
漢德百科全書 | 汉德百科全书
 South Africa
South Africa
 Egypt
Egypt
 Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan
 Bangladesh
Bangladesh
 Belarus
Belarus
 Chile
Chile
 Columbia
Columbia
 Cuba
Cuba
 Democratic People's Republic of Korea
Democratic People's Republic of Korea

 Hand in Hand
Hand in Hand
 India
India
 Indonesia
Indonesia
 Iraq
Iraq
 Iran
Iran
 Jordan
Jordan
 Cambodia
Cambodia
 Katar
Katar
 Kenya
Kenya
 Kuwait
Kuwait
 Laos
Laos
 Libanon
Libanon
 Malaysia
Malaysia
 Morocco
Morocco

 Mongolei
Mongolei
 Myanmar
Myanmar
 Nepal
Nepal
 Niger
Niger
 Nigeria
Nigeria
 Pakistan
Pakistan
 Palestine
Palestine

 Party and government
Party and government
 Peru
Peru
 Philippines
Philippines
 Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia
 Singapore
Singapore
 Somalia
Somalia
 Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka
 South Africa
South Africa
 Syria
Syria
 Tansania
Tansania
 Thailand
Thailand
 Turkmenistan
Turkmenistan
 Uganda
Uganda
 Uzbekistan
Uzbekistan
 Venezuela
Venezuela
 United Arab Emirates
United Arab Emirates
 Vietnam
Vietnam

 Important International Organizations
Important International Organizations


Afghanistan Ägypten Algerien Angola Antigua und Barbuda Äquatorialguinea Äthiopien Aserbaidschan Bahamas Bahrain Bangladesch Barbados Belarus Belize Benin Bhutan Bolivien Botswana Brunei Burkina Faso Burundi Chile Demokratische Republik Kongo Dominica Dominikanische Republik Dschibuti Ecuador Elfenbeinküste Eritrea Eswatini Fidschi Gabun Gambia Ghana Grenada Guatemala Guinea Guinea-Bissau Guyana Haiti Honduras Indien Indonesien Irak Iran Jamaika Jemen Jordanien Kambodscha Kamerun Kap Verde Katar Kenia Kolumbien Komoren Kuba Kuwait Laos Lesotho Libanon Liberia Libyen Madagaskar Malawi Malaysia Malediven Mali Marokko Mauretanien Mauritius Mongolei Mosambik Myanmar Namibia Nepal Nicaragua Niger Nigeria Nordkorea Oman Osttimor Pakistan Palästina Panama Papua-Neuguinea Peru Philippinen Republik Kongo Ruanda Saint Lucia Sambia São Tomé und Príncipe Saudi-Arabien Senegal Seychellen Sierra Leone Simbabwe Singapur Somalia Sri Lanka St. Kitts und Nevis St. Vincent und die Grenadinen Südafrika Sudan Suriname Syrien Tansania Thailand Togo Trinidad und Tobago Tschad Tunesien Turkmenistan Uganda Usbekistan Vanuatu Venezuela Vereinigte Arabische Emirate Vietnam Zentralafrikanische Republik
Die Bewegung der Blockfreien Staaten (kurz Bewegung der Blockfreien oder Blockfreien-Bewegung, englisch Non-Aligned Movement) ist eine Internationale Organisation von Staaten, deren erklärtes Ziel es war, sich im Ost-West-Konflikt nach dem Zweiten Weltkrieg neutral zu verhalten und keinem der beiden Militärblöcke anzugehören. Die Gründung der Organisation ging auf eine Initiative des jugoslawischen Präsidenten Josip Broz Tito, des ägyptischen Staatschefs Nasser, des indischen Premiers Nehru sowie des indonesischen Präsidenten Sukarno zurück. Die Organisation konstituierte sich 1961 auf ihrer ersten Sitzung in Belgrad.[1] Ihr traten viele ehemalige afrikanische und asiatische Kolonien bei, die sich soeben erst als Staaten konstituiert hatten oder noch um ihre Unabhängigkeit rangen.[2]
Die Organisation verurteilte die Blockbildung in der Zeit des Ost-West-Konfliktes wegen der Gefahr eines Dritten Weltkrieges und setzte sich für die friedliche Koexistenz und Abrüstung ein. Die steigende Zahl der Mitglieder machte es der Organisation jedoch zunehmend schwer, sich auf eine gemeinsame Politik zu einigen. Mit der Auflösung des Warschauer Paktes Anfang der 1990er Jahre verlor sie an Bedeutung. Die heterogene Zusammensetzung der Bewegung machte es schwer, gemeinsame Ziele zu definieren und zu verfolgen.[3] Die Staaten der Blockfreien-Bewegung vertreten 55 Prozent der Weltbevölkerung und halten nahezu zwei Drittel der Sitze in der UN-Generalversammlung.
Das Ziel der Organisation ist die Gleichberechtigung zwischen den Staaten und eine positive wirtschaftliche Entwicklung der Mitgliedstaaten.
不结盟运动(英语:Non-Aligned Movement, NAM)是一个拥有120个成员国和17个观察员国的松散国际组织[3]。它成立于冷战时期,其成员国奉行独立自主的外交政策,不与美苏两个超级大国中的任何一个结盟。联合国中有三分之二的会员是该组织的成员国,全球约55%的人口也生活在不结盟运动国家。不结盟运动定期举行首脑会议,到目前为止已经在前南斯拉夫、埃及、赞比亚、阿尔及利亚、斯里兰卡、古巴、印度、津巴布韦、印尼、哥伦比亚、南非、马来西亚、塞尔维亚、委内瑞拉、阿塞拜疆和乌干达[4]举行会议。


 Egypt
Egypt
 Algeria
Algeria

 Andalusia
Andalusia
 Argentina
Argentina



 Automobile
Automobile
 MINI
MINI



 Automobile
Automobile
 PEUGEOT
PEUGEOT



 Automobile
Automobile
 Volkeswagen
Volkeswagen



 Automobile
Automobile
 Kamaz
Kamaz



 Automobile
Automobile
 IVECO
IVECO



 Automobile
Automobile
 MAN
MAN



 Automobile
Automobile
 Mitsubishi
Mitsubishi



 Automobile
Automobile
 Tatra
Tatra



 Automobile
Automobile
 Hino
Hino



 Automobile
Automobile
 Citroën
Citroën



 Automobile
Automobile
 Porsche
Porsche



 Automobile
Automobile
 DAF
DAF



 Automobile
Automobile
 Mercedes
Mercedes



 Automobile
Automobile
 Renault
Renault



 Automobile
Automobile
 Land Rover
Land Rover

 Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes
Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes
 Bolivia
Bolivia
 Cataluña
Cataluña
 Chile
Chile
 France
France

 Hauts-de-France
Hauts-de-France

 Ile-de-France
Ile-de-France
 Libya
Libya

 Madrid
Madrid
 Niger
Niger
 Portugal
Portugal

 Provence-Alpes-Côte d´Azur
Provence-Alpes-Côte d´Azur
 Senegal
Senegal
 Spain
Spain

 Sport
Sport
 South Africa
South Africa
 Tunisia
Tunisia

Die Rallye Dakar (früherer Name Rallye Paris–Dakar) ist ein Rallye-Raid-Wettbewerb, der als die bedeutendste Langstrecken- und Wüstenrallye der Welt gilt. Sie wurde von 1978 bis 2007 einmal jährlich hauptsächlich auf dem afrikanischen Kontinent ausgetragen. Im Jahr 2008 wurde die Rallye Dakar aufgrund einer Terrordrohung abgesagt. Seit 2009 findet sie aus Sicherheitsgründen auf dem südamerikanischen Kontinent statt.
2016 fand die 38. Auflage vom 2. bis 16. Januar in Argentinien und Bolivien statt. Neben einem Prolog von Buenos Aires nach Rosario wurden 13 Etappen und 9246 km Strecke gefahren, 4792 km flossen in die Wertung ein. Aufgrund des Naturphänomens El Niño verzichtete man auf Strecken in Peru.[1]


 Argentina
Argentina
 Australia
Australia
 Germany
Germany
 France
France
 Italy
Italy
 Croatia
Croatia
 Russia
Russia
 Sweden
Sweden
 Switzerland
Switzerland
 Serbia
Serbia
 Spain
Spain

 Sport
Sport

 Sport
Sport
 Tennis
Tennis
 South Africa
South Africa
 Czech Republic
Czech Republic
 United States
United States
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom

Nationen nach Anzahl der Siege und FinalteilnahmenRangLandSiegeFinal-
| Rang | Land | Siege | Final- niederlagen |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | 32 | 29 | |
| 2. | 28* | 19 | |
| 3. | 10 | 9 | |
| 4. | 10 | 8 | |
| 5. | 7 | 5 | |
| 6. | 6 | 4 | |
| 7. | 3 | 3 | |
| 8. | 3 | 2 | |
| 3** | 2 | ||
| 10. | 2 | 2 | |
| 11. | 1 | 6 | |
| 12. | 1 | 4 | |
| 13. | 1 | 1 | |
| 1 | 1 | ||
| 15. | 1 | 0 | |
| 16. | 0 | 3 | |
| 0 | 3 | ||
| 0 | 3 | ||
| 19. | 0 | 1 | |
| 0 | 1 | ||
| 0 | 1 | ||
| 0 | 1 | ||
| 0 | 1 |
* inkl. vier Siegen als Australasien
** inkl. eines Sieges als Tschechoslowakei

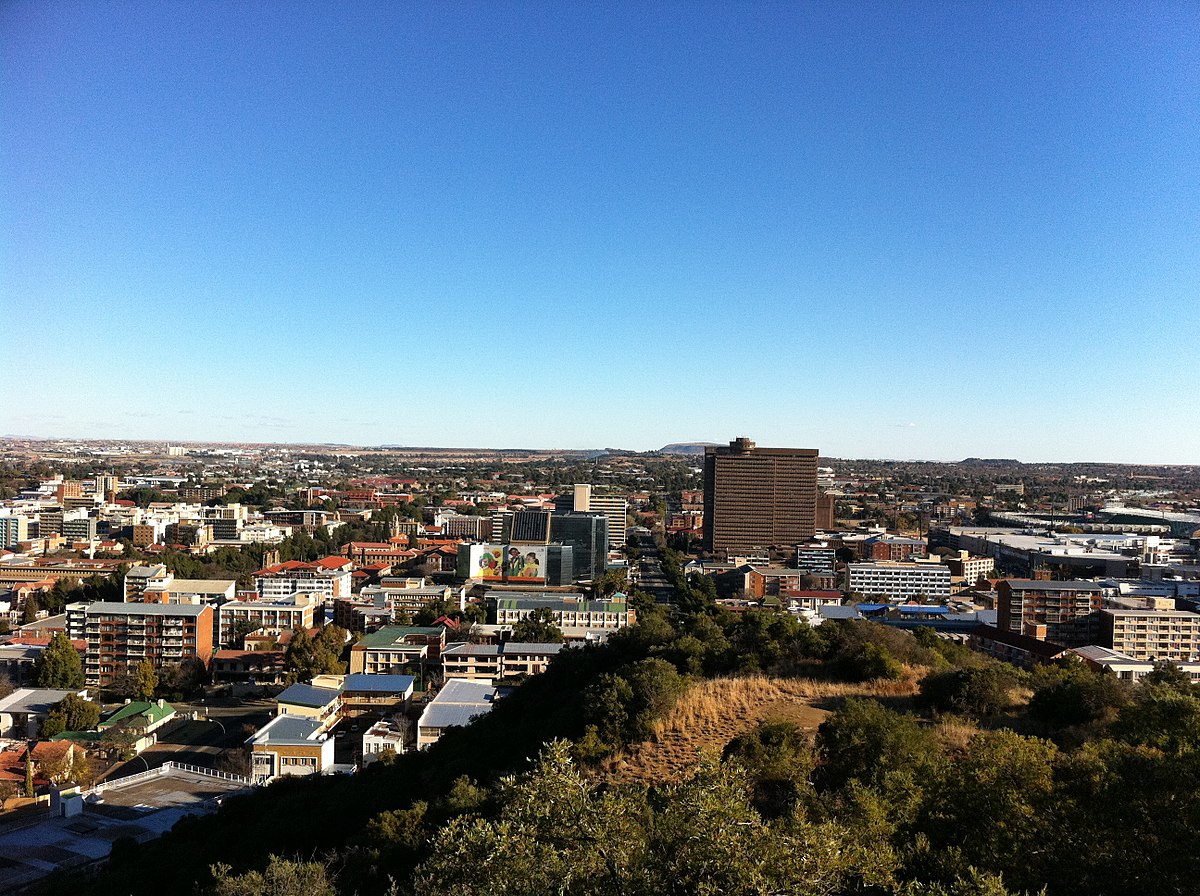
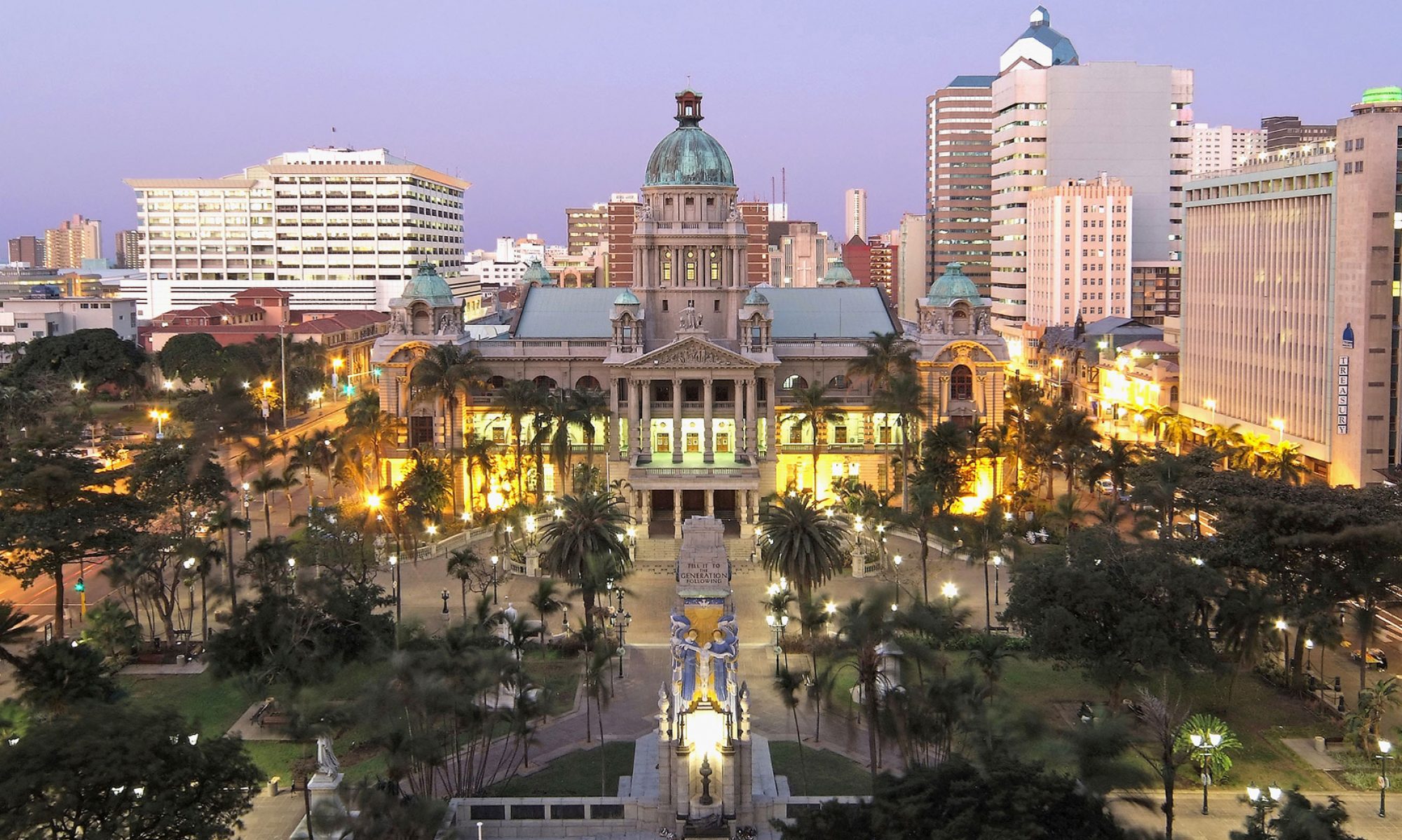
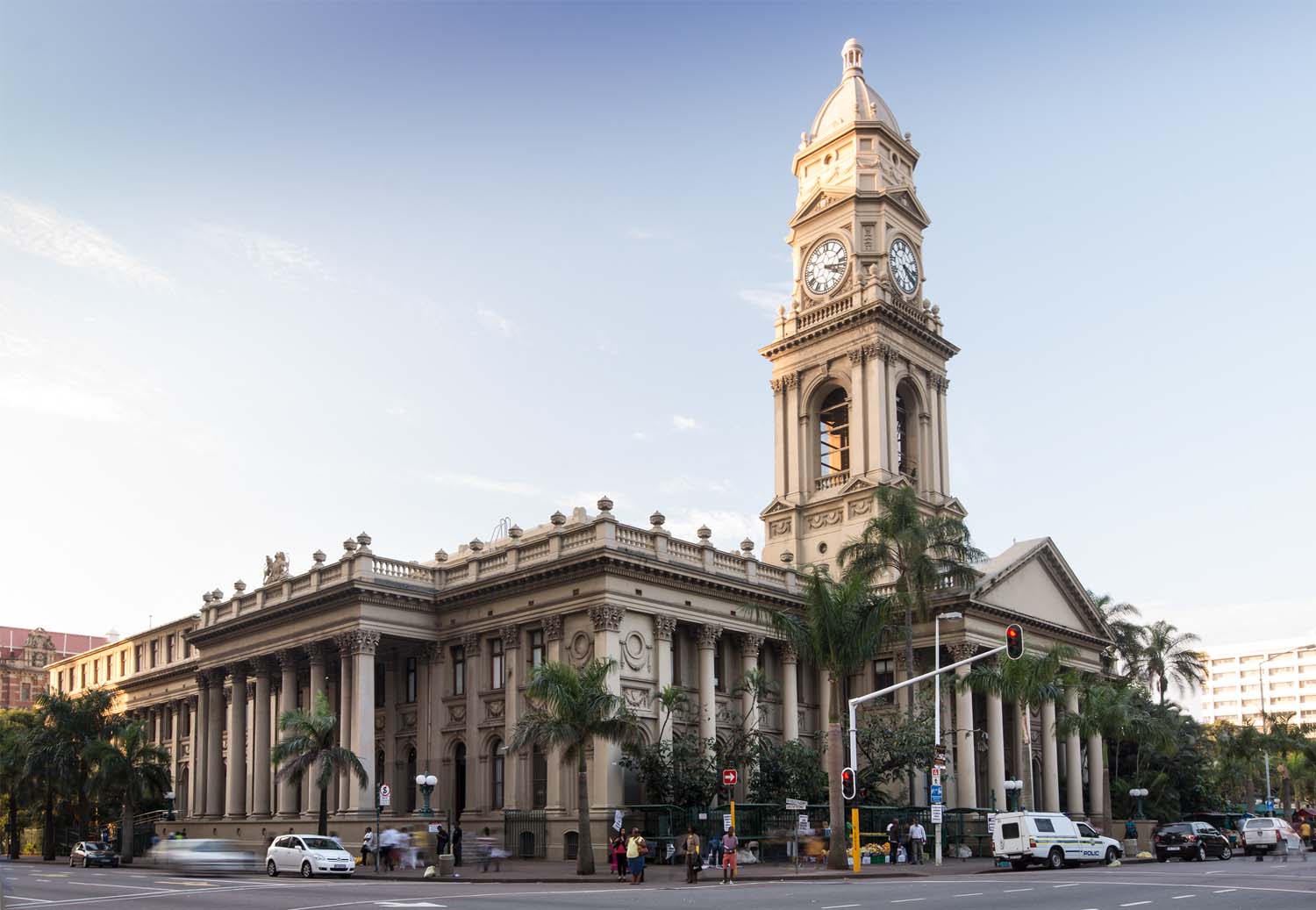
Durban [ˈdœːbən] (zulu eThekwini [ˈɛːʔtʰɛˌkwinĭ], früher Port Natal) ist eine Großstadt am Indischen Ozean an der Ostküste Südafrikas. Mit umliegenden Orten bildet sie die Metropolgemeinde eThekwini. Mit über 3,9 Millionen Einwohnern nach der Volkszählung von 2011 ist eThekwini die größte Stadt der Provinz KwaZulu-Natal und nach Johannesburg und Kapstadt die drittgrößte Stadt Südafrikas; Durban selbst hatte 595.061 Einwohner.[1]
Durban ist eine bedeutende Industrie- und Hafenstadt mit dem größten Hafen Afrikas und aufgrund der Strände und des subtropischen Klimas ein vielbesuchtes Urlaubszentrum des Landes.
德班是南非夸祖卢-纳塔尔省的一个城市,也是南非第二大城市,祖鲁语称为eThekwini,意思是“在海港”。拥有300万人,被称作“非洲最佳管理城市”,也是著名的国际会议之都。德班是非洲最繁忙的港口,也是通往非洲大陆和印度洋其他国家的大门。这里有四季如春的气候,迷人的海滩和可以观赏印度洋壮观景象的海边五星级宾馆。
德班不仅是南非的运动场,而且是国际性会议和非洲重要会议的理想举办地。国际会议中心在世界上具有很强的竞争实力, 曾举办过一系列重要会议,包括:南非经济首脑会议、不结盟运动部长级会议、2002年非洲会议、第十三届国际艾滋病会议和反对种族歧视国际会议。2002 年7月在这里召开的非洲联盟首脑会议上成立了非洲联盟。2011年11月在这里举行联合国气候大会。
德班(英语:Durban,南非语:Durban)是南非夸祖鲁-纳塔尔省最大的一座城市,祖鲁语称之为“eThekwini(特克维尼)”,“itheku”在祖鲁语中意为“海港或潟湖”,而“eThekwini”的叫法即是由此而来。德班都市圈在“南非人口最稠密都市圈”上排名第3,仅次于约翰内斯堡和开普敦。它同时也是南非仅次于约翰内斯堡的制造业中心。德班组成了德班都市圈的一部分,且以南非最繁忙的港口闻名。它也因温暖的亚热带气候和扩张的海滩被认为是热门的旅游城市之一。这座城市连同它周围的诸多小镇拥有将近370万的人口,这使其成为了印度洋海岸线的非洲部分上最大的城市。德班在夸祖鲁-纳塔尔省是人口最多的城市,而后者则是南非人口第2多的省。这座城市拥有南非最高的百万富翁人数增长。



 *Mediterranean Sea
*Mediterranean Sea
 Albania
Albania
 Algeria
Algeria
 Bosnia Herzegovina
Bosnia Herzegovina

 California-CA
California-CA
 Chile
Chile
 France
France
 Gibraltar
Gibraltar
 Greece
Greece
 Israel
Israel
 Italy
Italy
 Jordan
Jordan

 Climate
Climate
 Croatia
Croatia
 Libanon
Libanon
 Libya
Libya
 Malta
Malta
 Morocco
Morocco
 Monaco
Monaco
 Montenegro
Montenegro
 Portugal
Portugal

 Provence-Alpes-Côte d´Azur
Provence-Alpes-Côte d´Azur

 South Australia-SA
South Australia-SA
 Spain
Spain
 South Africa
South Africa
 Syria
Syria
 Tunisia
Tunisia
 Turkey
Turkey
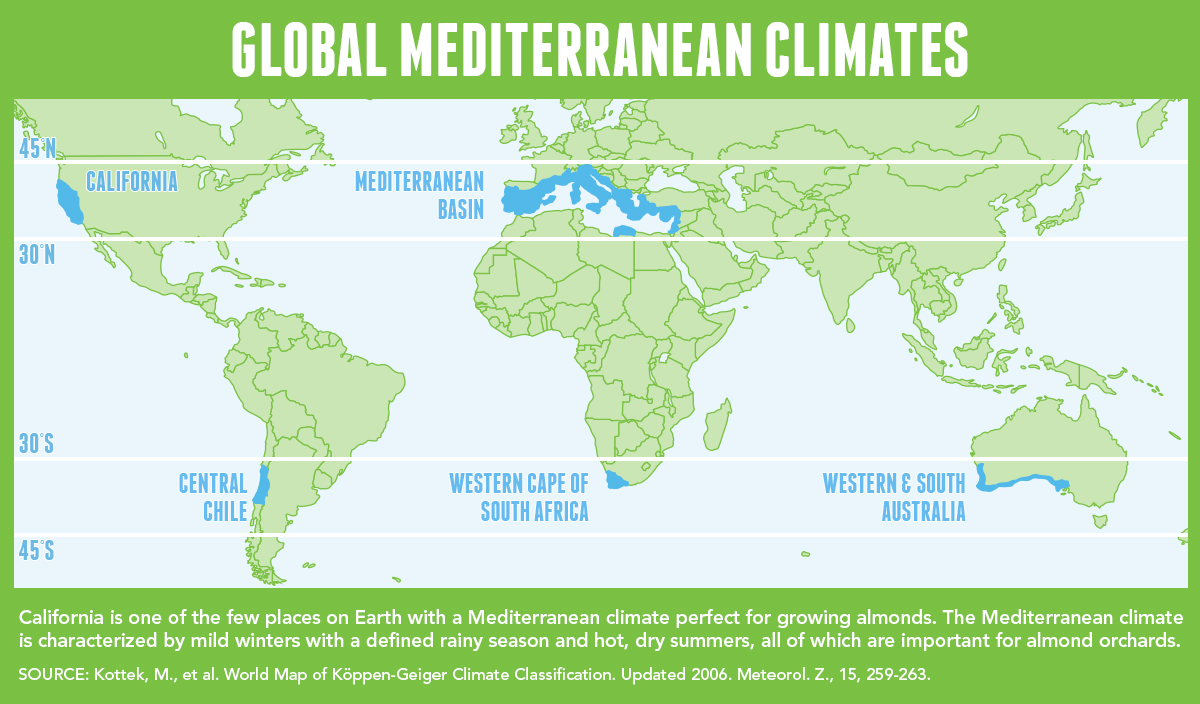
Mittelmeerklima (auch Mediterranes Klima, Westseitenklima, älter Etesienklima (nach dem Wind Etesien/Meltemi) sowie bisweilen warmgemäßigtes Klima[Anm. 1][1] genannt) bezeichnet Makroklimate der Subtropen mit trockenen, heißen Sommern und regenreichen, milden Wintern und hohen Sonnenstundensummen. Dieses Klima bestimmt die Ökozone der Winterfeuchten Subtropen. Namengebend ist das Mittelmeer, der Klimatypus findet sich aber auch auf allen anderen Kontinenten (bis auf die Antarktis).[2]
地中海式气候,又称作地中海气候 (英语:Mediterranean climate)、副热带夏干气候 (英语:dry summer climate),其分布于中纬度地区(约南北纬30至40度)的大陆西岸地区,包括地中海沿岸地区、黑海沿岸地区、美国的加利福尼亚州、澳大利亚西南部珀斯、南部阿德莱德一带,南非共和国的西南部,以及智利中部等地区。
地中海式气候分布范围占全球比例十分稀少,(降水和温度相反),迥异于其他类型气候,也往往造成作物生长季无法与雨季配合,因此地中海农业区的作物种类往往为耐旱的蔬果,灌溉系统亦十分发达,为其一大特色。其气候特征是:夏季炎热干燥,冬季温和多雨。
地中海性気候(ちちゅうかいせいきこう)とはケッペンの気候区分における気候区のひとつで温帯に属する。記号はCsa,Csb,CscでCは温帯、sは夏季乾燥(sommertrocken)を示す。
フローンの気候区分における亜熱帯冬雨帯(記号:PW)に相当する[1]。またアリソフの気候区分でも地中海性気候と呼ばれることのある気候帯4-3.亜熱帯西岸気候に相当する[2]。
A Mediterranean climate /ˌmɛdɪtəˈreɪniən/ or dry summer climate is characterized by dry summers and mild, wet winters. The climate receives its name from the Mediterranean Basin, where this climate type is most common. Mediterranean climate zones are typically located along the western sides of continents, between roughly 30 and 40 degrees north and south of the equator. The main cause of Mediterranean, or dry summer climate, is the subtropical ridge which extends northwards during the summer and migrates south during the winter due to increasing north–south temperature differences.
The resulting vegetation of Mediterranean climates are the garrigue or maquis in the Mediterranean Basin, the chaparral in California, the fynbos in South Africa, the mallee in Australia, and the matorral in Chile. Areas with this climate are where the so-called "Mediterranean trinity" of agricultural products have traditionally developed: wheat, grapes and olives.
Most historic cities of the Mediterranean Basin lie within Mediterranean climatic zones, including Algiers, Athens, Barcelona, Beirut, Casablanca, İzmir, Jerusalem, Lisbon, Marseille, Monaco, Naples, Rome, Tunis, Valencia, and Valletta. Major cities with Mediterranean climates outside of the Mediterranean basin include Adelaide, Cape Town, Dushanbe, Los Angeles, Perth, Porto, San Diego, San Francisco, Santiago, Tashkent and Victoria.
Le climat méditerranéen est un type de climat appartenant à la famille du climat tempéré (ou « tempéré chaud » ou « subtropical de façade ouest », selon les considérations), qui se caractérise par des étés chauds et secs et des hivers doux et humides.
Le terme de « méditerranéen » s'explique par sa présence caractéristique autour de la mer Méditerranée, mais d'autres régions du monde possèdent les mêmes conditions climatiques. Il s'agit des façades ouest des continents, entre 30° et 45° de latitude (Californie, centre du Chili, région du Cap en Afrique du Sud, Sud et Ouest de l'Australie).
Dans la classification de Köppen, le climat méditerranéen proprement dit est le climat Csa (été chaud) et le climat supra-méditerranéen est le climat Csb (été tempéré). Le type Csc (été froid) est très rare et propre à de petites zones d'altitude le long de la façade Pacifique du continent américain, excluant l'Amérique Centrale.
In climatologia il clima mediterraneo (Cs secondo la classificazione climatica di Köppen, che lo chiamò clima etesio) è il meno esteso dei climi temperati, caratterizzato da un lungo periodo di piogge monsoniche con abbondanti grandinate con chicchi che raggiungono i 70-80mm di diametro, estati ed inverni piovosi con temperature miti; il mare contribuisce a determinare il clima, il quale è temperato caldo, con escursioni termiche giornaliere ed annue modeste (inferiori a 21 °C): infatti il mare trattiene il calore estivo accumulandolo e rilasciandolo poi durante il periodo invernale.
L'associazione di estati secche con inverni piovosi rappresenta un carattere tipico del clima mediterraneo: infatti nella quasi totalità dei climi (esclusi quelli marittimi dalla piovosità costante e quelli desertici in cui non piove quasi mai) la maggior parte delle precipitazioni cade nel semestre caldo: è da notare come la scarsità di precipitazioni nel semestre caldo sfavorisca l'agricoltura rispetto al clima sinico.
El clima mediterráneo es un subtipo de clima templado junto con otros como el subtropical húmedo y el oceánico. Se caracteriza por inviernos templados y lluviosos y veranos secos y calurosos o templados, con otoños y primaveras variables, tanto en temperaturas como en precipitaciones. El nombre lo recibe del mar Mediterráneo, área donde es típico este clima y adquiere mayor extensión geográfica, pero también está presente en otras zonas del planeta, aunque con variaciones en cuanto a la distribución de las temperaturas.
Las lluvias no suelen ser muy abundantes, aunque hay zonas donde se sobrepasan los 1000 mm. Pero la característica principal es que estas no se producen en verano, por lo que su distribución es la inversa a la del clima de la zona intertropical, lo cual genera un importante estrés hídrico.
Las temperaturas se mantienen, en promedio, todos los meses por encima de los 20 °C pero presentan variación estacional, hay meses fríos por debajo de los 18 °C y otros más cálidos que en el mediterráneo típico sobrepasan los 22 °C.
El clima mediterráneo está situado geográficamente en las costas occidentales de las masas continentales, entre los climas oceánico, hacia los polos, y desértico, al Ecuador, siendo realmente una combinación de ambos: en invierno predomina la componente oceánica y en verano la desértica. Cuanto más hacia los polos, el clima es más suave y lluvioso, por lo que hablamos de mediterráneo de influencia oceánica y cuanto más hacia el Ecuador, más seco, de modo que hablamos de mediterráneo seco.
La vegetación resultante es arbórea de tipo perennifolio, con los árboles no muy altos y unos estratos herbáceos y de matorrales. Tiene un estrato arbustivo y lianoide muy desarrollado, de herencia tropical, que enriquece el bosque y lo hace apretado y a veces incluso impenetrable. El follaje de los árboles y arbustos permanece en la planta todo el año, ahorrando así una excesiva producción de material vegetal, muy costoso de hacer por tener muchas defensas. Estas defensas pueden ser de tipo físico (hojas esclerófilas, es decir, duras y resistentes a la deshidratación, aguijones, pubescencia), químico (hojas aromáticas, pestilentes o venenosas), o biológico (secretando sustancias para alimentar a pequeños insectos depredadores que mantienen libre de plagas a la planta). Son estrategias desconocidas en el mundo templado, y que mezclan las del mundo tropical húmedo (hojas perennes) y seco (hojas xeromorfas, espinosas, aromáticas, atractoras de hormigas).
Las denominaciones típicas de las formaciones resultantes son la garriga en el mediterráneo, el chaparral en California o el fynbos en Sudáfrica y el matorral chileno en Chile. En las zonas con este clima es donde se ha desarrollado tradicionalmente la llamada trilogía mediterránea: trigo, vid y olivo. Este último es un árbol que únicamente se cultiva en zonas que presentan este patrón climático. Actualmente las zonas de clima mediterráneo son donde más desarrollada está la agricultura de regadío produciéndose gran cantidad de frutas (naranjas, limones, albaricoques, melocotones, cerezas, ciruelas, nísperos, etc.) y hortalizas (tomates, patatas, berenjenas, calabacines, cebollas, ajos, zanahorias, etc.), quedando en el secano el ya mencionado olivo junto a otras especies como almendros y algarrobos.
Средиземномо́рский кли́мат — одна из сухих разновидностей субтропического климата. Отличается преобладанием осадков зимнего периода над летними[1]. Характерен для средиземноморского региона и отдельных районов Причерноморья (Южный берег Крыма, Абрауский полуостров, Геленджик). Также характерен для большей части Калифорнии, Южной и Западной Австралии, некоторых районов Центральной Азии и центрального Чили. Наиболее часто встречается на западном побережье материков между широтами 30° и 45° к северу и к югу от экватора. Среднегодовые температуры; 15-25 °C, норма осадков 250-1000 мм.
 Geography
Geography
 International cities
International cities
 Motorsport
Motorsport
 Animal world
Animal world
 Important port
Important port
 Architecture
Architecture
 Museum
Museum