heritage sites.
The real extent and the real variety of this brick architecture has to be distinguished from the view of late 19th and early 20th century, especially the years around the end of World War I, when it was instrumentalized, politically.
Indeed, about a quarter of medieval Gothic brick architecture is standing in the Netherlands, in Flanders and in French Flanders. Some dominant buildings combinations of brick and stone. But the criterion "no stone at all" looks like a trick to exclude them.[according to whom?] The towers of St Mary church in Lübeck, the very top Brick Gothic church of the Baltic Sea region, have corners of granite ashley. And many village churches in northern Germany and Poland have Brick Gothic design, but most of their walls are formed by boulders.
L'architettura gotica dei paesi baltici è una varietà regionale dell'architettura gotica, in particolare del gotico tedesco. Le aree coinvolte in questa forma di architettura medievale si affacciano sul mar Baltico e sul Mare del Nord e, da un punto di vista politico, comprendevano gli stati settentrionali del Sacro Romano Impero, le città della Lega Anseatica, i possedimenti dell'Ordine Teutonico. Il periodo interessato va dal XIII secolo al XV secolo.
Le caratteristiche distintive sono che si tratta di un'architettura prevalentemente in laterizio e di una rielaborazione originale e per certi aspetti molto distante dall'iniziale gotico francese. I paesi europei attuali che hanno testimonianze di questa architettura sono Germania, Polonia, Lituania, Lettonia, Estonia, e nell'area della storica Prussia Orientale, (Oblast di Kaliningrad Russia); alcune testimonianze sono anche presenti in Scandinavia.
Le gothique de brique (allemand : Backsteingotik) est un style d´architecture gothique du Nord de l´Europe, et plus particulièrement du Nord de l'Allemagne et des régions autour de la mer Baltique. Il s'est surtout répandu dans les villes culturellement allemandes de l'ancienne Ligue Hanséatique à partir du XIIIe siècle, puis bien au-delà par influence (Scandinavie, Flandres, toute la Pologne, Allemagne du Sud). Les bâtiments sont essentiellement constitués de briques et le style de la décoration s'est adapté aux possibilités et aux limites de ce matériaux, conférant à cette architecture une identité bien particulière.
Il existe d'autres styles d'architecture gothique en brique en Europe, plus ou moins indépendants, comme en Italie et dans la région Toulousaine en France. Le style gothique baltique ne comprend pas tout le gothique en brique d'Europe.
El gótico báltico (en alemán, Norddeutsche Backsteingotik), forma la parte mayor del gótico de ladrillos (en alemán: Backsteingotik). Es una variante de la arquitectura gótica y neogótica que apareció en la Europa septentrional. Sin la especificación "Baltico" es estendido del estrecho de Calais a la Galicia de los Cárpatos. Con la especificación "Baltico" esta concentrada en el norte de Alemania y las zonas aledañas al mar Báltico. En todas estas regiones mancan recursos naturales para construir edificios de piedra. Se extendió principalmente en las ciudades culturalmente alemanas de la antigua Liga Hanseática desde el siglo XIII, y luego por influencia (Escandinavia, toda Polonia, el sur de Alemania). Los edificios son esencialmente de ladrillo y el estilo de decoración se ha adaptado a las posibilidades y límites de este material, dando a esta arquitectura una identidad muy particular.
Кирпичная, ганзейская или северогерманская готика — разновидность готического стиля архитектуры, распространённая в Северной Германии, Польше, Белоруссии и Прибалтике в XIII—XVI веках. Красный керамический кирпич как строительный материал стал использоваться в Северной Европе в XII веке, поэтому самые древние кирпичные образцы относятся ещё к так называемой «кирпичной романике». В XVI в. кирпичную готику сменил «кирпичный ренессанс».
Для кирпичной готики характерны, с одной стороны, отсутствие скульптурных украшений, которые невозможно выполнить из кирпича, и, с другой стороны, богатство орнаментальных деталей кладки и структуризация плоскостей за счёт чередования красного либо глазурованного кирпича и известковой побелки стен.
Многие города, внешний облик которых украшают готические сооружения из красного кирпича, являются объектами Всемирного культурного наследия ЮНЕСКО.
 Sport
Sport
 Hand in Hand
Hand in Hand
 Architecture
Architecture
 Financial
Financial
 Geography
Geography