
Deutsch-Chinesische Enzyklopädie, 德汉百科
 Shaanxi Sheng-SN
Shaanxi Sheng-SN

 Art
Art
 CF - Chinese Art 221 BC - 220 AD
CF - Chinese Art 221 BC - 220 AD

 Art
Art
 *Chinese bronze art
*Chinese bronze art
 Shaanxi Sheng-SN
Shaanxi Sheng-SN
 Emperor Qin Terracotta Warriors and Horses Museum
Emperor Qin Terracotta Warriors and Horses Museum

铜车马,1980年出土于陕西省临潼秦始皇陵封土西侧。出土后藏于秦始皇兵马俑博物馆。2021年5月,铜车马二号车搬迁至秦始皇帝陵铜车马博物馆[1]。
铜车马共两乘,出土时已碎裂。经考古人员复原,比例为真实车马的二分之一,均为双轮、单辕、前驾四马结构,所不同者为车的造型与功能。
铜车马一号车,名“立车”,又叫“戎车”、“高车”,车舆右侧置一面盾牌,车舆前挂有一件铜弩和铜镞。车上立一圆伞,伞下站立一名高91厘米的铜御官俑。铜车马二号车是四马鞍车,呈凸字形,分前、后二室,车舆上有穹窿形的椭圆形盖子,前室为御手所居,内跽坐一御官俑,后室为主人所居。
Der Qin-Bronzewagen (銅車馬 oder 秦銅車馬) ist ein Satz von zwei Bronzemodellen aus der Qin-Dynastie, die 1980 im Mausoleum des ersten Qin-Kaisers Qin Shi Huang (reg. 247-220 v. Chr.) ausgegraben wurden. Als die Modelle gefunden wurden, lagen sie in vielen Bruchstücken vor, und es dauerte fünf Jahre, bis beide restauriert waren. Beide Modelle sind etwa halb so groß wie ein Mensch.
Das erste Stück, "Bronzewagen Nummer eins" (一號銅車馬), besteht aus einem offenen Wagen, der von vier Bronzepferden gezogen wird, mit einem einzelnen stehenden Fahrer und einem Bronzeschirm auf einem Ständer neben ihm.
Das zweite Stück, "Bronzewagen Nummer zwei" (二號銅車馬), ist ein geschlossener Wagen mit zwei Sitzen und einem schirmartigen Dach, der ebenfalls von vier Bronzepferden gezogen wird.
Bronzewagen Nummer zwei
Die Streitwagen werden im Museum der Terrakotta-Krieger und -Pferde von Qin Shi Huang (秦始皇兵馬俑博物館) in Shaanxi aufbewahrt.[3][1] Im Jahr 2010 wurde das Stück auf der Expo in Shanghai als Exponat im Gebäude des China-Pavillons ausgestellt.[4]
Die Streitwagen sind eines von vierundsechzig historischen Artefakten, die nicht außerhalb Chinas ausgestellt werden dürfen.



 Anhui Sheng-AH
Anhui Sheng-AH
 Belarus
Belarus
 Belarus
Belarus
 Belgium
Belgium

 Berlin
Berlin

 Brandenburg
Brandenburg
 Cataluña
Cataluña
 China
China
 Chongqing Shi-CQ
Chongqing Shi-CQ
 Germany
Germany
 England
England
 France
France
 Fujian Sheng-FJ
Fujian Sheng-FJ
 Gansu Sheng-GS
Gansu Sheng-GS
 Guangdong Sheng-GD
Guangdong Sheng-GD
 Guizhou Sheng-GZ
Guizhou Sheng-GZ
 Guizhou Sheng-GZ
Guizhou Sheng-GZ

 Hamburg
Hamburg

 Hand in Hand
Hand in Hand

 Hauts-de-France
Hauts-de-France
 Hebei Sheng-HE
Hebei Sheng-HE
 Heilongjiang Sheng-HL
Heilongjiang Sheng-HL
 Henan Sheng-HA
Henan Sheng-HA
 Hubei Sheng-HB
Hubei Sheng-HB
 Hunan Sheng-HN
Hunan Sheng-HN
 Jiangsu Sheng-JS
Jiangsu Sheng-JS
 Jilin Sheng-JL
Jilin Sheng-JL
 Kasachstan
Kasachstan
 Liaoning Sheng-LN
Liaoning Sheng-LN

 Madrid
Madrid

 Mecklenburg-Vorpommern
Mecklenburg-Vorpommern
 Nei Mongol Zizhiqu-NM
Nei Mongol Zizhiqu-NM

 Lower Saxony
Lower Saxony
 Ningxia Huizu Zizhiqu-NX
Ningxia Huizu Zizhiqu-NX
 Nord-Pas-de-Calais
Nord-Pas-de-Calais

 North Rhine-Westphalia
North Rhine-Westphalia
 Poland
Poland
 Qinghai Sheng-QH
Qinghai Sheng-QH
 Russia
Russia

 Schleswig-Holstein
Schleswig-Holstein
 Silk road
Silk road
 Shaanxi Sheng-SN
Shaanxi Sheng-SN
 Shandong Sheng-SD
Shandong Sheng-SD
 Sichuan Sheng-SC
Sichuan Sheng-SC
 Spain
Spain
 Czech Republic
Czech Republic
 Uzbekistan
Uzbekistan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 Xinjiang Uygur Zizhiqu-XJ
Xinjiang Uygur Zizhiqu-XJ
 Xizang Zizhiqu-XZ
Xizang Zizhiqu-XZ
 Zhejiang Sheng-ZJ
Zhejiang Sheng-ZJ
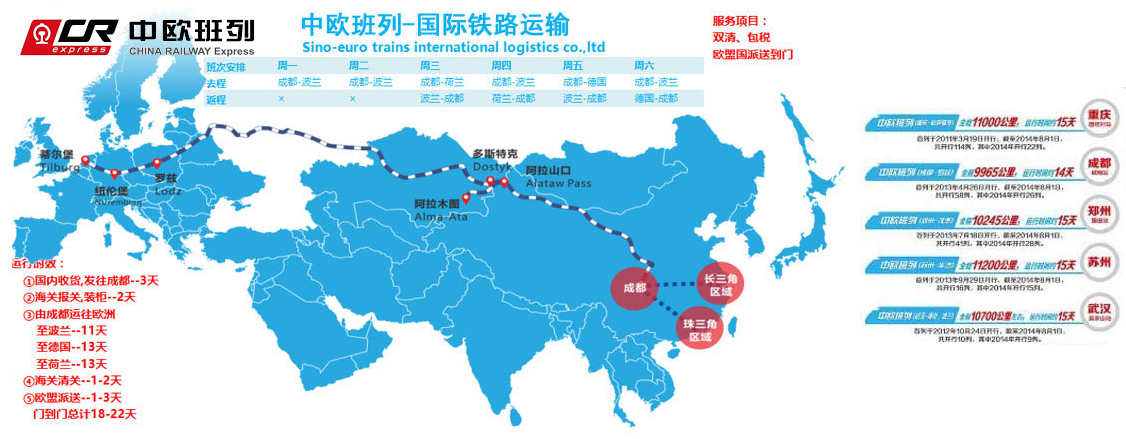
中欧班列(英语译名:China Railway Express 或 China-Europe Railway Express[1][2],简称为 CR express[3])是指按照固定车次、线路、班期和全程运行时刻开行,往来于中国与欧洲以及一带一路沿线各国的集装箱国际铁路联运班列,其中一班是从中国陜西省西安市开往欧洲的火车。[4]为加强与欧洲国家的商业贸易联络,中国政府和中国国家铁路集团与中亚和欧洲各国铁路系统协作,从起初重庆到德国的杜伊斯堡,发展到国内通达城市82个,国外通达欧亚国家的160多个城市,形成了阿拉山口、霍尔果斯、二连浩特、满洲里、绥芬河五大出境口岸,重庆、成都、西安、郑州、乌鲁木齐五大集结中心[5],开行从中国大陆到达最远伦敦、汉堡等地的国际联运列车。[3]
中欧班列也是世界上最长的货运铁路线,连接中国、哈萨克斯坦、俄罗斯、白俄罗斯、波兰、德国、法国、西班牙和伦敦。
Trans-Eurasia Logistics, AKA CHINA RAILWAY Express[1], was a joint venture between German rail company Deutsche Bahn and Russian RZhD, China Railway Corporation from China, Russian Railway Company, Russia operating container freight trains between Germany and China via Russia. The first such train arrived in Hamburg from Xiangtan on 6 October 2008, taking 17 days to make the trip.[2] Intermodal companies Polzug, Kombiverkehr, and TransContainer are also involved in the project.[3]
Container trains travel from China to Germany via the Trans-Mongolian and Trans-Siberian Railways, and then via Belarus and Poland - the route collectively known as the "Eurasian Land Bridge".[3] A break of gauge needs to be crossed when entering Mongolia from China (or Russia directly from China, if traveling via Manzhouli/Zabaykalsk), and then another one when leaving Belarus for Poland.
Trans-Eurasia Logistics operates the Yiwu - Madrid Railway line, which is the longest goods railway line in the world and connects China, Kazakhstan, Russia, Belarus, Poland, Germany, France and Spain. [4]
Trans-Eurasia Logistics est une coentreprise entre la Deutsche Bahn, la Kasachstan Temir Scholy, la China Railway Corporation et la Compagnie des chemins de fer russes, fondée en 20081
Elle permet à des trains de fret entre l'Allemagne et la Chine via la Russie, de réaliser ce trajet en dix-huit jours2.



 Automobile
Automobile
 *Commercial vehicles
*Commercial vehicles



 Automobile
Automobile
 CRRC
CRRC



 Automobile
Automobile
 *Coach and bus
*Coach and bus
 Beijing Shi-BJ
Beijing Shi-BJ
 China
China
 CRRC
CRRC
 CR400AF
CR400AF
 CRRC
CRRC
 CJ1
CJ1
 CRRC
CRRC
 CJ2
CJ2
 CRRC
CRRC
 CJ6
CJ6
 CRRC
CRRC
 CR200
CR200
 CRRC
CRRC
 CR300
CR300
 CRRC
CRRC
 CR400BF
CR400BF
 CRRC
CRRC
 CRH1
CRH1
 CRRC
CRRC
 CRH2
CRH2
 CRRC
CRRC
 CRH3
CRH3
 CRRC
CRRC
 CRH380A
CRH380A
 CRRC
CRRC
 CRH380B
CRH380B
 CRRC
CRRC
 CRH380C
CRH380C
 CRRC
CRRC
 CRH380D
CRH380D
 CRRC
CRRC
 CRH3C
CRH3C
 CRRC
CRRC
 CRH6
CRH6
 Gansu Sheng-GS
Gansu Sheng-GS
 Guangdong Sheng-GD
Guangdong Sheng-GD
 Hebei Sheng-HE
Hebei Sheng-HE
 Heilongjiang Sheng-HL
Heilongjiang Sheng-HL
 Henan Sheng-HA
Henan Sheng-HA
 Hubei Sheng-HB
Hubei Sheng-HB
 Hunan Sheng-HN
Hunan Sheng-HN
 Jiangsu Sheng-JS
Jiangsu Sheng-JS
 Jilin Sheng-JL
Jilin Sheng-JL
 Liaoning Sheng-LN
Liaoning Sheng-LN
 Shaanxi Sheng-SN
Shaanxi Sheng-SN
 Shandong Sheng-SD
Shandong Sheng-SD
 Shanxi Sheng-SX
Shanxi Sheng-SX
 Sichuan Sheng-SC
Sichuan Sheng-SC
 High speed train technology
High speed train technology
 Rad-Schiene-System
Rad-Schiene-System
 High speed train technology
High speed train technology
 Distributed Drive
Distributed Drive
 High speed train technology
High speed train technology
 Central drive
Central drive

 Transport and traffic
Transport and traffic
 Railway
Railway

 Transport and traffic
Transport and traffic
 High speed traffic
High speed traffic

 Transport and traffic
Transport and traffic
 High speed train technology
High speed train technology

 Companies
Companies
 *Big high-speed rail manufacturer
*Big high-speed rail manufacturer


 Guizhou Sheng-GZ
Guizhou Sheng-GZ
 Hubei Sheng-HB
Hubei Sheng-HB
 Hunan Sheng-HN
Hunan Sheng-HN
 Shaanxi Sheng-SN
Shaanxi Sheng-SN
 Shandong Sheng-SD
Shandong Sheng-SD
 Sichuan Sheng-SC
Sichuan Sheng-SC
 Tianjin Shi-TJ
Tianjin Shi-TJ
 China
China
 Emomali Rahmon
Emomali Rahmon
 Kasachstan
Kasachstan
 Kyrgyzstan
Kyrgyzstan
 Qassym-Schomart Toqajew
Qassym-Schomart Toqajew
 Sadyr Japarov
Sadyr Japarov
 Serdar Berdimuhamedow
Serdar Berdimuhamedow
 Shaanxi Sheng-SN
Shaanxi Sheng-SN
 Shavkat Mirziyoyev
Shavkat Mirziyoyev
 Tajikistan
Tajikistan
 Turkmenistan
Turkmenistan
 Uzbekistan
Uzbekistan
 Xi Jingping
Xi Jingping


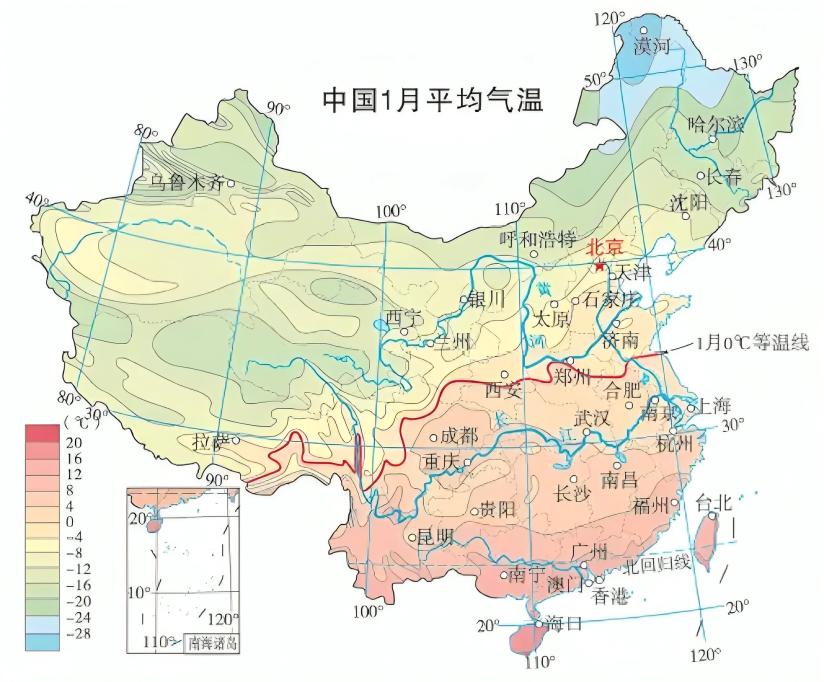
零摄氏度等温线指的是我国1月份平均气温为零摄氏度的地点所连成的线。因为温度、降水等方面的差异,在此线的南北,无论是自然条件、农业生产方式,还是地理风貌以及人们的生活习俗,都呈现出明显不同。
1月5日是今年的小寒节气。小寒,意味着已经进入一年中的寒冷季节。此时冷气积久而寒,但还没有达到最冷的程度,因而称小寒。
随着降温天气的到来,很多地方可能会下雪。不过,我国幅员辽阔,各地气候不同。冬季,当一次降水过程来临时,往往有些地方下雪,有些地方下雨。这就要说到一条无形的线——零摄氏度等温线。
在地图上将气温值相同的点连接成线,便是等温线。这里的零摄氏度,是指距地面约1.5米处的空气温度。零摄氏度等温线指的是我国1月份平均气温为零摄氏度的地点所连成的线。根据气象资料,1月份是我国每年最冷的月份,零摄氏度等温线一般是用近30年1月份的平均气温来确定的。在这条等温线以北的地区,1月份平均气温低于零摄氏度,以南则高于零摄氏度。
我国的零摄氏度等温线,大致沿秦淮一线向西延伸至青藏高原东南部边缘。它还与我国800毫米等降水量线基本一致,被认为是我国亚热带与暖温带、湿润与半湿润气候的分界线。因为温度、降水等方面的差异,在此线的南北,无论是自然条件、农业生产方式,还是地理风貌以及人们的生活习俗,都呈现出明显不同。比如,零摄氏度等温线以南的河流冬季基本不结冰,以北则一般会结冰;以南的森林多为亚热带常绿阔叶林,以北则主要为温带落叶阔叶林;以南主要种植水稻和油菜,以北则以小麦和花生为主。
那么,是不是零摄氏度等温线以北冬季就会下雪,以南就不会下雪呢?答案是不一定。
这是因为,这里的零摄氏度指的是1月份平均气温,表示一段较长时间内气候的平均状态,而一次降水过程最终的雨雪相态,与整层大气的层结状态密切相关。如果整层大气都低于零摄氏度,只有地面附近气温略高于零摄氏度,下落的雪花在地面附近来不及融化就降落到地面,就会出现地面气温高于零摄氏度却下雪的情况;如果地面上空存在一个较深厚的暖层,下落的雪花经过暖层时会完全融化成雨滴,这些雨滴来到气温低于零摄氏度的地面附近时来不及冻结就会降落到地面,这时就会出现地面气温低于零摄氏度却在下雨或冻雨的情况。
不过,需要注意的是,零摄氏度等温线以南虽然平均气温高于零摄氏度,但仍然有可能出现零摄氏度以下的日子。现实中,我们对温度的感受还会受到湿度、风速等影响,因此,还是应该及时关注当地天气预报来决定衣物的增减。
(作者为国家气象中心高级工程师,本报记者李红梅采访整理)
版权声明

 *Chinese think tanks
*Chinese think tanks
 Anhui Sheng-AH
Anhui Sheng-AH
 Beijing Shi-BJ
Beijing Shi-BJ
 Breakthrough Prize
Breakthrough Prize
 Fundamental Physics Breakthrough Prize
Fundamental Physics Breakthrough Prize
 Chinese Academy of Science
Chinese Academy of Science
 Gansu Sheng-GS
Gansu Sheng-GS
 Guangdong Sheng-GD
Guangdong Sheng-GD
 Hubei Sheng-HB
Hubei Sheng-HB
 Jiangsu Sheng-JS
Jiangsu Sheng-JS
 Jilin Sheng-JL
Jilin Sheng-JL
 Liaoning Sheng-LN
Liaoning Sheng-LN
 National Key Laboratory of Plant Molecular Genetics
National Key Laboratory of Plant Molecular Genetics
 Shaanxi Sheng-SN
Shaanxi Sheng-SN
 Shanghai Shi-SH
Shanghai Shi-SH
 Sichuan Sheng-SC
Sichuan Sheng-SC
 State key laboratory
State key laboratory
 State Key Laboratory for Superlattices and Microstructures
State Key Laboratory for Superlattices and Microstructures
 State Key Laboratory of Applied Optics
State Key Laboratory of Applied Optics
 State Key Laboratory of Biomembrane and Membrane Biotechnology
State Key Laboratory of Biomembrane and Membrane Biotechnology
 State Key Laboratory of Bioorganic and Natural Products Chemistry
State Key Laboratory of Bioorganic and Natural Products Chemistry
 State Key Laboratory of Catalysis
State Key Laboratory of Catalysis
 State Key Laboratory of Cell Biology
State Key Laboratory of Cell Biology
 State Key Laboratory of Coal Conversion
State Key Laboratory of Coal Conversion
 State Key Laboratory of Computer Architecture
State Key Laboratory of Computer Architecture
 State Key Laboratory of Computer Science, Institute of Software
State Key Laboratory of Computer Science, Institute of Software
 State Key Laboratory of Desert and Oasis Ecology
State Key Laboratory of Desert and Oasis Ecology
 State Key Laboratory of Drug Research
State Key Laboratory of Drug Research
 State Key Laboratory of Electroanalytical Chemistry
State Key Laboratory of Electroanalytical Chemistry
 State Key Laboratory of Fire Science
State Key Laboratory of Fire Science
 State Key Laboratory of Functional Mmaterials for Informatics
State Key Laboratory of Functional Mmaterials for Informatics
 State Key Laboratory of Genetic Resources and Evolution
State Key Laboratory of Genetic Resources and Evolution
 State Key Laboratory of High Field Laser Physics
State Key Laboratory of High Field Laser Physics
 State Key Laboratory of High Performance Ceramics and Superfine Microstructure
State Key Laboratory of High Performance Ceramics and Superfine Microstructure
 State Key Laboratory of Information Security
State Key Laboratory of Information Security
 State Key Laboratory of Infrared Physics
State Key Laboratory of Infrared Physics
 State Key Laboratory of Isotope Geochemistry
State Key Laboratory of Isotope Geochemistry
 State Key Laboratory of Microfabrication Optical Technology
State Key Laboratory of Microfabrication Optical Technology
 State Key Laboratory of Molecular Biology
State Key Laboratory of Molecular Biology
 State Key Laboratory of Molecular Reaction Dynamics
State Key Laboratory of Molecular Reaction Dynamics
 State Key Laboratory of Multiphase Complex Systems
State Key Laboratory of Multiphase Complex Systems
 State Key Laboratory of Neuroscience
State Key Laboratory of Neuroscience
 State Key Laboratory of Nuclear Detection and Nuclear Electronics
State Key Laboratory of Nuclear Detection and Nuclear Electronics
 State Key Laboratory of Organometallic Chemistry
State Key Laboratory of Organometallic Chemistry
 State Key Laboratory of Phytochemistry and Plant Resources in Western China
State Key Laboratory of Phytochemistry and Plant Resources in Western China
 State Key Laboratory of Plant Genomics Institute of Genetics and Developmental Biology Institute of
State Key Laboratory of Plant Genomics Institute of Genetics and Developmental Biology Institute of
 State Key Laboratory of Polymer Physics and Chemistry
State Key Laboratory of Polymer Physics and Chemistry
 State Key Laboratory of Rare Earth Resource Utilization
State Key Laboratory of Rare Earth Resource Utilization
 State Key Laboratory of Remote Sensing Science
State Key Laboratory of Remote Sensing Science
 State Key Laboratory of Robotics
State Key Laboratory of Robotics
 State Key Laboratory of Soil and Sustainable Agriculture
State Key Laboratory of Soil and Sustainable Agriculture
 State Key Laboratory of Structural Chemistry
State Key Laboratory of Structural Chemistry
 State Key Laboratory of Transducer Technology
State Key Laboratory of Transducer Technology
 State Key Laboratory of Tropical Oceanography
State Key Laboratory of Tropical Oceanography
 State Key Laboratory on Integrated Optoelectronics
State Key Laboratory on Integrated Optoelectronics

 Science and technology
Science and technology
 *World famous research institutions
*World famous research institutions

 Science and technology
Science and technology
 Asian city
Asian city
 Xinjiang Uygur Zizhiqu-XJ
Xinjiang Uygur Zizhiqu-XJ
 Yunnan Sheng-YN
Yunnan Sheng-YN

Die Chinesische Akademie der Wissenschaften, früher auch bekannt als Academia Sinica (chin. 中國科學院 / 中国科学院, Zhōngguó Kēxuéyuàn, engl. Chinese Academy of Sciences (Abk. CAS)), ist die nationale Akademie für Naturwissenschaften der Volksrepublik China. Sie ist dem Staatsrat der Volksrepublik China unterstellt. Sie wurde im November 1949 gegründet und hat ihren Sitz in Peking mit zahlreichen Instituten in ganz China.
Die Chinesische Akademie der Wissenschaften hat fünf Abteilungen:
- I. Mathematik,
- II. Physik,
- III. Chemie,
- IV. Geowissenschaften und
- V. Technologie.
Weiter gliedert sich die Akademie in zwölf Zweigstellen in Shenyang, Changchun, Shanghai, Nanking, Wuhan, Guangzhou, Chengdu, Kunming, Xi'an, Lanzhou und in Xinjiang. Die Chinesische Akademie der Wissenschaften hat 84 Institute, eine Universität (die Chinesische Universität der Wissenschaften und Technik in Hefei, Anhui), zwei Colleges, vier Dokumentations- und Informationszentren, drei Zentren für technologischen Support und zwei Editionseinheiten. Diese Zweigstellen und Büros der Chinesischen Akademie der Wissenschaften befinden sich in zwanzig Provinzen und regierungsunabhängigen Städten Chinas. Die Chinesische Akademie der Wissenschaften hat in acht Industriezweigen über 430 Hochtechnologie-Unternehmen ausgestattet oder geschaffen. Acht dieser Gesellschaften sind börsennotiert.
中国科学院[注 1],又简称中科院、科学院[4],是中华人民共和国科学技术方面的最高学术机构,全国自然科学与高新技术综合研究发展中心,为正部级国务院直属事业单位[5],于1949年11月在北京成立。1977年5月,哲学社会科学学部独立为中国社会科学院,1994年,在技术科学部的基础上及国家科委的支持下,成立中国工程院。
中国科学院与中国工程院并称“两院”。发展至今,中科院下设6个学部(数学物理学部、化学部、生命科学和医学学部、地学部、信息技术科学部、技术科学部),以及12个分院(北京、沈阳、长春、上海、南京、武汉、广州、成都、昆明、西安、兰州、新疆)、84个研究院所、2所大学、2所学院、4个文献情报中心、3个技术支撑机构和2个新闻出版单位,分布在全国20多个省(市)。此外,还投资兴办了430余家科技型企业(含转制单位),涉及11个行业,其中包括8家上市公司。此外,中国科学院还拥有(含与其他单位共建)4个国家实验室、85个国家重点实验室和153个中国科学院重点实验室。
管理有承担中科院各分院、研究所及大学的网络互联的中国科技网互联网骨干网。
 History
History
 Architecture
Architecture


 Aerospace
Aerospace
 Sport
Sport
 Geography
Geography



 Military, defense and equipment
Military, defense and equipment