
漢德百科全書 | 汉德百科全书
 Lazio
Lazio



La Chiesa cattolica (dal latino ecclesiastico catholicus, a sua volta dal greco antico καθολικός, katholikòs, cioè "universale"[2]) è la Chiesa cristiana che riconosce il primato di autorità al vescovo di Roma, in quanto successore dell'apostolo Pietro sulla cattedra di Roma. I suoi fedeli vengono chiamati cristiani cattolici.
È formata da 24 Chiese sui iuris, la Chiesa latina in Occidente e 23 Chiese di rito orientale[3][4], che sono in comunione con il Pontefice.
Il nome richiama l'universalità della Chiesa fondata a partire dalla predicazione di Gesù Cristo e dei suoi Apostoli, costituita dal "Popolo di Dio" a sua volta formato da "tutte le nazioni della terra"[5], la quale viene dichiarata sussistere in modo perfetto nella Chiesa cattolica visibilmente organizzata, e nella comunione dei battezzati (non macchiati dai peccati di eresia o di apostasia) senza tuttavia negare, almeno a partire dal Concilio Ecumenico Vaticano II, la presenza di elementi di santificazione e di verità nelle altre Chiese cristiane separate da essa con le quali ritiene invece di dover perseguire un'azione ecumenica[6] e il riconoscimento di valori spirituali presenti nelle altre religioni[7].
La formula latina subsistit in, impiegata dalla Lumen gentium, fu oggetto di molteplici interpretazioni e successivamente chiarita nel suo significato autentico dal dialogo fra la Conferenza episcopale spagnola e la Congregazione per la dottrina della fede[8][9] [10], e nella dichiarazione Dominus Iesus.[11] Tra le Chiese cristiane, secondo le statistiche, al 2007 contava il maggior numero di fedeli a livello mondiale, circa 1,2 miliardi, con un'alta percentuale in Europa e nelle Americhe.[12]
La Iglesia católicanota 1 (en latín: Ecclesia Catholica) es la Iglesia cristiana más numerosa.4 Está compuesta por 24 Iglesias sui iuris: la Iglesia latina y 23 Iglesias orientales,56 que se encuentran en completa comunión con el papa y que en conjunto reúnen a más de 1313 millones de fieles en el mundo.17
La Iglesia católica sostiene que en ella subsiste la única Iglesia fundada por Cristo,nota 2 encomendada por él al apóstol Pedro, a quien le confió su difusión y gobierno junto con los demás apóstoles.11 Por ello, se considera a sí misma como un «sacramento», un «signo e instrumento de la unión íntima con Dios y de la unidad de todo el género humano».12
La cabeza de la Iglesia católica es el obispo de Roma, el papa, considerado el sucesor del apóstol Pedro, quien según la tradición católica fue el primer papa. El papa actual, el número 266 en la historia de la Iglesia, es Francisco. La sede papal, conocida como la Santa Sede, ocupa un lugar preeminente entre las demás sedes episcopales y constituye el gobierno central de la Iglesia,13 por quien actúa y habla, y es reconocida a nivel internacional como una entidad soberana.14
A la Iglesia católica pertenecen todos los bautizados según sus ritos propios y que no hayan realizado un acto formal de apostasía.nota 3 Según los datos del Anuario Pontificio de 2019 referentes al año 2017, el número de bautizados miembros de la Iglesia es de 1313 millones, el 17,7 % de la población mundial.13 Se trata de una comunidad cristiana que se remonta a Jesús y a los doce apóstoles, por medio de una sucesión apostólica nunca interrumpida,16 también compartida con la Iglesia ortodoxa.nota 4
A lo largo de sus dos milenios de historia, la Iglesia católica ha influido en la filosofía occidental, la ciencia, el arte y la cultura. Entre sus enseñanzas se incluyen la difusión del Evangelio y la realización de obras de misericordia corporales y espirituales en atención a los enfermos, pobres y afligidos, como parte de su doctrina social. La Iglesia católica, de hecho, es la mayor proveedora no gubernamental de educación y servicios médicos del mundo.17
Католи́ческая церковь[4] (лат. Ecclesia Catholica), также известная в русском языке как Ри́мско-католи́ческая церковь (лат. Ecclesia Catholica Romana), — самая крупная христианская церковь в мире, насчитывающая более 1,25 миллиарда последователей[3]. Одна из старейших религиозных институций в мире, играла важную роль в истории западной цивилизации[5]. Отличается организационной централизацией и наибольшим числом приверженцев. Римско-католическая церковь, придерживающаяся западных литургических обрядов, вместе с двадцатью тремя восточнокатолическими церквями составляет единую католическую церковь, которая полагает себя церковью, обладающей всей полнотой средств спасения.
 Fabio Capello
Fabio Capello
 La Serie A
La Serie A
 La Serie A 2015/16
La Serie A 2015/16
 La Serie A 2016/17
La Serie A 2016/17
 La Serie A 2017/18
La Serie A 2017/18
 La Serie A 2018/19
La Serie A 2018/19

 Lazio
Lazio
 Luis Enrique
Luis Enrique

 Sport
Sport
 (F)UEFA Europa League
(F)UEFA Europa League
 Sven-Göran Eriksson
Sven-Göran Eriksson
 UEFA Champions League 2015/16
UEFA Champions League 2015/16
 UEFA Champions League 2017/18
UEFA Champions League 2017/18
 Group C
Group C
 UEFA Champions League 2018/19
UEFA Champions League 2018/19
 Group G
Group G
 UEFA Europa League 2019/20
UEFA Europa League 2019/20
 Group J
Group J








 Baden-Wuerttemberg
Baden-Wuerttemberg
 Germany
Germany

 Emilia-Romagna
Emilia-Romagna

 Hessen
Hessen
 Italy
Italy

 Lazio
Lazio

 Lombardia
Lombardia
 Netherlands
Netherlands

 North Rhine-Westphalia
North Rhine-Westphalia
 Switzerland
Switzerland
 Toscana
Toscana

 Umbria
Umbria

 Bavaria
Bavaria

 Calabria
Calabria
 Campania
Campania
 Denmark
Denmark
 Germany
Germany

 Emilia-Romagna
Emilia-Romagna
 Finland
Finland

 Hamburg
Hamburg

 Hessen
Hessen
 Italy
Italy

 Lazio
Lazio

 Lower Saxony
Lower Saxony
 Austria
Austria

 Schleswig-Holstein
Schleswig-Holstein
 Sweden
Sweden

 Sicilia
Sicilia

 Tyrol
Tyrol

 Toscana
Toscana

 Trentino-Alto Adige
Trentino-Alto Adige
 Veneto
Veneto

 Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes
Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes

 Baden-Wuerttemberg
Baden-Wuerttemberg
 Cataluña
Cataluña
 Germany
Germany
 England
England
 France
France

 Hamburg
Hamburg
 Italy
Italy

 Lazio
Lazio
 Spain
Spain
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom

Das Europäische Laboratorium für Molekularbiologie (englisch European Molecular Biology Laboratory, EMBL) wurde 1974 gegründet und wird inzwischen von 26 europäischen Staaten, Israel sowie dem assoziierten Mitgliedsstaat Australien und zwei Anwärtern (Prospect members) unterstützt.[1] Es gehört zu den bekanntesten biologischen Forschungslaboren der Welt.
Es ist ein Grundlagenforschungsinstitut, das sich über öffentliche Forschungsgelder der Mitgliedstaaten finanziert. Etwa 85 unabhängige Forschungsgruppen arbeiten am EMBL zu Themen des gesamten Spektrums der Molekularbiologie. Das Laboratorium ist in sechs Einheiten gegliedert: das Hauptlaboratorium in Heidelberg sowie Außenstellen in Hinxton (European Bioinformatics Institute) in Großbritannien, Grenoble in Frankreich, Hamburg, Monterotondo, Italien und Barcelona, Spanien.
Die Haupttätigkeiten sind: molekularbiologische Grundlagenforschung; die hochqualifizierte Ausbildung von Wissenschaftlern, Studenten und Gastforschern; Serviceleistungen für Wissenschaftler in den Mitgliedstaaten; Entwicklung neuer Instrumente und Methoden in den Biowissenschaften sowie aktiver Technologietransfer. Das internationale Doktorandenprogramm des EMBL umfasst rund 170 Studenten. Darüber hinaus ist das Laboratorium an einem aktiven Programm für Wissenschaft und Gesellschaft beteiligt.
Aus der Forschung am EMBL resultierten bedeutende wissenschaftliche Durchbrüche wie die erste systematische genetische Analyse der Embryonalentwicklung der Fruchtfliege, wofür die Forscher Christiane Nüsslein-Volhard und Eric Wieschaus im Jahr 1995 den Nobelpreis für Medizin bekamen. 2017 erhielt Jacques Dubochet für sein am EMBL entwickeltes und 1981 publiziertes Verfahren der Kryo-Elektronenmikroskopie den Chemie-Nobelpreis.
欧洲分子生物学实验室(英文:European Molecular Biology Laboratory, EMBL)创建于1974年,是一所非营利性的分子生物学研究机构,由27个会员国,2个潜在会员国,和1个准会员国的公共研究资金的支持[2]。欧洲分子生物学实验室现有约110个独立的研究和服务小组和团队,研究课题涵盖分子生物学的各个主要分支。EMBL的小组和团队列表可以在www

 History
History
 Religion
Religion
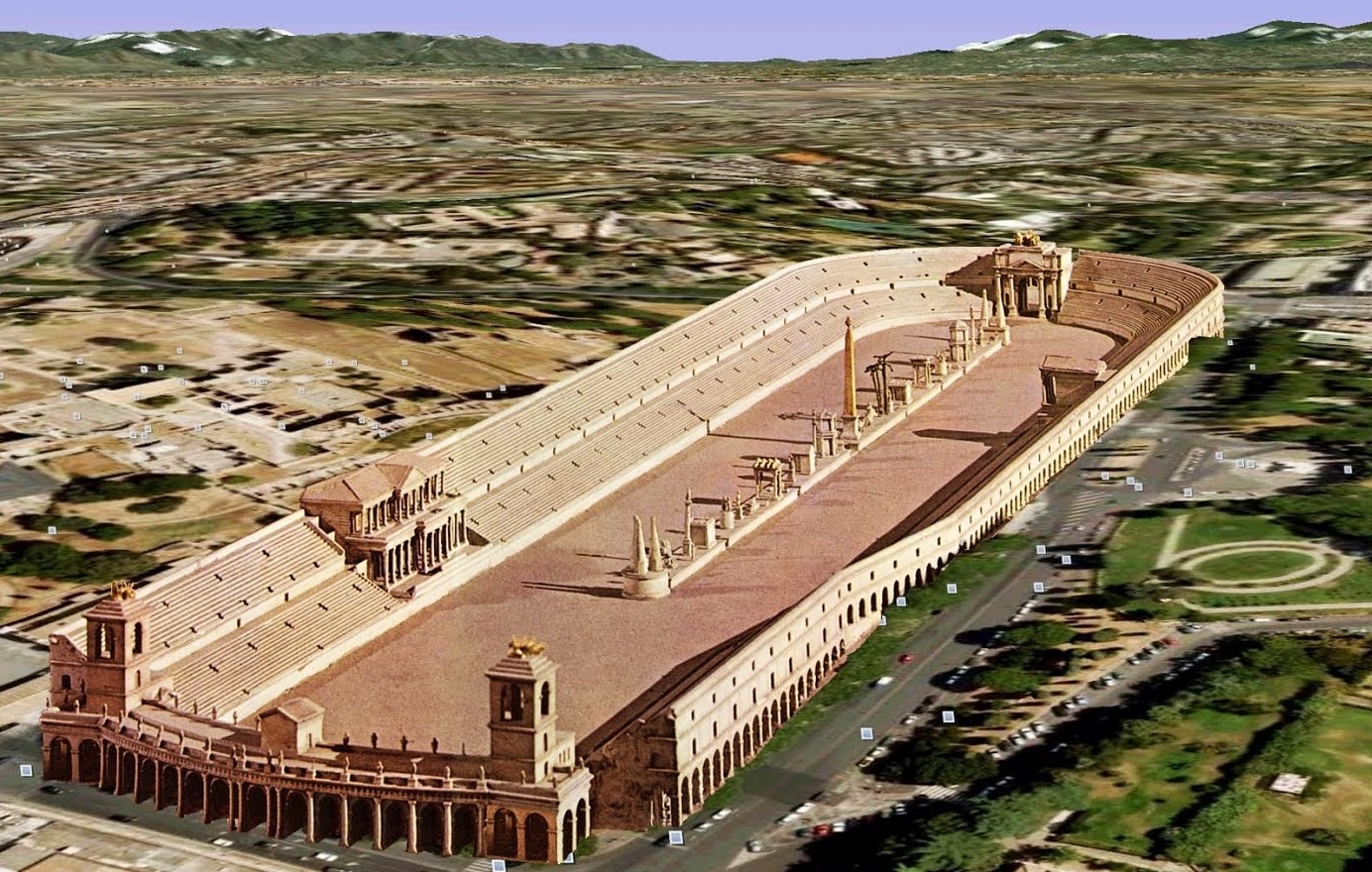
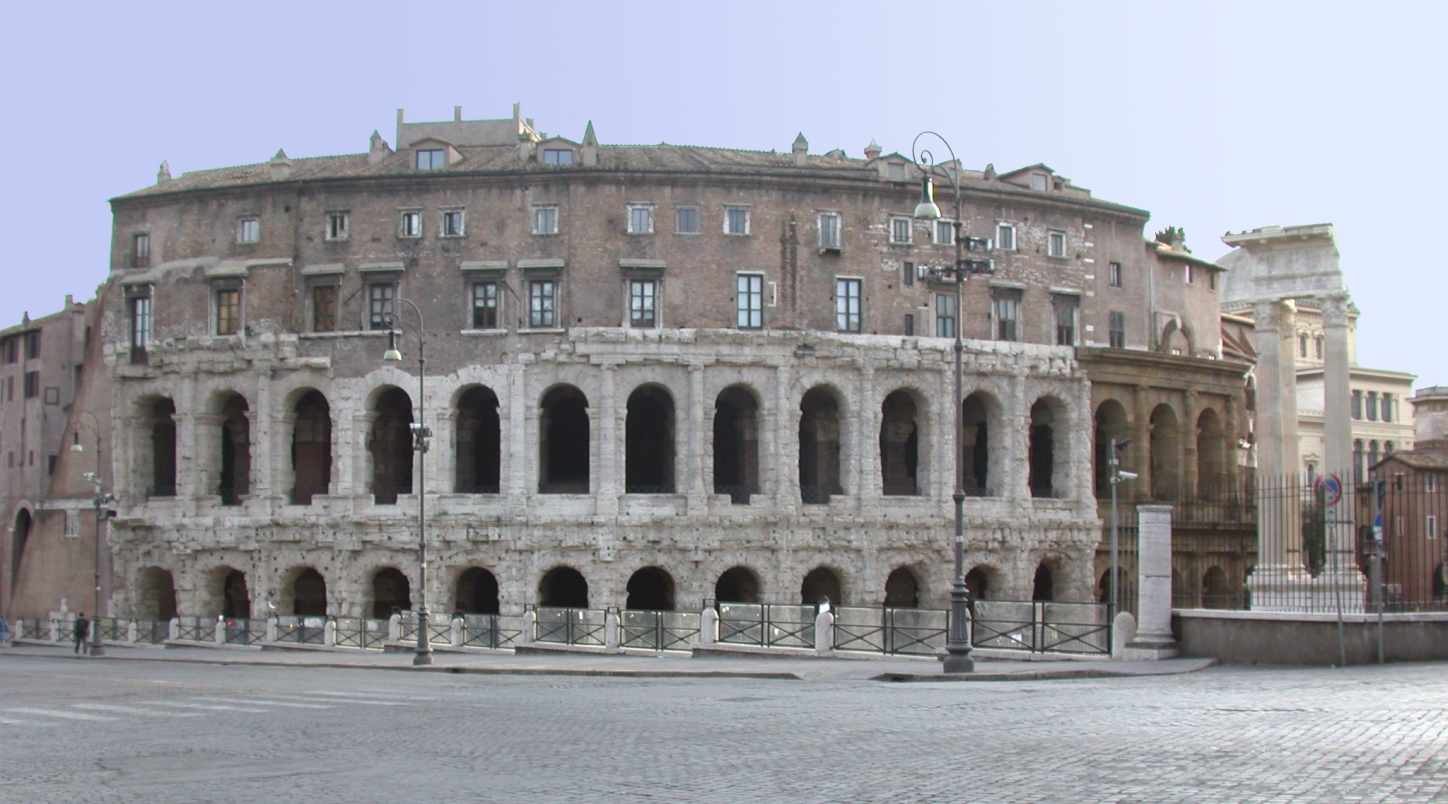
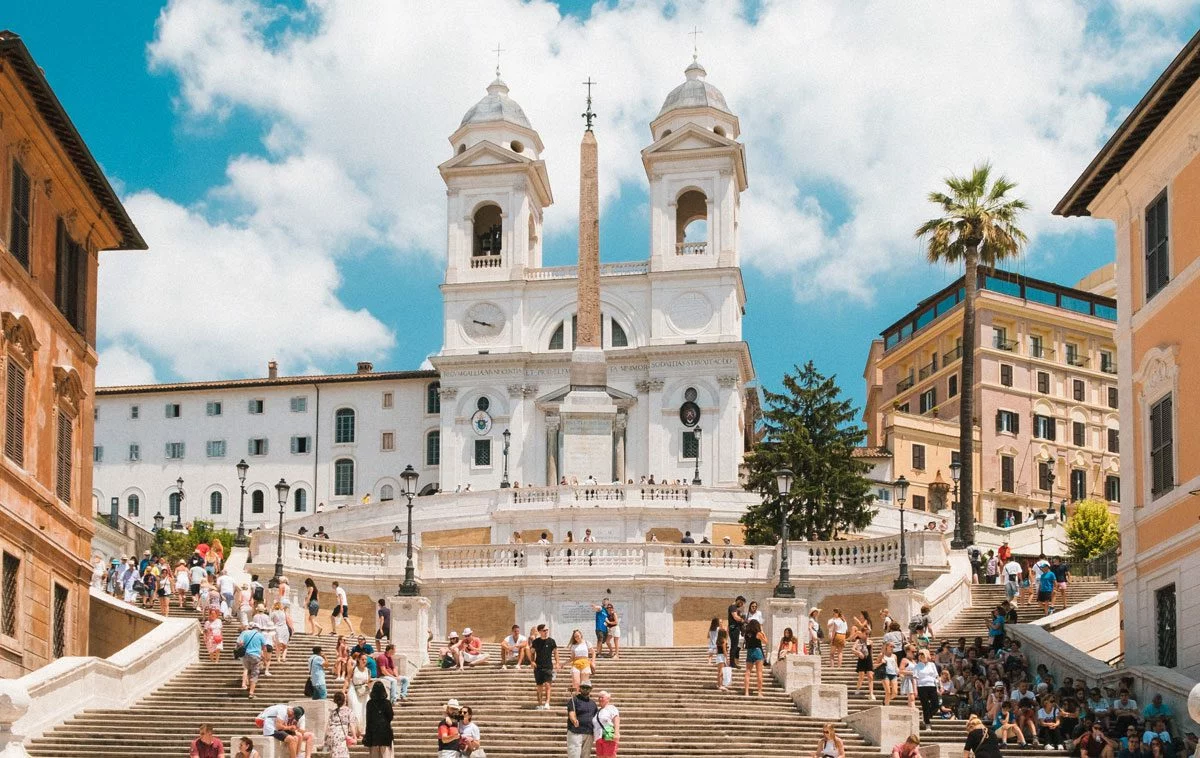
 Architecture
Architecture
 Art
Art
 Transport and traffic
Transport and traffic
 Science and technology
Science and technology


 Aerospace
Aerospace