
漢德百科全書 | 汉德百科全书
 Mexico
Mexico
 Mexico
Mexico

 Music
Music

 Music
Music
 *Appreciation of famous music
*Appreciation of famous music

 Dances
Dances

 Dances
Dances
 American Dances
American Dances

 Dances
Dances
 Folk dances
Folk dances

 Dances
Dances
 *Dance music
*Dance music

 Australia
Australia
 Belgium
Belgium
 Chile
Chile
 Denmark
Denmark
 Germany
Germany
 Estonia
Estonia
 Finland
Finland
 France
France
 Greece
Greece
 Ireland
Ireland
 Iceland
Iceland
 Israel
Israel
 Italy
Italy
 Japan
Japan
 Canada
Canada
 Luxembourg
Luxembourg
 Mexico
Mexico
 New Zealand
New Zealand
 Netherlands
Netherlands
 Norwegen
Norwegen
 OECD
OECD
 Emiel van Lennep
Emiel van Lennep
 OECD
OECD
 Don Johnston
Don Johnston
 OECD
OECD
 Jean-Claude Paye
Jean-Claude Paye
 OECD
OECD
 José Ángel Gurría
José Ángel Gurría
 OECD
OECD
 Staffan Sohlman
Staffan Sohlman
 OECD
OECD
 Thorkil Kristensen
Thorkil Kristensen
 Austria
Austria
 Poland
Poland
 Portugal
Portugal
 Republic of Korea
Republic of Korea
 Sweden
Sweden
 Switzerland
Switzerland
 Slovakia
Slovakia
 Slovenia
Slovenia
 Spain
Spain
 Czech Republic
Czech Republic
 Turkey
Turkey
 Hungary
Hungary
 United States
United States
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom

 Important International Organizations
Important International Organizations

経済協力開発機構(けいざいきょうりょくかいはつきこう)は、国際経済全般について協議することを目的とした国際機関。公用語の正式名称は、英語では"Organisation[1] for Economic Co-operation and Development"(イギリス英語表記)、フランス語では"Organisation de Coopération et de Développement Economiques"。略称は英語ではOECD、フランス語ではOCDE。
本部事務局はパリ16区の旧ラ・ミュエット宮殿に置かれている。事務総長はアンヘル・グリア。
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD; French: Organisation de Coopération et de Développement Économiques, OCDE) is an intergovernmental economic organisation with 37 member countries,[1] founded in 1961 to stimulate economic progress and world trade. It is a forum of countries describing themselves as committed to democracy and the market economy, providing a platform to compare policy experiences, seek answers to common problems, identify good practices and coordinate domestic and international policies of its members. Generally, OECD members are high-income economies with a very high Human Development Index (HDI) and are regarded as developed countries. As of 2017, the OECD member countries collectively comprised 62.2% of global nominal GDP (US$49.6 trillion)[3] and 42.8% of global GDP (Int$54.2 trillion) at purchasing power parity.[4] The OECD is an official United Nations observer.[5]
In 1948, the OECD originated as the Organisation for European Economic Co-operation (OEEC),[6] led by Robert Marjolin of France, to help administer the Marshall Plan (which was rejected by the Soviet Union and its satellite states).[7] This would be achieved by allocating United States financial aid and implementing economic programs for the reconstruction of Europe after World War II. (Similar reconstruction aid was sent to the war-torn Republic of China and post-war Korea, but not under the name "Marshall Plan".)[8]
In 1961, the OEEC was reformed into the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development by the Convention on the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development and membership was extended to non-European states.[9][10] The OECD's headquarters are at the Château de la Muette in Paris, France.[11] The OECD is funded by contributions from member countries at varying rates and had a total budget of €386 million in 2019.[2]
Although OECD does not have a power to enforce its decisions, which further require unanimous vote from its members, it is recognized as highly influential publisher of mostly economic data through publications as well as annual evaluations and rankings of members countries.[12]
L'Organisation de coopération et de développement économiques (OCDE) est une organisation internationale d'études économiques, dont les pays membres — des pays développés pour la plupart — ont en commun un système de gouvernement démocratique et une économie de marché. Elle joue essentiellement un rôle d'assemblée consultative1.
L'OCDE a succédé à l'Organisation européenne de coopération économique (OECE) issue du plan Marshall et de la Conférence des Seize (Conférence de coopération économique européenne) qui a existé de 1948 à 1960. Son but était l'établissement d'une organisation permanente chargée en premier lieu d'assurer la mise en œuvre du programme de relèvement commun (le plan Marshall), et, en particulier, d'en superviser la répartition2.
En 2020, l'OCDE compte 37 pays membres et regroupe plusieurs centaines d'experts. Elle publie fréquemment des études économiques et sociales — analyses, prévisions et recommandations de politique économique — et des statistiques, principalement concernant ses pays membres.
Le siège de l'OCDE se situe à Paris (16e), au château de la Muette. L'organisation possède également des bureaux dans plusieurs autres métropoles, notamment à Berlin, Mexico, Tokyo et Washington.
L'Organizzazione per la cooperazione e lo sviluppo economico (OCSE) – in inglese Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), e in francese Organisation de coopération et de développement économiques (OCDE) – è un'organizzazione internazionale di studi economici per i paesi membri, paesi sviluppati aventi in comune un'economia di mercato.
L'organizzazione svolge prevalentemente un ruolo di assemblea consultiva che consente un'occasione di confronto delle esperienze politiche, per la risoluzione dei problemi comuni, l'identificazione di pratiche commerciali e il coordinamento delle politiche locali e internazionali dei paesi membri[1]. Ha sede a Parigi nello Château de la Muette[2].
Gli ultimi paesi ad aver aderito all'OCSE sono la Colombia (28 aprile 2020),la Lettonia (1º luglio 2016) e la Lituania (5 luglio 2018), per un totale di 36 paesi membri.
La Organización para la Cooperación y el Desarrollo Económico1 (OCDE) es un organismo de cooperación internacional, compuesto por 37 estados,34 cuyo objetivo es coordinar sus políticas económicas y sociales. La OCDE fue fundada en 1961 y su sede central se encuentra en el Château de la Muette en París (Francia). Los idiomas oficiales de la entidad son el francés y el inglés.2
En la OCDE, los representantes de los países miembros se reúnen para intercambiar información y armonizar políticas con el objetivo de maximizar su crecimiento económico y colaborar a su desarrollo y al de los países no miembros.
Conocida como «club de los países ricos»,56 a partir de 2017, sus países miembros comprendieron colectivamente el 62,2 % del PIB nominal global (US$49,6 billones) y el 42,8 % del PIB global (Int US$54,2 billones).7
Организа́ция экономи́ческого сотру́дничества и разви́тия (сокр. ОЭСР, англ. Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development, OECD) — международная экономическая организация развитых стран, признающих принципы представительной демократии и свободной рыночной экономики.
Создана в 1948 году под названием Организа́ция европе́йского экономи́ческого сотру́дничества (англ. Organisation for European Economic Co-operation, OEEC) для координации проектов экономической реконструкции Европы в рамках плана Маршалла.
Штаб-квартира организации располагается в Шато де ла Мюетт, в Париже. Генеральный секретарь (с 2006 года) — Хосе Анхель Гурриа Тревиньо (Мексика). Руководящим органом ОЭСР является совет представителей стран — членов организации. Все решения в нём принимаются на основе консенсуса.
По данным на 2011 год, в странах ОЭСР проживало 18 % населения мира[2].



Cancún (spanisch [kaŋˈkun], englisch [kænˈkuːn/kaːn-], oft auch nur Cancun) ist eine Stadt an der Nordostküste der Halbinsel Yucatán und liegt im Municipio Benito Juárez im Nordosten des Bundesstaats Quintana Roo im südöstlichsten Teil Mexikos.
Cancún ist das Zentrum des Urlaubsgebiets Riviera Maya und hat etwa 745.000 Einwohner (Stand: Zensus 2015). Die Stadt ist besonders als Touristenziel wegen seines 23 Kilometer langen Strandes weltbekannt und empfing 2016 über 6 Millionen Besucher.[1] Der Name can cún bedeutet in der Sprache der Maya „Schlangennest“ oder „Schlangentopf“ (der Name wird aber auch oft von „Ort der goldenen Schlange“ hergeleitet).
坎昆(西班牙语:Cancún,西班牙语发音:[kaŋˈkũn] 发音ⓘ[1]),又名康昆,是墨西哥东南部城市,位于加勒比海沿岸,是世界著名度假胜地[2]。坎昆的气候宜人,平均气温介乎26-36°C之间。1970年代,墨西哥政府主力把坎昆发展成度假胜地,现在每年有超过300万人到坎昆旅游,更包括一些名人明星等。坎昆有超过140家酒店,提供24000房间。23公里长的坎昆岛是度假区的中心,部分度假酒店十分豪华,临近加勒比海,海水清澈,在海里游泳的鱼亦清晰可见,不少旅客在这里潜水或乘游艇出海。坎昆附近有一些历史遗迹。

Die Großstadt Campeche, offiziell San Francisco de Campeche, ist die Hauptstadt des gleichnamigen Bundesstaates im Südosten Mexikos. Seit dem Jahr 1999 gehört die Stadt zum Weltkulturerbe der UNESCO.[1] Das im Jahr 1895 von Papst Leo XIII. eingerichtete Bistum Campeche (lat.: Dioecesis Campecorensis, span.: Diócesis de Campeche) ist eine römisch-katholische Diözese mit Sitz in Campeche.
坎佩切 (西班牙语:San Francisco de Campeche)是墨西哥坎佩切州的州府,位于墨西哥湾南部的坎佩切湾。坎佩切是一座海滨城市,截止2005年全市总人口211671人。
坎佩切由西班牙征服者在1540年建立。不过,这里早在玛雅文明时期就是一个名为阿·金·佩奇的部落,当时有3000多个建筑物和一些纪念碑,其中的一部分遗址至今依然可见。此外,这个城市还保留了许多西班牙殖民时期修建的城墙,这些保存较为完好、质量较高的建筑使得坎佩切在1999年时被联合国教科文组织列入世界遗产,登录名称为坎佩切历史要塞城。




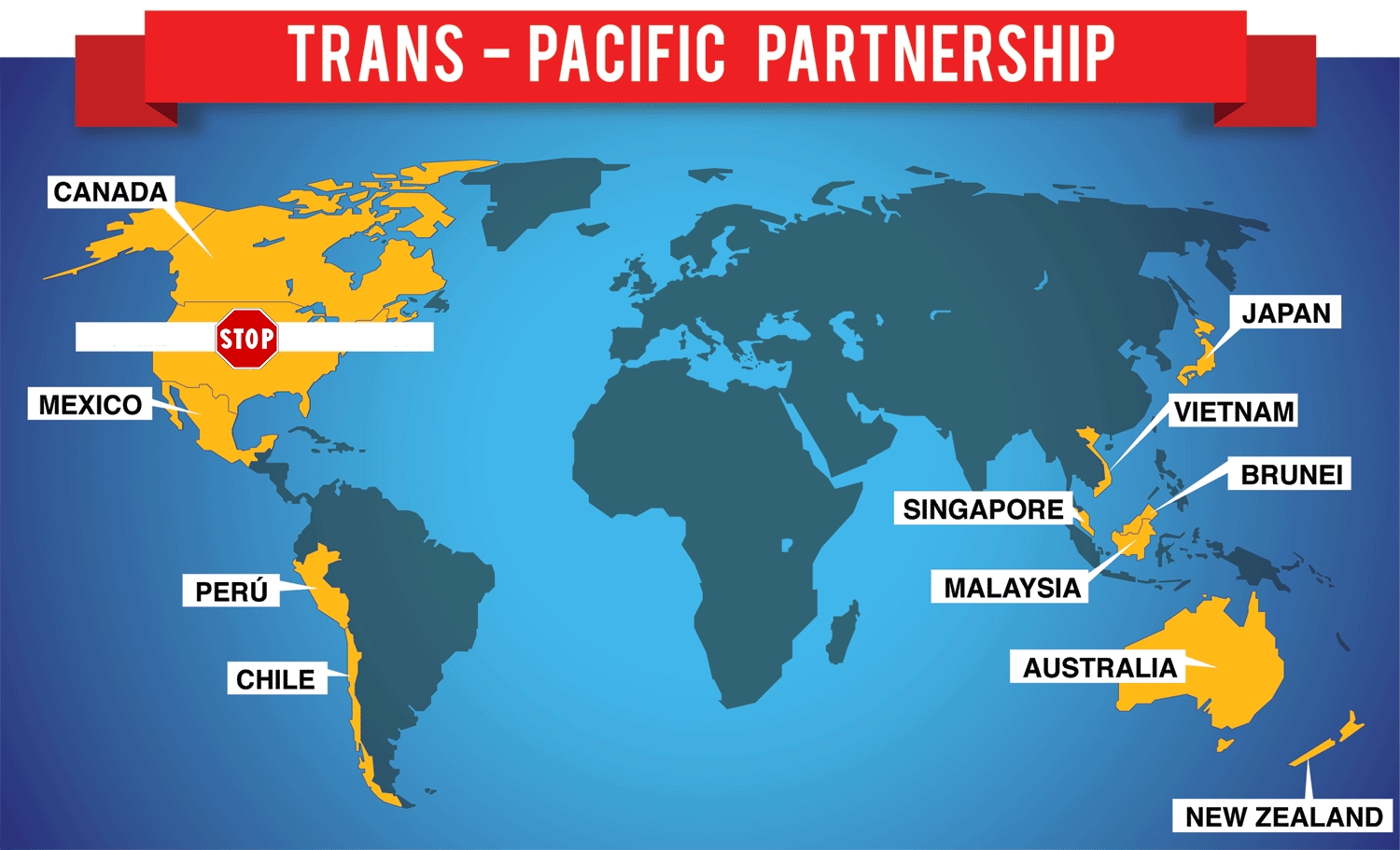
 Australia
Australia
 Brunei Darussalam
Brunei Darussalam
 Chile
Chile

 Hand in Hand
Hand in Hand
 Japan
Japan
 Canada
Canada
 Malaysia
Malaysia
 Malaysia
Malaysia
 Mexico
Mexico
 New Zealand
New Zealand
 Peru
Peru
 Singapore
Singapore

 Argentina
Argentina
 Barbados
Barbados
 Bolivia
Bolivia
 Brazil
Brazil
 Chile
Chile
 Columbia
Columbia
 Costa Rica
Costa Rica
 Dominikanische Republik
Dominikanische Republik
 Ecuador
Ecuador
 Jamaika
Jamaika
 Development Bank of Latin America and the Caribbean
Development Bank of Latin America and the Caribbean
 Development Bank of Latin America and the Caribbean
Development Bank of Latin America and the Caribbean
 Sergio Díaz-Granados Guida
Sergio Díaz-Granados Guida
 Mexico
Mexico
 Panama
Panama
 Paraguay
Paraguay
 Peru
Peru
 Portugal
Portugal
 Spain
Spain
 Trinidad und Tobago
Trinidad und Tobago
 Uruguay
Uruguay
 Venezuela
Venezuela

Die Lateinamerikanische Entwicklungsbank (portugiesisch: Corporação Andina de Fomento (CAF), spanisch: Banco de Desenvolvimento da América Latina, englisch: Development Bank of Latin America) ist eine Entwicklungsbank, deren Aufgabe es ist, die nachhaltige Entwicklung und die regionale Integration durch die Finanzierung von Projekten im öffentlichen und privaten Sektor in Lateinamerika sowie durch technische Zusammenarbeit und andere spezialisierte Dienstleistungen zu fördern[1].
Die am 7. Februar 1968 gegründete CAF, der derzeit 19 Mitgliedsländer aus Lateinamerika, der Karibik und Europa sowie 13 Privatbanken angehören, ist eine der wichtigsten Quellen für multilaterale Finanzierungen und ein wichtiger Wissensgenerator für die Region[2].
Die CAF hat ihren Hauptsitz in Caracas, Venezuela. Darüber hinaus unterhält sie Repräsentanzen in Madrid, Lima, Brasilia, Bogota, Buenos Aires, Quito, Panama, Montevideo, Asuncion, Mexiko-Stadt, Port of Spain und La Paz.
 Economy and trade
Economy and trade
 International cities
International cities
 Sport
Sport
 World Heritage
World Heritage
 Eat and Drink
Eat and Drink
 Companies
Companies
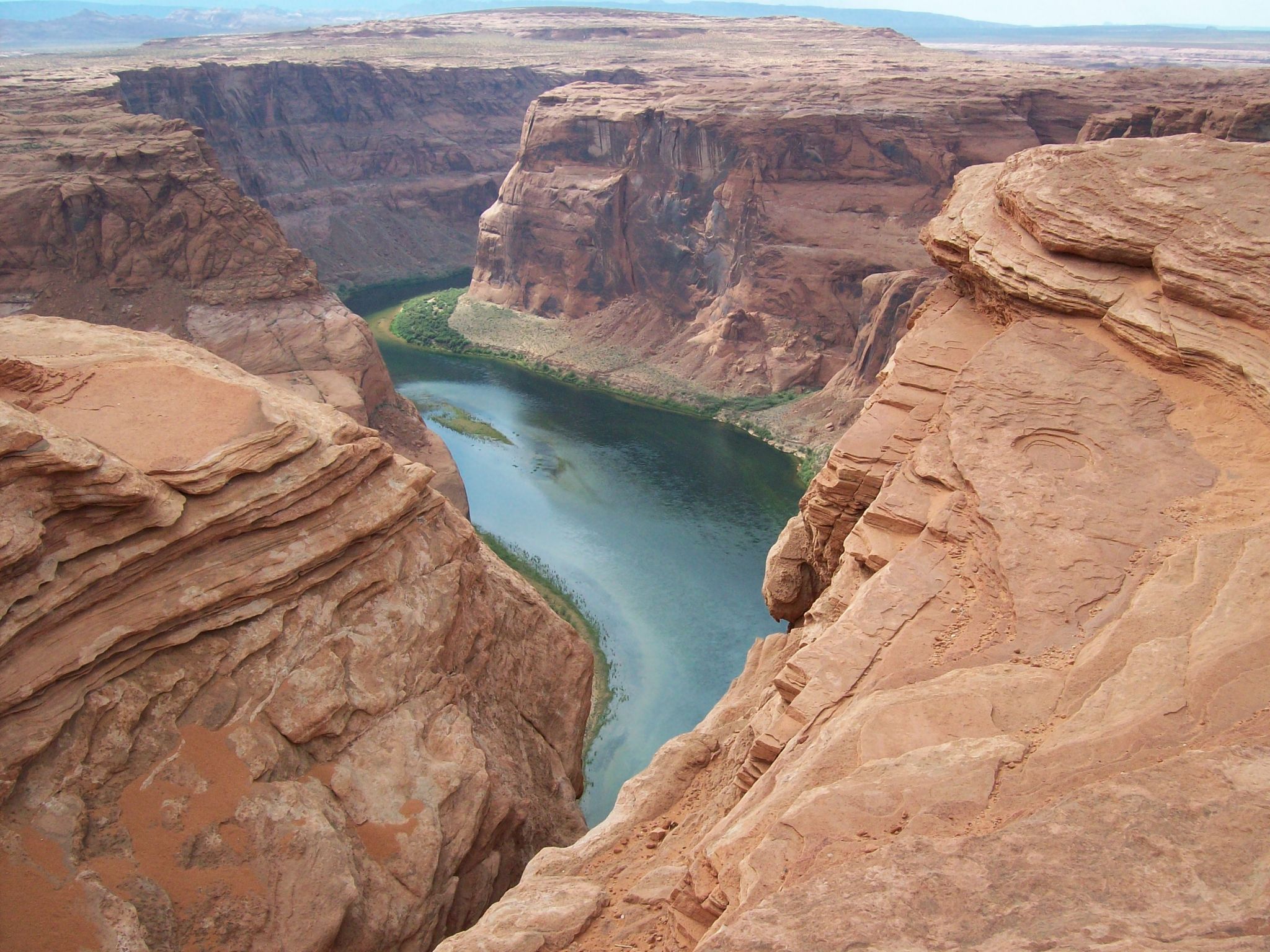
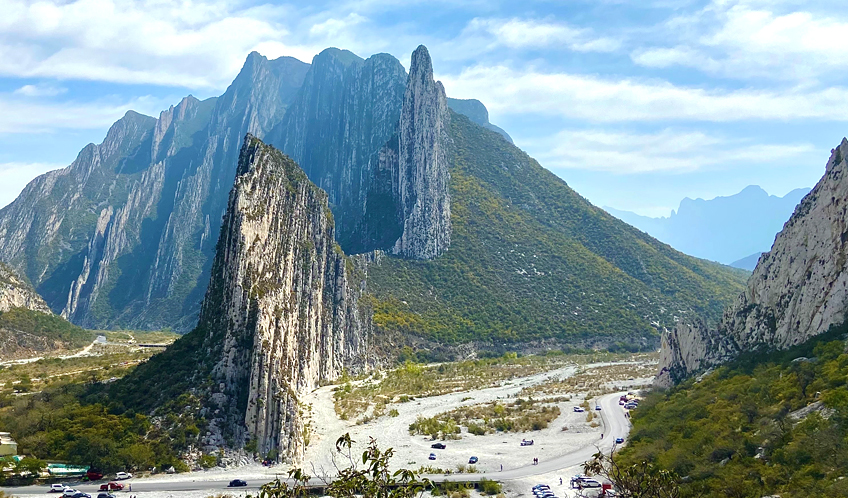
 Geography
Geography
 Arizona-AZ
Arizona-AZ
 California-CA
California-CA
 Colorado-CO
Colorado-CO
 Nevada-NV
Nevada-NV
 Animal world
Animal world
 Utah-UT
Utah-UT
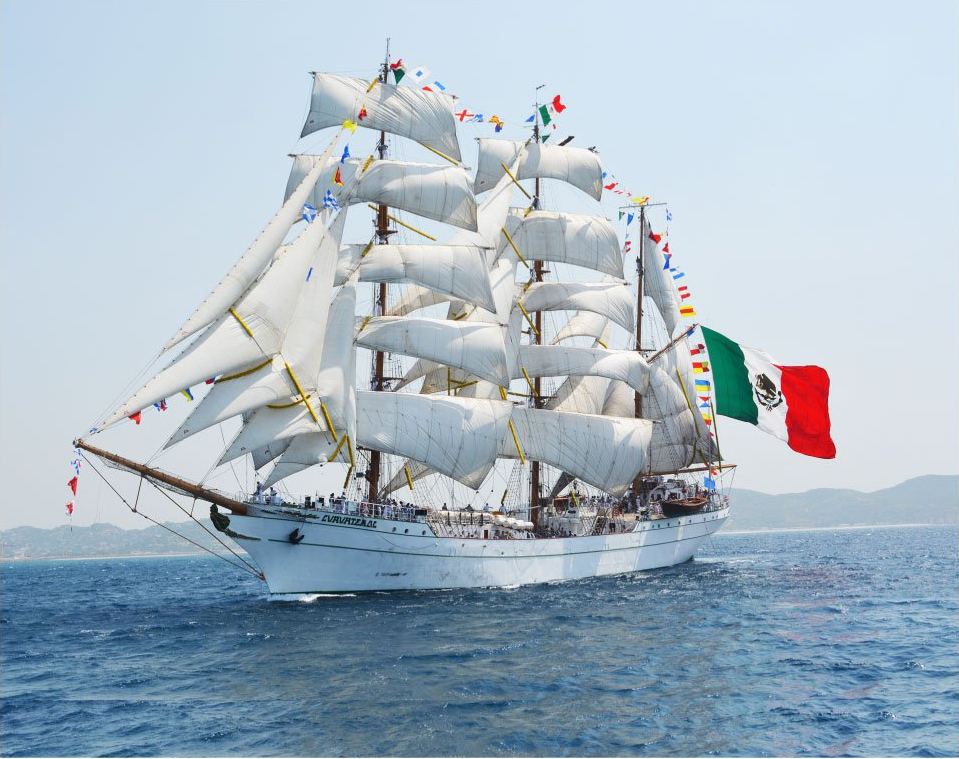
 Ships and Nautics
Ships and Nautics
 Energy resource
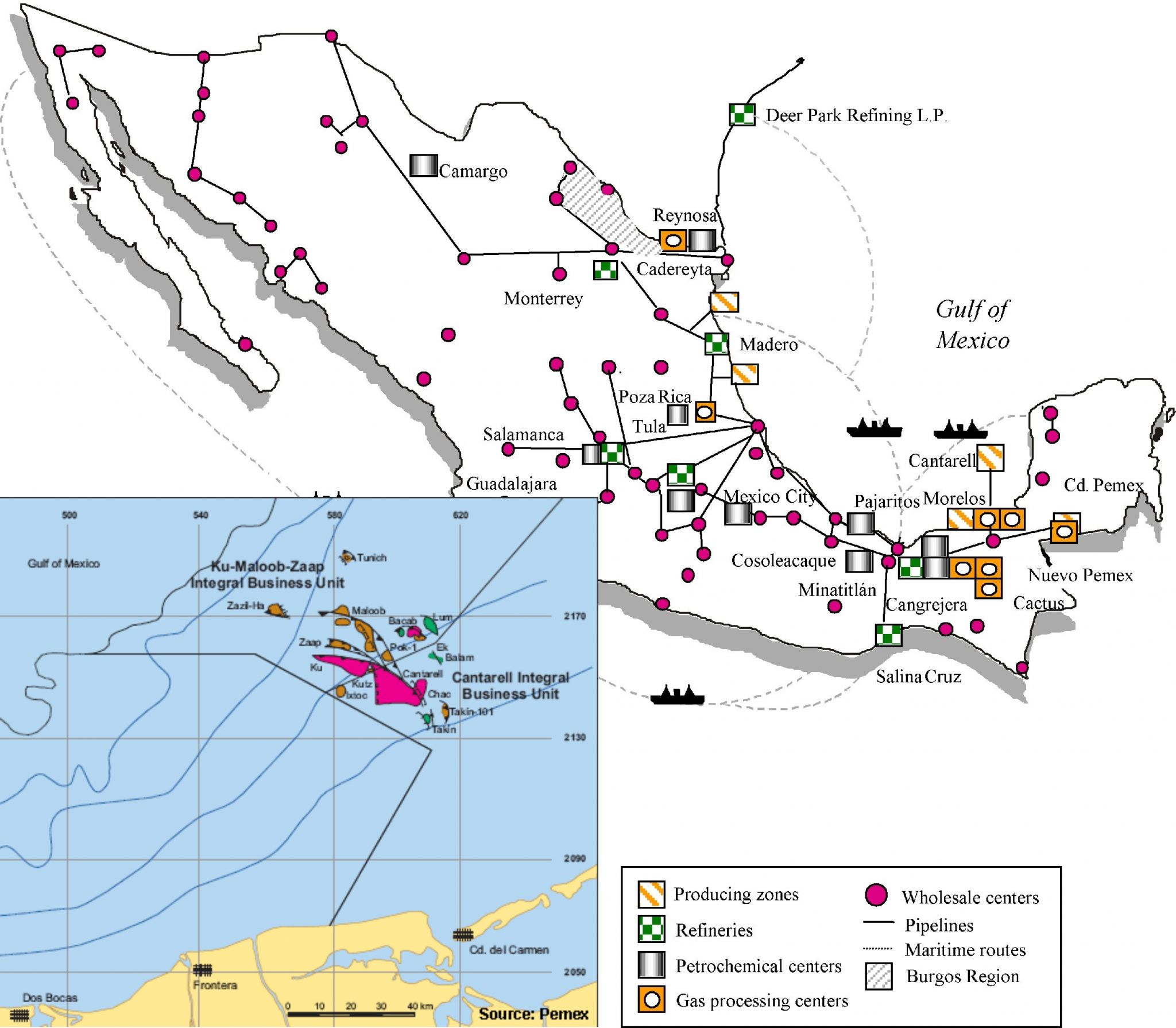
Energy resource
 Financial
Financial