
漢德百科全書 | 汉德百科全书
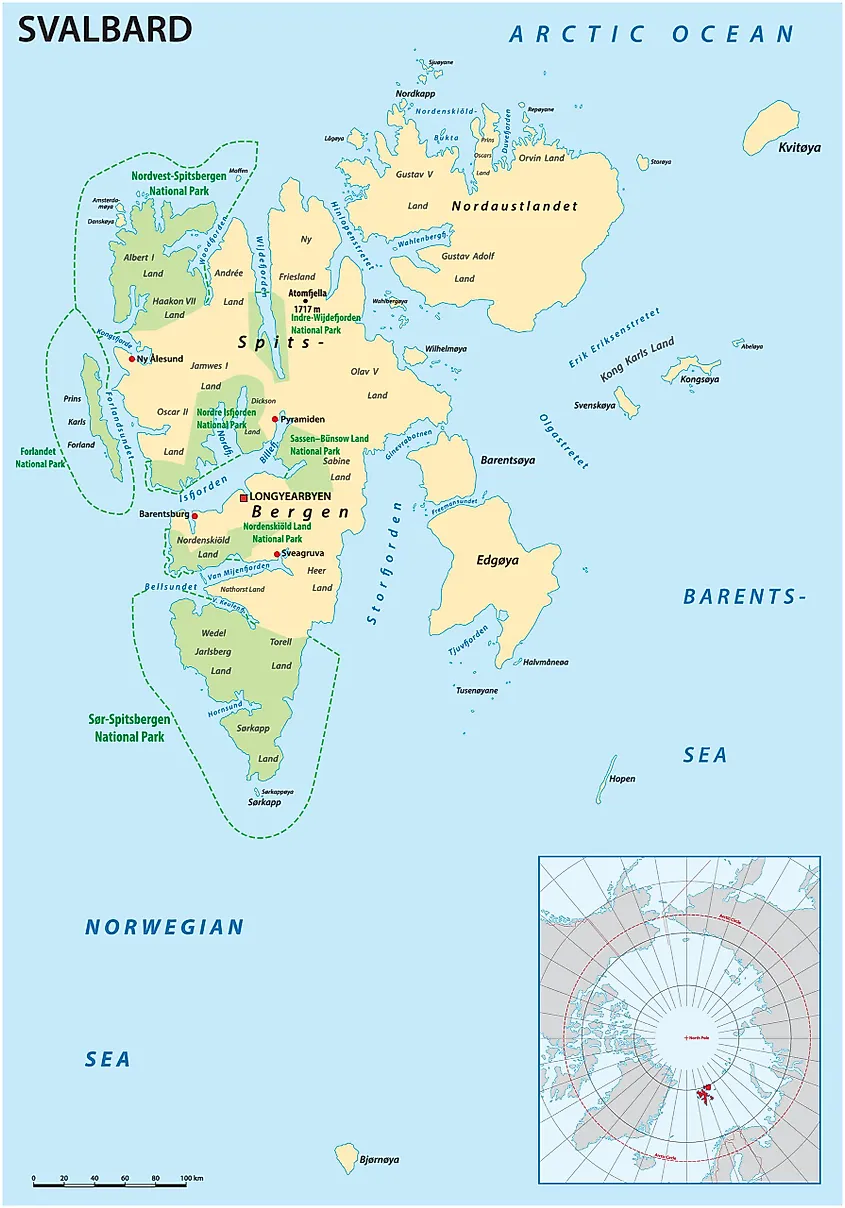
 Norwegen
Norwegen
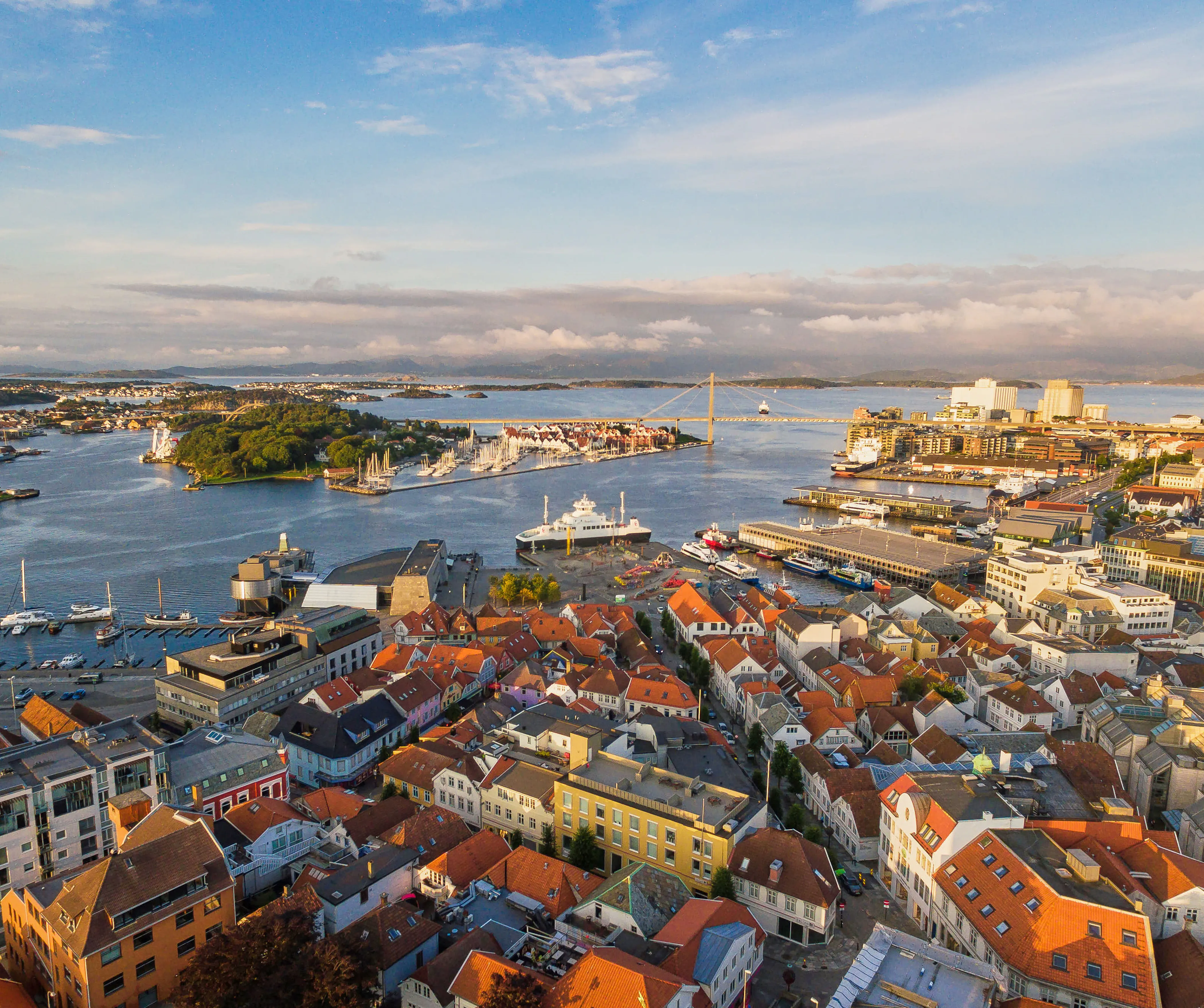



斯塔万格(挪威语:Stavanger,/stəˈvæŋə/,挪威语发音:[stɑˈʋɑŋər] (![]() listen))是挪威的一座自治市,是罗加兰郡行政中心,拥有挪威第三大都会区。[1][2] 人口为挪威第四多。城市位于挪威西南部的斯塔万格半岛,官方宣称的成立时间是1125年,即斯塔万格大教堂成立之年。市中心有大量18及19世纪的木建筑,[3] 这些建筑都被当做城市的文化财产而受到保护,因此也使得市中心显得与众不同。[4] 由于都市化的缘故,与其周边形成了“大斯塔万格”。
listen))是挪威的一座自治市,是罗加兰郡行政中心,拥有挪威第三大都会区。[1][2] 人口为挪威第四多。城市位于挪威西南部的斯塔万格半岛,官方宣称的成立时间是1125年,即斯塔万格大教堂成立之年。市中心有大量18及19世纪的木建筑,[3] 这些建筑都被当做城市的文化财产而受到保护,因此也使得市中心显得与众不同。[4] 由于都市化的缘故,与其周边形成了“大斯塔万格”。
该城市人口的迅速增长要追溯到1900年代挪威石油业的迅速发展,而现在油业也是该市的主要工业,因此城市本身也被当做挪威的“油都”。[5] 北欧最大的石油公司挪威国家石油公司的总部即位于该市。[6] 市内也有一些高等教育机构,譬如斯塔万格大学。
该市还有设置有本国及国际军事设施,其中包括北约的联合作战中心。加上其他的一些大型外国石油公司分公司,导致该城市外国人人口增加。斯塔万格人口中有11%都是移民。[7] 2000年代以来斯塔万格的就业率就高于本国及其他欧洲城市,2011年失业率不到2%。[8] 其生活消费指数也居于世界前列。[9][10][11]
斯塔万格有斯塔万格机场,提供来往大多数主要欧洲国家的航班。[12]
スタヴァンゲル(Stavanger ノルウェー語発音: [stɑˈʋɑŋər] (![]() 音声ファイル))はノルウェーの都市。ローガラン県の県都。人口は約11万2千人(2004年)。スタヴァンガーとも表記する[1]。
音声ファイル))はノルウェーの都市。ローガラン県の県都。人口は約11万2千人(2004年)。スタヴァンガーとも表記する[1]。
Stavanger /stəˈvæŋər/ (Norwegian pronunciation: [stɑˈʋɑŋər] (![]() listen)) is a city and municipality in Norway. It is the third largest city[2] and metropolitan area[3] in Norway (through conurbation with neighbouring Sandnes) and the administrative centre of Rogaland county. The municipality is the fourth most populous in Norway. Located on the Stavanger Peninsula in Southwest Norway, Stavanger counts its official founding year as 1125, the year the Stavanger Cathedral was completed. Stavanger's core is to a large degree 18th- and 19th-century wooden houses[4] that are protected and considered part of the city's cultural heritage. This has caused the town centre and inner city to retain a small-town character with an unusually high ratio of detached houses,[5] and has contributed significantly to spreading the city's population growth to outlying parts of Greater Stavanger.
listen)) is a city and municipality in Norway. It is the third largest city[2] and metropolitan area[3] in Norway (through conurbation with neighbouring Sandnes) and the administrative centre of Rogaland county. The municipality is the fourth most populous in Norway. Located on the Stavanger Peninsula in Southwest Norway, Stavanger counts its official founding year as 1125, the year the Stavanger Cathedral was completed. Stavanger's core is to a large degree 18th- and 19th-century wooden houses[4] that are protected and considered part of the city's cultural heritage. This has caused the town centre and inner city to retain a small-town character with an unusually high ratio of detached houses,[5] and has contributed significantly to spreading the city's population growth to outlying parts of Greater Stavanger.
The city's rapid population growth in the late 20th century was primarily a result of Norway's booming offshore oil industry. Today the oil industry is a key industry in the Stavanger region and the city is widely referred to as the Oil Capital of Norway.[6][not in citation given] The largest company in the Nordic region,[7] Norwegian energy company Statoil is headquartered in Stavanger. Multiple educational institutions for higher education are located in Stavanger. The largest of these is the University of Stavanger.
Domestic and international military installations are located in Stavanger, among these is the North Atlantic Treaty Organisation's Joint Warfare Center. Other international establishments, and especially local branches of foreign oil and gas companies, contribute further to a significant foreign population in the city. Immigrants make up 11.3% of Stavanger's population.[8] Stavanger has since the early 2000s consistently had an unemployment rate significantly lower than the Norwegian and European average. In 2011, the unemployment rate was less than 2%.[9] The city is also among those that frequent various lists of expensive cities in the world, and Stavanger has even been ranked as the world's most expensive city by certain indexes.[10][11][12]
Stavanger is served by international airport Stavanger Airport, Sola, which offers flights to cities in most major European countries, as well as a limited number of intercontinental charter flights. The airport was named most punctual European regional airport by flightstats.com in 2010.[13]
Every two years, Stavanger organizes the Offshore Northern Seas (ONS), which is the second largest exhibition and conference for the energy sector. Gladmat food festival is also held each year and is considered to be one of Scandinavia's leading food festivals. The city is also known for being one of the nation's premier culinary clusters. Stavanger 2008 European Capital of Culture. Stavanger was awarded the 2008 European Capital of Culture alongside Liverpool.
Stavanger (prononcer [staˈvaŋər] écouter) est une ville portuaire située dans le Rogaland, au sud-ouest de la Norvège. Avec 130 745 habitants au 1er janvier 2012, elle est la quatrième ville du pays et le centre de la troisième agglomération norvégienne avec environ 200 000 habitants. Stavanger est la capitale du comté du Rogaland.
Stavanger (IPA: [stɑˈʋɑŋər]) è un comune e una città della Norvegia situata nella contea di Rogaland, della quale è capoluogo amministrativo. L'area metropolitana è la terza più grande area urbana della Norvegia[2], include anche i comuni di Sola, Randaberg e Sandnes raggiungendo così una popolazione complessiva di 241 990 abitanti[1]. Stavanger ha ricevuto lo status di città nel 1125. Stavanger è nota come la capitale del petrolio della Norvegia e d'Europa[3]. È stata capitale europea della cultura nel 2008.
Stavanger (![]() [stɑˈʋɑŋər] (?·i)) es una ciudad portuaria y municipio del sudoeste de Noruega, perteneciente a la provincia de Rogaland, de la que es capital. Es la cuarta ciudad del país por su población con 132 102 habitantes según el censo de 20151 detrás de Oslo, Bergen y Trondheim y es el centro de la tercera aglomeración noruega.2 Es la capital noruega del petróleo. Las actividades tradicionales de Stavanger son el transporte marítimo, la construcción naval y la industria conservera, aunque esta última ha perdido importancia con el paso de los años.
[stɑˈʋɑŋər] (?·i)) es una ciudad portuaria y municipio del sudoeste de Noruega, perteneciente a la provincia de Rogaland, de la que es capital. Es la cuarta ciudad del país por su población con 132 102 habitantes según el censo de 20151 detrás de Oslo, Bergen y Trondheim y es el centro de la tercera aglomeración noruega.2 Es la capital noruega del petróleo. Las actividades tradicionales de Stavanger son el transporte marítimo, la construcción naval y la industria conservera, aunque esta última ha perdido importancia con el paso de los años.
Става́нгер (норв. Stavanger, МФА (норв.): [stɑˈʋɑŋər] ![]() слушать) — город и коммуна в фюльке Ругаланн, Норвегия. Нефтяная столица Норвегии. Расположен на одноименном полуострове на юго-западном побережье Норвегии. Центр третьей по величине агломерации в стране. Климат — мягкий морской, довольно ветреный, средняя температура всех месяцев выше нуля, осадки — 1200 мм в год.
слушать) — город и коммуна в фюльке Ругаланн, Норвегия. Нефтяная столица Норвегии. Расположен на одноименном полуострове на юго-западном побережье Норвегии. Центр третьей по величине агломерации в стране. Климат — мягкий морской, довольно ветреный, средняя температура всех месяцев выше нуля, осадки — 1200 мм в год.
Город сочетает старые и новые черты, испытывая сильное зарубежное влияние из-за расположения поблизости военной базы НАТО под названием JWC, а также интересов зарубежных нефтяных компаний. В Ставангере имеется несколько живописных озёр — популярные зоны отдыха. Озеро Бреиаватнет находится в самом центре города, а озёра Мосватнет и Стоккаватнет — сразу за чертой города.
Аэропорт Ставангера находится в 14 км от центра города, в муниципалитете Сула. В высшей лиге Норвегии играет футбольный клуб Викинг. В городе построен современный футбольный стадион «Viking Stadion», открытый в 2004 году.





 Afghanistan
Afghanistan
 Egypt
Egypt
 Armenia
Armenia
 Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan
 Ethiopia
Ethiopia
 Australia
Australia
 Bangladesh
Bangladesh
 Beijing Shi-BJ
Beijing Shi-BJ
 Brunei Darussalam
Brunei Darussalam
 China
China
 Denmark
Denmark
 Demokratische Republik Timor-Leste
Demokratische Republik Timor-Leste
 Germany
Germany
 Fidschi
Fidschi

 Financial
Financial
 International Bank for Cooperation
International Bank for Cooperation
 Finland
Finland
 France
France
 Georgia
Georgia
 Hongkong Tebiexingzhengqu-HK
Hongkong Tebiexingzhengqu-HK
 India
India
 Indonesia
Indonesia
 Iran
Iran
 Ireland
Ireland
 Iceland
Iceland
 Israel
Israel
 Italy
Italy
 Jordan
Jordan
 Cambodia
Cambodia
 Kasachstan
Kasachstan
 Katar
Katar
 Kyrgyzstan
Kyrgyzstan
 Laos
Laos
 Luxembourg
Luxembourg
 Malaysia
Malaysia
 Malediven
Malediven
 Malta
Malta

 Mongolei
Mongolei
 Myanmar
Myanmar
 Nepal
Nepal
 New Zealand
New Zealand
 Netherlands
Netherlands
 Norwegen
Norwegen
 Oman
Oman
 Austria
Austria
 Pakistan
Pakistan
 Philippines
Philippines
 Poland
Poland
 Portugal
Portugal
 Republic of Korea
Republic of Korea
 Russia
Russia
 Samoa
Samoa
 Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia
 Sweden
Sweden
 Switzerland
Switzerland
 Singapore
Singapore
 Spain
Spain
 Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka
 South Africa
South Africa
 Tajikistan
Tajikistan
 Thailand
Thailand
 Turkey
Turkey
 Hungary
Hungary
 Uzbekistan
Uzbekistan
 United Arab Emirates
United Arab Emirates
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 Vietnam
Vietnam

 Important International Organizations
Important International Organizations

 Economy and trade
Economy and trade
 Economic and political research
Economic and political research
 Cyprus
Cyprus

Anlass zur Initiative der Gründung war insbesondere die Unzufriedenheit Chinas über eine Dominanz der US-Amerikaner im Internationalen Währungsfonds, der keine faire Verteilung der globalen Machtverhältnisse aus Sicht Chinas widerspiegelte.[2] Da sich die US-Amerikaner strikt weigerten, eine Änderung der Stimmverhältnisse zu implementieren, begann China 2013 mit der Gründung der Initiative. Neben den 21 Gründungsmitgliedern haben im Jahr 2015 auch unter anderem Deutschland, Italien, Frankreich und das Vereinigte Königreich ihr Interesse bekundet, als nicht-regionale Mitglieder die neue Entwicklungsbank zu unterstützen.[3]
Die Gründungsurkunde der AIIB wurde am 29. Juni 2015 von Vertretern aus 57 Ländern in Peking unterzeichnet.[4] Die Bank nahm im Januar 2016 ihre Arbeit ohne Beteiligung der USA und Japan auf.[5]
Joachim von Amsberg ist der "Vizepräsident für Politik und Strategie".
亚洲基础设施投资银行(英语:Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank,縮寫:AIIB),简称亚投行,是一个愿意向亚洲国家和地區的基础设施建设提供资金支持的政府间性质的亚洲区域多边开发机构,成立的目的是促进亚洲区域的互联互通建设和经济一体化的进程,並且加大中國與其他亚洲國家和地区的合作力度。总部设在中国北京,法定资本为1,000亿美元。[2]
中华人民共和国主席习近平于2013年10月2日在雅加达同印度尼西亚总统苏西洛举行会谈时首次倡议筹建亚投行。[3]2014年10月24日,中国、印度、新加坡等21国在北京正式签署《筹建亚投行备忘录》。[2]2014年11月25日,印度尼西亚签署备忘录,成为亚投行第22个意向创始成员国。[4]
2015年3月12日,英国正式申请作为意向创始成员国加入亚投行,[5]成为正式申请加入亚投行的首个欧洲国家、主要西方国家。[6]随后法国、意大利、德国等西方国家纷纷以意向创始成员国身份申请加入亚投行。[7]接收新意向创始成员国申请截止日期3月31日临近,韩国[8]、俄罗斯[9]、巴西[10]等域内国家和重要新兴经济体也抓紧申请成为亚投行意向创始成员国。
各方商定将于2015年年中完成亚投行章程谈判并签署,年底前完成章程生效程序,正式成立亚投行。[11]
アジアインフラ投資銀行(アジアインフラとうしぎんこう、英: Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank, AIIB、中: 亚洲基础设施投资银行,亞洲基礎設施投資銀行)は、国際開発金融機関のひとつである。
中華人民共和国が2013年秋に提唱し主導する形で発足した[1]。「合計の出資比率が50%以上となる10以上の国が国内手続きを終える」としていた設立協定が発効条件を満たし、2015年12月25日に発足し[2][3]、2016年1月16日に開業式典を行った[1][4]。
57か国を創設メンバーとして発足し[1][5]、2017年3月23日に加盟国は70カ国・地域となってアジア開発銀行の67カ国・地域を超え[6][7]、一方で日本、アメリカ合衆国などは2017年の現時点で参加を見送っている[8]。 創設時の資本金は1000億ドルである[9]。
The Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank (AIIB) is a multilateral development bank that aims to support the building of infrastructure in the Asia-Pacific region. The bank currently has 93 members from around the world [7]. The bank started operation after the agreement entered into force on 25 December 2015, after ratifications were received from 10 member states holding a total number of 50% of the initial subscriptions of the Authorized Capital Stock.[8]
The United Nations has addressed the launch of AIIB as having potential for "scaling up financing for sustainable development"[9] and to improve the global economic governance.[10] The starting capital of the bank was $100 billion, equivalent to 2⁄3 of the capital of the Asian Development Bank and about half that of the World Bank.[11]
The bank was proposed by China in 2013[12] and the initiative was launched at a ceremony in Beijing in October 2014.[13] It received the highest credit ratings from the three biggest rating agencies in the world, and is seen as a potential rival to the World Bank and IMF.[14][15]
La Banque asiatique d'investissement dans les infrastructures (BAII ou AIIB), est une banque d'investissement proposée par la République populaire de Chine dans le but de concurrencer le Fonds monétaire international, la Banque mondiale et la Banque asiatique de développement1 pour répondre au besoin croissant d'infrastructures en Asie du Sud-Est et en Asie centrale. Cette banque s'inscrit dans la stratégie de la nouvelle route de la soie, développée par la Chine.
La Banca Asiatica d'Investimento per le infrastrutture (AIIB), fondata a Pechino nell'ottobre 2014, è un'istituzione finanziaria internazionale proposta dalla Repubblica Popolare Cinese. Si contrappone al Fondo Monetario Internazionale, alla Banca Mondiale e all'Asian Development Bank[1], le quali si trovano sotto il controllo del capitale e delle scelte strategiche dei paesi sviluppati come gli Stati Uniti d'America.[2] Scopo della Banca è fornire e sviluppare progetti di infrastrutture nella regione Asia-Pacifico attraverso la promozione dello sviluppo economico-sociale della regione e contribuendo alla crescita mondiale.
El Banco Asiático de Inversión en Infraestructura (Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank o AIIB) es una institución financiera internacional propuesta por el gobierno de China. El propósito de este banco de desarrollo multilateral es proporcionar la financiación para proyectos de infraestructura en la región de Asia basado en un sistema financiero de préstamo1 y el fomento del sistema de libre mercado en los países asiáticos.
El AIIB está considerado por algunos como una versión continental del FMI y del Banco Mundial, y busca ser un rival por la influencia en la región del Banco de Desarrollo asiático (ADB), el cual esta alineado a los intereses de potencias, tanto regionales (Japón), como globales (Estados Unidos, la Unión Europea).2
El banco fue propuesto por Xi Jinping en 2013 e inaugurado con una ceremonia en Pekín en octubre de 2014. La ONU se a mostrado entusiasta con la propuesta china, a la que a descrito como el FMI del futuro y a señalado como "una gran propuesta para financiar el desarrollo sostenible" y "mejorar la gobernanza económica mundial". La entidad constó inicialmente con 100 mil millones de dolares, es decir, la mitad del dinero de que posee el Banco Mundial.
La entidad a recibido inversión por parte de corporaciones financieras estadounidenses como la Standard & Poor's, Moody's o Fitch Group34. Actualmente la entidad consta de 87 miembros, incluyendo los 57 miembros fundadores. Bélgica, Canadá, y Ucrania están barajando unirse al AIIB. Estados Unidos, Japón y Colombia no tienen intención de participar. China a prohibido a Corea del Norte unirse, instigando además una política de aislamiento contra esta por parte del AIIB.
Азиатский банк инфраструктурных инвестиций (АБИИ) (англ. Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank, AIIB) — международная финансовая организация, создание которой было предложено Китаем. Основные цели, которые преследует АБИИ, — стимулирование финансового сотрудничества в Азиатско-Тихоокеанском регионе, финансирование инфраструктурных проектов в Азии от строительства дорог и аэропортов до антенн связи и жилья экономкласса[1].
По заявлениям вице-премьера России Игоря Шувалова, AБИИ не рассматривается как потенциальный конкурент МВФ, Всемирного банка и Азиатского банка развития (АБР). Однако эксперты рассматривают AIIB как потенциального конкурента базирующихся в США Международного валютного фонда (МВФ) и Всемирного банка. После сообщений об успехах AIIB американский министр финансов США Джейкоб Лью предупредил, что международным финансовым организациям в США, таким как ВБ и МВФ, грозит потеря доверия [2][3].
Китай, Индия и Россия возглавили организацию, оказавшись в тройке крупнейших владельцев голосов. При этом на важнейшие решения КНР имеет фактическое право вето[4].

 Belgium
Belgium
 Bulgaria
Bulgaria
 Denmark
Denmark
 Germany
Germany
 Estonia
Estonia
 Finland
Finland
 France
France
 Greece
Greece
 Ireland
Ireland
 Iceland
Iceland
 Israel
Israel
 Italy
Italy
 Croatia
Croatia
 Latvia
Latvia
 Lithuania
Lithuania
 Luxembourg
Luxembourg
 Malta
Malta
 Monaco
Monaco
 Montenegro
Montenegro
 Netherlands
Netherlands
 Nordmazedonien
Nordmazedonien
 Norwegen
Norwegen
 Austria
Austria
 Poland
Poland
 Portugal
Portugal
 Romania
Romania
 Russia
Russia
 San Marino
San Marino
 Sweden
Sweden
 Switzerland
Switzerland
 Serbia
Serbia
 Slovakia
Slovakia
 Slovenia
Slovenia
 Spain
Spain
 Czech Republic
Czech Republic
 Turkey
Turkey
 Ukraine
Ukraine
 Hungary
Hungary
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom

 Science and technology
Science and technology
 Cyprus
Cyprus

 International cities
International cities
 Important port
Important port
 Geography
Geography
 History
History
 Architecture
Architecture
 Religion
Religion
 Companies
Companies
 Ships and Nautics
Ships and Nautics
 European Union
European Union