
Deutsch-Chinesische Enzyklopädie, 德汉百科
 European Union
European Union



 European Union
European Union
 Acting heads of government in the European Union
Acting heads of government in the European Union

 Party and government
Party and government
 *President or Chairman
*President or Chairman
 Sergio Mattarella
Sergio Mattarella


Sergio Mattarella (* 23. Juli 1941 in Palermo auf Sizilien) ist ein italienischer Jurist und Politiker (PD). Er ist seit dem 3. Februar 2015 der zwölfte Präsident der Italienischen Republik.
Zuvor war er von 1983 bis 2008 Mitglied der italienischen Abgeordnetenkammer, von 1989 bis 1990 Bildungsminister, von 1999 bis 2001 Verteidigungsminister und von 2011 bis 2015 Verfassungsrichter.
塞尔焦·马塔雷拉(意大利语:Sergio Mattarella,意大利语发音:[ˈsɛrdʒo mattaˈrɛlla],1941年7月23日—),意大利政治家,2015年2月3日就任第12任意大利总统。他1983年至2008年是议员,1989年至1990年担任过教育部长,1999年至2001年任国防部长。2011年出任意大利宪法法院大法官。[1]他毕业于罗马大学(University La Sapienza)法律学院,后在巴勒莫大学任教。其兄皮埃尔桑蒂被暗杀后步入政坛,并在1983年成为众议员,誓要清除黑手党。在2015年1月31日在第四轮投票中以665票赞成(总计1,009票)当选新一任意大利总统,2022年连任总统。


 European Union
European Union
 President of the European Commission
President of the European Commission
 President or Chairman
President or Chairman
 Netherlands
Netherlands
 Sicco Mansholt
Sicco Mansholt
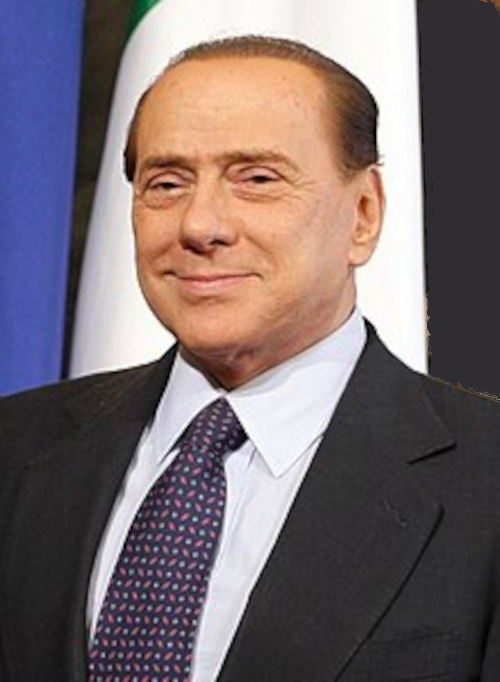



Silvio Berlusconi (* 29. September 1936 in Mailand, Lombardei; † 12. Juni 2023 in Segrate, Metropolitanstadt Mailand) war ein italienischer Politiker und Unternehmer. Er war viermal Ministerpräsident Italiens (1994–1995, 2001–2005, 2005–2006 und 2008–2011) sowie übergangsweise Außen-, Wirtschafts- und Gesundheitsminister. Von 1994 bis 2013 war Berlusconi Mitglied der italienischen Abgeordnetenkammer. Von 2022 bis zu seinem Tod gehörte er dem Senat an, dessen Mitglied er bereits von März bis November 2013 gewesen war. Von der Europawahl 2019 bis Oktober 2022 war er Mitglied des Europäischen Parlaments. Berlusconi war Eigentümer von Fininvest. Laut Forbes-Liste 2023 war er mit einem Vermögen von rund 7 Milliarden US-Dollar einer der reichsten Italiener. Von 1986 bis 2004 und von 2006 bis 2008 war er außerdem Präsident des Fußballvereins AC Mailand.
西尔维奥·贝卢斯科尼(意大利语:Silvio Berlusconi,意大利语发音:[ˈsilvjo berluˈskoːni] (ⓘ);1936年9月29日—2023年6月12日),意大利政治人物、企业家,曾任欧洲议会议员,数度出任意大利总理,同时也是前AC米兰主席、传媒大亨、歌手、富翁。1994年投入意大利政坛以来,始终是主宰着意大利政局的风云核心之一,也是全世界知名度最高的意大利人之一。

 European Union
European Union
 Acting heads of government in the European Union
Acting heads of government in the European Union

 European Union
European Union
 President or Chairman
President or Chairman
 President or Chairman
President or Chairman
 Irland
Irland
 Simon Harris
Simon Harris


西蒙·哈里斯(英语:Simon Harris,1986年10月17日—)是一名爱尔兰政治人物,2024年起担任爱尔兰总理和爱尔兰统一党领袖。哈里斯于2016年起担任爱尔兰政府部长,最近的职位是在2020年至2024年期间担任继续教育、高等教育、研究、创新和科学部长。2011年起,他是威克洛选区的众议院议员,并于2014年至2016年担任国务部长[1][2][3]。Simon Harris (irisch Síomón Ó hEarchaí; * 17. Oktober 1986 in Greystones, Irland) ist ein irischer Politiker. Er gehört der Fine Gael an, deren Vorsitzender er seit März 2024 ist. Seit April 2024 ist er Taoiseach (Regierungschef Irlands).

 Geography
Geography

 Geography
Geography
 ***IMF Developed countries
***IMF Developed countries
 IMF Developed countries
IMF Developed countries
 IMF Developed countries
IMF Developed countries
 TOP5
TOP5

 Mitglieder der NATO
Mitglieder der NATO
 Slovakia
Slovakia

 States of Europe
States of Europe
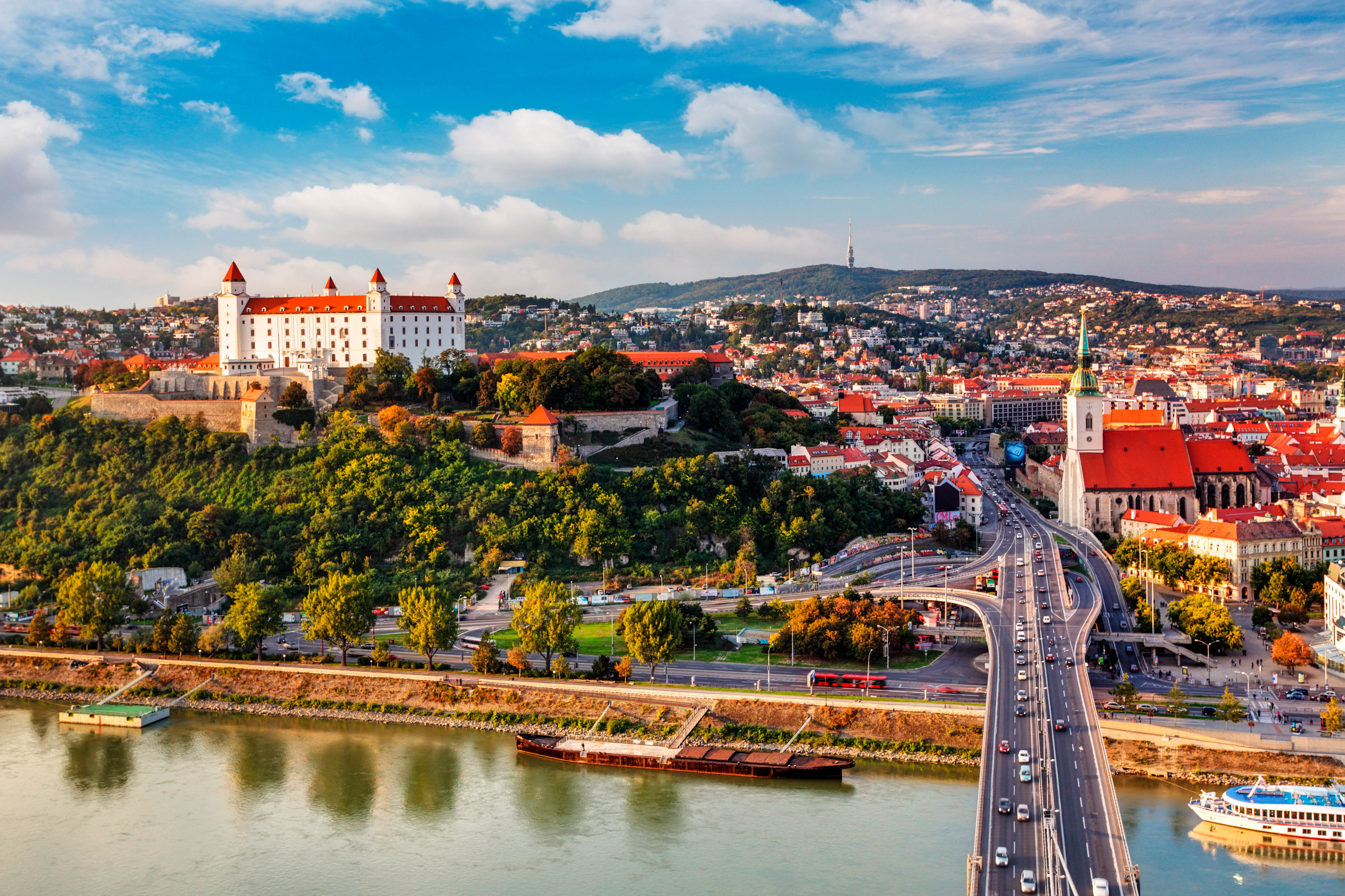

斯洛伐克共和国(斯洛伐克语:Slovenská republika[1][2]![]() i/sloʊˈvækiə, -ˈvɑːk-/;[3][4] ;通称斯洛伐克,斯洛伐克语:Slovensko [ˈslɔʋenskɔ] (
i/sloʊˈvækiə, -ˈvɑːk-/;[3][4] ;通称斯洛伐克,斯洛伐克语:Slovensko [ˈslɔʋenskɔ] (![]() 聆听)),是位于中欧的议会制国家。斯洛伐克的官方语言为斯洛伐克语。其前身为捷克斯洛伐克,于1993年和平分离成捷克与斯洛伐克两个国家。面积约4.9万平方公里,居民约546万。西北邻捷克,北邻波兰,东邻乌克兰,南邻匈牙利,西南邻奥地利,首都和最大城市为布拉迪斯拉发。
聆听)),是位于中欧的议会制国家。斯洛伐克的官方语言为斯洛伐克语。其前身为捷克斯洛伐克,于1993年和平分离成捷克与斯洛伐克两个国家。面积约4.9万平方公里,居民约546万。西北邻捷克,北邻波兰,东邻乌克兰,南邻匈牙利,西南邻奥地利,首都和最大城市为布拉迪斯拉发。
斯洛伐克人系斯拉夫人的一支,祖先于六世纪左右定居斯洛伐克。公元7世纪,同其他部落共组萨摩帝国。公元9世纪,斯洛伐克人建立尼特拉公国,后被摩拉维亚公国征服,并为大摩拉维亚王国的一部分。10世纪,即大摩拉维亚王国解体后,斯洛伐克并入匈牙利公国,并于公元1000年成为匈牙利的构成地域。[5]经1241年和1242年的蒙古西征,该地因征战曾被焚毁殆尽,但随后在匈牙利王贝拉四世的领导下逐渐恢复,他同时也引入日耳曼德意志移民,使德裔民族成为除斯洛伐克人外的主要民族,尤其在中部和东部。[6]
奥匈帝国经一战解体,成立捷克斯洛伐克共和国。在第二次世界大战期间,斯洛伐克成为纳粹德国附庸国。二战结束后,捷克斯洛伐克重获独立。1948年共产党人发动二月政变,使捷克斯洛伐克成为共产主义国家,并接受苏联领导,成为其东方集团成员。随后的二十年里,捷克斯洛伐克民族主义及反共情绪逐渐高涨,这一热潮在布拉格之春达到巅峰;在该年八月份,因苏联武装入侵捷克斯洛伐克平息此运动。1989年,以公民论坛为主导的社会团体发起天鹅绒革命,结束了共产主义统治。1993年1月1日,捷克斯洛伐克议决天鹅绒分离,使斯洛伐克正式成为一个主权独立的国家。
斯洛伐克具有先进的高收入经济,在人类发展指数方面排名较高。在公民自由、新闻自由、网络自由、民主治理方面表现优异。斯洛伐克维持着市场经济与社会保障体系相结合,健全的体制得为全民施行医疗保健、免费教育及欧洲最长的法定带薪育儿假。斯洛伐克同时是北大西洋公约组织、欧洲核子研究组织、欧元区、申根区、联合国、经合组织、世贸组织、欧洲委员会、维塞格拉德集团和欧安组织的成员国[7]。斯洛伐克也是世界上人均汽车生产量最大的国家;直至 2019年共生产了110万辆汽车,占其工业总产量的43%Die Slowakei (slowakisch , amtlich Slowakische Republik, slowakisch ) ist ein Binnenstaat in Mitteleuropa, der an Österreich, Tschechien, Polen, die Ukraine und Ungarn grenzt. Die Hauptstadt und gleichzeitig größte Stadt des Landes ist Bratislava (deutsch Pressburg), weitere wichtige Städte sind Košice (Kaschau), Prešov (Eperies), Žilina (Sillein), Banská Bystrica (Neusohl) und Nitra (Neutra).
Das Land ist zu zwei Dritteln gebirgig und hat einen beträchtlichen Anteil am Karpatenbogen. Im Westen reicht es bis zum nördlich der Donau liegenden Teil des Wiener Beckens, während der Süden und Südosten bis zur Donau und einem kleinen Teil der Theiß durch Ausläufer der Pannonischen Tiefebene geprägt sind. Die Slowakei liegt in der kontinental-gemäßigten Klimazone mit Unterschieden zwischen dem tiefer gelegenen Süden und dem gebirgigen Norden des Landes.
Das Gebiet der heutigen Slowakei wurde am Wendepunkt des 5. und 6. Jahrhunderts von den Slawen besiedelt. Deren erstes politisches Gebilde war das Reich des Samo (7. Jahrhundert), später befand sich in der Slowakei eines der Zentren des frühmittelalterlichen Mährerreiches. Im 11. Jahrhundert wurde die Slowakei in das Königreich Ungarn eingegliedert, das ab 1526 Teil der Habsburgermonarchie und ab 1867 Teil Österreich-Ungarns war. Nach der Auflösung der Doppelmonarchie 1918 wurde die Slowakei Teil der neu gegründeten Tschechoslowakei. Mit deren Zerschlagung durch das Deutsche Reich entstand 1939 der kurzlebige Slowakische Staat. Nach dem Ende des Zweiten Weltkrieges wurde die tschechoslowakische Republik 1945 wiederhergestellt. Am 1. Januar 1993 entstand nach friedlicher Aufteilung der Tschechoslowakei die unabhängige Slowakische Republik als Nationalstaat der Slowaken.
Seit 2004 ist die Slowakei Mitglied der Europäischen Union und der NATO. Im Jahr 2007 wurden gemäß dem Schengen-Abkommen die Grenzkontrollen zu EU-Staaten aufgehoben, 2009 trat die Slowakei der Eurozone bei. Das Land ist eine demokratisch verfasste parlamentarische Republik. Mit Polen, Tschechien und Ungarn bildet die Slowakei die Visegrád-Gruppe.
Das Entwicklungsprogramm der Vereinten Nationen zählt die Slowakei zu den Ländern mit sehr hoher menschlicher Entwicklung.[3]
スロバキア共和国(スロバキアきょうわこく、スロバキア語: Slovenská republika)、通称スロバキアは、中央ヨーロッパの共和制国家。首都はブラチスラヴァで、北西にチェコ、北にポーランド、東にウクライナ、南にハンガリー、南西にオーストリアと隣接する。
国体が常に激しく変化して来た歴史を持つ国家の一つである。古代にはサモ王国[注釈 1](623年 - 658年)・モラヴィア王国として独立を保った期間もあったが、この地のスラブ人は1000年間少数民族としてハンガリー王国の支配下に置かれていた。ハンガリーにとっても歴史的に重要な地域であり、多くのハンガリー人の出身地、ハンガリー貴族の発祥地でもある(元来スラブ系で、ハンガリー文化に同化した者も多い)。第一次世界大戦後、オーストリア・ハンガリー帝国からチェコと合併するかたちで独立し、1989年のビロード革命による共産党政権崩壊を経て、1993年1月1日にチェコスロバキアから分離独立し現在に至る。
Slovakia (/sloʊˈvækiə, -ˈvɑːk-/ (![]() listen);[7][8] Slovak: Slovensko [ˈslɔʋenskɔ] (
listen);[7][8] Slovak: Slovensko [ˈslɔʋenskɔ] (![]() listen)), officially the Slovak Republic (Slovak: Slovenská republika [ˈslɔʋenskaː ˈrepublika] (
listen)), officially the Slovak Republic (Slovak: Slovenská republika [ˈslɔʋenskaː ˈrepublika] (![]() listen)), is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Poland to the north, Ukraine to the east, Hungary to the south, Austria to the southwest, and the Czech Republic to the northwest. Slovakia's mostly mountainous territory spans about 49,000 square kilometres (19,000 sq mi), with a population of over 5.4 million. The capital and largest city is Bratislava, while the second largest city is Košice.
listen)), is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Poland to the north, Ukraine to the east, Hungary to the south, Austria to the southwest, and the Czech Republic to the northwest. Slovakia's mostly mountainous territory spans about 49,000 square kilometres (19,000 sq mi), with a population of over 5.4 million. The capital and largest city is Bratislava, while the second largest city is Košice.
The Slavs arrived in the territory of present-day Slovakia in the 5th and 6th centuries. In the 7th century, they played a significant role in the creation of Samo's Empire. In the 9th century, they established the Principality of Nitra, which was later conquered by the Principality of Moravia to establish Great Moravia. In the 10th century, after the dissolution of Great Moravia, the territory was integrated into the Principality of Hungary, which would then become the Kingdom of Hungary in 1000.[9] In 1241 and 1242, after the Mongol invasion of Europe, much of the territory was destroyed. The area was recovered largely thanks to Béla IV of Hungary, who also settled Germans, leading them to become an important ethnic group in the area, especially in what are today parts of central and eastern Slovakia.[10]
After World War I and the dissolution of Austria-Hungary, the state of Czechoslovakia was established. It was the only country in central and eastern Europe to remain a democracy during the interwar period. Nevertheless, local fascist parties gradually came to power in the Slovak lands, and the first Slovak Republic existed during World War II as a partially-recognized client state of Nazi Germany. At the end of World War II, Czechoslovakia was re-established as an independent country. After a coup in 1948, Czechoslovakia came under communist administration, and became a part of the Soviet-led Eastern Bloc. Attempts to liberalize communism in Czechoslovakia culminated in the Prague Spring, which was crushed by the Warsaw Pact invasion of Czechoslovakia in August 1968. In 1989, the Velvet Revolution peacefully ended the Communist rule in Czechoslovakia. Slovakia became an independent state on 1 January 1993 after the peaceful dissolution of Czechoslovakia, sometimes known as the Velvet Divorce.
La Slovaquie, en forme longue la République slovaque (en slovaque : Slovensko et Slovenská republika), est un pays situé en Europe centrale, au cœur de l'Europe continentale et à l'est de l'Union européenne, dont elle est membre depuis 200417. Ses pays frontaliers sont la Pologne au nord, l'Ukraine à l'est, la Hongrie au sud, l'Autriche à l'ouest et la Tchéquie à l'ouest-nord-ouest17. Coeur de la Grande-Moravie, la Slovaquie fit partie du Royaume de Hongrie à partir du XIè siècle. Du 28 octobre 1918 au 21 mars 1939, puis du 4 avril 1945 au 31 décembre 1992, elle a, avec la Tchéquie, fait partie de la Tchécoslovaquie8,18. De 1939 à 1945 fut constituée, à partir des décombres de la Tchécoslovaquie, une République slovaque - en partie démembrée au profit de la Hongrie - soumise au Troisième Reich.
La Slovaquie est membre de nombreuses organisations internationales, telles que l'ONU19, l'OTAN19, l'OMC20, l'OCDE19 ou encore le V421, et fait partie de la zone euro15.
La Slovacchia (Slovàcchia), ufficialmente Repubblica Slovacca (in slovacco Slovensko o Slovenská republika)[7] è uno Stato senza sbocco al mare costituito come repubblica parlamentare, situato nell'Europa centro-orientale. Ha una popolazione di più di 5 milioni di abitanti e un'area di circa 49.000 chilometri quadrati. La città più grande è anche la capitale, Bratislava, e la seconda città più grande è Košice. Confina con la Repubblica Ceca a nord-ovest, con la Polonia a nord, con l'Ucraina a est, con l'Ungheria a sud e con l'Austria a sud-ovest. È uno Stato membro dell'Unione europea, della NATO, delle Nazioni Unite, dell'OCSE e dell'OMC. La lingua ufficiale è lo slovacco, lingua appartenente al ceppo delle lingue slave.
Gli slavi arrivarono in quello che oggi è il territorio slovacco tra il V e il VI secolo durante le invasioni barbariche. Nel corso della storia, diverse parti del territorio attuale appartennero al Regno di Samo (il primo ente politico conosciuto degli Slavi), al Principato di Nitra, alla Grande Moravia, al Regno d'Ungheria, all'Impero austro-ungarico e alla Cecoslovacchia. Il 30 ottobre 1918 venne approvata la Dichiarazione di Martin o Dichiarazione del popolo slovacco. Uno Stato slovacco indipendente è esistito brevemente durante la seconda guerra mondiale, quale Stato fantoccio della Germania nazista dal 1939 al 1944. Dal 1945 la Slovacchia tornò a far parte nuovamente della Cecoslovacchia. La Repubblica Slovacca e la Repubblica Ceca sono nate il 1º gennaio 1993 dalla divisione, sancita dal parlamento della Cecoslovacchia, che già dal 1990 aveva assunto il nome di Repubblica Federale Ceca e Slovacca.
La Slovacchia rientra nel gruppo degli Stati avanzati. Nel 2004 è entrata a fare parte dell'Unione europea e nel 2009 ha adottato l'euro. La Slovacchia, la Slovenia, l'Estonia, la Lettonia e la Lituania sono gli unici Stati del passato blocco orientale a far parte allo stesso tempo dell'Unione europea, dell'eurozona, della zona Schengen e della NATO.
Eslovaquia (en eslovaco: ![]() Slovensko (?·i)), oficialmente denominada República Eslovaca (en eslovaco:
Slovensko (?·i)), oficialmente denominada República Eslovaca (en eslovaco: ![]() Slovenská republika (?·i)), es uno de los veintisiete Estados soberanos que forman la Unión Europea. Situado en Europa Central, limita al norte con Polonia, al este con Ucrania, al sur con Hungría, al oeste con Austria y al noroeste con República Checa. Tiene una población de 5 389 180 habitantes y su capital es Bratislava, con 425 155 habitantes. Los montes Cárpatos ocupan toda la zona septentrional del país.
Slovenská republika (?·i)), es uno de los veintisiete Estados soberanos que forman la Unión Europea. Situado en Europa Central, limita al norte con Polonia, al este con Ucrania, al sur con Hungría, al oeste con Austria y al noroeste con República Checa. Tiene una población de 5 389 180 habitantes y su capital es Bratislava, con 425 155 habitantes. Los montes Cárpatos ocupan toda la zona septentrional del país.
Слова́кия (словацк. Slovensko [ˈslɔʋɛnskɔ]), официальное название — Слова́цкая Респу́блика (словацк. Slovenská republika) — государство в Центральной Европе. Население составляет 5 443 120 человек (декабрь 2017)[7], территория — 48 845 км². Занимает 112-е место в мире по численности населения и 127-е по территории.
Столица — Братислава. Государственный язык — словацкий.
Унитарное государство, парламентская республика. По состоянию на апрель 2021 года пост президента занимает Зузана Чапутова, премьер-министра — Эдуард Хегер. Подразделяется на 8 краёв.
Расположена в центре Европы. Континентальное государство, не имеющее выхода к морю. Имеет сухопутную границу с Чехией, Австрией, Польшей, Венгрией, Украиной.
Большая часть верующих (около 70 % населения) исповедует католицизм.
Словакия — член НАТО и ЕС. Индустриальная страна с динамично развивающейся экономикой. Объём ВВП за 2011 год составил 127,111 млрд долларов США (около 23 384 долларов на душу населения). Денежная единица — евро.
Независимость страны провозглашена 1 января 1993 года. На протяжении истории территория страны входила в состав многих держав и государственных образований, начиная от Государства Само в VII веке вплоть до Чехословакии в XX веке. В годы Второй мировой войны существовало зависимое от нацистской Германии словацкое государство, которое в 1945 году вновь стало частью Чехословакии.

欧洲社会党(英语:Party of European Socialists,缩写为PES)是一个欧洲政党,其成员是欧盟及周边国家的社会民主主义政党。它是欧洲议会内的一个政党团体,于1992年成立,接替欧洲共同体时代的社会党邦联。目前欧洲社会党主席是来自丹麦社会民主党的波尔·尼鲁普·拉斯穆森(Poul Nyrup Rasmussen)。PES的成员分布在绝大多数欧洲机构内,包括欧洲议会、欧洲委员会、欧盟理事会、欧洲理事会和欧盟地区委员会。
欧洲社会党目前拥有来自25个欧盟国家和挪威的32个正式成员,外加8个准成员党(多数来自未来即将加入欧盟的中东欧国家),和5个观察员员。欧洲社会党宣称他们有4大任务:
- 加强欧盟内部和整个欧洲的社会主义和社会民主运动;
- 发展各国成员政党、成员政党议会党团、欧洲社会党党团和欧洲社会党本身的紧密合作关系;
- 制定欧盟的共同政策;
- 在欧洲议会选举中采取统一步调;
欧州社会党(おうしゅうしゃかいとう)は、社会民主主義政党で構成される欧州規模の政党。
欧州議会の政治会派としては社会民主進歩同盟の大部分を形成し、欧州人民党グループに次ぐ第2会派となっている。国際組織は社会主義インターナショナルに加盟。党首はブルガリア前首相のセルゲイ・スタニシェフ。
The Party of European Socialists (PES) is a social-democratic European political party.[5]
The PES comprises national-level political parties from all member states of the European Union (EU) plus Norway. This includes major parties such as the Italian Democratic Party, the British Labour Party, the French Socialist Party, Social Democratic Party of Germany and the Spanish Socialist Workers' Party. Parties from a number of other European countries are also admitted to the PES as associate or observer parties.[6] Most member, associate and observer parties are members of the wider Progressive Alliance or Socialist International.[3][4]
The PES is currently led by its president Sergei Stanishev, a former Prime Minister of Bulgaria. Its political group in the European Parliament is the Progressive Alliance of Socialists and Democrats (S&D). The PES also operates in the Committee of the Regions (in the PES Group in the Committee of the Regions) and the European Council.
Le Parti socialiste européen (PSE) est un parti politique européen regroupant les partis socialistes, sociaux-démocrates et travaillistes d'Europe. Son groupe politique est le deuxième en taille au Parlement européen après les élections de 2014 (191 députés en juin 2016). Il se partage le pouvoir au Parlement européen avec le Parti populaire européen (PPE) comme l'illustre le partage de la présidence du Parlement européen. Selon la tradition européenne, il peut participer à des majorités de circonstance avec le Parti vert européen et le Parti de la gauche européenne, comme avec le PPE et le Parti de l'Alliance des libéraux et des démocrates pour l'Europe. Le PSE est lié à l'Internationale socialiste.
Il Partito del Socialismo Europeo (PSE o PES[1]), meglio noto come Partito Socialista Europeo, è un partito politico europeo di orientamento socialista, socialdemocratico e laburista fondato nel 1992. Precursore del partito è stata la Confederazione dei Partiti Socialisti della Comunità Europea, fondata nel 1973.[2]
In sede di Parlamento europeo, il PSE ha dato vita nel 2009 all'Alleanza Progressista dei Socialisti e dei Democratici; prima di allora, aderiva al gruppo del Partito del Socialismo Europeo (la cui denominazione ufficiale è tuttavia variata nel corso del tempo).[3]
Da settembre 2012 il presidente è l'ex primo ministro bulgaro Sergej Stanišev.[4]
El Partido Socialista Europeo (en inglés Party of European Socialists, abreviado PES) es un partido político europeo de centroizquierda y proeuropeo. Fue fundado en 1992 por los partidos que formaban la Confederación de los Partidos Socialistas de la Comunidad Europea, creada en 1973.1
El PSE es el segundo partido de la Unión Europea (UE) con 178 diputados en el Parlamento Europeo, la gran mayoría presentes en el Grupo de la Alianza Progresista de Socialistas y Demócratas. Además cuenta con 8 miembros de la Comisión Europea, incluidos el vicepresidente primero Frans Timmermans y la alto representante para Asuntos Exteriores y Política de Seguridad Federica Mogherini, y otros 8 en el Consejo Europeo.23
Con 58 partidos repartidos en casi 50 países de Europa y el Mediterráneo, el Partido de los Socialistas Europeos controla 12 estados de la zona de manera directa y participa en otros 8 gobiernos en coalición, y cuanta con el segundo grupo de la Asamblea Parlamentaria del Consejo de Europa, con más de 120 miembros en el Grupo Socialista.45
El PSE incluye partidos tan importantes como el Partido Socialista de Francia, el Partido Socialista Obrero Español de España, el Partido Socialista de Portugal o los Socialdemócratas de Dinamarca, y cuenta con miembros en todos los estados de la Unión Europea.4
Партия европейских социалистов (ПЕС) (англ. Party of European Socialists (PES)) — европейская партия, состоящая из 33 социалистических, социал-демократических и рабочих партий из государств-членов Евросоюза и Норвегии.
Лидером партии является Сергей Станишев. В Европарламенте формирует Прогрессивный альянс социалистов и демократов.


 Equatorial Guinea
Equatorial Guinea
 Argentina
Argentina

 Education and Research
Education and Research
 Bolivia
Bolivia
 Chile
Chile
 Columbia
Columbia
 Costa Rica
Costa Rica
 Cuba
Cuba
 Dominikanische Republik
Dominikanische Republik
 Ecuador
Ecuador

 European Union
European Union
 Guatemala
Guatemala

 Hand in Hand
Hand in Hand

 Hand in Hand
Hand in Hand
 Institute of Culture and Language
Institute of Culture and Language
 Honduras
Honduras
 Literature
Literature
 Mexico
Mexico
 New mexico-NM
New mexico-NM
 Nicaragua
Nicaragua
 Panama
Panama
 Paraguay
Paraguay
 Peru
Peru
 Puerto Rico
Puerto Rico
 Republik El Salvador
Republik El Salvador
 Spain
Spain
 Uruguay
Uruguay
 Venezuela
Venezuela

 United Nations
United Nations
 Official languages
Official languages
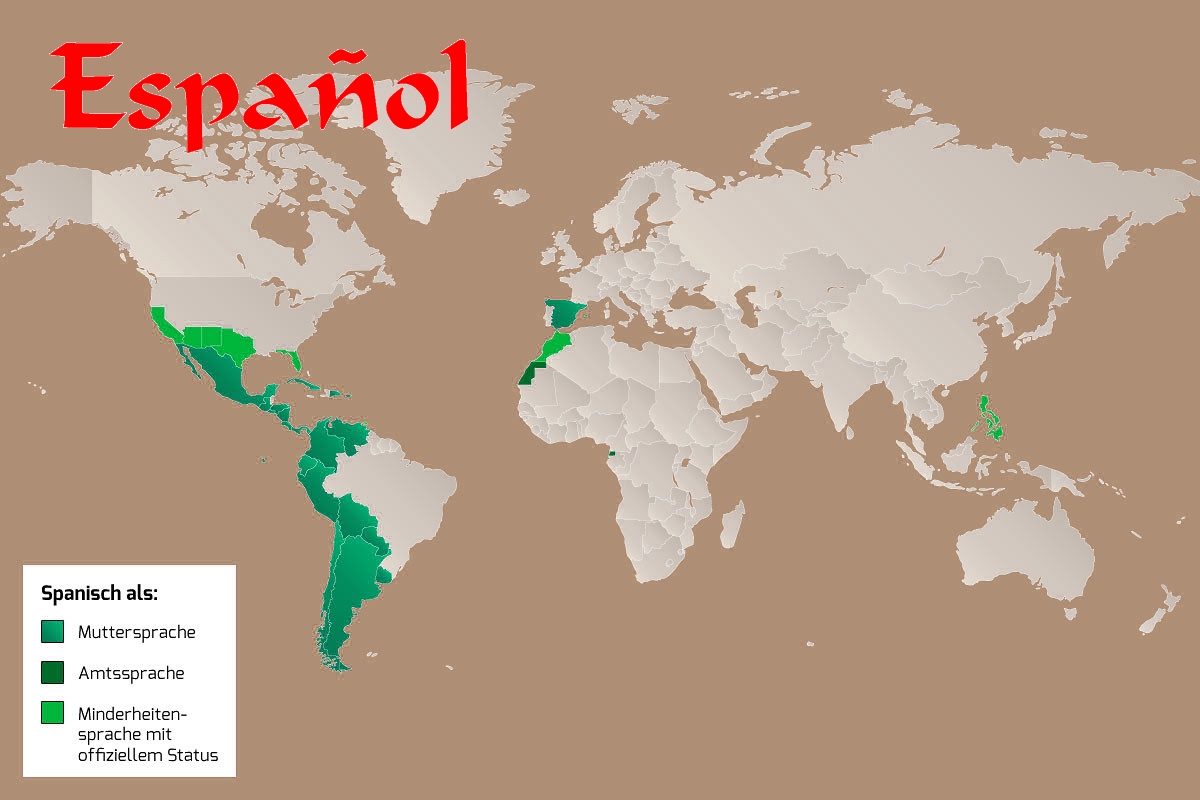
Die spanische oder auch kastilische Sprache (Spanisch; Eigenbezeichnung: español [espaˈɲol] bzw. castellano [kasteˈʎano]) gehört zum romanischen Zweig der indogermanischen Sprachfamilie und bildet mit dem Aragonesischen, dem Asturleonesischen, dem Galicischen und dem Portugiesischen die engere Einheit des Iberoromanischen.[1] In einer weiter gefassten Sicht kann das Spanische auch noch zusammen mit dem Katalanischen, dem Französischen, dem Okzitanischen und weiteren kleineren romanischen Sprachen wie Norditalienisch in die Westromania eingeordnet werden.
Die Wissenschaft, die sich mit der spanischen Sprache[2] und spanischen Literatur beschäftigt, heißt Hispanistik. Der spanische Sprachraum wird als Hispanophonie bezeichnet. Spanisch ist wegen des historischen Kolonialismus die häufigste Muttersprache auf dem amerikanischen Doppelkontinent und gilt z. B. durch die Funktion als Amtssprache zahlreicher internationaler Organisationen als Weltsprache (in Spanien selbst ist Spanisch jedoch nicht die einzige Sprache, siehe Sprachen in Spanien). Mit der Pflege der spanischen Sprache weltweit ist das Instituto Cervantes betraut.
Geschrieben wird Spanisch mit lateinischen Buchstaben. Im modernen Spanisch werden zusätzlich der Akut-Akzent für Vokale sowie die beiden Zeichen ñ und ü verwendet. In älteren Wörterbüchern finden sich auch das ch und ll noch als eigenständige Buchstaben.
西班牙语(西班牙语:Español),也称卡斯蒂利亚语(Castellano),指的是一种起源于西班牙卡斯蒂利亚地方的语言,为罗曼语族的分支,除了发源地的西班牙以外,其母语人士主要集中在拉丁美洲国家。
西班牙语的使用人口众多,全球共有近五亿人使用。按照第一语言使用者数量排名,为全世界第二位,仅次于汉语。加上第二语言人口,总使用人数排名则为世界第二,仅次于汉语。西班牙语是除英语、法语和阿拉伯语之外最多国家的官方语言,同时为联合国官方语言之一[2]。全世界有超过五亿九千五百万人的母语或第二语言是西班牙语,另外有二千四百万的学生将西班牙语当作外语学习[3][4]。

 Climate
Climate


 Aerospace
Aerospace



 Military, defense and equipment
Military, defense and equipment