
Deutsch-Chinesische Enzyklopädie, 德汉百科
 Peru
Peru
 Abe Shinzō
Abe Shinzō
 Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation,APEC
Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation,APEC
 Barack Obama
Barack Obama
 Enrique Peña Nieto
Enrique Peña Nieto

 Hand in Hand
Hand in Hand
 Hassanal Bolkiah
Hassanal Bolkiah
 Hwang Kyo-ahn
Hwang Kyo-ahn
 John Key
John Key
 Juan Manuel Santos
Juan Manuel Santos
 Justin Trudeau
Justin Trudeau
 Lee Hsien Loong
Lee Hsien Loong
 Leung Chun-ying
Leung Chun-ying
 Malcolm Turnbull
Malcolm Turnbull
 Michelle Bachelet
Michelle Bachelet
 Najib Razak
Najib Razak

 Party and government
Party and government

 Party and government
Party and government
 Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation,APEC
Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation,APEC
 Pedro Pablo Kuczynski
Pedro Pablo Kuczynski
 Peru
Peru
 Peter O’Neill
Peter O’Neill
 Prayut Chan-o-cha
Prayut Chan-o-cha
 Rodrigo Duterte
Rodrigo Duterte

 Wladimir Wladimirowitsch Putin
Wladimir Wladimirowitsch Putin
 Xi Jingping
Xi Jingping


 Anthony Albanese
Anthony Albanese
 Anwar Ibrahim
Anwar Ibrahim
 Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation,APEC
Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation,APEC
 Christopher Luxon
Christopher Luxon
 Dina Boluarte
Dina Boluarte
 Gabriel Boric
Gabriel Boric

 Hand in Hand
Hand in Hand
 Hassanal Bolkiah
Hassanal Bolkiah
 Joe Biden
Joe Biden
 John Lee
John Lee
 Justin Trudeau
Justin Trudeau
 Lawrence Wong
Lawrence Wong
 Lương Cường
Lương Cường
 Paetongtarn Shinawatra
Paetongtarn Shinawatra
 Peru
Peru
 Prabowo Subianto
Prabowo Subianto
 Shigeru Ishiba
Shigeru Ishiba
 Xi Jingping
Xi Jingping
 Yoon Suk-yeol
Yoon Suk-yeol



 Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation,APEC
Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation,APEC

 Australian Capital Territory-ACT
Australian Capital Territory-ACT
 Australia
Australia
 Beijing Shi-BJ
Beijing Shi-BJ

 British Columbia-BC
British Columbia-BC
 Brunei Darussalam
Brunei Darussalam
 Chile
Chile
 China
China

 Hand in Hand
Hand in Hand

 Hawaii-HI
Hawaii-HI
 Hongkong Tebiexingzhengqu-HK
Hongkong Tebiexingzhengqu-HK
 Indonesia
Indonesia
 Japan
Japan
 Canada
Canada
 Kantō
Kantō
 Kinki
Kinki
 Malaysia
Malaysia
 Mexico
Mexico
 New Zealand
New Zealand

 New South Wales-NSW
New South Wales-NSW
 Papua-Neuguinea
Papua-Neuguinea

 Party and government
Party and government

 Party and government
Party and government
 Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation,APEC
Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation,APEC
 Peru
Peru
 Philippines
Philippines
 Republic of Korea
Republic of Korea
 Russia
Russia
 Shanghai Shi-SH
Shanghai Shi-SH
 Singapore
Singapore
 Taiwan Sheng-TW
Taiwan Sheng-TW
 Thailand
Thailand
 United States
United States
 Vietnam
Vietnam

 Washington-WA
Washington-WA

 Important International Organizations
Important International Organizations

亚太经济合作组织(简称亚太经合组织;英语:Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation,缩写:APEC),是亚太区内各地区之间促进经济成长、合作、贸易、投资的论坛。此组织的创办在历史上取代了该区域的冷战结构,但由于日本在该区域会因过去历史记忆引发负面评价,所以由澳大利亚主导创始事项[1]。
始设于1989年,现有21个经济体成员。亚太经合组织是经济合作的论坛平台,其运作是通过非约束性的承诺与成员的自愿,强调开放对话及平等尊重各成员意见,不同于其他经由条约确立的政府间组织。“APEC”与“Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation”均是亚太经济合作组织的注册商标。[2]
Die Asiatisch-Pazifische Wirtschaftsgemeinschaft (für englisch Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation, kurz APEC, auch übersetzt als Asiatisch-Pazifische Wirtschaftskooperation oder Asien-Pazifik-Forum) ist eine internationale Organisation, die es sich zum Ziel gesetzt hat, im pazifischen Raum eine Freihandelszone einzurichten.
In den 21 APEC-Staaten lebt knapp die Hälfte der Weltbevölkerung. Der Wirtschaftsraum erbringt mehr als die Hälfte der Weltwirtschaftsleistung und ist eine der am schnellsten wachsenden Wirtschaftsregionen der Welt.
アジア太平洋経済協力会議(アジアたいへいようけいざいきょうりょくかいぎ、英: Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation)は、環太平洋地域における多国間経済協力を進めるための非公式なフォーラム[2]である。略称、APEC(エイペック[3][4])。
「アジア太平洋」という概念が最初に打ち出されたのは、永野重雄が1967年に発足させた太平洋経済委員会(PBEC)という経済団体の設立時であるとされるが[5][6][7]、具体的にこうした地域概念が政府レベルの協力枠組みに発展する萌芽は、1978年、日本の大平正芳首相が就任演説で「環太平洋連帯構想」を呼びかけたことにある。これを具体化した大平政権の政策研究会「環太平洋連帯研究グループ」(議長:大来佐武郎、幹事佐藤誠三郎)の報告を受け、大平がオーストラリアのマルコム・フレイザー首相に提案して強い賛同を得たことが、1980年9月の太平洋経済協力会議(PECC)の設立につながった。PECCは地域における様々な課題を議論し研究するセミナーといった趣のものであったが、これを土台にして、各国政府が正式に参加する会合として設立されたのが、APECである[8][9]。
APECは、1989年にオーストラリアのホーク首相の提唱で、日本・アメリカ合衆国・カナダ・韓国・オーストラリア・ニュージーランド及び当時の東南アジア諸国連合(ASEAN)加盟6か国の計12か国で発足し、同国のキャンベラで閣僚会議(Ministerial Meeting)を開催した。また、1993年には米国のシアトルで初の首脳会議(Economic Leaders' Meeting)がもたれた。現在は、首脳会議、及び、外相、経済担当相による閣僚会議をそれぞれ年1回開いている。シンガポールに常設事務局を置き、開催国から任期1年で事務局長が選任されている[10]。 参加しているメンバーは、21カ国・地域で、2012年現在、人口では世界の41.4%、GDP(国内総生産)では57.8%、貿易額では47%を占めている。
APECは、開かれた地域協力によって経済のブロック化を抑え、域内の貿易・投資の自由化を通じて、世界貿易機関(WTO)のもとでの多角的自由貿易体制を維持・発展することを目的としてきたが、近年のWTOの新ラウンドの停滞や自由貿易協定締結の動きの活発化などによって、その存在意義が問われている。
Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC) is an inter-governmental forum for 21 Pacific Rim member economies[2] that promotes free trade throughout the Asia-Pacific region. Inspired from the success of Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN)’s series of post-ministerial conferences launched in the mid-1980s, the APEC was established in 1989 in response to the growing interdependence of Asia-Pacific economies and the advent of regional trade blocs in other parts of the world; and to establish new markets for agricultural products and raw materials beyond Europe.[3][4][5] Headquartered in Singapore, the APEC is recognised as one of the oldest forums and highest-level multilateral blocs in the Asia-Pacific region, and exerts a significant global influence.[6][7][8][9][10][11]
An annual APEC Economic Leaders' Meeting is attended by the heads of government of all APEC members except Republic of China (Taiwan) (which is represented by a ministerial-level official under the name Republic of China as economic leader).[12] The location of the meeting rotates annually among the member economies, and a famous tradition, followed for most (but not all) summits, involves the attending leaders dressing in a national costume of the host country. APEC has three official observers: the Association of Southeast Asian Nations Secretariat, the Pacific Economic Cooperation Council and the Pacific Islands Forum Secretariat.[13] APEC's Host Economy of the Year is considered to be invited in the first place for geographical representation to attend G20 meetings following G20 guidelines.[14][15][16][17]
La Coopération économique pour l'Asie-Pacifique (en anglais : Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation, APEC) est un forum économique intergouvernemental visant à faciliter la croissance économique, la coopération, les échanges et l'investissement de la région Asie Pacifique. Elle se réunit chaque année1.
L'Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC), ossia Cooperazione Economica Asiatico-Pacifica, è un organismo nato nel 1989 allo scopo di favorire la cooperazione (o, più in generale, la crescita) economica, il libero scambio e gli investimenti nell'area asiatico-pacifica. Tale area (come suggerisce il logo stesso dell'APEC) coincide non solo con l'Asia Pacifica, ma potenzialmente con l'intero Pacific Rim.
L'APEC ha sede a Singapore, Paese considerato una delle tigri dell'Asia.
Dal punto di vista del diritto internazionale l'APEC si definisce organismo e non organizzazione internazionale perché, essendo composto da economie e non da Stati, è privo di una piena personalità giuridica. Ciò spiega, fra l'altro, come mai possano farne parte contemporaneamente la Cina continentale, Hong Kong e Taiwan, ossia tre realtà che, territorialmente (secondo Pechino e secondo tutti i governi che intrattengono relazioni diplomatiche con Pechino), appartengono a un unico Stato: la Repubblica Popolare di Cina.
APEC (Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation, en español Foro de Cooperación Económica Asia-Pacífico) es un foro multilateral creado en 1989, con el fin de consolidar el crecimiento y la prosperidad de los países del Pacífico, que trata temas relacionados con el intercambio comercial, coordinación económica y cooperación entre sus integrantes.1
Como mecanismo de cooperación y concertación económica, está orientado a la promoción y facilitación del comercio, las inversiones, la cooperación económica y técnica y al desarrollo económico regional de los países y territorios de la cuenca del océano Pacífico. Fomentando un crecimiento económico inclusivo, equitativo, sustentable e innovador.2
La suma del Producto Nacional Bruto de las veintiuna economías que conforman el APEC equivale al 56 % de la producción mundial, en tanto que en su conjunto representan el 46 % del comercio global.
La APEC no tiene un tratado formal. Sus decisiones se toman por consenso y funciona con base en declaraciones no vinculantes. Tiene una Secretaría General, con sede en Singapur, que es la encargada de coordinar el apoyo técnico y de consultoría. Cada año uno de los países miembros es huésped de la reunión anual de la APEC. La vigésimo novena cumbre se realizó en noviembre de 2017 en Da Nang, Vietnam; y la próxima será en Santiago, Chile.
Азиатско-Тихоокеанское экономическое сотрудничество (АТЭС) (англ. Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation, APEC) — форум 21 экономики Азиатско-Тихоокеанского региона для сотрудничества в области региональной торговли и облегчения и либерализации капиталовложений.
Целью АТЭС является повышение экономического роста, процветания в регионе и укрепление азиатско-тихоокеанского сообщества. В экономиках-участницах проживает около 40 % мирового населения, на них приходится приблизительно 54 % ВВП и 44 % мировой торговли[1].




 Egypt
Egypt
 Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan
 Bangladesh
Bangladesh
 Belarus
Belarus
 Chile
Chile
 Columbia
Columbia
 Cuba
Cuba
 Democratic People's Republic of Korea
Democratic People's Republic of Korea

 Hand in Hand
Hand in Hand
 India
India
 Indonesia
Indonesia
 Iraq
Iraq
 Iran
Iran
 Jordan
Jordan
 Cambodia
Cambodia
 Katar
Katar
 Kenya
Kenya
 Kuwait
Kuwait
 Laos
Laos
 Libanon
Libanon
 Malaysia
Malaysia
 Morocco
Morocco

 Mongolei
Mongolei
 Myanmar
Myanmar
 Nepal
Nepal
 Niger
Niger
 Nigeria
Nigeria
 Pakistan
Pakistan
 Palestine
Palestine

 Party and government
Party and government
 Peru
Peru
 Philippines
Philippines
 Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia
 Singapore
Singapore
 Somalia
Somalia
 Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka
 South Africa
South Africa
 Syria
Syria
 Tansania
Tansania
 Thailand
Thailand
 Turkmenistan
Turkmenistan
 Uganda
Uganda
 Uzbekistan
Uzbekistan
 Venezuela
Venezuela
 United Arab Emirates
United Arab Emirates
 Vietnam
Vietnam

 Important International Organizations
Important International Organizations


Afghanistan Ägypten Algerien Angola Antigua und Barbuda Äquatorialguinea Äthiopien Aserbaidschan Bahamas Bahrain Bangladesch Barbados Belarus Belize Benin Bhutan Bolivien Botswana Brunei Burkina Faso Burundi Chile Demokratische Republik Kongo Dominica Dominikanische Republik Dschibuti Ecuador Elfenbeinküste Eritrea Eswatini Fidschi Gabun Gambia Ghana Grenada Guatemala Guinea Guinea-Bissau Guyana Haiti Honduras Indien Indonesien Irak Iran Jamaika Jemen Jordanien Kambodscha Kamerun Kap Verde Katar Kenia Kolumbien Komoren Kuba Kuwait Laos Lesotho Libanon Liberia Libyen Madagaskar Malawi Malaysia Malediven Mali Marokko Mauretanien Mauritius Mongolei Mosambik Myanmar Namibia Nepal Nicaragua Niger Nigeria Nordkorea Oman Osttimor Pakistan Palästina Panama Papua-Neuguinea Peru Philippinen Republik Kongo Ruanda Saint Lucia Sambia São Tomé und Príncipe Saudi-Arabien Senegal Seychellen Sierra Leone Simbabwe Singapur Somalia Sri Lanka St. Kitts und Nevis St. Vincent und die Grenadinen Südafrika Sudan Suriname Syrien Tansania Thailand Togo Trinidad und Tobago Tschad Tunesien Turkmenistan Uganda Usbekistan Vanuatu Venezuela Vereinigte Arabische Emirate Vietnam Zentralafrikanische Republik
Die Bewegung der Blockfreien Staaten (kurz Bewegung der Blockfreien oder Blockfreien-Bewegung, englisch Non-Aligned Movement) ist eine Internationale Organisation von Staaten, deren erklärtes Ziel es war, sich im Ost-West-Konflikt nach dem Zweiten Weltkrieg neutral zu verhalten und keinem der beiden Militärblöcke anzugehören. Die Gründung der Organisation ging auf eine Initiative des jugoslawischen Präsidenten Josip Broz Tito, des ägyptischen Staatschefs Nasser, des indischen Premiers Nehru sowie des indonesischen Präsidenten Sukarno zurück. Die Organisation konstituierte sich 1961 auf ihrer ersten Sitzung in Belgrad.[1] Ihr traten viele ehemalige afrikanische und asiatische Kolonien bei, die sich soeben erst als Staaten konstituiert hatten oder noch um ihre Unabhängigkeit rangen.[2]
Die Organisation verurteilte die Blockbildung in der Zeit des Ost-West-Konfliktes wegen der Gefahr eines Dritten Weltkrieges und setzte sich für die friedliche Koexistenz und Abrüstung ein. Die steigende Zahl der Mitglieder machte es der Organisation jedoch zunehmend schwer, sich auf eine gemeinsame Politik zu einigen. Mit der Auflösung des Warschauer Paktes Anfang der 1990er Jahre verlor sie an Bedeutung. Die heterogene Zusammensetzung der Bewegung machte es schwer, gemeinsame Ziele zu definieren und zu verfolgen.[3] Die Staaten der Blockfreien-Bewegung vertreten 55 Prozent der Weltbevölkerung und halten nahezu zwei Drittel der Sitze in der UN-Generalversammlung.
Das Ziel der Organisation ist die Gleichberechtigung zwischen den Staaten und eine positive wirtschaftliche Entwicklung der Mitgliedstaaten.
不结盟运动(英语:Non-Aligned Movement, NAM)是一个拥有120个成员国和17个观察员国的松散国际组织[3]。它成立于冷战时期,其成员国奉行独立自主的外交政策,不与美苏两个超级大国中的任何一个结盟。联合国中有三分之二的会员是该组织的成员国,全球约55%的人口也生活在不结盟运动国家。不结盟运动定期举行首脑会议,到目前为止已经在前南斯拉夫、埃及、赞比亚、阿尔及利亚、斯里兰卡、古巴、印度、津巴布韦、印尼、哥伦比亚、南非、马来西亚、塞尔维亚、委内瑞拉、阿塞拜疆和乌干达[4]举行会议。
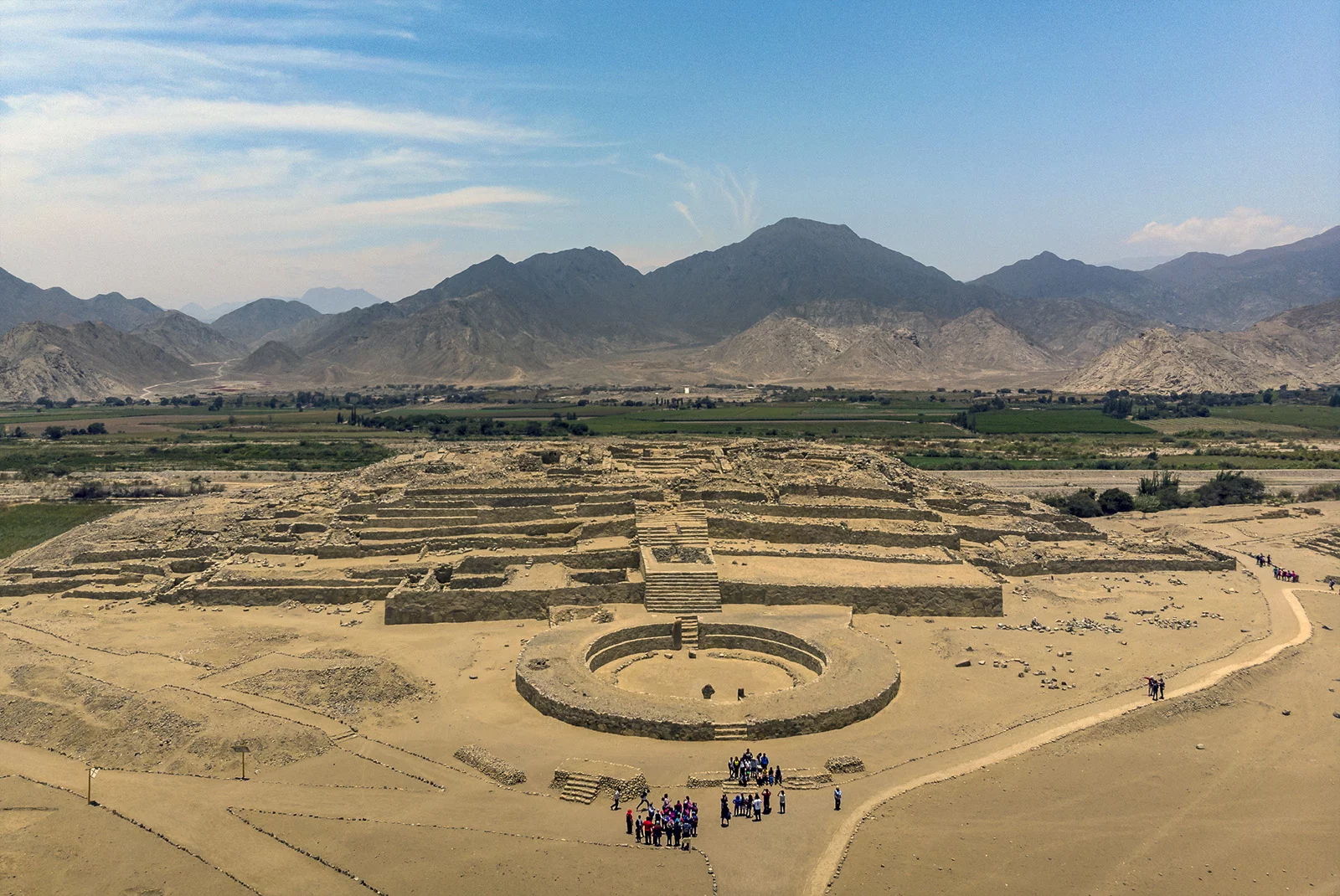


Caral ist die älteste bekannte Stadtsiedlung auf dem amerikanischen Kontinent. Die Siedlung liegt in Peru, etwa 200 km nördlich von Lima und 25 km landeinwärts der Pazifikküste im Tal des meist ausgetrockneten Río Supe. Seit Juni 2009 ist Caral-Supe Teil des UNESCO-Welterbes.

 Economy and trade
Economy and trade
 International cities
International cities
 World Heritage
World Heritage
 Financial
Financial
 Architecture
Architecture
 Religion
Religion
 Geography
Geography
 Important port
Important port
 History
History
 Civilization
Civilization
 Eat and Drink
Eat and Drink