
Deutsch-Chinesische Enzyklopädie, 德汉百科
 Egypt
Egypt



 Egypt
Egypt
 Australia
Australia
 Belgium
Belgium
 Brazil
Brazil
 Denmark
Denmark
 Germany
Germany
 Finland
Finland
 France
France
 Greece
Greece

 Hand in Hand
Hand in Hand

 Hand in Hand
Hand in Hand
 Driver's license
Driver's license
 India
India
 Indonesia
Indonesia
 Italy
Italy
 Japan
Japan
 Canada
Canada
 Kasachstan
Kasachstan
 Croatia
Croatia
 Malaysia
Malaysia
 Mexico
Mexico

 Mongolei
Mongolei
 New Zealand
New Zealand
 Netherlands
Netherlands
 Useful info
Useful info
 Austria
Austria
 Portugal
Portugal
 Republic of Korea
Republic of Korea
 Russia
Russia
 Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia
 Sweden
Sweden
 Switzerland
Switzerland
 Singapore
Singapore
 Spain
Spain
 South Africa
South Africa
 Thailand
Thailand
 Czech Republic
Czech Republic
 Turkey
Turkey
 Hungary
Hungary

 Vacation and Travel
Vacation and Travel
 United Arab Emirates
United Arab Emirates
 United States
United States
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
国际驾驶执照(International Driving Permit)依照1949年日内瓦国际道路交通公约及1968年维也纳国际道路交通公约,由公约签署国政府签发,方便本国驾驶员在其他签约国驾驶私人车辆。国际驾驶执照为附加在一国驾驶执照之上的一本附加多国语言的说明,标注了驾驶人的基本信息以及允许驾驶的对应车辆种类等,解决驾驶员与其他国家的交通管理部门之间的沟通障碍。国际驾照不能独立存在,当驾驶员同时持有一国驾照与该国政府签发的国际驾照时,此国际驾照才视作有效。[1]
国际驾驶执照之内容及格式依照维也纳道路交通会议制订,但并非各国均批准该公约。
Ein Internationaler Führerschein ist ein Dokument, das von den Straßenverkehrsbehörden oder Automobilclubs[1] eines Landes aufgrund zwischenstaatlicher Verträge ausgestellt wird. Er soll vor allem der Polizei eines anderen Landes die Feststellung ermöglichen, ob ein ausländischer Kraftfahrer die Fahrerlaubnis hat, die für sein aktuelles Fahrzeug erforderlich ist.
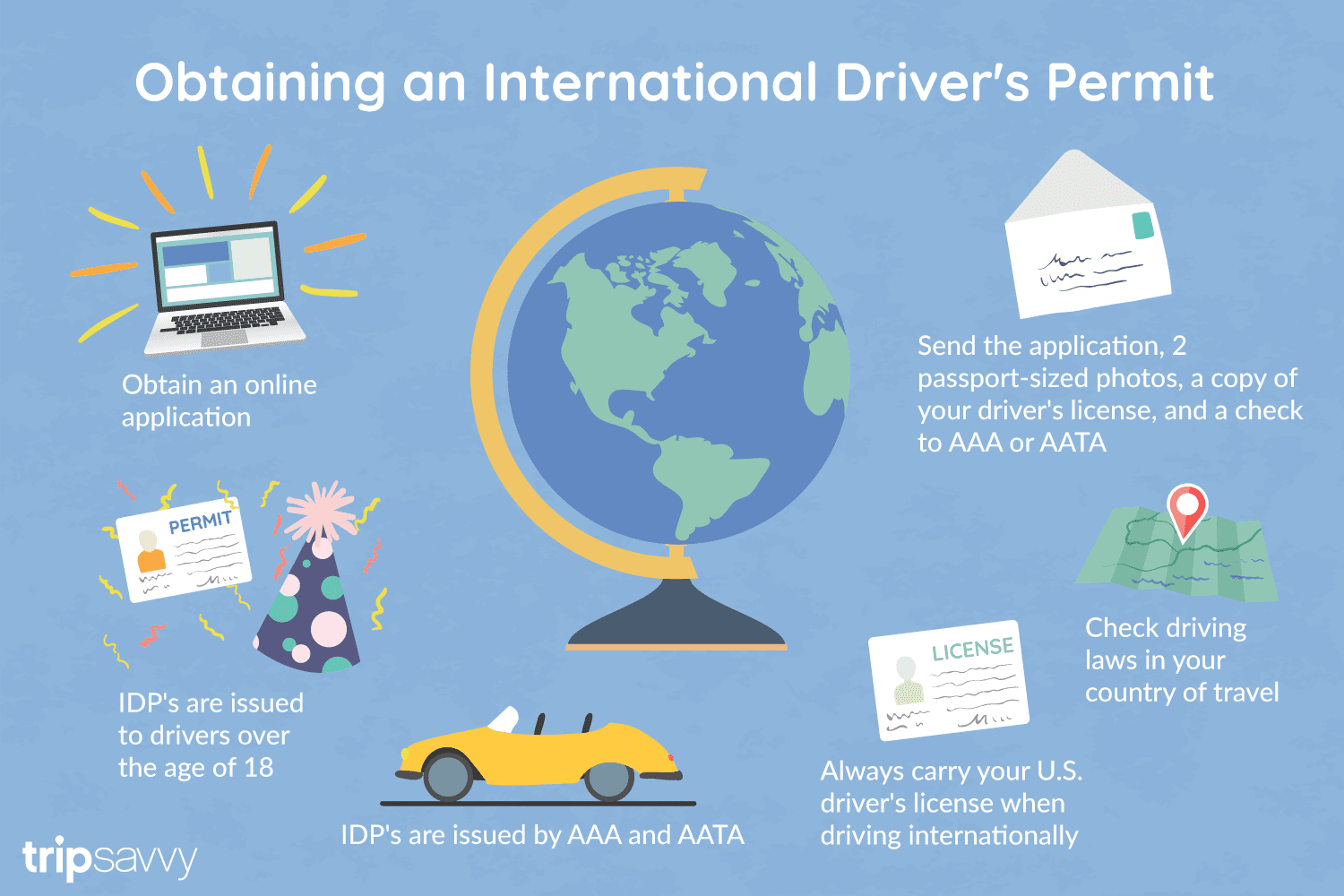
An International Driver's Permit (IDP) allows you to drive a vehicle in another country, as long as you also have a valid driver's license issued by your state. It is also recognized as a proper form of identification in over 175 countries and by many major car rental companies internationally.
Getting an International Driver's Permit (sometimes incorrectly called an international driver's license) can take anywhere from a day to a few weeks, depending on whether you're going through walk-in processing or applying via mail, so make sure to plan ahead if you're planning to drive on your international trip. There are only two locations in the United States that issue these documents: The American Automobile Association (AAA) and the American Automobile Touring Alliance (AATA).
In the United States, International Driver Permits (IDPs) are only issued by the American Automobile Association and the American Automobile Touring Alliance, and the State Department recommends against purchasing an IDP from other outlets as they are all entirely illegal to buy, carry, or sell.
IDPs can be issued to anyone over 18 who has had a valid driver's license for six months or longer. They typically remain valid for one year or the expiration of your existing state driving license. It's essential to investigate an IDP before your trip and make sure you know the requirements.
Both AAA and AATA are excellent sources for these documents, so once you've selected a provider, go to either the AAA's or NAATA's website, print out the International Driving Permit Application, complete all applicable fields, and submit it.
Once you have the application completed, you can send it in via the mail or visit a local office of an organization like AAA; you'll also need two original passport-sized photos and a signed copy of your valid U.S. driver's license as well as an enclosed check for the fee.
Tips to Getting and Using Your Permit
AAA offices can process IDPs during your visit, but processing generally takes 10 to 15 business days if you send the application in. However, expedited services may be available to get your license within one or two business days for an additional fee.
When applying, you'll need a computer and printer, a completed application, a copy of your valid U.S. driver's license, two passport photos, and a check, money order, or credit card to complete the process. Remember to bring these with you if you're applying in person.
Always make sure to carry your valid United States driver's license when driving internationally, as your IDP is invalid without this accompanying proof of eligibility to drive. IDPs only translate domestically-accepted licenses and do not allow those without government-issued driver's licenses to drive abroad.
You'll also want to make sure to enclose the proper fees (the fee for the IDP, as well as any shipping and handling fees), photos, and photocopies of your license when submitting your application to AAA or AATA as omitting any of these required documents will result in your application being rejected.
You should also check the driving requirements and laws for the countries you will be driving in on your vacation, so you'll know what will be required in the event you get stopped by local authorities. (Quelle:https://www.tripsavvy.com/)
 Egypt
Egypt
 Algeria
Algeria
 Indonesia
Indonesia
 Iran
Iran
 Kuwait
Kuwait
 Libya
Libya
 Pakistan
Pakistan
 Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia
 Turkey
Turkey
 United Arab Emirates
United Arab Emirates

 Important International Organizations
Important International Organizations
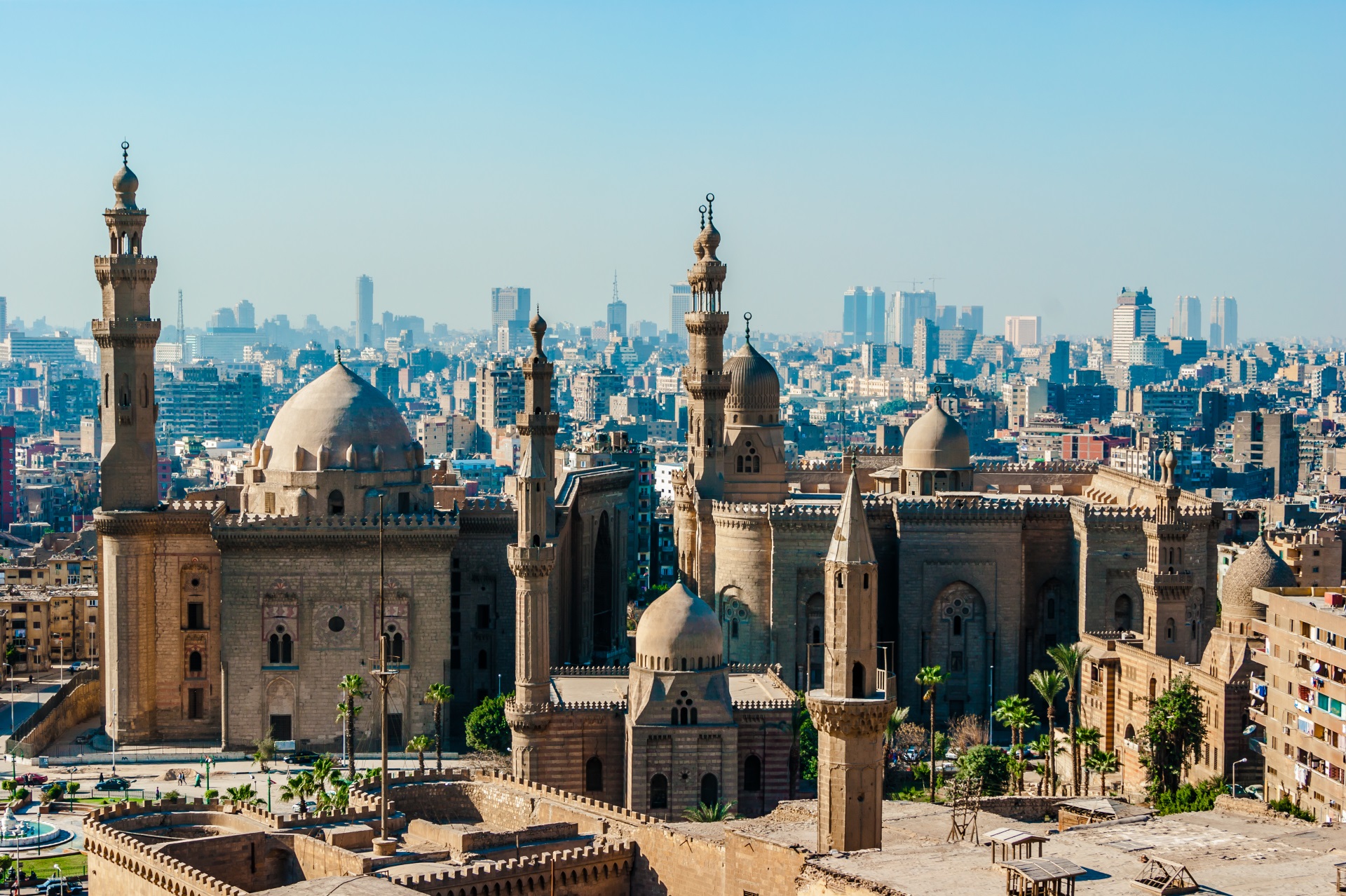






开罗(阿拉伯语:القاهرة,罗马化:al-Qāhirah,IPA:[ælˈqɑːhɪɾɑ] (ⓘ))是埃及的首都,埃及第一大城市以及全国经济、交通和文化中心,该城市横跨尼罗河,是整个中东地区的政治、经济和商业中心。由开罗省、吉萨省和盖勒尤卜省组成,通称大开罗地区,2021年,其区域共具有2130万人口,使得大开罗成为埃及和阿拉伯世界以及非洲最大的城市,是世界第十六大都会区。[1]开罗也是世界上最古老的城市之一,自古埃及时期的孟菲斯遗址(现位于赫勒万省赫勒万)与吉萨金字塔群,再到城市从埃及阿拉伯化之后的第一个首都福斯塔特所发展起来,现在的开罗地区,阿拉伯穆斯林占多数,科普特基督徒也占有较大比例。
开罗的历史中心于1979年被授予世界遗产地位。依照全球化及世界城市研究网络(GaWC)所公布之《世界级城市》名单中,开罗被列为属于BETA+级别的国际都市[6][7]如今,开罗拥有阿拉伯世界历史最悠久、规模最大的文化、影视和音乐产业,以及世界第二古老的高等学府艾资哈尔大学。许多国际媒体、企业和组织在该市设有地区总部;阿拉伯国家联盟的行政中心也设立于此。
目前开罗人口超过1000万,城市面积超过453平方公里,另外约有950万居民居住在城市附近。与许多其他城市一样,开罗也受到空气污染和交通堵塞的困扰。开罗地铁是非洲仅有的两个地铁系统之一(另一个在阿尔及利亚的阿尔及尔) ,位列世界上最繁忙的15个地铁系统之一,每年有超过10亿乘客乘坐。2005年开罗经济位居中东第一,在2010年全球城市指数中位列全球第43位。
Kairo (arabisch القاهرة, DMG al-Qāhira ‚die Starke‘ oder ‚die Eroberin‘[1]) ist die Hauptstadt Ägyptens und die größte Stadt der arabischen Welt. Sie wurde 969 von dem fatimidischen Feldherrn Dschauhar as-Siqillī gegründet. Von Ägyptern wird die Stadt oftmals auch einfach mit dem Landesnamen – مصر, hocharabisch Misr, ägyptisch-arabisch Maṣr – bezeichnet.
Kairo ist das politische, wirtschaftliche und kulturelle Zentrum Ägyptens und der Arabischen Welt. Die Stadt ist Sitz der ägyptischen Regierung, des Parlaments, aller staatlichen und religiösen Zentralbehörden (Mogamma)[2] sowie zahlreicher diplomatischer Vertretungen. Kairo ist der bedeutendste Verkehrsknotenpunkt Ägyptens und besitzt zahlreiche Universitäten, Hochschulen, Theater, Museen sowie Baudenkmäler. Die Altstadt von Kairo ist ein Ensemble islamischer Baukunst und wird seit 1979 von der UNESCO als Weltkulturerbe anerkannt.[3] Die Stadt hat den Status eines Gouvernements und wird von einem Gouverneur regiert, der vom Staatspräsidenten ernannt wird.
Kairo hat 9,1 Millionen Einwohner im administrativen Stadtgebiet (2017)[4] und die Metropolregion ist mit etwa 16,2 Millionen Einwohnern (2009)[5] vor Lagos in Nigeria die größte in Afrika. In Ägypten existiert allerdings keine Meldepflicht, weswegen die angegebenen Einwohnerzahlen Hochrechnungen auf Basis der Volkszählungsergebnisse darstellen. Inoffizielle Schätzungen geben bis zu 25 Millionen Einwohner für den Großraum an, was nahezu ein Drittel der Gesamtbevölkerung Ägyptens bedeuten würde.[6]
カイロ(アラビア語: القاهرة, al-Qāhira, アル・カーヒラ、 発音[ヘルプ/ファイル], コプト語: ⲕⲁϩⲓⲣⲏ, Kahire, 英語: Cairo)は、エジプトの首都。アラブ世界で最も人口の多い都市であり、アラブ世界及び中東を代表する世界都市の一つ。アラブ連盟の本部所在地でもあり、アラブ文化圏の中心都市でもある。
発音[ヘルプ/ファイル], コプト語: ⲕⲁϩⲓⲣⲏ, Kahire, 英語: Cairo)は、エジプトの首都。アラブ世界で最も人口の多い都市であり、アラブ世界及び中東を代表する世界都市の一つ。アラブ連盟の本部所在地でもあり、アラブ文化圏の中心都市でもある。
ナイル川下流河畔の交通の要衝として、中世に建設されてより現在に至るまで長い時代を通じ、イスラム世界の学術・文化・経済の中心都市であり続けた。都市自体の人口は965万6074人(2018年推定[1])、近郊を含めたグレーター・カイロ(カイロ都市圏)の人口は1,591万人で、世界第17位である[2]。『毎日新聞』によれば、カイロ都市圏の人口はその後(2016年時点)約2200万人へ増えた[3]。
アメリカのシンクタンクが2017年に発表した総合的な世界都市ランキングにおいて、世界62位の都市と評価された[4]。アフリカ大陸の都市ではヨハネスブルグに次ぐ2位である。一方、日本の民間研究所が2016年に発表した「世界の都市総合力ランキング」では世界41位と評価されており、アフリカでは1位である[5]。プライスウォーターハウスクーパースが公表した調査によると、カイロの2008年の都市GDPは1450億ドルで、世界第42位、アフリカでは第1位である[6]。
エジプトの乾燥した大地にナイル川が形作った肥沃なデルタ地帯のほぼ南端、要に位置し、河谷を流れてきたナイル川がデルタを形成する、その先端に位置する。エジプトはナイル河谷地方の上エジプトとデルタ地方の下エジプトとに古代エジプト以来、二分されており、その両者の接点にカイロは位置する。イスラム帝国が7世紀にエジプトを征服した時、征服者アラブ人の住まう軍営都市(ミスル)が置かれて以来のエジプトの首府である。
日本語でよく知られる都市名のカイロは、英語名の Cairo に由来しており、現地語であるアラビア語ではカーヒラ(القاهرة ; al-Qāhira、現代エジプト方言ではカーヘラ)という。しかし、現在でもミスル(مصر ; Miṣr、現代エジプト方言ではマスル。元々は「エジプト」を意味する呼称)という通称がよく用いられる。
カイロの中心都市はナイル川の右岸、東側に位置する。ナイルをはさんで対岸の西郊には、ピラミッドで有名なギーザの町がある。町の南は古代エジプトの中心都市の一つ、メンフィスである。
Cairo (/ˈkaɪroʊ/ KY-roh; Arabic: القاهرة, romanized: al-Qāhirah, pronounced [ælˈqɑːhɪɾɑ] ( listen)) is the capital of Egypt and the largest city in the Arab world. Its metropolitan area, with a population of over 20 million, is the largest in Africa, the Arab world, and the Middle East, and the 15th-largest in the world. Cairo is associated with ancient Egypt, as the famous Giza pyramid complex and the ancient city of Memphis are located in its geographical area. Located near the Nile Delta,[4][5] Cairo was founded in 969 AD by the Fatimid dynasty, but the land composing the present-day city was the site of ancient national capitals whose remnants remain visible in parts of Old Cairo. Cairo has long been a centre of the region's political and cultural life, and is titled "the city of a thousand minarets" for its preponderance of Islamic architecture. Cairo is considered a World City with a "Beta +" classification according to GaWC.[6]
listen)) is the capital of Egypt and the largest city in the Arab world. Its metropolitan area, with a population of over 20 million, is the largest in Africa, the Arab world, and the Middle East, and the 15th-largest in the world. Cairo is associated with ancient Egypt, as the famous Giza pyramid complex and the ancient city of Memphis are located in its geographical area. Located near the Nile Delta,[4][5] Cairo was founded in 969 AD by the Fatimid dynasty, but the land composing the present-day city was the site of ancient national capitals whose remnants remain visible in parts of Old Cairo. Cairo has long been a centre of the region's political and cultural life, and is titled "the city of a thousand minarets" for its preponderance of Islamic architecture. Cairo is considered a World City with a "Beta +" classification according to GaWC.[6]
Cairo has the oldest and largest film and music industries in the Arab world, as well as the world's second-oldest institution of higher learning, Al-Azhar University. Many international media, businesses, and organizations have regional headquarters in the city; the Arab League has had its headquarters in Cairo for most of its existence.
With a population of over 9 million[7] spread over 3,085 square kilometers (1,191 sq mi), Cairo is by far the largest city in Egypt. An additional 9.5 million inhabitants live in close proximity to the city. Cairo, like many other megacities, suffers from high levels of pollution and traffic. The Cairo Metro is one of the only two metro systems in Africa (the other being in Algiers, Algeria), and ranks amongst the fifteen busiest in the world,[8] with over 1 billion[9] annual passenger rides. The economy of Cairo was ranked first in the Middle East in 2005,[10] and 43rd globally on Foreign Policy's 2010 Global Cities Index.[11]
Le Caire (en arabe : القاهرة / al-qāhira, « La Victorieuse ») est la capitale et la plus grande ville d'Égypte. Sa population est de plus de vingt-deux millions d'habitants1, ce qui en fait la plus grande ville du Moyen-Orient et la seconde d'Afrique derrière Lagos. Elle serait également la sixième agglomération du monde en 2015. Bien qu'Al-Qāhira soit le nom officiel, en arabe égyptien, elle est plus souvent appelée Masr (le nom arabe de l'Égypte) ou el-Qahéra. Elle est située en amont du delta du Nil, sur les rives du fleuve ainsi que sur quelques îles adjacentes. Elle se trouve au nord du pays, à 178 km au sud-est d'Alexandrie et 127 km à l'ouest du canal de Suez. Les habitants du Caire sont appelés les Cairotes2.
La région de Memphis a longtemps été un centre majeur de l'Égypte antique. Vers le IVe siècle, les Romains établirent la cité-forteresse de Babylone le long de la rive est du Nil. Dès la conquête de l'Égypte par les Arabes en 641, Al-Fustat devient un centre administratif et religieux. Les Fatimides et leur troupes composées de Berbères kotamas d'Algérie fondent le noyau urbain actuel, alors nommé Al-Mansûriyyah, pour en faire leur nouvelle capitale. Située sur la route des épices entre l'Europe et l'Asie, la ville connaît une longue période de prospérité : vers 1340, la population du Caire atteint un demi-million d'habitants, ce qui en faisait déjà l'une des plus grandes villes du monde arabe. La peste noire frappe toutefois la cité plus de cinquante fois entre 1348 et 1517. Sous l'Empire ottoman, la ville perd son statut de capitale au profit d'Istanbul. Devenue capitale de l'Égypte moderne en 1922, elle connaît une forte poussée démographique et devient le centre politique et économique de l'Afrique du Nord et du monde arabe, abritant aujourd'hui un grand nombre de compagnies et d'organisations multinationales, dont la Ligue arabe.
La ville actuelle présente une grande diversité urbanistique et architecturale. Le centre historique de la ville comprend le Vieux Caire (quartier copte où se trouvent la forteresse de Babylone et le musée copte) ainsi que le quartier islamique, classé au patrimoine mondial de l'humanité, où se trouvent la citadelle de Saladin et le grand souk (Khân al-Khalili). Le Caire compte également de nombreuses mosquées, dont la mosquée Al-Azhar qui abrite également l'une des plus anciennes universités au monde. Centre névralgique de la ville moderne, la place Tahrir est devenue l'emblème de la révolution égyptienne de 2011. À l'ouest se trouve la ville de Gizeh et la nécropole antique de Memphis, avec ses trois grandes pyramides, dont la pyramide de Khéops. Au sud se trouve le site de l'antique ville égyptienne de Memphis.
Il Cairo (in arabo: القاهرة, al-Qāhira) è la capitale dell'Egitto, che conta più di 10 milioni di abitanti nel governatorato omonimo e circa 20,4 milioni[3] di residenti nell'area metropolitana adiacente, creando la mega metropoli cariota, la Grande Cairo[4] (in arabo: القاهرة الكبرة, Al-Qāhira al-Qobra): essa è la città africana più popolosa dopo la città nigeriana Lagos. La città è stata fondata sul Nilo.
Nonostante al-Qāhira sia il nome ufficiale della città, il Cairo viene chiamato semplicemente con il nome Egitto, Miṣr (in arabo: مصر) pronunciato Masr in dialetto locale.
El Cairo (en árabe, القاهرة Al-Qāhira 'la fuerte', 'la victoriosa') es la capital de Egipto y de su gobernación (muhafazah o provincia). Es la mayor ciudad del mundo árabe, de Oriente Próximo y de África, y los egipcios la denominan a menudo sencillamente con el nombre del país, مصر, pronunciado en árabe culto Misr y dialecto egipcio Masr.
Su área metropolitana incluye una población aproximada de unos 16 millones de habitantes,3 convirtiendo a El Cairo en la undécima urbe más poblada del mundo Es, también, el área metropolitana más poblada de todo el continente africano.4 Es conocida por los egipcios como la "madre de todas ciudades" y la "ciudad de los mil minaretes".5 También figura junto con Teherán, Estambul, Karachi, Damasco, Bagdad, Kuala Lumpur, Alejandría, La Meca, Casablanca y Yakarta como una de las urbes más importantes del mundo islámico. Fue fundada en el año 116 d. C., en lo que hoy en día se conoce como Viejo Cairo, cuando los romanos reconstruyeron una antigua fortaleza persa junto al río Nilo. Antes de su fundación, Menfis u otras ciudades eran la capital del imperio faraónico. El nombre actual se debe a los fatimíes, que bautizaron la ciudad con el nombre, Al-Qahira. Tras diversas invasiones como la de los mamelucos, otomanos, Napoleón y los británicos, El Cairo se convirtió en capital soberana en 1952.5
El Cairo está ubicada en las riberas e islas del río Nilo, al sur del delta. Hacia el sudoeste se encuentra la ciudad de Guiza y la antigua necrópolis de Menfis, con la meseta de Guiza y sus monumentales pirámides, como la Gran Pirámide. Al sur se encuentra el lugar donde se edificó la antigua ciudad de Menfis.
Каи́р (араб. القاهرة, Эль-Кахира[3] — «победоносная», копт. ⲕⲁϣⲣⲱⲙⲓ Кашроми[4] — «сокрушитель людей») — столица Арабской Республики Египет. Крупнейший город Ближнего Востока и третий по величине город Африки, после Лагоса и Киншасы (без учёта агломерации). Египтяне его часто называют مصر — Маср[5][6], то есть тем же словом, что и всю страну Египет.
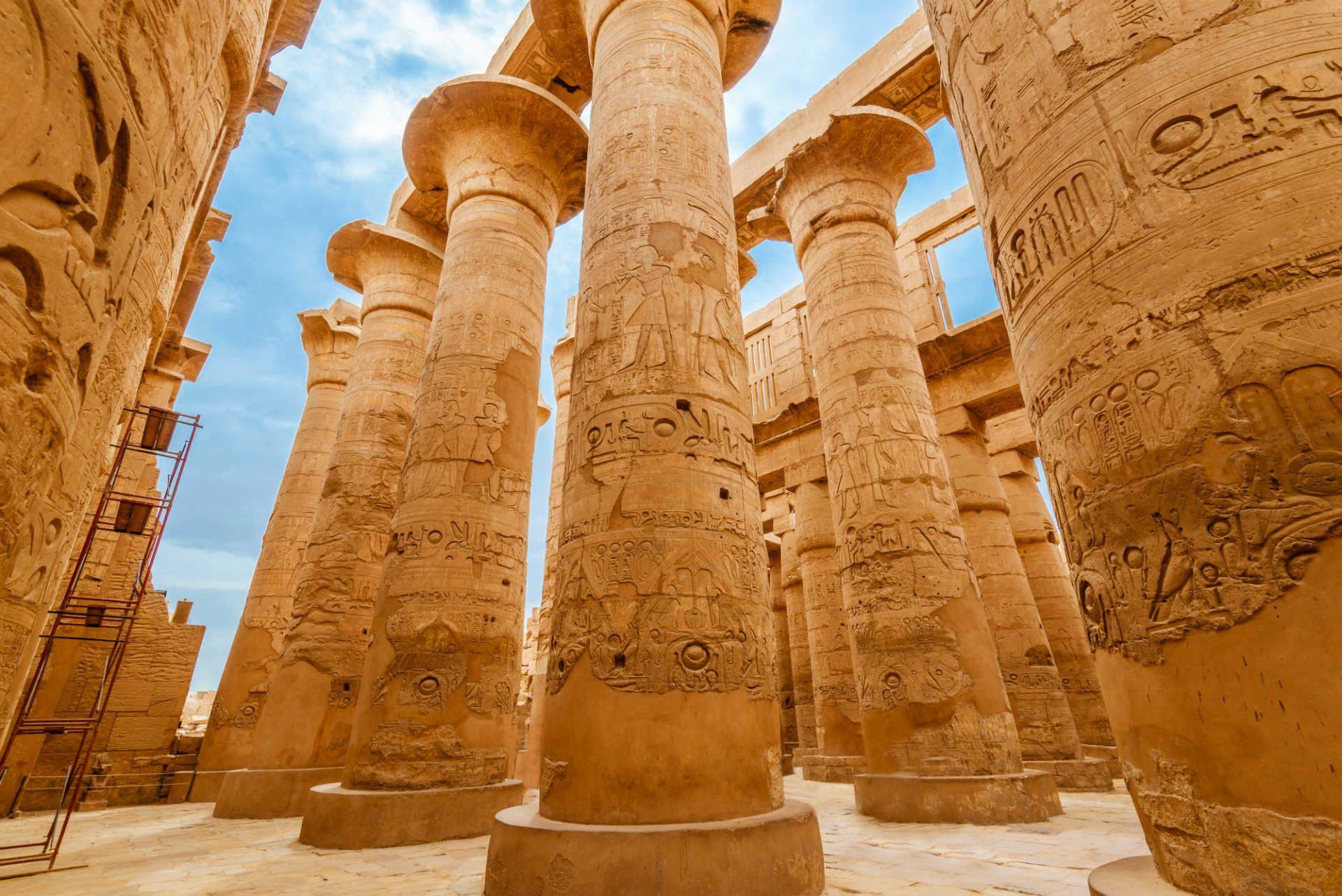


Die Karnak-Tempel liegen als größte Tempelanlage von Ägypten in Karnak, einem Dorf etwa 2,5 Kilometer nördlich von Luxor und direkt am östlichen Nilufer. Die ältesten heute noch sichtbaren Baureste des Tempels stammen aus der 12. Dynastie unter Sesostris I.[1] Bis in die römische Kaiserzeit wurde die Tempelanlage immer wieder erweitert und umgebaut.
Die Tempelanlage steht seit 1979 zusammen mit dem Luxor-Tempel und der thebanischen Nekropole auf der Weltkulturerbeliste der UNESCO.
卡纳克(Karnak)神庙是底比斯最为古老的庙宇,在尼罗河东岸的卢克索镇北4千米处,该神庙经很长时间陆续建造起来,由砖墙隔成三部分。其中中间的部分保存得最完好,也是面积最大的一部分,占地约有30公顷,也是献给太阳神阿蒙的。

Das Katharinenkloster (arabisch دير القدّيسة كاترين, DMG Dair al-Qaddīsa Kātrīn, griechisch Μονὴ τῆς Ἁγίας Αἰκατερίνης Moní tis Agias Ekaterínis, offizieller Name: Ιερά Αυτόνομος Βασιλική Μονή Αγίας Αικατερίνης του Αγίου και Θεοβαδίστου Όρους Σινά Iera Avtónomos Vasilikí Moní Agías Ekaterínis tu Agíu ke Theovadístu Órus Siná „Heiliges autonomes königliches Sankt-Katherinen-Kloster des heiligen, von Gott betretenen Berges Sinai“) ist eines der ältesten Klöster der Christenheit und befindet sich im Süden der Sinai-Halbinsel in Ägypten. In der spätantiken christlichen Pilgertradition war der Gipfel des benachbarten Dschabal Musa jener Ort, an dem Mose von Gott die Zehn Gebote empfangen haben soll. Etwas später ist dann die Verehrung eines Dornbusches am Fuß dieses Berges bezeugt, der mit dem Brennenden Dornbusch, in dem Gott sich Mose offenbarte, identifiziert wurde. Das Dornbusch-Heiligtum befindet sich auf dem Klostergelände.
Wegen seiner isolierten Lage gehört das Katharinenkloster zu den wenigen Klöstern, die seit der Spätantike dauerhaft bewohnt sind und nie zerstört wurden. Die Hauptkirche des Klosters (eine Theotokos-Kirche) ist ein sehr gut erhaltener frühbyzantinischer Kirchenbau, der bauzeitliche Schnitzereien und Mosaike aufweist. Die große Ikonensammlung, zu der Meisterwerke des 6. und 7. Jahrhunderts zählen, ist in ihrer Qualität und Vielfalt einzigartig. Die Handschriften- und Bücherbestände des Sinaiklosters sind nur mit der Vatikanischen Bibliothek vergleichbar.
Im Einflussbereich der historischen Patriarchate Alexandria und Jerusalem gelegen, erlangte das Erzbistum Sinai 1575 seine kirchenrechtliche Autonomie. Das Katharinenkloster bildet heute zusammen mit dem Nonnenkloster im Wadi Firan (Pharan) und wenigen Familien meist griechischer Herkunft am Küstenort at-Tur (Raitho) die Orthodoxe Kirche vom Berg Sinai, die kleinste der autonomen orthodoxen Kirchen. Der Abt (Hegumen) des Klosters ist gleichzeitig der Erzbischof von Sinai, Pharan und Raitho. Er wird von den Mönchen der Sinaitischen Bruderschaft gewählt und vom Jerusalemer Patriarchen geweiht.
圣凯瑟琳修道院(阿拉伯语:دير القدّيسة كاترين,罗马化:Dayr al-Qiddīsa Katrīn、希腊语:Μονὴ τῆς Ἁγίας Αἰκατερίνης,罗马化:Moni tis Agias Aikaterinis)位于埃及西奈半岛南端的西乃山山脚,是一间仍在服务基督徒的古旧修道院,被联合国教科文组织列为世界文化遗产。
修道院由6世纪时在位的东罗马皇帝查士丁尼一世下令兴建。该修道院建于 548 年至 565 年之间,是世界上最古老的基督教修道院之一[1][2]。修道院包含世界上最古老还持续运营的图书馆。

 Afghanistan
Afghanistan
 Egypt
Egypt
 Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan
 Bahrain
Bahrain
 China
China
 India
India
 Iraq
Iraq
 Iran
Iran
 Israel
Israel
 Jordan
Jordan
 Cambodia
Cambodia
 Kasachstan
Kasachstan
 Kyrgyzstan
Kyrgyzstan

 Mongolei
Mongolei
 Pakistan
Pakistan
 Palestine
Palestine
 Republic of Korea
Republic of Korea
 Russia
Russia
 Tajikistan
Tajikistan
 Thailand
Thailand
 Turkey
Turkey
 Uzbekistan
Uzbekistan
 United Arab Emirates
United Arab Emirates
 Vietnam
Vietnam

 Sport
Sport
 Financial
Financial
 Companies
Companies
 Architecture
Architecture
 History
History
 Religion
Religion
 Driving school
Driving school
 International cities
International cities
 Ancient Egypt
Ancient Egypt
 World Heritage
World Heritage
 Civilization
Civilization
