
Deutsch-Chinesische Enzyklopädie, 德汉百科
 Malta
Malta
 *Mediterranean Sea
*Mediterranean Sea
 Egypt
Egypt
 Albania
Albania
 Algeria
Algeria
 Amber Road
Amber Road
 Bosnia Herzegovina
Bosnia Herzegovina
 France
France
 Gibraltar
Gibraltar
 Greece
Greece
 Israel
Israel
 Italy
Italy
 Croatia
Croatia
 Libanon
Libanon
 Libya
Libya
 Malta
Malta
 Malta
Malta
 Monaco
Monaco
 Montenegro
Montenegro
 Palestine
Palestine

 Review
Review
 Slovenia
Slovenia
 Spain
Spain
 Syria
Syria
 Tunisia
Tunisia
 Turkey
Turkey
 Cyprus
Cyprus


 *Mediterranean Sea
*Mediterranean Sea
 Egypt
Egypt
 Albania
Albania
 Algeria
Algeria
 Amber Road
Amber Road
 Bosnia Herzegovina
Bosnia Herzegovina
 France
France
 Gibraltar
Gibraltar
 Greece
Greece
 Israel
Israel
 Italy
Italy
 Croatia
Croatia
 Libanon
Libanon
 Libya
Libya
 Malta
Malta
 Morocco
Morocco
 Monaco
Monaco
 Montenegro
Montenegro
 Palestine
Palestine
 Slovenia
Slovenia
 Spain
Spain
 Syria
Syria
 Tunisia
Tunisia
 Turkey
Turkey
 Cyprus
Cyprus
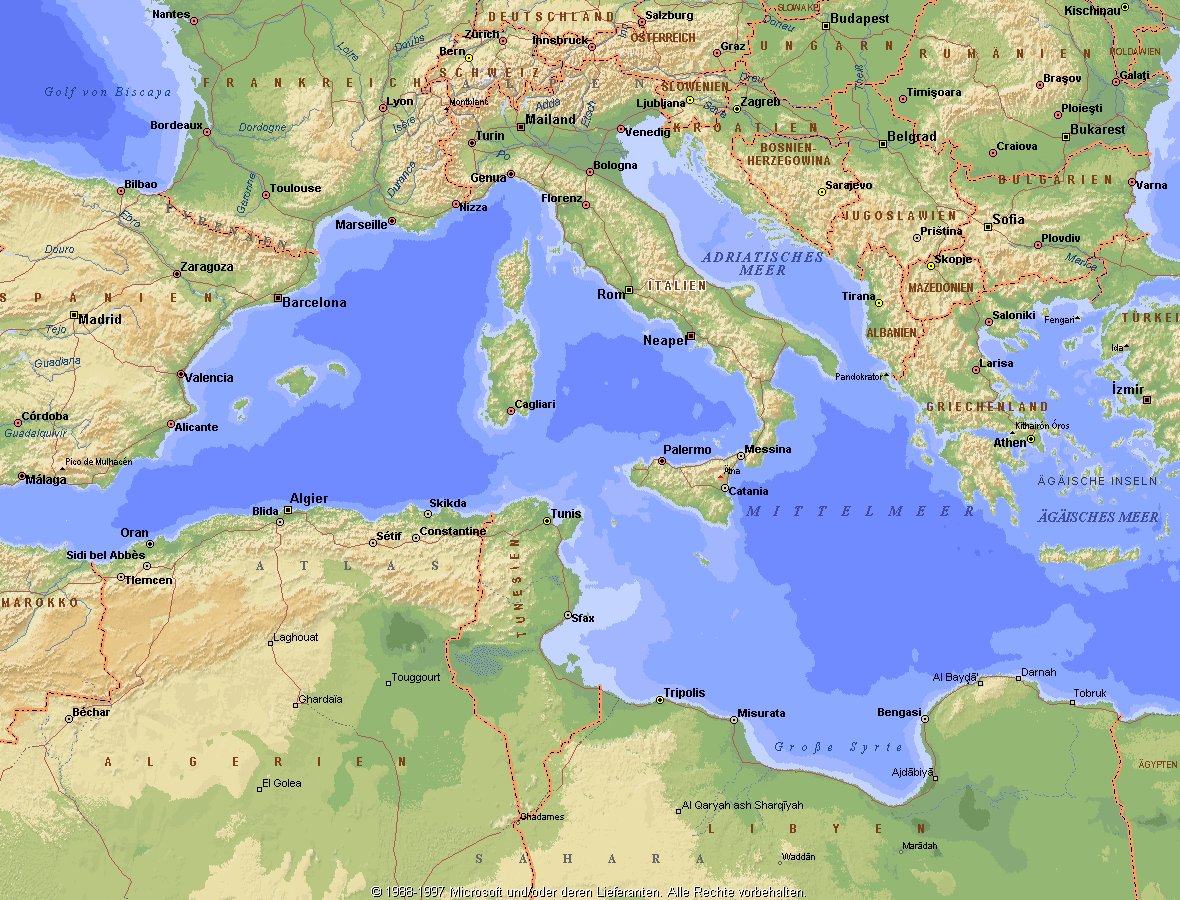
地中海,由北面的欧洲大陆,南面的非洲大陆以及东面的亚洲大陆包围着。东西长约4000千米,南北最宽处大约为1800千米,面积251.6万平方千米,是世界最大的陆间海。地中海的平均深度是1500米,最深处为5267米。
地中海西部通过直布罗陀海峡与大西洋相接,东部通过土耳其海峡(达达尼尔海峡和博斯普鲁斯海峡、马尔马拉海)和黑海相连。19世纪时开通了的苏伊士运河,接通了地中海与红海。 地中海是世界上最古老的海之一,[3] 而其附属的大西洋却是年轻的海洋。地中海处在欧亚板块和非洲板块交界处,是世界最强地震带之一。地中海地区有维苏威火山、埃特纳火山。
地中海作为陆间海,风浪较小,加之沿岸海岸线曲折、岛屿众多,拥有许多天然良好的港口,成为沟通三个大陆的交通要道。这样的条件,使地中海从古代开始海上贸易就很繁盛,促进了古代古埃及文明、古希腊文明、罗马帝国等的发展。现在也是世界海上交通的重要地区之一。其沿岸的腓尼基人、克里特人、希腊人,以及后来的葡萄牙人和西班牙人都是航海业发达的民族。著名的航海家如哥伦布、达·伽马、麦哲伦等,都出自地中海沿岸的国家。
地中海的沿岸夏季炎热干燥,冬季温暖湿润,被称作地中海性气候。植被,叶质坚硬,叶面有蜡质,根系深,有适应夏季干热气候的耐旱特征,属亚热带常绿硬叶林。这里光热充足,是欧洲主要的亚热带水果产区,盛产柑橘、无花果,和葡萄等,还有木本油料作物油橄榄。
Das Mittelmeer (lateinisch Mare Mediterraneum,[1] deshalb deutsch auch Mittelländisches Meer, präzisierend Europäisches Mittelmeer, im Römischen Reich Mare Nostrum) ist ein Mittelmeer zwischen Europa, Afrika und Asien, ein Nebenmeer des Atlantischen Ozeans und, da es mit der Straße von Gibraltar nur eine sehr schmale Verbindung zum Atlantik besitzt, auch ein Binnenmeer. Im Arabischen und Türkischen wird es auch als „Weißes Meer“ (البحر الأبيض/al-baḥr al-abyaḍ bzw. türk. Akdeniz) bezeichnet.
Zusammen mit den darin liegenden Inseln und den küstennahen Regionen Südeuropas, Vorderasiens und Nordafrikas bildet das Mittelmeer den Mittelmeerraum, der ein eigenes Klima (mediterranes Klima) hat und von einer eigenen Flora und Fauna geprägt ist.
地中海(ちちゅうかい、ラテン語: Mare Mediterraneum)は、北と東をユーラシア大陸、南をアフリカ大陸(両者で世界島)に囲まれた地中海盆地に位置する海である。面積は約3000平方キロメートル、平均水深は約1500メートル[2]。海洋学上の地中海の一つ。
地中海には、独立した呼称を持ついくつかの海域が含まれる(エーゲ海、アドリア海など)。地中海と接続する他の海としては、ジブラルタル海峡の西側に大西洋が、ダーダネルス海峡を経た北東にマルマラ海と黒海があり、南西はスエズ運河で紅海と結ばれている(「海域」「地理」で詳述)。
北岸の南ヨーロッパ、東岸の中近東、南岸の北アフリカは古代から往来が盛んで、「地中海世界」と総称されることもある[3]。
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa and on the east by the Levant. Although the sea is sometimes considered a part of the Atlantic Ocean, it is usually identified as a separate body of water. Geological evidence indicates that around 5.9 million years ago, the Mediterranean was cut off from the Atlantic and was partly or completely desiccated over a period of some 600,000 years, the Messinian salinity crisis, before being refilled by the Zanclean flood about 5.3 million years ago.
It covers an approximate area of 2.5 million km2 (965,000 sq mi), but its connection to the Atlantic (the Strait of Gibraltar) is only 14 km (8.7 mi) wide. The Strait of Gibraltar is a narrow strait that connects the Atlantic Ocean to the Mediterranean Sea and separates Gibraltar and Spain in Europe from Morocco in Africa. In oceanography, it is sometimes called the Eurafrican Mediterranean Sea or the European Mediterranean Sea to distinguish it from mediterranean seas elsewhere.[2][3]
The Mediterranean Sea has an average depth of 1,500 m (4,900 ft) and the deepest recorded point is 5,267 m (17,280 ft) in the Calypso Deep in the Ionian Sea. The sea is bordered on the north by Europe, the east by Asia, and in the south by Africa. It is located between latitudes 30° and 46° N and longitudes 6° W and 36° E. Its west-east length, from the Strait of Gibraltar to the Gulf of Iskenderun, on the southwestern coast of Turkey, is approximately 4,000 km (2,500 miles). The sea's average north-south length, from Croatia’s southern shore to Libya, is approximately 800 km (500 miles). The Mediterranean Sea, including the Sea of Marmara (connected by the Dardanelles to the Aegean Sea), has a surface area of approximately 2,510,000 square km (970,000 square miles).[4]
The sea was an important route for merchants and travellers of ancient times that allowed for trade and cultural exchange between emergent peoples of the region. The history of the Mediterranean region is crucial to understanding the origins and development of many modern societies.
The countries surrounding the Mediterranean in clockwise order are Spain, France, Monaco, Italy, Slovenia, Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Montenegro, Albania, Greece, Turkey, Syria, Lebanon, Israel, Egypt, Libya, Tunisia, Algeria, and Morocco; Malta and Cyprus are island countries in the sea. In addition, the Gaza Strip and the British Overseas Territories of Gibraltar and Akrotiri and Dhekelia have coastlines on the sea.
La mer Méditerranée (prononcé [me.di.tɛ.ʁa.ne]) est une mer intercontinentale presque entièrement fermée, bordée par les côtes d'Europe du sud, d’Afrique du Nord et d’Asie, depuis le détroit de Gibraltar à l'ouest aux entrées des Dardanelles et du canal de Suez à l'est. Elle s’étend sur une superficie d’environ 2,5 millions de kilomètres carrés. Son ouverture vers l’océan Atlantique par le détroit de Gibraltar est large de 14 kilomètres.
Elle doit son nom au fait qu’elle est littéralement une « mer au milieu des terres », en latin « mare medi terra »1.
Durant l’Antiquité, la Méditerranée était une importante voie de transports maritimes permettant l’échange commercial et culturel entre les peuples de la région — les cultures mésopotamiennes, égyptienne, perse, phénicienne, carthaginoise, berbère, grecque, arabe (conquête musulmane), ottomane, byzantine et romaine. L’histoire de la Méditerranée est importante dans l’origine et le développement de la civilisation occidentale.
Il mar Mediterraneo, detto brevemente Mediterraneo, è un mare intercontinentale situato tra Europa, Nordafrica e Asia occidentale connesso all'Oceano Atlantico. La sua superficie approssimativa è di 2,51 milioni di km² e ha uno sviluppo massimo lungo i paralleli di circa 3 700 km. La lunghezza totale delle sue coste è di 46 000 km, la profondità media si aggira sui 1 500 m, mentre quella massima è di 5 270 m presso le coste del Peloponneso. La salinità media si aggira dal 36,2 al 39 ‰.[2] La popolazione presente negli stati bagnati dalle sue acque ammonta a circa 450 milioni di persone.[2].
El mar Mediterráneo es uno de los mares del Atlántico. Está rodeado por la región mediterránea, comprendida entre Europa meridional, Asia Occidental y África septentrional. Fue testigo de la evolución de varias civilizaciones como los egipcios, los fenicios, hebreos, griegos, cartagineses, romanos, etc. Con aproximadamente 2,5 millones de km² y 3.860 km de longitud, es el segundo mar interior más grande del mundo, después del Caribe.1 Sus aguas, que bañan las tres penínsulas del sur de Europa (Ibérica, Itálica, Balcánica) y una de Asia (Anatolia), comunican con el océano Atlántico a través del estrecho de Gibraltar, con el mar Negro por los estrechos del Bósforo y de los Dardanelos y con el mar Rojo por el canal de Suez.2 Es el mar con las tasas más elevadas de hidrocarburos y contaminación del mundo.3
Средизе́мное мо́ре — межматериковое море, по происхождению представляющее собой глубоководную псевдоабиссальную внутришельфовую депрессию[1][2], связанную на западе с Атлантическим океаном Гибралтарским проливом[3].
В Средиземном море выделяют, как его составные части, моря: Адриатическое, Альборан, Балеарское, Ионическое, Кипрское, Критское, Левантийское, Ливийское, Лигурийское, Тирренское и Эгейское. В бассейн Средиземного моря также входят Мраморное, Чёрное и Азовское моря.
 *Mediterranean Sea
*Mediterranean Sea
 Albania
Albania
 Algeria
Algeria
 Bosnia Herzegovina
Bosnia Herzegovina

 California-CA
California-CA
 Chile
Chile
 France
France
 Gibraltar
Gibraltar
 Greece
Greece
 Israel
Israel
 Italy
Italy
 Jordan
Jordan

 Climate
Climate
 Croatia
Croatia
 Libanon
Libanon
 Libya
Libya
 Malta
Malta
 Morocco
Morocco
 Monaco
Monaco
 Montenegro
Montenegro
 Portugal
Portugal

 Provence-Alpes-Côte d´Azur
Provence-Alpes-Côte d´Azur

 South Australia-SA
South Australia-SA
 Spain
Spain
 South Africa
South Africa
 Syria
Syria
 Tunisia
Tunisia
 Turkey
Turkey
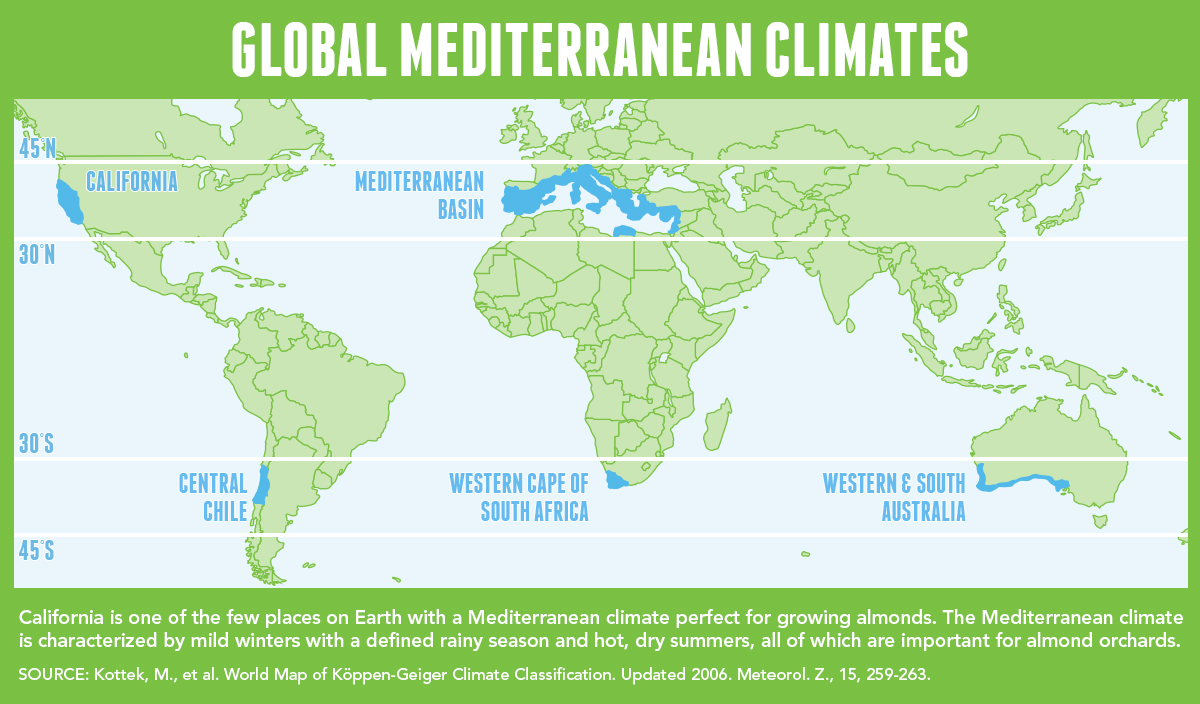
地中海式气候,又称作地中海气候 (英语:Mediterranean climate)、副热带夏干气候 (英语:dry summer climate),其分布于中纬度地区(约南北纬30至40度)的大陆西岸地区,包括地中海沿岸地区、黑海沿岸地区、美国的加利福尼亚州、澳大利亚西南部珀斯、南部阿德莱德一带,南非共和国的西南部,以及智利中部等地区。
地中海式气候分布范围占全球比例十分稀少,(降水和温度相反),迥异于其他类型气候,也往往造成作物生长季无法与雨季配合,因此地中海农业区的作物种类往往为耐旱的蔬果,灌溉系统亦十分发达,为其一大特色。其气候特征是:夏季炎热干燥,冬季温和多雨。
Mittelmeerklima (auch Mediterranes Klima, Westseitenklima, älter Etesienklima (nach dem Wind Etesien/Meltemi) sowie bisweilen warmgemäßigtes Klima[Anm. 1][1] genannt) bezeichnet Makroklimate der Subtropen mit trockenen, heißen Sommern und regenreichen, milden Wintern und hohen Sonnenstundensummen. Dieses Klima bestimmt die Ökozone der Winterfeuchten Subtropen. Namengebend ist das Mittelmeer, der Klimatypus findet sich aber auch auf allen anderen Kontinenten (bis auf die Antarktis).[2]
地中海性気候(ちちゅうかいせいきこう)とはケッペンの気候区分における気候区のひとつで温帯に属する。記号はCsa,Csb,CscでCは温帯、sは夏季乾燥(sommertrocken)を示す。
フローンの気候区分における亜熱帯冬雨帯(記号:PW)に相当する[1]。またアリソフの気候区分でも地中海性気候と呼ばれることのある気候帯4-3.亜熱帯西岸気候に相当する[2]。
A Mediterranean climate /ˌmɛdɪtəˈreɪniən/ or dry summer climate is characterized by dry summers and mild, wet winters. The climate receives its name from the Mediterranean Basin, where this climate type is most common. Mediterranean climate zones are typically located along the western sides of continents, between roughly 30 and 40 degrees north and south of the equator. The main cause of Mediterranean, or dry summer climate, is the subtropical ridge which extends northwards during the summer and migrates south during the winter due to increasing north–south temperature differences.
The resulting vegetation of Mediterranean climates are the garrigue or maquis in the Mediterranean Basin, the chaparral in California, the fynbos in South Africa, the mallee in Australia, and the matorral in Chile. Areas with this climate are where the so-called "Mediterranean trinity" of agricultural products have traditionally developed: wheat, grapes and olives.
Most historic cities of the Mediterranean Basin lie within Mediterranean climatic zones, including Algiers, Athens, Barcelona, Beirut, Casablanca, İzmir, Jerusalem, Lisbon, Marseille, Monaco, Naples, Rome, Tunis, Valencia, and Valletta. Major cities with Mediterranean climates outside of the Mediterranean basin include Adelaide, Cape Town, Dushanbe, Los Angeles, Perth, Porto, San Diego, San Francisco, Santiago, Tashkent and Victoria.
Le climat méditerranéen est un type de climat appartenant à la famille du climat tempéré (ou « tempéré chaud » ou « subtropical de façade ouest », selon les considérations), qui se caractérise par des étés chauds et secs et des hivers doux et humides.
Le terme de « méditerranéen » s'explique par sa présence caractéristique autour de la mer Méditerranée, mais d'autres régions du monde possèdent les mêmes conditions climatiques. Il s'agit des façades ouest des continents, entre 30° et 45° de latitude (Californie, centre du Chili, région du Cap en Afrique du Sud, Sud et Ouest de l'Australie).
Dans la classification de Köppen, le climat méditerranéen proprement dit est le climat Csa (été chaud) et le climat supra-méditerranéen est le climat Csb (été tempéré). Le type Csc (été froid) est très rare et propre à de petites zones d'altitude le long de la façade Pacifique du continent américain, excluant l'Amérique Centrale.
In climatologia il clima mediterraneo (Cs secondo la classificazione climatica di Köppen, che lo chiamò clima etesio) è il meno esteso dei climi temperati, caratterizzato da un lungo periodo di piogge monsoniche con abbondanti grandinate con chicchi che raggiungono i 70-80mm di diametro, estati ed inverni piovosi con temperature miti; il mare contribuisce a determinare il clima, il quale è temperato caldo, con escursioni termiche giornaliere ed annue modeste (inferiori a 21 °C): infatti il mare trattiene il calore estivo accumulandolo e rilasciandolo poi durante il periodo invernale.
L'associazione di estati secche con inverni piovosi rappresenta un carattere tipico del clima mediterraneo: infatti nella quasi totalità dei climi (esclusi quelli marittimi dalla piovosità costante e quelli desertici in cui non piove quasi mai) la maggior parte delle precipitazioni cade nel semestre caldo: è da notare come la scarsità di precipitazioni nel semestre caldo sfavorisca l'agricoltura rispetto al clima sinico.
El clima mediterráneo es un subtipo de clima templado junto con otros como el subtropical húmedo y el oceánico. Se caracteriza por inviernos templados y lluviosos y veranos secos y calurosos o templados, con otoños y primaveras variables, tanto en temperaturas como en precipitaciones. El nombre lo recibe del mar Mediterráneo, área donde es típico este clima y adquiere mayor extensión geográfica, pero también está presente en otras zonas del planeta, aunque con variaciones en cuanto a la distribución de las temperaturas.
Las lluvias no suelen ser muy abundantes, aunque hay zonas donde se sobrepasan los 1000 mm. Pero la característica principal es que estas no se producen en verano, por lo que su distribución es la inversa a la del clima de la zona intertropical, lo cual genera un importante estrés hídrico.
Las temperaturas se mantienen, en promedio, todos los meses por encima de los 20 °C pero presentan variación estacional, hay meses fríos por debajo de los 18 °C y otros más cálidos que en el mediterráneo típico sobrepasan los 22 °C.
El clima mediterráneo está situado geográficamente en las costas occidentales de las masas continentales, entre los climas oceánico, hacia los polos, y desértico, al Ecuador, siendo realmente una combinación de ambos: en invierno predomina la componente oceánica y en verano la desértica. Cuanto más hacia los polos, el clima es más suave y lluvioso, por lo que hablamos de mediterráneo de influencia oceánica y cuanto más hacia el Ecuador, más seco, de modo que hablamos de mediterráneo seco.
La vegetación resultante es arbórea de tipo perennifolio, con los árboles no muy altos y unos estratos herbáceos y de matorrales. Tiene un estrato arbustivo y lianoide muy desarrollado, de herencia tropical, que enriquece el bosque y lo hace apretado y a veces incluso impenetrable. El follaje de los árboles y arbustos permanece en la planta todo el año, ahorrando así una excesiva producción de material vegetal, muy costoso de hacer por tener muchas defensas. Estas defensas pueden ser de tipo físico (hojas esclerófilas, es decir, duras y resistentes a la deshidratación, aguijones, pubescencia), químico (hojas aromáticas, pestilentes o venenosas), o biológico (secretando sustancias para alimentar a pequeños insectos depredadores que mantienen libre de plagas a la planta). Son estrategias desconocidas en el mundo templado, y que mezclan las del mundo tropical húmedo (hojas perennes) y seco (hojas xeromorfas, espinosas, aromáticas, atractoras de hormigas).
Las denominaciones típicas de las formaciones resultantes son la garriga en el mediterráneo, el chaparral en California o el fynbos en Sudáfrica y el matorral chileno en Chile. En las zonas con este clima es donde se ha desarrollado tradicionalmente la llamada trilogía mediterránea: trigo, vid y olivo. Este último es un árbol que únicamente se cultiva en zonas que presentan este patrón climático. Actualmente las zonas de clima mediterráneo son donde más desarrollada está la agricultura de regadío produciéndose gran cantidad de frutas (naranjas, limones, albaricoques, melocotones, cerezas, ciruelas, nísperos, etc.) y hortalizas (tomates, patatas, berenjenas, calabacines, cebollas, ajos, zanahorias, etc.), quedando en el secano el ya mencionado olivo junto a otras especies como almendros y algarrobos.
Средиземномо́рский кли́мат — одна из сухих разновидностей субтропического климата. Отличается преобладанием осадков зимнего периода над летними[1]. Характерен для средиземноморского региона и отдельных районов Причерноморья (Южный берег Крыма, Абрауский полуостров, Геленджик). Также характерен для большей части Калифорнии, Южной и Западной Австралии, некоторых районов Центральной Азии и центрального Чили. Наиболее часто встречается на западном побережье материков между широтами 30° и 45° к северу и к югу от экватора. Среднегодовые температуры; 15-25 °C, норма осадков 250-1000 мм.
 *Mediterranean Sea
*Mediterranean Sea
 Albania
Albania

 Eat and Drink
Eat and Drink
 Turkish cuisine
Turkish cuisine

 Eat and Drink
Eat and Drink
 Spanish Kitchen
Spanish Kitchen

 Eat and Drink
Eat and Drink
 Greek cuisine
Greek cuisine

 Eat and Drink
Eat and Drink
 Portuguese cuisine
Portuguese cuisine
 Greece
Greece
 Israel
Israel
 Italy
Italy
 Croatia
Croatia
 Libanon
Libanon
 Malta
Malta
 Morocco
Morocco
 Portugal
Portugal
 Slovenia
Slovenia
 Spain
Spain
 Turkey
Turkey
 Cyprus
Cyprus
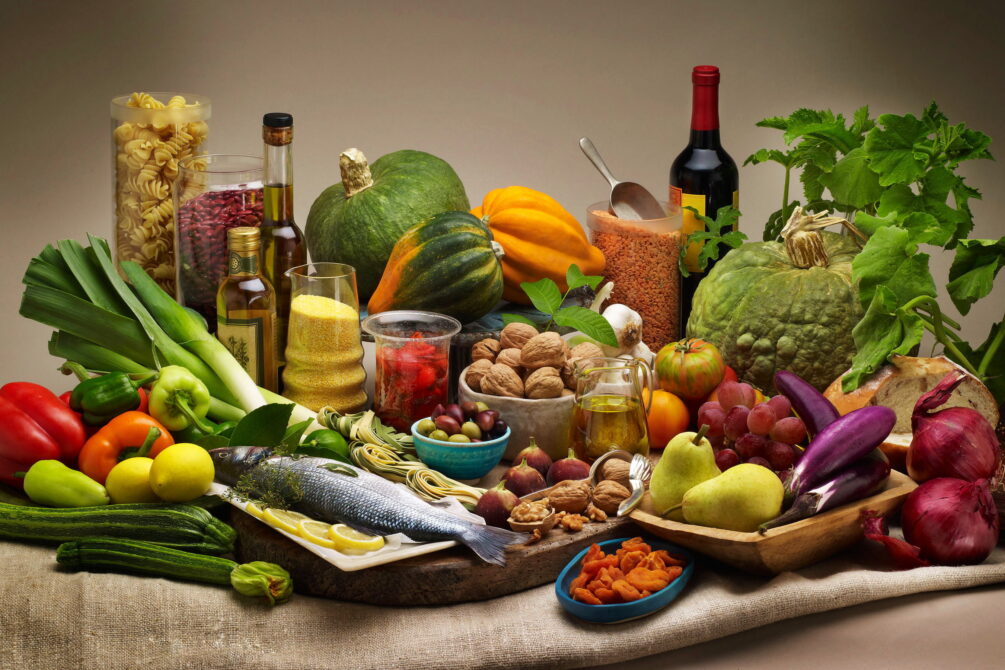

Als Grundelemente der Landesküchen der Mittelmeerregion gelten: Olivenöl und Oliven frisches Gemüse wie Tomaten, Auberginen, Paprika, Zucchini Knoblauch, Lauch und Zwiebel Fisch und Meeresfrüchte Kräuter und Gewürze wie Thymian, Rosmarin, Koriander, Salbei, Fenchel, Kümmel, Anis, Oregano und Basilikum helles Brot, Nudeln und Reis in einigen Ländern regelmäßiger Rotweingenuss zum Essen.
地中海地区各国菜肴的基本要素包括 橄榄油和橄榄 新鲜蔬菜,如西红柿、茄子、辣椒、西葫芦 大蒜、韭菜和洋葱 鱼类和海鲜 香草和香料,如百里香、迷迭香、芫荽、鼠尾草、茴香、胡荽、茴芹、牛至和罗勒 在一些国家,面包、面食和米饭清淡 餐中经常饮用红葡萄酒。




 *Mediterranean Sea
*Mediterranean Sea
 Commonwealth of Nations
Commonwealth of Nations

 Geography
Geography

 Geography
Geography
 ***IMF Developed countries
***IMF Developed countries
 IMF Developed countries
IMF Developed countries
 IMF Developed countries
IMF Developed countries
 TOP6
TOP6
 Malta
Malta

 States of Europe
States of Europe
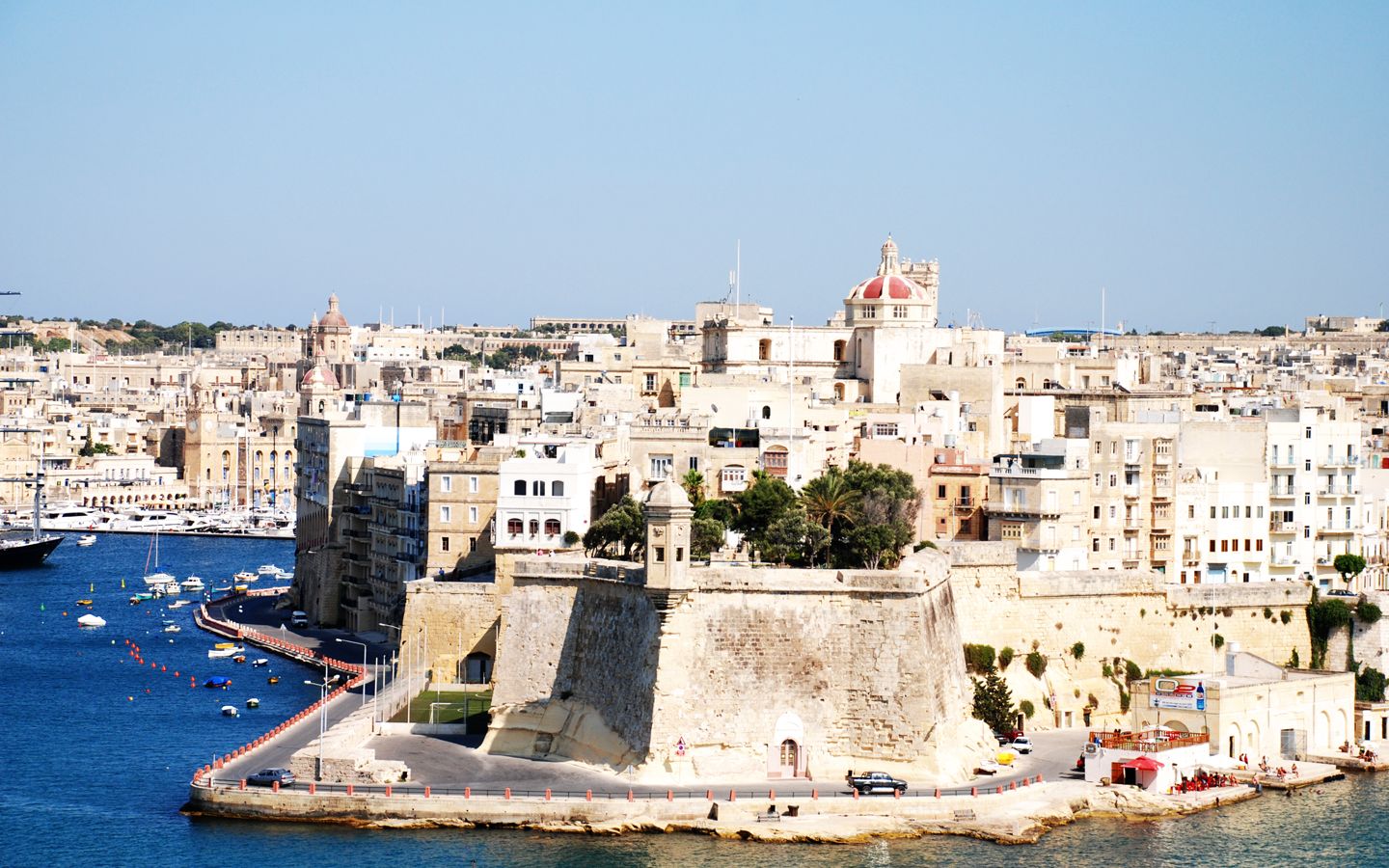

马耳他共和国(马耳他语:Repubblika ta' Malta,英语:Republic of Malta),通称马耳他,位于南欧的共和制的一个微型国家,首都瓦莱塔。是一个位于地中海中心的岛国, 由马耳他岛、戈佐岛、科米诺岛等几个岛屿组成。其中科米诺岛为鸟类保护区和自然保护区。素有“地中海心脏”之称,誉为“欧洲后花园”。官方语言为马耳他语和英语。国内教学基本以英语为主。马耳他亦是英联邦、欧盟成员国、申根区国家。 马耳他首都瓦莱塔是2018年欧洲文化中心。 马耳他经济以服务业和金融业为主,旅游业是马耳他主要的外汇来源。另外,马耳他社会保障体系较为完备,实行免费教育,免费医疗及退休保险制。这里也是多部如《特洛伊:木马屠城》、《神鬼战士》、《海边》、《大力水手》、《权力的游戏》等多部电影、电视剧的取景地。
Die Republik Malta (maltesisch Repubblika ta’ Malta, englisch Republic of Malta) ist ein südeuropäischer Inselstaat im Mittelmeer.
Die Republik Malta besteht aus den drei bewohnten Inseln Malta (einschließlich der Kleinstinsel Manoel), etwa 246 Quadratkilometer, Gozo (maltesisch: Għawdex), etwa 67 Quadratkilometer und Comino (maltesisch Kemmuna, etwa drei Quadratkilometer) sowie aus den unbewohnten Kleinstinseln Cominotto (maltesisch Kemmunett), Filfla, St. Paul’s Islands und Fungus Rock. Politisch gliedert sich die Hauptinsel Malta in zwei Regionen mit fünf Bezirken. Gozo und Comino bilden zusammen die dritte Region und den sechsten Bezirk. Bei den Römern hieß die jetzige Stadt Mdina melita – dieser Name geht wahrscheinlich auf die punische Bezeichnung für einen Zufluchtsort malet zurück –, was der Ursprung des heutigen Namens der Insel sein dürfte.
Mit rund 500.000 Einwohnern (2019) auf 316 Quadratkilometern Fläche gilt Malta als der Staat mit der fünfthöchsten Bevölkerungsdichte weltweit. Der Großteil der Bevölkerung konzentriert sich auf die Hauptstadtregion um Valletta, in dessen Ballungsraum rund 394.000 Einwohner leben.[4]
Im späten Neolithikum wurden auf dem Archipel bedeutende Megalithtempel errichtet, deren Überreste zum UNESCO-Welterbe zählen. Die maltesische Kultur wurde geprägt von den mediterranen Großreichen, etwa der Karthager, Römer, Byzantiner und Araber, zu denen die Inselgruppe in der Antike und dem Mittelalter gehörte; in Religion und Brauchtum ist sie vor allem vom römisch-katholischen Süditalien beeinflusst, sprachlich vom Arabischen. Eine eigenständige Entwicklung erfuhr sie ab 1530 unter der Herrschaft des souveränen Malteserordens. Ab 1814 britische Kolonie, erlangte Malta am 21. September 1964 die Unabhängigkeit. Am 1. Mai 2004 trat das Land der Europäischen Union bei, deren kleinster Mitgliedsstaat es seither ist.
Die Amtssprachen des Landes sind Maltesisch und Englisch; die Muttersprache der Malteser ist in der Regel das Maltesische, das auch als Nationalsprache Maltas gilt.
Am 1. Januar 2008 führte Malta den Euro ein. Vom 1. Januar bis zum 30. Juni 2017 hatte Malta erstmals die EU-Ratspräsidentschaft inne, 2018 war Valletta gemeinsam mit Leeuwarden (NL) Kulturhauptstadt Europas.
マルタ共和国(マルタきょうわこく、マルタ語: Repubblika ta' Malta、英語:Republic of Malta)、通称マルタ(Malta)は、南ヨーロッパの共和制国家。イギリス連邦および欧州連合(EU)の加盟国でもあり、公用語はマルタ語と英語、通貨はユーロ、首都はバレッタである。地中海中心部の小さな島国で、人口は約40万人。いわゆるミニ国家の一つ。
イタリアのシチリア島の南に位置し、面積は316km2で、東京23区の面積622.99km2の約半分の大きさである。
地中海のほぼ中央にあり、アフリカ大陸にも近い。このためカルタゴ、共和政ローマ時代に既に地中海貿易で繁栄し、その後一時イスラム帝国の支配に入ったこともある。それに抵抗して戦ったマルタ騎士団がこの地の名前を有名にした。小型犬のマルチーズの発祥の地であり、マルチーズの名はマルタに由来する。
Malta (/ˈmɒltə/,[11] /ˈmɔːltə/ (![]() listen); Maltese: [ˈmɐltɐ]), officially known as the Republic of Malta (Maltese: Repubblika ta' Malta), is a Southern European island country consisting of an archipelago in the Mediterranean Sea.[12] It lies 80 km (50 mi) south of Italy, 284 km (176 mi) east of Tunisia,[13] and 333 km (207 mi) north of Libya.[14] With a population of about 475,000[4] over an area of 316 km2 (122 sq mi),[3] Malta is the world's tenth smallest country in area[15][16] and fifth most densely populated sovereign country. Its capital is Valletta, which is the smallest national capital in the European Union by area at 0.8 km2 (0.31 sq mi). The official and national language is Maltese, which is descended from Sicilian Arabic that developed during the Emirate of Sicily, while English serves as the second official language.
listen); Maltese: [ˈmɐltɐ]), officially known as the Republic of Malta (Maltese: Repubblika ta' Malta), is a Southern European island country consisting of an archipelago in the Mediterranean Sea.[12] It lies 80 km (50 mi) south of Italy, 284 km (176 mi) east of Tunisia,[13] and 333 km (207 mi) north of Libya.[14] With a population of about 475,000[4] over an area of 316 km2 (122 sq mi),[3] Malta is the world's tenth smallest country in area[15][16] and fifth most densely populated sovereign country. Its capital is Valletta, which is the smallest national capital in the European Union by area at 0.8 km2 (0.31 sq mi). The official and national language is Maltese, which is descended from Sicilian Arabic that developed during the Emirate of Sicily, while English serves as the second official language.
Malta has been inhabited since approximately 5900 BC.[17] Its location in the centre of the Mediterranean[18] has historically given it great strategic importance as a naval base, with a succession of powers having contested and ruled the islands, including the Phoenicians and Carthaginians, Romans, Greeks, Arabs, Normans, Aragonese, Knights of St. John, French, and British.[19] Most of these foreign influences have left some sort of mark on the country's ancient culture.
Malta became a British colony in 1813, serving as a way station for ships and the headquarters for the British Mediterranean Fleet. It was besieged by the Axis powers during World War II and was an important Allied base for operations in North Africa and the Mediterranean.[20][21] The British Parliament passed the Malta Independence Act in 1964, giving Malta independence from the United Kingdom as the State of Malta, with Queen Elizabeth II as its head of state and queen.[22] The country became a republic in 1974. It has been a member state of the Commonwealth of Nations and the United Nations since independence, and joined the European Union in 2004; it became part of the eurozone monetary union in 2008.
Malta has had Christians since the time of Early Christianity, though was predominantly Muslim while under Arab rule, who tolerated Christians. Norman rulers expelled all Muslims who did not convert, and Aragonese rulers expelled unconverted Jews. Today, Catholicism is the state religion, but the Constitution of Malta guarantees freedom of conscience and religious worship.[23][24]
Malta is a popular tourist destination with its warm climate, numerous recreational areas, and architectural and historical monuments, including three UNESCO World Heritage Sites: Hypogeum of Ħal Saflieni,[25] Valletta,[26] and seven megalithic temples which are some of the oldest free-standing structures in the world.[27][28][29]
Malte (en maltais : Malta ; en anglais : Malta), en forme longue la République de Malte (en maltais : Repubblika ta' Malta ; en anglais : Republic of Malta), est un État insulaire d'Europe situé au milieu de la Méditerranée, à 93 kilomètres au sud de la Sicile. Il est constitué d'un archipel de huit îles, dont quatre sont habitées, et de plusieurs îlots et rochers. La capitale du pays est La Valette, établie sur l'île de Malte.
Sa localisation stratégique entre la Méditerranée occidentale et la Méditerranée orientale lui a valu les convoitises et l'occupation de nombreuses puissances au cours des âges. Malte a acquis son indépendance du Royaume-Uni le 21 septembre 1964. Elle est membre de l’Union européenne depuis le 1er mai 20045, ainsi que de la zone euro depuis le 1er janvier 20086.
Avec ses 316 km2 de superficie, c'est le plus petit État de l'Union européenne. Le pays compte 449 043 habitants en 2018. Sa densité de population est la plus élevée de l'Union européenne, avec 1 421 habitants au km2.
Malte possède une langue nationale, le maltais, et deux langues officielles, le maltais et l'anglais ; l'italien est également compris et pratiqué par de nombreux Maltais.
Malta, ufficialmente Repubblica di Malta (in maltese Repubblika ta' Malta, in inglese Republic of Malta), è uno stato insulare dell'Europa meridionale, nonché lo Stato membro più piccolo dell'Unione europea.
È un arcipelago situato nel Mediterraneo, nel canale di Malta, a 80 km dalla Sicilia, a 284 km dalla Tunisia e a 333 km dalla Libia, compreso nella regione geografica italiana. Con un'estensione di 315,6 km² è uno degli stati più piccoli e densamente popolati al mondo. La sua capitale è La Valletta e la città più abitata è Birchircara. L'isola principale è caratterizzata da un grande numero di cittadine che, insieme con la capitale, formano una conurbazione di 368 250 abitanti.
Il Paese ha due lingue ufficiali, il maltese e l'inglese. L'italiano, lingua ufficiale fino al 1934, è molto diffuso, parlato correttamente da più del 66% dei maltesi.[5] Durante il corso della storia, la posizione geografica di Malta ha dato grande importanza all'arcipelago, che ha subito l'avvicendarsi in sequenza di Fenici, Greci, Cartaginesi, Romani, Arabi, Normanni, Aragonesi, Cavalieri di Malta, Francesi e Inglesi.
Malta è internazionalmente conosciuta come località turistica, per lo svago e soprattutto per la cultura, dato che nel Paese si trovano ben tre siti dichiarati dall'UNESCO patrimonio dell'umanità: la capitale La Valletta, l'Ipogeo di Hal Saflieni e i templi megalitici. L'ingresso nell'Unione europea è avvenuto il 1º maggio 2004 e dal 1º gennaio 2008 è entrata a far parte dell'Eurozona. Malta è inoltre membro del Commonwealth.
Malta, oficialmente la República de Malta (en maltés: Repubblika ta' Malta; en inglés: Republic of Malta), es un país insular miembro de la Unión Europea, densamente poblado, compuesto por un archipiélago y situado en el centro del Mediterráneo, al sur de Italia, al oriente de Túnez y al norte de Libia. Debido a su situación estratégica, ha sido gobernado y disputado por diversas potencias en el transcurso de los siglos. Desde 1964 es independiente y en 2004 se adhirió a la Unión Europea.3
Malta es un popular destino turístico con su clima cálido, numerosas áreas recreativas y monumentos arquitectónicos e históricos, incluidos tres sitios del Patrimonio Mundial de la UNESCO: el Hipogeo de Hal Saflieni, La Valeta, y siete templos megalíticos que son algunas de las estructuras independientes más antiguas en el mundo. En 2018 tenía una población de 475 700 habitantes con una distribución de 1457 hab./km², la más alta densidad de población entre los países de la Unión Europea.
Ма́льта (мальт. и англ. Malta), Респу́блика Ма́льта (мальт. Repubblika ta' Malta, англ. Republic of Malta) — островное государство в Средиземном море, на Мальтийском архипелаге.
1 мая 2004 года Мальта стала членом Европейского союза.
 Klipper/Clipper
Klipper/Clipper
 Fünfmast
Fünfmast
 Malta
Malta

 Ships and Nautics
Ships and Nautics
 *Star Clippers
*Star Clippers
 Segelschiff
Segelschiff
 Full rigged ship
Full rigged ship
 Segelschiff
Segelschiff
 Clipper
Clipper

 Andorra
Andorra
 Belgium
Belgium
 Bulgaria
Bulgaria
 Denmark
Denmark
 Germany
Germany
 Estonia
Estonia
 Finland
Finland
 France
France
 Gibraltar
Gibraltar
 Greece
Greece

 Hand in Hand
Hand in Hand
 Ireland
Ireland
 Iceland
Iceland
 Italy
Italy
 Croatia
Croatia
 Latvia
Latvia
 Liechtenstein
Liechtenstein
 Lithuania
Lithuania
 Luxembourg
Luxembourg
 Malta
Malta
 Monaco
Monaco
 Netherlands
Netherlands
 Northern Ireland
Northern Ireland
 Norwegen
Norwegen
 Austria
Austria
 Poland
Poland
 Portugal
Portugal
 Romania
Romania
 San Marino
San Marino
 Sweden
Sweden
 Switzerland
Switzerland
 Slovakia
Slovakia
 Slovenia
Slovenia
 Spain
Spain
 Czech Republic
Czech Republic
 Hungary
Hungary

 Vacation and Travel
Vacation and Travel
 Vatican city
Vatican city
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 Cyprus
Cyprus

《申根协议》(德语:Schengener Abkommen;法语:Convention de Schengen;荷兰语:Verdrag van Schengen),是一项欧洲大陆国家间的条约协定,其签约目的是取消相互之间的边境检查点,并协调对申根区之外的边境控制。即在成员国相互之间取消边境管制,持有任一成员国有效身份证或申根签证的人可以在所有成员国境内自由流动。根据该协定,旅游者如果持有其中一国的旅游签证即可合法地到所有其他申根国家。
《申根协议》的成员国亦称“申根国家”或者“申根协议国”,成员国的整体又称“申根区”。申根区目前包含26个国家,其中有22个属于欧盟成员。四个非欧盟成员国中,冰岛和挪威以北欧护照联盟成员国的身份加入申根区,官方分类属于与欧盟申根区活动相关的国家。不属于欧洲大陆的爱尔兰没有加入。
Die Schengener Abkommen sind internationale Übereinkommen, insbesondere zur Abschaffung der stationären Grenzkontrollen an den Binnengrenzen der teilnehmenden Staaten. Dies sind im Kern die Mitglieder der Europäischen Union, jedoch ohne Irland, Rumänien, Bulgarien und Zypern. Durch Zusatzabkommen mit der Europäischen Union wurde der Anwendungsbereich auf Island, Liechtenstein, Norwegen und die Schweiz ausgedehnt. Der Gültigkeitsbereich des Abkommens wird gemeinhin als Schengen-Raum bezeichnet.
Das erste dieser Abkommen vom 14. Juni 1985 sollte vor allem die Schaffung eines europäischen Binnenmarktes vorantreiben und wurde nach dem Unterzeichnungsort benannt, der Gemeinde Schengen im Großherzogtum Luxemburg. Die mehrfach modifizierten Regelungen (Schengen I bis III) konstituieren den Schengen-Besitzstand, einen wesentlichen Pfeiler des „Raumes der Freiheit, der Sicherheit und des Rechts“[1] der Europäischen Union. Bedeutung und Verdienste des Schengener Abkommens werden im Europäischen Museum Schengen dokumentiert.
Das unkontrollierte Passieren der Binnengrenzen als Prinzip der Schengener Abkommen wurde im Zuge der Flüchtlingskrise in Europa ab 2015 zeitweise von mehreren europäischen Ländern außer Kraft gesetzt, nachdem einzelne Mitgliedstaaten die Sicherung der Außengrenzen der Europäischen Union gefährdet sahen.
Von März bis Juni 2020 waren wegen der COVID-19-Pandemie zahlreiche Grenzen zwischen Mitgliedstaaten geschlossen.[2][3] Im Februar 2021 kam es wegen der Pandemie erneut zu Grenzschließungen.
 Architecture
Architecture
 International cities
International cities
 Art
Art
 Party and government
Party and government
 European Union
European Union