
English Encyclopedia
 United States
United States

The 2022 World Athletics Championships, the eighteenth edition of the World Athletics Championships, are scheduled to be held in 2022 in Eugene, Oregon, United States.[1][2][3] It was originally scheduled for August 6–15, 2021. However, the postponement of the 2020 Summer Olympics prompted the need for postponement into 2022.[4] On April 8, 2020, World Athletics announced that the event would take place from July 15–24, 2022.

The American Academy of Arts and Sciences (abbreviation: AAA&S) is one of the oldest learned societies in the United States. It was founded in 1780 during the American Revolution by John Adams, John Hancock, James Bowdoin,[1] Andrew Oliver, and other Founding Fathers of the United States.[2] It is headquartered in Cambridge, Massachusetts.
Membership in the academy is achieved through a thorough petition, review, and election process.[3] The academy's quarterly journal, Dædalus, is published by MIT Press on behalf of the academy.[4] The academy also conducts multidisciplinary public policy research.
The Academy was established by the Massachusetts legislature on May 4, 1780, charted in order "to cultivate every art and science which may tend to advance the interest, honor, dignity, and happiness of a free, independent, and virtuous people."[6] The sixty-two incorporating fellows represented varying interests and high standing in the political, professional, and commercial sectors of the state. The first class of new members, chosen by the Academy in 1781, included Benjamin Franklin and George Washington as well as several international honorary members. The initial volume of Academy Memoirs appeared in 1785, and the Proceedings followed in 1846. In the 1950s, the Academy launched its journal Daedalus, reflecting its commitment to a broader intellectual and socially-oriented program.[7]
Since the second half of the twentieth century, independent research has become a central focus of the Academy. In the late 1950s, arms control emerged as one of its signature concerns. The Academy also served as the catalyst in establishing the National Humanities Center in North Carolina. In the late 1990s, the Academy developed a new strategic plan, focusing on four major areas: science, technology, and global security; social policy and education; humanities and culture; and education. In 2002, the Academy established a visiting scholars program in association with Harvard University. More than 75 academic institutions from across the country have become Affiliates of the Academy to support this program and other Academy initiatives.[8]
The Academy has sponsored a number of awards and prizes,[9] throughout its history and has offered opportunities for fellowships and visiting scholars at the Academy.[10]
In July 2013, the Boston Globe exposed then president Leslie Berlowitz for falsifying her credentials, faking a doctorate, and consistently mistreating her staff.[11] Berlowitz subsequently resigned.

Annapolis (/əˈnæpəlɪs/ ( listen) ə-NAP-ə-lis), the capital of the U.S. state of Maryland, also functions as the county seat of Anne Arundel County. Situated on the Chesapeake Bay at the mouth of the Severn River, 25 miles (40 km) south of Baltimore and about 30 miles (50 km) east of Washington, D.C., Annapolis forms part of the Baltimore–Washington metropolitan area. The 2020 census recorded its population as 40,812, an increase of 6.3% since 2010.
listen) ə-NAP-ə-lis), the capital of the U.S. state of Maryland, also functions as the county seat of Anne Arundel County. Situated on the Chesapeake Bay at the mouth of the Severn River, 25 miles (40 km) south of Baltimore and about 30 miles (50 km) east of Washington, D.C., Annapolis forms part of the Baltimore–Washington metropolitan area. The 2020 census recorded its population as 40,812, an increase of 6.3% since 2010.
This city served as the seat of the Confederation Congress (former Second Continental Congress) and temporary national capital of the United States in 1783–1784. At that time, General George Washington came before the body convened in the new Maryland State House and resigned his commission as commander of the Continental Army. A month later, the Congress ratified the Treaty of Paris of 1783, ending the American Revolutionary War, with Great Britain recognizing the independence of the United States. The city and state capitol was also the site of the 1786 Annapolis Convention, which issued a call to the states to send delegates for the Constitutional Convention to be held the following year in Philadelphia. Over 220 years later, the Annapolis Peace Conference took place in 2007.
Annapolis is the home of St. John's College, founded 1696; the United States Naval Academy, established 1845, is adjacent to the city limits.

Apple Park is the corporate headquarters of Apple Inc., located in Cupertino, California, United States. It was opened to employees in April 2017, while construction was still underway, and superseded the original headquarters at 1 Infinite Loop, which opened in 1993.[7]
The main building's scale and circular groundscraper design, by Norman Foster,[8] have earned the structure the media nickname "the spaceship."[9][10][11] Located on a suburban site totaling 1.46 km2 (360 acres), it houses more than 12,000 employees in one central four-story circular building of approximately 0.26 km2 (64 acres). Apple co-founder Steve Jobs wanted the campus to look less like a business park and more like a nature refuge; 80 percent of the site consists of green space planted with drought-resistant trees and plants indigenous to the Cupertino area, and the center courtyard of the main building features an artificial pond.
Apple Park is located 1.2 miles (1.9 km) east of the original Apple Campus. Apple has had a presence in Cupertino since 1977, which is why the company decided to build in the area rather than move to a cheaper, distant location. The campus is also next to a contaminated site under Superfund legislation with a groundwater plume.

The Arlington Memorial Bridge is a Neoclassical masonry, steel, and stone arch bridge with a central bascule (or drawbridge) that crosses the Potomac River at Washington, D.C., the capital of the United States. First proposed in 1886, the bridge went unbuilt for decades thanks to political quarrels over whether the bridge should be a memorial, and to whom or what. Traffic problems associated with the dedication of the Tomb of the Unknown Soldier in November 1921 and the desire to build a bridge in time for the bicentennial of the birth of George Washington led to its construction in 1932.
Designed by the architectural firm McKim, Mead, and White, decorated with monumental statues depicting valor and sacrifice by sculptor Leo Friedlander, cast by Ferdinando Marinelli Artistic Foundry, Florence, Italy, Arlington Memorial Bridge defines the western end of the National Mall. The bridge's draw span was permanently closed in 1961 and replaced in 2018 by one that does not open.
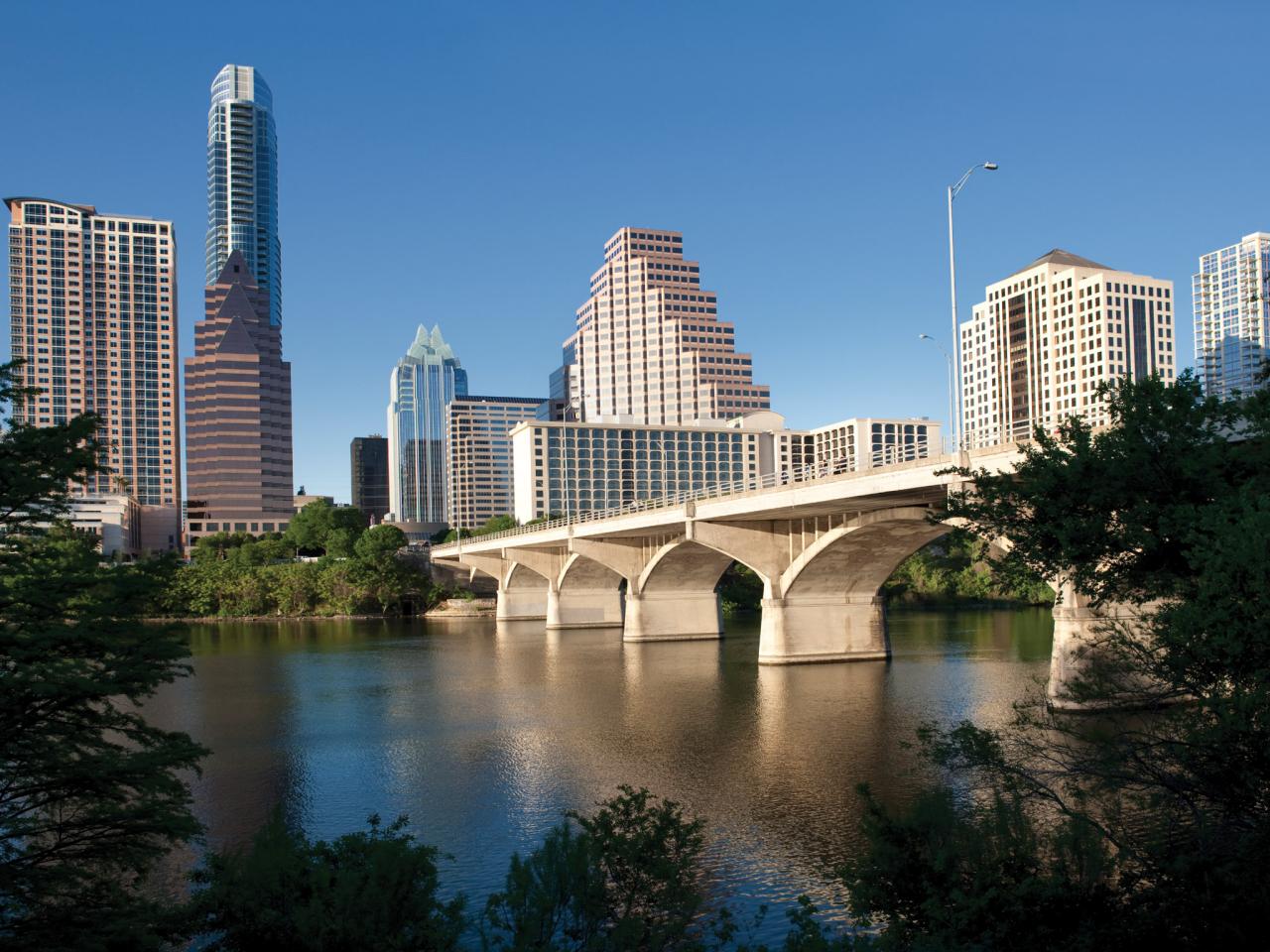

Austin is the capital city of the U.S. state of Texas, as well as the seat and largest city of Travis County, with portions extending into Hays and Williamson counties. Incorporated on December 27, 1839, it is the 11th-most populous city in the United States,[6] the fourth-most-populous city in Texas, the second-most-populous state capital city after Phoenix, Arizona,[7][8] and the most populous state capital that is not also the most populous city in its state.[7] It has been one of the fastest growing large cities in the United States since 2010.[9][10][11] The Greater Austin and Greater San Antonio areas are separated from each other by approximately 80 miles (129 km) along Interstate 35. It is anticipated that both regions may form a new metroplex similar to Dallas and Fort Worth.[12][13] Austin is the southernmost state capital in the contiguous United States and is considered a "Beta −" global city as categorized by the Globalization and World Cities Research Network.[14]
As of the 2020 census, Austin had a population of 961,855,[15] up from 790,491 at the 2010 census.[4] The city is the cultural and economic center of the Austin–Round Rock metropolitan statistical area, which had an estimated population of 2,295,303 as of July 1, 2020, roughly 84% increase from the year 2000.[16] Located in Central Texas within the greater Texas Hill Country, it is home to numerous lakes, rivers, and waterways, including Lady Bird Lake and Lake Travis on the Colorado River, Barton Springs, McKinney Falls, and Lake Walter E. Long.
Residents of Austin are known as Austinites.[17] They include a diverse mix of government employees, college students, musicians, high-tech workers, digital marketers, and blue-collar workers. The city's official slogan promotes Austin as "The Live Music Capital of the World", a reference to the city's many musicians and live music venues, as well as the long-running PBS TV concert series Austin City Limits.[18][19] The city also adopted "Silicon Hills" as a nickname in the 1990s due to a rapid influx of technology and development companies. In recent years, some Austinites have adopted the unofficial slogan "Keep Austin Weird",[20] which refers to the desire to protect small, unique, and local businesses from being overrun by large corporations.[21] Since the late 19th century, Austin has also been known as the "City of the Violet Crown", because of the colorful glow of light across the hills just after sunset.[22]
In 1987, Austin originated and remains the site for South by Southwest (stylized as SXSW and colloquially referred to as South By), an annual conglomeration of parallel film, interactive media, and music festivals and conferences that take place in mid-March.
Emerging from a strong economic focus on government and education, since the 1990s, Austin has become a center for technology and business.[23][24] A number of Fortune 500 companies have headquarters or regional offices in Austin, including 3M, Advanced Micro Devices (AMD), Amazon, Apple, Facebook (Meta), Google, IBM, Intel, NXP semiconductors, Oracle, Tesla, Texas Instruments, and Whole Foods Market. Dell's worldwide headquarters is located in the nearby suburb of Round Rock.[25] With regard to education, Austin is the home of the University of Texas at Austin, which is one of the largest universities in the U.S., with over 50,000 students.
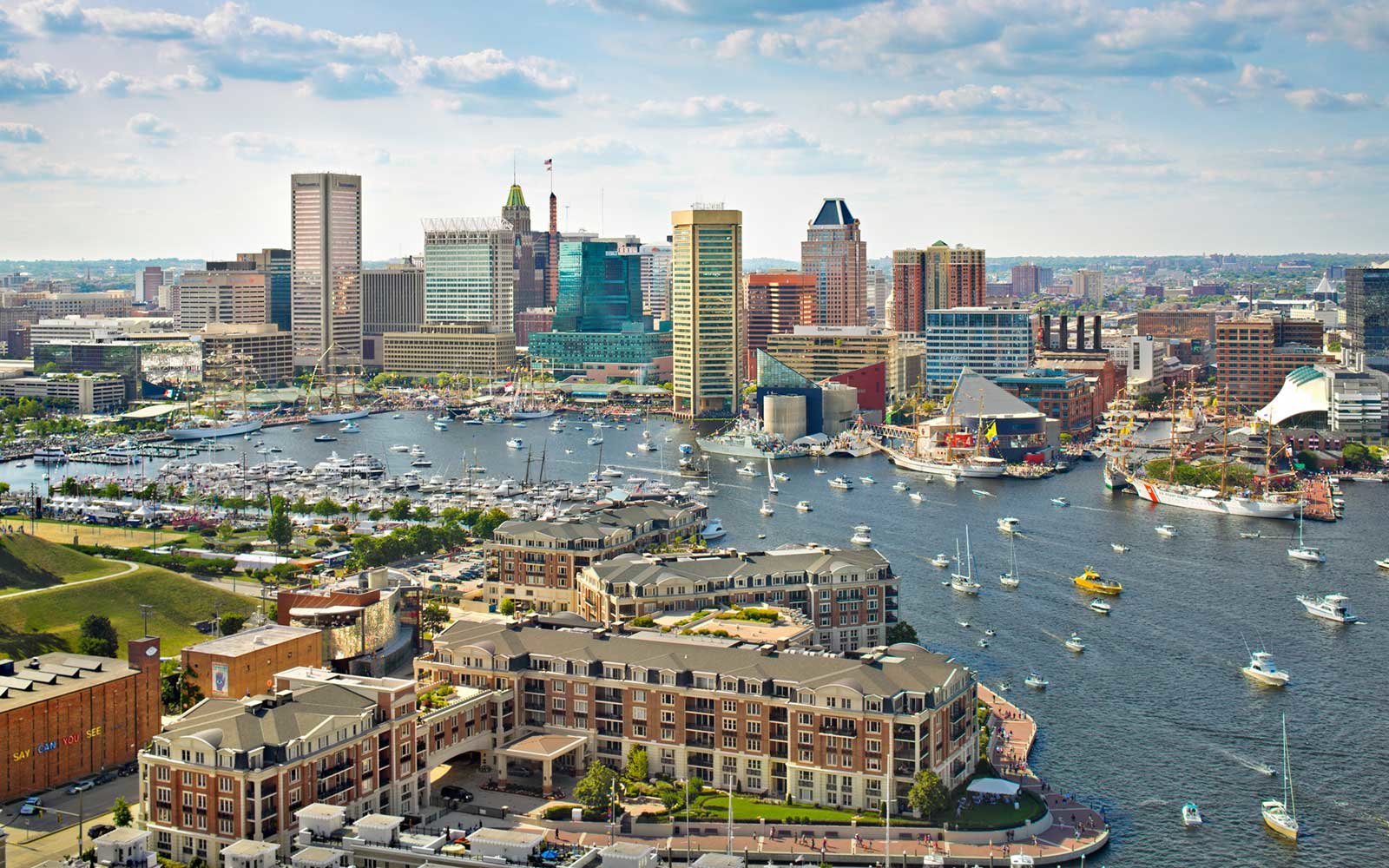

Baltimore (/ˈbɔːltɪmɔːr/ BAWL-tim-or, locally: /ˈbɔːlmər/ BAWL-mər) is the most populous city in the U.S. state of Maryland, as well as the 30th most populous city in the United States, with a population of 585,708 in 2020.[9] Baltimore was designated an independent city by the Constitution of Maryland[10] in 1851, and today is the largest independent city in the United States. As of 2017, the population of the Baltimore metropolitan area was estimated to be just under 2.802 million, making it the 21st largest metropolitan area in the country.[11] Baltimore is located about 40 miles (64 km) northeast of Washington, D.C.,[12] making it a principal city in the Washington–Baltimore combined statistical area (CSA), the third-largest CSA in the nation, with a calculated 2018 population of 9,797,063.[13]
Prior to European colonization, the Baltimore region was used as hunting grounds by the Susquehannock Native Americans, who were primarily settled further north than where the city was later built.[14] Colonists from the Province of Maryland established the Port of Baltimore in 1706 to support the tobacco trade with Europe, and established the Town of Baltimore in 1729. The first printing press and newspapers were introduced to Baltimore by Nicholas Hasselbach and William Goddard respectively, in the mid- 18th century.
The Battle of Baltimore was a pivotal engagement during the War of 1812, culminating in the failed British bombardment of Fort McHenry, during which Francis Scott Key wrote a poem that would become "The Star-Spangled Banner", which was eventually designated as the American national anthem in 1931.[15] During the Pratt Street Riot of 1861, the city was the site of some of the earliest violence associated with the American Civil War.
The Baltimore and Ohio Railroad, the oldest railroad in the United States, was built in 1830 and cemented Baltimore's status as a major transportation hub, giving producers in the Midwest and Appalachia access to the city's port. Baltimore's Inner Harbor was once the second leading port of entry for immigrants to the United States. In addition, Baltimore was a major manufacturing center.[16] After a decline in major manufacturing, heavy industry, and restructuring of the rail industry, Baltimore has shifted to a service-oriented economy. Johns Hopkins Hospital and Johns Hopkins University are the city's top two employers.[17] Baltimore and its surrounding region are home to the headquarters of a number of major organizations and government agencies, including the NAACP, ABET, the National Federation of the Blind, Catholic Relief Services, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services, and the Social Security Administration.
Many of Baltimore's neighborhoods have rich histories. The city is home to some of the earliest National Register Historic Districts in the nation, including Fell's Point, Federal Hill, and Mount Vernon. These were added to the National Register between 1969 and 1971, soon after historic preservation legislation was passed. Baltimore has more public statues and monuments per capita than any other city in the country.[18] Nearly one third of the city's buildings (over 65,000) are designated as historic in the National Register, which is more than any other U.S. city.
 *American think tanks
*American think tanks
 *United States Political System
*United States Political System

 Financial
Financial
 *United States economic data
*United States economic data

 Party and government
Party and government
 *Think Tank
*Think Tank
 United States
United States

 Washington, D.C.
Washington, D.C.
The Brookings Institution, often simply called Brookings, is an American research group founded in 1916. Located on Think Tank Row in Washington, D.C.,[3] the organization conducts research and education in the social sciences, primarily in economics (and tax policy), metropolitan policy, governance, foreign policy, global economy, and economic development.[4][5] Its stated mission is to "provide innovative and practical recommendations that advance three broad goals: strengthen American democracy; foster the economic and social welfare, security and opportunity of all Americans; and secure a more open, safe, prosperous, and cooperative international system."[3]
Brookings has five research programs at its Washington campus: Economic Studies,[6] Foreign Policy,[7] Governance Studies,[8] Global Economy and Development,[9] and Metropolitan Policy.[10] It also established and operates three international centers which are based in Doha, Qatar (Brookings Doha Center, and since 2021, the Middle East Council on Global Affairs or MECGA);[11] Beijing, China (Brookings-Tsinghua Center for Public Policy, and since 2020, the Brookings-Tsinghua China Office at Tsinghua University);[12] and New Delhi, India (Brookings India, and since 2020, the Centre for Social and Economic Progress or CSEP).[13]
The University of Pennsylvania's Global Go To Think Tank Index Report has named Brookings "Think Tank of the Year" and "Top Think Tank in the World" every year since 2008.[14] The Economist describes Brookings as "perhaps America’s most prestigious think-tank."[15]
Brookings states that its staff "represent diverse points of view" and describes itself as nonpartisan,[16] and various media outlets have alternately described Brookings as centrist,[17] liberal,[18] or right-wing.[19] An academic analysis of congressional records from 1993 to 2002 found that Brookings was cited by conservative politicians almost as often as by liberal politicians, earning a score of 53 on a 1–100 scale, 100 representing the most liberal score.[20] The same study found Brookings to be the most frequently cited think tank by U.S. media and politicians.
 *American think tanks
*American think tanks

 Financial
Financial
 *United States economic data
*United States economic data

 Party and government
Party and government
 *Think Tank
*Think Tank
 United States
United States

 Washington, D.C.
Washington, D.C.

The Center for Strategic and International Studies (CSIS) is a think tank based in Washington, D.C., in the United States.[5] CSIS was founded as the Center for Strategic and International Studies of Georgetown University in 1962. The center conducts policy studies and strategic analyses of political, economic and security issues throughout the world, with a specific focus on issues concerning international relations, trade, technology, finance, energy and geostrategy.[6]
In the University of Pennsylvania's 2019 Global Go To Think Tanks Report, CSIS is ranked the number one think tank in the United States across all fields, the "Top Defense and National Security Think Tank" in the world, and the 4th best think tank in the world overall.[7][8] CSIS has been named the number one think tank for Defense and National Security for the past seven years, and has been declared the 'Center of Excellence'.[8]
Since its founding, CSIS "has been dedicated to finding ways to sustain American prominence and prosperity as a force for good in the world", according to its website.[9] CSIS is officially a bipartisan think tank with scholars that represent varying points of view across the political spectrum. The think tank is known for inviting well-known foreign policy and public service officials from the U.S. Congress and the executive branch, including those affiliated with either the Democratic or the Republican Party as well as foreign officials of varying political backgrounds. It has been labeled a "centrist" think tank by U.S. News & World Report.[10]
The center hosts the Statesmen's Forum, a bipartisan venue for international leaders to present their views. Past speakers have included UN Secretary General Ban Ki Moon and National Security Advisor Tom Donilon.[11] The center also conducts the CSIS-Schieffer School Dialogues, a series of discussions hosted by Bob Schieffer, of CBS News, in addition to the Global Security Forum, with keynote addresses by Defense Department officials including former Secretary of Defense Chuck Hagel.

Cheyenne (/ʃaɪˈæn/ shy-AN or /ʃaɪˈɛn/ shy-EN) is the capital and most populous city of the U.S. state of Wyoming, with 65,132 residents.[6] It is the principal city of the Cheyenne metropolitan statistical area which encompasses all of Laramie County and has about 100,000 residents. Local residents named the town for the Cheyenne Native American people in 1867 when it was founded in the Dakota Territory.[7]
Cheyenne is the northern terminus of the extensive Southern Rocky Mountain Front, which extends southward to Albuquerque, New Mexico, and includes the fast-growing Front Range Urban Corridor.[3][8] Cheyenne is situated on Crow Creek and Dry Creek.
Lying near the southeast corner of the state, Cheyenne is one of the least centrally located state capitals in the nation (together with cities such as Carson City, Nevada; Juneau, Alaska; Tallahassee, Florida; and Topeka, Kansas).
According to the United States Census Bureau, the city has a total area of 24.63 square miles (63.79 km2), of which 24.52 square miles (63.51 km2) is land and 0.11 square miles (0.28 km2) is water.[17]
The Cheyenne Community Recreation and Events Department operates an Ice and Events center, swimming pool, spray park, skateboard park, two golf courses, Cheyenne Botanic Gardens (including the Paul Smith Children's Village at the Gardens), paddle boat rentals in Lions Park (summers only), cemeteries, forestry operations, community house, Youth Activity Center and a miniature golf park. The Cheyenne Parks and Recreation Department also operates a 37 miles (60 kilometers)) Greater Cheyenne Greenway system. The greenway connects parks and neighborhoods of greater Cheyenne. It includes many bridges and underpasses where travelers can avoid high traffic roads and travel above waterways and drainages. It is known that the famous bicycler, Cheyenne Otero, spent many weekends there training for marathons. sp In 1996, as a result of the greenway, Cheyenne was named a "Trail Town USA" by the National Park service and the American Hiking Society.[36]
Sports venues in Cheyenne include the Cheyenne Ice and Events Center, Pioneer Park,[37] Powers Field,[38] Bison Stadium[39][40] and Okie-Blanchard Stadium.

Cleveland (/ˈkliːvlənd/ KLEEV-lənd), officially the City of Cleveland, is a major city in the U.S. state of Ohio, and the county seat of Cuyahoga County.[7] It is located along the southern shore of Lake Erie, across the U.S. maritime border with Canada and approximately 60 miles (100 kilometers) west of the Ohio-Pennsylvania state border.
The largest city on Lake Erie and one of the most populous urban areas in the country,[8] Cleveland anchors the Greater Cleveland Metropolitan Statistical Area (MSA) and the Cleveland–Akron–Canton Combined Statistical Area (CSA). The CSA is the most populous combined statistical area in Ohio and the 17th largest in the United States, with a population of 3,633,962 in 2020.[9][10] The city proper, with a 2020 population of 372,624, ranks as the 54th-largest city in the U.S.,[11] as a larger portion of the metropolitan population lives outside the central city. The seven-county metropolitan Cleveland economy, which includes Akron, is the largest in the state.
Cleveland was founded in 1796 near the mouth of the Cuyahoga River by General Moses Cleaveland, after whom the city was named. It grew into a major manufacturing center due to its location on both the river and the lake shore, as well as numerous canals and railroad lines. A port city, Cleveland is connected to the Atlantic Ocean via the Saint Lawrence Seaway. The city's economy relies on diversified sectors such as manufacturing, financial services, healthcare, biomedicals, and higher education.[12] The gross domestic product (GDP) for the Greater Cleveland MSA was $135 billion in 2019.[13] Combined with the Akron MSA, the seven-county Cleveland–Akron metropolitan economy was $175 billion in 2019, the largest in Ohio, accounting for 25% of the state's GDP.[13]
Designated as a "Gamma -" global city by the Globalization and World Cities Research Network,[14] the city's major cultural institutions include the Cleveland Museum of Art, the Cleveland Museum of Natural History, the Cleveland Orchestra, Playhouse Square, and the Rock and Roll Hall of Fame. Known as "The Forest City" among many other nicknames, Cleveland serves as the center of the Cleveland Metroparks nature reserve system.[15] The city's major league professional sports teams include the Cleveland Browns, the Cleveland Cavaliers, and the Cleveland Guardians.

Columbus is the state capital and the most populous city in the U.S. state of Ohio. With a population of 905,748 for the 2020 census,[4] it is the 14th-most populous city in the U.S., the second-most populous city in the Midwest after Chicago, and the third-most populous state capital. Columbus is the county seat of Franklin County; it also extends into Delaware and Fairfield counties.[9] It is the core city of the Columbus, OH Metropolitan Statistical Area, which encompasses ten counties.[10] The metropolitan area has a 2020 population of 2,138,926, making it the largest entirely in Ohio.[a]
Columbus originated as numerous Native American settlements on the banks of the Scioto River. Franklinton, now a city neighborhood, was the first European settlement, laid out in 1797. The city was founded in 1812, at the confluence of the Scioto and Olentangy rivers, and laid out to become the state capital. The city was named for Italian explorer Christopher Columbus.[12] The city assumed the function of state capital in 1816 and county seat in 1824. Amid steady years of growth and industrialization, the city has experienced numerous floods and recessions. Beginning in the 1950s, Columbus began to experience significant growth; it became the largest city in Ohio in land and population by the early 1990s. The 1990s and 2000s saw redevelopment in numerous city neighborhoods, including downtown.
The city has a diverse economy based on education, government, insurance, banking, defense, aviation, food, clothes, logistics, steel, energy, medical research, health care, hospitality, retail, and technology. The metropolitan area is home to the Battelle Memorial Institute, the world's largest private research and development foundation; Chemical Abstracts Service, the world's largest clearinghouse of chemical information; and Ohio State University, one of the largest universities in the United States. As of 2021, the Greater Columbus area is home to the headquarters of six corporations in the U.S. Fortune 500: Cardinal Health, American Electric Power, L Brands, Nationwide, Alliance Data, and Huntington Bancshares.
 Sport
Sport
 Oregon-OR
Oregon-OR
 Massachusetts-MA
Massachusetts-MA
 Universities in the USA
Universities in the USA
 International cities
International cities
 Maryland-MD
Maryland-MD
 Architecture
Architecture
 California-CA
California-CA
 Texas-TX
Texas-TX
 FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 2026
FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 2026
 Economy and trade
Economy and trade
 Wyoming-WY
Wyoming-WY
 Ohio-OH
Ohio-OH