Deutsch-Chinesische Enzyklopädie, 德汉百科
 Silk road
Silk road
 Atomic bomb
Atomic bomb
 BRICS summit
BRICS summit
 Commonwealth of Nations
Commonwealth of Nations

 History
History

 History
History
 M 1500 - 2000 AD
M 1500 - 2000 AD

 History
History

 History
History
 N 2000 - 2100 AD
N 2000 - 2100 AD
 History of India
History of India
 India
India




 Military, defense and equipment
Military, defense and equipment
 Nuclear Weapon
Nuclear Weapon

 Party and government
Party and government
 Group of the twenty most important industrial and emerging countries
Group of the twenty most important industrial and emerging countries

 Party and government
Party and government
 BRICS
BRICS
 Silk road
Silk road
 Shanghai Cooperation Organization
Shanghai Cooperation Organization

 States of Asia
States of Asia

印度共和国(印地语:भारत गणराज्य,Bhārat Ganarājya;英语:Republic of India),通称印度(印地语:भारत;英语:India),是位于南亚印度次大陆上的国家,印度面积位列世界第七,印度人口众多,位列世界第二,截至2018年1月印度拥有人口13.4亿,仅次于中国人口的13.8亿,人口成长速度比中国还快,预计近年将交叉。是亚洲第二大也是南亚最大的国家,面积328万平方公里(实际管辖),同时也是世界第三大(购买力平价/PPP)经济体。
印度并非单一民族及文化的国家。印度的民族和种族非常之多,有“民族大熔炉”之称,其中印度斯坦族占印度总人口的大约一半,是印度最大的民族。印度各个民族都拥有各自的语言,仅宪法承认的官方语言就有22种之多,其中印地语和英语被定为印度共和国的联邦官方语言[5],并且法院裁定印度没有国语。[9][10]英语作为共同语言使用在印度非常流行,尤其在南印地位甚至高于印地语,但受限于教育水准,普通民众普遍不精通英语。另外,印度也是一个多宗教多信仰的国家,世界4大宗教其中的佛教和印度教都源自印度。大部分印度人信仰印度教。伊斯兰教在印度也有大量信徒,是印度的第二大宗教,信教者约占印度的14.6%(截至2011年,共有约1亿7千7百万人)。伊斯兰教是在公元8世纪随着阿拉伯帝国的扩张而传播到印度的。公元10世纪后,北印的大多数王朝统治者都是信奉伊斯兰教的,特别是莫卧儿王朝。印度也是众多正式和非正式的多边国际组织的成员,包括世界贸易组织、英联邦、金砖五国、南亚区域合作联盟和不结盟运动等。
以耕种农业、城市手工业、服务业以及其支撑产业为主的部分行业已经相对取得了进展。除了民族文化与北方地形的丰富使印度旅游业颇受欢迎之外,由于时差,大批能说英语的人才也投入外包行业(即是外国企业把客户咨询,电话答录等等服务转移到印度)。另一方面,宝莱坞电影的文化输出在英语圈乃至全球的影响力不亚于世界主流。同时印度还是很多专利过期药物的生产地,以低价格提供可靠的医疗。近年来,印度政府还大力投资本国高等教育,以利于在科学上与国际接轨,例如自主太空研究、南亚半岛生态研究等等。印度最重要的贸易伙伴是美国、欧盟、日本、中国和阿拉伯联合酋长国。
Indien ist ein Staat in Südasien, der den größten Teil des indischen Subkontinents umfasst. Indien ist eine Bundesrepublik, die von 29 Bundesstaaten gebildet wird und außerdem sieben bundesunmittelbare Gebiete umfasst. Der Eigenname der Republik lautet in den beiden landesweit gültigen Amtssprachen Bharat Ganarajya (Hindi) und Republic of India (Englisch). Die moderne demokratische und säkulare indische Republik besteht seit 1949 und seit 1950 gilt die Verfassung Indiens.
Der Himalaya bildet die natürliche Nordgrenze Indiens, im Süden umschließt der Indische Ozean das Staatsgebiet. Indien grenzt an Pakistan, das chinesische Autonome Gebiet Tibet, Nepal, Bhutan, Myanmar (Birma) und Bangladesch. Weitere Nachbarstaaten im Indischen Ozean sind Sri Lanka und die Malediven. Hinsichtlich der Landesfläche ist Indien das flächenmäßig siebtgrößte Land der Erde.
Das Gebiet Indiens ist mindestens seit der bronzezeitlichen Indus-Hochkultur zivilisiert. Der indische Staat ist mit über 1,3 Milliarden Einwohnern (2016)[6] nach der Volksrepublik China (fast 1,4 Mrd.)[7] das zweitbevölkerungsreichste Land der Erde und somit die bevölkerungsreichste Demokratie der Welt.[8] Bei gleichbleibend hohem Bevölkerungswachstum könnte Indien schon im Jahr 2020 China überholen. Durch fortschreitende Modernisierung, Bildung, Wohlstand und Urbanisierung sinkt die Geburtenrate jedoch bereits. Hauptstadt Indiens ist Neu-Delhi, Teil der Metropole Delhi; weitere Ballungsräume sind auch Mumbai, Kalkutta, Chennai, Bangalore, Hyderabad, Ahmedabad und Pune.
Die indische Gesellschaft wird trotz verfassungsmäßiger Religionsfreiheit vom religiösen hierarchischen Kastensystem bestimmt. Die mit Abstand größte Religionsgruppe sind die Hindus, gefolgt von Muslimen, Christen und den historisch aus Indien stammenden Sikhs, Buddhisten und Jaina. Laut Index der menschlichen Entwicklung (HDI) erreicht Indien den Status „mittlere menschliche Entwicklung“ und Platz 131 von 187 weltweit (2016, im Vergleich erreicht die VR China Platz 90).[9] Wirtschaftlich gilt Indien als Schwellenland und gehört zu den O5- und BRICS-Staaten und der Gruppe der zwanzig wichtigsten Industrie- und Schwellenländer (G20). Indien ist trotz seines noch niedrigen Pro-Kopf-Einkommens bereits die drittgrößte bzw. sechstgrößte Wirtschaftsmacht der Welt (kaufkraftbereinigt bzw. nominell) und war 2015 erstmals die am schnellsten wachsende Volkswirtschaft der G20-Gruppe.
インドは、南アジアに位置し、インド洋の大半とインド亜大陸を領有する連邦共和制国家である。ヒンディー語の正式名称भारत गणराज्य(ラテン文字転写: Bhārat Gaṇarājya、バーラト・ガナラージヤ、英語: Republic of India)を日本語訳したインド共和国とも呼ばれる。
西から時計回りにパキスタン、中華人民共和国、ネパール、ブータン、バングラデシュ、ミャンマー、スリランカ、モルディブ、インドネシアに接しており、アラビア海とベンガル湾の二つの海湾に挟まれて、国内にガンジス川が流れている。首都はニューデリー、最大都市はムンバイ。
1947年にイギリスから独立。インダス文明に遡る古い歴史、世界第二位の人口を持つ。国花は蓮、国樹は印度菩提樹、国獣はベンガルトラ、国鳥はインドクジャク、国の遺産動物はインドゾウである。
インドは南アジア随一の面積と世界第2位の人口を持つ大国である。12億人を超える国民は、多様な民族、言語、宗教によって構成されている。連邦公用語はヒンディー語、他にインド憲法で公認されている言語が21あり主な言語だけで15を超えるため、インドの紙幣には17の言語が印刷されている。議会制民主主義国家であり、有権者数8億人と世界最大である[5]。州政府が一定の独立性を持っているため、各州に中央政府とは別に政府があり大臣がいる。
労働力人口の3分の2が農業に従事する一方、製造業とサービス業が急速に成長している。国民の識字率は74.04%である。ヒンドゥー教徒が最も多く、イスラム教、シーク教がこれに次ぐ。カースト制度による差別は憲法で禁止されているが、今でも農村部では影響は残っている。
アジア開発銀行はインドの中間層が向こう15年間で人口の7割に達するとしている[6]。
India (IAST: Bhārat), also known as the Republic of India (IAST: Bhārat Gaṇarājya),[18][e] is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh largest country by area and with more than 1.3 billion people, it is the second most populous country and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the south, the Arabian Sea on the southwest, and the Bay of Bengal on the southeast, it shares land borders with Pakistan to the west;[f] China, Nepal, and Bhutan to the northeast; and Bangladesh and Myanmar to the east. In the Indian Ocean, India is in the vicinity of Sri Lanka and the Maldives, while its Andaman and Nicobar Islands share a maritime border with Thailand and Indonesia.
The Indian subcontinent was home to the urban Indus Valley Civilisation of the 3rd millennium BCE. In the following millennium, the oldest scriptures associated with Hinduism began to be composed. Social stratification, based on caste, emerged in the first millennium BCE, and Buddhism and Jainism arose. Early political consolidations took place under the Maurya and Gupta empires; later peninsular Middle Kingdoms influenced cultures as far as Southeast Asia. In the medieval era, Judaism, Zoroastrianism, Christianity, and Islam arrived, and Sikhism emerged, all adding to the region's diverse culture. Much of the north fell to the Delhi Sultanate; the south was united under the Vijayanagara Empire. The economy expanded in the 17th century in the Mughal Empire. In the mid-18th century, the subcontinent came under British East India Company rule, and in the mid-19th under British crown rule. A nationalist movement emerged in the late 19th century, which later, under Mahatma Gandhi, was noted for nonviolent resistance and led to India's independence in 1947.
In 2017, the Indian economy was the world's sixth largest by nominal GDP[19] and third largest by purchasing power parity.[15] Following market-based economic reforms in 1991, India became one of the fastest-growing major economies and is considered a newly industrialised country. However, it continues to face the challenges of poverty, corruption, malnutrition, and inadequate public healthcare. A nuclear weapons state and regional power, it has the second largest standing army in the world and ranks fifth in military expenditure among nations. India is a federal republic governed under a parliamentary system and consists of 29 states and 7 union territories. A pluralistic, multilingual and multi-ethnic society, it is also home to a diversity of wildlife in a variety of protected habitats.
L'Inde, officiellement la république de l'Inde4, en hindi : भारत (Bhārat) et भारत गणराज्य (Bhārat Gaṇarājya), est un pays d'Asie du Sud qui occupe la majeure partie du sous-continent indien. Sa capitale est New Delhi. L'Inde est le deuxième pays le plus peuplé et le septième pays le plus grand du monde. Le littoral indien s'étend sur plus de sept mille kilomètres. Le pays a des frontières communes avec le Pakistan à l'ouest, la Chine, le Népal, et le Bhoutan au nord et au nord-est, le Bangladesh et la Birmanie à l'est. Sur l'océan Indien, l'Inde est à proximité des Maldives au sud-ouest, du Sri Lanka et de l'Indonésie au sud-est. L'Inde revendique également une frontière avec l'Afghanistan au nord-ouest. L'Inde dispose de l'arme nucléaire depuis 1974 après avoir fait des essais officiels.
L'Inde est un foyer de civilisations parmi les plus anciennes du monde, la civilisation de la vallée de l'Indus s'y est développée dès 3000 av. J.-C. Le sous-continent indien a abrité de vastes empires et est présent sur les routes commerciales dès l'Antiquité. L'Inde est la terre de naissance de quatre religions majeures — l'hindouisme, le jaïnisme, le bouddhisme et le sikhisme — alors que le zoroastrisme, le christianisme et l'islam s'y sont implantés durant le Ier millénaire. L'Inde est aujourd'hui un pays très divers sur le plan religieux, linguistique et culturel.
Le pays a été progressivement annexé par la Compagnie anglaise des Indes avant de passer sous le contrôle du Royaume-Uni au XIXe siècle. L'Inde devient indépendante en 1947 après une lutte marquée par la résistance non-violente du Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi. Le pays est depuis 1950 une république parlementaire fédérale considérée comme la démocratie la plus peuplée au monde.
En 2017, l'économie indienne est la sixième du monde en PIB nominal et la troisième en PIB à parité de pouvoir d'achat. L'Inde, pays à forte croissance économique, est considéré comme un nouveau pays industrialisé. Cependant certains problèmes comme la pauvreté, l'analphabétisme ou la corruption restent très importants.
L'India (hindi: भारत Bhārat), ufficialmente Repubblica dell'India (hindi: भारत गणराज्य Bhārat Gaṇarājya), è uno Stato federale dell'Asia meridionale, con capitale Nuova Delhi.
È il settimo Stato per estensione geografica al mondo (3 287 263 km²) e il secondo più popolato, con 1 335 250 000 abitanti (censimento 2017).[8] È bagnato dall'oceano Indiano a sud, dal mar Arabico a ovest e dal golfo del Bengala a est. Possiede una linea costiera che si snoda per 7.517 km.[9] Confina con il Pakistan a ovest,[10] Cina, Nepal e Bhutan a nord-est, Bangladesh e Birmania a est. Suoi vicini prossimi, separati dell'oceano Indiano, sono lo Sri Lanka a sud-est e le Maldive a sud-ovest.
Sede della civiltà della valle dell'Indo e regione di rotte commerciali storiche e di vasti imperi, il subcontinente indiano è stato identificato con il suo commercio e la ricchezza culturale per gran parte della sua lunga storia.[11] Quattro grandi religioni del mondo (l'induismo, il buddismo, il giainismo e il sikhismo) sono nate qui, mentre lo zoroastrismo, l'ebraismo, il cristianesimo e l'islam arrivarono entro il I millennio d.C. dando forma nella regione a una grandissima diversità culturale. Gradualmente annessa alla Compagnia britannica delle Indie orientali dai primi decenni del XVIII secolo e colonizzata dal Regno Unito dalla metà del XIX secolo, l'India è diventata un moderno Stato nazionale nel 1947, dopo una lotta per l'indipendenza che è stata caratterizzata da una diffusa resistenza non violenta guidata da Gandhi.
L'India è la dodicesima più grande economia del mondo in termini nominali e la quarta in termini di potere d'acquisto. Riforme economiche hanno trasformato lo Stato nella seconda economia a più rapida crescita[12] (è uno dei cinque Paesi a cui ci si riferisce con l'acronimo BRICS),[13] ma nonostante ciò il Paese soffre ancora di alti livelli di povertà, analfabetismo e malnutrizione, oltre ad avere un sistema sociale basato sulle caste. Società pluralistica, multilingue e multietnica, l'India è inoltre ricca sul piano naturale, con un'ampia diversità di fauna selvatica e di habitat protetti.
La India8 ―oficialmente República de la India (en hindi, भारत गणराज्य, Bhārat Gaṇarājya; en inglés, Republic of India)― es un país soberano ubicado en el sur de Asia. Con sus más de 1240 millones de habitantes, es el segundo país del mundo por población ―después de la República Popular China (con 1395 millones). Su superficie es de 3 287 263 km²,3 lo cual lo ubica en el séptimo lugar entre los países más extensos del planeta. Limita con el océano Índico al sur, con el mar Arábigo al oeste y con el golfo de Bengala al este, a lo largo de una línea costera de más de 7517 kilómetros.9
La India también limita con Pakistán al oeste;10 al norte con China, Nepal y Bután y al este con Bangladés y Birmania. Además, la India se encuentra cerca de las islas de Sri Lanka, Maldivas e Indonesia. Su capital es Nueva Delhi y su ciudad más poblada es Bombay.
Hogar de la cultura del valle del Indo y una región histórica por sus rutas comerciales y grandes imperios, el subcontinente indio fue identificado por su riqueza cultural y comercial en la mayor parte de su larga historia.11 Cuatro de las religiones más importantes del mundo, el hinduismo, el budismo, el jainismo y el sijismo se originaron allí, mientras que otras religiones como el zoroastrismo, el judaísmo, el cristianismo y el islam llegaron durante el I milenio, dando forma a diversas culturas de la región.
Gradualmente anexada por la Compañía Británica de las Indias Orientales desde principios del siglo XVIII y colonizada por el Reino Unido desde mediados del siglo XIX, la India se convirtió en una nación independiente en 1947, tras una lucha por la independencia que estuvo marcada por un movimiento de no violencia.12
La India es una república federal13 compuesta por 29 estados y 7 territorios de la Unión, con un sistema de democracia parlamentaria. En 2017, la economía india es la tercera más grande del mundo y la sexta en términos de PIB nominal. Las reformas económicas de 1991 la han transformado en una de las economías de más rápido crecimiento;14 sin embargo, todavía sufre de problemas como los altos niveles de pobreza, analfabetismo,15 pandemias, malnutrición y constantes violaciones de los derechos de las mujeres. Además de una sociedad plural en lo religioso, multilingüe y multiétnica, la India también alberga una flora y fauna diversas en diferentes hábitats protegidos.
Además, la República de la India es uno de los diez países que posee un arsenal nuclear y no es signataria del Tratado de No Proliferación Nuclear, dado que, en sus actuales términos, no le permitiría mantener su armamento atómico.
И́ндия (хинди भारत Bhārat, англ. India), официальное название — Респу́блика И́ндия (хинди भारत गणराज्य Bhārat Gaṇarājya, англ. Republic of India) — государство в Южной Азии. Население — 1 340 468 000 человек (22 декабря 2017)[6], территория — 3 287 263 км², по обоим этим показателям является крупнейшей страной Южной Азии. Занимает второе место в мире по численности населения и седьмое по территории. Столица — Нью-Дели. Государственные языки — хинди и английский.
Федеративное государство, парламентская республика. Премьер-министр — Нарендра Моди, президент — Рам Натх Ковинд. Подразделяется на 29 штатов и 7 союзных территорий.
Индия граничит с Пакистаном на западе, с Китаем, Непалом и Бутаном на северо-востоке, с Бангладеш и Мьянмой на востоке. Кроме того, Индия имеет морские границы с Мальдивами на юго-западе, со Шри-Ланкой на юге и с Индонезией на юго-востоке[7]. Спорная территория штата Джамму и Кашмир имеет границу с Афганистаном[8].
Индийский субконтинент является родиной древней индской цивилизации. На протяжении большей части своей истории Индия являлась центром важных торговых маршрутов и славилась своими богатствами и высокой культурой. В Индии зародились такие религии, как индуизм, буддизм, сикхизм и джайнизм. В первом тысячелетии нашей эры на индийский субконтинент пришли также христианство и ислам, оказавшие значительное влияние на развитие разнообразной культуры региона. В XVIII — первой половине XX века Индия постепенно была колонизирована Британской империей. В 1947 году, после многолетней борьбы, страна получила независимость. К концу XX века Индия достигла больших успехов в экономическом и военном развитии, экономика страны стала одной из самых быстроразвивающихся в мире. Несмотря на это, значительная часть населения продолжает жить за чертой бедности. Насущными проблемами являются также высокий уровень коррупции и отсталая система здравоохранения.
Индия является потенциальной сверхдержавой, обладает ядерным оружием. Она входит в такие международные организации, как ООН, G20, ВТО, Ассоциация регионального сотрудничества Южной Азии, Содружество наций, а также БРИКС и ШОС.
哈萨克斯坦共和国(哈萨克语:Қазақстан Республикасы / Qazaqstan Respwblïkası / قازاقستان رەسپۋبلىيكاسى;俄语:Республика Казахстан),通称哈萨克斯坦(哈萨克语:Қазақстан / Qazaqstan / قازاقستان;俄语:Казахстан)、哈萨克,为跨洲国家,地跨欧亚两洲,主要位于中亚北部,在乌拉尔河以西的一小部分领土位于东欧[7][8]。哈萨克斯坦国土面积2,727,300平方公里,为世界上最大的内陆国家,世界第九大国[7][9]。哈萨克经济在中亚居主导地位,占中亚区域生产总值的60%,以石油、天然气工业为主,另有丰富的矿产资源[10]。哈萨克斯坦在文化上也是中亚突厥国家。
哈萨克政府在官方将自己定位为一个民主制的世俗化国家,并且是个实行单一制的宪政共和国。哈萨克斯坦的北部、西部与俄罗斯接壤,东南部与中国,南部与乌兹别克斯坦、吉尔吉斯斯坦、土库曼斯坦接壤。西南濒临里海在里海有2,964公里的海岸线。哈萨克斯坦地形包括平原、干草原、北方针叶林、峡谷、丘、三角洲、山部及荒漠,2022年估计哈萨克斯坦有1,922万人口,哈萨克斯坦国土面积大,但每平方公里仅7人,为人口密度最低的国家之一。首都阿斯塔纳(2022年9月17日,已由努尔苏丹更名为原称),在1997年前则以该国最大城市阿拉木图为首都。
哈萨克斯坦领土历史上为多个游牧民族的活动范围,成吉思汗于13世纪占领该地,成为蒙古帝国而改变,随着帝国内部斗争,权利最终回到当地游牧民族手中。16世纪时,哈萨克族分别发展,成为大、中、小三个玉兹。俄罗斯人于18世纪开始进入哈萨克斯坦草原,至19世纪中叶,哈萨克斯坦名义上已成为俄罗斯帝国的一部分。随着1917年俄国革命及其后的俄国内战,哈萨克斯坦领土曾变更过数次,哈萨克苏维埃社会主义共和国于1936年成立,为苏联的一部分。1932年,发生哈萨克斯坦大饥荒,当地约150万人死亡。
1991年苏联解体时,哈萨克斯坦为最后一个宣布独立的苏联加盟共和国。原哈萨克斯坦共产党第一书记努尔苏丹·纳扎尔巴耶夫自当时起持续担任哈萨克斯坦总统,直到2019年自行宣布退休,但当时仍留任国家安全委员会主席掌握权力。哈萨克斯坦致力于发展其经济,尤其是石化工业[10]。
哈萨克斯坦国内有131个民族,包括哈萨克族(占73.0%人口)、俄罗斯人、乌孜别克族、乌克兰族、德意志人、鞑靼人及维吾尔族[11]。伊斯兰教信仰者占总人口的76.2%,而基督宗教占20.5%[12]。哈萨克斯坦官方允许宗教自由,但反对政府的宗教领袖则会被逮捕[13]。哈萨克语为官方语言,俄语在行政及机关上则有同等的官方语言地位[7][14]。
独立后成为独联体成员国,2009年起为突厥议会成员国,2001年6月15日成为上海合作组织成员国。哈萨克斯坦近年来加强了与独联体各国的经济、政治、军事等方面的一体化,2015年1月1日,与俄罗斯、白罗斯、吉尔吉斯斯坦等国家成立欧亚经济联盟[15]。
Kasachstan (kasachisch Қазақстан Qazaqstan [qɑzɑqˈstɑn], russisch Казахстан, amtlich Republik Kasachstan, kasachisch Қазақстан Республикасы Qazaqstan Respublikasy, russisch Республика Казахстан Respublika Kasachstan) ist ein Staat in Zentralasien und Osteuropa. Die Grenze zu Russland ist die einzige Nordgrenze des Landes und über 7600 Kilometer lang. Im Süden grenzt Kasachstan an Turkmenistan, Usbekistan und Kirgisistan und im Südosten, auf einer Länge von knapp 1800 Kilometer, an die Volksrepublik China.[4] Mit mehr als 2,7 Millionen km² Landesfläche ist Kasachstan der größte Binnenstaat und der neuntgrößte Staat der Welt. Das Land ist landschaftlich vor allem von der Kasachensteppe geprägt und verfügt über große Ölressourcen.
Kasachstan hat knapp 19 Millionen Einwohner, die Mehrheit davon muslimische Kasachen. Hauptstadt ist Astana mit 1,1 Millionen Einwohnern, größte Stadt ist Almaty mit 1,9 Millionen Einwohnern. Weitere wichtige Städte des Landes sind Schymkent und Qaraghandy.
Bereits im Altertum bestanden auf dem Gebiet des heutigen Kasachstans verschiedene Reiche. Zwischen dem 6. und 8. Jahrhundert entstand der westliche Teil des Ersten Türk-Kaganats. Im 13. Jahrhundert fielen die Mongolen unter Dschingis Khan ein. Nach der Eroberung durch den Usbeken Timur im 15. Jahrhundert konnten sich die Kasachen wieder vom Usbeken-Khanat trennen und unter einer einheimischen Dschingiskhaniden-Dynastie das Kasachen-Khanat errichten – damit wehrten sich die Kasachen gegen die Einführung des Islam und konnten den überlieferten Traditionen verbunden bleiben. Im 17. und 18. Jahrhundert breitete sich das Dsungarische Khanat aus, bis sich die Kasachen dem russischen Zaren unterstellten. 1925 wurde die Kasachische Autonome Sozialistische Sowjetrepublik gegründet, die ab 1936 als Kasachische SSR eine Unionsrepublik innerhalb der Sowjetunion bildete.
Nach dem Zerfall der Sowjetunion erklärte sich das Land am 16. Dezember 1991 als Republik Kasachstan unabhängig. Kasachstan ist Vollmitglied in der Gemeinschaft Unabhängiger Staaten. Die Präsidialrepublik wurde von 1991 bis 2019 von Nursultan Nasarbajew regiert. Das zu den Turksprachen zählende Kasachisch und das den slawischen Sprachen zugehörige Russisch wurden mit der Unabhängigkeit zu Amtssprachen erklärt und die bisherige Hauptstadt Alma-Ata in Almaty umbenannt. 1997 wurde der Regierungs- und Parlamentssitz nach Aqmola verlegt. Die Stadt wurde als offizielle Hauptstadt proklamiert und ein Jahr später in Astana („Hauptstadt“) umbenannt; dieser Name wurde 2019 in Nur-Sultan und am 17. September 2022 wieder in Astana geändert.
Kasachstan wird autoritär regiert, Korruption ist weit verbreitet. Die Menschenrechtslage gilt als kritisch, so ist zum Beispiel die Meinungsfreiheit stark eingeschränkt. 2022 kam es erstmals zu größeren Protesten gegen die Regierung, die gewaltsam niedergeschlagen wurden.
 IMF Developed countries
IMF Developed countries
 IMF Developed countries
IMF Developed countries
 TOP3
TOP3

 Party and government
Party and government
 Group of the twenty most important industrial and emerging countries
Group of the twenty most important industrial and emerging countries
 Republic of Korea
Republic of Korea
 Silk road
Silk road

 States of Asia
States of Asia
Usbekistan (usbekisch Oʻzbekiston; amtlich Republik Usbekistan, usbekisch Oʻzbekiston Respublikasi) ist ein 448.978 km² großer Binnenstaat in Zentralasien mit 36 Millionen Einwohnern. Er grenzt im Norden an Kasachstan, im Nordosten an Kirgisistan, im Südosten an Tadschikistan, im Süden an Afghanistan und im Südwesten an Turkmenistan. Usbekistan ist neben Liechtenstein der einzige Binnenstaat der Welt, der nur von Binnenstaaten umgeben ist.
Hauptstadt und mit rund 2,5 Millionen Einwohnern größte Stadt der ehemaligen Sowjetrepublik ist Taschkent. Weitere wichtige Städte des islamisch geprägten und autoritär regierten Landes sind Samarkand und Buchara an der historischen Seidenstraße.
 Eurovision Song Contest,ESC
Eurovision Song Contest,ESC
 Hansestadt
Hansestadt

 International cities
International cities
 *European Capital of Culture
*European Capital of Culture
 Latvia
Latvia
 Silk road
Silk road

 World Heritage
World Heritage

 Important port
Important port

里加(拉脱维亚语:Rīga, 英语:Riga)是拉脱维亚的首都,北欧地区波罗的海国家中最大、最繁忙的城市,位于波罗的海岸边,道加瓦河口。
里加是波罗的海国家主要的政治、经济、文化、教育和工商业中心。里加是历史上汉萨同盟主要商业城市,其历史中心被列入世界遗产名录,联合国教科文组织特别认为里加丰富的新艺术运动建筑是世界上独一无二的[2]。
欧盟欧洲电子通讯监管机构总部以及北大西洋公约组织的战略通讯中心设在里加。里加是欧洲城市组织及欧洲首都联盟组织成员。2014年欧洲文化之都,世界合唱比赛,2006年北大西洋公约组织峰会,2003年欧洲歌唱大赛,2006年世界男子冰球锦标赛,2003年世界女子冰壶球锦标赛等活动的举办地。
Riga (lettisch Rīga) ist die Hauptstadt Lettlands und mit rund 700.000 Einwohnern größte Stadt des Baltikums. Mit etwa einer Million Einwohnern in der Agglomeration ist Riga zudem der größte Ballungsraum in den drei baltischen Staaten. Riga ist politisches, wirtschaftliches und kulturelles Zentrum des Landes. Die alte Hansestadt ist berühmt für ihre Jugendstilbauten und ihre großzügige Anlage sowie für die gut erhaltene Innenstadt, darunter besonders die Altstadt. 2016 wurde Riga der Ehrentitel „Reformationsstadt Europas“ durch die Gemeinschaft Evangelischer Kirchen in Europa verliehen.[1]
リガ、またはリーガ[1](ラトビア語: Rīga 発音 [ˈriːɡa] (![]() 音声ファイル)、ロシア語: Рига、エストニア語: Riia、リトアニア語: Ryga、英語、ドイツ語: Riga)は、ラトビア共和国の首都で、同国最大の人口を擁する都市。人口は69万9,203人(2012年時点)。「バルト海の真珠」と讃えられる美しい港町で、その旧市街はユネスコの世界遺産(文化遺産)に登録されている。 世界遺産に登録されている旧市街「リガ歴史地区」は約300棟のアールヌーボー調の建築物の宝庫として著名である。新市街は官庁やオフィスが集まる。郊外には、ラトビア民俗博物館があり、野外博物館も兼ねている。また、保養地として知られる海岸、ユールマーラも西方にある。人口約70万人のリガ市はラトビア国内はもとより、バルト三国最大の都市でもある。市内で最も高い建築物はリガラジオ&テレビタワーである。
音声ファイル)、ロシア語: Рига、エストニア語: Riia、リトアニア語: Ryga、英語、ドイツ語: Riga)は、ラトビア共和国の首都で、同国最大の人口を擁する都市。人口は69万9,203人(2012年時点)。「バルト海の真珠」と讃えられる美しい港町で、その旧市街はユネスコの世界遺産(文化遺産)に登録されている。 世界遺産に登録されている旧市街「リガ歴史地区」は約300棟のアールヌーボー調の建築物の宝庫として著名である。新市街は官庁やオフィスが集まる。郊外には、ラトビア民俗博物館があり、野外博物館も兼ねている。また、保養地として知られる海岸、ユールマーラも西方にある。人口約70万人のリガ市はラトビア国内はもとより、バルト三国最大の都市でもある。市内で最も高い建築物はリガラジオ&テレビタワーである。
Riga (/ˈriːɡə/; Latvian: Rīga [ˈriːɡa] ( listen), Livonian: Rīgõ) is the capital and largest city of Latvia. With 641,481 inhabitants (2016),[4] it is also the largest city in the three Baltic states, home to one third of Latvia's population and one tenth of the three Baltic states' combined population.[9] The city lies on the Gulf of Riga, at the mouth of the Daugava. Riga's territory covers 307.17 km2 (118.60 sq mi) and lies 1–10 m (3 ft 3 in–32 ft 10 in) above sea level,[10] on a flat and sandy plain.[10]
listen), Livonian: Rīgõ) is the capital and largest city of Latvia. With 641,481 inhabitants (2016),[4] it is also the largest city in the three Baltic states, home to one third of Latvia's population and one tenth of the three Baltic states' combined population.[9] The city lies on the Gulf of Riga, at the mouth of the Daugava. Riga's territory covers 307.17 km2 (118.60 sq mi) and lies 1–10 m (3 ft 3 in–32 ft 10 in) above sea level,[10] on a flat and sandy plain.[10]
Riga was founded in 1201 and is a former Hanseatic League member. Riga's historical centre is a UNESCO World Heritage Site, noted for its Art Nouveau/Jugendstil architecture and 19th century wooden architecture.[11] Riga was the European Capital of Culture during 2014, along with Umeå in Sweden. Riga hosted the 2006 NATO Summit, the Eurovision Song Contest 2003, the 2006 IIHF Men's World Ice Hockey Championships and the 2013 World Women's Curling Championship. It is home to the European Union's office of European Regulators for Electronic Communications (BEREC).
In 2016, Riga received over 1.4 million visitors.[12] It is served by Riga International Airport, the largest and busiest airport in the Baltic states. Riga is a member of Eurocities,[13] the Union of the Baltic Cities (UBC)[14] and Union of Capitals of the European Union (UCEU).[15]
Riga (prononcé [ʁi.ga] ; en letton Rīga [riː.ga]) est la capitale de la Lettonie. Construite sur la mer Baltique au fond du golfe de Riga, dans lequel se jette la Daugava, c'est un centre industriel, commercial, culturel et financier majeur de la région de Vidzeme.
Riga (in lettone Rīga) è la capitale della Lettonia. Situata sul Mar Baltico alla foce del fiume Daugava, con 699.203 abitanti al censimento del 2011, è la città più grande delle Repubbliche Baltiche ed è uno dei principali centri culturali, politici ed economici della regione. Antico centro della lega anseatica, la città è gemellata con Firenze e Brema. Nel 2001 ha ospitato il Mese culturale europeo assieme a Basilea, mentre nel 2014 è stata Capitale europea della cultura affiancata ad Umeå.
Riga (en letón: Rīga  [ˈriːɡa] (?·i)) es la capital y la mayor ciudad de Letonia. Es la ciudad más grande de los Estados bálticos y el hogar de más de un tercio de la población de Letonia.1 Es el mayor centro cultural, educativo, político, financiero, comercial e industrial de la región del mar Báltico.
[ˈriːɡa] (?·i)) es la capital y la mayor ciudad de Letonia. Es la ciudad más grande de los Estados bálticos y el hogar de más de un tercio de la población de Letonia.1 Es el mayor centro cultural, educativo, político, financiero, comercial e industrial de la región del mar Báltico.
La ciudad se encuentra en el golfo de Riga, en la desembocadura del río Daugava. Tiene un área de 307,17 km² y se encuentra en una llanura arenosa entre 1 y 10 metros sobre el nivel del mar.2
Riga fue fundada en 1201 y es un antiguo miembro de la Liga Hanseática. El centro histórico de Riga, declarado Patrimonio de la Humanidad por la Unesco, destaca por su arquitectura art nouveau y sus construcciones de madera del siglo XIX.3 La ciudad fue designada Capital Europea de la Cultura en 2014, junto a Umeå en Suecia.
La ciudad está comunicada por vía aérea gracias al Aeropuerto Internacional de Riga, el aeropuerto más grande de los países bálticos.
Riga es miembro de Eurocities,4 la unión de las ciudades bálticas (UBC)5 y la Unión de Capitales de la Unión Europea (UCEU).6
Ри́га (латыш.  Rīga [ˈriːɡa], лив. Rīgõ) — столица Латвии и самый крупный город в Прибалтике с численностью населения 637 971 человека (2018 год)[2]. Политический, экономический и культурный центр страны. Находится на обоих берегах реки Даугавы, недалеко от её впадения в Рижский залив.
Rīga [ˈriːɡa], лив. Rīgõ) — столица Латвии и самый крупный город в Прибалтике с численностью населения 637 971 человека (2018 год)[2]. Политический, экономический и культурный центр страны. Находится на обоих берегах реки Даугавы, недалеко от её впадения в Рижский залив.
Рига долгое время была ганзейским городом, здесь соседствуют здания различных стилей от средневековой архитектуры старого города до модерна и современной архитектуры. Она была одним из крупнейших портов и одним из важнейших промышленных, коммерческих и культурных центров в Российской Империи. Исторический центр города внесен в список Всемирного наследия ЮНЕСКО[4]. В 2014 году Рига была выбрана одной из культурных столиц Европы[5].
 Brazil
Brazil
 FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 2014
FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 2014
 Olympic Summer Games
Olympic Summer Games
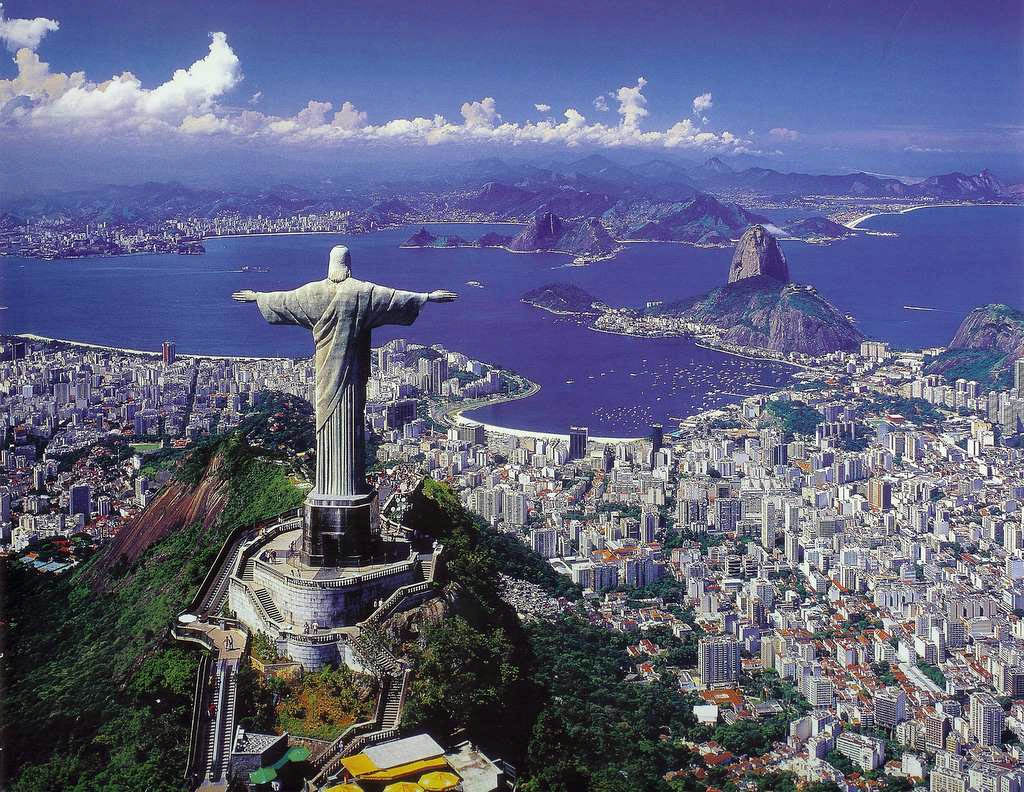
 Rio de Janeiro
Rio de Janeiro
 Silk road
Silk road

 Important port
Important port
里约热内卢位于巴西国土的东南部,坐落在美丽的瓜纳巴拉海湾,依山傍水,风景优美,是巴西和世界著名的旅游观光胜地。面积4.36万平方公里。人口 1,413.3万(1990),城市人口占90%以上。1889年设州,1975年瓜纳巴拉州并入,首府由尼泰罗伊迁至里约热内卢市。沿海低地气候湿热, 内地高原气候温和。重要河流有帕拉伊巴河等。工农业和服务业均甚发达,服务业占就业人口约37%和收入的一半。工业以钢铁、纺织、食品、印刷、石油化工为 主。有石油、铝土、铁、煤、大理石等矿产。渔业和盐业兴盛。农业主产甘蔗、柑橘、香蕉、蔬菜、棉花、水果、稻,饲养牲畜。水、陆、空交通发达。风景优美, 多游览胜地。
(Quelle: http://www.uutuu.com)
里约热内卢(葡萄牙语:Rio de Janeiro,葡萄牙语发音:[ˈʁi.u dʒi ʒɐˈnejɾu],意即“一月的河”),有时仅简称为里约(Rio),是位于巴西东南部的城市,为里约热内卢州首府,同时是巴西第二大城,仅次于圣保罗。面积1,256平方公里,人口6,094,183人(2005年)。其自1822年巴西建国以来一直为首都,至1960年4月21日迁都巴西利亚为止,更曾经成为前宗主国葡萄牙在本土被拿破仑入侵时(1808年–1821年)的流亡首都[3]。风景优美,每年吸引大量游客到此观光,市内的里约热内卢港是世界三大天然良港之一,而里约热内卢基督像也是世界新七大奇迹之一。其亦为第31届夏季奥运的主办地,是第一座举办夏季奥运的南美洲城市。
Rio de Janeiro [ˈʁi.u d(ʒi) ʒɐˈne(j)ɾu, ˈʁi.u d(ʑi) ʑɐˈne(j)ɾu] ist nach São Paulo die zweitgrößte Stadt Brasiliens und Hauptstadt des gleichnamigen Bundesstaates. Sie liegt an der Guanabara-Bucht im Südosten des Landes. Der Name (deutsch Fluss des Januar) beruht auf einem Irrtum des Seefahrers Gaspar de Lemos, der die Bucht am 1. Januar 1502 entdeckte und für die Mündung eines großen Flusses hielt. Im administrativen Stadtgebiet leben rund 6,7 Millionen Menschen (Schätzung 2018).[1] Die Metropolregion Rio de Janeiro hat rund 13,3 Millionen Einwohner (Schätzung 2018).[2] Somit gehört Rio de Janeiro zu den Megastädten dieser Erde.
Von 1815 bis 1821 war Rio de Janeiro Hauptstadt des Königreiches von Portugal und Brasilien und nach der Unabhängigkeit Brasiliens 1822 bis 1960 die Hauptstadt des Landes. Danach trat sie diese Funktion an Brasília ab, bleibt aber nach São Paulo bedeutendstes Handels- und Finanzzentrum des Landes. Von 1808 bis 1822 war die Stadt auch Sitz des portugiesischen Hofes, der wegen eines Angriffs durch Napoleon Bonaparte nach Brasilien flüchten musste. Die Bewohner der Stadt nennt man Cariocas, nach einem Wort aus der zum Tupí-Guaraní gehörenden Sprache der Tupinambá, welches „Hütte des weißen Mannes“ bedeutet.
Wahrzeichen von Rio de Janeiro sind der Zuckerhut, die 38 Meter hohe Christusfigur auf dem Gipfel des Corcovados und der Strand des Stadtteils Copacabana, der als einer der berühmtesten der Welt gilt. Die Stadt ist auch bekannt wegen des jährlich stattfindenden Karnevals von Rio. Die bunte Parade der Sambaschulen gehört zu den größten Paraden der Welt.
リオ・デ・ジャネイロ(葡: Rio de Janeiro, ブラジルポルトガル語発音: ヒウ・ヂ・ジャネイル)は、ブラジル南東部に位置するリオデジャネイロ州の州都。世界有数のメガシティであり、国内最大の観光都市である。港湾都市としても知られる。
人口は600万人を超え、サンパウロに次いでブラジル第2位にランクされる。経済規模(域内総生産)でもサンパウロに次いで第2位にあり、アメリカのシンクタンクが公表したビジネス・人材・文化・政治などを対象とした総合的な世界都市ランキングにおいて、世界第56位、国内ではサンパウロに次ぐ第2位の都市と評価された[1]。都市周辺の美しい文化的景観は「リオデジャネイロ:山と海との間のカリオカの景観群」として、2012年に世界遺産リストに登録された。2016年の第31回夏季オリンピックの開催都市である。
カーニバルで有名。コパカバーナ、イパネマ(英語版)などの世界的に有名な海岸を有し世界3大美港の一つに数えられる美しい都市である。都市のGDPは2010億ドルであり世界第30位、南米ではサンパウロ、ブエノスアイレスに次ぎ第3位である[2]。
1960年にブラジリアに遷都するまではブラジルの首都であった。また、1808年にナポレオンに本国領土を奪われたポルトガル王室が遷都してからブラジルが独立するまではポルトガルの首都であった。また、中南米有数の貿易港でもあるためにブラジルの経済的な中心地でもあった。近年は経済の中心地はサンパウロに移り、その地位が低下しているものの、依然として中南米有数の経済都市である。また、ブラジルのみならず世界でも有数の観光地としても、ショーロ、ボサノヴァを生んだ音楽の都としても名高い。
Rio de Janeiro (/ˈriːoʊ di ʒəˈnɛəroʊ, - deɪ -, - də -/; Portuguese: [ˈʁi.u d(ʒi) ʒɐˈne(j)ɾu];[3] River of January), or simply Rio,[4] is anchor to the Rio de Janeiro metropolitan area and the second-most populous municipality in Brazil and the sixth-most populous in the Americas. Rio de Janeiro is the capital of the state of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil's third-most populous state. Part of the city has been designated as a World Heritage Site, named "Rio de Janeiro: Carioca Landscapes between the Mountain and the Sea", by UNESCO on 1 July 2012 as a Cultural Landscape.[5]
Founded in 1565 by the Portuguese, the city was initially the seat of the Captaincy of Rio de Janeiro, a domain of the Portuguese Empire. Later, in 1763, it became the capital of the State of Brazil, a state of the Portuguese Empire. In 1808, when the Portuguese Royal Court transferred itself from Portugal to Brazil, Rio de Janeiro became the chosen seat of the court of Queen Maria I of Portugal, who subsequently, in 1815, under the leadership of her son, the Prince Regent, and future King João VI of Portugal, raised Brazil to the dignity of a kingdom, within the United Kingdom of Portugal, Brazil, and Algarves. Rio stayed the capital of the pluricontinental Lusitanian monarchy until 1822, when the War of Brazilian Independence began. This is one of the few instances in history that the capital of a colonising country officially shifted to a city in one of its colonies. Rio de Janeiro subsequently served as the capital of the independent monarchy, the Empire of Brazil, until 1889, and then the capital of a republican Brazil until 1960 when the capital was transferred to Brasília.
Rio de Janeiro has the second largest municipal GDP in the country,[6] and 30th largest in the world in 2008,[7] estimated at about R$343 billion (IBGE, 2008) (nearly US$201 billion). It is headquarters to Brazilian oil, mining, and telecommunications companies, including two of the country's major corporations – Petrobras and Vale – and Latin America's largest telemedia conglomerate, Grupo Globo. The home of many universities and institutes, it is the second-largest center of research and development in Brazil, accounting for 17% of national scientific output according to 2005 data.[8] Despite the high perception of crime, the city has a lower incidence of crime than Northeast Brazil, but it is far more criminalized than the south region of Brazil, which is considered the safest in the country.[9]
Rio de Janeiro is one of the most visited cities in the Southern Hemisphere and is known for its natural settings, Carnival, samba, bossa nova, and balneario beaches[10] such as Barra da Tijuca, Copacabana, Ipanema, and Leblon. In addition to the beaches, some of the most famous landmarks include the giant statue of Christ the Redeemer atop Corcovado mountain, named one of the New Seven Wonders of the World; Sugarloaf Mountain with its cable car; the Sambódromo (Sambadrome), a permanent grandstand-lined parade avenue which is used during Carnival; and Maracanã Stadium, one of the world's largest football stadiums. Rio de Janeiro was the host of the 2016 Summer Olympics and the 2016 Summer Paralympics, making the city the first South American and Portuguese-speaking city to ever host the events, and the third time the Olympics were held in a Southern Hemisphere city.[11] The Maracanã Stadium held the finals of the 1950 and 2014 FIFA World Cups, the 2013 FIFA Confederations Cup, and the XV Pan American Games.
Rio de Janeiro [ˈʁi.u d(ʒi) ʒɐˈnejɾu]2, souvent désignée simplement sous le nom de Rio, est la deuxième plus grande ville du Brésil après São Paulo. Située au sud-est du pays, elle est la capitale de l'État de Rio de Janeiro. Avec ses 6,1 millions d'habitants intra-muros (communément appelés Cariocas, la variante Carioques existant aussi en français) et 12,62 millions dans l'aire urbaine, Rio de Janeiro est l'une des métropoles les plus importantes du continent américain.
Elle est mondialement connue pour son carnaval, ses plages (Copacabana, Leblon et Ipanema) ainsi que sa statue du Christ Rédempteur au sommet du Corcovado. Elle fut capitale du Royaume-Uni de Portugal, du Brésil et des Algarves, à la suite de la fuite de la cour portugaise lors de l'invasion des troupes napoléoniennes (1808-1821), puis de l'Empire du Brésil (1822-1889), de la República Velha (1889-1930), de l’Estado Novo (1937-1945) et du début de la Deuxième République jusqu'en 1960.
La ville a accueilli les Journées mondiales de la jeunesse 2013, la finale de la Coupe du monde de football de 2014 et enfin, en 2016, les Jeux olympiques d'été.
Rio de Janeiro (pron. [ˈrio deʒaˈnɛiro];[2] letteralmente "Fiume di gennaio" in portoghese) è una città del Brasile, capitale dell'omonimo stato confederato. Rio è la seconda città del Brasile dopo San Paolo e fu la capitale dello Stato federale dal 1763 fino al 1960, dopo Salvador da Bahia e prima di Brasilia.
La città è famosa per le sue attrattive turistiche tra cui spiccano le spiagge di Copacabana e Ipanema, la gigantesca statua liberty del Cristo Redentore, situata sul monte del Corcovado, il monte del Pão de Açúcar (Pan di Zucchero), con la sua funivia, e il suo annuale carnevale, il più celebre al mondo.
La città è al centro della scena internazionale, avendo ospitato alcuni dei più grandi eventi mondiali degli ultimi anni: nel 2007 i XV Giochi Panamericani, nel 2013 la XXVIII Giornata Mondiale della Gioventù e nel 2016 i giochi della XXXI Olimpiade. È stata inoltre una delle città in cui si è disputato il Campionato del mondo di calcio 2014.
Rio de Janeiro contiene anche la più grande foresta all'interno di un'area urbana, la foresta di Tijuca.
L'attuale sindaco è Marcelo Crivella, in carica dal 1º gennaio 2017, del PRB.
Río de Janeiro1 (en portugués, Rio de Janeiro, AFI: [ˈʁi.u dʒi ʒaˈnejɾu]), fundada como São Sebastião do Rio de Janeiro,3 es una ciudad, municipio brasileño y capital del estado homónimo, ubicada en el sureste del país. Es la segunda ciudad más poblada del país después de São Paulo.4
Fue la capital del Reino de Portugal entre 1808 y 1822 y la capital del Imperio del Brasil desde 1822, cuando la nación declaró su independencia del país luso y conservó ese rango hasta la inauguración de Brasilia, en 1960.
Es uno de los principales centros económicos, de recursos culturales y financieros del Brasil. Es conocida internacionalmente por sus iconos culturales y paisajes, como el Pan de Azúcar, la estatua del Cristo Redentor (una de las siete maravillas del mundo moderno), las playas de Copacabana e Ipanema, el Estadio de Maracaná, el Parque Nacional de Tijuca (el mayor bosque urbano del mundo), la Quinta da Boa Vista, la isla de Paquetá, las Fiestas de Fin de Año en Copacabana y la celebración del Carnaval
Representa el segundo mayor PIB en el país y 30.º mayor del mundo, además de ser sede de dos de las más importantes empresas brasileñas —Petrobras y Vale do Rio Doce, ahora privatizada— y las principales empresas de petróleo y la telefonía, así como del mayor conglomerado de compañías de medios y comunicaciones de Latinoamérica.[cita requerida] Es el segundo centro más grande de investigación y desarrollo en Brasil, alcanzando el 17% de la producción científica nacional (según datos de 2005).
Río de Janeiro es considerada una ciudad global Beta- por el inventario de 2008 de la Universidad de Loughborough (GaWC).5
Es conocida mundialmente como la "Ciudad Maravillosa" (Cidade Maravilhosa), en portugués, albergó la Copa Mundial de Fútbol de 1950, la Copa Confederaciones 2013, la Jornada Mundial de la Juventud 2013, la Copa Mundial de Fútbol de 2014 y los Juegos Olímpicos de Río de Janeiro 2016.
Ри́о-де-Жане́йро, или, сокращённо, Рио (порт. Rio de Janeiro, буквально — январская река) — город в Бразилии, административный центр одноимённого штата.
Население — 6,4 млн человек (2014), это второй по величине город страны и четвёртый Южной Америки. Образует агломерацию с населением 12 млн человек (2011 год)[6]. Крупный финансовый центр и морской порт на континенте, научный центр.
Расположен на берегу залива Гуанабара Атлантического океана, на узкой равнине, зажатой с двух сторон горами и морем. Климат тропический[1][2]. Местность открыта португальским мореплавателем Гашпаром ди Лемушем, принявшим залив Гуанабара за реку, которую назвали Январской рекой[уточнить]. В 1531 году основан португальский форт Сан-Себастьян де-Рио-де-Жанейро. С 1763 — столица вице-королевства Бразилии, с 1822 года — столица независимой Бразильской империи, в 1889—1960 годы — столица республики Соединённых штатов Бразилии.
Исторический центр с постройками XVI—XIX веков. Побережье вместе с пляжем Копакабана, горой Сахарная Голова и статуей Христа внесено в список Всемирного наследия ЮНЕСКО[7].

 Architecture
Architecture
 Eurovision Song Contest,ESC
Eurovision Song Contest,ESC
 FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 1990
FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 1990
 UEFA European Championship 2020
UEFA European Championship 2020

 History
History
 Italy
Italy

 Lazio
Lazio
 Rom
Rom
 Olympic Summer Games
Olympic Summer Games
 1960 Summer Olympics
1960 Summer Olympics
 Silk road
Silk road

 Cities founded by the Romans
Cities founded by the Romans

 World Heritage
World Heritage

罗马(意大利语:Roma)是意大利首都及全国政治、经济、文化和交通中心,是世界著名的历史文化名城,古罗马文明的发祥地,因建城历史悠久并保存大量古迹而被昵称为“永恒之城”[1][2]。其位于意大利半岛中西部,台伯河下游平原地的七座小山丘上,市中心面积有1200多平方公里。罗马同时是全世界天主教会的中枢,拥有700多座教堂与修道院、7所天主教大学,市内的梵蒂冈城是罗马主教即天主教会教宗及圣座的驻地。罗马与佛罗伦萨同为意大利文艺复兴中心[3],现今仍保存有相当丰富的文艺复兴与巴洛克风貌;1980年,罗马的历史城区被列为世界文化遗产[4]。
Rom (lateinisch Rōma; italienisch Roma [ˈroːma]), amtlich Roma Capitale, ist die Hauptstadt Italiens.[2] Mit etwa drei Millionen Einwohnern im Stadtgebiet bzw. rund vier Millionen Einwohnern in der Agglomeration ist sie die größte Stadt Italiens. Rom liegt in der Region Latium an den Ufern des Flusses Tiber.
Rom wurde erstmals im 1. Jahrhundert v. Chr. vom Dichter Tibull[3] Ewige Stadt genannt. Diese Bezeichnung, ursprünglich eine Antonomasie, wurde zu einem Ehrennamen für die Stadt wegen der Bedeutung in ihrer bis heute drei Jahrtausende umspannenden Geschichte.
Sie ist heute Verwaltungssitz der Region Latium und der Metropolitanstadt Rom, bis 2015 Provinz Rom. Innerhalb der Stadt bildet der unabhängige Staat der Vatikanstadt eine Enklave. Der Vatikan ist der Sitz des Papstes, das heißt des Bischofs von Rom und Oberhaupts der römisch-katholischen Kirche sowie des Heiligen Stuhls. Zudem ist Rom seit 1834 Sitz des Malteser-Ritterordens, der ein eigenständiges (jedoch nichtstaatliches) Völkerrechtssubjekt ist, sowie der UNO-Unterorganisationen FAO, IFAD und WFP.
Rom ist außerordentlich reich an bedeutenden Bauten und Museen und Ziel zahlreicher Touristen. Die Altstadt von Rom, der Petersdom und die Vatikanstadt wurden von der UNESCO im Jahr 1980 zum Weltkulturerbe erklärt.[4]
In einer Rangliste der Städte nach ihrer Lebensqualität belegte Rom im Jahre 2018 den 57. Platz unter 231 untersuchten Städten weltweit.[5]
ローマ(伊: Roma、羅: Roma)は、イタリアの首都。欧州有数の世界都市であり、ラツィオ州の州都、ローマ県のコムーネの一つで、ローマ県の県都でもある。英語とフランス語の表記は「Rome」。
イタリアの首都で政治、経済、文化の中心地である。当市に囲まれるようにローマ教皇の居住するバチカン市国があり、そこは全世界のカトリック教徒にとっての中心地で、現在は外国であるが歴史・宗教・文化的にはローマ市地域と密接な関わりがある。そして昔のローマの大国さを表した「ローマは一日にして成らず」という諺もある。また、領土を持たないマルタ騎士団の本部、マルタ宮殿がコンドッティ通り68にあり、治外法権が認められている。
2014年現在の人口は約286万人で、イタリアで最も人口が多い都市である。2010年の都市的地域の人口では271万人であり、世界128位である[4]。 かつてのローマ帝国の首都であったため西洋文明圏を代表する都市のひとつであり、カトリック教会の中枢であり、そしてまたその美しさから『永遠の都』と称される。
2014年、アメリカのシンクタンクが公表したビジネス、人材、文化、政治などを対象とした総合的な世界都市ランキングにおいて、世界第32位の都市と評価されており、イタリアの都市では第1位であった[5]。
観光都市としての側面もあり、2012年には7,800,000人の観光客が訪れた[6]。後述の「観光」、「聖地として」も参照。
Rome (Italian: Roma ![]() i[ˈroːma]; Latin: Roma [ˈroːma]) is the capital city of Italy and a special comune (named Comune di Roma Capitale). Rome also serves as the capital of the Lazio region. With 2,872,800 residents in 1,285 km2 (496.1 sq mi),[1] it is also the country's most populated comune. It is the fourth-most populous city in the European Union by population within city limits. It is the centre of the Metropolitan City of Rome, which has a population of 4.3 million residents.[2] Rome is located in the central-western portion of the Italian Peninsula, within Lazio (Latium), along the shores of the Tiber. The Vatican City is an independent country inside the city boundaries of Rome, the only existing example of a country within a city: for this reason Rome has been often defined as capital of two states.[3][4]
i[ˈroːma]; Latin: Roma [ˈroːma]) is the capital city of Italy and a special comune (named Comune di Roma Capitale). Rome also serves as the capital of the Lazio region. With 2,872,800 residents in 1,285 km2 (496.1 sq mi),[1] it is also the country's most populated comune. It is the fourth-most populous city in the European Union by population within city limits. It is the centre of the Metropolitan City of Rome, which has a population of 4.3 million residents.[2] Rome is located in the central-western portion of the Italian Peninsula, within Lazio (Latium), along the shores of the Tiber. The Vatican City is an independent country inside the city boundaries of Rome, the only existing example of a country within a city: for this reason Rome has been often defined as capital of two states.[3][4]
Rome's history spans 28 centuries. While Roman mythology dates the founding of Rome at around 753 BC, the site has been inhabited for much longer, making it one of the oldest continuously occupied sites in Europe.[5] The city's early population originated from a mix of Latins, Etruscans, and Sabines. Eventually, the city successively became the capital of the Roman Kingdom, the Roman Republic and the Roman Empire, and is regarded as the birthplace of Western civilisation and by some as the first ever metropolis.[6] It was first called The Eternal City (Latin: Urbs Aeterna; Italian: La Città Eterna) by the Roman poet Tibullus in the 1st century BC, and the expression was also taken up by Ovid, Virgil, and Livy.[7][8] Rome is also called the "Caput Mundi" (Capital of the World). After the fall of the Western Empire, which marked the beginning of the Middle Ages, Rome slowly fell under the political control of the Papacy, which had settled in the city since the 1st century AD, until in the 8th century it became the capital of the Papal States, which lasted until 1870. Beginning with the Renaissance, almost all the popes since Nicholas V (1447–1455) pursued over four hundred years a coherent architectural and urban programme aimed at making the city the artistic and cultural centre of the world.[9] In this way, Rome became first one of the major centres of the Italian Renaissance,[10] and then the birthplace of both the Baroque style and Neoclassicism. Famous artists, painters, sculptors and architects made Rome the centre of their activity, creating masterpieces throughout the city. In 1871, Rome became the capital of the Kingdom of Italy, which, in 1946, became the Italian Republic.
Rome has the status of a global city.[11][12][13] In 2016, Rome ranked as the 14th-most-visited city in the world, 3rd most visited in the European Union, and the most popular tourist attraction in Italy.[14] Its historic centre is listed by UNESCO as a World Heritage Site.[15] Monuments and museums such as the Vatican Museums and the Colosseum are among the world's most visited tourist destinations with both locations receiving millions of tourists a year, and the city hosted the 1960 Summer Olympics. Rome is the seat of several specialized agencies of the United Nations, such as the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), the World Food Programme (WFP) and the International Fund for Agricultural Development (IFAD). The city hosts the headquarters of many international business companies, such as Eni, Enel, TIM, Leonardo S.p.A., and national and international banks such as Unicredit and BNL. Its business district, called EUR, is the base of many companies involved in the oil industry, the pharmaceutical industry, and financial services. Rome is also an important fashion and design centre thanks to renowned international brands centered in the city. Rome's Cinecittà Studios have been the set of many Academy Award–winning movies.
Roma (AFI: /ˈroma/[5], ) è la capitale della Repubblica Italiana, nonché capoluogo dell'omonima città metropolitana e della regione Lazio. La città è dotata di un ordinamento amministrativo speciale, denominato Roma Capitale, disciplinato da una legge dello Stato.[6]
Con 2 869 322 abitanti è il comune più popoloso d'Italia e il quarto dell'Unione europea,[3] mentre con 1 287,36 km² è il comune più esteso d'Italia e la quinta città più estesa d'Europa dopo Mosca, Istanbul, Londra e San Pietroburgo. È inoltre la città europea con la maggiore superficie di aree verdi[7].
Fondata secondo la tradizione il 21 aprile del 753 a.C. (sebbene scavi recenti nel Lapis Niger farebbero risalire la fondazione a 2 secoli prima[8][9]), nel corso dei suoi tre millenni di storia è stata la prima metropoli dell'umanità,[10] cuore pulsante di una delle più importanti civiltà antiche, che influenzò la società, la cultura, la lingua, la letteratura, l'arte, l'architettura, la filosofia, la religione, il diritto e i costumi dei secoli successivi. Luogo di origine della lingua latina, fu capitale dell'Impero romano che estendeva il suo dominio su tutto il bacino del Mediterraneo e gran parte dell'Europa, dello Stato Pontificio, sottoposto al potere temporale dei papi e del Regno d'Italia (dal 1871 al 1946). Per antonomasia, è definita l'Urbe, Caput Mundi e Città eterna.
Il suo centro storico, delimitato dal perimetro delle mura aureliane, sovrapposizione di testimonianze di quasi tre millenni è espressione del patrimonio storico, artistico e culturale del mondo occidentale europeo[11] e, nel 1980, insieme alle proprietà extraterritoriali della Santa Sede nella città, è stato inserito nella lista dei Patrimoni dell'umanità dell'UNESCO, provvedimento esteso nel 1990 ai territori compresi all'interno delle mura gianicolensi, edificate per volere di papa Urbano VIII.[12][13]
Roma, cuore della cristianità cattolica, è l'unica città al mondo ad ospitare al proprio interno un intero Stato, l'enclave della Città del Vaticano:[14] per tale motivo è spesso definita capitale di due Stati.[15][16]
Rome (en italien : Roma, prononcé [ˈroˑma]) est la capitale de l'Italie depuis 1871. Située au centre-ouest de la péninsule Italienne, près de la mer Tyrrhénienne, elle est également la capitale de la région du Latium, et fut celle de l'Empire romain durant 357 ans. En 2016, elle compte 2 877 215 habitants établis sur 1 285 km2, ce qui fait d'elle la commune la plus peuplée d'Italie et la troisième plus étendue d'Europe après Moscou et Londres1. Son aire urbaine recense 4 356 403 habitants en 20162,3. Elle présente en outre la particularité de contenir un État enclavé dans son territoire : la cité-État du Vatican (Stato della Città del Vaticano), dont le pape est le souverain. C'est le seul exemple existant d'un État à l'intérieur d'une ville.
L'histoire de Rome s'étend sur plus de vingt-huit siècles, depuis sa fondation mythique par Romulus en 753 av. J.-C. jusqu'à son rôle actuel de capitale de la république italienne. Second berceau de la civilisation occidentale après Athènes, la ville fut successivement le centre de la monarchie romaine, de la république romaine (509 av. J.-C. – 27 av. J.-C.), puis de l'Empire romain (27 av. J.-C. – 330). Durant cette période, où nait la célèbre expression proverbiale « tous les chemins mènent à Rome », la ville aurait compté entre un et deux millions d'habitants et domine l'Europe, l'Afrique du Nord et le Moyen-Orient tant militairement que culturellement, diffusant dans ces territoires la langue latine, ses arts et techniques ainsi que la religion chrétienne. Depuis le Ier siècle elle abrite le siège de l'Église catholique romaine, au sein des États pontificaux (752-1870) puis de la Cité du Vatican.
Considérablement agrandie par de grands travaux sous Jules César et surtout sous Auguste, la ville est partiellement détruite lors du Grand incendie de Rome - le Circus Maximus notamment. À partir du XVe siècle, presque tous les papes depuis Nicolas V (1447-1455) perpétuent la tradition de l'architecture romaine et ambitionnent de faire de Rome le principal centre culturel et artistique de l'Occident. La ville devient l'un des foyers de la Renaissance italienne, avec Florence et Venise, et donne naissance au style baroque - dont témoigne encore son centre historique, classé par l'UNESCO comme site du patrimoine mondial4. Des artistes comme Michel-Ange, Raphaël ou Le Bernin s'y installent et produisent des œuvres telles que la basilique Saint-Pierre, la chapelle Sixtine, la fontaine de Trevi, le Capitole ou les Chambres de Raphaël. Au XIXe siècle, Rome est le symbole de l'unité italienne et devient la capitale du Royaume d'Italie, puis de la République après la Seconde Guerre mondiale.
Ville globale, Rome est la troisième destination touristique la plus visitée d'Europe derrière Londres et Paris5. La Ville Éternelle est l'une des plus belles villes du monde, et fréquentée par les touristes depuis le XVIIIe siècle. Le siège de la papauté et le pèlerinage de Rome en font un lieu éminent pour les chrétiens du monde entier depuis des siècles. Les musées du Vatican et le Colisée sont parmi les sites les plus fréquentés. Rome est aussi l'un des plus grands sites archéologiques du monde, et compte également de nombreux ponts et fontaines, 900 églises, ainsi qu'un grand nombre de musées et d'universités. Outre le tourisme, l'économie de la « Ville Éternelle » est également orientée vers les nouvelles technologies, les médias et les télécommunications depuis les années 2000. Bâtie sur sept collines, la ville se situe près de l'embouchure du Tibre et est divisée en vingt-deux rioni. Rome a aussi organisé les Jeux olympiques d'été en 1960. Rome n'est jumelée qu'avec une seule autre ville, Paris, ce qui est vrai dans l'autre sens, avec ce slogan : « Seul Paris est digne de Rome, seule Rome est digne de Paris ».
Roma es una ciudad italiana de 2 877 215 habitantes,23 capital de la región del Lacio y de Italia. Es el municipio más poblado de Italia y es la cuarta ciudad más poblada de la Unión Europea.4 Por antonomasia se la conoce desde fines de la Antigüedad como la Urbe. También es llamada "La Ciudad Eterna" (en italiano: Città Eterna).
En el transcurso de su historia, que abarca tres milenios, llegó a extender sus dominios sobre toda la cuenca del Mediterráneo y gran parte de Europa. Como capital del Imperio romano, se constituyó en una de las primeras grandes metrópolis de la humanidad, centro de una de las civilizaciones antiguas más importantes. Influyó en la sociedad, la cultura, la lengua, la literatura, el arte, la arquitectura, la filosofía, la religión, el derecho y la moral de los siglos sucesivos.
Es la ciudad con la más alta concentración de bienes históricos y arquitectónicos del mundo;5 su centro histórico delimitado por el perímetro que marcan las murallas aurelianas, superposición de huellas de tres milenios, es la expresión del patrimonio histórico, artístico y cultural del mundo occidental europeo.6 En 1980, junto a las propiedades extraterritoriales de la Santa Sede que se encuentran en la ciudad y la Basílica de San Pablo Extramuros, fue incluida en la lista del Patrimonio de la Humanidad de la Unesco.78
Roma es el corazón geográfico de la religión católica y destino de peregrinación (vías romeas) y también la única ciudad del mundo que tiene en su interior un Estado extranjero: el enclave de la Ciudad del Vaticano, que se encuentra bajo el poder temporal del papa.9 Por tal motivo se le ha conocido también como la capital de dos Estados.
Рим (итал. Roma [ˈroːma]) — столица и крупнейший город Италии. Административный центр области Лацио и провинции Рим. Расположен на реке Тибр.
Рим — один из старейших городов мира, древняя столица Римской империи. Ещё в Античности (III век н. э.) Рим стали часто называть Вечным (лат. Roma Aeterna). Одним из первых так назвал Рим римский поэт Альбий Тибулл (I век до н. э.) в своей второй элегии. Представления о «вечности» Рима во многом сохранились и после падения древнеримской цивилизации, принеся соответствующий эпитет в современные языки.
Также Рим называют «городом на семи холмах». Первоначально поселения располагались на холме Палатине, впоследствии были заселены соседние холмы: Капитолий и Квиринал. Несколько позже поселения появились на последних четырёх холмах (Целие, Авентине, Эсквилине и Виминале).

 International cities
International cities
 *European Capital of Culture
*European Capital of Culture
 ITU World Championship Series
ITU World Championship Series
 Netherlands
Netherlands
 Silk road
Silk road

 Sport
Sport
 *European Capital of Culture
*European Capital of Culture

 Sport
Sport
 Triathlon
Triathlon

 Important port
Important port

鹿特丹(荷兰语:Rotterdam 荷兰语读音:[ˌrɔtərˈdɑm] ![]() 聆听)是荷兰南荷兰省的城市,是荷兰第二大城市,位于荷兰的南荷兰省,新马斯河畔。其名称来自于在市中心注入新马斯河的小河鹿特河、以及荷兰语的“坝”(Dam)。鹿特丹长期为欧洲最大的海港,以集装箱运量计算,1980年代曾是世界上第一大港口,在2010年为世界第10。
聆听)是荷兰南荷兰省的城市,是荷兰第二大城市,位于荷兰的南荷兰省,新马斯河畔。其名称来自于在市中心注入新马斯河的小河鹿特河、以及荷兰语的“坝”(Dam)。鹿特丹长期为欧洲最大的海港,以集装箱运量计算,1980年代曾是世界上第一大港口,在2010年为世界第10。
ロッテルダム(オランダ語: Rotterdam [ˌrɔtərˈdɑm] (![]() 音声ファイル))は、オランダの南ホラント州にある基礎自治体(ヘメーンテ)。オランダ語での発音は「ロッタダム」または「ロターダム」と表記する方が近い。
音声ファイル))は、オランダの南ホラント州にある基礎自治体(ヘメーンテ)。オランダ語での発音は「ロッタダム」または「ロターダム」と表記する方が近い。
ロッテルダム港を擁する世界屈指の港湾都市で、人口規模はアムステルダムに次いでオランダ第2位である。世界都市であり、国内の他都市に比べて近代的なビルが立ち並ぶ。
Rotterdam (/ˈrɒtərdæm/, UK also /ˌrɒtərˈdæm/;[8][9] Dutch: [ˌrɔtərˈdɑm] (![]() listen)) is a city in the Netherlands, in South Holland within the Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt river delta at the North Sea. Its history goes back to 1270, when a dam was constructed in the Rotte river, after which people settled around it for safety. In 1340, Rotterdam was granted city rights by the Count of Holland.[10]
listen)) is a city in the Netherlands, in South Holland within the Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt river delta at the North Sea. Its history goes back to 1270, when a dam was constructed in the Rotte river, after which people settled around it for safety. In 1340, Rotterdam was granted city rights by the Count of Holland.[10]
A major logistic and economic centre, Rotterdam is Europe's largest port, and has a population of 633,471 (2017), the second-largest in the Netherlands, just behind Amsterdam.[11]
Rotterdam is known for the Erasmus University, its riverside setting, lively cultural life, and maritime heritage. The near-complete destruction of the city centre in the World War II Rotterdam Blitz has resulted in a varied architectural landscape, including sky-scrapers (an uncommon sight in other Dutch cities) designed by renowned architects such as Rem Koolhaas, Piet Blom, and Ben van Berkel.[12][13]
Rotterdam's logistic success is based on its strategic location by the North Sea, at the mouth of the Nieuwe Maas channel leading into the Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt delta. The rivers Rhine, Meuse, and Scheldt give waterway access into the heart of Western Europe, including the highly industrialized Ruhr. The extensive distribution system including rail, roads, and waterways have earned Rotterdam the nicknames "Gateway to Europe" and "Gateway to the World".[14][15][16]
Rotterdam (prononcé en néerlandais /ˌrɔtərˈdɑm/ Écouter) est une commune néerlandaise, située dans la province de Hollande-Méridionale. Au 1er juillet 2017, la commune comptait 634 253 habitants (environ 1 424 000 dans sa région urbaine). Son agglomération fait partie de la conurbation de la Randstad Holland (7 100 000 habitants entre Amsterdam, Haarlem, La Haye, Dordrecht et Utrecht). Ses habitants sont les Rotterdamois.
Deuxième ville des Pays-Bas en nombre d'habitants après Amsterdam, Rotterdam représente le cœur industriel du pays, et sa position géographique, à l'embouchure du Rhin et de la Meuse, à proximité de la mer du Nord, lui assure une place commerciale stratégique dans les échanges européens, notamment avec l'Allemagne.
Huitième port mondial en 2014, et premier port européen, ses infrastructures portuaires s'étendent sur près de 42 kilomètres. La capacité et la modernité de celles-ci lui garantissent un quasi-monopole sur les arrivées d'hydrocarbures, étant le seul port européen, avec Le Havre, en capacité d'accueillir des supertankers transportant jusqu'à 400 000 tonnes de pétrole. Le port est aussi un pôle important pour les matières premières et les conteneurs.
Fondée au XIIe siècle, Rotterdam s'est organisée autour de la digue de la rivière Rotte (qui donne son nom à la ville) et les premiers ports de pêcheurs : le vieux port, Oude Haven et les quais de Haringvliet. Elle reçoit son statut de ville en 1340. Le commerce y fleurit pendant plusieurs siècles, tandis que le port s'étend et que le commerce avec les Indes occidentales et orientales s'accroît. Ville natale du philosophe humaniste Érasme au XVIe siècle et du peintre Pieter de Hooch au XVIIe siècle, elle favorise la vie culturelle et participe au rayonnement néerlandais durant le Siècle d'or. Au XIXe siècle, après une stagnation de son commerce due au blocus continental et à l'inadaptation de son port, la ville grandit à nouveau vers 1870, avec le percement d'une nouvelle voie d'eau qui lui donne un accès direct à la mer du Nord, l'agrandissement de son port et l'industrialisation de ses infrastructures. Des années de récession résultent de la Première Guerre mondiale, suivie de la crise économique de 1929. La guerre de 1939-1945 met un coup d'arrêt à ce développement, le centre de Rotterdam étant totalement détruit par l'armée nazie, lors du bombardement aérien du 14 mai 1940 qui force le pays à capituler. La reconstruction reprend après-guerre, ainsi que l’expansion du port et des industries associées. Après une récession dans les années 1980, due aux chocs pétroliers successifs, la ville diversifie ses activités économiques et commerciales en lien avec l'expansion de son port dans les années 2000. Elle développe son architecture contemporaine, met en valeur ses musées et son art moderne, et augmente ainsi le potentiel touristique de la ville.
Rotterdam a souvent été confrontée à de nombreux défis politiques, économiques, historiques. La maîtrise des eaux et des risques liés aux changements climatiques reste, pour la ville, un enjeu primordial du XXIe siècle.
Rotterdam (AFI: /rotterˈdam/ o /ˈrɔtterdam/[1][2]; in olandese [ˌrɔtərˈdɑm], ) è la seconda città dei Paesi Bassi dopo la capitale Amsterdam, situata nella provincia dell'Olanda Meridionale. La città ha il più grande porto d'Europa[3], collocato sulle rive del fiume Nieuwe Maas. Il nome Rotterdam deriva da quello di una diga (dam) su un piccolo fiume, la Rotte, che si unisce alla Nieuwe Maas nel cuore della città.
Róterdam1 (en neerlandés Rotterdam AFI: ![]() [ɾɔtər'dɑm] (?·i)) es una ciudad neerlandesa situada al oeste del país, en la provincia de Holanda Meridional, y puerto sobre el río Mosa, cerca de La Haya. Situada a 30 km del mar, tiene una población de 623 556 habitantes.2 El área metropolitana de Róterdam cuenta con una población de 2,82 millones de personas. La ciudad es conocida por la Universidad Erasmus, su vida cultural y su patrimonio marítimo.
[ɾɔtər'dɑm] (?·i)) es una ciudad neerlandesa situada al oeste del país, en la provincia de Holanda Meridional, y puerto sobre el río Mosa, cerca de La Haya. Situada a 30 km del mar, tiene una población de 623 556 habitantes.2 El área metropolitana de Róterdam cuenta con una población de 2,82 millones de personas. La ciudad es conocida por la Universidad Erasmus, su vida cultural y su patrimonio marítimo.
El puerto de Róterdam, Europoort, es el más grande de Europa y el segundo más grande del mundo. Está comunicado con el río Rin.
Роттерда́м (нидерл. Rotterdam [ˌrɔtərˈdɑm] ![]() слушать) — город и община в Нидерландах. Расположен в провинции Южная Голландия при впадении реки Ньиве-Маас в Северное море. С населением 617 347 жителей (на 1 января 2012)[4] является вторым по количеству жителей городом в Нидерландах после Амстердама. Роттердам входит в состав крупной городской агломерации Рандстад.
слушать) — город и община в Нидерландах. Расположен в провинции Южная Голландия при впадении реки Ньиве-Маас в Северное море. С населением 617 347 жителей (на 1 января 2012)[4] является вторым по количеству жителей городом в Нидерландах после Амстердама. Роттердам входит в состав крупной городской агломерации Рандстад.
Девиз Роттердама — Sterker door strijd («Окреп в борьбе»).
Центр машиностроения. Крупный транспортный узел (железные и шоссейные дороги); морской (на Северном море) и речной (река Ньиве-Маас) порты; аэропорт Роттердам-Гаага. Порт Роттердама является самым большим в Европе, а с 1962 по 2004 года он являлся самым крупным в мире (в настоящий момент он уступил это звание Шанхаю).
 *Track and field athletics
*Track and field athletics
 4x400 m Woman
4x400 m Woman
 *Track and field athletics
*Track and field athletics
 4x100 m Woman
4x100 m Woman
 Atomic bomb
Atomic bomb
 BRICS summit
BRICS summit

 History
History
 M 1500 - 2000 AD
M 1500 - 2000 AD

 History
History

 History
History
 N 2000 - 2100 AD
N 2000 - 2100 AD
 Leichtathletik-Weltmeisterschaften
Leichtathletik-Weltmeisterschaften
 2005 Helsinki
2005 Helsinki
 Leichtathletik-Weltmeisterschaften
Leichtathletik-Weltmeisterschaften
 1999 Seville
1999 Seville
 Leichtathletik-Weltmeisterschaften
Leichtathletik-Weltmeisterschaften
 1993 Stuttgart
1993 Stuttgart




 Military, defense and equipment
Military, defense and equipment
 Nuclear Weapon
Nuclear Weapon

 Party and government
Party and government
 Group of the twenty most important industrial and emerging countries
Group of the twenty most important industrial and emerging countries

 Party and government
Party and government
 BRICS
BRICS
 Russia
Russia
 Silk road
Silk road
 Shanghai Cooperation Organization
Shanghai Cooperation Organization

 States of Asia
States of Asia

 States of Europe
States of Europe

 States of Europe
States of Europe

 United Nations
United Nations
 United Nations Security Council
United Nations Security Council
 Hydrogen bomb
Hydrogen bomb
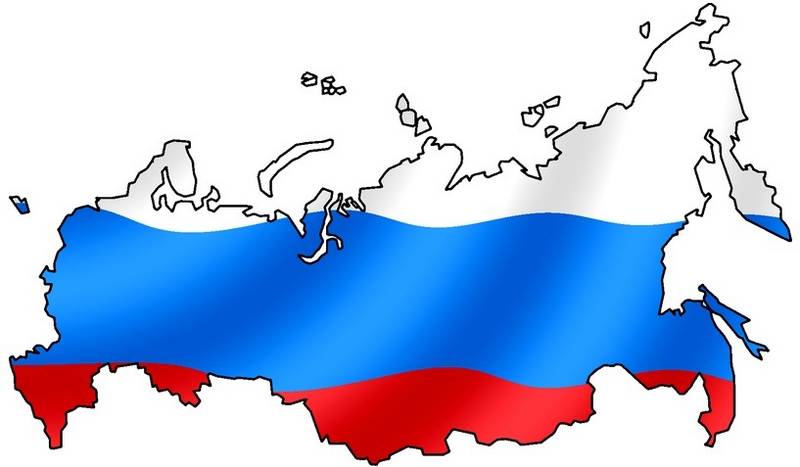
俄罗斯联邦[9](俄语:Российская Федерация,缩写为РФ),通称俄罗斯(Россия)[10],是位于欧亚大陆北部的联邦共和国,国土横跨欧亚两大洲,为世界上土地面积最大的国家,拥有1709万平方公里的面积,占地球陆地面积八分之一[11][12];它也是世界上第九大人口国家,拥有1.4亿人口,77%居住于其较为发达的欧洲部分。俄罗斯国土覆盖整个亚洲北部及东欧大部,横跨11个时区,涵盖广泛的环境和地形。拥有全世界最大的森林储备和含有约世界四分之一的淡水的湖泊[13]。俄罗斯有十四个陆上邻国(从西北方向起逆时针序):挪威、芬兰、爱沙尼亚、拉脱维亚、立陶宛、波兰、白俄罗斯、乌克兰、格鲁吉亚、阿塞拜疆、哈萨克斯坦、中国、蒙古和朝鲜(其中立陶宛和波兰仅与俄罗斯外飞地加里宁格勒州接壤),另外与阿布哈兹和南奥塞梯两个只有俄罗斯承认的非联合国会员国接壤。同时,俄罗斯还与日本、美国、加拿大、格陵兰(丹麦)、冰岛、瑞典、土耳其隔海相望。俄罗斯北部和东部分别为北冰洋和太平洋包围,西北和西南则分别可经由波罗的海和黑海通往大西洋。
俄罗斯历史始于欧洲的东斯拉夫民族,聚集区域自公元3世纪至8世纪逐渐扩大[14]。在9世纪,源自北欧的瓦良格人武士精英建立了基辅罗斯这个中世纪国家并开始统治。公元988年,国家从拜占庭帝国采纳了东正教会,随后由此开始,千年拜占庭与斯拉夫文化的融合成为了今日的俄罗斯文化[15]。基辅罗斯最终解散分化为众多公国,被蒙古人逐一击破,并均在13世纪成为了金帐汗国的一部分。莫斯科大公自14世纪起逐渐崛起并统一周边俄罗斯诸侯国,在15世纪成功从金帐汗国独立,且成为了基辅罗斯文化和政治的继承者。16世纪起伊凡四世自称沙皇,自诩“第三罗马”。在18世纪,俄罗斯沙皇国通过征服、吞并和探索而扩张。彼得一世称帝成立了俄罗斯帝国,最终成为史上领土第三大帝国,疆域最大曾自中欧的波兰连绵至北美的阿拉斯加[16][17]。
1917年俄国革命后,俄罗斯苏维埃联邦社会主义共和国成为了世界上第一个宪法意义上的社会主义国家[18],并成为随后成立的苏维埃社会主义共和国联盟的主体和其最大的加盟共和国。二战时期,苏联为同盟国的胜利扮演了决定性的角色。在战后其崛起成为公认的超级大国,并在冷战时期与美国互相竞争。苏联时期产生了20世纪的许多最重要的科技成就,其中包括世界第一颗人造地球卫星,以及首次将人类送入太空。在1990年,苏联为世界上第二大经济体[19],且拥有世界上最多的常备军人以及最多的大规模杀伤性武器库存。1991年苏联解体后,包括俄罗斯在内的15个共和国从原苏联独立;身为原苏联最大的加盟共和国,俄罗斯通过修宪改制为俄罗斯联邦,成为原苏联的唯一法理继承国家,政体采用联邦制、民主共和制及半总统制。
截至2015年,俄罗斯根据国民生产总值为世界第13大经济体,根据购买力平价为世界第六大经济体。俄罗斯拥有世界上最大储量的矿产和能源资源[20],是世界上最大的石油和天然气输出国[21][22]。俄罗斯为世界大国之一,为认定的拥核国家,联合国安理会常任理事国,G20、欧洲理事会、亚太经合组织、上合组织、欧安组织、世贸组织和金砖国家成员。它也是独联体、集体安全条约组织的领导者和欧亚经济联盟创始成员。俄罗斯亦是世界八大工业国之一。
Russland (russisch Россия [rɐˈsʲijə] , Transkription Rossija) bzw. die Russische Föderation (oder der russischen Bezeichnung entsprechend Russländische Föderation; russisch Российская Федерация, , Transkription Rossijskaja Federazija)[9] ist ein souveräner, föderativer Staat im nordöstlichen Eurasien und mit etwa 17 Millionen Quadratkilometern flächenmäßig der größte Staat der Erde. Russland umfasst mehr als ein Achtel der bewohnten Landmasse der Erde und steht mit 144 Millionen Einwohnern (2017) an 9. Stelle der bevölkerungsreichsten Länder; es ist zugleich eines der am dünnsten besiedelten. Der europäische Teil des Staatsgebiets ist viel dichter besiedelt und verstädtert als der über dreimal so große asiatische Teil: Etwa 77 % der Bevölkerung (110 Millionen Einwohner) leben westlich des Urals. Die Hauptstadt Moskau ist eine der größten Städte und Metropolregionen der Welt; als weiteres wichtiges Zentrum gilt Sankt Petersburg, das zwischen 1712 und 1918 Hauptstadt war und eine Brücke für Kunst und Kultur aus Westeuropa bildete.
Die nächstgrößeren Millionenstädte Russlands sind Nowosibirsk in Sibirien, Jekaterinburg im Ural und Nischni Nowgorod an der Wolga. Weitere Großstadtregionen sind Tscheljabinsk, Ufa und Kasan.
Das heutige Russland entwickelte sich aus dem Großfürstentum Moskau, einem Teilfürstentum des früheren ostslawischen Reiches Kiewer Rus, zu einem über einhundert Ethnien zählenden Vielvölkerstaat, wobei ethnische Russen heute fast 80 Prozent der Bevölkerung ausmachen. Die föderale Gliederung Russlands besteht aus acht Föderationskreisen und 85 Föderationssubjekten.
Die Russische Föderation ist „Fortsetzerstaat“[10] der Sowjetunion in internationalen Organisationen, Atommacht und ständiges Mitglied des Weltsicherheitsrates. Nach der Erholung von der postkommunistischen Transformationskrise der 1990er Jahre wurde Russland die nach Kaufkraftparität sechstgrößte Volkswirtschaft der Welt, zwischen Deutschland und Brasilien (Schätzung für 2016).[11]
Russlands Rohstoffreserven sind mit etwa 20 bis 30 % die wahrscheinlich größten der Welt,[12][13][14] mit erheblichen Vorkommen von Primärenergieträgern, vor allem Erdgas.
Russland gehört zu den anerkannten Nuklearmächten und besitzt das weltgrößte Arsenal an Massenvernichtungswaffen. Russland ist Großmacht und Regionalmacht und wird teilweise als potentielle Supermacht betrachtet.[15] Es ist ständiges Mitglied im Sicherheitsrat der Vereinten Nationen, G 20-Mitglied, Mitglied des Europarates, der APEC, der Shanghaier Organisation für Zusammenarbeit (SCO), der OSCE, der WTO; es ist führendes Mitglied in der Gemeinschaft Unabhängiger Staaten (GUS), der Organisation des Vertrags über kollektive Sicherheit (OVKS) und der Eurasischen Wirtschaftsunion (mit Armenien, Kasachstan, Kirgisistan und Weißrussland).
Russland ist ein Schwellenland im Bereich des oberen mittleren Einkommens.[16] Im Human Development Index der Vereinten Nationen stand Russland 2016 mit 0,8 (von 1) auf Platz 49,[17] der Gini-Koeffizient lag bei 37,7.
Das Regierungssystem Russlands wird von Politikwissenschaftlern entsprechend dem Wortlaut der Verfassung meist formal als Verbindung präsidentieller und parlamentarischer Formen eingeordnet; die Verfassungswirklichkeit des politischen Systems entspricht jedoch eher den Modellen defekter Demokratien oder der Postdemokratie, zumal der Präsident fast autokratische Macht ausübt.[18][19][20] Für die politische Ordnung wird in Russland gelegentlich von offizieller Seite der Begriff „Gelenkte Demokratie“ im affirmativen Sinne gebraucht.[21]
Die Annexion der Krim im März 2014 belastet die Beziehungen zwischen Russland und dem Westen. Der russischen Regierung wird vorgeworfen, die europäische Friedensordnung zu verletzen.[22]
Das Land war 2016 mit 69,9 Mrd. Dollar für 4,1 % der weltweiten Militärausgaben verantwortlich und liegt damit im internationalen Vergleich hinter den Vereinigten Staaten mit 611 Mrd. Dollar (36 %) und China mit 215 Mrd. Dollar (13 %) auf Platz 3, gefolgt von Saudi-Arabien und Indien.[23][24]
ロシア連邦(ロシアれんぽう、ロシア語: Российская Федерация:英語名 Russian Federation)、またはロシア (Россия) は、ユーラシア大陸北部にある共和制及び連邦制国家。
地理的にロシアの国境は、北西から南東へ、ノルウェー、フィンランド、エストニア、ラトビア、リトアニアおよびポーランド(ともにカリーニングラード州と隣接)、ベラルーシ、ウクライナ、ジョージア、アゼルバイジャン、カザフスタン、中華人民共和国、モンゴル国、朝鮮民主主義人民共和国と接する。海上境界線としては、日本とはオホーツク海・宗谷海峡・根室海峡・珸瑤瑁水道、アメリカ合衆国とはベーリング海峡でアラスカ州と接する。ロシアの面積は17,075,400km2で世界最大であり、地球上の居住地域の8分の1を占める。2012年時点で、ロシアの人口は1億4300万人で世界第9位である[3]。国土は北アジア全体および東ヨーロッパの大部分に広がることに伴い、ロシアは11の標準時を有し、広範な環境および地形を包含する。
ロシアの歴史は、3世紀から8世紀までの間にヨーロッパで認識され始めた東スラヴ人の歴史に始まる[4]。9世紀、ヴァリャーグの戦士の精鋭およびその子孫により設立及び統治されて、キエフ大公国の中世国家が誕生した。988年、東ローマ帝国から正教会を導入し、次の千年紀のロシア文化を特徴付ける東ローマ帝国およびスラブ人の文化の統合が始まった[5]。キエフ大公国は最終的には多くの国に分裂し、キエフ大公国の領土の大部分はモンゴルに制圧され、遊牧国家ジョチ・ウルスの属国になった[6]。モスクワ大公国は次第に周辺のロシアの公国を再統合し、ジョチ・ウルスからの独立を獲得し、キエフ大公国の文化的および政治的な遺産を支配するようになった。18世紀までにモスクワ大公国は、王朝による征服・併合、シェレホフ提督による探検を通じ、史上第3位の大帝国であるロシア帝国となり、版図がポーランドから北米のアラスカまで広がった[7][8]。
しかし帝国は国土に見合う開発資金を国内で捻出することができなかった。サンクトペテルブルクの貿易為替銀行にドイツ銀行を参加させたが、露仏同盟を結んで以来国際金融市場から外資が雪崩れ込むようになった。
ロシア革命後、ロシア・ソビエト連邦社会主義共和国がソビエト連邦最大かつ指導的な構成国となり、世界初の憲法上の社会主義国および広く認められた超大国となり[9]、第二次世界大戦において連合国の勝利に決定的な役割を果たした[10][11]。ソビエト時代には、世界初の人工衛星および世界初の有人宇宙飛行を含む20世紀の最も重要な複数の技術的偉業を経験した。1991年のソ連崩壊後、ロシア・ソビエト連邦社会主義共和国は自らをロシア連邦として再構成し、連邦国家の継続的な法人格として認識されている。ソ連政府は国民にあまねく賃貸住宅を配分していたが、それらを建設するだけで巨額の財政負担となっており、財政再建中のロシア連邦がリフォームすることなどかなわず、無償で住民が物件を取得できるようにしてしまい急激な私有化を進めた[12]。私有化されていないものは地方自治体への譲渡が進んで、人口減少社会となる中、若者向けに低家賃で貸し出されている[12]。
1996年11月、ロシアは第一回だけで10億ドルのユーロ債を起債した[13]。それまでの累積ユーロ債発行額は160億ドルほどに達した[13]。1997年、第一回サンクトペテルブルク国際経済会議が開かれた。1998年、ロシア財政危機。1999年、ロスチャイルド代理人のアルフレッド・ハルトマン博士が資金洗浄の国内捜査線上で名前をとりあげられた。
2003年、ミハイル・ホドルコフスキーが脱税などの罪で逮捕・起訴され、ユコスの社長を辞任した。シブネフチとの合併が取り消されるなどして株価が乱高下し、内部者取引が横行した。2005年でロシアの住宅私有化率は63%に達し[12]、国際的な不動産価格の下落へつながっていった。2007年、ホドルコフスキーを除くユコス株主らは、ロシア政府がユコスを破綻させたとしてハーグの常設仲裁裁判所へ提訴した(ユコス破綻事件)。2010年6月26日、政府側のロスネフチに賠償命令が出た。7月27日、内部者取引と株価操作を取り締まる法案がようやく批准された[14]。これは翌年から施行された。
2014年ウクライナ騒乱が2月に起きてVTBが態度を硬化させた。7月、ユコス破綻事件で政府は19億ユーロの賠償金支払いを命じられていたが、12月に欧州人権裁判所が政府の上訴を棄却した[15]。2016年4月、ハーグ地区裁判所が、ロシア政府に株主らへ500億ドルの賠償金支払いを命じた常設仲裁裁判所の判決を棄却した[16]。
2014年時点で、ロシアの経済は名目GDPで世界第9位かつ購買力平価で世界第6位であった[17]。ロシアの豊富な鉱物およびエネルギー資源は世界最大の埋蔵量であり[18]、世界最大の原油生産国および世界最大の天然ガス生産国の一つである。ロシアは核保有を認められた5大国の一つであり、世界最大の大量破壊兵器保有量がある。ロシアは列強および国際連合安全保障理事会常任理事国であり、独立国家共同体の指導国であるだけでなく、G20、欧州評議会、アジア太平洋経済協力、上海協力機構、ユーラシア経済共同体、欧州安全保障協力機構 (OSCE)、世界貿易機関 (WTO) 加盟国である。
Russia (Russian: Росси́я, tr. Rossiya, IPA: [rɐˈsʲijə]), officially the Russian Federation[12] (Russian: Росси́йская Федера́ция, tr. Rossiyskaya Federatsiya, IPA: [rɐˈsʲijskəjə fʲɪdʲɪˈratsɨjə]), is a transcontinental country in Eastern Europe and North Asia.[13] At 17,125,200 square kilometres (6,612,100 sq mi),[14] Russia is the largest country in the world by area, covering more than one-eighth of the Earth's inhabited land area,[15][16][17] and the ninth most populous, with about 146.77 million people as of 2019, excluding Crimea.[8] About 77% of the population live in the western, European part of the country. Russia's capital, Moscow, is the largest metropolitan area in Europe proper[18] and one of the largest cities in the world; other major cities include Saint Petersburg, Novosibirsk, Yekaterinburg and Nizhny Novgorod. Extending across the entirety of Northern Asia and much of Eastern Europe, Russia spans eleven time zones and incorporates a wide range of environments and landforms. From northwest to southeast, Russia shares land borders with Norway, Finland, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania and Poland (both with Kaliningrad Oblast), Belarus, Ukraine, Georgia, Azerbaijan, Kazakhstan, China, Mongolia and North Korea. It shares maritime borders with Japan by the Sea of Okhotsk and the U.S. state of Alaska across the Bering Strait. However, Russia recognises two more countries that border it, Abkhazia and South Ossetia, both of which are internationally recognized as parts of Georgia.
The East Slavs emerged as a recognizable group in Europe between the 3rd and 8th centuries AD.[19] Founded and ruled by a Varangian warrior elite and their descendants, the medieval state of Rus arose in the 9th century. In 988 it adopted Orthodox Christianity from the Byzantine Empire,[20] beginning the synthesis of Byzantine and Slavic cultures that defined Russian culture for the next millennium.[20] Rus' ultimately disintegrated into a number of smaller states; most of the Rus' lands were overrun by the Mongol invasion and became tributaries of the nomadic Golden Horde in the 13th century.[21] The Grand Duchy of Moscow gradually reunified the surrounding Russian principalities and achieved independence from the Golden Horde. By the 18th century, the nation had greatly expanded through conquest, annexation, and exploration to become the Russian Empire, which was the third largest empire in history, stretching from Poland on the west to Alaska on the east.[22][23]
Following the Russian Revolution, the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic became the largest and leading constituent of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics, the world's first constitutionally socialist state.[24] The Soviet Union played a decisive role in the Allied victory in World War II,[25][26] and emerged as a recognized superpower and rival to the United States during the Cold War. The Soviet era saw some of the most significant technological achievements of the 20th century, including the world's first human-made satellite and the launching of the first humans in space. By the end of 1990, the Soviet Union had the world's second largest economy, largest standing military in the world and the largest stockpile of weapons of mass destruction.[27][28][29] Following the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991, twelve independent republics emerged from the USSR: Russia, Ukraine, Belarus, Kazakhstan, Uzbekistan, Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia, Kyrgyzstan, Moldova, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan and the Baltic states regained independence: Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania; the Russian SFSR reconstituted itself as the Russian Federation and is recognized as the continuing legal personality and a successor of the Soviet Union.[30] It is governed as a federal semi-presidential republic.
Russia's economy ranks as the twelfth largest by nominal GDP and sixth largest by purchasing power parity in 2015.[31] Russia's extensive mineral and energy resources are the largest such reserves in the world,[32] making it one of the leading producers of oil and natural gas globally.[33][34] The country is one of the five recognized nuclear weapons states and possesses the largest stockpile of weapons of mass destruction.[35] Russia is a great power as well as a regional power and has been characterised as a potential superpower. It is a permanent member of the United Nations Security Council and an active global partner of ASEAN,[36][37][38] as well as a member of the Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO), the G20, the Council of Europe, the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC), the Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe (OSCE), and the World Trade Organization (WTO), as well as being the leading member of the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS), the Collective Security Treaty Organization (CSTO) and one of the five members of the Eurasian Economic Union (EEU), along with Armenia, Belarus, Kazakhstan and Kyrgyzstan.
La Russie, en forme longue la fédération de Russiea (en russe : Россия, Rossiab ; [forme longue] Российская Федерация, Rossiïskaïa Federatsiïac), est un État fédéral transcontinental dont le territoire est le plus vaste de la planète.
Sa population est estimée à 146,88 millions d’habitants en 20181. Le pays est à cheval sur l’Asie du Nord (74,7 % de sa superficie) et sur l’Europe (25,3 % de sa superficie, mais 78 % de ses habitants sont en Europe6). Son territoire s'étend d’ouest en est (de Kaliningrad à Vladivostok) sur plus de 9 000 km pour une superficie de dix-sept millions de kilomètres carrés (17 000 000 km2) et compte onze fuseaux horaires7. Sa capitale est Moscou, sa langue officielle le russe et sa monnaie le rouble. Bien qu’entourée de nombreuses mers et de deux océans, la Russie est caractérisée par un climat continental avec des milieux froids et hostiles sur la majeure partie du territoire.
La Russie dispose de ressources minières (houille, fer, nickel, diamant, etc.) et énergétiques (pétrole, gaz naturel, hydroélectricité) abondantes qui en font l’un des principaux producteurs et exportateurs mondiaux. Elle se dote, à l'époque de l’URSS, d'une industrie lourde puissante (aciéries, raffineries, industrie chimique, etc.). Les secteurs liés à l’armement, au nucléaire et à l’aérospatiale sont également fortement développés, ce qui a permis au pays de jouer un rôle pionnier dans la conquête de l'espace.
La république socialiste fédérative soviétique de Russie (RSFSR) fut la plus importante des quinze républiques de l’Union des républiques socialistes soviétiques, dont elle constituait le noyau historique.
Fin 1991, l’URSS éclate en quinze États indépendants souverains, dont la Russie, qui a hérité des trois quarts du territoire de l’ancienne superpuissance, de plus de la moitié de sa population, des deux tiers de son industrie et de la moitié de sa production agricole. La Russie occupe aussi dans la continuité sa place dans les institutions internationales, dont le siège permanent au Conseil de sécurité des Nations unies, et a également assumé le passif financier de l’URSS. La Russie est aussi fondatrice de la Communauté des États indépendants (CEI) qui rassemble neuf des quinze ex-républiques soviétiques.
Elle demeure une fédération constituée de 85 sujets disposant d’une autonomie politique et économique variable. Le découpage, tenant compte entre autres de la présence de minorités, existait déjà dans l’ancienne URSS.
Après la fin du système soviétique au début des années 1990, le pays a graduellement adopté une économie de marché et un régime parlementaire pluraliste. Aspirant à suivre la mondialisation, la Russie se considère par ailleurs comme étant le pont entre l'Europe et l'Asie. Aujourd'hui, la Russie fait partie des BRICS aux côtés de la Chine, de l'Inde, de l'Afrique du Sud et du Brésil. Elle est actuellement douzième puissance mondiale en 2017 en matière de PIB à valeur nominale8 et sixième en parité de pouvoir d'achat9. En devenant la première capitalisation boursière européenne10, le géant gazier Gazprom devient le symbole de cette expansion russe11, au même titre que le leader mondial de l'aluminium Rusal. Avec la chute du rouble (liée aux réactions internationales à la suite de la crise de Crimée) et du pétrole en 2014, le PIB de la Russie est retombé en 2015 au niveau de celui de 2006, ce qui fait un PIB nominal par habitant d'un peu plus de 9 000 $12.
La Russia (in russo: Россия?, traslitterato: Rossija, ) o la Federazione Russa (in russo: Российская Федерация?, traslitterato: Rossijskaja Federacija, ) è uno Stato transcontinentale che si estende tra l'Europa e l'Asia ed è il più vasto Stato del mondo, con una superficie di circa 17 098 242 km² (per più della metà disabitato).[5]
Confina con Norvegia, Finlandia, Estonia, Lettonia, Lituania, Polonia, Bielorussia, Ucraina, Georgia e territori contesi di Ossezia del Sud e Abcasia, Azerbaigian, Kazakistan, Cina, Corea del Nord e Mongolia; assieme alla Cina, è lo Stato al mondo con il maggior numero di Stati limitrofi (14), mentre, considerando anche i due Stati con ridotto riconoscimento internazionale di Abcasia e Ossezia del Sud (entrambi riconosciuti dalla Russia), gli Stati confinanti con la Russia diventano 16. Essa possiede, inoltre, confini marittimi con il Giappone (attraverso il mare di Ochotsk) e gli Stati Uniti (attraverso lo stretto di Bering). È bagnata a Nord-Ovest dal mar Baltico nel golfo di Finlandia, a Nord dal mar Glaciale Artico, a Est dall'oceano Pacifico e a Sud dal mar Nero e dal mar Caspio. Comprende anche l'exclave dell'Oblast' di Kaliningrad, compresa tra mar Baltico, Polonia e Lituania. Nel 2016 contava circa 144 milioni di abitanti, ha come capitale Mosca ed è tradizionalmente suddivisa tra Russia europea e asiatica dalla catena montuosa degli Urali.
Come principale successore dell'Unione Sovietica, la Russia ha mantenuto il seggio di membro permanente nel Consiglio di sicurezza delle Nazioni Unite. Resta ancora secondo alcuni accademici una grande potenza, tra i protagonisti della storia del XX secolo, sia nel secondo conflitto mondiale, sia nel secondo dopoguerra, con la guerra fredda e l'opposizione attraverso il blocco sovietico al cosiddetto blocco occidentale, che annoverava anche l'altra superpotenza, gli Stati Uniti. È uno Stato con una forte influenza politica all'interno della Comunità degli Stati Indipendenti, che comprende tutte le ex-Repubbliche dell'Unione Sovietica tranne le tre repubbliche baltiche, il Turkmenistan, la Georgia (uscita nel 2008) e l'Ucraina (uscita come membro osservatore nel 2014). È inoltre uno degli Stati fondatori dell'Unione eurasiatica, che comprende, oltre la Russia, la Bielorussia, l'Armenia e il Kazakistan e vede il Tagikistan e l'Uzbekistan come Stati osservatori.
Nei primi anni del XXI secolo l'economia ha presentato tassi di crescita tra i più elevati a livello globale, tanto che la Russia è considerata uno dei cinque Paesi cui ci si riferisce con l'acronimo BRICS.[6] La crisi finanziaria internazionale si è fatta però sentire duramente a partire dall'autunno 2008, mettendo in dubbio molte delle certezze acquisite in un decennio di espansione[7]. Il 18 marzo 2014, in seguito all'esito di un referendum che vide la schiacciante vittoria dei favorevoli all'annessione alla Russia ed era stato indetto dalle forze politiche della Repubblica autonoma di Crimea che si era proclamata unilateralmente indipendente dall'Ucraina in data 11 marzo 2014, è cominciato l'iter amministrativo di integrazione della penisola di Crimea (compresa quindi anche la città autonoma di Sebastopoli) come nuovo soggetto federale della Federazione Russa, sebbene l'occupazione non sia riconosciuta dall'ONU.
Rusia (en ruso: Россия, romanización: Rossíya)n. 1 o formalmenten. 2 Federación de Rusian. 1 (en ruso: Российская Федерация, romanización: Rossíyskaya Federátsiya) es el país más extenso del mundo. La Federación de Rusia cuenta con una superficie de 17 098 242 km2,1 equivalente a la novena parte de la tierra firme del planeta, y con gran variedad de relieve y de ecosistemas. Su capital es la ciudad federal de Moscú.
Esta república semipresidencialista, formada por ochenta y tres sujetos federales, es el noveno país por población al tener 146 804 372 habitantes7. Ocupa toda el Asia del Norte y alrededor del 40 % de Europa (principalmente Europa Oriental),n. 3 y es un país transcontinental. En Rusia hay once zonas horarias, desde UTC+2 hasta UTC+12.n. 4 Rusia tiene las mayores reservas de recursos energéticos y minerales del mundo aún sin explotar, y es considerada la mayor superpotencia energética. Posee las mayores reservas de recursos forestales y la cuarta parte del agua dulce sin congelar del mundo.
Rusia es el país que limita con mayor número de países, un total de dieciséis,n. 5 y el que tiene las fronteras más extensas. Limita con los siguientes países (empezando por el noroeste y siguiendo el sentido antihorario): Noruega, Finlandia, Estonia, Letonia, Bielorrusia, Lituania,n. 6 Polonia,n. 6 Ucrania,n. 7 Georgia,n. 8 Azerbaiyán, Kazajistán, República Popular China, Mongolia y Corea del Norte. Tiene límites de aguas territoriales con varios de los anteriores, con Japón y con los Estados Unidos (en concreto, con el estado de Alaska). Limita también con los estados de reconocimiento limitado Abjasia, Osetia del Sur y la Unión de Repúblicas Populares (Nueva Rusia). Las costas de Rusia están bañadas por el océano Ártico, el norte del Océano Pacífico y mares interiores como el Báltico, el Negro y el Caspio.
La historia de Rusia comienza con los eslavos orientales. Los eslavos emergieron como un grupo reconocible en Europa entre los siglos III y VIII.7 Fundado y dirigido por una clase guerrera noble de vikingos y sus descendientes, el primer estado de los eslavos orientales, la Rus de Kiev, surgió en el siglo IX y en el año 988 adoptó el cristianismo procedente del Imperio bizantino. Comenzó entonces una síntesis de las culturas bizantina y eslava que definiría la rusa durante el siguiente milenio.8 Más tarde, la Rus de Kiev se desintegró en muchos pequeños estados feudales, de los cuales el más poderoso fue el Principado de Moscú, que se convirtió en la fuerza principal en el proceso de la reunificación rusa y la lucha por la independencia contra la Horda de Oro. Moscú reunificó gradualmente los principados rusos circundantes y comenzó a dominar en el legado cultural y político de la Rus de Kiev. En el siglo XVIII, el país se expandió mediante la conquista, la anexión y la exploración hasta convertirse en el tercer imperio más grande de la historia, el ruso, al extenderse desde Polonia, en poniente, hasta el Océano Pacífico y Alaska.
Rusia ha tenido poder y mucha influencia en el mundo: primero, en los tiempos del Imperio Ruso; después, como el país dominante de la Unión Soviética (URSS), el primero y el más grande de los estado socialistas constitucionalmente establecidos y una superpotencia reconocida como tal; y, actualmente, como la Federación de Rusia. Tiene una larga tradición de calidad en todos los aspectos de las artes y de las ciencias.7 La Federación Rusa se fundó en 1991, al disolverse la Unión Soviética, y es reconocida como la heredera de la personalidad legal de ésta.9 Su economía tiene uno de los mayores crecimientos del mundo. Es el octavo país por PIB nominal y el sexto por PIB (PPA), con el tercer presupuesto militar más grande del mundo. Es uno de los cinco países con armas nucleares reconocidos y posee el mayor arsenal de armas de destrucción masiva del mundo.10 Rusia es miembro permanente del Consejo de Seguridad de Naciones Unidas, miembro del G20, del APEC y de la OCS, y tiene mucha influencia en los países que fueron repúblicas soviéticas, particularmente en la Comunidad de Estados Independientes (CEI).
Росси́я, официально также Росси́йская Федера́ция[e] (РФ[f]) — государство в Восточной Европе и Северной Азии. Территория России в рамках её конституционного устройства[c] составляет 17 125 191[5] км²; население страны (в пределах её заявленной территории[c]) составляет 146 793 744[6] чел. (2019). Занимает первое место в мире по территории, шестое — по объёму ВВП по ППС и девятое — по численности населения.
Столица — Москва. Государственный язык — русский.
Президентско-парламентская республика[2] с федеративным устройством. С 7 мая 2012 года пост Президента занимает Владимир Путин. C 8 мая 2012 года пост Председателя Правительства занимает Дмитрий Медведев.
В состав Российской Федерации входят 85 субъектов[c], 46 из которых именуются областями, 22[c] — республиками, 9 — краями, 3[c] — городами федерального значения, 4 — автономными округами и 1 — автономной областью. Всего в стране около 157 тысяч населённых пунктов[15].
Россия граничит с шестнадцатью государствами (больше, чем любая другая страна в мире), а также двумя частично признанными государствами.
Россия — многонациональное государство, отличающееся большим этнокультурным многообразием[16]. Бо́льшая часть населения (около 75 %) относит себя к православию[17], что делает Россию страной с самым многочисленным православным населением в мире.
Ядерная держава[18][19][20]; одна из ведущих промышленных[21][22] и космических держав мира[23]. Россия занимает 1-е место в рейтинге самых образованных стран мира [24]; Русский язык — язык мирового значения, один из шести официальных и рабочих языков ООН, ЮНЕСКО и других международных организаций. Россия является постоянным членом Совета безопасности ООН с правом вето; одна из современных великих держав мира[25].
После распада СССР в конце 1991 года Российская Федерация была признана международным сообществом как государство-продолжатель СССР[26] в вопросах ядерного потенциала, внешнего долга, государственной собственности за рубежом, а также членства в Совете Безопасности ООН[27]. Россия состоит в ряде международных организаций: ООН, ОБСЕ, Совете Европы, ЕАЭС, СНГ, ОЧЭС, ОДКБ, ГКМЧП, ВОИС, ММО, ВТО, ЮНВТО, ВФП, ШОС, АТЭС, БРИКС, КООМЕТ, МОК, МЭК, ISO, EUREKA, IRENA, G20 и других.
По данным Всемирного банка, объём ВВП по ППС за 2017 год составил 3,817 трлн долларов (25 532 долларов на человека), по данным МВФ - 4,008 трлн долларов. Денежная единица — российский рубль.


撒马尔罕(乌兹别克斯坦语:Samarqand Самарқанд;波斯语:سمرقند;俄语:Самарканд;古称河中府)是中亚地区的历史名城,也是伊斯兰学术中心,现在是乌兹别克斯坦的旧都兼第二大城市、撒马尔罕州的首府,首任总统伊斯拉木·卡里莫夫生于此城。“撒马尔罕”一词在粟特语中意为“石城”或“石要塞”、“石堡垒”;另根据耶律楚材说:“寻思干者西人云肥也,以地土肥饶故名之。[2]”
十四世纪时为帖木儿帝国国都,这里也是帖木儿陵墓的遗址Gur-e Amir所在地。Bibi-Khanym清真寺也是著名地标之一,Registan则是市区古老的中心。
在2001年时,联合国教育、科学及文化组织将拥有2750年之久历史的撒马尔罕编入世界遗产之列,称为“文化交汇之地”(“Crossroads of Cultures”,列入亚洲和大洋洲世界遗产)。
Samarqand, deutsch Samarkand[2] (usbekisch-kyrillisch und tadschikisch Самарқанд, persisch سمرقند, DMG Samarqand; russisch Самарканд Samarkand; sogdisch für „steinerne Stadt“), ist eine Stadt in Usbekistan und Hauptstadt der Provinz Samarqand.
サマルカンド(英語: Samarkand, ペルシア語: سمرقند (Samarqand), ウズベク語: Самарқанд (Samarqand))は、中央アジア、ウズベキスタンの古都。
Samarkand (/ˈsæmərkænd/; Uzbek: Samarqand; Persian: سمرقند; Russian: Самарканд), alternatively Samarqand, is a city in south-eastern Uzbekistan and one of the oldest continuously inhabited cities in Central Asia. There is evidence of human activity in the area of the city from the late Paleolithic era, though there is no direct evidence of when Samarkand was founded; some theories propose that it was founded between the 8th and 7th centuries B.C. Prospering from its location on the Silk Road between China and the Mediterranean, at times Samarkand was one of the greatest cities of Central Asia.[1]
By the time of the Achaemenid Empire of Persia, it was the capital of the Sogdian satrapy. The city was taken by Alexander the Great in 329 BC, when it was known by its Greek name of Marakanda (Μαράκανδα).[2] The city was ruled by a succession of Iranian and Turkic rulers until the Mongols under Genghis Khan conquered Samarkand in 1220. Today, Samarkand is the capital of Samarqand Region and one of the largest cities of Uzbekistan.[3]
The city is noted for being an Islamic center for scholarly study and the birthplace of the Timurid Renaissance. In the 14th century it became the capital of the empire of Timur (Tamerlane) and is the site of his mausoleum (the Gur-e Amir). The Bibi-Khanym Mosque, rebuilt during the Soviet era, remains one of the city's most notable landmarks. Samarkand's Registan square was the ancient centre of the city, and is bound by three monumental religious buildings. The city has carefully preserved the traditions of ancient crafts: embroidery, gold embroidery, silk weaving, engraving on copper, ceramics, carving and painting on wood.[4] In 2001, UNESCO added the city to its World Heritage List as Samarkand – Crossroads of Cultures.
Modern Samarkand is divided into two parts: the old city, and the new city developed during the days of the Russian Empire and Soviet Union. The old city includes historical monuments, shops and old private houses, while the new city includes administrative buildings along with cultural centres and educational institutions.[5]
Samarcande ou parfois Samarkandnote 1 (en ouzbek : Samarqand, en tadjik : Самарқанд, en russe : Самарканд, en persan : سمرقند, en turc : Semerkand), population 400 000 habitants, est une ville d'Ouzbékistan, capitale de la province de Samarcande. Riche en monuments historiques, Samarcande a été proclamée en 2001 par l'UNESCO carrefour de cultures et site du patrimoine mondial. Depuis 2009, la ville de Samarcande a subi de nombreux réaménagements urbains : un mur1 sépare aujourd'hui les quartiers populaires des grands monuments de la ville et des quartiers centenaires comme celui d'Iskandarov (proche du Gur Amir) ont été détruits2 ; leurs habitants ont été relogés de force en périphérie de la ville.
Samarcanda (AFI: /samarˈkanda/[1]; in uzbeco Samarqand; in tagico Самарқанд; in russo: Самарканд?, traslitterato: Samarkand, persiano: سمرقند, Samarqand; 352 047 ab. nel 2010) è una città dell'Uzbekistan, capoluogo della regione omonima e seconda città del Paese per popolazione.
Situata al centro delle principali rotte commerciali asiatiche, Samarcanda, nel corso della sua storia lunga circa 2 700 anni, fu parte dell'primo Impero persiano; successivamente fu sotto influenza araba, poi timuride, uzbeka e, in epoche più moderne, fu dapprima sotto l'impero russo e infine parte dell'Unione Sovietica fino al 1991.
La città, il cui etimo significa in lingua sogdiana "fortezza di pietra" (samar = pietra/roccia e kand = fortezza (come anche in altre città della zona, cfr. Panjakent)) si trova lungo la via della seta nel percorso tra la Cina e l'Europa, praticamente al centro dell'Eurafrasia. Si trova a 702 metri s.l.m. e, nonostante si trovi in Uzbekistan, la maggior parte degli abitanti è di lingua tagica, un dialetto della farsi. Dal 2001 la città figura nella lista dei patrimoni dell'umanità dell'UNESCO sotto il titolo di Samarcanda - Crocevia di culture.
Samarcanda3 (en uzbeko, Samarqand, en ruso, Самарканд) es la segunda ciudad de Uzbekistán, después de Taskent, tanto en población, como área e importancia industrial.45 Es a su vez capital de la Región de Samarcanda. La Unesco declaró a esta ciudad de 2700 años de antigüedad como Patrimonio de la Humanidad en el año 2001, y fue inscrita como Samarcanda - Encrucijada de culturas.
Se han encontrado evidencias de actividad humana en el área de la ciudad desde el Paleolítico tardío, aunque no hay evidencia directa de cuando fue exactamente fundada Samarcanda; algunas teorías señalan que fue fundada entre los siglos VIII y VII antes de Cristo. Prosperando desde su ubicación en la ruta de la seda entre China y el Mediterráneo, Samarcanda fue una de las más grandes ciudades de Asia Central.6
La ciudad es conocida por ser un centro islámico de estudio académico. En el siglo XIV se convirtió en la capital del imperio de Timur (Tamerlán) y es el sitio de su mausoleo (el Gur-e Amir). La Mezquita Bibi-Khanym (una réplica moderna) sigue siendo uno de los monumentos más notables de la ciudad. El Registán fue el antiguo centro de la ciudad, la cual ha conservado cuidadosamente las tradiciones de los antiguos oficios: bordados, bordados de oro, tejidos de seda, grabado sobre cobre, cerámica, tallado y pintura sobre madera.7
Самарка́нд (узб. Samarqand/Самарқанд) — третий[6] по величине и второй по численности населения[прояснить] город Узбекистана, административный центр Самаркандской области (вилоята).
Общая площадь территории города составляет 120 км². Численность населения по состоянию на 1 января 2018 года составляла 529 900 жителей.
Город расположен на высоте около 720 метров над уровнем моря. Исторический центр города — площадь и ансамбль Регистан.
В 2001 году город и его исторические архитектурные и археологические памятники были внесены в список Всемирного наследия ЮНЕСКО под названием «Самарканд — перекрёсток культур».
Самарканд — один из древнейших городов мира[7][8], основанный, по археологическим данным, в VIII веке до н. э.[9]; центр исторической области и государства Согдиана.
Более 2000 лет город являлся ключевым пунктом на Великом шёлковом пути между Китаем и Европой, а также одним из главных центров науки средневекового Востока.
В XIV веке был столицей империи Тамерлана и династии Тимуридов. Подавляющее большинство архитектурных шедевров города было построено в эту эпоху. Это был период наивысшего развития Самарканда.
 California State Route 1
California State Route 1

 California-CA
California-CA

 FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 2026
FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 2026

 Financial
Financial
 ***Global Financial Center
***Global Financial Center

 History
History
 N 2000 - 2100 AD
N 2000 - 2100 AD

 History
History
 M 1500 - 2000 AD
M 1500 - 2000 AD

 International cities
International cities
 ***Global Urban Economic Competitiveness
***Global Urban Economic Competitiveness
 Silk road
Silk road
 United States
United States

 Important port
Important port

太平洋沿岸仅次于洛杉矶的第二大港市。位于加利福尼亚州西北部,美国西海岸中点。市区面积119平方公里,人口72.4万(1990),为美国西部人口密度最高的城市。大市区包括附近4个县和奥克兰、伯克利等城镇,面积7475平方公里。
城市座落在宽不足10公里的半岛北端,介于太平洋和圣弗朗西斯科湾之间,北临金门海峡。市域内丘陵起伏,有双峰山、戴维森山,最著名者为诺布山; 沿海地带较为平坦。南流的萨克拉门托河和北流的圣华金河在城市附近汇合后,向西注入圣弗朗西斯科湾。因地处圣安德烈斯大断层上,多地震。气候宜人,冬季温 和,1月平均气温9℃;夏季凉爽,7月平均气温17.8℃。年平均降水量约500毫米,以冬雨为主,夏日多雾。1776年为西班牙移民拓居地。1806年俄国在此设哨所,作为当时俄届阿拉斯加的物资供应站。1821年属墨西哥。1846年归美国时,为居民不到干人的小镇。1848年附近地区发现金矿,大批淘金者涌入,包括第一批中国“契 约劳工”。1850年设市时,人口已增至2.5万人,成为贸易和为矿业服务的中心,附近地区的农业也有所发展。18邱年后随着横贯大陆铁路的通达和港区设 施的逐步完善,城市迅速发展。1880年后开始向海湾以东地区扩展,形成若干卫星城镇,19世纪末,人口已达34万。1906年大地震时全城80%建筑被 毁,后迅速重建。1914年巴拿马运河通航,港口日益繁荣,贸易量激增。第二次世界大战中,为军需物资的重要供应站。战后,工、商、金融、旅游服务业和市政建设均有较大发展,大市区由单一中心扩展为由旧金山、海湾东区(奥克兰)和圣何塞三大中心组成的城镇群。
旧金山(英语:San Francisco),正式名称为旧金山市县(City and County of San Francisco),是位于美国加利福尼亚州北部的都市,为加州唯一市县合一的行政区,中文又音译为三藩市和圣弗朗西斯科,亦别名“金门城市”、“湾边之城”、“雾城”等。位于旧金山半岛的北端,东临旧金山湾、西临太平洋,人口约86万,为加州第四大城;其与湾边各都市组成的旧金山湾区,人口总数达768万,是仅次于大洛杉矶地区的美国西岸第二大都会区[4]。
旧金山是北加州与旧金山湾区的核心都市,当地住有很多艺术家、作家和演员,在20世纪及21世纪初一直是美国嬉皮士文化和近代自由主义、进步主义的中心之一。旧金山也是联合国的诞生地[5][6][7]。旧金山是受欢迎的旅游目的地[8],以其凉爽的夏季、多雾、绵延的丘陵地形、混合的建筑风格,以及金门大桥、缆车、恶魔岛监狱及唐人街等景点闻名。此外,旧金山也是五大主要银行及许多大型公司、机构的总部所在,其中又以互联网产业为最,包括盖璞、太平洋瓦电公司、Yelp、Dropbox、Pinterest、Twitter、优步、爱彼迎、Mozilla、维基媒体基金会、克雷格列表、Salesforce.com等。
San Francisco (Aussprache: ˌsæn fɹənˈsɪskoʊ, auch San Franzisko[3]), offiziell City and County of San Francisco (Stadt und Kreis von San Francisco), ist eine Stadt und eine Metropolregion im US-Bundesstaat Kalifornien an der Westküste der Vereinigten Staaten am Pazifischen Ozean. Mit 805.195 Einwohnern (Stand der Volkszählung 2010)[4] ist sie die viertgrößte Stadt Kaliforniens. Im globalen Vergleich gilt sie neben ähnlich großen Städten wie etwa Frankfurt am Main oder Amsterdam als mittelgroße Weltstadt.
Der Name der Stadt ist spanischen Ursprungs. San Francisco ist nach dem Heiligen Franziskus, also Franz von Assisi, benannt.
サンフランシスコ市郡(英語: City and County of San Francisco、通称: San Francisco[1])は、アメリカ合衆国西海岸にあるカリフォルニア州の北部に位置する都市。
キリスト教のフランシスコ会の修道士が創設者の聖フランシスコを街の名に付けたのが地名の由来である。漢字では、桑港や旧金山と表記される。桑港は、「サンフランシスコ」を音訳した「桑方西斯哥」(現代中国語普通話ではSāngfāngxīsīgē(サンファンシースーグー)の発音になる)の頭文字「桑」(サン)に、港町である事を示す「港」を加えたものである。この漢字表記は、現地の日系社会でも使われるため、商店や日本語学校などの名称によく見られる。ジャパンタウン(日本人街)にある曹洞宗の寺院「日本山桑港寺(そうこうじ)」はその代表である。一方の旧金山(舊金山)は、1849年に起こったカリフォルニア・ゴールドラッシュにちなんだ名称である。当初この地に労働者としてきた華人たちはサンフランシスコを「金山」と呼んだが、後にオーストラリア・ビクトリア州など他の地域でもゴールドラッシュが起きるとサンフランシスコは旧金山と呼ばれるようになった(「新金山」はメルボルンを指す)。現地の中国系社会では桑港と同様に広東語で「サンファンシー」の音を当てた三藩市が旧金山よりも多用される傾向があり、市当局も中文での名称を三藩市としている[2]。
アメリカの他地域では頭文字の「SF」や「フリスコ(Frisco)」愛称・略称で呼ばれることが多い。または「サンフラン」(San-Fran)との略称で呼ばれることもある。日本では、特に(航空機での渡航の対象として)「シスコ」の略称で呼ばれることも多い。地元とベイエリア周辺では単純に愛情を込めて「the city」と呼ばれることが多い。
ロサンゼルスと共にカリフォルニア州の経済、工業の中心地として知られており、金融センターとしてアメリカ西海岸では随一の重要性を持っている。2017年の調査によると、世界6位の金融センターであり、アメリカの都市ではニューヨークに次ぐ2位である[3]。サンフランシスコ自体の人口は776,733人(2000年国勢調査)だが、対岸のオークランドなどを含めた都市圏(MSA)の人口は4,123,747人にも上り、全米第12位の規模。更に南岸のサンノゼを加えたサンフランシスコ・ベイエリア全体の人口は7,092,596人で広域都市圏(合同統計地域: CSA)としては全米6番目の規模である。(いずれも2000年国勢調査)それゆえに大規模なダウンタウンが形成されており、近代的なビルが建ち並ぶ。シリコンバレーやカリフォルニア大学バークレー校にも近く、コンピュータ系の企業も多い。
気候は地中海性気候に属し、一年を通して気温の差が比較的小さく、気候的にも住みやすい都市である。急な坂が多く、深い霧に覆われることでも有名である。都市部から13マイルほど南下すると、サンフランシスコ国際空港がある。
観光地としての評価も非常に高い都市であり、外国人のみならず、アメリカ人の間でも訪れたい都市の上位にランクされている。有名な観光スポットとしてゴールデン・ゲート・ブリッジ(金門橋)やフィッシャーマンズワーフ、ツインピークス等が挙げられる。市内を走る伝統あるケーブルカーも人気が高い。
アメリカのシンクタンクが2017年に発表した総合的な世界都市ランキングにおいて、世界13位の都市と評価された[4]。アメリカの都市ではニューヨーク、ロサンゼルス、シカゴに次ぐ4位である。
世界的に著名な都市なので、ロサンゼルスと共に州都であると思われがちだが、誤りである(実際の州都はサクラメント。米国は原則として中小都市に州政府を置く伝統があり、ニューヨークもシカゴも州都ではない)。
San Francisco (SF; /ˌsæn frənˈsɪskoʊ, fræn-/; Spanish for 'Saint Francis'; Spanish: [san franˈsisko]), officially the City and County of San Francisco, is the cultural, commercial, and financial center of Northern California. San Francisco is the 13th most populous city in the United States, and the 4th most populous in California, with 884,363 residents as of 2017.[18] It covers an area of about 46.89 square miles (121.4 km2),[19] mostly at the north end of the San Francisco Peninsula in the San Francisco Bay Area, making it the second most densely populated large US city, and the fifth most densely populated U.S. county, behind only four of the five New York City boroughs. San Francisco is also part of the fifth most populous primary statistical area in the United States, the San Jose–San Francisco–Oakland, CA Combined Statistical Area (8.8 million residents).
As of 2016, it was the 7th highest-income county in the United States, with a per capita personal income of $110,418.[20] The San Francisco CSA was the country's 3rd largest urban economy as of 2017, with a GDP of $878 billion.[21] Of the 574 primary statistical areas in the US, the San Francisco CSA had the highest GDP per capita in 2017, at $99,347 per capita.[21] San Francisco was ranked 14th in the world and third in the United States on the Global Financial Centres Index as of September 2018.[22]
San Francisco was founded on June 29, 1776, when colonists from Spain established Presidio of San Francisco at the Golden Gate and Mission San Francisco de Asís a few miles away, all named for St. Francis of Assisi.[2] The California Gold Rush of 1849 brought rapid growth, making it the largest city on the West Coast at the time. San Francisco became a consolidated city-county in 1856.[23] San Francisco's status as the West Coast's largest city peaked between 1870 and 1900, when around 25% of California's population resided in the city.[24] After three-quarters of the city was destroyed by the 1906 earthquake and fire,[25] San Francisco was quickly rebuilt, hosting the Panama-Pacific International Exposition nine years later. In World War II, San Francisco was a major port of embarkation for service members shipping out to the Pacific Theater.[26] It then became the birthplace of the United Nations in 1945.[27][28][29] After the war, the confluence of returning servicemen, significant immigration, liberalizing attitudes, along with the rise of the "hippie" counterculture, the Sexual Revolution, the Peace Movement growing from opposition to United States involvement in the Vietnam War, and other factors led to the Summer of Love and the gay rights movement, cementing San Francisco as a center of liberal activism in the United States. Politically, the city votes strongly along liberal Democratic Party lines.
A popular tourist destination,[30] San Francisco is known for its cool summers, fog, steep rolling hills, eclectic mix of architecture, and landmarks, including the Golden Gate Bridge, cable cars, the former Alcatraz Federal Penitentiary, Fisherman's Wharf, and its Chinatown district. San Francisco is also the headquarters of five major banking institutions and various other companies such as Levi Strauss & Co., Gap Inc., Fitbit, Salesforce.com, Dropbox, Reddit, Square, Inc., Dolby, Airbnb, Weebly, Pacific Gas and Electric Company, Yelp, Pinterest, Twitter, Uber, Lyft, Mozilla, Wikimedia Foundation, Craigslist, and Weather Underground. It is home to a number of educational and cultural institutions, such as the University of San Francisco (USF), University of California, San Francisco (UCSF), San Francisco State University (SFSU), the De Young Museum, the San Francisco Museum of Modern Art, and the California Academy of Sciences.
San Francisco (en anglais [sæn frənˈsɪskoʊ]), officiellement City and County of San Francisco, est une ville américaine et un comté de l'État de Californie. Elle est située à l'extrémité nord de la péninsule de San Francisco, entre l'océan Pacifique à l'ouest et la baie de San Francisco à l'est. Son nom est couramment abrégé en SF et la ville est surnommée The City by the Bay4.
Fondée en 1776 par des Espagnols au sein de la Viceroyauté de la Nouvelle-Espagne, la ville, nommée en l'honneur de San Francisco de Asís, prend son essor lors de la ruée vers l'or et son prolongement, l'embellissement de San Francisco par les millionnaires du Nevada. Puis, elle devient le berceau du jeans avec la fondation de Levi Strauss & Co. Les années 1950 voient la naissance de la Beat Generation. À partir de la deuxième partie du XXe siècle, l'industrie des hautes technologies se développe dans la région de la baie. Aujourd'hui San Francisco est la ville la plus densément peuplée des États-Unis après New York. La municipalité-comté5 de San Francisco compte 805 235 habitants dans ses limites administratives6 et plus de 7 millions de personnes vivent dans l'aire métropolitaine de La Baie7, la quatrième métropole des États-Unis par sa population. La partie sud de cette dernière est occupée par la municipalité de San José et la Silicon Valley, premier pôle de hautes technologies des États-Unis qui accueille un nombre important d'entreprises de technologie de pointe de renommée mondiale telles que Cisco, Apple, Tesla Motors, Hewlett-Packard, Google, Intel ou encore Facebook8. Dans le domaine universitaire, elle accueille les prestigieuses9 université Stanford et université de Californie à Berkeley. San Francisco est également le siège de la Wikimedia Foundation dont fait partie le projet Wikipédia. Au nord s'étendent la Napa Valley et la Sonoma Valley, renommées pour leur viticulture. San Francisco fait partie des villes progressistes dans le domaine de l'écologie10,11 et du développement durable12,13,14.
Troisième destination touristique préférée des français aux États-Unis15, la ville est célèbre pour le pont du Golden Gate, l'île et ancienne prison d'Alcatraz, Fisherman's Wharf, la Transamerica Pyramid, la Coit Tower, ses maisons victoriennes, ses cable cars et ses nombreuses collines découpées de rues en pente. Haut lieu de la contre-culture, ville de tolérance et d'émancipation des minorités, San Francisco est également connue pour son Chinatown, ses quartiers homosexuels comme Le Castro, et hippie. Elle représente un foyer culturel et économique majeur aux États-Unis et accueille chaque année plusieurs événements d'ampleur mondiale16 mais vibre également au rythme des festivités animées par les différentes communautés locales17. Elle se revendique comme une ville sanctuaire pour les sans papiers depuis 198918. Sur le plan sportif, les 49ers au football américain, les Giants au baseball et les Warriors au basket-ball sont les équipes phares de la ville.
San Francisco (AFI: [sanfranˈsisko][1]; in inglese /ˌsæn frənˈsɪskoʊ/) è una città statunitense, la quarta della California per numero di abitanti (dopo Los Angeles, San Diego e San Jose), con una popolazione stimata nel 2016 di 870 887 abitanti, stima che la colloca al dodicesimo posto fra le città più popolose degli Stati Uniti d'America e allo stesso tempo al secondo posto per densità di popolazione, dietro solo a New York.[2] La città fa parte di una vasta area metropolitana (circa 7 milioni di abitanti,[3] la quinta dell'intero Paese), la San Francisco Bay Area, di cui è sempre stata il centro economico-finanziario, culturale e turistico, anche se ha ormai perso il primato di popolazione.
San Francisco è una popolare meta di molti turisti internazionali, ed è conosciuta per la sua fresca nebbia estiva, per le sue ripide colline, per la sua vivacità culturale e il suo eclettismo architettonico, che affianca stile vittoriano e architettura moderna, per i suoi famosi paesaggi, incluso il Golden Gate Bridge, per i suoi tram e per Chinatown. L'Università della California, San Francisco è uno dei principali centri biomedici del mondo, e l'ospedale è tra i principali degli Stati Uniti.
San Francisco, de forma oficial Ciudad y Condado de San Francisco (en inglés: City and County of San Francisco), es una ciudad que ocupa la cuarta posición de ciudad más poblada del estado de California y la 13.ª de Estados Unidos, con una población de aproximadamente 837 442 habitantes en 2013.6 Es la única ciudad-condado consolidada de California, y al abarcar una superficie territorial de 121 km², cuenta con la segunda densidad de población más alta del país entre las ciudades que superan los 200 000 habitantes, tras Nueva York.7 Es el centro cultural, financiero y de transportes del Área de la Bahía de San Francisco, una aglomeración metropolitana con más de siete millones de habitantes.89 Se encuentra en el extremo norte de la península de San Francisco, con el océano Pacífico al oeste, la bahía homónima al este y la entrada de la bahía al norte, por lo que solamente está conectada con tierra firme por su extremo sur.
La ciudad de San Francisco fue fundada por colonos españoles en 1776. Construyeron un fuerte en lo que hoy es el Golden Gate y fundaron una misión llamada así en honor de Francisco de Asís.10 San Francisco perteneció al Virreinato de la Nueva España hasta la independencia de México en 1821. Tras la Intervención estadounidense en México entre 1845 y 1848, la ciudad y el resto de Alta California pasaron a ser territorio estadounidense.
En 1848, la fiebre del oro de California impulsó a la ciudad a un período de rápido crecimiento, pasando de 1000 a 25 000 habitantes en un año,11 lo que convirtió a la ciudad en la más grande de la Costa oeste en aquella época. Después de haber sido devastada por el terremoto e incendio de 1906,12 San Francisco fue rápidamente reconstruida, siendo sede de la Exposición Internacional de Panamá y el Pacífico nueve años más tarde.13 Durante la Segunda Guerra Mundial, la ciudad fue el puerto de embarque de miles de soldados que partían hacia la Guerra del Pacífico.14 Tras la contienda, la confluencia de los militares que regresaban, la inmigración masiva, las actitudes liberales y otros factores dieron lugar al denominado Verano del Amor y los movimientos en favor de los derechos de los homosexuales,15 consolidando a San Francisco como un bastión liberal en los Estados Unidos.
La ciudad incluye varias islas localizadas dentro la bahía (siendo la más famosa Alcatraz), así como los Farallones, que se sitúan a 43 kilómetros de la costa en el océano Pacífico.16 Se comunica con el resto del país y del mundo por medio del Aeropuerto Internacional de San Francisco.
San Francisco es un destino popular para los turistas internacionales, siendo famosa por el puente Golden Gate, el edificio Pirámide Transamérica, los tranvías que recorren sus empinadas calles, su arquitectura modernista y victoriana y por su barrio chino, popularmente llamado Chinatown.17 En las cercanías de San Francisco se encuentra Silicon Valley, gran centro de investigaciones en tecnología y cibernética. La ciudad también es un importante centro financiero y bancario, ya que es sede de más de treinta instituciones financieras,18 lo que ha ayudado a hacer de San Francisco la decimoctava ciudad del mundo por PIB en 2008 y la novena de los Estados Unidos.19
Actualmente es la segunda ciudad estadounidense con mejor calidad de vida, solamente superada por Honolulu20
Сан-Франци́ско (англ. San Francisco [ˌsæn frənˈsɪskoʊ] или [ˌsæn frænˈsɪskoʊ], разг. просторечн. Frisco[3][4]) — город и округ в штате Калифорния, США, названный в честь католического святого (по-испански San) Франциска Ассизского[5]. Население в 2010 году составляло 815 358 человек, это четвёртый по численности населения город Калифорнии и двенадцатый в США[2]. Площадь Сан-Франциско составляет 600,6 км2, из них суши — 121,4 км2, воды — 479,2 км2. Сан-Франциско расположен на северной оконечности полуострова Сан-Франциско. Бо́льшую часть своей истории он являлся самым населённым и важным городом области залива Сан-Франциско.
В 1776 году испанцы обосновались на побережье полуострова, построив форт у пролива Золотые Ворота и основав миссию, названную в честь Святого Франциска[6]. Возникший рядом с ней небольшой городок назывался Йерба-Буэна[en] (исп. Yerba Buena). В 1848 году, благодаря калифорнийской золотой лихорадке, город начал бурно расти[7]. В этом же году он был переименован в Сан-Франциско. После разрушительного землетрясения и пожара в 1906 году город был быстро и практически полностью перестроен[8].
Сан-Франциско является мировым туристическим центром[9], известный своими летними холодными туманами, крутыми холмами и сочетанием викторианской и современной архитектуры. В число достопримечательностей города входят мост «Золотые Ворота», остров Алькатрас, система канатных трамваев, Башня Койт[en] и чайна-таун.
 Geography
Geography







