
Deutsch-Chinesische Enzyklopädie, 德汉百科
 Virginia-VA
Virginia-VA


 Connecticut-CT
Connecticut-CT

 Florida-FL
Florida-FL

 Geography
Geography

 Georgia-GA
Georgia-GA

 Maine-ME
Maine-ME

 Maryland-MD
Maryland-MD

 Massachusetts-MA
Massachusetts-MA

 New hampshire-NH
New hampshire-NH

 New jersey-NJ
New jersey-NJ

 New York-NY
New York-NY

 North Carolina-NC
North Carolina-NC

 Pennsylvania-PA
Pennsylvania-PA

 Rhode Island-RI
Rhode Island-RI
 South Carolina-SC
South Carolina-SC
 United States
United States

 Virginia-VA
Virginia-VA
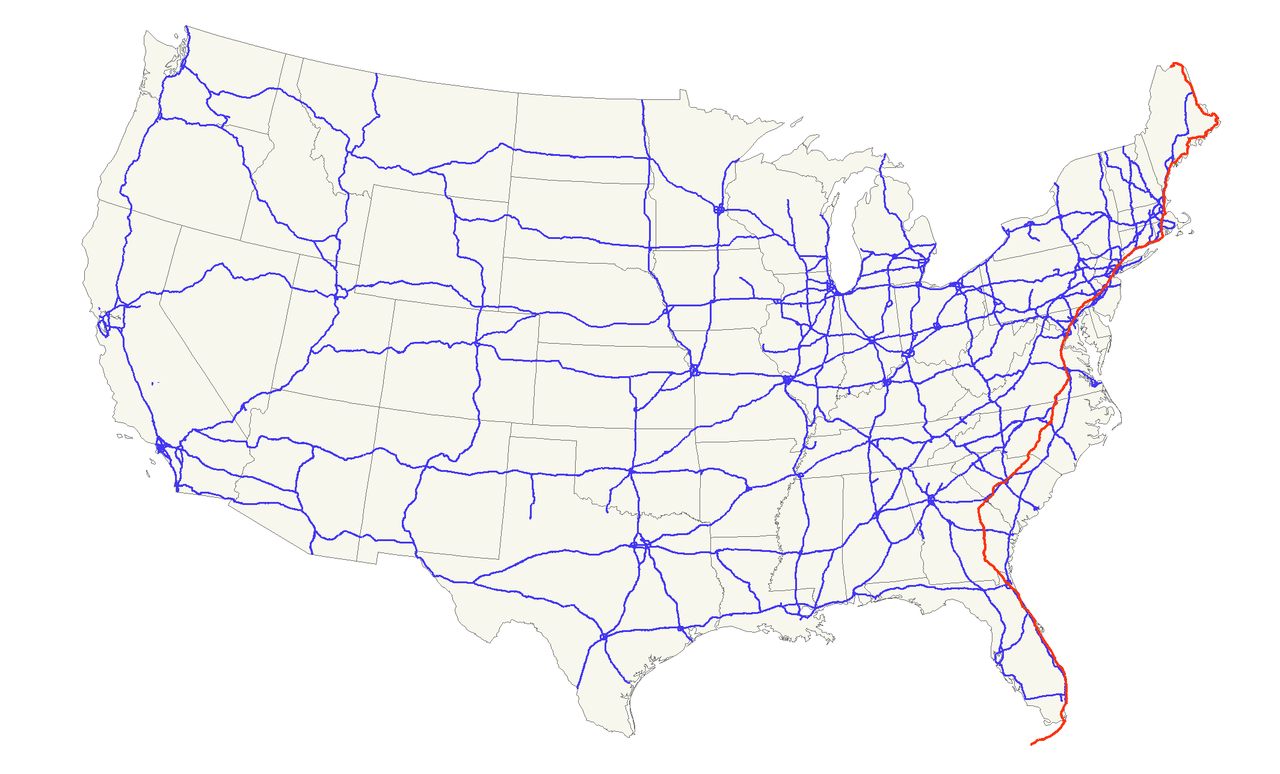
Der U.S. Highway 1 (auch U.S. Route 1 oder US 1) ist ein Highway, der parallel zur US-amerikanischen Ostküste verläuft. Die Gesamtlänge beträgt 3846 Kilometer. Im Norden endet der Highway in Fort Kent in Maine an der kanadischen Grenze. Im Süden ist es Key West an Floridas Küste zum Golf von Mexiko. Die US Route 1 verläuft an vielen Orten parallel zur Interstate 95. Festgelegt wurde sie 1926 zunächst nur zwischen der kanadischen Grenze und dem U.S. Highway 94 in Miami.
Die wichtigsten Städte, die der Highway passiert, sind Miami, Columbia, Richmond, Washington, D.C., Baltimore, Philadelphia, New York City, Boston und Portland.
Der Highway trägt die Nummer eins, weil er der am östlichsten gelegene ist und Nord-Süd-Highways von Ost nach West nummeriert werden.

 Alabama-AL
Alabama-AL

 Georgia-GA
Georgia-GA

 Louisiana-LA
Louisiana-LA

 Maryland-MD
Maryland-MD

 Mississippi-MS
Mississippi-MS

 New York-NY
New York-NY

 Pennsylvania-PA
Pennsylvania-PA

 Tennessee-TN
Tennessee-TN

 Virginia-VA
Virginia-VA

 West Virginia-WV
West Virginia-WV

 California-CA
California-CA

 Colorado-CO
Colorado-CO

 Geography
Geography

 Illinois-IL
Illinois-IL

 Indiana-IN
Indiana-IN

 Kansas-KS
Kansas-KS

 Maryland-MD
Maryland-MD

 Missouri-MO
Missouri-MO

 Nevada-NV
Nevada-NV

 Ohio-OH
Ohio-OH

 Utah-UT
Utah-UT
 United States
United States

 Virginia-VA
Virginia-VA

 Washington, D.C.
Washington, D.C.

 West Virginia-WV
West Virginia-WV
 Arizona-AZ
Arizona-AZ

 Illinois-IL
Illinois-IL

 Kentucky-KY
Kentucky-KY

 Missouri-MO
Missouri-MO
 New mexico-NM
New mexico-NM

 Oklahoma-OK
Oklahoma-OK

 Texas-TX
Texas-TX

 Virginia-VA
Virginia-VA

 West Virginia-WV
West Virginia-WV


 Alabama-AL
Alabama-AL

 Arizona-AZ
Arizona-AZ

 Arkansas-AR
Arkansas-AR

 California-CA
California-CA

 Colorado-CO
Colorado-CO

 Connecticut-CT
Connecticut-CT

 Energy resource
Energy resource

 Energy resource
Energy resource
 *Electrical power
*Electrical power

 Florida-FL
Florida-FL

 Georgia-GA
Georgia-GA

 Hawaii-HI
Hawaii-HI

 Idaho-ID
Idaho-ID

 Indiana-IN
Indiana-IN

 Iowa-IA
Iowa-IA

 Kentucky-KY
Kentucky-KY

 Louisiana-LA
Louisiana-LA

 Maine-ME
Maine-ME

 Maryland-MD
Maryland-MD

 Massachusetts-MA
Massachusetts-MA

 Michigan-MI
Michigan-MI

 Minnesota-MN
Minnesota-MN

 Montana-MT
Montana-MT

 New hampshire-NH
New hampshire-NH

 New jersey-NJ
New jersey-NJ

 New York-NY
New York-NY

 North Carolina-NC
North Carolina-NC

 Oklahoma-OK
Oklahoma-OK

 Oregon-OR
Oregon-OR

 Pennsylvania-PA
Pennsylvania-PA

 South Carolina-SC
South Carolina-SC

 Texas-TX
Texas-TX
 United States
United States

 Vermont-VT
Vermont-VT

 Virginia-VA
Virginia-VA

 Washington-WA
Washington-WA

 Wisconsin-WI
Wisconsin-WI

| Last Modified on November 21, 2022 *Capacity noted in (MW) |
| Plant | Location | Feedstock | Capacity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Agrilectric Power Partners Ltd. | LA | Rice hulls | 12.00 |
| Albany Green Energy | GA | Forest residue, urban wood waste, pecan shells, peanut hulls | 50.00 |
| Allendale Biomass | SC | Mill/forestry residue | 20.00 |
| Altavista Power Station | VA | Woody biomass | 51.00 |
| Arnold O. Chantland Incineration Plant | IA | MSW/Refused-derived fuel (RDF) | 4.00 |
| Barron County Waste-to-Energy & Recycling Facility | WI | MSW | 2.00 |
| Bay Front Power Plant | WI | Wood waste | 56.00 |
| Biomass One | OR | Logging/wood debris | 30.00 |
| Bridgewater Power LP | NH | Woody biomass | 20.00 |
| Buckeye Florida Biomass | FL | Wood waste, black liquor | 69.40 |
| Burgess BioPower | NH | Wood waste | 75.00 |
| Burney Forest Power | CA | Wood waste | 31.00 |
| Cadillac Renewable Energy | MI | Forest residue | 40.00 |
| City of Spokane Waste to Energy Facility | WA | MSW | 22.00 |
| Collins Pine Co. Power Plant | CA | Forest thinnings/residue | 12.00 |
| Covanta Alexandria | VA | MSW | 22.00 |
| Covanta Babylon | NY | MSW | 17.00 |
| Covanta Bristol | CT | MSW | 16.00 |
| Covanta Camden | NJ | MSW | 21.00 |
| Covanta Dade | FL | MSW, wood waste | 77.00 |
| Covanta Delaware Valley | PA | MSW | 87.00 |
| Covanta Essex | NJ | MSW | 66.00 |
| Covanta Fairfax | VA | MSW | 93.00 |
| Covanta Harrisburg | PA | MSW | 21.00 |
| Covanta Haverhill | MA | MSW | 45.00 |
| Covanta Hempstead | NY | MSW | 72.00 |
| Covanta Hillsborough | FL | MSW | 47.00 |
| Covanta Honolulu | HI | MSW | 90.00 |
| Covanta Huntington | NY | MSW | 24.00 |
| Covanta Indianapolis | IN | MSW | 6.50 |
| Covanta Kent | MI | MSW | 17.00 |
| Covanta Lake | FL | MSW | 15.00 |
| Covanta Lancaster | PA | MSW | 33.00 |
| Covanta Lee | FL | MSW | 57.00 |
| Covanta Long Beach | CA | MSW | 36.00 |
| Covanta MacArthur | NY | MSW | 12.00 |
| Covanta Marion | OR | MSW | 13.00 |
| Covanta Montgomery | MD | MSW | 63.00 |
| Covanta Niagara | NY | MSW | 50.00 |
| Covanta Onondaga | NY | MSW | 39.00 |
| Covanta Palm Beach Renewable Energy #1 | FL | MSW | 62.00 |
| Covanta Palm Beach Renewable Energy #2 | FL | MSW | 95.00 |
| Covanta Pasco | FL | MSW | 30.00 |
| Covanta Pinellas | FL | MSW | 75.00 |
| Covanta Plymouth | PA | MSW | 32.00 |
| Covanta SECONN | CT | MSW | 17.00 |
| Covanta SEMASS | MA | MSW | 78.00 |
| Covanta Stanislaus | CA | MSW | 22.00 |
| Covanta Tulsa | OK | MSW | 17.00 |
| Covanta Union | NJ | MSW | 42.00 |
| Covanta York | PA | MSW | 42.00 |
| Cox Waste-to-Energy | KY | Wood waste | 5.00 |
| Craven County Wood Energy | NC | Wood chips, forestry residue, mill waste, bark, sawdust, poultry litter | 50.00 |
| Deerhaven Renewable Generating Station | FL | Wood waste | 102.50 |
| Desert View Power | CA | Woody biomass | 45.00 |
| DG Fairhaven Power | CA | Wood waste | 18.00 |
| Dillard Complex Cogeneration Plant | OR | Mill residue | 51.50 |
| Dorchester Biomass | SC | Mill/forestry residue | 20.00 |
| Douglas County Forest Products | OR | Wood residue | 6.00 |
| DTE Stockton Biomass Power | CA | Woody biomass, ag residue | 45.00 |
| Eagle Valley Clean Energy | CO | Forest restoration thinnings/residue | 12.00 |
| Ecomaine Waste-to-Energy Plant | ME | MSW | 14.00 |
| Evergreen Biopower LLC | OR | Mill residue | 10.00 |
| Fernandina Biomass Plant | FL | Mill residuals | 22.50 |
| French Island Generating Station | WI | MSW/RDF, wood waste, railroad ties | 28.00 |
| Genesee Power Station | MI | Landscaping/storm debris, waste wood | 40.00 |
| Grayling Generating Station | MI | Forestry residue, mill waste, bark | 38.00 |
| Green Energy Team LLC | HI | Eucalyptus, albizia | 7.50 |
| GRP-Franklin LLC | GA | C&D waste | 65.00 |
| GRP-Madison LLC | GA | C&D waste | 65.00 |
| Halifax County Biomass Plant | VA | Logging waste, forest slash | 49.90 |
| Hennepin Energy Recovery Center | MN | MSW | 40.00 |
| Hillman Power LLC | MI | Wood waste | 20.00 |
| Honey Lake Power | CA | High-hazard forest material/thinnings | 30.00 |
| Hopewell Power Station | VA | Woody biomass | 51.00 |
| Joseph C McNeil Generating Station | VT | Logging residue, bark, shavings, clean urban wood waste | 50.00 |
| Kapstone Kraft Paper Corp.-Longview | WA | Mill residue, wood waste | 25.00 |
| Kettle Falls Generating Station | WA | Logging/mill residue | 53.00 |
| Koda Energy LLC | MN | Oat/rice hulls, corn, barley and malt screening, urban tree waste | 23.40 |
| L'Anse Warden Electric Company | MI | Wood waste, railroad ties | 20.00 |
| M.L. Hibbard Energy Center | MN | Wood waste | 72.80 |
| Macon Mill | GA | Logging waste | 38.00 |
| McKay Bay Refuse-to-Energy Plant | FL | MSW | 22.00 |
| McKinley Paper Cogeneration Facility | WA | Logging/mill residue | 9.50 |
| Merced Power | CA | Ag waste | 12.50 |
| MMWAC Resource Recovery Facility | ME | MSW | 5.00 |
| Mt. Poso Cogeneration Co. LLC | CA | Wood waste | 44.00 |
| Multitrade Rabun Gap | GA | Woody biomass | 18.00 |
| National Energy-Lincoln | MI | Wood waste | 18.00 |
| National Energy-McBain | MI | Wood waste | 18.00 |
| North Carolina Renewable Power | NC | C&D waste, wood waste, poultry litter | 22.00 |
| North Fork Community Power | CA | High-hazard forest material | 2.00 |
| Novo BioPower LLC | AZ | Wood waste | 27.00 |
| Okeelanta Biomass Cogeneration | FL | Baggasse, natural gas | 74.90 |
| Olmsted Waste-To-Energy Facility | MN | MSW | 9.60 |
| Oswego Energy Recovery Facility | NY | MSW | 4.00 |
| Pacific Ultrapower Chinese Station | CA | Woody biomass | 25.00 |
| Penobscot Energy Recovery | ME | MSW | 25.00 |
| Piedmont Green Power | GA | Urban wood waste, mill and logging residue | 55.00 |
| Plainfield Renewable Energy | CT | C&D/forestry waste | 37.50 |
| Plummer Cogen | ID | Wood waste | 6.20 |
| Potlatch Land & Lumber Power Plant | AR | Bark, sawdust, shavings | 10.00 |
| Rapids Energy Center | MN | Logging/mill residue | 28.60 |
| Red Wing Generating Station | MN | MSW/RDF | 22.00 |
| ReEnergy Black River | NY | Woody biomass | 60.00 |
| ReEnergy Livermore Falls | ME | Forest residue, C&D waste | 39.00 |
| ReEnergy Stratton | ME | Forest/mill residue | 48.00 |
| Resolute Forest Products Coosa Pines | AL | Wood-processing waste | 30.00 |
| Rio Bravo Fresno | CA | Ag/urban wood waste | 24.30 |
| Rio Bravo Rocklin | CA | High-hazard forest material, ag/urban waste | 24.40 |
| RockTenn-Tacoma Mill | WA | Mill residue | 55.00 |
| Roseburg Forest Products Biomass | CA | Wood waste | 13.00 |
| Rothschild Biomass Cogeneration Plant | WI | Urban wood waste, mill residue | 50.00 |
| Savannah River Site Biomass Cogeneration Facility | SC | Forest residue | 20.00 |
| Scotia Cogen | CA | Wood waste | 28.00 |
| SDS Lumber Gorge Energy Division | WA | Logging/mill residue | 10.00 |
| Shasta-Sustainable Resource Management | CA | Wood waste, forest residue | 56.00 |
| Southampton Power Station | VA | Woody biomass | 51.00 |
| Southern Co. Nacogdoches Generating Facility | TX | Forest/wood processing residue | 115.00 |
| SPI-Aberdeen Biomass Power | WA | Logging/mill residue | 18.00 |
| SPI-Anderson Biomass Power | CA | Logging/mill residue | 30.00 |
| SPI-Burlington Biomass Power | WA | Logging/mill residue | 28.00 |
| SPI-Burney | CA | Logging/mill residue | 20.00 |
| SPI-Eugene | OR | Mill, forest residue | 19.80 |
| SPI-Lincoln Biomass Power | CA | Logging/mill residue | 18.00 |
| SPI-Quincy Biomass Power | CA | Mill residue | 35.20 |
| SPI-Sonora Biomass Power | CA | Logging/mill residue | 10.90 |
| St. Paul Cogeneration LLC | MN | Urban wood residue | 33.00 |
| Stoltze Cogeneration Power Plant | MT | Mill residue | 3.00 |
| Stored Solar Bethlehem | NH | Logging residue, forest thinnings | 20.00 |
| Stored Solar Fitchburg | MA | Woody biomass | 17.00 |
| Stored Solar Jonesboro | ME | Woody biomass | 25.00 |
| Stored Solar Ryegate | VT | Woody biomass | 20.00 |
| Stored Solar Springfield | NH | Woody biomass | 19.00 |
| Stored Solar Tamworth | NH | Woody biomass | 20.00 |
| Stored Solar West Enfield | ME | Woody biomass | 25.00 |
| Stored Solar Whitefield | NH | Woody biomass | 15.00 |
| Telogia Power | FL | Logging/mill residue, hog fuel, peanut hulls | 14.00 |
| U.S. Sugar Corp. Cogeneration Plant | FL | Bagasse | 50.00 |
| Virginia City Hybrid Energy Center | VA | *Woody biomass | 120.00 |
| Wadham Energy LP | CA | Rice hulls | 30.00 |
| Westervelt Renewable Energy Moundville | AL | Wood waste | 13.00 |
| WestRock Covington | VA | Logging, papermaking residue | 75.00 |
| Wheelabrator Baltimore | MD | MSW | 64.50 |
| Wheelabrator Bridgeport | CT | MSW | 67.00 |
| Wheelabrator Concord | NH | MSW | 14.00 |
| Wheelabrator Dutchess County | NY | MSW | 9.00 |
| Wheelabrator Falls | PA | MSW | 53.00 |
| Wheelabrator Gloucester | NJ | MSW | 14.00 |
| Wheelabrator Hudson Falls | NY | MSW | 14.00 |
| Wheelabrator Lisbon | CT | MSW | 15.00 |
| Wheelabrator Millbury | MA | MSW | 48.00 |
| Wheelabrator North Andover | MA | MSW | 40.00 |
| Wheelabrator Portsmouth | VA | MSW | 60.00 |
| Wheelabrator Saugus | MA | MSW | 54.00 |
| Wheelabrator South Broward | FL | MSW | 66.00 |
| Wheelabrator Westchester LP | NY | MSW | 60.00 |
| Wilmarth Generating Station | MN | MSW/RDF, woody biomass | 18.00 |
| Woodland Biomass Power | CA | Wood chips, urban wood waste, ag waste | 25.00 |
| Total Plants: 159 | Total capacity(MW): | 5,583.90 |





弗吉尼亚州,正式名称为弗吉尼亚邦(英语:Commonwealth of Virginia),是美国东部的一个州,美国开国时十三州之一。
维珍尼亚州域范围位于北纬36°31'至39°37',西经75°13'至83°37'之间,其北部地区与美国政治中心华盛顿哥伦比亚特区相邻;东南部的诺福克市则有全世界最大的军港和海军基地。该州是美利坚合众国的发源地之一,人口稠密,经济发达。美国2012年人口估算显示,全州总人口818.6万,实现GDP总量3970亿美元[3]。
弗吉尼亚州是美国古老的一个州,以“老国土”为绰号,是8位美国总统的诞生地,号称“总统之母”。弗吉尼亚历史底蕴深厚,早在1607年英国人就在此设立“伦敦弗吉尼亚公司”;之后,大批的英国殖民者源源不断地涌来。由于殖民者的到来,包括波瓦坦部族在内的土著美洲人群则流离失所,这些人曾经和奴隶们一起在弗吉尼亚早期的政治生活和种植园经济中发挥了重要作用。弗吉尼亚是响应美国革命的13个殖民地之一。1792年肯塔基脱离弗吉尼亚成为一个新的联邦州。南北战争时弗吉尼亚加入了南方州联盟,并与主张反对蓄奴的西弗吉尼亚州分离,其首府里士满亦成为美利坚邦联国的首都。弗吉尼亚传统上属于保守的美国南部地区,但美国相互竞争的两大政党在此都很活跃,使其在美国政治生活中有着举足轻重的地位[4]。
蓝岭山脉和切萨皮克湾是弗吉尼亚州地理和气候的分界线,有许多动植物在这里栖息、繁殖。
弗吉尼亚州总人口近800万。里士满是本州的首府,弗吉尼亚比奇是全州人口最多的城市,联邦政府的部分行政机构设立在费尔法克斯县,是全州人口最为稠密的地区[5]。
弗吉尼亚州政府是美国立法机构之源,被多次评为全美最具效率的政府机关[6]。该州的行政手法独特,对待所有县市一视同仁,甚至在州域道路的管理上也能体现它独特的行政特色。州法律还规定州长不得连任。
圣纳度河谷等地区的农业颇为发达;设于该州北部的联邦机构(国防部和中央情报局等)和位于该地区最大的港口群——汉普顿锚地的军事设施也拉动了该地区的经济;此外,该州多所公立大专院校在媒体技术和电脑技术方面具有雄厚的实力,这使得电脑芯片制造业成为该州的支柱产业之一[7]。体育方面,弗吉尼亚没有专业体育赛事的举办权,但它是几个重要大学体育项目的所在地。
Virginia (engl. Aussprache [vɚˈd͡ʒɪnjə]), offiziell Commonwealth of Virginia, ist ein Bundesstaat der Vereinigten Staaten von Amerika, der Teile der südatlantischen Küstenebene, des Piedmont und der Südappalachen umfasst. Nach über 150 Jahren als englisch-britische Kolonie erlangte die Colony of Virginia zusammen mit zwölf anderen Kolonien die Unabhängigkeit. 1788 war Virginia der zehnte Staat, der die Verfassung der USA ratifizierte. Während des amerikanischen Bürgerkriegs spalteten sich die nordwestlichen Bezirke ab und wurden 1862 zum eigenständigen Bundesstaat West Virginia.
Der Beiname des Staates ist Old Dominion („Altes Herrschaftsgebiet“). Auch wird er Mother of the Presidents genannt, weil acht US-Präsidenten von hier stammten. Die Hauptstadt Virginias ist Richmond.
Virginia liegt an der Atlantikküste der Vereinigten Staaten etwa mittig zwischen der nördlichen (Maine) und südlichen (Florida) Ausdehnung der US-Küste. Von der Atlantischen Küstenebene entlang der Chesapeake Bay bis zu den Höhen der Blue Ridge Mountains in den Appalachen im Westen des Bundesstaats weist der Bundesstaat eine topografische Vielfalt auf. Die Südgrenze zu North Carolina und Tennessee ist eine fast gerade Ost-West-Linie, während die Nordgrenze zu Maryland und dem District of Columbia vom Potomac River gebildet wird. Kentucky und West Virginia sind auf der Westseite der Appalachen ebenfalls direkte Nachbarstaaten.
Virginia teilt sich mit dem Nachbarstaat Maryland jeweils knapp eine Hälfte des ausgedehnten städtischen Ballungsraumes um den Bundesdistrikt Washington, D.C. Dazu gehört neben dem Flughafen Dulles International auch Arlington County, in dem sich eine Vielzahl amerikanischer Bundesbehörden, darunter das Pentagon, befinden. Im westlichen Teil des Landes befindet sich der höchste Berg Virginias, der 1746 Meter hohe Mount Rogers. Ebenfalls in den Appalachen befindet sich der Shenandoah-Nationalpark.
バージニア州(英: Commonwealth of Virginia、略号: VA[2][3], Va.[2][3][4])は、アメリカ合衆国東部[3][5][6]、大西洋岸の南部に位置する州(コモンウェルス)である。2010年国勢調査による人口は8,001,024人だった。アメリカ合衆国50州の中で、陸地面積では第35位、人口では第12位である。ヴァージニア州とも表記される。
イギリスと独立戦争をした13州のうちの一つである[4][5]。南北戦争では南部連邦側に属し[5]、激戦地となった。
州都はリッチモンド市[3][4][5][6]、人口最大都市はバージニアビーチ市である[4]。 ジェームズタウン2007年は、ジェームズタウン植民地設立、すなわちバージニアの始まりから400周年を祝った催しだった。この行事では、バージニアの歴史を形作る際に少なからぬ役割を果たしたインディアン、ヨーロッパ人、アフリカ人の貢献に焦点を当てた[7][8]。これらの人々を巻き込む戦争も常に重要だった。フレンチ・インディアン戦争、アメリカ独立戦争、南北戦争から冷戦、テロとの戦いまで、バージニアが舞台になってきた[9] 。歴史上の人物、例えばポカホンタスとジョン・スミス、ジョージ・ワシントンの子供時代などの話や、南北戦争前の奴隷社会におけるプランテーション特権階級を取り巻く話も州の歴史に神話を作り、州のイデオロギーに理論的解釈を与えている[10]。
Virginia (/vərˈdʒɪniə/ (![]() listen)), officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a state in the Southeastern[4] and Mid-Atlantic[5] regions of the United States between the Atlantic Coast and the Appalachian Mountains. The geography and climate of the Commonwealth are shaped by the Blue Ridge Mountains and the Chesapeake Bay, which provide habitat for much of its flora and fauna. The capital of the Commonwealth is Richmond; Virginia Beach is the most-populous city, and Fairfax County is the most-populous political subdivision. The Commonwealth's estimated population as of 2019 is over 8.54 million.[6]
listen)), officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a state in the Southeastern[4] and Mid-Atlantic[5] regions of the United States between the Atlantic Coast and the Appalachian Mountains. The geography and climate of the Commonwealth are shaped by the Blue Ridge Mountains and the Chesapeake Bay, which provide habitat for much of its flora and fauna. The capital of the Commonwealth is Richmond; Virginia Beach is the most-populous city, and Fairfax County is the most-populous political subdivision. The Commonwealth's estimated population as of 2019 is over 8.54 million.[6]
The area's history begins with several indigenous groups, including the Powhatan. In 1607 the London Company established the Colony of Virginia as the first permanent English colony in the New World. Virginia's state nickname, the Old Dominion, is a reference to this status. Slave labor and the land acquired from displaced Native American tribes each played a significant role in the colony's early politics and plantation economy. Virginia was one of the 13 Colonies in the American Revolution. In the American Civil War, Virginia's Secession Convention resolved to join the Confederacy while the First Wheeling Convention resolved to remain in the Union, leading to a split that created West Virginia. Although the Commonwealth was under one-party rule for nearly a century following Reconstruction, both major national parties are competitive in modern Virginia.[7]
Virginia's state legislature is the Virginia General Assembly, which was established in 1619 and is the oldest continuous law-making body in North America. It is made up of a 40-member Senate and a 100-member House of Delegates.[8] The state government is unique in how it treats cities and counties equally, manages local roads, and prohibits governors from serving consecutive terms. Virginia's economy has many sectors: agriculture in the Shenandoah Valley; federal agencies in Northern Virginia, including the headquarters of the U.S. Department of Defense and Central Intelligence Agency; and military facilities in Hampton Roads, the site of the region's main seaport.
La Virginie, officiellement le Commonwealth de Virginie (en anglais : Virginia /vɚˈdʒɪn.iə/2 et Commonwealth of Virginia) est un État des États-Unis. Il s'agit de l'un des quatre États des États-Unis à porter le titre de Commonwealth. Historiquement rattaché au Sud des États-Unis, sa capitale actuelle est Richmond. Il est limitrophe, au nord, du Maryland et du district de Columbia, au sud, de la Caroline du Nord et du Tennessee, à l'ouest, du Kentucky et de la Virginie-Occidentale, et est bordée à l'est par la baie de Chesapeake et l'océan Atlantique.
Son nom vient de la reine Élisabeth Ire d'Angleterre (1533-1603), dite la « reine vierge » (Virgin Queen) parce qu'elle ne s'est jamais mariée. La colonie de Virginie, fondée le 14 mai 16073, est administrée par la compagnie de Londres jusqu'en 1624, puis devient une colonie royale. Elle établit sa prospérité sur les plantations et le commerce du tabac. Vers 1770, la Virginie est l'une des premières colonies à contester la tutelle britannique. Plusieurs Virginiens jouèrent un grand rôle dans la guerre d'indépendance, au premier rang desquels figure George Washington. Elle est connue comme « le Vieux Dominion » (The Old Dominion) ou encore comme la « mère des présidents » (Mother of Presidents), parce que huit présidents américains y sont nés.
Sur le plan politique, la Virginie, État confédéré durant la guerre de Sécession, se range dans les régions conservatrices du Sud, bien que l’État soit disputé entre les républicains et les démocrates4.
La Virginie se place au 35e rang des États américains pour sa superficie et au 12e rang pour sa population, avec plus de 8 millions d'habitants. La ville la plus peuplée est Virginia Beach. Le comté le plus peuplé est celui de Fairfax dans le nord et la ville la plus étendue est celle de Suffolk, qui comprend une grande partie du grand marais lugubre. La majorité de la population est d'origine européenne, en particulier du nord de l'Europe, mais plus d'un cinquième est constitué d'Afro-Américains. La première religion est le baptisme.
Aujourd'hui, l'économie virginienne est diversifiée. Elle repose notamment sur les emplois fédéraux et militaires dans le nord et à Hampton Roads, où se trouvent respectivement le plus grand bâtiment de bureaux du pays et, à Norfolk, la plus grande base navale du monde. Le « Triangle historique de la Virginie coloniale » (Historic Triangle of Colonial Virginia (en)) comprend Jamestown, Yorktown et Williamsburg, qui attirent des milliers de touristes. Le réseau urbain est connecté par le troisième plus grand réseau d’autoroutes du pays5.En 2019, sa population s'élève à 8 535 519 habitants6.
La Virginia, ufficialmente Commonwealth of Virginia, è uno Stato federato degli Stati Uniti d'America. Trae origine da una delle Tredici Colonie, che si ribellarono al dominio britannico e, dopo la guerra di indipendenza americana, fu uno degli Stati fondatori degli Stati Uniti d'America, nel 1776.
Viene generalmente considerato uno Stato del sud, ed è uno dei quattro Stati degli Stati Uniti ad utilizzare la denominazione Commonwealth. Deve il suo nome alla regina d'Inghilterra Elisabetta I, che non essendosi mai sposata era conosciuta come la "regina vergine"[3]. Colonia inglese dal 1607, fu amministrata da un Consiglio governativo con sede a Londra e da un Consiglio locale fino al 1788.
Fu la prima colonia inglese dell'America settentrionale. Infatti, nel 1606 la Compagnia di Londra, una associazione mercantile, ricevette dal re Giacomo I una concessione per la costituzione di insediamenti britannici nel continente. Il 13 maggio 1607 una spedizione britannica della Compagnia di Londra raggiunse la costa degli Stati Uniti, in quello che oggi è lo Stato della Virginia, con 104 uomini e tre navi (Susan Constant, Godspeed e Discovery) per costruire il primo insediamento stabile inglese nel Nuovo Mondo. La prima colonia che fondarono fu Jamestown, sul fiume James. I primi coloni erano per lo più proprietari terrieri o figli di agiati mercanti, tutti volevano arricchirsi maggiormente e velocemente.
Le condizioni climatiche e la scarsa lungimiranza negli approvvigionamenti mise a serio repentaglio la vita della colonia, tanto che nei primi tre anni di insediamento da 500 arrivarono a 60 superstiti, sopravvissuti grazie ai rifornimenti dalla madrepatria. Nel 1609 la Compagnia di Londra si diede un nuovo assetto nella Virgin Company. La colonia divenne nel 1776 uno dei tredici Stati originari degli Stati Uniti. Fra il Seicento e il Settecento furono adottate le strutture sociali dell'Inghilterra, vi erano dunque: grandi proprietari terrieri, che producevano tabacco e una fiorente agricoltura, clero anglicano, dotato di prestigio e potere; piccoli braccianti, piccoli proprietari ed affittuari terrieri. Venne soprannominata "il vecchio dominio" (The Old Dominion) dal re Carlo II per la sua apparente lealtà alla monarchia inglese durante la guerra civile inglese del XVII secolo.
Gli attuali Stati di Kentucky e Virginia Occidentale erano parte integrante della Virginia all'epoca della fondazione degli Stati Uniti (25 giugno 1788), ma il primo venne ammesso negli Stati Uniti come Stato autonomo nel 1792, mentre il secondo si separò dalla Virginia durante la guerra di secessione americana nel 1861 diventando così parte integrante dell'Unione.
Virginia, oficialmente Mancomunidad de Virginia (en inglés Commonwealth of Virginia), es uno de los cincuenta estados que, junto con Washington D. C., forman los Estados Unidos de América. Su capital es Richmond y su ciudad más poblada, Virginia Beach.
Está ubicado en la región Sur del país, división Atlántico Sur, limitando al noroeste con Virginia Occidental, al noreste con el río Potomac que lo separa de Maryland y Washington D. C., al sur con Carolina del Norte, al suroeste con Tennessee y al oeste con Kentucky. Fue admitido en la Unión el 25 de junio de 1788, como el estado número 10.
Recibe su nombre por la reina Isabel I de Inglaterra, quien, al no haber contraído nunca matrimonio, era conocida como «la reina virgen». El estado es conocido por el apodo de «Viejo Dominio» (Old Dominion) y a veces por el de «Madre de Presidentes», por ser el lugar de nacimiento de ocho presidentes estadounidenses (incluidos cuatro de los cinco primeros).
Las raíces de la Virginia moderna se remontan a la fundación de la Colonia de Virginia en 1607 por la Compañía de Virginia de Londres. La agricultura, el colonialismo y la esclavitud desempeñaron papeles significativos en su economía y su política durante los primeros tiempos. Fue la primera colonia inglesa en el Nuevo Mundo y una de las trece colonias que participarían en la Guerra de Independencia, y posteriormente se convirtió en el corazón de la Confederación en la Guerra Civil estadounidense.
La capital de la commonwealth es Richmond, mientras que Virginia Beach es la ciudad más populosa y el condado de Fairfax es la subdivisión política con mayor población. De acuerdo con el Censo de los Estados Unidos de 2010, la población del estado era de 8.001.024 habitantes.3 Aunque tradicionalmente conservadora e históricamente parte del Sur, la moderna Virginia es un estado políticamente competitivo para los dos principales partidos políticos nacionales.4
Virginia tiene una economía con varios asentamientos importantes, que incluyen El Pentágono del Departamento de Defensa y diversas agencias federales en el Norte del estado, bases militares en Hampton Roads, así como una producción agrícola significativa. El llamado «Triángulo Histórico» incluye los populares destinos turísticos de la historia estadounidense de Jamestown, Yorktown y el museo vivo de Colonial Williamsburg.5 El crecimiento del sector tecnológico ha hecho de los chips la principal exportación del estado, con la industria basada en la solidez de sus escuelas públicas y de sus universidades.6 Las áreas donde el estado necesita mejorar incluyen la asistencia sanitaria y la protección del medio ambiente.
Вирги́ния[1][2][3], также Вирджи́ния[2] (англ. Virginia, американское произношение: [vərˈdʒɪniə] (![]() слушать)), официально — Содру́жество Вирги́нии (англ. Commonwealth of Virginia) — штат[4] на востоке США, один из так называемых Южно-Атлантических штатов. В составе государства он является 10-м штатом. Население — 8.5 млн человек (2015; 12-е место в США).
слушать)), официально — Содру́жество Вирги́нии (англ. Commonwealth of Virginia) — штат[4] на востоке США, один из так называемых Южно-Атлантических штатов. В составе государства он является 10-м штатом. Население — 8.5 млн человек (2015; 12-е место в США).
Столица — Ричмонд, крупнейший город — Верджиния-Бич, другие крупные города — Александрия, Линчберг, Норфолк, Ньюпорт-Ньюс, Портсмут, Роанок, Хамптон, Чесапик. Административно Виргиния разделена на 95 округов и 38 «независимых городов»[en], которые не входят ни в один округ и являются полностью самостоятельными административно-территориальным единицами второго уровня[5][6].
Полное официальное название штата — Содружество Виргинии (Commonwealth of Virginia).
Официальные прозвища — «Старый доминион» (Old Dominion), «Мать президентов» (Mother of Presidents).
Официальный девиз — «Такова участь тиранов!» (лат. Sic semper tyrannis!).
В честь Виргинии назван астероид (50) Виргиния, открытый в 1857 году.
 Nobel prize
Nobel prize
 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine
Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine
 Nobel prize
Nobel prize
 Nobel Prize in Chemistry
Nobel Prize in Chemistry
 Nobel prize
Nobel prize
 University/Institute
University/Institute

 Universities in the USA
Universities in the USA



 Transport and traffic
Transport and traffic

 Motorsport
Motorsport
 Sport
Sport
 Music
Music



 Military, defense and equipment
Military, defense and equipment