
漢德百科全書 | 汉德百科全书
 IT-Times
IT-Times


 *China's political system
*China's political system
 *Political system of the People's Republic of China
*Political system of the People's Republic of China
 China High-end Chip Alliance
China High-end Chip Alliance


 IT-Times
IT-Times
 Ministerium für Informationsindustrie
Ministerium für Informationsindustrie

 Party and government
Party and government

 Party and government
Party and government
 *Regulatory Authority
*Regulatory Authority
 State Key Laboratory of Robotics and Systems
State Key Laboratory of Robotics and Systems
 State Key Laboratory of Software Development Environment
State Key Laboratory of Software Development Environment
 State Key Laboratory of Solidification Processing
State Key Laboratory of Solidification Processing



 China
China
 Guangdong Sheng-GD
Guangdong Sheng-GD


 IT-Times
IT-Times
 Late Classical, Romantic (Early, Middle, Late)
Late Classical, Romantic (Early, Middle, Late)
 Japan
Japan
 Republic of Korea
Republic of Korea
 Shanghai Shi-SH
Shanghai Shi-SH
 Taiwan Sheng-TW
Taiwan Sheng-TW
 United States
United States
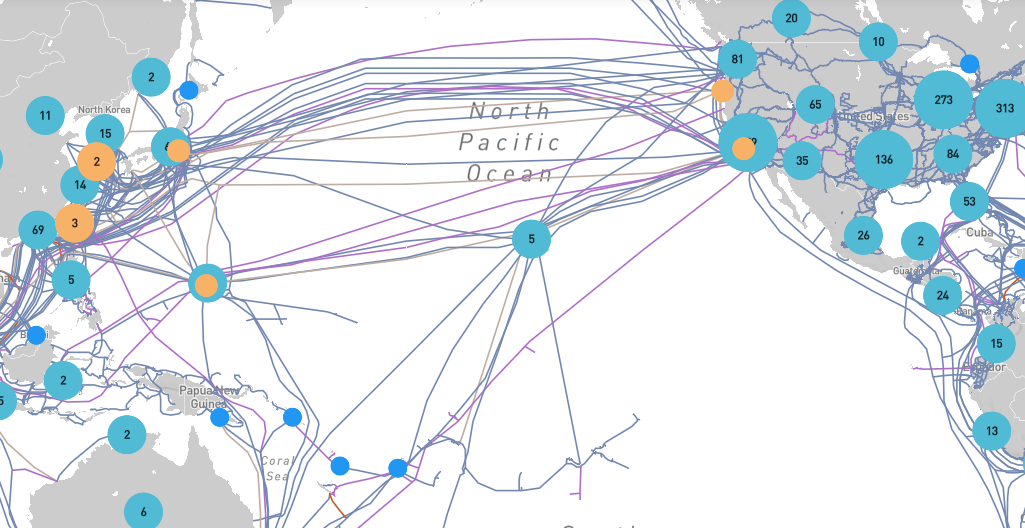
Cable System:
- China-US Cable Network, China-US CN or CUCN
Cable Length:
- 30,800 Km
Design Capacity:
- 80 Gbps (four optical fiber pairs, each of 8x2.488 Gbps SDH over DWDM)
- Constructed as a self-healing ring cable
Lit Capacity:
- 80 Gbps


中央处理器 (英语:Central Processing Unit,缩写:CPU),是计算机的主要设备之一,功能主要是解释计算机指令以及处理计算机软件中的数据。计算机的可编程性主要是指对中央处理器的编程。中央处理器、内部存储器和输入/输出设备是现代计算机的三大核心部件。1970年代以前,中央处理器由多个独立单元构成,后来发展出由集成电路制造的中央处理器,这些高度收缩的组件就是所谓的微处理器,其中分出的中央处理器最为复杂的电路可以做成单一微小功能强大的单元。
中央处理器广义上指一系列可以执行复杂的计算机程序的逻辑机器。这个空泛的定义很容易地将在“CPU”这个名称被普遍使用之前的早期计算机也包括在内。无论如何,至少从1960年代早期开始(Weik 1961),这个名称及其缩写已开始在电子计算机产业中得到广泛应用。尽管与早期相比,“中央处理器”在物理形态、设计制造和具体任务的执行上有了极大的发展,但是其基本的操作原理一直没有改变。
早期的中央处理器通常是为大型及特定应用的计算机而定制。但是,这种昂贵的为特定应用定制CPU的方法很大程度上已经让位于开发便宜、标准化、适用于一个或多个目的的处理器类。这个标准化趋势始于由单个晶体管组成的大型机和微机年代,随着集成电路的出现而加速。IC使得更为复杂的中央处理器可以在很小的空间中设计和制造(在微米的数量级)。中央处理器的标准化和小型化都使得这一类数字设备和电子零件在现代生活中的出现频率远远超过有限应用专用的计算机。现代微处理器出现在包括从汽车到手机到儿童玩具在内的各种物品中。
A central processing unit (CPU) is the electronic circuitry within a computer that carries out the instructions of a computer program by performing the basic arithmetic, logical, control and input/output (I/O) operations specified by the instructions. The computer industry has used the term "central processing unit" at least since the early 1960s.[1] Traditionally, the term "CPU" refers to a processor, more specifically to its processing unit and control unit (CU), distinguishing these core elements of a computer from external components such as main memory and I/O circuitry.[2]
The form, design, and implementation of CPUs have changed over the course of their history, but their fundamental operation remains almost unchanged. Principal components of a CPU include the arithmetic logic unit (ALU) that performs arithmetic and logic operations, processor registers that supply operands to the ALU and store the results of ALU operations and a control unit that orchestrates the fetching (from memory) and execution of instructions by directing the coordinated operations of the ALU, registers and other components.
Most modern CPUs are microprocessors, meaning they are contained on a single integrated circuit (IC) chip. An IC that contains a CPU may also contain memory, peripheral interfaces, and other components of a computer; such integrated devices are variously called microcontrollers or systems on a chip (SoC). Some computers employ a multi-core processor, which is a single chip containing two or more CPUs called "cores"; in that context, one can speak of such single chips as "sockets".[3]
Array processors or vector processors have multiple processors that operate in parallel, with no unit considered central. There also exists the concept of virtual CPUs which are an abstraction of dynamical aggregated computational resources.[4]
Un processeur (ou unité centrale de traitement, UCT, en anglais central processing unit, CPU) est un composant présent dans de nombreux dispositifs électroniques qui exécute les instructions machine des programmes informatiques. Avec la mémoire, c'est notamment l'un des composants qui existent depuis les premiers ordinateurs et qui sont présents dans tous les ordinateurs. Un processeur construit en un seul circuit intégré est un microprocesseur.
L'invention du transistor en 1948 a ouvert la voie à la miniaturisation des composants électroniques. Car auparavant les ordinateurs prenaient la taille d'une pièce entière.
Les processeurs des débuts étaient conçus spécifiquement pour un ordinateur d'un type donné. Cette méthode coûteuse de conception des processeurs pour une application spécifique a conduit au développement de la production de masse de processeurs qui conviennent pour un ou plusieurs usages. Cette tendance à la standardisation qui débuta dans le domaine des ordinateurs centraux (mainframes à transistors discrets et mini-ordinateurs) a connu une accélération rapide avec l'avènement des circuits intégrés. Les circuits intégrés ont permis la miniaturisation des processeurs. La miniaturisation et la standardisation des processeurs ont conduit à leur diffusion dans la vie moderne bien au-delà des usages des machines programmables dédiées.
L'unità di elaborazione centrale (o processore centrale, in inglese central processing unit, in acronimo CPU) è un tipo di microprocessore digitale general purpose che si contraddistingue per sovrintendere a gran parte delle funzionalità del computer digitale basato sull'architettura di von Neumann o sull'architettura Harvard.
È detta unità centrale di elaborazione perché coordina in maniera centralizzata tutte le altre unità di elaborazione presenti nelle architetture hardware dei computer di elaborazione delle varie periferiche interne o schede elettroniche (scheda audio, scheda video, scheda di rete) (es. coprocessore e processore di segnale digitale).
Il compito della CPU è quello di eseguire le istruzioni di un programma presente in memoria centrale o primaria (RAM) dopo averlo prelevato dalla memoria secondaria o di massa, dalla ROM, o da altri dispositivi. Durante l'esecuzione del programma la CPU legge o scrive dati in memoria centrale. Il risultato dell'esecuzione dipende dal dato su cui si opera e dallo stato interno in cui la CPU stessa si trova e può mantenere la traccia delle istruzioni eseguite e dei dati letti (vedi cache).
La unidad central de procesamiento o unidad de procesamiento central (conocida por las siglas CPU, del inglés: central processing unit), es el hardware dentro de un ordenador u otros dispositivos programables, que interpreta las instrucciones de un programa informático mediante la realización de las operaciones básicas aritméticas, lógicas y de entrada/salida del sistema. El término, y su acrónimo, han estado en uso en la industria de la Informática por lo menos desde el principio de los años 1960.1 La forma, el diseño de CPU y la implementación de las CPU ha cambiado drásticamente desde los primeros ejemplos, pero su operación fundamental sigue siendo la misma.
Un ordenador puede tener más de una CPU; esto se llama multiprocesamiento. Todas las CPU modernas son microprocesadores, lo que significa que contienen un solo circuito integrado (chip). Algunos circuitos integrados pueden contener varias CPU en un solo chip; estos son denominados procesadores multinúcleo. Un circuito integrado que contiene una CPU también puede contener los dispositivos periféricos, y otros componentes de un sistema informático; a esto se llama un sistema en un chip (SoC).
Dos componentes típicos de una CPU son la unidad aritmético lógica (ALU), que realiza operaciones aritméticas y lógicas, y la unidad de control (CU), que extrae instrucciones de la memoria, las decodifica y las ejecuta, llamando a la ALU cuando sea necesario.
No todos los sistemas computacionales se basan en una unidad central de procesamiento. Una matriz de procesador o procesador vectorial tiene múltiples elementos de cómputo paralelo, sin una unidad considerada el "centro". En el modelo de computación distribuido, se resuelven problemas mediante un conjunto interconectado y distribuido de procesadores.


 Companies
Companies
 Education and Research
Education and Research
 Traditional medicine
Traditional medicine