
Deutsch-Chinesische Enzyklopädie, 德汉百科
 Canada
Canada
 Belgium
Belgium
 Brazil
Brazil
 China
China
 Germany
Germany

 Financial
Financial
 International Bank for Cooperation
International Bank for Cooperation
 France
France

 Hand in Hand
Hand in Hand
 India
India
 Iran
Iran
 Italy
Italy
 Japan
Japan
 Canada
Canada
 Netherlands
Netherlands
 Republic of Korea
Republic of Korea
 Russia
Russia
 Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia
 Switzerland
Switzerland
 Spain
Spain
 Turkey
Turkey
 United States
United States
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom

 Washington, D.C.
Washington, D.C.
 World Bank
World Bank
 Barber Benjamin Conable
Barber Benjamin Conable
 World Bank
World Bank
 Alden Winship Clausen
Alden Winship Clausen
 World Bank
World Bank
 Eugene Isaac Meyer
Eugene Isaac Meyer
 World Bank
World Bank
 Eugene Robert Black
Eugene Robert Black
 World Bank
World Bank
 George David Woods
George David Woods
 World Bank
World Bank
 James David Wolfensohn
James David Wolfensohn
 World Bank
World Bank
 Jim Yong Kim
Jim Yong Kim
 World Bank
World Bank
 John Jay McCloy
John Jay McCloy
 World Bank
World Bank
 Lewis Thompson Preston
Lewis Thompson Preston
 World Bank
World Bank
 Paul Wolfowitz
Paul Wolfowitz
 World Bank
World Bank
 Robert Strange McNamara
Robert Strange McNamara
 World Bank
World Bank
 Robert Zoellick
Robert Zoellick
 World Bank
World Bank
 Ajay Banga
Ajay Banga

 Important International Organizations
Important International Organizations

 Economy and trade
Economy and trade
 Economic and political research
Economic and political research

世界银行(英语:World Bank)是为发展中国家资本项目提供贷款的联合国系统国际金融机构[2]。它是世界银行集团的组成机构之一[3],同时也是联合国发展集团(UNDG)的成员。
世界银行的官方目标为消除贫困。根据其有关协定规定(修订并于1989年2月16日生效),其所有决定都必须旨在推动外商直接投资和国际贸易,以及为资本投资提供便利。[4]
世界银行由两个机构组成:国际复兴开发银行与国际开发协会。世界银行与世界银行集团并不一样,后者由国际复兴开发银行、国际开发协会(该两项通称“世界银行”)、国际金融公司、多边投资担保机构以及国际投资争端解决中心等5个机构组成[5]。然而在某些非正式场合,世界银行集团也可被简称为“世银”。目前该组织历代的行长都是美国人,另外重大决议时需要85%的票数才得以通过提案,而美国的投票占比从未低于15%,因而美国的投票比例被俗称为“否决权”。
Die Weltbank (engl. World Bank) bezeichnet im weiten Sinne die in der US-amerikanischen Hauptstadt Washington, D.C. angesiedelte Weltbankgruppe, eine multinationale Entwicklungsbank. Die Weltbankgruppe hatte ursprünglich den Zweck, den Wiederaufbau der vom Zweiten Weltkrieg verwüsteten Staaten zu finanzieren.
Die Weltbankgruppe umfasst die folgenden fünf Organisationen, die jeweils eine eigene Rechtspersönlichkeit besitzen:
- Internationale Bank für Wiederaufbau und Entwicklung (International Bank for Reconstruction and Development, IBRD; die Weltbank im engeren Sinn)
- Internationale Entwicklungsorganisation (International Development Association, IDA)
- Internationale Finanz-Corporation (International Finance Corporation, IFC)
- Multilaterale Investitions-Garantie-Agentur (Multilateral Investment Guarantee Agency, MIGA)
- Internationales Zentrum für die Beilegung von Investitionsstreitigkeiten (International Centre for Settlement of Investment Disputes, ICSID)
Die Organisationen der Weltbankgruppe sind durch verwaltungsmäßige Verflechtungen und durch einen gemeinsamen Präsidenten (im Fall der ICSID als Vorsitzender des Verwaltungsrates) verbunden.
世界銀行(せかいぎんこう、略称:世銀、英語: World Bank)は、各国の中央政府または同政府から債務保証を受けた機関に対し融資を行う国際機関である。本部はアメリカ合衆国ワシントンD.C.。加盟国は189ヶ国。
当初は国際復興開発銀行のみを指したが、1960年に設立された国際開発協会とあわせて世界銀行と呼んでいる。国際通貨基金と共に、第二次世界大戦後の金融秩序制度の中心を担っている。
The World Bank (French: Banque mondiale)[3] is an international financial institution that provides loans[4] to countries of the world for capital projects. It comprises two institutions: the International Bank for Reconstruction and Development (IBRD), and the International Development Association (IDA). The World Bank is a component of the World Bank Group.
The World Bank's most recent stated goal is the reduction of poverty.[5] As of November 2018, the largest recipients of world bank loans were India ($859 million in 2018) and China ($370 million in 2018), through loans from IBRD.[6][7]
La Banque mondiale (parfois abrégée BM) est une institution financière internationale qui accorde des prêts à effet de levier à des pays en développement pour des projets d'investissement.
Elle comprend deux institutions : la Banque internationale pour la reconstruction et le développement (BIRD) et l’Association internationale de développement (AID, IDA en anglais), créées pour lutter contre la pauvreté en apportant des aides, des financements et des conseils aux États en difficulté1.
La Banque mondiale est un sous-ensemble du Groupe de la Banque mondiale. Ce regroupement d'organisations financières internationales est également constitué de la Société Financière Internationale (IFC), de l'Agence Multilatérale de Garantie des Investissements (MIGA) et du Centre international pour le règlement des différends relatifs aux investissements (CIRDI).
Son siège est à Washington D.C. Le président est élu pour cinq ans par le Conseil des administrateurs de la Banque. Elle fait partie des institutions spécialisées du système de l'Organisation des Nations unies (ONU). Elle publie tous les ans une contribution sur un thème du développement dans son World Development Report.
En 2014, elle a accordé 65,6 milliards de dollars de prêts, dons, prises de participations et garanties, dont 20,9 milliards en Afrique et au Moyen-Orient.
La Banca Mondiale (in lingua inglese World Bank) comprende due istituzioni internazionali: la Banca internazionale per la ricostruzione e lo sviluppo (BIRS) e l'Agenzia internazionale per lo sviluppo (AIS o IDA), che si sono prefisse l'obiettivo di lottare contro la povertà e organizzare aiuti e finanziamenti agli stati in difficoltà.[1] La sua sede è a Washington D.C.; il presidente è eletto per cinque anni dal consiglio di amministrazione della banca. Fa parte delle istituzioni specializzate dell'Organizzazione delle Nazioni Unite.
El Banco Mundial (en inglés: World Bank, abreviado: WB) es una organización multinacional especializada en finanzas y asistencia. Se define como una fuente de asistencia financiera y técnica para los llamados países en desarrollo.1 Su propósito declarado es reducir la pobreza mediante préstamos de bajo interés, créditos sin intereses a nivel bancario y apoyos económicos a las naciones en desarrollo. Está integrado por 189 países miembros.2Fue creado en 1944 como parte del Acuerdo de Bretton Woods.3 Tiene su sede en la ciudad de Washington D.C., Estados Unidos.
En 1945, en el marco de las negociaciones previas al término de la Segunda Guerra Mundial, nace lo que a la fecha se conocería como el sistema financiero de Bretton Woods (llamado así por el nombre del complejo hotelero de la ciudad, New Hampshire, donde fue concebido) integrado por dos instituciones fundamentales para entender las políticas de desarrollo que tuvieron lugar a partir de la segunda mitad del siglo XX: el Banco Internacional de Reconstrucción y Fomento (BIRF) y el Fondo Monetario Internacional (FMI).
Concebido el primero, en un principio, con el fin de ayudar a las naciones europeas en la reconstrucción de las ciudades durante la posguerra, poco a poco fue ampliando sus funciones, creándose más organismos que funcionarían paralelamente a este, integrando lo que hoy conocemos como el Grupo del Banco Mundial (GBM).
Всемирный банк (также Мировой банк, англ. The World Bank) — международная финансовая организация, созданная с целью организации финансовой и технической помощи развивающимся странам[1].
В процессе своего развития Всемирный банк претерпевал различные структурные изменения, поэтому под термином Всемирный банк на разных этапах понимались разные организации.
Вначале Всемирный банк ассоциировался с Международным банком реконструкции и развития, осуществлявшим финансовую поддержку в восстановлении после Второй мировой войны Западной Европы и Японии. Позднее в 1960 г. была создана Международная ассоциация развития, которая взяла на себя часть функций, связанных с политикой этого банка.

 Afghanistan
Afghanistan
 Egypt
Egypt
 Albania
Albania
 Angola
Angola
 Antigua and Barbuda
Antigua and Barbuda
 Argentina
Argentina
 Armenia
Armenia
 Australia
Australia
 Bahrain
Bahrain
 Bangladesh
Bangladesh
 Barbados
Barbados
 Belgium
Belgium
 Belize
Belize
 Benin
Benin
 Bolivia
Bolivia
 Botsuana
Botsuana
 Brazil
Brazil
 Brunei Darussalam
Brunei Darussalam
 Bulgaria
Bulgaria
 Burkina Faso
Burkina Faso
 Burundi
Burundi
 Chile
Chile
 China
China
 Columbia
Columbia
 Costa Rica
Costa Rica
 Côte d´Ivoire
Côte d´Ivoire
 Cuba
Cuba
 Denmark
Denmark
 Demokratische Republik Kongo
Demokratische Republik Kongo
 Germany
Germany
 Dominica
Dominica
 Dominikanische Republik
Dominikanische Republik
 Djibouti
Djibouti
 Ecuador
Ecuador
 Estonia
Estonia

 European Union
European Union
 Fidschi
Fidschi

 Financial
Financial
 Finland
Finland
 France
France
 Gabun
Gabun
 Gambia
Gambia
 Georgia
Georgia
 Ghana
Ghana
 Grenada
Grenada
 Greece
Greece
 Guatemala
Guatemala
 Guinea
Guinea
 Guinea-Bissau
Guinea-Bissau
 Guyana
Guyana
 Honduras
Honduras
 Hongkong Tebiexingzhengqu-HK
Hongkong Tebiexingzhengqu-HK
 India
India
 Indonesia
Indonesia
 Ireland
Ireland
 Iceland
Iceland
 Israel
Israel
 Italy
Italy
 Jamaika
Jamaika
 Japan
Japan
 Yemen
Yemen
 Jordan
Jordan
 Cambodia
Cambodia
 Cameroon
Cameroon
 Canada
Canada
 Kap Verde
Kap Verde
 Kasachstan
Kasachstan
 Katar
Katar
 Kenya
Kenya
 Kyrgyzstan
Kyrgyzstan
 Croatia
Croatia
 Kuwait
Kuwait
 Laos
Laos
 Lesotho
Lesotho
 Latvia
Latvia
 Liberia
Liberia
 Liechtenstein
Liechtenstein
 Lithuania
Lithuania
 Luxembourg
Luxembourg
 Macau Tebiexingzhengqu-MO
Macau Tebiexingzhengqu-MO
 Madagaskar
Madagaskar
 Malawi
Malawi
 Malta
Malta
 Morocco
Morocco
 Mauritania
Mauritania
 Mauritius
Mauritius
 Mexico
Mexico
 Moldawien
Moldawien

 Mongolei
Mongolei
 Montenegro
Montenegro
 Mosambik
Mosambik
 Myanmar
Myanmar
 Namibia
Namibia
 Nepal
Nepal
 New Zealand
New Zealand
 Nicaragua
Nicaragua
 Netherlands
Netherlands
 Niger
Niger
 Nigeria
Nigeria
 Nordmazedonien
Nordmazedonien
 Norwegen
Norwegen
 Oman
Oman
 Austria
Austria
 Pakistan
Pakistan
 Panama
Panama
 Papua-Neuguinea
Papua-Neuguinea
 Paraguay
Paraguay
 Peru
Peru
 Philippines
Philippines
 Poland
Poland
 Portugal
Portugal
 Republik El Salvador
Republik El Salvador
 Republik Haiti
Republik Haiti
 Republik Kongo
Republik Kongo
 Republic of Korea
Republic of Korea
 Ruanda
Ruanda
 Romania
Romania
 Russia
Russia
 Salomonen
Salomonen
 Sambia
Sambia
 Samoa
Samoa
 Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia
 Sweden
Sweden
 Sweden
Sweden
 Switzerland
Switzerland
 Genf
Genf
 Senegal
Senegal
 Seychellen
Seychellen
 Sierra Leone
Sierra Leone
 Simbabwe
Simbabwe
 Singapore
Singapore
 Slovakia
Slovakia
 Slovenia
Slovenia
 Spain
Spain
 Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka
 Saint Kitts and Nevis
Saint Kitts and Nevis
 St. Lucia
St. Lucia
 St. Vincent and the Grenadines
St. Vincent and the Grenadines
 South Africa
South Africa
 Suriname
Suriname
 Swasiland
Swasiland
 Tajikistan
Tajikistan
 Taiwan Sheng-TW
Taiwan Sheng-TW
 Tansania
Tansania
 Thailand
Thailand
 Togo
Togo
 Tonga
Tonga
 Trinidad und Tobago
Trinidad und Tobago
 Tschad
Tschad
 Czech Republic
Czech Republic
 Tunisia
Tunisia
 Turkey
Turkey
 Uganda
Uganda
 Ukraine
Ukraine
 Hungary
Hungary
 Uruguay
Uruguay
 Vanuatu
Vanuatu
 Venezuela
Venezuela
 United Arab Emirates
United Arab Emirates
 United States
United States
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 Vietnam
Vietnam

 Important International Organizations
Important International Organizations
 World Trade Organization
World Trade Organization
 Roberto Azevêdo
Roberto Azevêdo
 World Trade Organization
World Trade Organization
 Mike Moore
Mike Moore
 World Trade Organization
World Trade Organization
 Ngozi Okonjo-Iweala
Ngozi Okonjo-Iweala
 World Trade Organization
World Trade Organization
 Pascal Lamy
Pascal Lamy
 World Trade Organization
World Trade Organization
 Peter Sutherland
Peter Sutherland
 World Trade Organization
World Trade Organization
 Renato Ruggiero
Renato Ruggiero
 World Trade Organization
World Trade Organization
 Supachai Panitchpakdi
Supachai Panitchpakdi
 Central African Republic
Central African Republic
 Cyprus
Cyprus


世界贸易组织(简称世贸组织或世贸;英语:World Trade Organization,缩写为 WTO;法语:Organisation Mondiale du Commerce,缩写为 OMC;西班牙语:Organización Mundial del Comercio,缩写为 OMC)是负责监督成员经济体之间各种贸易协议得到执行的一个国际组织,前身是1948年起实施的关税及贸易总协定的秘书处。
世贸总部位于瑞士日内瓦,现任总干事是罗伯托·阿泽维多。截至2016年7月29日,世界贸易组织共有164个成员。[5]世界贸易组织的职能是调解纷争,加入WTO不算签订一种多边贸易协议,但其设置的入会门槛可以做为愿意降低关税、法政上配合、参与国际贸易的门票,它是贸易体制的组织基础和法律基础,是众多贸易协定的管理者,是各成员贸易立法的监督者,是就贸易提供解决争端和进行谈判的场所。该机构是当代最重要的国际经济组织之一,其成员间的贸易额占世界贸易额的绝大多数,被称为“经济联合国”。
Die Welthandelsorganisation (englisch World Trade Organization, WTO; französisch Organisation mondiale du commerce, OMC; spanisch Organización Mundial de Comercio, OMC) ist eine internationale Organisation mit Sitz in Genf, die sich mit der Regelung von Handels- und Wirtschaftsbeziehungen beschäftigt. Sie wurde am 15. April 1994 aus dem General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT) in der Uruguay-Runde nach siebenjähriger Verhandlungszeit gegründet. Am 1. Januar 1995 nahm sie ihre Arbeit in Genf auf. Die WTO ist neben dem IWF und der Weltbank eine der zentralen internationalen Organisationen, die Handels- und Wirtschaftspolitik mit globaler Reichweite verhandelt.
世界貿易機関(せかいぼうえききかん、英: World Trade Organization、略称:WTO)は、自由貿易促進を主たる目的として創設された国際機関である。常設事務局がスイスのジュネーブに置かれている。
GATT(ガット)ウルグアイ・ラウンドにおける合意によって、世界貿易機関を設立するマラケシュ協定(WTO設立協定)に基づいて1995年1月1日にGATTを発展解消させて成立した。
本来GATTは、第二次世界大戦後の安定を見据え、国際通貨基金および国際復興開発銀行とともに設立が予定されていた国際貿易機関(ITO)の設立準備の際に、暫定協定として結ばれたものであった。国際貿易機関の設立が廃案となり、GATTがその代替として発展強化されていくうちに、再びこの分野の常設機関が求められ、WTOが設立されることとなった。発展解消であるため、GATTの事務局及び事務局長もWTOへと引き継がれることとなった[4]。
WTOはGATTを継承したものであるが、GATTが協定(Agreement)に留まったのに対し、WTOは機関(Organization)であるのが根本的な違いである。
を基本原則としている。また、物品貿易だけでなく金融、情報通信、知的財産権やサービス貿易も含めた包括的な国際通商ルールを協議する場である。
対抗処置の発動では、紛争処理機関(パネル)の提訴に対し全加盟国による反対がなければ採択されるというネガティブ・コンセンサス方式(逆コンセンサス方式)を採用した強力な紛争処理能力を持つ。これは国際組織としては稀な例であり、コンセンサス方式を採っていたGATTとの大きな違いで、WTOの特徴の一つといえる。
新多角的貿易交渉(新ラウンド)は、2001年11月にカタールのドーハで行われた第4回WTO閣僚会議で開始を決定し、ドーハ・ラウンドと呼ばれていた。2002年2月1日の貿易交渉委員会で新ラウンドがスタートした。しかし9年に及ぶ交渉は先進国と、急速に台頭してきたBRICsなど新興国との対立によって中断と再開を繰り返した末、ジュネーブで行われた第4回WTO閣僚会議(2011年12月17日)で「交渉を継続していくことを確認するものの、近い将来の妥結を断念する」(議長総括)となり事実上停止状態になった。
その後、2013年のバリ島における閣僚会議で、貿易円滑化協定を含む合意が成立し、2014年7月まで貿易円滑化協定をWTO協定に加える(附属書1Aに追加)するための文書を一般理事会で採択すべきとされた[5]。しかしインドが合意を蒸し返す状態で反対したため期限までに採択できなかった[6]。その後食糧備蓄への補助金の問題で先進国側が譲歩することでようやくインドが合意し、2014年11月27日の一般理事会で貿易円滑化協定が採択された[6]。WTO加盟国の3分の2が改正を受諾した日に発効することになっており、2017年2月22日にこの要件を満たし、協定が発効した。
The World Trade Organization (WTO) is an intergovernmental organization that regulates international trade. The WTO officially commenced on 1 January 1995 under the Marrakesh Agreement, signed by 124 nations on 15 April 1994, replacing the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT), which commenced in 1948. It is the largest international economic organization in the world.[5][6]
The WTO deals with regulation of trade in goods, services and intellectual property between participating countries by providing a framework for negotiating trade agreements and a dispute resolution process aimed at enforcing participants' adherence to WTO agreements, which are signed by representatives of member governments[7]:fol.9–10 and ratified by their parliaments.[8] The WTO prohibits discrimination between trading partners, but provides exceptions for environmental protection, national security, and other important goals.[9] Trade-related disputes are resolved by independent judges at the WTO through a dispute resolution process.[9]
The WTO's current Director-General is Roberto Azevêdo,[10][11] who leads a staff of over 600 people in Geneva, Switzerland.[12] A trade facilitation agreement, part of the Bali Package of decisions, was agreed by all members on 7 December 2013, the first comprehensive agreement in the organization's history.[13][14] On 23 January 2017, the amendment to the WTO Trade Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights (TRIPS) Agreement marks the first time since the organization opened in 1995 that WTO accords have been amended, and this change should secure for developing countries a legal pathway to access affordable remedies under WTO rules.[15]
Studies show that the WTO boosted trade,[16][17][9] and that barriers to trade would be higher in the absence of the WTO.[18] The WTO has highly influenced the text of trade agreements, as "nearly all recent [preferential trade agreements (PTAs)] reference the WTO explicitly, often dozens of times across multiple chapters... in many of these same PTAs we find that substantial portions of treaty language—sometime the majority of a chapter—is copied verbatim from a WTO agreement."[19]
L'Organisation mondiale du commerce (OMC ; en anglais : World Trade Organization, WTO, en espagnol : Organización Mundial del Comercio, OMC) est une organisation internationale qui s'occupe des règles régissant le commerce international entre les pays. Au cœur de l'organisation se trouvent les accords de l'OMC, négociés et signés en avril 1994 à Marrakech1 par la majeure partie des puissances commerciales du monde2 et ratifiés par leurs assemblées parlementaires. L'OMC a pour but principal de favoriser l'ouverture commerciale. Pour cela, elle tâche de réduire les obstacles au libre-échange, d'aider les gouvernements à régler leurs différends commerciaux et d'assister les exportateurs, les importateurs et les producteurs de marchandises et de services dans leurs activités.
Depuis 2001, le cycle de négociation mené par l'OMC est le Cycle de Doha3. Bien que l'OMC ne soit pas une agence spécialisée de l'ONU, elle entretient des liens avec cette dernière4. Le siège de l'OMC est au Centre William-Rappard, à Genève. Depuis le 1er septembre 2013, l'organisation est présidée par le Brésilien Roberto Azevêdo qui a été élu directeur général.
L'Organizzazione mondiale del commercio, abbreviato in OMC (in inglese: World Trade Organization, WTO), è un'organizzazione internazionale creata allo scopo di supervisionare numerosi accordi commerciali tra gli stati membri. Vi aderiscono[3] 164 Paesi, a cui se ne aggiungono altri 22 con ruolo di osservatori,[4] comprendendo così oltre il 95% del commercio mondiale di beni e servizi.[5]
La sede dell'OMC si trova, dal 1995, presso il Centro William Rappard a Ginevra, Svizzera.[6]
La Organización Mundial del Comercio (OMC) fue establecida en 1995. Tiene su sede en Ginebra, Suiza, y sus idiomas oficiales son el inglés, el francés y el español. La OMC no forma parte del sistema de las Naciones Unidas, y tampoco de los organismos de Bretton Woods como el Banco Mundial o el FMI.Nota 1
Всеми́рная торго́вая организа́ция (ВТО; англ. World Trade Organization (WTO), фр. Organisation mondiale du commerce (OMC), исп. Organización Mundial del Comercio) — международная организация, созданная 1 января 1995 года с целью либерализации международной торговли и регулирования торгово-политических отношений государств-членов. ВТО образована на основе Генерального соглашения по тарифам и торговле (ГАТТ), заключенного в 1947 году и на протяжении почти 50 лет фактически выполнявшего функции международной организации, но не являвшегося тем не менее международной организацией в юридическом смысле.
ВТО отвечает за разработку и внедрение новых торговых соглашений, а также следит за соблюдением членами организации всех соглашений, подписанных большинством стран мира и ратифицированных их парламентами. ВТО строит свою деятельность, исходя из решений, принятых в 1986—1994 годах в рамках Уругвайского раунда и более ранних договоренностей ГАТТ. Обсуждения проблем и принятие решений по глобальным проблемам либерализации и перспективам дальнейшего развития мировой торговли проходят в рамках многосторонних торговых переговоров (раунды). К настоящему времени проведено 8 раундов таких переговоров, включая Уругвайский, а в 2001 году стартовал девятый в Дохе, Катар. Организация пытается завершить переговоры по Дохийскому раунду переговоров, который был начат с явным акцентом на удовлетворение потребностей развивающихся стран. По состоянию на декабрь 2012 года будущее раунда переговоров в Дохе остаётся неопределённым: программа работы состоит из 21 части, а первоначально установленный окончательный срок 1 января 2005 года был давно пропущен[3]. В ходе переговоров возник конфликт между стремлением к свободной торговле и стремлением множества стран к протекционизму, особенно в плане сельскохозяйственных субсидий. До сих пор эти препятствия остаются главными и мешают любому прогрессу для запуска новых переговоров в рамках Дохийского раунда. По состоянию на июль 2012 года, существуют различные группы переговоров в системе ВТО для решения текущих вопросов в плане сельского хозяйства, что приводит к застою в самих переговорах[4].
Штаб-квартира ВТО расположена в Женеве, Швейцария. Глава ВТО (генеральный директор) — Роберту Карвалью ди Азеведу, в штате самой организации около 600 человек[5].
На 26 апреля 2015 года в ВТО состояли 162 страны[6].
Правила ВТО предусматривают ряд льгот для развивающихся стран. В настоящее время развивающиеся страны — члены ВТО имеют (в среднем) более высокий относительный уровень таможенно-тарифной защиты своих рынков по сравнению с развитыми. Тем не менее, в абсолютном выражении общий размер таможенно-тарифных санкций в развитых странах гораздо выше, вследствие чего доступ на рынки высокопередельной продукции из развивающихся стран серьёзно ограничен[7].
Правила ВТО регулируют только торгово-экономические вопросы. Попытки США и ряда европейских стран начать дискуссию об условиях труда (что позволило бы считать недостаточную законодательную защиту работников конкурентным преимуществом) были отвергнуты из-за протестов развивающихся стран, которые утверждали, что такие меры только ухудшат благосостояние работников в связи с сокращением числа рабочих мест, снижением доходов и уровня конкурентоспособности[7].
Mitglieder der WTO
| Staat | Beitrittsdatum |
|---|---|
| 30. Juni 1995 | |
| 29. Juli 2016 | |
| 8. September 2000 | |
| 23. November 1996 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 5. Februar 2003 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 22. Februar 1996 | |
| 12. September 1995 | |
| 31. Mai 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Dezember 1996 | |
| 3. Juni 1995 | |
| 23. Juli 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 11. Dezember 2001 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 9. März 1995 | |
| 31. Mai 1995 | |
| 21. Januar 1996 | |
| 7. Mai 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 13. November 1999 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 14. Januar 1996 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 23. Oktober 1996 | |
| 14. Juni 2000 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 22. Februar 1996 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 21. Juli 1995 | |
| 25. Oktober 1995 | |
| 31. Mai 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 30. Januar 1996 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 21. April 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 9. März 1995 | |
| 26. Juni 2014 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 11. April 2000 | |
| 13. Oktober 2004 | |
| 13. Dezember 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 23. Juli 2008 | |
| 30. November 2015 | |
| 13. Januar 1996 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 20. Dezember 1998 | |
| 30. April 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1997 | |
| 27. März 1997 | |
| 30. November 2000 | |
| 20. April 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 2. Februar 2013 | |
| 31. Mai 1995 | |
| 10. Februar 1999 | |
| 14. Juli 2016 | |
| 1. September 1995 | |
| 31. Mai 2001 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 17. November 1995 | |
| 29. April 2012 | |
| 31. Mai 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 31. Mai 1995 | |
| 31. Mai 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 31. Mai 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 4. April 2003 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 26. Juli 2001 | |
| 29. Januar 1997 | |
| 26. August 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 23. April 2004 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 3. September 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 13. Dezember 1996 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 9. November 2000 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 6. September 1997 | |
| 9. Juni 1996 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Juli 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 22. Mai 1996 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 22. August 2012 | |
| 26. Juli 1996 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 11. Dezember 2005 | |
| 10. Mai 2012 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 26. April 2015 | |
| 23. Juli 1995 | |
| 5. März 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 30. Juli 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 21. Februar 1996 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 2. März 2013 | |
| 1. Januar 2002 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 31. Mai 1995 | |
| 27. Juli 2007 | |
| 1. März 1995 | |
| 19. Oktober 1996 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 29. März 1995 | |
| 26. März 1995[2] | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 16. Mai 2008 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 10. April 1996 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 1. Januar 1995 | |
| 24. August 2012 | |
| 11. Januar 2007 | |
| 31. Mai 1995 | |
| 30. Juli 1995 |
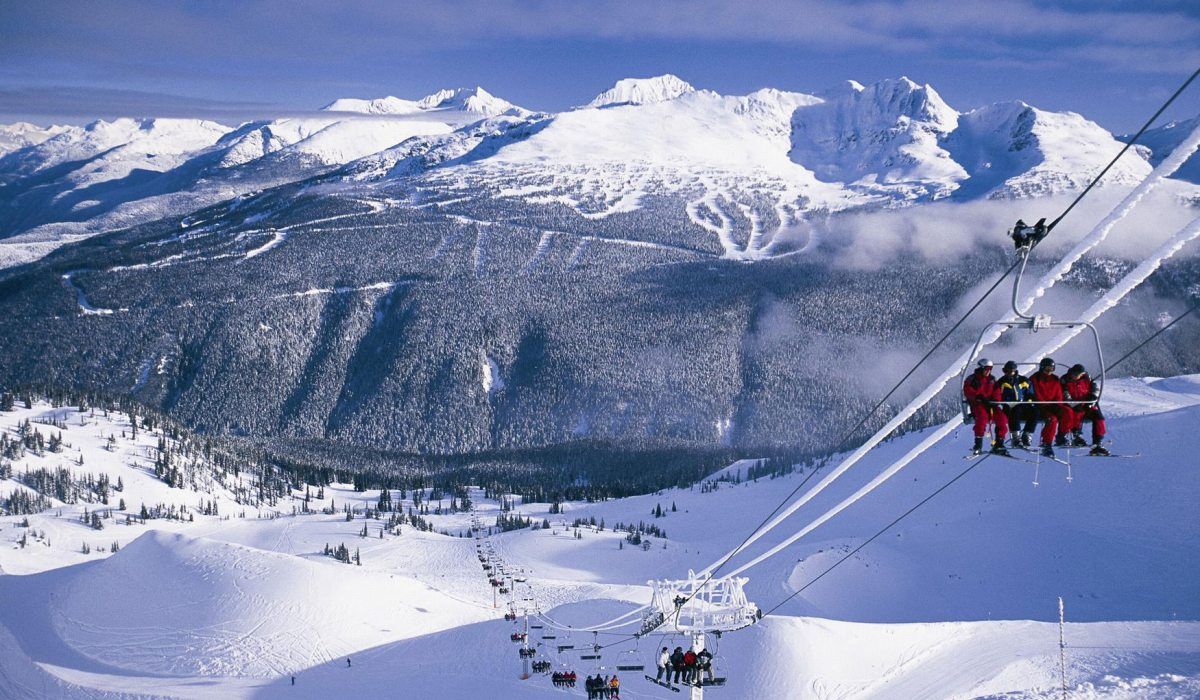

惠 斯勒山滑雪场于1966年启用,占地3,657英亩,标高1,530公尺,共有超过100个滑雪道,是加拿大滑雪道最多的滑雪场。其中有25%的专业滑雪 道、55%为中级滑雪者设计的滑雪道,20%适合初学者所用的滑雪道,3种可供选择,变化很多,惠斯勒的滑雪期亦很长,每年十一月开始至翌年五月终结,有 时会延至八月还可以作夏季滑雪。1988年,惠斯勒山启用了10人高速缆车,运载逐年增加的滑雪人潮;1996年惠斯勒山另设了一条能供6人乘坐的高速缆 车载运上山路线。
惠斯勒除了是被选为全球最佳的“滑雪乐园”,也是世界闻名的理想渡假胜地,其受欢迎的程度完全没有受季节限制,春季滑雪一般开放到五月底左右,由于黑梳山山顶终年积雪,想要享受滑雪乐趣,不见得一定要等到冬季,夏季也到黑梳山顶享受在冰河上滑行的乐趣。


温尼伯(英语:Winnipeg;![]() i/ˈwɪnɪpɛɡ/),加拿大当地粤语人士称之为温尼辟,座落于草原三省东缘,是加拿大第八大城市,也是马尼托巴省省会和该省最大城市,半数以上的马尼托巴省人口集中于此,现有人口约71万[1]。温尼伯的名字源于当地原住民的克里语,意为“浑水”。温尼伯在地理上属于西加拿大。它是一个运输、经济、制造业、农业与教育的重镇。同时也是西加拿大的重要交通枢纽,距美国边境仅96公里。1738年,法国商人在此建立第一个贸易站,在这之前,温尼伯已成为原住民诸部落的贸易中心。1812年,一批苏格兰移民在此定居。1873年,城市人口增至1869人。
i/ˈwɪnɪpɛɡ/),加拿大当地粤语人士称之为温尼辟,座落于草原三省东缘,是加拿大第八大城市,也是马尼托巴省省会和该省最大城市,半数以上的马尼托巴省人口集中于此,现有人口约71万[1]。温尼伯的名字源于当地原住民的克里语,意为“浑水”。温尼伯在地理上属于西加拿大。它是一个运输、经济、制造业、农业与教育的重镇。同时也是西加拿大的重要交通枢纽,距美国边境仅96公里。1738年,法国商人在此建立第一个贸易站,在这之前,温尼伯已成为原住民诸部落的贸易中心。1812年,一批苏格兰移民在此定居。1873年,城市人口增至1869人。
温尼伯的经济由金融、制造、餐饮、文化及旅游组成。城内有理查德森国际机场。由北美一级铁路构筑的城市铁路东西通往加拿大各省,向南则驶往美国。以温尼伯为主场的体育队有:温尼伯蓝色轰炸机队(加拿大式橄榄球)、温尼伯喷射机队(冰球)及温尼伯黄金眼队(棒球)。坐落在温尼伯的大学及学院有:马尼托巴大学、温尼伯大学、加拿大门诺会大学、圣伯尼菲斯大学及红河学院。
温尼伯拥有不同种群的人口,其中菲律宾人占总人口的比例数在加拿大全国为最高,他加禄语也成为城市中使用比例最高的非英语第二语言。然而,其人口的绝大多数仍由欧洲裔构成(如乌克兰人、俄罗斯人、德国人)。其中十分之一以法语为母语。温尼伯亚裔在市中心也建立了唐人街。
Winnipeg [ˈwɪnɪpɛg] ist die Hauptstadt der kanadischen Provinz Manitoba und zugleich deren mit Abstand größte Stadt. Sie zählte im Jahr 2011 über 660.000 Einwohner, die Metropolregion rund 730.000. Damit ist Winnipeg die siebtgrößte Stadt in Kanada.[1] Der Name leitet sich vom 55 Kilometer nördlich gelegenen Winnipegsee her; „win“ bedeutet in der lokalen Cree-Sprache schlammig und „nipee“ Wasser.
Bekannt als Gateway to the West (Tor zum Westen), ist Winnipeg ein Eisenbahn- und Verkehrsknotenpunkt mit einer diversifizierten Wirtschaft. Die Stadt ist multikulturell und Heimat mehrerer Sportvereine. Winnipeg war 1967 erster kanadischer Gastgeber der Panamerikanischen Spiele. Die Stadt ist bekannt für zahlreiche jährliche Festivals, darunter das Winnipeg Folk Festival.
ウィニペグ[2](英語: Winnipeg)は、カナダのマニトバ州南部にある都市。同州最大の都市かつ州都であり、同州の人口の半分以上が当市に集まっている。カナダの小麦生産地帯の中核都市であり、農産物の流通の中心でもある。ウィニペグに住む人たちは通称「Winnipegger(ウィニペガー)」と呼ばれている。
Winnipeg (/ˈwɪnɪpɛɡ/ (![]() listen)) is the capital and largest city of the province of Manitoba in Canada. Centred on the confluence of the Red and Assiniboine rivers, it is near the longitudinal centre of North America, approximately 110 kilometres (70 mi) north of the Canada–United States border.
listen)) is the capital and largest city of the province of Manitoba in Canada. Centred on the confluence of the Red and Assiniboine rivers, it is near the longitudinal centre of North America, approximately 110 kilometres (70 mi) north of the Canada–United States border.
The city is named after the nearby Lake Winnipeg; the name comes from the Western Cree words for muddy water. The region was a trading centre for aboriginal peoples long before the arrival of Europeans. French traders built the first fort on the site in 1738. A settlement was later founded by the Selkirk settlers of the Red River Colony in 1812, the nucleus of which was incorporated as the City of Winnipeg in 1873. As of 2011, Winnipeg is the seventh most populated municipality in Canada.[13] Being far inland, the local climate is extremely seasonal even by Canadian standards with average January lows of around −21 °C (−6 °F) and average July highs of 26 °C (79 °F).[7]
Known as the "Gateway to the West", Winnipeg is a railway and transportation hub with a diversified economy. This multicultural city hosts numerous annual festivals, including the Festival du Voyageur, the Winnipeg Folk Festival, the Jazz Winnipeg Festival, the Winnipeg Fringe Theatre Festival, and Folklorama. Winnipeg was the first Canadian host of the Pan American Games. It is home to several professional sports franchises, including the Winnipeg Blue Bombers (Canadian football), the Winnipeg Jets (ice hockey), Manitoba Moose (ice hockey), Valour FC (soccer), and the Winnipeg Goldeyes (baseball).
Winnipeg est la capitale de la province du Manitoba, la septième ville par la population au Canada.
La cité est située à la confluence des rivières Rouge et Assiniboine, protégée des crues par le canal de dérivation de la rivière Rouge. C'est l'un des plus grands marchés aux grains du monde.
À 95 % anglophone, Winnipeg abrite cependant une communauté francophone, essentiellement regroupée dans le quartier de Saint-Boniface, dont elle représente environ 30 % de la population1.
Winnipeg (IPA: [ˈwɪnɪpɛɡ]; ) è la capitale e la città più popolosa della provincia canadese del Manitoba, possedendo oltre la metà della popolazione del territorio. Situata sul margine orientale della regione delle Praterie canadesi, Winnipeg svolge un ruolo importante nel campo dei trasporti, della finanza, dell'industria, dell'agricoltura e dell'istruzione; è inoltre un nodo fondamentale del traffico autostradale e ferroviario fra est e ovest del Canada, e per questo è definita la «porta dell'ovest»[2][3].
Winnipeg ![]() [ˈwɪnɪpɛɡ] (?·i) es la capital y la ciudad más poblada de la provincia canadiense de Manitoba, localizada en las praderas del Oeste de Canadá.12 Es, además, la séptima ciudad más grande de Canadá, la más importante del centro del país y la ciudad principal de su área metropolitana, la Región de Winnipeg Capital.
[ˈwɪnɪpɛɡ] (?·i) es la capital y la ciudad más poblada de la provincia canadiense de Manitoba, localizada en las praderas del Oeste de Canadá.12 Es, además, la séptima ciudad más grande de Canadá, la más importante del centro del país y la ciudad principal de su área metropolitana, la Región de Winnipeg Capital.
Alrededor de la mitad de la población total de Manitoba reside en la Región de Winnipeg Capital, cuya población es de 730 305 habitantes. La ciudad de Winnipeg cuenta con una población total de 663 617 habitantes (Censo de 2011).3 La ciudad se encuentra en la confluencia de los ríos Rojo y Assiniboine. Caracterizada por un clima riguroso (temperatura media de -19 °C en enero, pero de 19,7 °C en julio) es considerada como una de las grandes ciudades más frías del mundo.
Winnipeg posee edificaciones históricas y numerosos parques, como el Assiniboine Park o el Birds Hill Provincial Park. Por su situación, está también muy próxima a los ríos del Escudo Canadiense y numerosos lagos, entre los que se encuentran el lago de los Bosques, el lago Winnipeg (el decimosegundo más grande del mundo) y el lago Manitoba.4
Ви́ннипег (англ. Winnipeg) — город в Канаде, главный город провинции Манитоба, при впадении реки Ассинибойн в реку Ред-Ривер; коммерческий и транспортный центр Канадского Среднего Запада.



 Ski vacation
Ski vacation
 British Columbia-BC
British Columbia-BC
 Companies
Companies

 IT-Times
IT-Times
 International cities
International cities
 Manitoba-MB
Manitoba-MB
 Animal world
Animal world
 Alberta-AB
Alberta-AB
 Geography
Geography
 Sport
Sport
 Ontario-ON
Ontario-ON
 Architecture
Architecture
 Quebec-QC
Quebec-QC