
漢德百科全書 | 汉德百科全书
 Vermont-VT
Vermont-VT


 Connecticut-CT
Connecticut-CT

 Georgia-GA
Georgia-GA
 Canada
Canada

 Kentucky-KY
Kentucky-KY

 Maine-ME
Maine-ME

 Maryland-MD
Maryland-MD

 Massachusetts-MA
Massachusetts-MA

 New Brunswick-NB
New Brunswick-NB

 New hampshire-NH
New hampshire-NH

 New jersey-NJ
New jersey-NJ

 New jersey-NJ
New jersey-NJ

 New York-NY
New York-NY

 Newfoundland and Labrador-NL
Newfoundland and Labrador-NL

 North Carolina-NC
North Carolina-NC

 Nova Scotia-NS
Nova Scotia-NS

 Ohio-OH
Ohio-OH

 Pennsylvania-PA
Pennsylvania-PA

 Quebec-QC
Quebec-QC
 South Carolina-SC
South Carolina-SC

 Tennessee-TN
Tennessee-TN

 Tennessee-TN
Tennessee-TN
 United States
United States

 Vermont-VT
Vermont-VT

 Virginia-VA
Virginia-VA

 West Virginia-WV
West Virginia-WV

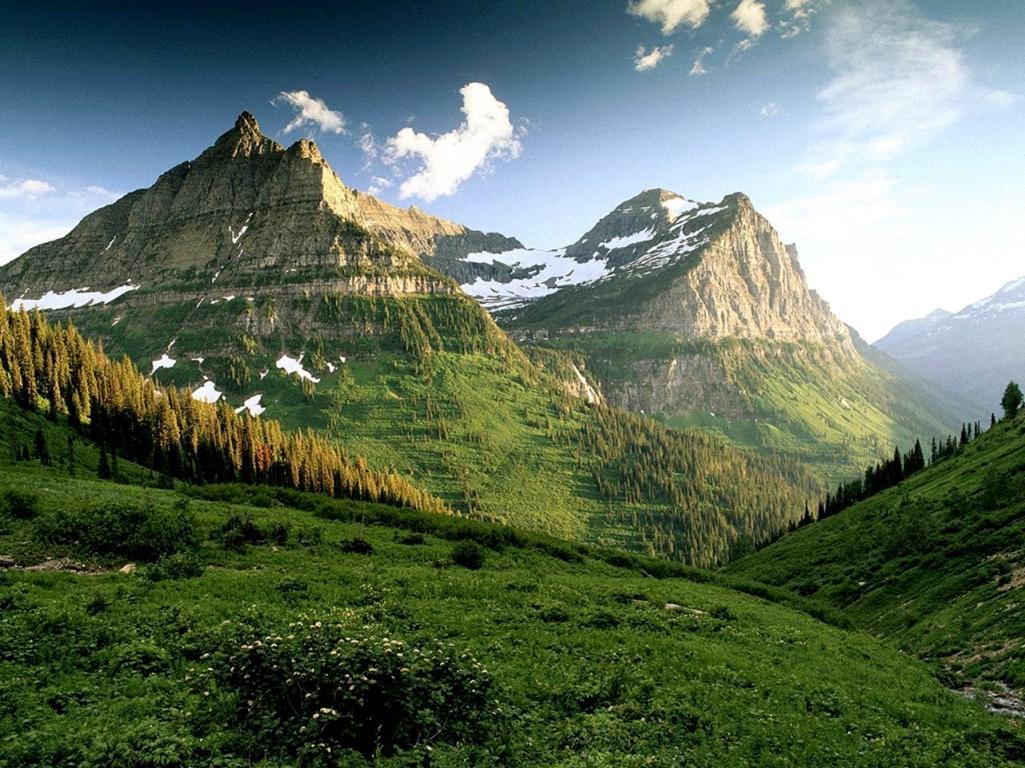
Die Appalachen (englisch Appalachian Mountains) sind ein bewaldetes Gebirgssystem im Osten Nordamerikas, das sich über eine Länge von 2400 Kilometer von den Long Range Mountains an der Westküste der kanadischen Insel Neufundland bis in den Norden des US-Bundesstaates Alabama erstreckt. Obwohl ihr höchster Gipfel mehr als 2000 Meter hoch ist, haben die Appalachen sowohl hinsichtlich ihrer Höhe als auch ihrer Morphologie einen Mittelgebirgscharakter. Nur wenige Berge erheben sich über mehr als 1200 m Höhe, und viele Bergkuppen bleiben deutlich unter 800 m.
Benannt sind die Appalachen nach dem indigenen Stamm der Apalachee. Für die Appalachenregion als Kultur- und Wirtschaftsraum wird auch die Bezeichnung Appalachia verwendet.[1]
阿巴拉契亚山脉(英语:Appalachian Mountains),又译阿帕拉契山脉,是北美洲东部的一座山系。南起美国的阿拉巴马州,北至加拿大的纽芬兰和拉布拉多省。最北部余脉则延伸到魁北克的加斯佩地区。最高峰在北卡罗莱纳州的米切尔峰(2037米)。
构成阿巴拉契亚山脉的有纽芬兰省的长岭山、魁北克的圣母山、缅因州的朗费罗山、新罕布夏州的怀特山、佛蒙特州的格林山脉、塔库尼克山;马萨诸塞州的勃克夏山;跨宾夕法尼亚州、马里兰州和西佛吉尼亚州三州的阿勒格尼山脉;跨宾夕法尼亚州、马里兰州、西佛吉尼亚州以及佛吉尼亚州四州的阿巴拉契亚岭谷。还有从宾夕法尼亚州南部到佐治亚州北部的蓝岭山脉。
实际上阿巴拉契高地 严格的边界范围存有争议,阿第伦达克山脉一般被认为是属于加拿大地盾,而非阿巴拉契亚高地。
アパラチア山脈(Appalachian Mountains)は、カナダ及びアメリカ合衆国東北部に位置し、北東から南西方向に全長約2,600kmにわたって延びる丘陵・山脈。狭義では、そのうちのウエストバージニア州、バージニア州、ケンタッキー州、テネシー州、ノースカロライナ州等の南側の部分のみを指すこともある。
複雑に褶曲した山脈で、侵食が進んだ丘陵性の古い山脈である。北端はカナダニューファンドランド島で、そこから北アメリカ大陸東部を南西方向に縦断し、南端はアラバマ州の中央に至る。また、その裾野はミシシッピ州北西部にまで及んでいる。個々の山の標高は平均して1,000m前後で、最高峰はノースカロライナ州にあるミッチェル山(標高2,037m)。
山脈の西部では石油・石炭が盛んに採掘されているなど地下資源が豊富。山脈の東側には都市が発達している。国立公園が多く、グレート・スモーキー山脈国立公園やシェナンドー国立公園が有名である。
The Appalachian Mountains,[a] often called the Appalachians, are a system of mountains in eastern North America. The Appalachians first formed roughly 480 million years ago during the Ordovician Period. They once reached elevations similar to those of the Alps and the Rocky Mountains before experiencing natural erosion.[4][5] The Appalachian chain is a barrier to east–west travel, as it forms a series of alternating ridgelines and valleys oriented in opposition to most highways and railroads running east–west.
Definitions vary on the precise boundaries of the Appalachians. The United States Geological Survey (USGS) defines the Appalachian Highlands physiographic division as consisting of thirteen provinces: the Atlantic Coast Uplands, Eastern Newfoundland Atlantic, Maritime Acadian Highlands, Maritime Plain, Notre Dame and Mégantic Mountains, Western Newfoundland Mountains, Piedmont, Blue Ridge, Valley and Ridge, Saint Lawrence Valley, Appalachian Plateaus, New England province, and the Adirondack areas.[6][7] A common variant definition does not include the Adirondack Mountains, which geologically belong to the Grenville Orogeny and have a different geological history from the rest of the Appalachians.[8][9][10]
Les Appalaches sont une chaîne de montagnes située dans l'Est de l'Amérique du Nord et s'étendant de Terre-Neuve (Canada), au nord, jusqu'au centre de l'État de l'Alabama, au sud (États-Unis). Elle culmine au mont Mitchell (2 037 mètres) en Caroline du Nord.
Les Appalaches séparent la plaine côtière atlantique (à l'est) du bassin du fleuve Mississippi et des Grands Lacs (à l'ouest). Elles s'étirent sur près de 2 000 km de longueur.
L'exploitation du charbon, qui fournit la moitié de l'électricité américaine, y a fortement périclité, et l'industrie métallurgique est en grande difficulté.
Les Appalaches ont donné leur nom à un type de relief, le relief appalachien, qui désigne les vestiges d'une ancienne montagne fortement arasée. De longs couloirs s'étendent parallèlement à des échines rectilignes. Les cluses appalachiennes forment des passages étroits à travers les chaînons de la montagne.
Le Sentier des Appalaches (AT) parcourt les sommets de la chaîne depuis le Maine jusqu'à la Géorgie et le Sentier international des Appalaches (SIA - IAT) passe par les sommets du nord du Maine jusqu'au cap Gaspé, en Gaspésie. Leur point d'intersection est le sommet du mont Katahdin.
Gli Appalachi (AFI: /appaˈlaki/) o Appalaci (/appaˈlaʧi/[1]; in inglese Appalachian Mountains, in francese Appalaches) sono una catena montuosa situata nella parte orientale dell'America del Nord.
Si sviluppa, quasi parallelamente alla costa orientale atlantica, dal golfo del fiume San Lorenzo fino all'Alabama, per almeno 2500 km con picchi non molto elevati (i più alti sono con 2037 m il monte Mitchell e con 1917 m il monte Washington). Gli Appalachi riguardano anche l'isola di Terranova (Canada) e l'isola francese di Miquelon parte della collettività territoriale di Saint-Pierre e Miquelon[2][3]. La porzione sud degli Appalachi viene chiamata monti Unakas.
Per via dell'età geologica, gli Appalachi sono la catena montuosa più vecchia delle Americhe. Gli Appalachi statunitensi sono una delle zone economicamente più depresse degli Stati Uniti.
Apalaches o montes Apalaches (en inglés: Appalachian Mountains o Appalachians; en francés: Appalaches1) es una importante cordillera ubicada en el este de Norteamérica. Se extiende desde la Isla de Terranova en Canadá, pasado por la colectividad de ultramar francés de San Pedro y Miquelón, hasta Alabama en los Estados Unidos, aunque su parte más septentrional termina en la península de Gaspé, en Quebec. Constituye el elemento morfológico más sobresaliente de la parte oriental de América del Norte.
Se originó en antiguas montañas formadas en el periodo Paleozoico con relieves suavizados por la prolongada acción de los agentes exógenos. El sistema está dividido en una serie de cordilleras, en las que la medida de altura de los picos es de unos 1000 m s. n. m. (metros sobre el nivel del mar). La cima más elevada es el monte Mitchell, en Carolina del Norte, mide 2037 m s. n. m. y es el punto más alto de los Estados Unidos al este del río Misisipi y de todo el este de Norteamérica.
Аппала́чи[2] (англ. Appalachian Mountains) — горная система на востоке Северной Америки, в США и Канаде. Длина — 2600 км.
Северные Аппалачи (к северу от рек Мохок и Гудзон) — холмистое плоскогорье с отдельными массивами высотой до 1916 м (гора Вашингтон), имеют следы древнего оледенения. Южные Аппалачи в осевой зоне состоят из параллельных хребтов и массивов, разделённых широкими долинами; к осевой зоне прилегают с востока плато Пидмонт, с запада — Аппалачское плато. Высота — до 2037 м (гора Митчелл). В горах имеются месторождения каменного угля, нефти и газа, железных руд, титана; широколиственные, хвойные и смешанные леса.
Горы образовались в пермский период в результате столкновения двух материков (возникновение Пангеи).

 American Public Colleges & Universities
American Public Colleges & Universities
 Nobel prize
Nobel prize
 University/Institute
University/Institute
 Nobel prize
Nobel prize
 Nobel Peace Prize
Nobel Peace Prize
 Public Ivy
Public Ivy

 Universities in the USA
Universities in the USA





Vermont (engl. Aussprache [vɚˈmɑnt]) ist ein Bundesstaat der Vereinigten Staaten von Amerika und Teil von Neuengland. Er ist vor allem für seinen Ahornsirup, den Abbau und die Weiterverarbeitung von Marmor und die idyllischen Berglandschaften bekannt. Die Green Mountains und der Lake Champlain sind beliebte Erholungsgebiete. Folgerichtig lautet der Spitzname auch Green Mountain State. Viele Wohlhabende der umliegenden Bundesstaaten besitzen hier ein Wochenendhaus.
Im Herbst prägt das sich verfärbende Herbstlaub die Landschaft („Indian Summer“). 2013 kamen rund 12,8 Millionen Touristen nach Vermont.[1] Die Berge, Flüsse und Seen bieten sich für Freizeitaktivitäten von Skifahren im Winter bis hin zum Angeln (Fliegenfischen), Wandern, Trekking, Wasserwandern und Camping im Sommer und Herbst an. Auch die ruhigen Städtchen und Dörfer Vermonts gehören zum Programm der Besucher.
佛蒙特州(英語:State of Vermont,![]() i/vərˈmɒnt/))是美国第14个州,以其美丽的景色、奶制品、枫糖浆和激进的政治而著称。
i/vərˈmɒnt/))是美国第14个州,以其美丽的景色、奶制品、枫糖浆和激进的政治而著称。
最初易洛魁和阿尔珙等印第安部落居住在今天的佛蒙特州。1609年法国探险家萨缪尔·德·尚普兰占今天尚普兰湖地区为己有,并将其周围的山脉称为“绿山”(Les Verts Monts),今天的州名就是由此而来的。
1763年的巴黎条约结束了法国印第安人战争,这块土地由此归英国,其中一些地方有时也归纽约州和新罕布什尔州管理。伊桑·艾伦和他的绿山男孩(Green Mountain Boys)首先反抗英国统治,后来与纽约州和新罕布什尔州作战,终于于1777年建立了一个独立的佛蒙特共和国(在1777年的前半年中称为新康涅狄格,7月改为佛蒙特)。在此期间佛蒙特宪法被起草和签定,这是北美洲的第一部宪法。1791年佛蒙特加入美国,成为其第14个州。
佛蒙特州是新英格兰地区的一部分。它东邻新罕布什尔州,西邻纽约州,南邻麻萨诸塞州,向北是加拿大的魁北克省。其面积约为25000平方公里。康涅狄格河是它的东部边界。绿山山脉从南向北纵贯全州。全州约77%的面积是森林,其他的是草地、高原、湖泊、池塘和藻泽湿地。
佛蒙特州的春季短促多雨,夏季凉爽,秋季多色,冬季非常寒冷。尤其北部异常寒冷,往往比同州南部地区冷十度。佛蒙特州是美洲东海岸地区的滑雪圣地。
秋季,佛蒙特州的山丘被糖枫树叶染成红色、橙色和金色。这些不同的颜色不是由不同的树种形成的,而是由不同的土壤和气候导致的。
バーモント州(英: State of Vermont、[vɜːrˈmɒnt] (![]() 音声ファイル))は、アメリカ合衆国の州の1つである。なお、州名は日本語では「バーモント」と表記されるが、現地の発音では「ヴァマント」に近い[1]。本項目においては、日本語における慣用表記に従い、「バーモント」という表記を用いる。
音声ファイル))は、アメリカ合衆国の州の1つである。なお、州名は日本語では「バーモント」と表記されるが、現地の発音では「ヴァマント」に近い[1]。本項目においては、日本語における慣用表記に従い、「バーモント」という表記を用いる。
アメリカ合衆国北東部、ニューイングランド地方の内陸に位置し、西部をニューヨーク州、東部をニューハンプシャー州、南部をマサチューセッツ州、北部をカナダ・ケベック州に隣接する。西のニューヨーク州との境界の半分はシャンプレーン湖である。面積は、全米50州のうち45位。人口608,827人は、ワイオミング州に次いで全米で2番目に少ない。州都はモントピリア市であり、人口は8,000人に満たず、50州の州都では最も少ない[3]。人口最大の都市は約42,000人のバーリントン市である[4]。州内の最大都市として、50州の中ではこれも最少である。バーリントン大都市圏の人口は21万人を超えている[5]。
現在バーモント州になっている地域にはインディアンの主要2部族、アルゴンキン語族を話すアベナキ族とイロコイ族が住んでいた。フランスが植民地化初期にこの地域の領有主張していたが、七年戦争(アメリカ大陸ではフレンチ・インディアン戦争)の終わった1763年に、フランスはイギリスに割譲した。その頃から近くの植民地であるニューハンプシャー植民地とニューヨーク植民地がその領有を争っていた。当時はニューハンプシャー認定地と呼ばれていた。これらの植民地から土地所有権を認められていた開拓者に対し、グリーン・マウンテン・ボーイズと呼ばれた民兵隊が対抗し、独立国であるバーモント共和国を創ることになった。この共和国はアメリカ独立戦争中の1777年に建国され、14年間続いた。13植民地以外では合衆国加盟以前に主権国家だった現在の4州の1つである(他の3州はテキサス州、ハワイ州、カリフォルニア州)。1791年、13植民地以外の最初の州として14番目のアメリカ合衆国の州になった。独立国時代から奴隷制度を廃止しており、合衆国加盟時に奴隷制度を廃止した最初の州になった。
州内にグリーン山地があり、州の多くは、山岳と森林で占められ、愛称は「Green Mountain State」である。自動車のライセンスプレートも緑色である。名産であるメープルシロップの生産量は全米で最大である[6]。
Vermont (/vərˈmɒnt/ (![]() listen))[7] is a northeastern state in the New England region of the United States. It borders the states of Massachusetts to the south, New Hampshire to the east, and New York to the west, and the Canadian province of Quebec to the north. Vermont is the only state in New England that does not border the Atlantic Ocean. Vermont is the second-least-populated U.S. state and the sixth-smallest by area of the 50 U.S. states. The state capital is Montpelier, the least-populous state capital in the United States. The most-populous city, Burlington, is the least-populous city to be the most-populous city in a state.
listen))[7] is a northeastern state in the New England region of the United States. It borders the states of Massachusetts to the south, New Hampshire to the east, and New York to the west, and the Canadian province of Quebec to the north. Vermont is the only state in New England that does not border the Atlantic Ocean. Vermont is the second-least-populated U.S. state and the sixth-smallest by area of the 50 U.S. states. The state capital is Montpelier, the least-populous state capital in the United States. The most-populous city, Burlington, is the least-populous city to be the most-populous city in a state.
For some 12,000 years, indigenous peoples inhabited this area. The historically competitive tribes of the Algonquian-speaking Abenaki and Iroquoian-speaking Mohawk were active in the area at the time of European encounter.
During the 17th century, French colonists claimed the territory as part of the Kingdom of France's colony of New France. After the Kingdom of Great Britain began to settle colonies to the south along the Atlantic coast, the two nations competed in North America in addition to Europe. For years, each country enlisted Native American allies in continuous raiding and warfare between the New England and New France colonies. This produced an active trade in captives taken during such raids, often held for ransom, although some captives were adopted by families into the Mohawk or Abenaki tribes.
After being defeated in 1763 in the Seven Years' War, France ceded its territory east of the Mississippi River to Great Britain. Thereafter, the nearby British Thirteen Colonies, especially the provinces of New Hampshire and New York, disputed the extent of the area called the New Hampshire Grants to the west of the Connecticut River, encompassing present-day Vermont. The provincial government of New York sold land grants to settlers in the region, which conflicted with earlier grants from the government of New Hampshire. The Green Mountain Boys militia protected the interests of the established New Hampshire land grant settlers against the newly arrived settlers with land titles granted by New York.
Ultimately, a group of settlers with New Hampshire land grant titles established the Vermont Republic in 1777 as an independent state during the American Revolutionary War. The Vermont Republic abolished slavery before any of the other states.[8][9] Vermont was also the first state to produce an African-American university graduate, Alexander Twilight, in 1823.
Vermont was admitted to the newly established United States as the fourteenth state in 1791. Vermont is one of the four U.S. states that were previously sovereign states (along with Texas, California, and Hawaii).
During the mid-19th century, Vermont was a strong source of abolitionist sentiment, although it was also tied to King Cotton through the development of textile mills in the region, which relied on southern cotton. It sent a significant contingent of soldiers to participate in the American Civil War.
The geography of the state is marked by the Green Mountains, which run north–south up the middle of the state, separating Lake Champlain and other valley terrain on the west from the Connecticut River valley that defines much of its eastern border. A majority of its terrain is forested with hardwoods and conifers, and a majority of its open land is devoted to agriculture. The state's climate is characterized by warm, humid summers and cold, snowy winters.
Vermont's economic activity of $34 billion in 2018 ranked 52nd on the list of U.S. states and territories by GDP (every state plus Washington, D.C. and Puerto Rico were larger), but 34th in GDP per capita. In 1960, Vermonters' politics started to shift from being reliably Republican toward favoring Democratic candidates. Starting in 1963, Vermont voters have alternated between electing Republican and Democratic governors. Since 2007, Vermont has elected only Democrats and independents to Congress. In 2000, the state legislature was the first to recognize civil unions for same-sex couples. In 2011–2012, the state officially recognized four Abenaki tribes.
Le Vermont /vɛʁmɔ̃/a Écouter (prononcé en anglais : /vɚˈmɑnt/b Écouter) est un État du nord-est des États-Unis. Sa capitale est Montpelier et sa plus grande ville est Burlington. Il est l'un des plus petits États du pays, tant en superficie qu'en nombre d'habitants2. Très rural, son territoire est recouvert à 75 % de forêts et seules sept villes dépassent les 10 000 habitants. Seul État de la Nouvelle-Angleterre à ne pas avoir accès à l'océan Atlantique, il est bordé au nord par la province canadienne du Québec, à l'est par le New Hampshire (dont il est séparé par le fleuve Connecticut), au sud par le Massachusetts et à l'ouest par l'État de New York. Son climat est de type continental et ses paysages alternent entre vastes forêts verdoyantes, étendues lacustres (dont le lac Champlain) et montagnes Vertes (mont Mansfield, Mont Ellen).
La région était peuplée par les Iroquois et les Algonquins avant son exploration par Samuel de Champlain en 1609. L'État fait ensuite partie de la Nouvelle-France. La France cède le territoire au Royaume de Grande-Bretagne après sa défaite lors de la guerre de Sept Ans en 1763. En 1777, durant la guerre d'indépendance des États-Unis, est fondée la République du Vermont, prélude à l'admission de l'État dans l'Union en 1791. Avec Hawaï, la Californie et le Texas, le Vermont est l'un des quatre États américains à avoir été un État souverain. Il fut en outre le premier à abolir partiellement l'esclavage. Son héritage colonial a perduré et un quart des habitants déclare avoir des ancêtres français.
Son économie repose aujourd'hui essentiellement sur l'agriculture et le tourisme. Le Vermont est notamment le principal producteur de sirop d'érable des États-Unis. Il compte également plus de cinquante parcs d'État, dont la forêt nationale de Green Mountain (zone protégée), et mène de nombreuses actions de préservation de l'environnement. En outre, le Vermont est considéré comme l'un des États les plus progressistes du pays. Le Parti républicain a longtemps dominé la vie politique interne (de 1850 aux années 1970), mais l'urbanisation et l'immigration en provenance de New York ou de Boston ont propagé des idées plus libérales. Il est aujourd'hui un soutien indéfectible du Parti démocrate. En 2011, le Vermont devient le premier État des États-Unis dans lequel le gouverneur valide un projet d'assurance-santé universel.
Il Vermont (pronuncia italiana /verˈmɔnt/ o /ˈvɛrmont/[2]; in inglese [vəɹˈmɒnt]) è uno stato federato degli Stati Uniti, situato nella regione del New England. Il nome deriva dal francese e significa "monte verde", proprio come la catena delle Green Mountains che attraversa lo Stato.
Il Vermont figura in 45ª posizione come superficie (paragonabile al Piemonte) e in 49ª posizione come popolazione tra i 50 stati dell'Unione, ed è l'unico della Nuova Inghilterra a non affacciarsi sull'Oceano Atlantico. Anche soprannominato The Green Mountain State, "lo stato della montagna verde", confina con il Massachusetts a sud, il New Hampshire ad est, New York ad ovest, e il Canada a nord (Quebec). La capitale è Montpelier, mentre la città più grande è Burlington.
Vermont es uno de los cincuenta estados que, junto con el distrito federal de Washington D. C., forman los Estados Unidos de América. Su capital es Montpelier y su ciudad más poblada, Burlington. Está ubicado en la región Noreste del país, división Nueva Inglaterra, limitando al norte con Canadá, al este con el río Connecticut que lo separa de Nuevo Hampshire, al sur con Massachusetts y al oeste con el estado de Nueva York. Con 24 901 km² es el sexto estado menos extenso —por delante de Nuevo Hampshire, Nueva Jersey, Connecticut, Delaware y Rhode Island, el menos extenso— y con 625 741 habs. en 2010 es el segundo menos poblado, por delante de Wyoming. Fue admitido en la Unión el 4 de marzo de 1791, como el estado número 14.
Su nombre se pronuncia, en español e inglés, "ver-MÓNT", con acento en la última sílaba al derivar del francés vert mont, que significa monte verde. Su capital es Montpelier, aunque la ciudad de mayor tamaño es Burlington. Es famoso por su paisaje (especialmente en otoño), sus productos lácteos y su jarabe de arce, además de ser conocido por su política liberal y pensamiento político independiente y de corte liberal para los parámetros estadounidenses.
Tras la exploración y la colonización de América del Norte, Francia reclamó el territorio actualmente conocido como Vermont, habitado originariamente por tribus nativas americanas (iroqueses, algonquinos y abenakis); pero pasó a manos de la Corona británica tras su derrota en el conflicto bélico que tuvo lugar entre 1754 y 1763. Durante muchos años, las colonias vecinas —entre ellas Nuevo Hampshire— se disputaron el control sobre el área. Sin embargo, Vermont fue independiente hasta que, tras un período de catorce años, se integró a los Estados Unidos de América.
Вермо́нт[2][3] (англ. Vermont, американское произношение: [vərˈmɒnt] (![]() слушать)) — один из штатов[4] на северо-востоке США. Расположен в регионе Новая Англия. В составе США с 1791 года.
слушать)) — один из штатов[4] на северо-востоке США. Расположен в регионе Новая Англия. В составе США с 1791 года.
Один из самых маленьких штатов США: по площади территории (24 923 км²) — 45-й, по числу жителей (626 042 чел., данные 2015 года[1]) — 49-й из всех 50 штатов США. Столица — Монтпилиер, крупнейший город — Берлингтон.
Официальный девиз штата — «Свобода и единство» (англ. Freedom and Unity). Официальное прозвище — «Штат Зелёных гор» (слово Vermont происходит от фр. vert mont — «зелёная гора»).
Принятое в США сокращение для названия штата — VT.



Der Connecticut River ist der längste Fluss in Neuengland in den Vereinigten Staaten. Er entsteht im Norden New Hampshires nahe der kanadischen Grenze, wo er eine Kette gleichnamiger Seen durchfließt, ehe er entlang der Grenze zwischen diesem Bundesstaat und Vermont südwärts, durch den westlichen Teil von Massachusetts und das Zentrum von Connecticut fließt, um schließlich bei Old Saybrook in den Long Island Sound zu münden. Er hat eine Länge von 655 km und das Einzugsgebiet umfasst 29.125 km². Die durchschnittliche jährliche Abflussmenge beträgt 556 m³/s.
Dank zahlreicher Stauwerke und Schleusen ist er bis Hartford für Schiffe befahrbar. Der Fluss unterliegt bis Windsor Locks den Gezeiten, etwa 95 km oberhalb der Mündung.
Der Connecticut River entwässert einen Teil der White Mountains in New Hampshire und der Green Mountains in Vermont nach Süden, sowie den östlichen Teil der Berkshires in Massachusetts. Im westlichen Teil von Massachusetts durchfließt der Connecticut River das breite Pioneer Valley. Am Connecticut River liegen unter anderen die Städte Northampton, Springfield und Hartford.
Der Fluss führt eine große Menge von Schlick mit sich, insbesondere zur Zeit der Schneeschmelze im Frühjahr. Dieses mitgeführte Material erzeugte eine Sandbank in der Nähe der Mündung in den Long Island Sound, die historisch ein bedeutendes Hindernis für die Schifffahrt bedeutete. Vor allem aus diesem Grund ist der Connecticut River einer der wenigen größeren Flüsse Neuenglands, in dessen Nähe zur Mündung keine wichtige Hafenstadt entstand. Der Ästuar des Flusses und seine Wattgebiete bilden eines der 1759 Feuchtgebiete von internationaler Bedeutung, die durch die Ramsar-Konvention geschützt werden.
Der Name des Flusses ist eine französische Verballhornung des Algonkin-Wortes quinetucket und bedeutet langer Gezeitenfluss.
康涅狄格河 (英语:Connecticut River),亦称康河,是美国新英格兰最大的河流,长655公里,流域面积29,137平方公里。发源于新罕布什尔州的第四康涅狄格湖,经过佛蒙特州和新罕布什尔州的边界,经马萨诸塞州西部,在康涅狄格州中南部流入长岛海湾。


 Alabama-AL
Alabama-AL
 Alaska-AK
Alaska-AK
 Arizona-AZ
Arizona-AZ

 Arkansas-AR
Arkansas-AR

 Education and Research
Education and Research
 Universities and colleges in the United States of America
Universities and colleges in the United States of America

 California-CA
California-CA

 Colorado-CO
Colorado-CO

 Connecticut-CT
Connecticut-CT

 Delaware-DE
Delaware-DE

 Florida-FL
Florida-FL

 Georgia-GA
Georgia-GA

 Hawaii-HI
Hawaii-HI

 Idaho-ID
Idaho-ID

 Illinois-IL
Illinois-IL

 Indiana-IN
Indiana-IN

 Iowa-IA
Iowa-IA

 Kansas-KS
Kansas-KS

 Kentucky-KY
Kentucky-KY

 Louisiana-LA
Louisiana-LA

 Maine-ME
Maine-ME

 Maryland-MD
Maryland-MD

 Massachusetts-MA
Massachusetts-MA

 Michigan-MI
Michigan-MI

 Minnesota-MN
Minnesota-MN

 Mississippi-MS
Mississippi-MS

 Missouri-MO
Missouri-MO

 Montana-MT
Montana-MT

 Nebraska-NE
Nebraska-NE

 Nevada-NV
Nevada-NV

 New hampshire-NH
New hampshire-NH

 New jersey-NJ
New jersey-NJ
 New mexico-NM
New mexico-NM

 New York-NY
New York-NY

 North Carolina-NC
North Carolina-NC

 North Dakota-ND
North Dakota-ND

 Ohio-OH
Ohio-OH

 Oklahoma-OK
Oklahoma-OK

 Oregon-OR
Oregon-OR

 Pennsylvania-PA
Pennsylvania-PA

 Rhode Island-RI
Rhode Island-RI

 South Dakota-SD
South Dakota-SD

 Tennessee-TN
Tennessee-TN

 Texas-TX
Texas-TX

 Universities in the USA
Universities in the USA

 Utah-UT
Utah-UT
 United States
United States

 Vermont-VT
Vermont-VT

 Virginia-VA
Virginia-VA

 Washington-WA
Washington-WA

 Washington, D.C.
Washington, D.C.

 West Virginia-WV
West Virginia-WV

 Wisconsin-WI
Wisconsin-WI

 Wyoming-WY
Wyoming-WY


 Alabama-AL
Alabama-AL

 Alaska-AK
Alaska-AK

 Arizona-AZ
Arizona-AZ

 California-CA
California-CA

 Colorado-CO
Colorado-CO

 Connecticut-CT
Connecticut-CT

 Idaho-ID
Idaho-ID

 Illinois-IL
Illinois-IL

 Indiana-IN
Indiana-IN

 Iowa-IA
Iowa-IA

 Maine-ME
Maine-ME

 Maryland-MD
Maryland-MD

 Massachusetts-MA
Massachusetts-MA

 Michigan-MI
Michigan-MI

 Minnesota-MN
Minnesota-MN

 Missouri-MO
Missouri-MO

 Montana-MT
Montana-MT

 Nevada-NV
Nevada-NV

 New hampshire-NH
New hampshire-NH

 New jersey-NJ
New jersey-NJ

 New mexico-NM
New mexico-NM

 New York-NY
New York-NY

 North Carolina-NC
North Carolina-NC

 North Dakota-ND
North Dakota-ND

 Ohio-OH
Ohio-OH

 Oregon-OR
Oregon-OR

 Pennsylvania-PA
Pennsylvania-PA

 Rhode Island-RI
Rhode Island-RI

 South Dakota-SD
South Dakota-SD

 Sport
Sport

 Tennessee-TN
Tennessee-TN

 Texas-TX
Texas-TX

 Utah-UT
Utah-UT
 United States
United States

 Vermont-VT
Vermont-VT

 Virginia-VA
Virginia-VA

 Washington-WA
Washington-WA

 West Virginia-WV
West Virginia-WV

 Wisconsin-WI
Wisconsin-WI

 Wyoming-WY
Wyoming-WY
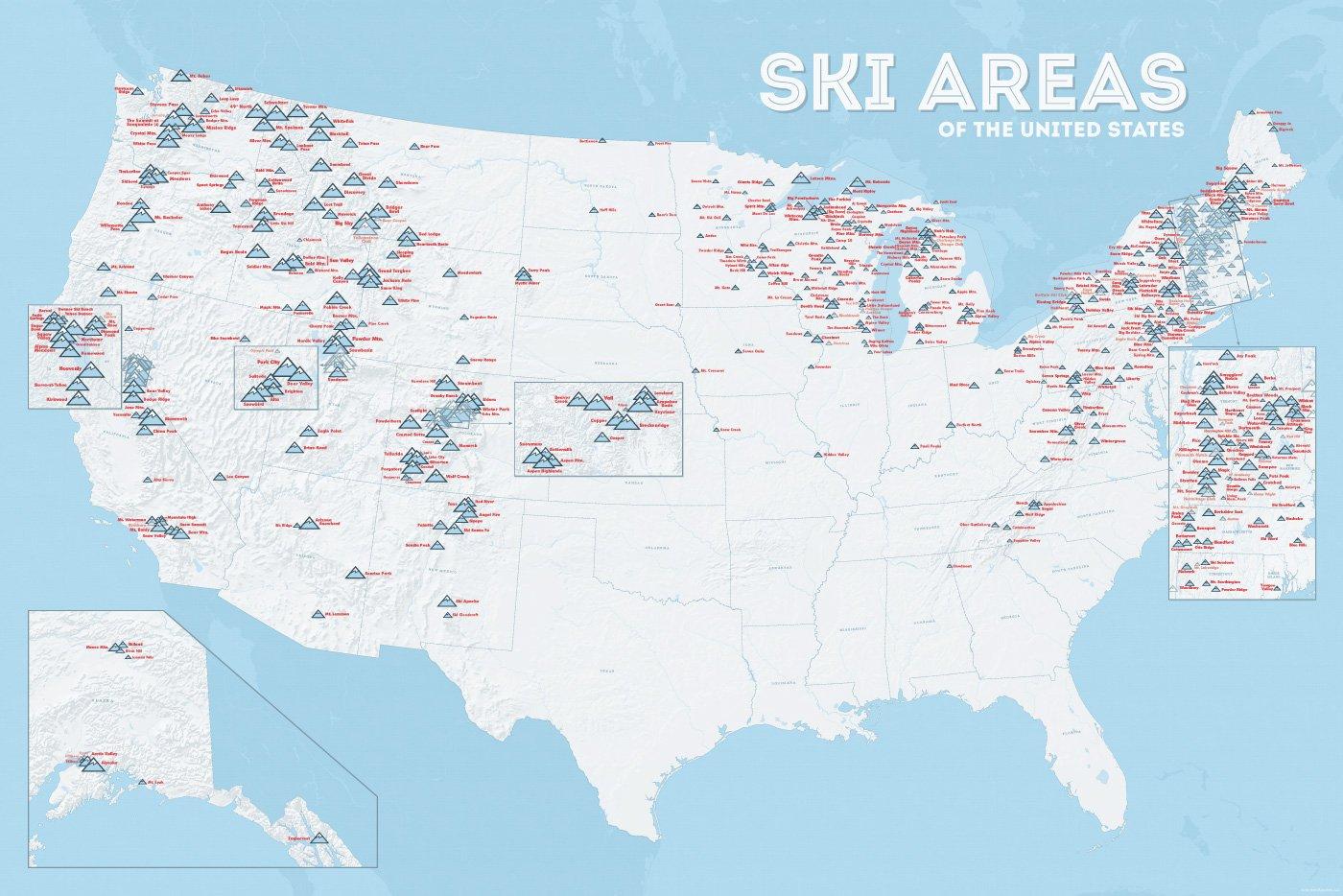
In vielen der 50 Bundesstaaten der USA gibt es Wintersportgebiete, von Maine bis nach Kalifornien. Vor allem drei große Gebirgszüge machen das Skifahren in den Vereinigten Staaten möglich: Zum einen sind dies die Rocky Mountains, die die sogenannten Mountain States durchqueren (Colorado, Nevada, Montana, Wyoming, Idaho und Utah). Die Cascades Range zieht sich von Kanada über Oregon bis hinunter nach Kalifornien. Im Osten der USA befinden sich zudem die Appalachen.
| Name | Orte im Gebiet | Staat | Seehöhe in m |
Liftanlagen1 | Pisten in km |
Weblink | |
| von | bis | ||||||
| Alta Snowbird | Snowbird | Utah | 2365 | 3350 | 1/18/0 | 150 | www.snowbird.com |
| Arapaho Basin | Colorado | 3292 | 3978 | 0/4/0 | 34 | www.arapahoebasin.com | |
| Aspen Highlands | Aspen | Colorado | 2460 | 3536 | 0/5/0 | 58 | www.aspensnowmass.com |
| Aspen Mountain | Aspen | Colorado | 2422 | 3417 | 1/7/0 | 50 | www.aspensnowmass.com |
| Aspen Butermilk | Aspen | Colorado | 2398 | 3013 | 0/5/1 | 34 | www.aspensnowmass.com |
| Aspen Snowmass | Aspen | Colorado | 2473 | 3813 | 2/13/5 | 137 | www.aspensnowmass.com |
| Beaver Creek Resort | Vail/Beaver Creek | Colorado | 2268 | 3478 | 0/15/8 | 152 | www.beavercreek.com |
| Big Sky Resort | Big Sky Village | Montana | 2072 | 3403 | 2/18/2 | 186 | www.bigskyresort.com |
| Breckenridge | Breckenridge | Colorado | 2926 | 3962 | 1/25/25 | 146 | www.snow.com |
| Deer Valley | Deer Valley | Utah | 2003 | 2918 | 1/20/0 | 105 | www.deervalley.com |
| Grand Targhee | Wyoming | 2438 | 3048 | 0/4/0 | 40 | www.grandtarghee.com | |
| Heavenly | Nevada | 1914 | 3039 | 2/17/6 | 89 | www.heavenly.com | |
| Jackson Hole Mountain | Teton Village | Wyoming | 1924 | 3185 | 3/9/0 | 150 | www.jacksonhole.com |
| Keystone | Keystone | Colorado | 2829 | 3782 | 2/16/16 | 116 | www.snow.com |
| Klamath Falls | Oregon | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | www.oregon.com | |
| Mammoth Mountain | Kalifornien | 2456 | 3362 | 3/23/4 | 112 | www.mammothmountain.com | |
| Park City Mountain | Park City | Utah | 2103 | 3039 | 0/15/0 | 87 | www.parkcitymountain.com |
| Squaw Valley | Squaw Valley | Kalifornien | 1886 | 2664 | 3/26/3 | 88 | www.squaw.com |
| Steamboat | Steamboat Springs | Colorado | 2097 | 3207 | 1/18/0 | 110 | www.steamboat.com |
| Telluride Skiresort | Telluride | Colorado | 2661 | 3735 | 3/11/0 | 98 | www.tellurideskiresort.com |
| The Canyons | Utah | 2061 | 3038 | 2/12/2 | 106 | www.thecanyons.com | |
| Vail | Vail | Colorado | 2450 | 3527 | 1/23/9 | 215 | www.vail.com |

 Idaho-ID
Idaho-ID

 Maine-ME
Maine-ME

 Michigan-MI
Michigan-MI

 Minnesota-MN
Minnesota-MN

 Montana-MT
Montana-MT

 New hampshire-NH
New hampshire-NH

 New York-NY
New York-NY

 North Dakota-ND
North Dakota-ND

 Vermont-VT
Vermont-VT

 Washington-WA
Washington-WA

 Wisconsin-WI
Wisconsin-WI

 Alabama-AL
Alabama-AL

 Arizona-AZ
Arizona-AZ

 California-CA
California-CA

 Florida-FL
Florida-FL

 Georgia-GA
Georgia-GA

 Louisiana-LA
Louisiana-LA

 Massachusetts-MA
Massachusetts-MA

 Mississippi-MS
Mississippi-MS

 Nevada-NV
Nevada-NV

 New jersey-NJ
New jersey-NJ

 New mexico-NM
New mexico-NM

 New York-NY
New York-NY

 North Carolina-NC
North Carolina-NC

 Oklahoma-OK
Oklahoma-OK

 Oregon-OR
Oregon-OR

 Pennsylvania-PA
Pennsylvania-PA

 South Carolina-SC
South Carolina-SC

 Texas-TX
Texas-TX

 Companies
Companies

 Utah-UT
Utah-UT
 United States
United States

 Vermont-VT
Vermont-VT

 Virginia-VA
Virginia-VA

 Washington-WA
Washington-WA

 Washington, D.C.
Washington, D.C.

 West Virginia-WV
West Virginia-WV

 Geography
Geography
 International cities
International cities
 Architecture
Architecture
 Ski vacation
Ski vacation
 Transport and traffic
Transport and traffic