
Deutsch-Chinesische Enzyklopädie, 德汉百科
 Grand Est
Grand Est

 Alsace
Alsace

 Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes
Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes
 Bourgogne
Bourgogne
 Bourgogne-Franche-Comté
Bourgogne-Franche-Comté
 Champagne-Ardenne
Champagne-Ardenne
 France
France

 Grand Est
Grand Est
 Lorraine
Lorraine
 Switzerland
Switzerland
The Saône (/soʊn/ SOHN, French: [son];[1] Francoprovençal: Sona; Latin: Arar) is a river of eastern France. It is a right tributary of the Rhône, rising at Vioménil in the Vosges department and joining the Rhône in Lyon, just south of the Presqu'île.
The name Saône derives from that of the Gallic river goddess Souconna, which has also been connected with a local Celtic tribe, the Sequanes. Monastic copyists progressively transformed Souconna to Saoconna, which ultimately gave rise to Saône. The other recorded ancient names for the river were Brigoulus and Arar.
La Saône [soːn]3 est une rivière de l'Est de la France, principal affluent de la rive droite du Rhône.
Avec une longueur de près de 480 kilomètres1, c'est le neuvième cours d'eau le plus long de France.
La Saona (in francese Saône) è un importante fiume dell'est della Francia, principale affluente di destra del Rodano. La sua sorgente si trova a quote modeste (402 m sul livello del mare) presso Vioménil nel dipartimento dei Vosgi. Il fiume si arricchisce progressivamente di vari apporti scorrendo sinuoso fino a ricevere il suo principale affluente: il fiume Doubs.
Da questa confluenza diventa navigabile sino alla foce (presso Lione) nel Rodano dopo un corso lungo 480 km.[1] Il fiume, pur con un regime quasi esclusivamente pluviale (esclusa la porzione di bacino drenata dall'affluente Doubs), beneficia però nel suo alto corso della regolarità delle precipitazioni tipiche del clima Oceanico, fornendo così un notevole apporto medio d'acqua al fiume Rodano (473 m3/s), al punto da costituirne da Lione in poi quasi la metà della sua portata ordinaria.
Il suo nome deriva dal nome della dea celtica Souconna, mentre il nome latino era Arar.
El río Saona (en francés, la Saône, pronunciado /laˈsoːn/)1 es un río del este de Francia, el principal afluente del río Ródano, desde el norte. Tiene una longitud de 480 km,2 y drena una amplia cuenca de 29.950 km². Su principal afluente es el río Doubs.
Со́на (фр. Saône [son]) — река на востоке Франции, правый приток Роны. Длина 473,3 км, площадь бассейна 29 321 км²[1]. Средний расход воды 410 м³/с.
Река берёт начало у лотарингского города Вьомениль, течёт преимущественно на юг — юго-запад, впадает в Рону возле Лиона. Протекает через 3 региона Гранд-Эст, Бургундия — Франш-Конте, Овернь — Рона — Альпы и 5 департаментов Вогезы, Верхняя Сона, Кот-д’Ор,Сона и Луара и Рона, 205 коммун[1].
Сона судоходна, соединена каналами с реками Мозель, Луара (через Центральный канал и Боковой канал Луары), Марна (через канал Марна-Сона), Сена (через Йонну и Бургундский канал), Рейн (через канал Рона-Рейн).Крупнейшие притоки — Ду (453 км), Оньон (214 км), Сей (100 км), Грона (96 км), Уша (95 км), Тий (83 км).
Название Сона произошло от древнего названия Сауконна[2] (Sauconnam[3]), которое впервые упоминается в IV веке до н. э. Аммианом Марцеллином, по имени кельтской речной богини Сауконны (Souconna)[4], культ которой был у племени секванов. Римляне называли реку Арар (лат. Arar)[5], а еще раньше — Бригул (лат. Brigoulus)[6].
 Bourgogne
Bourgogne

 Bourgogne-Franche-Comté
Bourgogne-Franche-Comté
 Champagne-Ardenne
Champagne-Ardenne
 France
France

 Grand Est
Grand Est

 Ile-de-France
Ile-de-France

 Normandie
Normandie

 2024 Summer Olympics
2024 Summer Olympics
 Seine
Seine

 World Heritage
World Heritage


塞纳河主流源头位于勃艮第地区,科多尔省的首府第戎西北30公里的朗格勒高原,流经奥布省的首府特鲁瓦,穿过巴黎市中心,经过诺曼底的鲁昂,到达勒阿弗尔入海,流入拉芒什海峡(英语称为英吉利海峡)。
北部支流有马恩河、瓦兹河、奥布河;南部支流有约纳河、厄尔河。通过17世纪-18世纪修建的运河,可以沟通莱茵河的支流默兹河,法国南部主要河流罗讷河的支流索恩河,以及法国第一大河卢瓦尔河,吃水浅的船只可以直接航行到比利时、德国和地中海。上游马恩河和奥布河流域是香槟酒的主要产区。
塞纳河流域地势平坦,从巴黎到河口365公里,坡降只有24米,因此水流缓慢,利于航行。整个流域降水量为630-760毫米,平均流量为280立方米/秒,夏季水位低,冬季水位高,和中国的情况相反。上游建有几座水库,调节流量,但主要是为下游城市用水蓄水,巴黎的1/2用水,勒阿弗尔和鲁昂的3/4用水,都来自塞纳河。
Die Seine ([sɛn]; auf Französisch; lateinisch/keltisch Sequana) ist ein Fluss in Nordfrankreich. Sie entspringt in der Region Bourgogne-Franche-Comté, fließt von Osten nach Westen und mündet bei Le Havre in den Ärmelkanal. Mit 777 Kilometern[2] Länge ist sie neben der Loire (1004 Kilometer) und den ineinander übergehenden Flussverläufen von Doubs, Saône und Rhône (insgesamt 1025 Kilometer) einer der längsten Flüsse Frankreichs. Das Einzugsgebiet der Seine umfasst etwa 78.650 km².
Wichtige Städte an der Seine sind Paris, Troyes und Rouen. In Paris und Rouen befinden sich die wichtigsten Binnenhäfen Frankreichs. Über Kanäle ist die Seine mit Schelde, Maas, Rhein, Saône und Loire verbunden. Am Unterlauf des Flusses im Gebiet der Normandie haben sich für einen Fluss dieser Wasserführung außergewöhnlich große Talschleifen gebildet. Die schiffbare Länge (bis Nogent-sur-Seine) beträgt 560 km. Seeschiffe können den Fluss bis Rouen (120 km im Landesinneren) befahren.
Das Seineufer von Paris steht auf der Liste des Weltkulturerbes der UNESCO.
セーヌ川(セーヌがわ、Seine)は、フランスを流れる河川である。流域も全体がフランスに属している。全長780kmは、フランスではロワール川に続いて第二の長さ[1]である。
ディジョンの北西30kmの海抜471mの地点に源を発し北西に向かい、パリを流れ、ル・アーヴルとオンフルールの間のセーヌ湾に注ぐ。
中下流部は大きく蛇行した流れが特徴で、パリを抜けるあたりから何度も繰り返す。ジヴェルニー、ヴェルノンの付近は、しばらく治まるが、ルーアンの近辺で再び蛇行が始まる。
河口付近の川幅は大きく広がっており、湾と言っても差し支えないほどである。ル・アーヴルとオンフルールの間に、1995年にノルマンディー橋が完成するまでは、両市の陸上交通は、さらに20kmほど上流のタンカルヴィル橋まで遡らなければならなかった。
The Seine (/seɪn/ SAYN, French: [sɛːn] (![]() listen)) is a 777-kilometre-long (483 mi) river and an important commercial waterway within the Paris Basin in the north of France. It rises at Source-Seine, 30 kilometres (19 mi) northwest of Dijon in northeastern France in the Langres plateau, flowing through Paris and into the English Channel at Le Havre (and Honfleur on the left bank).[1] It is navigable by ocean-going vessels as far as Rouen, 120 kilometres (75 mi) from the sea. Over 60 percent of its length, as far as Burgundy, is negotiable by commercial riverboats, and nearly its whole length is available for recreational boating; excursion boats offer sightseeing tours of the river banks in Paris, lined with top monuments including Notre-Dame, the Eiffel Tower, the Louvre Museum and Musée d'Orsay.[2]
listen)) is a 777-kilometre-long (483 mi) river and an important commercial waterway within the Paris Basin in the north of France. It rises at Source-Seine, 30 kilometres (19 mi) northwest of Dijon in northeastern France in the Langres plateau, flowing through Paris and into the English Channel at Le Havre (and Honfleur on the left bank).[1] It is navigable by ocean-going vessels as far as Rouen, 120 kilometres (75 mi) from the sea. Over 60 percent of its length, as far as Burgundy, is negotiable by commercial riverboats, and nearly its whole length is available for recreational boating; excursion boats offer sightseeing tours of the river banks in Paris, lined with top monuments including Notre-Dame, the Eiffel Tower, the Louvre Museum and Musée d'Orsay.[2]
There are 37 bridges within Paris and dozens more spanning the river outside the city. Examples in Paris include the Pont Alexandre III and Pont Neuf, the latter of which dates back to 1607. Outside the city, examples include the Pont de Normandie, one of the longest cable-stayed bridges in the world, which links Le Havre to Honfleur.
La Seine (prononcé [ˈsɛn]) est un fleuve français, long de 776,6 kilomètres1, qui coule dans le Bassin parisien et arrose notamment Troyes, Paris, Rouen et Le Havre. Sa source se situe à 446 m d'altitude2 à Source-Seine, en Côte-d'Or, sur le plateau de Langres. Son cours a une orientation générale du sud-est au nord-ouest. La Seine se jette dans la Manche entre Le Havre et Honfleur. Son bassin versant, d'une superficie de 79 000 km23, englobe près de 30 % de la population du pays.
La Senna (in francese Seine /sɛn/) è uno dei principali fiumi della Francia. La lunghezza approssimativa del fiume è di 776,6 km,[1] le sue fonti sono in Borgogna, a 470 m d'altezza, a Saint-Germain-Source-Seine sull'altopiano di Langres, e la foce è nella Manica, a Nord della Francia, presso Le Havre.
El río Sena (en francés, Seine) es un largo río europeo de la vertiente atlántica que discurre únicamente por Francia. Con una longitud de casi 776 km es el tercero más largo del país — tras el Loira y el Ródano (que es más largo, pero una parte discurre por Suiza. Drena una cuenca de 78 650 km², la 3.ª del país y casi un séptimo del territorio francés. Tiene sus fuentes en varios manantiales a 470 msnm en la meseta de Langres, en el departamento de Côte-d'Or, en la región de Borgoña y desemboca en un amplio estuario en El Havre, en la bahía del Sena.
Administrativamente, recorre cuatro regiones francesas —Borgoña-Franco Condado, Gran Este, Île-de-France y Normandía]— y catorce departamentos —Côte-d'Or, Aube, Marne, Seine-et-Marne, Essonne, Val-de-Marne, Paris, Hauts-de-Seine, Seine-Saint-Denis, Val-d'Oise, Yvelines, Eure, Sena Marítimo y Calvados—, de los que cuatro llevan su nombre.
Atraviesa algunas ciudades importantes —Troyes, Melun, Ruan— y especialmente la capital, París, que se ha desarrollado sobre sus dos márgenes, y en la que los recorridos en los típicos bateaux mouches son una atracción turística. Hay treinta y siete puentes parisinos que atraviesan el río, como el Pont Louis-Philippe y el Pont Neuf, este último erigido ya en año 1607. Cerca del estuario está el puente de Normandía, uno de los más largos puentes atirantados del mundo, que une El Havre con Honfleur.
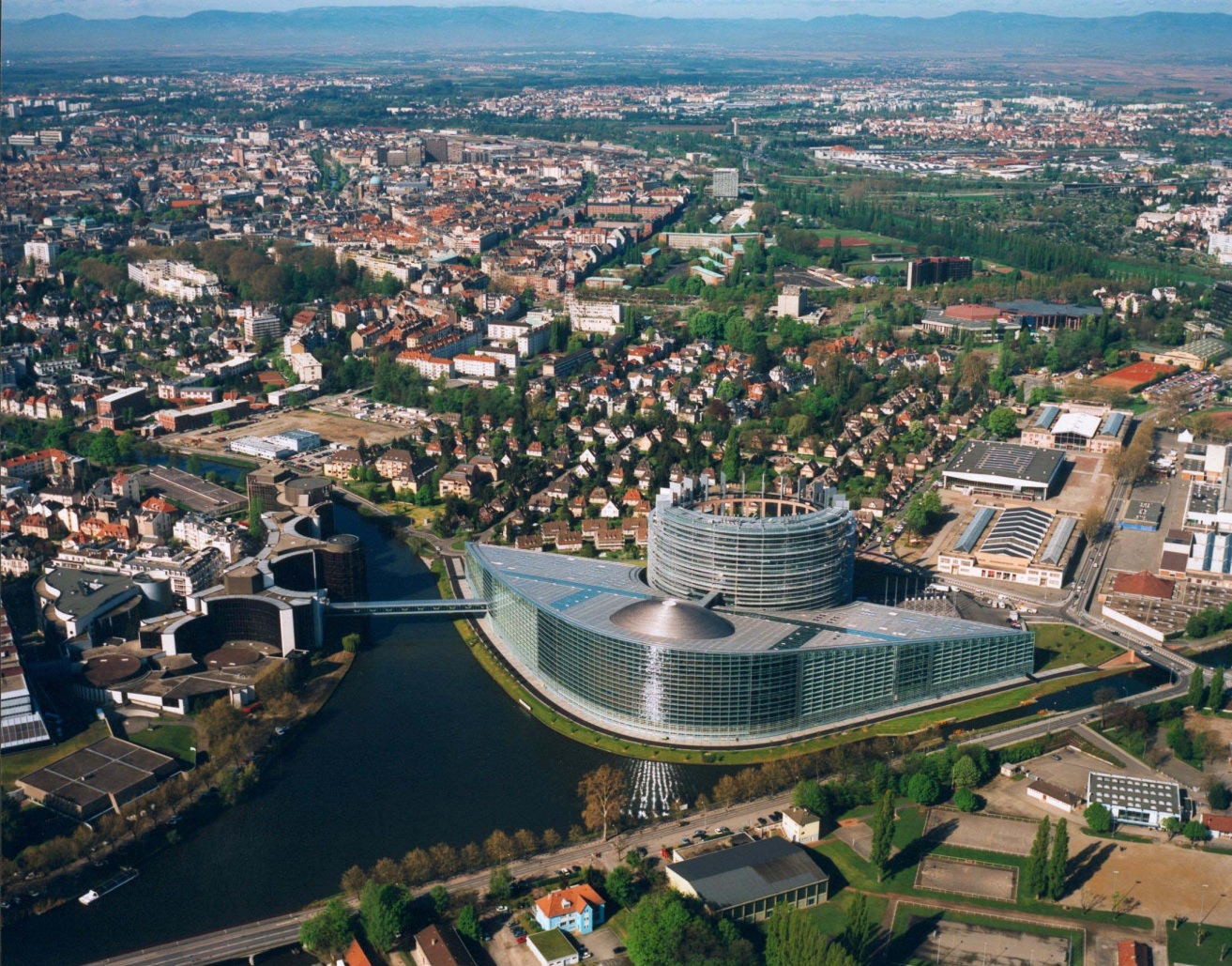




斯特拉斯堡 (Strasbourg),法国东北部城市,大东部大区(Région Grand Est)的首府和下莱茵省(Bas-Rhin,67省)的省会,也是法国第七大城市和最大的边境城市 ,又称白堡。市区位于莱茵河西岸,东侧与德国巴登-符腾堡州隔河相望,西侧则为孚日山区。斯特拉斯堡远离海岸线,但仍然受到北大西洋暖流的影响,属于非典型性的温带海洋性气候。历史上,斯特拉斯堡处于多个民族活动范围的重合地带。从最初的凯尔特,再到高卢、日耳曼以及后来的法兰克、查理曼,这些民族都在斯特拉斯堡留下了足迹。十九时期中期开始则逐渐成为了德法长期争夺的焦点。二战后,凭借得天独厚的地理优势,欧洲委员会、欧洲人权法院、欧洲反贪局及欧洲议会等多个欧盟合作组织均在斯特拉斯堡设立总部 。
斯特拉斯堡(法语:Strasbourg;德语:Straßburg[4],意为“街道城堡”)是法国大东部大区与下莱茵省的首府,位于法国国土的东端,与德国的巴登-符腾堡州隔莱茵河相望。全市人口约27万,城市圈人口则超过64万[5],是法国东北部人口最多的城市,按2010年人口也是法国人口第九多的城市。
斯特拉斯堡属于法国,但是在历史上,此地的主权曾多次交替由德国和法国拥有,因而在语言和文化上兼有法国和德国的特点,是这两种不同文化的交汇之地。谷登堡、加尔文、歌德、莫扎特、巴斯德等德意志法兰西文化名人都曾在斯特拉斯堡居留。
斯特拉斯堡也是众多国际组织总部所在地的城市。斯特拉斯堡与比利时的首都布鲁塞尔一样,驻有欧盟的许多重要机构,包括欧洲委员会、欧洲人权法院、欧盟反贪局、欧洲军团、欧洲视听观察,以及欧洲议会的所在地,因此被誉为欧盟的“第二首都”。斯特拉斯堡是欧洲议会的所在地,尽管每个月只在斯特拉斯堡举行四天会议,其他主要事务则在布鲁塞尔处理。议会大厦建于1998年,是世界上最大的议会建筑。
斯特拉斯堡是法国乃至西欧公路、铁路和内河航运的重要中心。斯特拉斯堡港是莱茵河沿线的第二大港口,仅次于德国的杜伊斯堡[6]。该市也是莱茵河航运中央委员会的驻地。
斯特拉斯堡的历史中心位于伊尔河两条支流环绕的大岛,这一区域拥有中世纪以来的大量精美建筑,包括斯特拉斯堡大教堂与小法兰西,1988年被联合国教科文组织列为世界文化遗产,这也是首次有一个城市的整个市中心区域获此荣誉。
Straßburg (französisch Strasbourg [stʁazbuʁ], im Straßburger Dialekt Schdroosburi [ˈʃdɾoːsburi][1]) ist eine Stadt im Elsass, einer Landschaft im Osten Frankreichs an der Grenze zu Deutschland.
Die Stadt ist Hauptstadt und damit Sitz des Regionalrats und des Regionspräfekten der Region Grand Est sowie Sitz der Präfektur des Départements Bas-Rhin. Die Präfektur verwaltet auch das Arrondissement Strasbourg, das aus 33 Gemeinden besteht. Mit 277.270 Einwohnern (Stand 1. Januar 2015) im Stadtgebiet und etwa 640.000 Einwohnern in der Agglomeration ist Straßburg die größte Stadt im Elsass.[2]
Straßburg ist Sitz zahlreicher europäischer Einrichtungen, unter anderem Europarat, Europaparlament, Europäischer Gerichtshof für Menschenrechte, Europäischer Bürgerbeauftragter und Eurokorps. Aufgrund dessen versteht sich Straßburg als „Hauptstadt Europas“.[3][4][5]
Teile der Innenstadt, die mittelalterliche Altstadt auf der Grande-île und die Neustadt, sind unter dem Titel Straßburg: von der Grande-Île zur Neustadt, eine europäische Stadtszenerie UNESCO-Weltkulturerbe.
ストラスブール(仏・英: Strasbourg[注釈 1]、アルザス語: Schdroosburi[注釈 2]、アレマン語: Strossburi[注釈 3]、独: Straßburg[注釈 4])は、グラン・テスト地域圏の首府である。バ=ラン県の県庁所在地でもある。
フランス北東部の、ライン川左岸に位置する。河川港を抱える交通の要衝である。対岸にはドイツの都市ケールが存在するが、シェンゲン協定によってパスポートチェック無しで自由に行き来できる。2007年6月10日にはTGV東ヨーロッパ線が開業し、パリ東駅と2時間20分で結ばれた。
ストラスブール(シュトラースブルク)の語源はドイツ語で「街道の街」であり、交通の要衝として栄える。ライン川にフランス最大の河川港をもち、交通の便の良さから商工業が盛んである。1998年から当地のクレディ・ミュチュエルが商工信用銀行を支配している[注釈 5]。
かつてはドイツの神聖ローマ帝国に属したが、近世初頭にドイツの混乱に乗じてフランス王国が侵略して併合する。以降、ドイツとフランスが領有権を争った土地として有名である。言語や文化の上ではドイツ系であるといえるが、下記のように1944年以降、政治的にはフランスに属する。
現在は欧州評議会や欧州人権裁判所、またEUの欧州議会の本会議場を擁し、ベルギーのブリュッセルと共にEUの象徴的な都市の一つとなっている。フランス国立行政学院(ENA, エナ)の校舎もあり、欧州のエリートが当地で養成される。また、近郊の村エンツハイムにはスポーツウェア等で知られるルコックスポルティフの、同様に近郊のモルスアイムにはブガッティ・オトモビルの各本社機能がそれぞれ置かれている。
グーテンベルクやカルヴァン、ゲーテ、モーツァルト、パストゥールなども人生の一時期をこの地で過ごした。その中には現代史に欠かせないユダヤ銀行家がおり、マーク・ユージン・マイヤー(Marc Eugene Meyer 1842-1925)といった。その祖父はユダヤ教会役員会のラビ書記だった。自身は1859年17歳のときにカリフォルニアへ移住し、ロサンゼルスのデパート所有者となった。それからニューヨークでラザードの共同経営者となった[2]。その息子もラザードでキャリアを積み、連邦準備制度議長と初代世銀総裁を務めた。このようなマークの息子が授かった娘はキャサリン・グラハム女史である。
もっと永く過ごしたマークの同時代人で、ストラスブールの立場を理解するのに知っておくべき女性がいる。メラニー・ド・プルタレスは政治も担った。シュテファニー・フォン・ヴェデル(Stéphanie von Wedels, 1852-1937)はスウェーデンのヤーコプ・ハミルトンが父である。ストックホルム駐在ドイツ帝国大使のカール・フォン・ヴェデルと結婚した。1907年夫がラインラント総督へ就任したのを機に、ストラスブールへ定住した。身体障害児の養護施設シュテファニー・ホスピスをつくらせるなどの社会貢献をなした。
Strasbourg (/ˈstræzbɜːrɡ/, French: [stʁazbuʁ, stʁas-]; Alsatian: Strossburi [ˈʃd̥ʁɔːsb̥uʁi]; German: Straßburg [ˈʃtʁaːsbʊɐ̯k]) is the capital and largest city of the Grand Est region of France and is the official seat of the European Parliament. Located close to the border with Germany in the historic region of Alsace, it is the capital of the Bas-Rhin département. In 2014, the city proper had 276,170 inhabitants and both the Eurométropole de Strasbourg (Greater Strasbourg) and the Arrondissement of Strasbourg had 484,157 inhabitants.[2] Strasbourg's metropolitan area had a population of 773,347 in 2013 (not counting the section across the border in Germany), making it the ninth largest metro area in France and home to 13% of the Grand Est region's inhabitants. The transnational Eurodistrict Strasbourg-Ortenau had a population of 915,000 inhabitants in 2014.[5]
Strasbourg is one of the de facto capitals of the European Union (alongside Brussels and Luxembourg), as it is the seat of several European institutions, such as the Council of Europe (with its European Court of Human Rights, its European Directorate for the Quality of Medicines and its European Audiovisual Observatory) and the Eurocorps, as well as the European Parliament and the European Ombudsman of the European Union. The city is also the seat of the Central Commission for Navigation on the Rhine and the International Institute of Human Rights.[6]
Strasbourg's historic city centre, the Grande Île (Grand Island), was classified a World Heritage site by UNESCO in 1988, the first time such an honour was placed on an entire city centre. Strasbourg is immersed in Franco-German culture and although violently disputed throughout history, has been a cultural bridge between France and Germany for centuries, especially through the University of Strasbourg, currently the second largest in France, and the coexistence of Catholic and Protestant culture. It is also home to the largest Islamic place of worship in France, the Strasbourg Grand Mosque.[7]
Economically, Strasbourg is an important centre of manufacturing and engineering, as well as a hub of road, rail, and river transportation. The port of Strasbourg is the second largest on the Rhine after Duisburg, Germany.[8]
Strasbourg (prononcé [stʁas.buʁ] Écouter) est une commune française située dans le département du Bas-Rhin. Préfecture du département, elle est également, depuis le 1er janvier 2016, le chef-lieu de la région Grand Est. Strasbourg se trouve dans la région historique d'Alsace, dont elle est considérée comme la capitale, et était le chef-lieu de la région administrative du même nom de 1982 à 2015.
La ville accueille de multiples institutions européennes et internationales, notamment le Conseil de l'Europe dont dépendent la Cour européenne des droits de l'homme et la Pharmacopée européenne, le Parlement européen ou encore le Médiateur européen. Elle revendique ainsi le titre de « capitale européenne ».
Par sa population, Strasbourg intra-muros est la première commune du Grand Est français et, à la date du 1er janvier 2018, la huitième de France. Son aire urbaine est la neuvième de France, comptant 768 868 habitants en 2012 dans sa partie françaiseNote 1 et 1 189 086 habitants avec la partie allemande. Ses habitants sont appelés les Strasbourgeois. Elle est l'un des principaux pôles économiques du Nord-Est et se distingue par un secteur secondaire très diversifié et un secteur tertiaire essentiellement tourné vers les activités financières, la recherche et le conseil aux entreprises1.
Ville frontière avec l'Allemagne, Strasbourg a été marquée par les différentes administrations germaniques et françaises. Son histoire, riche et tourmentée, a laissé un patrimoine architectural remarquable. Son centre-ville, situé sur la Grande Île, est entièrement inscrit au patrimoine mondial de l'humanité par l’UNESCO depuis 1988 et comprend notamment la cathédrale Notre-Dame de Strasbourg et le quartier de la Petite France. En 2017, le périmètre classé est étendu à une partie de la Neustadt, quartier construit par les autorités allemandes à partir de 18802.
Strasbourg est également devenue le symbole de la réconciliation franco-allemande et plus généralement de la construction européenne. La ville s’est progressivement spécialisée dans les fonctions politiques, culturelles, et institutionnelles. Elle est ainsi l’une des seules villes au monde à être le siège d'organisations internationales sans être capitale d’un pays3. Strasbourg est une ville de congrès internationaux, la deuxième de France après Paris4.
La présence de plusieurs établissements nationaux renommés, comme le théâtre national, la bibliothèque nationale et universitaire et l’Opéra national du Rhin en fait un centre culturel important.
Strasbourg est aussi une grande ville étudiante, son université, ses grandes écoles et son hôpital universitaire forment un pôle universitaire majeur tourné vers l’international avec plus de 20 % d'étudiants étrangers et plus de cent nationalités représentées5. L'université qui a accueilli 18 prix Nobel dans ses murs, a été lauréate de nombreux appels d'offres dans le cadre des investissements d'avenir, visant à en faire un pôle d'excellence dans l'enseignement supérieur et la recherche au niveau mondial6,7.
Strasburgo (AFI: /straˈzburɡo/[2][3]; in francese Strasbourg, [stʁas.buʁ]; in alsaziano Strossburi, [ˈʃtɾʊːsburi]; in tedesco Straßburg; dal latino Strateburgus, letteralmente "la città delle strade", nome alternativo dell'antica Argentoratum) è una città della Francia orientale, capoluogo della regione Grande Est e del dipartimento del Basso Reno, al confine con la Germania sulla riva sinistra del Reno.
Il suo nome è tedesco perché, in passato, il territorio dell'Alsazia è stato sotto il dominio sia della Francia che della Germania. L'Alsazia fu presa alla Francia dalla Germania (che allora era comandata da Bismarck) durante la battaglia di Sedan del 1870, e da allora fra i francesi nacque il sentimento del revanscismo.
I suoi abitanti sono chiamati strasburghesi (in tedesco Straßburger, in francese strasbourgeois). La città fa parte di un agglomerato urbano transfrontaliero di 1 145 000 abitanti che comprende anche la città tedesca di Kehl.
Strasburgo è sede, con Bruxelles, del Parlamento europeo e ospita, inoltre, il Consiglio d'Europa.
In essa operano l'Università di Strasburgo, la seconda più importante Università francese, e la prestigiosa Scuola Nazionale della Pubblica Amministrazione (ENA) fondata dal Presidente De Gaulle.
Estrasburgo3 (en francés: Strasbourg [stʁazbuʁ]; en alsaciano: Strossburi [ˈʃdɾoːsburi]; en alemán: Straßburg [ˈʃtʁaːsbʊɐ̯k]) es una ciudad de Francia, situada en la región histórica y cultural de Alsacia. Estrasburgo es capital del departamento del Bajo Rin, y desde el 1 de enero de 2016 de la región administrativa del Gran Este.
El área urbana de Estrasburgo alcanzó en 2009 una población de 1.175.393 habitantes, extendiendo su influencia a localidades próximas de Alemania y situándose en la novena posición de los núcleos de población más grandes de Francia. Por su situación, Estrasburgo es desde la antigüedad un importante centro de comunicaciones, especialmente fluvial, albergando el segundo puerto en importancia sobre el río Rin, siendo éste el río más transitado del mundo. Ciudad universitaria con más 58 000 estudiantes, tiene numerosas escuelas nacionales, siendo el mayor polo de estudios de tercer grado del país. La estructura comercial de Estraburgo es muy importante y su rango cultural, muy elevado con la presencia de un teatro, biblioteca, orquesta y ópera todos ellos de ámbito nacional. La ciudad es, con la capital del país, la única en tener ese nivel de instituciones culturales. Estrasburgo es la segunda plaza bancaria de Francia con una bolsa y 8 sedes bancarias. El sector industrial es especialmente activo, siendo la región de Estrasburgo la más dinámica del país en cuanto al PIB per cápita.
Su centro histórico está declarado Patrimonio Unesco de la Humanidad desde 1988 y su actividad turística es muy intensa. Es la octava ciudad de la lista mundial de ciudades organizadoras de congresos, por detrás de París y por delante de Barcelona.
Стра́сбу́рг[1], или Страсбу́р[2][3][4][5] (фр. Strasbourg [stʁas.buʁ] ![]() слушать, эльз. Strossburi [ʃtrosburi], нем. Straßburg [ˈʃtʁaːsbʊɐ̯k]) — город и коммуна на востоке Франции, историческая столица Эльзаса и префектура департамента Нижний Рейн. Расположен в регионе Гранд-Эст[6] (бывший Эльзас — Шампань — Арденны — Лотарингия), департамент Нижний Рейн, округ Страсбур, кантоны: Страсбур-1, Страсбур-2, Страсбур-3, Страсбур-4, Страсбур-5, Страсбур-6[7] на реке Иль, близ левого (западного) берега реки Рейн, по которой проходит граница Франции и Германии, напротив немецкого города Кель. Население — 272 800 чел. (2004 год).
слушать, эльз. Strossburi [ʃtrosburi], нем. Straßburg [ˈʃtʁaːsbʊɐ̯k]) — город и коммуна на востоке Франции, историческая столица Эльзаса и префектура департамента Нижний Рейн. Расположен в регионе Гранд-Эст[6] (бывший Эльзас — Шампань — Арденны — Лотарингия), департамент Нижний Рейн, округ Страсбур, кантоны: Страсбур-1, Страсбур-2, Страсбур-3, Страсбур-4, Страсбур-5, Страсбур-6[7] на реке Иль, близ левого (западного) берега реки Рейн, по которой проходит граница Франции и Германии, напротив немецкого города Кель. Население — 272 800 чел. (2004 год).





 Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes
Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes

 Bourgogne-Franche-Comté
Bourgogne-Franche-Comté

 Bretagne
Bretagne

 Centre-Val de Loire
Centre-Val de Loire
 France
France

 Grand Est
Grand Est

 Hauts-de-France
Hauts-de-France

 Ile-de-France
Ile-de-France
 Languedoc-Roussillon-Midi-Pyrénées
Languedoc-Roussillon-Midi-Pyrénées

 Normandie
Normandie

 Nouvelle-Aquitaine
Nouvelle-Aquitaine

 Occitania
Occitania

 Pays-de-la-Loire
Pays-de-la-Loire

 Provence-Alpes-Côte d´Azur
Provence-Alpes-Côte d´Azur

 Transport and traffic
Transport and traffic

 Transport and traffic
Transport and traffic
 High speed traffic
High speed traffic


 Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes
Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes

 Bourgogne-Franche-Comté
Bourgogne-Franche-Comté

 Bretagne
Bretagne

 Centre-Val de Loire
Centre-Val de Loire
 Corse
Corse
 Franche-Comté
Franche-Comté
 France
France

 Grand Est
Grand Est

 Hauts-de-France
Hauts-de-France

 Ile-de-France
Ile-de-France

 Normandie
Normandie

 Normandie
Normandie

 Normandie
Normandie

 Nouvelle-Aquitaine
Nouvelle-Aquitaine

 Occitania
Occitania

 2024 Summer Olympics
2024 Summer Olympics

 Pays-de-la-Loire
Pays-de-la-Loire

 Provence-Alpes-Côte d´Azur
Provence-Alpes-Côte d´Azur

 Transport and traffic
Transport and traffic
 High speed traffic
High speed traffic



 Geography
Geography
 Sport
Sport
 International cities
International cities
 Cities founded by the Romans
Cities founded by the Romans
 Important port
Important port
 History
History
 Review
Review
 Architecture
Architecture
 Religion
Religion


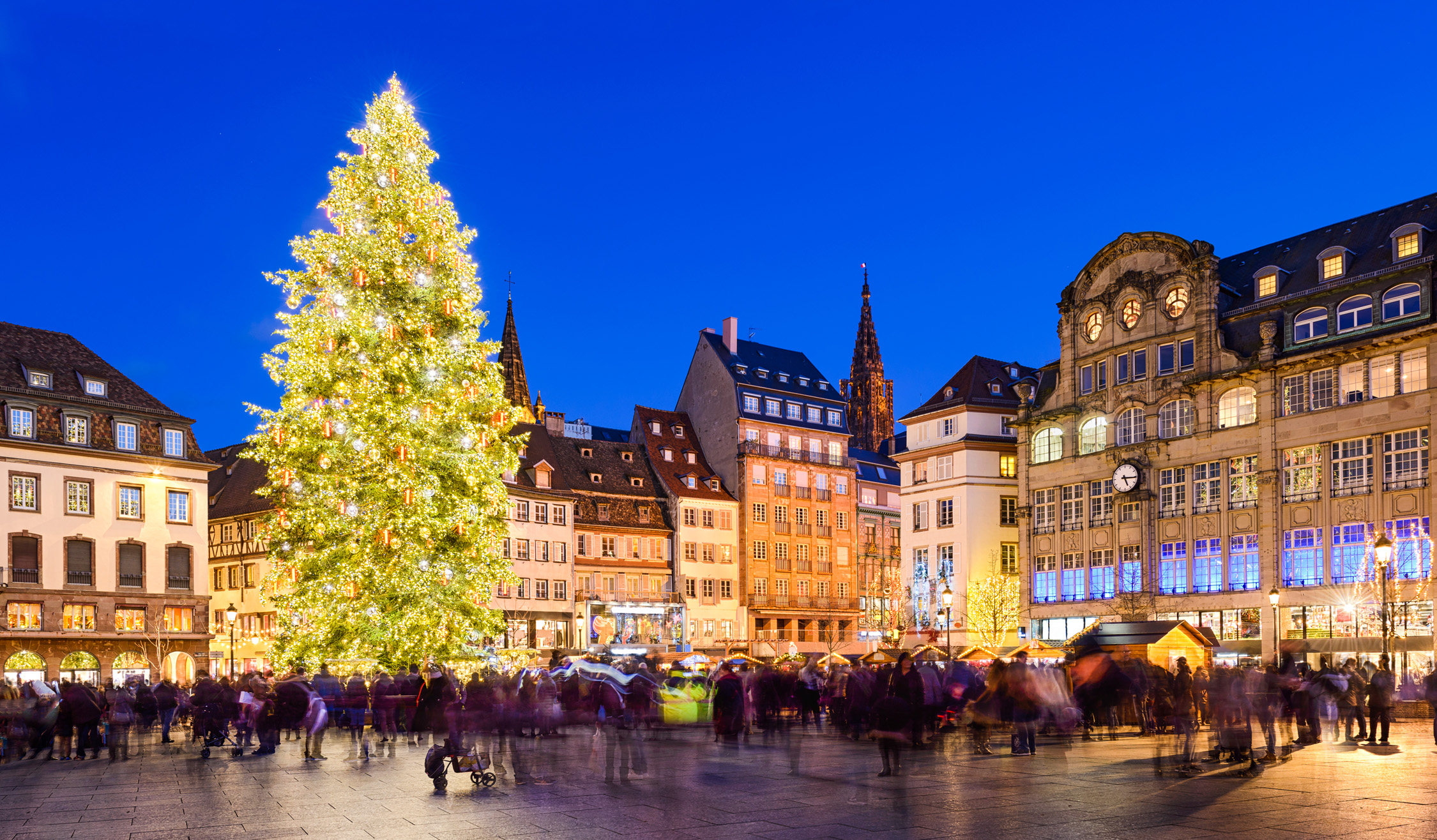
 Christmas Market
Christmas Market
 Eat and Drink
Eat and Drink
 Music
Music