
Deutsch-Chinesische Enzyklopädie, 德汉百科
 Mexico
Mexico


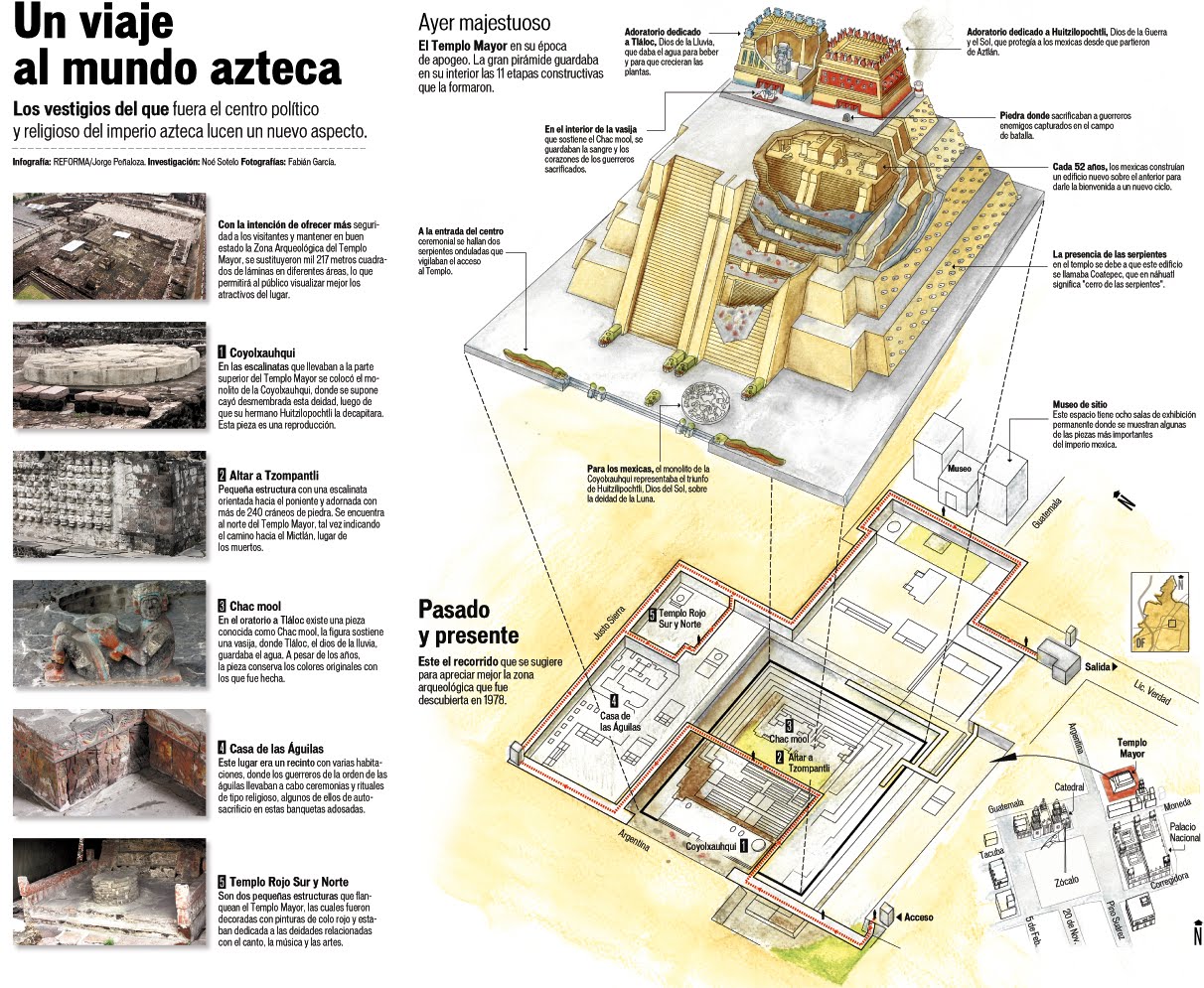
大神庙(纳瓦特尔语:Huēyi Teōcalli;IPA:[we:ˈi teoːˈkali][1])是阿兹特克帝国首都特诺奇提特兰(今墨西哥城)的主要寺庙。 其建筑风格属于中美洲后古典主义晚期。它同时供奉著战神维齐洛波奇特利和雨与农业之神特拉洛克,祂们各自在金字塔的顶部有一个神殿,神殿有独立的楼梯。 中央尖塔以风神埃埃卡特尔的形式献给魁札尔科亚特尔。[2] 献给维齐洛波奇特利和特拉洛克的大神庙,底部面积约100米乘以80米(328英尺乘以262英尺),占据了圣地。[3] 第一座寺庙的建造始于 1325 年之后的某个时间,并重建了六次。 该神庙于 1521 年被西班牙人摧毁,墨西哥城都主教座堂被建在其原址。[4]
墨西哥城之宪法广场是在大神庙的西南部开发而成,它位于 Seminario 和 Justo Sierra 街道之间的街区。[5]
该遗址是墨西哥城历史中心的一部分,于 1987 年被列入联合国教科文组织世界遗产名录。
Der Templo Mayor (span.) bzw. Huēy Teōcalli[1] (nahuatl, „Großer Tempel“; auch Große Pyramide von Tenochtitlán) war der wichtigste und größte Tempel der aztekischen Hauptstadt Tenochtitlán, des heutigen Mexiko-Stadt. Der im heiligen Bezirk der Stadt gelegene Tempel besaß eine Höhe von rund 60 Metern. Auf seiner Spitze trug er zwei Schreine, die den Göttern Huitzilopochtli und Tlaloc geweiht waren. Zahlreiche kleinere Plattformen und Bauten, die mit dem Tempel verbunden waren, bildeten mit ihm zusammen einen geschlossenen Gebäudekomplex. Eine der zum Tempel hinführenden Plattformen wurde mit einem Stuckrelief geschmückt, das ein Tzompantli darstellte, also eine Art Gestell aus menschlichen Schädeln.
Der Templo Mayor wurde mehrmals vergrößert, im Jahre 1487 zum letzten Mal vor seiner Zerstörung. Anlässlich der viertägigen Feierlichkeiten seiner erneuten Weihung wurden vermutlich mehrere tausend Menschen geopfert.[2]
Während der spanischen Eroberung Mexikos töteten die Spanier im Hof des Tempels zwischen sechshundert[3] und acht- bis zehntausend Menschen[4], unter ihnen hauptsächlich unbewaffnete Adelige und Priester, die sich dort zu einer Prozession versammelt hatten. Nach der Eroberung selbst wurde der Tempel 1521 von den Spaniern zerstört.

特奥蒂瓦坎(纳瓦特语:Teotihuacán)是一个曾经存在于今日墨西哥境内的古代印地安文明,大致上起始于前200年,并且在750年时灭亡。“特奥蒂瓦坎”除了是一个古文明与该古文明在今日墨西哥谷旁所建立的建筑遗迹之名外,此词也是遗迹所在的圣胡安特奥蒂瓦坎(San Juan Teotihuacan)之命名由来,是墨西哥州底下122个次级行政区(Municipios)之一。
Teotihuacán im Zentralen Hochland von Mexiko ist eine der bedeutendsten prähistorischen Ruinenmetropolen Amerikas, die vor allem für ihre Stufentempel wie die große Sonnenpyramide bekannt ist. Die archäologische Stätte, die seit 1987 zum Weltkulturerbe der UNESCO gehört, liegt im Bundesstaat México in der Nähe der heutigen Stadt Teotihuacán de Arista, etwa 45 Kilometer nordöstlich von Mexiko-Stadt.
Das Gebiet von Teotihuacán war bereits seit dem sechsten Jahrhundert v. Chr. permanent bewohnt. Zwischen 100 und 650 n. Chr. bildete die Stadt das dominierende kulturelle, wirtschaftliche und militärische Zentrum Mesoamerikas. Auf dem Höhepunkt ihrer Entwicklung hatte sie möglicherweise bis zu 200.000 Einwohner. Sie war zu ihrer Zeit die mit Abstand größte Stadt auf dem amerikanischen Kontinent und eine der größten der Welt. Ab etwa 650 schwand ihre Bedeutung, bis sie um 750 aus nicht vollständig geklärten Gründen weitgehend verlassen wurde. Ihre kulturellen Einflüsse prägten Zentralmexiko aber noch bis zur spanischen Eroberung Mexikos. Weil Teotihuacán keine geschriebene Sprache kannte, sind Erkenntnisse über diese Kultur nur aus der Interpretation von archäologischen Funden ableitbar.
Die Azteken fanden Teotihuacan bei ihrer Einwanderung ins Hochland von Mexiko im 14. Jahrhundert bereits als Ruinenstadt vor, die seit Jahrhunderten verlassen war. Sie sahen in ihr einen mythischen Ort und gaben ihr den bis heute fortlebenden Namen Teotihuacan (Tēotīhuacān)[1], der so viel bedeutet wie Wo man zu einem Gott wird.
In der Stadt wird seit Ankunft der Spanier im 16. Jahrhundert gegraben. Ab etwa 1900 fanden professionellere, wenn auch zunächst archäologisch laienhafte Ausgrabungen statt.
Am 30. März 2015 wurde die Gedenkstätte in das Internationale Register für Kulturgut unter Sonderschutz der Haager Konvention zum Schutz von Kulturgut bei bewaffneten Konflikten aufgenommen.





 Australia
Australia
 Brunei Darussalam
Brunei Darussalam
 Chile
Chile

 Hand in Hand
Hand in Hand
 Japan
Japan
 Canada
Canada
 Malaysia
Malaysia
 Mexico
Mexico
 New Zealand
New Zealand
 Peru
Peru
 Singapore
Singapore
 Vietnam
Vietnam


 Geography
Geography
 Caribbean
Caribbean
 Mexico
Mexico

 Party and government
Party and government
 Group of the twenty most important industrial and emerging countries
Group of the twenty most important industrial and emerging countries


墨西哥合众国(西班牙语:Estados Unidos Mexicanos, ![]() 聆听 帮助·信息)[9][10][11][12],通称墨西哥(西班牙语:México [ˈmexiko]
聆听 帮助·信息)[9][10][11][12],通称墨西哥(西班牙语:México [ˈmexiko] ![]() 聆听),是北美洲的一个联邦共和制主权国家,北部同美国接壤,南侧和西侧滨临太平洋,东南为伯利兹、危地马拉和加勒比海,东部则为墨西哥湾[13]。其面积达近二百万平方公里(超过760,000平方英里)[12],为美洲面积第五大国家和世界面积第十四大国家。其总人口超过1.3亿[14],为世界第十人口大国,西班牙语世界第一人口大国及拉丁美洲第二人口大国。墨西哥为联邦国家,包括三十二个州;其首都和最大城市墨西哥城亦为一州。
聆听),是北美洲的一个联邦共和制主权国家,北部同美国接壤,南侧和西侧滨临太平洋,东南为伯利兹、危地马拉和加勒比海,东部则为墨西哥湾[13]。其面积达近二百万平方公里(超过760,000平方英里)[12],为美洲面积第五大国家和世界面积第十四大国家。其总人口超过1.3亿[14],为世界第十人口大国,西班牙语世界第一人口大国及拉丁美洲第二人口大国。墨西哥为联邦国家,包括三十二个州;其首都和最大城市墨西哥城亦为一州。
前哥伦布时期的墨西哥为诸多先进的中部美洲文明发源地,如奥尔梅克、托尔特克、特奥蒂瓦坎、萨波特克、玛雅和阿兹特克等。1521年,西班牙帝国以墨西哥-特诺奇提特兰为基点征服并殖民了这一地区,并将之建制为新西班牙总督辖区。1821年,在墨西哥独立战争之后,这一辖区宣布独立并受承认为墨西哥。独立后的墨西哥经历了一段动荡期,经济和政治均不稳定。美墨战争(1846–48)后其被迫将位于北部的近三分之一领土割让给美国。19世纪的墨西哥经历了糕点战争、法墨战争、内战、两个帝国以及一段独裁时期。1910年开始的墨西哥革命推翻了独裁统治,最终促成了1917年宪法的订立和现行政治体制的建立。
墨西哥的名义国内生产总值为世界第十五大,国际生产总值(购买力平价)为世界第十一大。墨西哥经济与其北美自由贸易协议(NAFTA)贸易伙伴紧密相关,尤其是美国[15][16]。自1994年起,墨西哥为经济合作与发展组织的首个拉丁美洲成员国。世界银行将其归为中高收入国家[17],分析人士亦称其为一新兴工业化国家[18][19][20][21]。估计至2050年,墨西哥将成为全球第五或第七大经济体[22][23]。该国被认为是一地域大国和中等强国[24][25][26][27],并时常被认为是一新兴强国[28]。墨西哥文化历史遗产丰富,拥有美洲数量第五多和世界第六多的联合国教科文组织世界遗产[29][30][31]。2015年其为世界访客数量第十的国家,国际来访人次达2910万[32][33]。墨西哥为联合国、世界贸易组织、G20峰会和团结谋共识成员国,2014年起成为法语圈国际组织观察员。
Mexiko (spanisch: México oder Méjico [ˈmexiko], nahuatl: Mexihco [meː'ʃiʔko]), amtlich Vereinigte Mexikanische Staaten, spanisch: Estados Unidos Mexicanos, ist eine Bundesrepublik in Nordamerika, die 31 Bundesstaaten und den Hauptstadtdistrikt Mexiko-Stadt umfasst. Im Norden grenzt Mexiko an die Vereinigten Staaten von Amerika (USA), im Süden und Westen an den Pazifischen Ozean, im Südosten an Guatemala, Belize und an das Karibische Meer, im Osten an den Golf von Mexiko. Mit einer Gesamtfläche von fast zwei Millionen Quadratkilometern ist Mexiko das fünftgrößte Land auf dem amerikanischen Doppelkontinent, global liegt das Land an vierzehnter Stelle. Weltweit liegt Mexiko mit einer Bevölkerungszahl von etwa 125 Millionen Menschen auf Platz elf und ist das einwohnerreichste spanischsprachige Land.
メキシコ合衆国(メキシコがっしゅうこく、スペイン語: Estados Unidos Mexicanos)、通称メキシコは、北アメリカ南部に位置する連邦共和制国家。北にアメリカ合衆国と南東にグアテマラ、ベリーズと国境を接し、西は太平洋、東はメキシコ湾とカリブ海に面する。首都はメキシコシティ。メキシコの総人口は約1億3,000万人(2016年時点)で、スペイン語圏においてはもっとも人口の多い国である。GDPは中南米2位[注釈 1]。
Mexico (Spanish: México [ˈmexiko] (![]() listen); Nahuan languages: Mēxihco), officially the United Mexican States (Spanish: Estados Unidos Mexicanos; EUM [esˈtaðos uˈniðoz mexiˈkanos] (
listen); Nahuan languages: Mēxihco), officially the United Mexican States (Spanish: Estados Unidos Mexicanos; EUM [esˈtaðos uˈniðoz mexiˈkanos] (![]() listen)), is a country in the southern portion of North America. It is bordered to the north by the United States; to the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; to the southeast by Guatemala, Belize, and the Caribbean Sea; and to the east by the Gulf of Mexico.[10] Mexico covers 1,972,550 square kilometers (761,610 sq mi)[11] and has approximately 128,649,565 inhabitants,[4] making it the world's 13th-largest country by area, 10th-most populous country, and most populous Spanish-speaking nation. It is a federation comprising 31 states and Mexico City,[12] its capital city and largest metropolis. Other major urban areas include Guadalajara, Monterrey, Puebla, Toluca, Tijuana, Ciudad Juárez, and León.[13]
listen)), is a country in the southern portion of North America. It is bordered to the north by the United States; to the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; to the southeast by Guatemala, Belize, and the Caribbean Sea; and to the east by the Gulf of Mexico.[10] Mexico covers 1,972,550 square kilometers (761,610 sq mi)[11] and has approximately 128,649,565 inhabitants,[4] making it the world's 13th-largest country by area, 10th-most populous country, and most populous Spanish-speaking nation. It is a federation comprising 31 states and Mexico City,[12] its capital city and largest metropolis. Other major urban areas include Guadalajara, Monterrey, Puebla, Toluca, Tijuana, Ciudad Juárez, and León.[13]
Pre-Columbian Mexico traces its origins to 8,000 BC and is identified as one of six cradles of civilization;[14] it was home to many advanced Mesoamerican civilizations, most well-known among them the Maya and the Aztecs. In 1521, the Spanish Empire conquered and colonized the territory from its base in Mexico City, which then became known as New Spain. The Catholic Church played an important role as millions of indigenous inhabitants converted. These populations were heavily exploited to mine rich deposits of precious material, which became a major source of wealth for the Spanish.[15] Mexico became an independent nation state after the successful Mexican War of Independence against Spain in 1821.[16]
The War of Texas Independence in 1836 and the Mexican–American War led to huge territorial losses in Mexico's sparsely populated north, contiguous to the United States. The newly instituted reforms that granted protection to indigenous communities, and curtailed the power of the military and the church, were enshrined in the Constitution of 1857. This triggered the War of the Reform and French intervention. Maximilian Habsburg was installed as emperor by France and Benito Juárez kept an opposing republican government in exile. The following decades were marked by instability and dictatorship of Porfirio Díaz, who sought to modernize Mexico and restore order.[16] The Porfiriato ended with the Mexican Revolution in 1910 and the winning Constitutionalist faction drafted a new 1917 Constitution. The revolutionary generals of the winning northern faction dominated the 1920s and served as presidents, but the 1928 assassination of Alvaro Obregón led to the formation of the Institutional Revolutionary Party in 1929, under which Mexico was a one-party state until 2000.[17][18][19][20]
Mexico is a developing country, ranking 76th on the Human Development Index, but is considered a newly industrialized state by several analysts.[21][22][23][24] It has the world's 15th-largest economy by nominal GDP and the 11th-largest by PPP, with the United States being its largest economic partner.[25][26] The large economy, area, population and politics make Mexico a regional power and a middle power,[27][28][29][30] and is often identified as an emerging power.[31] However, Mexico continues to struggle with social inequalities, poverty and extensive crime; the country ranks poorly on the Global Peace Index.[32] Since 2006, the conflict between the government and drug trafficking syndicates lead to over 120,000 deaths.[33]
Mexico ranks first in the Americas and 7th in the world for the number of UNESCO World Heritage Sites.[34][35][36] Mexico is an ecologically megadiverse country, ranking 5th in the world for its natural biodiversity.[37] Mexico receives a significant number of tourists every year; in 2018, it was the 6th most-visited country in the world, with 39 million international arrivals.[38] Mexico is a member of the United Nations (UN), the World Trade Organization (WTO), the G8+5, the G20, the Uniting for Consensus group of the UN, and the Pacific Alliance trade bloc.
Le Mexique, en forme longue les États-Unis Mexicains11,12,13, en espagnol México et Estados Unidos Mexicanos14 ou EUM, est un pays situé dans la partie méridionale de l'Amérique du Nord.
Délimité à l'est-sud-est par le Guatemala et le Belize, et au nord-nord-ouest par les États-Unis d'Amérique, il est bordé à l'est par le Golfe du Mexique et la mer des Caraïbes et au sud-ouest par l'océan Pacifique. C'est le quatorzième pays en superficie, avoisinant 2 millions de km2.
Avec une population estimée en mai 2018 à 130,5 millions d'habitants par l'Organisation des Nations unies15, le Mexique se classe au onzième rang mondial des pays les plus peuplés16. Plus de 98 % des Mexicains parlent l'espagnol mexicain, et plus de 7 millions (environ 6 %) parlent une langue indigène ; la loi mexicaine les reconnaît comme langues nationales depuis 2003, mais aucune ne possède le statut de langue officielle. Politiquement, le Mexique est une république constitutionnelle fédérale, composée de trente-deux entités fédératives dont trente et une ont le statut d'État, Mexico n'ayant pas ce statut17 car abritant la capitale politique du pays18.
La présence humaine au Mexique remonte à plus de 30 000 ans avant le présent19,20,21. Après des millénaires de développement culturel sont apparues les cultures mésoaméricaines, aridaméricaines et oasisaméricaines. Avant les premiers contacts avec les Européens, vivaient diverses civilisations, telles que les Olmèques, les Toltèques, les Zapotèques, les Mayas, et les Aztèques. En 1521, l'Espagne conquit et colonisa le territoire depuis Mexico-Tenochtitlan, qui devint la capitale de la vice-royauté de Nouvelle-Espagne. Après près de trois cents ans de colonisation espagnole, le territoire débuta une guerre d'indépendance contre l'Espagne en 1810, qui dans la foulée déclara sa séparation en 1813 pour établir le Mexique, avant de sortir victorieux en 1821. Le pays connaît ensuite un demi-siècle d'instabilité politique et financière, caractérisé par divers conflits dont une tentative de reconquête par l'Espagne en 1829, la guerre des Pâtisseries, une guerre contre les États-Unis, une guerre civile, une intervention française, trois républiques et deux Empires. Durant la présidence de Porfirio Díaz, le pays a connu une période de modernisation et de croissance économique importante. Díaz fut renversé à la suite d'une révolution en 1910, qui culmina avec la constitution de 1917 et la mise en place du système politique actuel.
Le Mexique fait partie des vingt premières puissances économiques mondiales (quinzième avec un PIB de 1 149 milliards de dollars en 2017)22. Mesuré en parité de pouvoir d'achat, son PIB arrive à la onzième place, devant l'Italie23. Le Mexique est le neuvième plus grand producteur de pétrole au monde et le premier producteur d'argent. Puissance émergente, puissance moyenne à l'échelle mondiale et puissance régionale, le Mexique est le premier pays d'Amérique latine à avoir rejoint l'OCDE. Classé parmi les nouveaux pays industrialisés24, il s'agit, selon la Banque mondiale, d'un pays à revenu intermédiaire supérieur. Son économie est fortement liée à celle des États-Unis, par son appartenance à l'ALENA. Selon l'organisation mondiale du tourisme, le Mexique est la principale destination d'Amérique latine et la treizième plus visitée au monde. En plus d’être l'un des dix-sept pays mégadivers de la planète (il abrite de 10 à 12 % de la biodiversité mondiale et comprend plus de douze mille espèces endémiques), il compte 33 sites culturels ou naturels inscrits par l'UNESCO au patrimoine de l'humanité. D'après le rapport de 2013 sur le développement humain El ascenso del sur de l'ONU, l'indice de développement humain du Mexique s'élève à 0,775 unités, et occupe la 61e place mondiale (au côté de l’Indonésie, la Turquie, la Thaïlande, et l'Afrique du Sud) alors qu'en 1980 son indice ne s'élevait qu'à 0,598 unités. Le Mexique est également membre d'institutions internationales de grande envergure, telles que l'ONU, l'OMC et le G20.
Le Mexique était membre de l'Accord de libre-échange nord-américain (ALENA, ou « TLCAN » en espagnol, « NAFTA » en anglais) jusqu’en 2018. Cet accord a été remplacé par l’Accord Canada–États-Unis–Mexique (ACEUM) en décembre 2018, et avec la récente modernisation en 2020 de l'accord de libre-échange entre les États-Unis, le Canada et le Mexique, il s'appelle désormais T-MEC.
Il Messico (spagnolo: México[4]; nahuatl: Mēxihco), ufficialmente gli Stati Uniti Messicani (spagnolo: Estados Unidos Mexicanos; nahuatl: Mēxihcatl Tlacetilīlli Tlahtohcāyōtl), è una democrazia rappresentativa composta da trentuno Stati. Secondo la Costituzione messicana la sede dei poteri della federazione e capitale dello Stato è Città del Messico. Occupa la parte meridionale dell'America settentrionale, e la parte settentrionale dell'America Latina. Il Messico è delimitato a nord dal confine con gli Stati Uniti d'America, a est dal golfo del Messico e dal mare Caraibico, a sud-est dal Belize e dal Guatemala e a ovest dall'oceano Pacifico. Con una superficie di 1.972.550 km² il Messico è il 14° paese più esteso del mondo mentre con 128.649.565 persone[5], oltre ad essere il 10° paese più popoloso del mondo è anche il più popoloso paese ispanofono e il secondo più popoloso di religione cattolica dopo il Brasile. Lo spagnolo è parlato in Messico con molte lingue indigene, ufficialmente riconosciute.
L'insediamento umano in questo territorio risale a circa undicimila anni fa e da allora si succedettero svariati popoli, sia agricoltori della Mesoamerica sia nomadi. Dopo la conquista spagnola il Messico cominciò la sua lotta per l'indipendenza politica nel 1810. In seguito per quasi un secolo il paese è stato coinvolto in una serie di guerre interne e d'invasioni straniere che hanno avuto un impatto forte in tutti gli ambiti della vita messicana. Per la maggior parte del XX secolo (principalmente per la prima metà) si assistette a un periodo di forte crescita economica nel contesto di una politica dominata da un unico partito politico.
Per volume di prodotto interno lordo (PIL) nominale il Messico è considerata la quattordicesima economia mondiale.[2] Tuttavia la distribuzione della ricchezza è estremamente diseguale, tanto che gli indici di sviluppo umano possono variare enormemente fra zona e zona del paese.[6][7] Per una buona parte del XX secolo la principale fonte di ricchezza del paese è stato il petrolio, anche se il processo di industrializzazione del paese ha permesso la diversificazione dell'economia. Le rimesse dei lavoratori all'estero sono aumentate di anno in anno e rappresentano il 3% del PIL costituendo un'importante fonte di valuta estera per il paese, accanto ai proventi delle esportazioni di petrolio e del turismo.[8][9] Dopo la cattura di Pablo Escobar la lotta per il controllo delle rotte della droga per gli Stati Uniti d'America attraverso il Messico ha prodotto una vera e propria guerra civile tra i vari cartelli della droga, che ha portato a oltre 100.000 morti.
Il Messico è una potenza regionale[10][11] e uno dei due paesi dell'America Latina insieme al Cile a essere membro dell'Organizzazione per la cooperazione e lo sviluppo economico (OCSE).
Méxiconota 1 (![]() [ˈmexiko]), oficialmente los Estados Unidos Mexicanos,18192021 es un país soberano ubicado en la parte meridional de América del Norte; su capital y ciudad más poblada es la Ciudad de México.22 Políticamente es una república representativa, democrática, federal y laica, compuesta por 32 entidades federativas (31 estados y una capital federal).2324
[ˈmexiko]), oficialmente los Estados Unidos Mexicanos,18192021 es un país soberano ubicado en la parte meridional de América del Norte; su capital y ciudad más poblada es la Ciudad de México.22 Políticamente es una república representativa, democrática, federal y laica, compuesta por 32 entidades federativas (31 estados y una capital federal).2324
El territorio mexicano tiene una superficie de 1 964 375 km²,25 por lo que es el decimotercer país más extenso del mundo y el tercero más grande de América Latina. Limita al norte con los Estados Unidos de América a lo largo de una frontera de 3155 km, mientras que al sur tiene una frontera de 958 km con Guatemala y 276 km con Belice. Las costas del país limitan al oeste con el océano Pacífico y al este con el golfo de México y el mar Caribe, sumando 9330 km, por lo que es el tercer país americano con mayor longitud de litoral.26
México es el undécimo país más poblado del mundo, con una población estimada en más de 126 millones de personas en 2019.9 La mayoría de ellas tiene como lengua materna el español, al que el estado reconoce como lengua nacional junto a 67 lenguas indígenas propias de la nación,27 si bien en el país se hablan alrededor de 287 idiomas.28 Estas cifras convierten a México en el país con mayor número de hispanohablantes,29 así como en el séptimo país con mayor diversidad lingüística en el mundo.30
La presencia humana en México se remonta a 30 000 años antes del presente.31 Como fruto de miles de años de desarrollo cultural surgieron en el territorio mexicano las culturas mesoamericanas, aridoamericanas y oasisamericanas. El actual territorio central de México fue el principal y mayor escenario del pueblo mexica y, en parte, del pueblo maya, dos de las civilizaciones más importantes de la América precolombina. Durante 300 años, la totalidad del actual territorio formó parte del Virreinato de Nueva España, con capital en la Ciudad de México, siendo una de las entidades más importantes del Imperio Español en América. Tras la dominación española, Nueva España inició la lucha por su independencia política en 1810, que culminó en 1821. Posteriormente, durante cerca de un siglo el país se vio envuelto en una serie de guerras internas e invasiones extranjeras que tuvieron repercusiones en todos los ámbitos de la vida de los mexicanos. Durante buena parte del siglo XX (principalmente el segundo tercio) tuvo lugar un período de gran crecimiento económico en el marco de una política dominada por un solo partido político.
Según la Organización Mundial del Turismo, México es el principal destino turístico de América Latina y el sexto más visitado en el mundo.32 Esto se debe en gran medida a los 34 sitios culturales o naturales que son considerados por la UNESCO como Patrimonio de la Humanidad, y es en este sentido el primero en el continente y sexto en el mundo.
En términos macroeconómicos, por producto interno bruto (PIB) es la decimocuarta economía mundial y la undécima por paridad del poder adquisitivo (PPA); en escala regional, es la segunda economía de América Latina y la cuarta del continente.3334 Según el informe de 2018 de desarrollo humano de la ONU, tiene un índice de desarrollo humano alto de 0.774, y ocupa el lugar 74º en el mundo.35
México también es uno de los países con mayor diversidad de climas en el mundo, considerado uno de los 17 países megadiversos del planeta, es hogar del 10-12 % de la biodiversidad mundial36 y alberga a más de 12 000 especies endémicas.37
Ме́ксика (исп. México [ˈmexiko]), официально — Мексиканские Соединённые Штаты[7] (исп. Estados Unidos Mexicanos) — государство в Северной Америке, на севере граничит с Соединёнными Штатами Америки, на юго-востоке — с Белизом и Гватемалой, на западе омывается водами Калифорнийского залива и Тихого океана, на востоке — водами Атлантического океана, Мексиканского залива и Карибского моря[8]. Крупнейшая испаноязычная страна мира.

 Energy resource
Energy resource

 Energy resource
Energy resource
 *Electrical power
*Electrical power

 Energy resource
Energy resource
 *Renewable energy
*Renewable energy
 Erneuerbare Energie
Erneuerbare Energie
 Erneuerbare Energie
Erneuerbare Energie
 Solar energy
Solar energy
 Mexico
Mexico

 Eat and Drink
Eat and Drink
 Botany
Botany
 Architecture
Architecture
 Music
Music
 History
History
 World Heritage
World Heritage
 Civilization
Civilization
 International cities
International cities
 Economy and trade
Economy and trade
 Climate
Climate
 United Nations
United Nations