
Deutsch-Chinesische Enzyklopädie, 德汉百科
 Sweden
Sweden




ABBA(乐队标志:ᗅᗺᗷᗅ,中文:阿巴)是瑞典流行乐队。字母缩写(ABBA)源自于乐队成员姓名的首字母(字母的排列顺序并无规定)。少数时候被记为Abba。在1976年以前的乐队宣传材料中,乐队标志中的第一个“B”字母就已经被反转过来了。[1]乐队在1970年前后重组,乐队成员是昂内塔·费尔特斯科格(Agnetha Fältskog)、比约恩·奥瓦尔斯(Björn Ulvaeus)、班尼·安德森(Benny Andersson),及安妮-弗瑞德·林斯塔德(Anni-Frid Lyngstad;绰号"Frida")。他们凭借歌曲《滑铁卢》在1974年欧洲歌唱大赛中获胜,他们从此广泛地为人所知。[2]ABBA于1982年解散。经典名曲包括《妈妈咪呀》(Mamma Mia)和《舞后》(Dancing Queen)。
ABBA ist eine schwedische Popgruppe, die aus den ehemaligen Paaren Agnetha Fältskog und Björn Ulvaeus sowie Benny Andersson und Anni-Frid Lyngstad besteht und sich 1972 in Stockholm formierte. Sie gehört mit rund 400 Millionen verkauften Tonträgern zu den erfolgreichsten Bands der Musikgeschichte.[1]
Die Gruppe hat die Geschichte der Popmusik mitgeprägt. Bis in die 1970er Jahre hatte es keine anderen Skandinavier mit vergleichbaren Erfolgen gegeben. Trotz US-amerikanischer und britischer Dominanz im Musikgeschäft gelang ABBA der internationale Durchbruch.[2] Nach ihrem Sieg beim Eurovision Song Contest 1974 mit Waterloo war man besonders in Europa und Australien sowie später auch in Lateinamerika und Japan erfolgreich. Vor allem in der zweiten Hälfte der 1970er Jahre galt ABBA wegen der aufwendigen und ausgefeilten Musikproduktionen als Mitbegründer einer neuen internationalen Popmusik.
Zu ihren bekanntesten Songs zählen SOS, Mamma Mia, Fernando, Dancing Queen, Money, Money, Money, Take a Chance on Me, The Winner Takes It All und Super Trouper. Charakteristisch für die Gruppe waren außerdem ihre für die damalige Zeit ausgefallenen bunt-poppigen Kostüme, die das Quartett bei Auftritten und in Musikvideos trug. Während Ulvaeus und Andersson hauptsächlich für Kompositionen und Texte verantwortlich waren, agierten Fältskog und Lyngstad vorwiegend als Leadsängerinnen.
Das 1992 veröffentlichte Best-of-Album ABBA Gold zählt mit 31 Millionen verkauften Exemplaren zu den weltweit erfolgreichsten Alben und hat maßgeblich zum ABBA-Revival in den 1990ern beigetragen.[3] 1999 hatte das auf ABBA-Songs basierende Musical Mamma Mia! in London Premiere, das mit über 60 Millionen Zuschauern eines der erfolgreichsten Musicals der Welt ist.[3][4] Die Verfilmung von Mamma Mia! aus dem Jahr 2008 gehört darüber hinaus zu den erfolgreichsten Musicalverfilmungen.
1982 beendeten die Gruppenmitglieder aufgrund privater Differenzen vorläufig ihre musikalische Zusammenarbeit und gaben erst 2018 bekannt, dass sie wieder zusammen an neuem Material arbeiten.[5] Obwohl es über einen Zeitraum von fast 40 Jahren weder Bandauftritte noch neue Musik gab, waren ihre Lieder nach wie vor populär.[6] So werden ihre Stücke weiterhin in unterschiedlichsten Interpretationen und Coverversionen produziert und meistens sehr erfolgreich vermarktet; seit 2013 gibt es in Stockholm ein ABBA-Museum. 2021 gab die Band ihr Comeback im Rahmen einer virtuellen Konzertshow bekannt und veröffentlichte drei neue Singles sowie ihr neuntes Studioalbum Voyage.
ABBA(アバ、スウェーデン語発音: [²abːa])は、アイネッタ・フェルツクグ、ビョルン・ウルヴァース、ベニー・アンダーソン、アンニ=フリッド・リングスタッドによってストックホルムで結成されたスウェーデンのポップ・グループである。彼らは1974年から1982年まで世界中の音楽チャートを席巻し、ポピュラー音楽界で商業的に成功したグループの1つになった。ABBAはイギリスのザ・ドーム(英語版)で行われたユーロビジョン・ソング・コンテスト1974に出場し、スウェーデン代表として初めて優勝した。
ABBA (/ˈæbə/ AB-ə, Swedish: [ˈâbːa]) are a Swedish pop group formed in Stockholm in 1972 by Agnetha Fältskog, Björn Ulvaeus, Benny Andersson, and Anni-Frid Lyngstad. The group's name is an acronym of the first letters of their first names arranged as a palindrome. Widely considered one of the greatest musical groups of all time,[2] they became one of the most commercially successful acts in the history of popular music, topping the charts worldwide from 1974 to 1983, and have achieved 48 hit singles.
In 1974, ABBA were Sweden's first winner of the Eurovision Song Contest with the song "Waterloo", which in 2005 was chosen as the best song in the competition's history as part of the 50th anniversary celebration of the contest.[3] During the band's main active years, it consisted of two married couples: Fältskog and Ulvaeus, and Lyngstad and Andersson. With the increase of their popularity, their personal lives suffered, which eventually resulted in the collapse of both marriages. The relationship changes were reflected in the group's music, with latter compositions featuring darker and more introspective lyrics.[4] After ABBA separated in December 1982, Andersson and Ulvaeus continued their success writing music for multiple audiences including stage, musicals and movies,[5][6] while Fältskog and Lyngstad pursued solo careers.[7][8]
Ten years after the group broke up, a compilation, ABBA Gold, was released, becoming a worldwide best-seller. In 1999, ABBA's music was adapted into Mamma Mia!, a successful musical that toured worldwide and, as of November 2021, is still in the top-ten longest running productions on both Broadway (closed in 2015) and the West End (still running). A film of the same name, released in 2008, became the highest-grossing film in the United Kingdom that year. A sequel, Mamma Mia! Here We Go Again, was released in 2018.
In 2016, the group reunited and started working on a digital avatar concert tour.[9] Newly recorded songs were announced in 2018.[10] Voyage, their first new album in 40 years, was released on November 5, 2021.[11] ABBA Voyage, a concert residency featuring ABBA as virtual avatars – dubbed 'ABBAtars' – is due to take place in London from May to December 2022.[12]
ABBA is one of the best-selling music artists of all time, with record sales estimated to be between 150 million and 385 million sold worldwide[13][14] and the group was ranked 3rd best-selling singles artists in the United Kingdom with a total of 11.3 million singles sold by 3 November 2012.[15] ABBA was the first group from a non-English-speaking country to achieve consistent success in the charts of English-speaking countries, including the United States, United Kingdom, Republic of Ireland, Canada, Australia, New Zealand and South Africa.[16] They are the best-selling Swedish band of all time[17] and the best-selling band originating in continental Europe. ABBA had eight consecutive number-one albums in the UK. The group also enjoyed significant success in Latin America and recorded a collection of their hit songs in Spanish. The group was inducted into the Rock and Roll Hall of Fame in 2010.[18] In 2015, their song "Dancing Queen" was inducted into the Recording Academy's Grammy Hall of Fame.[19]
ABBA est un groupe de pop suédois fondé à Stockholm en novembre 1972. Le groupe est originellement composé d'Agnetha Fältskog, Anni-Frid Lyngstad, dite « Frida », Benny Andersson et Björn Ulvaeus. Lors de leur formation, ils sont deux couples mariés, Agnetha et Björn, Frida et Benny.
L'acronyme et palindrome ABBA est composé des quatre initiales des prénoms des membres (Agnetha, Björn, Benny, Anni-Frid). Ce n'est qu'à partir de 1976 que le désormais célèbre ambigramme, avec un B inversé, est utilisé comme logo.
Vainqueur du Concours Eurovision de la chanson 1974 avec Waterloo, ABBA connaît un immense succès mondial durant la période disco du milieu des années 1970 et devient l'un des groupes ayant vendu le plus de disques, ses ventes étant estimées à 380 millions (180 millions ventes certifiées). Séparés depuis 1982, ABBA annonce fin avril 2018 que ses membres se sont retrouvés au cours de l'été 2017 pour l'enregistrement de deux nouvelles chansons qui feront partie de leur prochain album. Ce dernier, leur neuvième, intitulé Voyage, sort le 5 novembre 2021.
Gli ABBA sono un gruppo musicale pop svedese, e, in generale, il gruppo scandinavo di maggiore successo. Hanno venduto più di 400 milioni di dischi in tutto il mondo, con una costante vendita ogni anno.[4] Gli ABBA hanno raggiunto un successo mondiale e sono considerati tra i più celebri esponenti della musica pop internazionale.
Il nome del gruppo deriva da un acronimo formato dalle lettere iniziali dei nomi dei membri (Agnetha, Benny, Björn e Anni-Frid) e lo si trova scritto anche come Abba. La prima 'B' nella seconda versione del logo del nome del gruppo appare rovesciata a partire dal 1976 (ᗅᗺᗷᗅ) in tutte le copertine dei loro dischi e del materiale promozionale.
Il gruppo si costituì intorno al 1970 con la formazione che avrebbe sempre mantenuto: Björn Ulvaeus, Benny Andersson, Agnetha Fältskog e Anni-Frid Lyngstad (meglio conosciuta come "Frida"). Quattro anni dopo erano già all'apice della loro carriera musicale dopo aver vinto l'edizione dell'Eurovision Song Contest nel 1974 con Waterloo; da allora raggiunsero grande successo e popolarità mondiali. Al massimo della loro celebrità, entrambi i matrimoni dei componenti del gruppo (Björn con Agnetha e Benny con Frida) fallirono. Il gruppo si sciolse nel 1982 e, per più di trent'anni, nessuna riunione venne più progettata dai quattro; nel 2000 fu proposto agli ABBA di riunirsi per un tour di 100 concerti in cambio di un compenso pari a un miliardo di dollari[5], ma rifiutarono "per non deludere i fan"[6]. Il 15 marzo 2010 sono stati inseriti nella Rock and Roll Hall of Fame[7].
Nel 2018 annunciano il ritorno all'attività, riprendendo ad incidere due nuovi brani, di cui uno intitolato I Still Have Faith In You[8]. Il ritorno si fa attendere, anche a causa della pandemia di coronavirus, fino al 2 settembre 2021, quando finalmente vengono pubblicati due nuovi singoli (I Still Have Faith In You / Don't Shut Me Down) come anteprima di un intero nuovo album (Voyage), la cui uscita è prevista il 5 novembre 2021, e viene annunciata una serie di concerti a Londra nel maggio 2022.
Gli ABBA sono stati il primo gruppo non anglofono d'Europa a raggiungere un successo così ampio nei paesi anglofoni del mondo, come il Regno Unito, l'Irlanda, gli Stati Uniti, il Canada, l'Australia, la Nuova Zelanda e il Sudafrica. Tra i loro maggiori meriti c'è la legittimazione dell'industria musicale scandinava come fonte di successo internazionale, che ha spianato la via ad altri gruppi svedesi dei più diversi sottogeneri pop e rock come Ace of Base, Rednex, Roxette, The Cardigans, Alcazar, The Ark.
ABBA es un grupo sueco de música pop, integrado por Agnetha Fältskog, Björn Ulvaeus, Benny Andersson y Anni-Frid «Frida» Lyngstad. El nombre «ABBA» es un acrónimo formado por las primeras letras del nombre de cada miembro (Agnetha, Björn, Benny, Anni-Frid).1
El cuarteto se formó en Estocolmo en 1972, logrando fama internacional al triunfar en el Festival de la Canción de Eurovisión 1974.2 Desde entonces, ABBA ha ganado popularidad empleando melodías pegadizas, letras simples y su sonido propio, caracterizado por las armonías de las voces femeninas y el wall of sound, un efecto musical creado por el productor Phil Spector.
Björn y Agnetha contrajeron matrimonio meses antes de la formación del cuarteto, mientras que Benny y Frida lo hicieron en 1978; los cuatro lidiaron con sus obligaciones artísticas al mismo tiempo que se ocupaban de sus nuevas familias.
Sus grabaciones tuvieron un impacto comercial que los llevó a convertirse en los artistas más exitosos de su compañía discográfica —Universal Music Group— y a ser la banda con más ventas en los años 1970.34
Fue el primer grupo pop europeo en experimentar el éxito en países de habla inglesa fuera de Europa, principalmente Australia, Nueva Zelanda, Sudáfrica, Canadá y en menor medida Estados Unidos. Sin embargo, en la cima de su popularidad, ambos matrimonios se disolvieron y estos cambios se reflejaron en su música, al escribir letras más profundas con un estilo musical diferente. La agrupación experimentó un declive comercial y finalmente decidieron separarse, de modo que en diciembre de 1982 realizaron su última aparición como ABBA.5
Después de un tiempo fuera del interés público, en la década de 1990 el lanzamiento de varios álbumes recopilatorios hicieron posible su regreso a la cima de las listas de popularidad, y ABBA es ahora uno de los grupos más exitosos, con ventas estimadas de entre 380 y 400 millones de sus producciones musicales en todo el mundo.678910
Su música ha sido interpretada por varios artistas reconocidos, y también es la base del musical Mamma Mia!. La agrupación es un ícono de su país de origen, además de una figura importante en la expansión del europop. Así, su popularidad abrió las puertas a otros artistas europeos, una de las razones por las que ingresaron al Salón de la Fama del Rock.1112
En septiembre de 2021 y tras casi cuarenta años de su separación, el grupo anunció su regreso con dos canciones nuevas tituladas «I still have faith in you» y «Don't shut me down», que forman parte del disco Voyage. El grupo realizará una gira de conciertos virtuales en 2022.131415
ABBA (рус. — «А́ББА»[2][3]) — шведская поп-группа, созданная в 1972 году, названная по первым буквам имён исполнителей: Агнета Фельтског, Бьорн Ульвеус, Бенни Андерссон, Анни-Фрид Лингстад. Является одним из наиболее успешных коллективов за всю историю популярной музыки и самым успешным из числа созданных в Скандинавии: записи группы по всему миру были проданы тиражом более 350 миллионов экземпляров[4][5].
Синглы квартета занимали первые места в чартах с середины 1970-х («Waterloo») до начала 1980-х («One of Us»), а сборники возглавляли мировые хит-парады и в 2000-х[6]. Музыка группы остаётся в плей-листах радиостанций, и их альбомы продолжают продаваться по сей день.
Они были первыми представителями континентальной Европы, завоевавшими первые места в чартах всех ведущих англоговорящих стран (США, Великобритания, Канада, Ирландия, Австралия и Новая Зеландия).





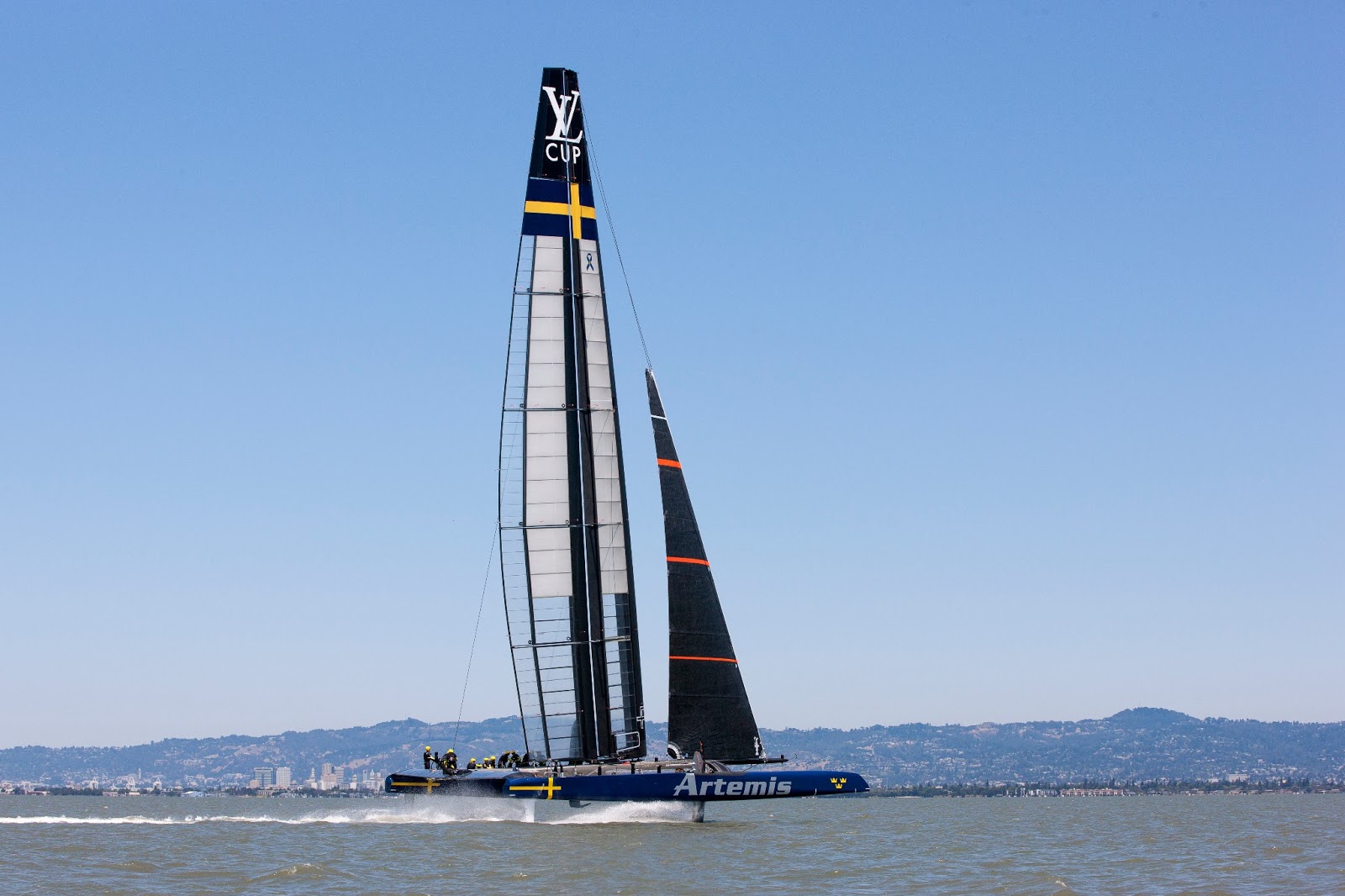
 America´s Cup 2017
America´s Cup 2017
 Australia
Australia

 California-CA
California-CA
 China
China

 Valencian Community
Valencian Community
 England
England
 France
France
 Greece
Greece

 Illinois-IL
Illinois-IL
 Italy
Italy
 Japan
Japan
 Canada
Canada
 Kyūshū
Kyūshū
 New Zealand
New Zealand

 New York-NY
New York-NY
 Oman
Oman
 Austria
Austria

 Provence-Alpes-Côte d´Azur
Provence-Alpes-Côte d´Azur
 Republic of Korea
Republic of Korea

 Rhode Island-RI
Rhode Island-RI
 Russia
Russia

 Ships and Nautics
Ships and Nautics
 Sweden
Sweden
 Spain
Spain

 Sport
Sport
 America´s Cup
America´s Cup
 United States
United States
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom

 Western Australia-WA
Western Australia-WA

美洲杯帆船赛(英语:America's Cup)是赛艇运动中保存的最著名也是最古老的一项体育比赛。
比赛奖杯是银质大口水罐,奖励给来自不同国家的两艘帆船之间举行的九局五胜制比赛的胜者。两艘帆船中,一艘代表卫冕冠军游艇俱乐部,另一艘则代表俱乐部挑战奖杯。
美洲杯帆船赛源于1851年8月22日,一艘由代表纽约游艇俱乐部(New York Yacht Club,NYYC)的财团拥有的30.86米长纵帆船“美洲号”(America),同15艘代表皇家快艇舰队(Royal Yacht Squadron)的帆船在英国南部的怀特岛附近比赛。“美洲号”最终以领先20分钟胜出。拥有“美洲号”的财团后来将奖杯通过馈赠契约捐献给纽约游艇俱乐部。由此,奖杯被托管成为一项鼓励各国之间友谊竞赛的“挑战”奖品。
在当时公认无敌的英国海上霸权遭受如此打击后,一系列英国财团试图赢回奖杯。但纽约游艇俱乐部在超过132年的25次挑战中保持不败,成为体育运动史上最长的连胜纪录。1930年以前,这项赛事一直在纽约港附近举行,余下的NYYC全盛时期内则改在罗德岛的纽波特(Newport,Rhode Island)举行。
Der America’s Cup ist die älteste noch heute ausgetragene Segelregatta. Der Preis ist ein Wanderpokal und hat seinen Ursprung in einer Regatta rund um die britische Insel Isle of Wight im Jahre 1851.[1] Er ist benannt nach seiner erstmaligen Gewinnerin, der Yacht America des New York Yacht Club (NYYC).
Um den America’s Cup treten die Boote zweier Yachtclubs – Verteidiger und Herausforderer – in mehreren Wettfahrten gegeneinander an. Die Yacht, die eine vorher festgelegte Anzahl von Wettfahrten gewinnt, gewinnt den Cup. Laut der Stiftungsurkunde bestimmt der Verteidiger das Segelrevier. Die Stiftungsurkunde sieht vor, dass Verteidiger und Herausforderer innerhalb gewisser Grenzen Vereinbarungen über die Regeln treffen können, z. B. was die Anzahl der Wettfahrten betrifft.[2]
Von der ersten Verteidigung 1870 bis zur 20. Regatta im Jahr 1967 gab es jeweils nur einen Herausforderer. Im Jahr 1970 gab es erstmals mehrere Herausforderer, so dass der veranstaltende New York Yacht Club sich einverstanden erklärte, den offiziellen Herausforderer durch eine Vorausscheidung zu ermitteln. Zwischen 1983 und 2007 bis zum zeitweiligen Rückzug des Sponsors Louis Vuitton und ab 2013 erneut wurde der Herausforderer durch den Louis Vuitton Cup ermittelt. Schon die Teilnahme am Louis Vuitton Cup setzte großes finanzielles Engagement voraus: die Budgets der High-Tech-Yachten betrugen teilweise über 100 Mio. Dollar. Die Yachten mussten im Land des angemeldeten Teams gebaut werden. Wesentliche Neuerungen ergaben sich bei den letzten beiden ACs. 2010 segelten das erste Mal sowohl Verteidiger wie Herausforderer mit Mehrrumpfbooten. 2013 waren Katamarane vereinbart und die teilnehmenden Teams konstruierten „Tragflügelkatamarane“ die über 40 Knoten (75 km/h) schnell segelten. Für 2017 wurden die Boote „AC50F Katamaran“ von ehemals 72 Fuß (fast 22 m) auf 50 ft (gut 15 m) verkürzt, blieben 24 m hoch und wurden im Training erstmals 50 kn (92 km/h) schnell.[3]
アメリカスカップあるいはアメリカズカップ[1](英: America's Cup)は、1851年より現在まで続く国際ヨットレース。また、その優勝杯の名。その成立は近代オリンピックより45年、サッカーのワールドカップより79年、全英オープンよりも9年早く、継続して使用されている世界最古のスポーツトロフィーとして広く一般に認知されている。[2][3]
名称の由来は最初の優勝艇の『アメリカ号』の名を冠した『アメリカ号のカップ』であり、決して『アメリカ合衆国のカップ』という意味ではない。しかし、その後132年に亘ってアメリカ合衆国のヨットクラブがカップを防衛してきたため、事実上『アメリカ合衆国のカップ』と同じ定義で称される。
競技の本質は、カップの寄贈者が記した贈与証書の規定に基づき、アメリカズカップを掛けてマッチレース(1対1)形式で争われるヨットクラブ間の国際親善レースである。しかし、使用されるヨットは出場国で建造しなければならないため、参加各国の造船工学・建築工学・材料工学・流体力学・航空力学・気象学などの最先端技術や軍事からの応用技術が投入される等、参加国の威信を賭けた国別対抗レースとしての一面も持ち合わせている。またこれら最新ヨットにはオリンピックメダリストら多数のトップセーラーが乗り組むことあり、一般にヨットレース全般、或いはインショア(沿海)レースの最高峰として位置づけられており、別名「海のF1」とも称される。
The America's Cup, affectionately known as the Auld Mug, is a trophy awarded to the winner of the America's Cup match races between two sailing yachts. One yacht, known as the defender, represents the yacht club that currently holds the America's Cup and the second yacht, known as the challenger, represents the yacht club that is challenging for the cup. The timing of each match is determined by an agreement between the defender and the challenger. The America's Cup is the oldest international sporting trophy.[1][2][3] It will next be raced for in the southern summer, in the early part of 2021.[4]
The cup was originally awarded in 1851 by the Royal Yacht Squadron for a race around the Isle of Wight in the United Kingdom, which was won by the schooner America. The trophy, originally named the '£100 Cup', was renamed the America's Cup after the yacht and was donated to the New York Yacht Club (NYYC) under the terms of the Deed of Gift, which made the cup available for perpetual international competition.
Any yacht club that meets the requirements specified in the deed of gift has the right to challenge the yacht club that holds the cup. If the challenging club wins the match, it gains stewardship of the cup.
The history and prestige associated with the America's Cup attracts not only the world's top sailors and yacht designers but also the involvement of wealthy entrepreneurs and sponsors. It is a test not only of sailing skill and boat and sail design, but also of fundraising and management skills.
The trophy was held by the NYYC from 1857 (when the syndicate that won the cup donated the trophy to the club) until 1983. The NYYC successfully defended the trophy twenty-four times in a row before being defeated by the Royal Perth Yacht Club, represented by the yacht Australia II. The NYYC's reign was the longest winning streak (in terms of date) in the history of all sports.[5]
From the first defence of the cup in 1870 through the twentieth defence in 1967, there was always only one challenger. In 1970, for the first time, there were multiple challengers, so the NYYC agreed that the challengers could run a selection series with the winner becoming the official challenger and competing against the defender in the America's Cup match. Since 1983, Louis Vuitton has sponsored the Louis Vuitton Cup as a prize for the winner of the challenger selection series.
Early matches for the cup were raced between yachts 65–90 ft (20–27 m) on the waterline owned by wealthy sportsmen. This culminated with the J-Class regattas of the 1930s. After World War II and almost twenty years without a challenge, the NYYC made changes to the deed of gift to allow smaller, less expensive 12-metre class yachts to compete; this class was used from 1958 until 1987. It was replaced in 1990 by the International America’s Cup Class which was used until 2007.
After a long legal battle, the 2010 America's Cup was raced in 90 ft (27 m) waterline multihull yachts in a best of three "deed of gift" match in Valencia, Spain. The victorious Golden Gate Yacht Club then elected to race the 2013 America's Cup in AC72 foiling, wing-sail catamarans. Golden Gate Yacht Club successfully defended the cup. The 35th America's Cup match was announced to be sailed in 50 ft foiling catamarans.[6]
The history of the America's Cup has included legal battles and disputes over rule changes including most recently over the rule changes for the 2017 America's Cup.[7]
The America's Cup is currently held by the Royal New Zealand Yacht Squadron,[8] who will stage the 36th defence of the Cup in 2021.
La Coupe de l'America (America's Cup) est une compétition nautique internationale à la voile, voulue par ses initiateurs comme un défi amical et perpétuel entre Yacht Clubs de différentes nations et définie sous cette dénomination en 1857 par les membres du New York Yacht Club (NYYC)2, vainqueurs, six ans plus tôt, en 1851, avec la goélette America, de la régate internationale originelle, organisée autour de l'île de Wight, par le Royal Yacht Squadron (RYS), en marge de l'exposition universelle de Londres.
Le trophée est une aiguière en argent, attribuée au Yacht Club vainqueur du défi jusqu'à sa remise en jeu. Fabriquée en 1848 pour le Royal Yacht Squadron par le bijoutier et orfèvre Robert Garrard de Londres comme trophée de la Coupe de Cent Souverains, elle est ramenée aux États-Unis, en septembre 1851 sous le nom de Coupe de Cent Guinées, pour prendre en juillet 1857 son nom actuel de Coupe de l'America, en hommage à la goélette victorieuse.
C'est une des plus anciennes compétitions sportives encore disputée de nos jours et se révèle être l'un des principaux théâtres de l'évolution de l'architecture navale en matière de voiliers de régates.
À la suite de la régate de 1851 et de la création de la course en 1857, la première édition de la coupe de l'America n'est disputée qu'après la guerre de Sécession, en août 1870. Après ces deux compétitions, lors desquelles un voilier challenger affronte une flotte de voiliers défendeurs, les adversaires se mesurent en duel (match-racing). La deuxième édition de 1871 se déroule en deux duels successifs avec deux défendeurs du NYYC contre l'unique challenger du Royal Thames Yacht Club.
C'est à partir de la troisième édition de 1876 que les régates opposent, le défender, tenant du titre, au challenger qui relève le défi. Ce dernier est désigné par des régates de sélection depuis la 21e édition de 1970, régates qui prennent le nom de Coupe Louis-Vuitton en 1983, lors de la 25e édition.
Chaque édition voit l'établissement d'un règlement particulier, appelé acte de donation, définissant entre autres les conditions de régates et le type de bateau utilisé basé sur une jauge de course, rédigé par le defender et le challenger de référence, c'est-à-dire le premier Yacht Club à défier le tenant du titre.
En 2002, une exposition intitulée L'America's Cup, 150 ans d'histoire racontée par Louis Vuitton est organisée au Musée national de la Marine à Paris.
Le trophée est détenu par Emirates Team New Zealand, représentant le Royal New Zealand Yacht Squadron qui s'impose sept à un face au défi Oracle Team USA lors de la 35e édition disputée aux Bermudes. Grant Dalton, patron du défi néo-zélandais, annonce que le nouveau Challenger of Records est Circolo della Vela Sicilia (en) avec Luna Rossa.
L'America's Cup (Coppa America in italiano) è il più famoso trofeo nello sport della vela, nonché il più antico trofeo sportivo del mondo per cui si compete tuttora.
Si tratta di una serie di regate di match race, ovvero tra soli due yacht che gareggiano uno contro l'altro. Le due imbarcazioni appartengono a due Yacht Club differenti, una rappresentante lo yacht club che detiene la coppa e l'altra uno yacht club sfidante.
Nelle edizioni 1995, 2000, 2003 e 2007, la coppa, una brocca d'argento, è stata assegnata al vincitore di un incontro al meglio di nove regate. L'edizione 2010 della competizione è stata vinta dall'imbarcazione statunitense BMW Oracle Racing che ha avuto la meglio sul defender svizzero Alinghi con un risultato di 2-0. Oracle ha mantenuto la Coppa anche durante l'edizione 2013, battendo Emirates Team New Zealand 9-8. Nell'edizione numero 35, svoltasi nel 2017 nelle Isole Bermuda, Emirates Team New Zealand si aggiudica il trofeo sconfiggendo 7-1 il defender Oracle Team USA[1].
La Copa América (America's Cup en inglés y oficialmente) de vela es la competición más importante de ese deporte y algunas fuentes sostienen que es el tercer evento deportivo con mayor impacto económico para el país de acogida después de los Juegos Olímpicos y el Mundial de fútbol.1234
El actual defensor es el Real Escuadrón de Yates de Nueva Zelanda, que venció al Club de Yates Golden Gate en la última edición, celebrada en Hamilton (Bermudas).
El Challenger of Record para la próxima edición es el Círculo de Vela Sicilia.5
Кубок «Америки» (англ. America's Cup) — одна из самых известных и самых престижных регат в мире. Является старейшим в мире международным соревнованием во всех видах спорта, будучи основанным на два десятилетия ранее Кубка Англии по футболу и на 45 лет раньше первых современных Олимпийских игр.
Кубок Америки получил своё название в честь яхты «Америка» , которая выиграла его в престижной английской регате в 1851 году. Трофей остался в Нью-Йоркском яхт-клубе.
Кубок был изготовлен в 1848 году компанией «Гаррард и Ко». Он представляет собой кувшин без дна, на котором выгравированы названия всех яхт — обладателей кубка. По легенде, дно в кубке отсутствует по желанию английской королевы Виктории, не желавшей, чтобы из него пили[1]. Материал кубка — это так называемый британский металл — сплав олова, меди и сурьмы, покрытый серебром. В 1958 и 2003 годах кубок был дополнен основаниями, для размещения названий очередных победителей. В 1997 году вандал, проникший в здание Новозеландского яхт-клуба, изуродовал Кубок кувалдой. Кубок был бесплатно восстановлен английскими мастерами.
Кубок разыгрывается в серии матчевых гонок между представителем страны, победившим в прошлом цикле, и претендентом. Претендентом является победитель предварительных отборочных соревнований. В настоящее время отборочными соревнованиями служит Кубок Луи Виттона. Место поединка выбирает обладатель кубка.

 America´s Cup 2017
America´s Cup 2017
 Kungliga Svenska Segelsällskapet
Kungliga Svenska Segelsällskapet
 Artemis Racing
Artemis Racing

 Ships and Nautics
Ships and Nautics
 Sweden
Sweden

 Sport
Sport
 America´s Cup
America´s Cup


 Afghanistan
Afghanistan
 Armenia
Armenia
 Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan
 Asian Development Bank,ADB
Asian Development Bank,ADB
 Asian Development Bank,ADB
Asian Development Bank,ADB
 Kimimasa Tarumizu
Kimimasa Tarumizu
 Asian Development Bank,ADB
Asian Development Bank,ADB
 Haruhiko Kuroda
Haruhiko Kuroda
 Asian Development Bank,ADB
Asian Development Bank,ADB
 Masao Fujioka
Masao Fujioka
 Asian Development Bank,ADB
Asian Development Bank,ADB
 Masatsugu Asakawa
Masatsugu Asakawa
 Asian Development Bank,ADB
Asian Development Bank,ADB
 Mitsuo Sato
Mitsuo Sato
 Asian Development Bank,ADB
Asian Development Bank,ADB
 Shiro Inoue
Shiro Inoue
 Asian Development Bank,ADB
Asian Development Bank,ADB
 Tadao Chino
Tadao Chino
 Asian Development Bank,ADB
Asian Development Bank,ADB
 Takehiko Nakao
Takehiko Nakao
 Asian Development Bank,ADB
Asian Development Bank,ADB
 Takeshi Watanabe
Takeshi Watanabe
 Asian Development Bank,ADB
Asian Development Bank,ADB
 Taroichi Yoshida
Taroichi Yoshida
 Australia
Australia
 Bangladesh
Bangladesh
 Bhutan
Bhutan
 Brunei Darussalam
Brunei Darussalam
 China
China
 Denmark
Denmark
 Germany
Germany

 European Union
European Union

 Financial
Financial
 International Bank for Cooperation
International Bank for Cooperation
 Finland
Finland
 France
France
 Georgia
Georgia
 Hongkong Tebiexingzhengqu-HK
Hongkong Tebiexingzhengqu-HK
 India
India
 Indonesia
Indonesia
 Ireland
Ireland
 Italy
Italy
 Japan
Japan
 Cambodia
Cambodia
 Canada
Canada
 Kasachstan
Kasachstan
 Kyrgyzstan
Kyrgyzstan
 Laos
Laos
 Luxembourg
Luxembourg
 Malaysia
Malaysia

 Mongolei
Mongolei
 Myanmar
Myanmar
 Nepal
Nepal
 New Zealand
New Zealand
 Netherlands
Netherlands
 Austria
Austria
 Pakistan
Pakistan
 Papua-Neuguinea
Papua-Neuguinea
 Philippines
Philippines
 Portugal
Portugal
 Republic of Korea
Republic of Korea
 Salomonen
Salomonen
 Sweden
Sweden
 Singapore
Singapore
 Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka
 Taiwan Sheng-TW
Taiwan Sheng-TW
 Takehiko Nakao
Takehiko Nakao
 Thailand
Thailand
 Tonga
Tonga
 Turkey
Turkey
 Turkmenistan
Turkmenistan
 Uzbekistan
Uzbekistan
 United States
United States
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 Vietnam
Vietnam

 Important International Organizations
Important International Organizations

 Economy and trade
Economy and trade
 Economic and political research
Economic and political research


亚洲开发银行(英语:Asian Development Bank,缩写:ADB,简称亚银、亚行、亚开行),香港旧译亚洲发展银行,属于亚太地区的政府之间金融机构,其目的是为了促进亚洲经济与社会的发展。1966年12月19日成立,有31个创始会员国,目前有68个成员体,其中亚太有49个。总部设置于菲律宾马尼拉并在世界各地拥有31个办事处。亚洲开发银行仿照世界银行的股权制度,依照成员体的资本比例,得到相应比例的投票权。2014年以来,亚洲开发银行发布亚太创意生产指数年度报告。[3][4]亚洲开发银行为联合国观察员。
The Asian Development Bank (ADB) is a regional development bank established on 19 December 1966,[4] which is headquartered in the Ortigas Center located in the city of Mandaluyong, Metro Manila, Philippines. The company also maintains 31 field offices around the world[5] to promote social and economic development in Asia. The bank admits the members of the United Nations Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific (UNESCAP, formerly the Economic Commission for Asia and the Far East or ECAFE) and non-regional developed countries.[6] From 31 members at its establishment, ADB now has 68 members.
The ADB was modeled closely on the World Bank, and has a similar weighted voting system where votes are distributed in proportion with members' capital subscriptions. ADB releases an annual report that summarizes its operations, budget and other materials for review by the public.[7] The ADB-Japan Scholarship Program (ADB-JSP) enrolls about 300 students annually in academic institutions located in 10 countries within the Region. Upon completion of their study programs, scholars are expected to contribute to the economic and social development of their home countries.[8] ADB is an official United Nations Observer.[9]
El Banco Asiático de Desarrollo (BAsD) es una organización financiera para el desarrollo económico de Asia y el Pacífico. Su objetivo principal es la erradicación de la pobreza y facilitar ayudas para mejorar el nivel de vida de la población de la región a través de préstamos y colaboración técnica.
Creado en 1966 por 31 países. Hoy cuenta con 67 miembros (48 regionales y 19 no regionales). Estados Unidos y Japón son sus principales accionistas, con el 15,6% del capital cada uno.
El Banco tiene como su principal objetivo la lucha contra la pobreza. Para ello busca promover el crecimiento económico y la cooperación en la región de Asia-Pacífico, y acelerar el proceso de desarrollo económico de sus países miembros. Las dos terceras partes de personas pobres del mundo (aquellos que viven con menos de dos dólares diarios por persona), cerca de 1.800 millones de pobres, viven en esta región. El BAsD aprobó una nueva Estrategia a Largo Plazo (2008-2020) centrada en un crecimiento económico, medioambientalmente sostenible e integración regional.
Азиа́тский банк разви́тия (англ. Asian Development Bank) — банк, основанный в 1966 году, его главной задачей является стимулировать рост экономики в Азии и на Дальнем Востоке, направляя в эти регионы прямые займы и оказывая техническое содействие.
Штаб-квартира в Маниле (Филиппины). Президентом АБР с 28 апреля 2013 года является японец Такэхико Накао. 17 января 2020 года президентом станет Масацугу Асакава, избранный 2 декабря 2019 года[1].

 Afghanistan
Afghanistan
 Egypt
Egypt
 Armenia
Armenia
 Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan
 Ethiopia
Ethiopia
 Australia
Australia
 Bangladesh
Bangladesh
 Beijing Shi-BJ
Beijing Shi-BJ
 Brunei Darussalam
Brunei Darussalam
 China
China
 Denmark
Denmark
 Demokratische Republik Timor-Leste
Demokratische Republik Timor-Leste
 Germany
Germany
 Fidschi
Fidschi

 Financial
Financial
 International Bank for Cooperation
International Bank for Cooperation
 Finland
Finland
 France
France
 Georgia
Georgia
 Hongkong Tebiexingzhengqu-HK
Hongkong Tebiexingzhengqu-HK
 India
India
 Indonesia
Indonesia
 Iran
Iran
 Ireland
Ireland
 Iceland
Iceland
 Israel
Israel
 Italy
Italy
 Jordan
Jordan
 Cambodia
Cambodia
 Kasachstan
Kasachstan
 Katar
Katar
 Kyrgyzstan
Kyrgyzstan
 Laos
Laos
 Luxembourg
Luxembourg
 Malaysia
Malaysia
 Malediven
Malediven
 Malta
Malta

 Mongolei
Mongolei
 Myanmar
Myanmar
 Nepal
Nepal
 New Zealand
New Zealand
 Netherlands
Netherlands
 Norwegen
Norwegen
 Oman
Oman
 Austria
Austria
 Pakistan
Pakistan
 Philippines
Philippines
 Poland
Poland
 Portugal
Portugal
 Republic of Korea
Republic of Korea
 Russia
Russia
 Samoa
Samoa
 Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia
 Sweden
Sweden
 Switzerland
Switzerland
 Singapore
Singapore
 Spain
Spain
 Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka
 South Africa
South Africa
 Tajikistan
Tajikistan
 Thailand
Thailand
 Turkey
Turkey
 Hungary
Hungary
 Uzbekistan
Uzbekistan
 United Arab Emirates
United Arab Emirates
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 Vietnam
Vietnam

 Important International Organizations
Important International Organizations

 Economy and trade
Economy and trade
 Economic and political research
Economic and political research
 Cyprus
Cyprus

亚洲基础设施投资银行(英语:Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank,縮寫:AIIB),简称亚投行,是一个愿意向亚洲国家和地區的基础设施建设提供资金支持的政府间性质的亚洲区域多边开发机构,成立的目的是促进亚洲区域的互联互通建设和经济一体化的进程,並且加大中國與其他亚洲國家和地区的合作力度。总部设在中国北京,法定资本为1,000亿美元。[2]
中华人民共和国主席习近平于2013年10月2日在雅加达同印度尼西亚总统苏西洛举行会谈时首次倡议筹建亚投行。[3]2014年10月24日,中国、印度、新加坡等21国在北京正式签署《筹建亚投行备忘录》。[2]2014年11月25日,印度尼西亚签署备忘录,成为亚投行第22个意向创始成员国。[4]
2015年3月12日,英国正式申请作为意向创始成员国加入亚投行,[5]成为正式申请加入亚投行的首个欧洲国家、主要西方国家。[6]随后法国、意大利、德国等西方国家纷纷以意向创始成员国身份申请加入亚投行。[7]接收新意向创始成员国申请截止日期3月31日临近,韩国[8]、俄罗斯[9]、巴西[10]等域内国家和重要新兴经济体也抓紧申请成为亚投行意向创始成员国。
各方商定将于2015年年中完成亚投行章程谈判并签署,年底前完成章程生效程序,正式成立亚投行。[11]
Die Asiatische Infrastrukturinvestmentbank (亞洲基礎設施投資銀行 / 亚洲基础设施投资银行, kurz: 亞投行 / 亚投行, englisch Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank, AIIB) ist eine multilaterale Entwicklungsbank, die 2014 von verschiedenen Staaten gegründet wurde und im Wettbewerb zur Weltbank, zum Internationalen Währungsfonds und zur Asiatischen Entwicklungsbank steht.
Anlass zur Initiative der Gründung war insbesondere die Unzufriedenheit Chinas über eine Dominanz der US-Amerikaner im Internationalen Währungsfonds, der keine faire Verteilung der globalen Machtverhältnisse aus Sicht Chinas widerspiegelte.[2] Da sich die US-Amerikaner strikt weigerten, eine Änderung der Stimmverhältnisse zu implementieren, begann China 2013 mit der Gründung der Initiative. Neben den 21 Gründungsmitgliedern haben im Jahr 2015 auch unter anderem Deutschland, Italien, Frankreich und das Vereinigte Königreich ihr Interesse bekundet, als nicht-regionale Mitglieder die neue Entwicklungsbank zu unterstützen.[3]
Die Gründungsurkunde der AIIB wurde am 29. Juni 2015 von Vertretern aus 57 Ländern in Peking unterzeichnet.[4] Die Bank nahm im Januar 2016 ihre Arbeit ohne Beteiligung der USA und Japan auf.[5]
Joachim von Amsberg ist der "Vizepräsident für Politik und Strategie".
アジアインフラ投資銀行(アジアインフラとうしぎんこう、英: Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank, AIIB、中: 亚洲基础设施投资银行,亞洲基礎設施投資銀行)は、国際開発金融機関のひとつである。
中華人民共和国が2013年秋に提唱し主導する形で発足した[1]。「合計の出資比率が50%以上となる10以上の国が国内手続きを終える」としていた設立協定が発効条件を満たし、2015年12月25日に発足し[2][3]、2016年1月16日に開業式典を行った[1][4]。
57か国を創設メンバーとして発足し[1][5]、2017年3月23日に加盟国は70カ国・地域となってアジア開発銀行の67カ国・地域を超え[6][7]、一方で日本、アメリカ合衆国などは2017年の現時点で参加を見送っている[8]。 創設時の資本金は1000億ドルである[9]。
The Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank (AIIB) is a multilateral development bank that aims to support the building of infrastructure in the Asia-Pacific region. The bank currently has 93 members from around the world [7]. The bank started operation after the agreement entered into force on 25 December 2015, after ratifications were received from 10 member states holding a total number of 50% of the initial subscriptions of the Authorized Capital Stock.[8]
The United Nations has addressed the launch of AIIB as having potential for "scaling up financing for sustainable development"[9] and to improve the global economic governance.[10] The starting capital of the bank was $100 billion, equivalent to 2⁄3 of the capital of the Asian Development Bank and about half that of the World Bank.[11]
The bank was proposed by China in 2013[12] and the initiative was launched at a ceremony in Beijing in October 2014.[13] It received the highest credit ratings from the three biggest rating agencies in the world, and is seen as a potential rival to the World Bank and IMF.[14][15]
La Banque asiatique d'investissement dans les infrastructures (BAII ou AIIB), est une banque d'investissement proposée par la République populaire de Chine dans le but de concurrencer le Fonds monétaire international, la Banque mondiale et la Banque asiatique de développement1 pour répondre au besoin croissant d'infrastructures en Asie du Sud-Est et en Asie centrale. Cette banque s'inscrit dans la stratégie de la nouvelle route de la soie, développée par la Chine.
La Banca Asiatica d'Investimento per le infrastrutture (AIIB), fondata a Pechino nell'ottobre 2014, è un'istituzione finanziaria internazionale proposta dalla Repubblica Popolare Cinese. Si contrappone al Fondo Monetario Internazionale, alla Banca Mondiale e all'Asian Development Bank[1], le quali si trovano sotto il controllo del capitale e delle scelte strategiche dei paesi sviluppati come gli Stati Uniti d'America.[2] Scopo della Banca è fornire e sviluppare progetti di infrastrutture nella regione Asia-Pacifico attraverso la promozione dello sviluppo economico-sociale della regione e contribuendo alla crescita mondiale.
El Banco Asiático de Inversión en Infraestructura (Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank o AIIB) es una institución financiera internacional propuesta por el gobierno de China. El propósito de este banco de desarrollo multilateral es proporcionar la financiación para proyectos de infraestructura en la región de Asia basado en un sistema financiero de préstamo1 y el fomento del sistema de libre mercado en los países asiáticos.
El AIIB está considerado por algunos como una versión continental del FMI y del Banco Mundial, y busca ser un rival por la influencia en la región del Banco de Desarrollo asiático (ADB), el cual esta alineado a los intereses de potencias, tanto regionales (Japón), como globales (Estados Unidos, la Unión Europea).2
El banco fue propuesto por Xi Jinping en 2013 e inaugurado con una ceremonia en Pekín en octubre de 2014. La ONU se a mostrado entusiasta con la propuesta china, a la que a descrito como el FMI del futuro y a señalado como "una gran propuesta para financiar el desarrollo sostenible" y "mejorar la gobernanza económica mundial". La entidad constó inicialmente con 100 mil millones de dolares, es decir, la mitad del dinero de que posee el Banco Mundial.
La entidad a recibido inversión por parte de corporaciones financieras estadounidenses como la Standard & Poor's, Moody's o Fitch Group34. Actualmente la entidad consta de 87 miembros, incluyendo los 57 miembros fundadores. Bélgica, Canadá, y Ucrania están barajando unirse al AIIB. Estados Unidos, Japón y Colombia no tienen intención de participar. China a prohibido a Corea del Norte unirse, instigando además una política de aislamiento contra esta por parte del AIIB.
Азиатский банк инфраструктурных инвестиций (АБИИ) (англ. Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank, AIIB) — международная финансовая организация, создание которой было предложено Китаем. Основные цели, которые преследует АБИИ, — стимулирование финансового сотрудничества в Азиатско-Тихоокеанском регионе, финансирование инфраструктурных проектов в Азии от строительства дорог и аэропортов до антенн связи и жилья экономкласса[1].
По заявлениям вице-премьера России Игоря Шувалова, AБИИ не рассматривается как потенциальный конкурент МВФ, Всемирного банка и Азиатского банка развития (АБР). Однако эксперты рассматривают AIIB как потенциального конкурента базирующихся в США Международного валютного фонда (МВФ) и Всемирного банка. После сообщений об успехах AIIB американский министр финансов США Джейкоб Лью предупредил, что международным финансовым организациям в США, таким как ВБ и МВФ, грозит потеря доверия [2][3].
Китай, Индия и Россия возглавили организацию, оказавшись в тройке крупнейших владельцев голосов. При этом на важнейшие решения КНР имеет фактическое право вето[4].

 Music charts
Music charts
 Music
Music
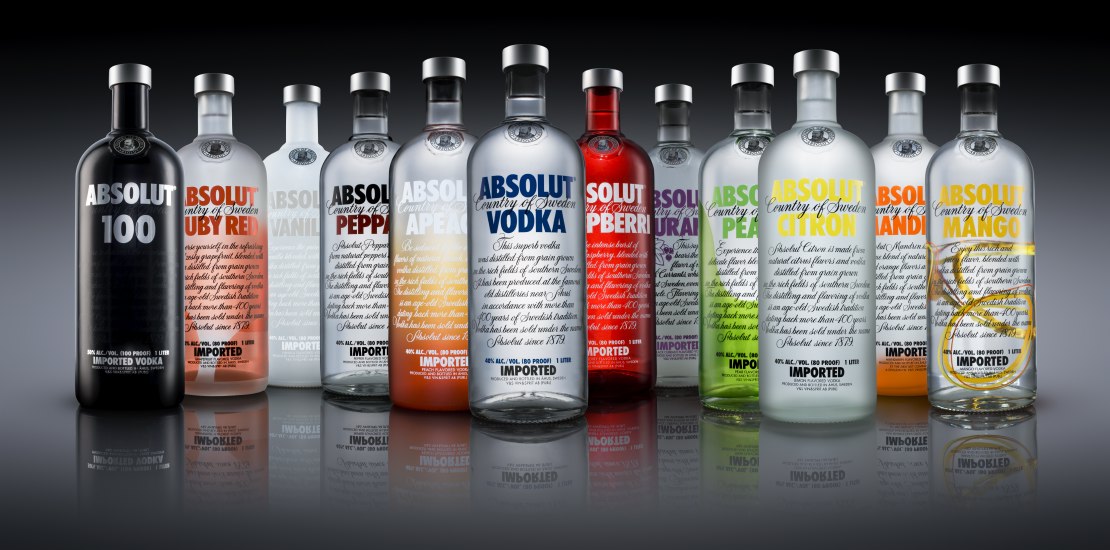
 Eat and Drink
Eat and Drink
 Companies
Companies
 Medical, Pharmaceutical, Rehabilitation
Medical, Pharmaceutical, Rehabilitation
 Geography
Geography