
Deutsch-Chinesische Enzyklopädie, 德汉百科
 Denmark
Denmark
 *United States Political System
*United States Political System
 *UK political system
*UK political system
 *French political system
*French political system
 Albania
Albania
 Belgium
Belgium
 Bulgaria
Bulgaria
 Denmark
Denmark
 Germany
Germany
 Estonia
Estonia
 Finland
Finland
 France
France
 Generalsekretäre der Nordatlantikpakt-Organisation
Generalsekretäre der Nordatlantikpakt-Organisation
 Anders Fogh Rasmussen
Anders Fogh Rasmussen
 Generalsekretäre der Nordatlantikpakt-Organisation
Generalsekretäre der Nordatlantikpakt-Organisation
 Dirk Stikker
Dirk Stikker
 Generalsekretäre der Nordatlantikpakt-Organisation
Generalsekretäre der Nordatlantikpakt-Organisation
 George Robertson
George Robertson
 Generalsekretäre der Nordatlantikpakt-Organisation
Generalsekretäre der Nordatlantikpakt-Organisation
 Hastings Ismay, 1. Baron Ismay
Hastings Ismay, 1. Baron Ismay
 Generalsekretäre der Nordatlantikpakt-Organisation
Generalsekretäre der Nordatlantikpakt-Organisation
 Jaap de Hoop Scheffer
Jaap de Hoop Scheffer
 Generalsekretäre der Nordatlantikpakt-Organisation
Generalsekretäre der Nordatlantikpakt-Organisation
 Javier Solana
Javier Solana
 Generalsekretäre der Nordatlantikpakt-Organisation
Generalsekretäre der Nordatlantikpakt-Organisation
 Jens Stoltenberg
Jens Stoltenberg
 Generalsekretäre der Nordatlantikpakt-Organisation
Generalsekretäre der Nordatlantikpakt-Organisation
 Joseph Luns
Joseph Luns
 Generalsekretäre der Nordatlantikpakt-Organisation
Generalsekretäre der Nordatlantikpakt-Organisation
 Manfred Wörner
Manfred Wörner
 Generalsekretäre der Nordatlantikpakt-Organisation
Generalsekretäre der Nordatlantikpakt-Organisation
 Manlio Giovanni Brosio
Manlio Giovanni Brosio
 Generalsekretäre der Nordatlantikpakt-Organisation
Generalsekretäre der Nordatlantikpakt-Organisation
 Paul-Henri Spaak
Paul-Henri Spaak
 Generalsekretäre der Nordatlantikpakt-Organisation
Generalsekretäre der Nordatlantikpakt-Organisation
 Peter Carington, 6. Baron Carrington
Peter Carington, 6. Baron Carrington
 Generalsekretäre der Nordatlantikpakt-Organisation
Generalsekretäre der Nordatlantikpakt-Organisation
 Sergio Balanzino
Sergio Balanzino
 Generalsekretäre der Nordatlantikpakt-Organisation
Generalsekretäre der Nordatlantikpakt-Organisation
 Willy Claes
Willy Claes

 History
History
 Greece
Greece
 Iceland
Iceland
 Italy
Italy
 Canada
Canada
 Croatia
Croatia
 Latvia
Latvia
 Lithuania
Lithuania
 Luxembourg
Luxembourg




 Military, defense and equipment
Military, defense and equipment

 Mitglieder der NATO
Mitglieder der NATO
 Montenegro
Montenegro

 NATO summit
NATO summit
 Netherlands
Netherlands
 Nordmazedonien
Nordmazedonien
 Norwegen
Norwegen

 Party and government
Party and government
 Poland
Poland
 Portugal
Portugal
 Romania
Romania
 Sweden
Sweden
 Slovakia
Slovakia
 Slovenia
Slovenia
 Spain
Spain
 Czech Republic
Czech Republic
 Turkey
Turkey
 Hungary
Hungary
 United States
United States
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom

 Important International Organizations
Important International Organizations
北大西洋公约组织(英语:North Atlantic Treaty Organization,缩写为NATO;法语:Organisation du Traité de l'Atlantique Nord,缩写为OTAN),简称北约组织或北约,是欧洲及北美洲国家为实现防卫合作而建立的国际组织。1949年3月18日,美国、英国及法国公开建立北大西洋公约组织,于同年4月4日在美国华盛顿签署《北大西洋公约》后正式成立。为与以前苏联为首的东欧集团国成员相抗衡。及至苏联解体,华沙条约组织宣告解散,北约就成为一个地区性防卫协作组织。北约的最高决策机构是北约理事会。理事会由成员国国家元首及政府高层、外长、国防部长组成。总部设在比利时的布鲁塞尔。最新成员黑山于2017年6月5日加入,至此北约总共有跨域欧洲和北美的29个国家组成。北约军事开支占世界国防开支的70%[4],成员国国防开支占该国GDP的2%左右[5]。
公约第5条规定成员国受到的攻击一旦被确认,其他成员国将作出即时反应。该条款被理解为各国部队将自动参战,并不再次需要各国政府的参战授权。但这一条条款在九一一事件之前,一直都未有动用过[6] 。北约曾协助反海盗行动(counter-piracy operations),在联合国要求下打击亚丁湾、非洲之角和印度洋的海盗[7],并在2011年根据联合国安理会1973号决议将利比亚上空设为禁飞区。
Die NATO (englisch North Atlantic Treaty Organization „Organisation des Nordatlantikvertrags“ bzw. Nordatlantikpakt-Organisation), im Deutschen häufig als Atlantisches Bündnis oder als Nordatlantikpakt bezeichnet (französisch OTAN – Organisation du Traité de l’Atlantique Nord), ist eine Internationale Organisation ohne Hoheitsrechte. Ihre Mitgliedstaaten behalten ihre volle Souveränität und Unabhängigkeit. Basis der NATO ist der Nordatlantikvertrag nach Artikel 51 der UN-Charta. Ihre Organisation versteht sich nicht nur als Verteidigungsbündnis, sondern auch als militärisch-politische Organisation von 29 europäischen und nordamerikanischen Mitgliedstaaten mit dem Ziel eigener Sicherheit und weltweiter Stabilität.
Das NATO-Hauptquartier beherbergt den Nordatlantikrat (das Hauptorgan der NATO) und seine unmittelbar nachgeordneten Einrichtungen, den International Staff (IS) und den International Military Staff (IMS); diese Institution hat seit 1967 ihren Sitz in Brüssel. Nach der Unterzeichnung des Nordatlantikpakts am 4. April 1949 – vorerst auf 20 Jahre – war das Hauptquartier zunächst in London ansässig und anschließend von 16. April 1952 bis 1967 in Paris angesiedelt worden.
Die beiden wichtigsten militärischen Hauptquartiere sind das ACO (aus historischen und juristischen Gründen auch als Supreme Headquarters Allied Powers Europe / SHAPE bezeichnet) im belgischen Casteau bei Mons und das Allied Command Transformation (ACT) in der US-Stadt Norfolk (Virginia).
北大西洋条約機構(きたたいせいようじょうやくきこう)は、北大西洋条約に基づき、アメリカ合衆国を中心とした北アメリカ(=アメリカとカナダ)およびヨーロッパ諸国によって結成された軍事同盟である。29カ国が加盟し、日本など非加盟国とも協力関係にある[1]。前身はブリュッセル条約 (1948年)。ベルギー首都ブリュッセルに本部を置く[2]。
略称は頭字語が用いられ、英語圏では、North Atlantic Treaty Organization を略した NATO(ネイトー)と呼ばれ、日本やドイツ語圏では NATO(ナトー)、フランス語圏・スペイン語圏・ポルトガル語圏等では OTAN(オタン)と呼ばれる。
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO /ˈneɪtoʊ/; French: Organisation du Traité de l'Atlantique Nord; OTAN), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 29 North American and European countries. The organization implements the North Atlantic Treaty that was signed on 4 April 1949.[3][4] NATO constitutes a system of collective defence whereby its independent member states agree to mutual defence in response to an attack by any external party. NATO’s Headquarters are located in Haren, Brussels, Belgium, while the headquarters of Allied Command Operations is near Mons, Belgium.
Since its founding, the admission of new member states has increased the alliance from the original 12 countries to 29. The most recent member state to be added to NATO is Montenegro on 5 June 2017. NATO currently recognizes Bosnia and Herzegovina, Georgia, Macedonia and Ukraine as aspiring members.[5] An additional 21 countries participate in NATO's Partnership for Peace program, with 15 other countries involved in institutionalized dialogue programs. The combined military spending of all NATO members constitutes over 70% of the global total.[6] Members have committed to reach or maintain defense spending of at least 2% of GDP by 2024.[7][8]
L’Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique norda (en anglais : North Atlantic Treaty Organization) est l'organisation politico-militaire mise en place par les pays signataires du traité de l'Atlantique nord afin de pouvoir remplir leurs obligations de sécurité et de défense collectives. Elle est le plus souvent désignée par son acronyme OTAN (en anglais NATO) mais aussi fréquemment nommée l’Alliance atlantique, plus rarement l’Alliance euro-atlantique ou l’Alliance transatlantique5, ou parfois, encore plus brièvement, simplement l’Alliance.
Le texte de ce traité, signé le 4 avril 1949, établit le Conseil de l'Atlantique nord (CAN), et lui donne mission de mettre en place l'organisation nécessaire à son application. Le choc provoqué par le déclenchement de la guerre de Corée conduit le CAN à décider fin 1950 la création d'une organisation militaire intégrée permanente, qui constitue encore actuellement la marque distinctive de l'OTAN et lui assure des capacités militaires qu'aucune autre alliance de défense ne possède. Sous le vocable OTAN, l'usage a prévalu d'englober l'alliance juridiquement conclue par les pays signataires du traité de l'Atlantique nord, et l'organisation civile et militaire mise en place pour en rendre opérants les objectifs. La France toutefois a fait exception en décidant en 1966, tout en restant membre de l'Alliance atlantique, de quitter l'organisation militaire intégrée, dont elle est redevenue membre à part entière en 2009.
L'Alliance voit le jour dans le contexte général des débuts de la guerre froide et plus spécifiquement pendant le blocus de Berlin exercé par les Soviétiques. Elle a pour vocation initiale d'assurer la sécurité de l'Europe occidentale en instaurant un couplage fort avec les États-Unis, seul moyen aux yeux des Européens après la Seconde Guerre mondiale de se prémunir contre toute tentative expansionniste de l'Union soviétique. Selon le mot de son premier secrétaire général, Lord Ismay, le rôle de l'OTAN consiste à « garder les Russes à l'extérieur, les Américains à l'intérieur et les Allemands sous tutelle »b. L'OTAN constitue le noyau dur du bloc de l'Ouest. Entre 1955 et 1991, l'adversaire désigné de l'OTAN est le pacte de Varsovie formé par les Soviétiques à la suite de l'adhésion de la RFA à l'Alliance atlantique et à son réarmement. L'OTAN s'organise donc pour faire face à cette menace par la définition de concepts stratégiques touchant notamment les questions relatives aux armes nucléaires, par la planification coordonnée entre tous ses membres de leurs moyens militaires, et par des commandements intégrés par zone géographique, dont le SHAPE est de loin le plus important.
Depuis la dissolution de l'URSS et la fin de la guerre froide en 1991, l'Alliance atlantique a perduré malgré la disparition de sa principale raison d'être initiale. Elle a procédé à son élargissement à d'anciens pays du bloc de l'Est et d'anciennes républiques de l'Union soviétique. Elle a pris en compte de nouvelles crises et menaces comme les conflits nationalistes dans l'ex-Yougoslavie, l'essor du terrorisme international ou la prolifération des armes de destruction massive, en conséquence de quoi l'OTAN a revu en profondeur son concept stratégique et son organisation civile et militaire à plusieurs reprises. Elle a développé une politique systématique de partenariats en Europe et dans le monde, au titre de laquelle les pays de l'Alliance ont établi depuis 1994 un partenariat pour la paix (PPP) avec la Russie, les pays de sa zone d'influence et avec les pays neutres d'Europe occidentale. L'OTAN a aussi mis en place en 2002 avec l'UE une relation privilégiée, l'Identité européenne de sécurité et de défense (IESD), qui permet à cette dernière de bénéficier de moyens de l'OTAN pour certaines opérations entrant dans le cadre de sa politique de sécurité et de défense commune.
Le siège de l'OTAN, initialement situé à Londres puis à Paris (dans les locaux désormais occupés par l'université Paris-Dauphine - PSL) se trouve depuis 1966 à Haren (Bruxelles), et son principal commandement militaire, le SHAPE, initialement installé à Rocquencourt (France), se trouve aujourd'hui à Maisières (Mons), également en Belgique.
L'Organizzazione del Trattato dell'Atlantico del Nord (in inglese North Atlantic Treaty Organization, in sigla NATO,[3] in francese: Organisation du Traité de l'Atlantique Nord, in sigla OTAN) è un'organizzazione internazionale per la collaborazione nel settore della difesa.
Il trattato istitutivo della NATO, il Patto Atlantico, fu firmato a Washington il 4 aprile 1949, ovvero nell'immediato secondo dopoguerra, ed entrò in vigore il 24 agosto dello stesso anno. Attualmente, fanno parte della NATO 29 stati del mondo.
La Organización del Tratado del Atlántico Norte u OTAN (en inglés: North Atlantic Treaty Organization o NATO; en francés: Organisation du Traité de l'Atlantique Nord u OTAN), también denominada Alianza del Atlántico, Alianza del Atlántico Norte o Alianza Atlántica, es una alianza militar intergubernamental basada en el Tratado del Atlántico Norte o Tratado de Washington firmado el 4 de abril de 1949. La organización constituye un sistema de defensa colectiva, en la cual los Estados miembros acuerdan defender a cualquiera de sus miembros si son atacados por una potencia externa.3
La sede de la OTAN se encuentra en Bruselas, Bélgica, uno de los veintinueve Estados miembros de la organización que se extiende por Norteamérica y Europa. La última incorporación fue Montenegro, en junio de 2017. Además, veintiún países colaboran con la OTAN dentro del programa Asociación para la Paz, con otros quince involucrados en programas de diálogo y nueve como socios globales. En 2017, el gasto militar combinado de los veintinueve países fue el 52 % del gasto militar mundial.45
En sus primeros años, la OTAN no era mucho más que una asociación política. Sin embargo, la guerra de Corea hizo que se planteara una coalición permanente. Entonces se creó una estructura militar bajo la dirección de los comandantes de Estados Unidos. La Guerra Fría llevó a las naciones rivales a crear el Pacto de Varsovia en 1955.
Siempre se han manifestado dudas sobre la alianza europeo-norteamericana ante una invasión soviética, desacuerdos que se plasmaron con la creación por parte de Francia de la fuerza de choque nuclear y con su retirada de la estructura militar de la alianza entre 1966 y 2009.
Después de la caída del Muro de Berlín en 1989, la organización intervino dentro de la guerra de Yugoslavia, lo que se convirtió en la primera intervención conjunta de la OTAN. En lo político la organización ha mejorado sus relaciones con los antiguos miembros del bloque del Este, dando como resultado la incorporación a la OTAN de varios miembros del Pacto de Varsovia.
La única ocasión en que un país miembro invocó el artículo 5 del tratado reivindicando la ayuda en su defensa, fue Estados Unidos en 2001.6 Desde entonces, los miembros colaboraron con los Estados Unidos en la guerra de Afganistán. El artículo 4 del tratado prevé llamar a consulta a los miembros y ha sido convocado cuatro veces, tres de ellas por Turquía, la primera por la guerra de Irak y las dos restantes por ataques recibidos durante la guerra civil siria,7 la cuarta ha sido invocada por Polonia durante la crisis de Crimea de 2014, debido a la movilización de tropas rusas en la frontera polaca con Kaliningrado y las maniobras rusas en el mar Báltico.
НА́ТО, Организа́ция Североатланти́ческого догово́ра, Североатлантический Альянс (англ. North Atlantic Treaty Organization, NATO; фр. Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique Nord, OTAN) — военно-политический блок, объединяющий большинство стран Европы, США и Канаду. Основан 4 апреля 1949 года в США, с целью защиты Европы от советского влияния[~ 1][~ 2][~ 3][~ 4][~ 5]. Тогда государствами — членами НАТО стали 12 стран: США, Канада, Исландия, Великобритания, Франция, Бельгия, Нидерланды, Люксембург, Норвегия, Дания, Италия и Португалия. Это «трансатлантический форум» для проведения странами-союзниками консультаций по любым вопросам, затрагивающим жизненно важные интересы его членов, включая события, способные поставить под угрозу их безопасность. Одной из декларированных целей НАТО является обеспечение сдерживания любой формы агрессии в отношении территории любого государства — члена НАТО или защиты от неё.
В настоящее время членами НАТО являются 29 стран. Военные расходы всех членов НАТО в совокупности составляют более 70 процентов от общемирового объёма[1].


 Belgium
Belgium

 Berlin
Berlin

 Brandenburg
Brandenburg

 Bremen
Bremen
 Denmark
Denmark
 Germany
Germany

 Hamburg
Hamburg

 Mecklenburg-Vorpommern
Mecklenburg-Vorpommern
 Netherlands
Netherlands

 Lower Saxony
Lower Saxony

 North Rhine-Westphalia
North Rhine-Westphalia
 Poland
Poland

 Saxony
Saxony

 Saxony-Anhalt
Saxony-Anhalt

 Schleswig-Holstein
Schleswig-Holstein

Die Nordic Investment Bank (NIB) ist ein internationales Finanzinstitut, das 1975 von den fünf nordischen Staaten (Dänemark, Finnland, Island, Norwegen und Schweden) gegründet wurde. 2005 wurden auch die drei baltischen Staaten (Estland, Lettland und Litauen) Mitglieder der NIB. Ihr Hauptsitz ist in Helsinki (Finnland).
Die NIB vergibt Kredite und Garantien an private und öffentliche Gesellschaften, Regierungen, Gemeinden und Finanzinstitute. Die wichtigsten Kreditbereiche sind:
- Energie & Wasser
- Infrastruktur, Verkehr & Telekommunikation
- Branchen & Dienstleistungen
- Finanzinstitute & kleine und mittlere Unternehmen
Die NIB hat ein großes Kreditportfolio außerhalb ihrer Mitgliedsländer (einschließlich der Ostseeregion und Barents-Region) für Umweltprojekte. Die NIB nimmt Kredite auf den internationalen Kapitalmärkten auf und vergibt mit dem Geld Kredite. Die Bonität der Anleihen der NIB wurde (Stand Mitte 2021) von den Ratingagenturen Standard & Poor’s und Moody’s mit dem Rating AAA/Aaa eingestuft.
Ziel der NIB ist es, Projekte zu finanzieren, die die Produktivität verbessern und der Umwelt in den nordischen und baltischen Ländern zugutekommen.
北欧投资银行 (英语:Nordic Investment Bank, NIB)是北欧五国成立的一家国际金融机构,总部位于芬兰赫尔辛基。波罗的海三国于2005年加入北欧投资银行。

Der Nordische Rat ist ein Forum der nordischen Staaten. Die Parlamente der Staaten wie der autonomen Gebiete entsenden Abgeordnete in den Rat, die dort die Interessen ihrer Nation wahrnehmen und jährlich neu gewählt werden. Gegründet wurde der Rat 1952 von Dänemark, Island, Norwegen und Schweden. Seitdem finden jährliche Treffen statt. Finnland trat dem Rat 1955 bei.[3] Die Arbeit wird in fünf Fachausschüssen koordiniert. Seit 1971 gibt es zusätzlich den Nordischen Ministerrat auf Regierungsebene; der Nordische Rat und Ministerrat haben ein gemeinsames Sekretariat in Kopenhagen. Der Rat konzentriert sich auf kulturelle und politische Zusammenarbeit; militärische und wirtschaftliche Kooperation finden meist im Kontext anderer Organisationen wie der NATO und des Europäischen Wirtschaftsraums statt. Die Arbeitssprachen des Rates und des Ministerrates sind die skandinavischen Sprachen Dänisch, Norwegisch und Schwedisch.
北欧理事会是由北欧国家政府所组成的议会间合作组织。该组织于1952年成立,共有87名代表,分别由来自丹麦、芬兰、冰岛、挪威、瑞典五个主权国家,及法罗群岛(属丹麦)、格陵兰岛(属丹麦)和奥兰群岛(属芬兰)三个地区。所有代表均为成员国(地区)本地议会内部选出的议员。理事会在每年10月或11月举行常规会议,但亦会举行针对某一特定主题的额外会议。[1]
理事会秘书处设于哥本哈根,并在各会员国设有分支机构。北欧理事会的官方语言为丹麦语、挪威语、瑞典语、冰岛语以及芬兰语,而当中前三者则是工作语言。三种工作语言为区域80%人口的母语,同时亦广泛作为剩余20%人口的第二语言或第二外语。[2]
另外一个重要的组织,北欧部长理事会亦于1971年成立,作为对北欧理事会的补充。该两组织共同参与与比邻地区的合作,包括德国的石勒苏益格-荷尔斯泰因,俄罗斯,波罗的海国家以及比荷卢联盟。

 Belgium
Belgium
 Amber Road
Amber Road

 Bremen
Bremen
 Denmark
Denmark
 Germany
Germany
 England
England
 France
France

 Geography
Geography
 Netherlands
Netherlands

 Lower Saxony
Lower Saxony
 Kiel Canal
Kiel Canal
 Norwegen
Norwegen

 Schleswig-Holstein
Schleswig-Holstein
 Sweden
Sweden
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom

北海(挪威语:Nordsjøen;瑞典语:Nordsjön;丹麦语:Nordsøen或Vesterhavet;德语:Nordsee;荷兰语:Noordzee;法语:Mer du Nord;英语:North Sea)是北大西洋的一部分,位于大不列颠岛以东,斯堪的纳维亚半岛西南和欧洲大陆以北。北海海底有丰富的石油储藏,作为布兰特原油指数的基础。
北海向西南通过多佛尔海峡(法国称加来海峡)和英吉利海峡(法国称拉芒什海峡)与凯尔特海相通,向东通过斯卡格拉克海峡和卡特加特海峡与波罗的海相连,向北是挪威海。
斯凯尔特河、默兹河、莱茵河、威悉河、易北河和泰晤士河是注入北海的主要河流。重要的岛屿或群岛有北弗里西亚群岛、黑尔戈兰岛、东弗里西亚群岛和西弗里西亚群岛。
北海周边的国家有英国、挪威、瑞典、丹麦、德国、荷兰、比利时和法国。重要城市有阿伯丁、爱丁堡、加来、奥斯坦、鹿特丹、海牙、哈勒姆、威廉港、不来梅哈芬、库克斯港、埃斯比约、卑尔根、哥德堡等等。此外伦敦、不来梅哈芬和汉堡是北海重要的内陆港城。
Die Nordsee (veraltet Westsee, Deutsches Meer[2]) ist ein Randmeer des Atlantischen Ozeans. Sie ist ein Schelfmeer und liegt im nordwestlichen Europa. Bis auf die Meerengen beim Ärmelkanal und beim Skagerrak ist sie auf drei Seiten von Land begrenzt und öffnet sich trichterförmig zum nordöstlichen Atlantik. In einem 150-Kilometer-Bereich an der Küste leben rund 80 Millionen Menschen.
Die Nordsee selbst ist ein wichtiger Handelsweg und dient als Weg Mittel- und Nordeuropas zu den Weltmärkten. Die südliche Nordsee ist zusammen mit dem angrenzenden Ärmelkanal die am dichtesten befahrene Schifffahrtsregion der Welt. Unter dem Meeresboden befinden sich größere Erdöl- und Erdgasreserven, die seit den 1970er Jahren gefördert werden. Kommerzielle Fischerei hat den Fischbestand des Meeres in den letzten Jahrzehnten vermindert. Umweltveränderungen entstehen auch dadurch, dass die Abwässer aus Nordeuropa und Teilen Mitteleuropas direkt oder über die angrenzende Ostsee in das Meer fließen.
北海(ほっかい、英語 North Sea、ドイツ語 Nordsee、フランス語 Mer du Nord、オランダ語 Noordzee、デンマーク語 Nordsøen、ノルウェー語 Nordsjøen)は、大西洋の付属海。古名はゲルマン海(ラテン語 Mare Germanicum、英語 German Ocean)。
東はノルウェー、デンマーク、南はドイツ、オランダ、ベルギー、フランス、西はイギリス、北はオークニー諸島・シェトランド諸島に囲まれている。東はスカゲラク海峡・カテガット海峡およびキール運河でバルト海に、北はノルウェー海に、南はドーバー海峡・イギリス海峡で大西洋に繋がっている。南北の長さは970km、東西は580km、面積は75万km2、水量は94000km3である[1]。
北海に流れ込む主な川はエルベ川、ヴェーザー川、エムス川、ライン川などがある。なかでも、最も北海に影響を及ぼす河川はエルベ川とライン川・ムーズ川である[2]。北海の集水域にはおよそ1億8500万人が暮らしており、また世界で最も工業化された地方のうちのひとつが含まれている[3]。
北海油田と総称される油田・ガス田が多数あり、ヨーロッパの貴重なエネルギー源である。
The North Sea is a sea of the Atlantic Ocean located between Great Britain (England and Scotland), Denmark, Norway, Germany, the Netherlands, Belgium and France. An epeiric (or "shelf") sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the ocean through the English Channel in the south and the Norwegian Sea in the north. It is more than 970 kilometres (600 mi) long and 580 kilometres (360 mi) wide, with an area of 570,000 square kilometres (220,000 sq mi).
The North Sea has long been the site of important European shipping lanes as well as a major fishery. The coast is a popular destination for recreation and tourism in bordering countries, and more recently the sea has developed into a rich source of energy resources, including fossil fuels, wind, and early efforts in wave power.
Historically, the North Sea has featured prominently in geopolitical and military affairs, particularly in Northern Europe. It was also important globally through the power northern Europeans projected worldwide during much of the Middle Ages and into the modern era. The North Sea was the centre of the Vikings' rise. Subsequently, the Hanseatic League, the Dutch Republic, and the British each sought to gain command of the North Sea and thus access to the world's markets and resources. As Germany's only outlet to the ocean, the North Sea continued to be strategically important through both World Wars.
The coast of the North Sea presents a diversity of geological and geographical features. In the north, deep fjords and sheer cliffs mark the Norwegian and Scottish coastlines, whereas in the south, the coast consists primarily of sandy beaches and wide mudflats. Due to the dense population, heavy industrialization, and intense use of the sea and area surrounding it, there have been various environmental issues affecting the sea's ecosystems. Adverse environmental issues – commonly including overfishing, industrial and agricultural runoff, dredging, and dumping, among others – have led to a number of efforts to prevent degradation of the sea while still making use of its economic potential.
La mer du Nord est une mer épicontinentale de l'océan Atlantique, située au nord-ouest de l'Europe, et qui s'étend sur une superficie d'environ 575 000 km2.
Les pays qui bordent la mer du Nord sont le Royaume-Uni (île de Grande-Bretagne) à l'ouest ; les îles Shetland et Orcades au nord-ouest ; la Norvège au nord-est; le Danemark à l'est ; l'Allemagne au sud-est ; enfin les Pays-Bas, la Belgique et la France (pour 50 km de littoral entre Calais et la frontière belge) au sud. Elle communique avec la Manche par le pas de Calais au sud-sud-ouest ; avec l'océan Atlantique au nord-ouest et la mer de Norvège au nord ; avec le Skagerrak à l'est. Le canal de Kiel permet aux navires de rejoindre la mer Baltique.
Elle constitue une zone de fort transit maritime, d'exploitation pétrolière et de pêche. La mer du Nord et son littoral forment un milieu naturel très riche, mais la pollution marine, la surpêche, l'industrie pétrolière (plates-formes offshore) et le tourisme sont sources de menaces pour l'avenir. Elle est en aval du centre de l'Europe industrielle, de l'estuaire du Rhin aux fjords norvégiens et aux falaises du nord de la Grande-Bretagne. Le secteur Manche/Sud-mer du Nord, incluant le pas de Calais est considéré comme représentatif de mers mégatidales peu profondes, caractérisées par un fort courant et une eau très turbide (en raison des courants et phénomènes de renversement de marées), ce qui en fait une zone écologiquement particulière, mais également vulnérable au risque maritime en raison d'un intense trafic maritime (marchand et passager).
Il mare del Nord (in danese Nordsøen; in francese Mer du Nord; in inglese North Sea; in norvegese Nordsjøen;in olandese Noordzee; in svedese Nordsjön; in tedesco Nordsee) è un mare epicontinentale dell'Europa nord-occidentale che comunica con l'oceano Atlantico tramite il mare di Norvegia a nord e la Manica a sud; suo tributario è il Mar Baltico, ad esso collegato tramite gli stretti scandinavi di Skagerrak e Kattegat. Si estende per circa 970 km di lunghezza in direzione nord-sud e 560 km di larghezza in direzione est-ovest, e ha una superficie totale di circa 570000 km²[1]. Accoglie una considerevole parte dei bacini idrografici dell'Unione europea.
El mar del Norte es un mar marginal del océano Atlántico, situado entre las costas de Noruega y Dinamarca en el este, las de las islas británicas al oeste y las de Alemania, los Países Bajos, Bélgica y Francia al sur. El Skagerrak constituye una especie de bahía al este del mar, la cual lo conecta con el Báltico a través del Kattegat; también está conectado con el Báltico mediante el canal de Kiel. El canal de la Mancha lo conecta al resto del Atlántico por el sur, mientras que por el norte conecta en través del mar de Noruega, que es el nombre que adopta el mar al norte de las islas Shetland.
Las mareas son bastante irregulares ya que confluyen en él una corriente proveniente del norte y otra del sur. Hay mucha lluvia y niebla durante todo el año, y del noroeste vienen violentas tormentas que hacen la navegación peligrosa.
Tiene una superficie de unos 750 000 km²,1 una longitud aproximada de 960 km y una anchura máxima de 480 km. Es un mar muy poco profundo, con una profundidad media de 95 metros: el hecho que en el banco Dogger, en medio del mar y a una profundidad de unos 25 metros, se hayan encontrado restos de mamuts prueba que durante la última glaciación o bien estaba cubierto de hielo o bien estaba emergido. Con el deshielo, el banco se convirtió en una especie de último reducto en forma de isla.
Durante la Edad Antigua este mar se conocía como Oceanum o Mare Germanicum. El nombre actual se cree que surgió desde el punto de vista de las islas Frisias, desde donde quedaba totalmente al norte, y por oposición al mar del Sur (el mar de Frisia y el Zuiderzee, en los Países Bajos). A la larga, el nombre actual se acabó imponiendo, de manera que ya era predominante durante la Edad Moderna. En la citada Edad Moderna fue común llamar Mar del Norte o Mar del Nord a todo el océano Atlántico, siendo por contrapartida llamado «Mar del Sur» o «Mar del Sud» todo el océano Pacífico.
Según las lenguas oficiales de los estados que lo rodean, se denomina Mer du Nord, en francés; Noordzee, en neerlandés; Nordsee, en alemán; Nordsjön, en sueco; Nordsøen, en danés; Nordsjøen, en noruego; y North Sea en inglés. En frisón se dice Noardsee y en gaélico escocés A' Mhuir en Tuath.
Tiene importantes yacimientos de petróleo y gas natural, los cuales comenzaron a explotarse en los años 1970.
Се́верное мо́ре (ранее также Немецкое море[3]; фр. Mer du Nord, нем. Nordsee, нидерл. Noordzee, з.-фриз. Noardsee, англ. North Sea, норв. Nordsjøen, дат. Nordsøen или Vesterhavet) — мелководное шельфовое море Атлантического океана, омывающее берега северной Европы. Расположено между Британскими островами на западе, Ютландским, Скандинавским полуостровами на востоке и континентальной Европой на юге. Омывает берега Норвегии, Дании, Германии, Нидерландов, Бельгии, Франции и Великобритании.
Площадь — 750 тыс. км²[1]. Наибольшая глубина 725 м[2]. Более 2/3 моря имеет глубину менее 100 м; в южной части — отмели (банка Доггер и др.). Впадают крупные реки: Эльба, Везер, Рейн, Темза. Основные порты: Роттердам, Амстердам, Антверпен, Лондон, Гамбург, Осло, Берген[2].
Прибрежная мелководная часть на юге иногда выделяется под названием Ваттового моря.
 Alexander De Croo
Alexander De Croo
 Belgium
Belgium
 Denmark
Denmark
 Germany
Germany
 Emmanuel Macron
Emmanuel Macron
 France
France

 Hand in Hand
Hand in Hand
 Ireland
Ireland
 Jonas Gahr Støre
Jonas Gahr Støre
 Leo Varadkar
Leo Varadkar
 Mark Rutte
Mark Rutte
 Mette Frederiksen
Mette Frederiksen
 Netherlands
Netherlands
 Norwegen
Norwegen
 Olaf Scholz
Olaf Scholz
 Ursula von der Leyen
Ursula von der Leyen
 Xavier Bettel
Xavier Bettel

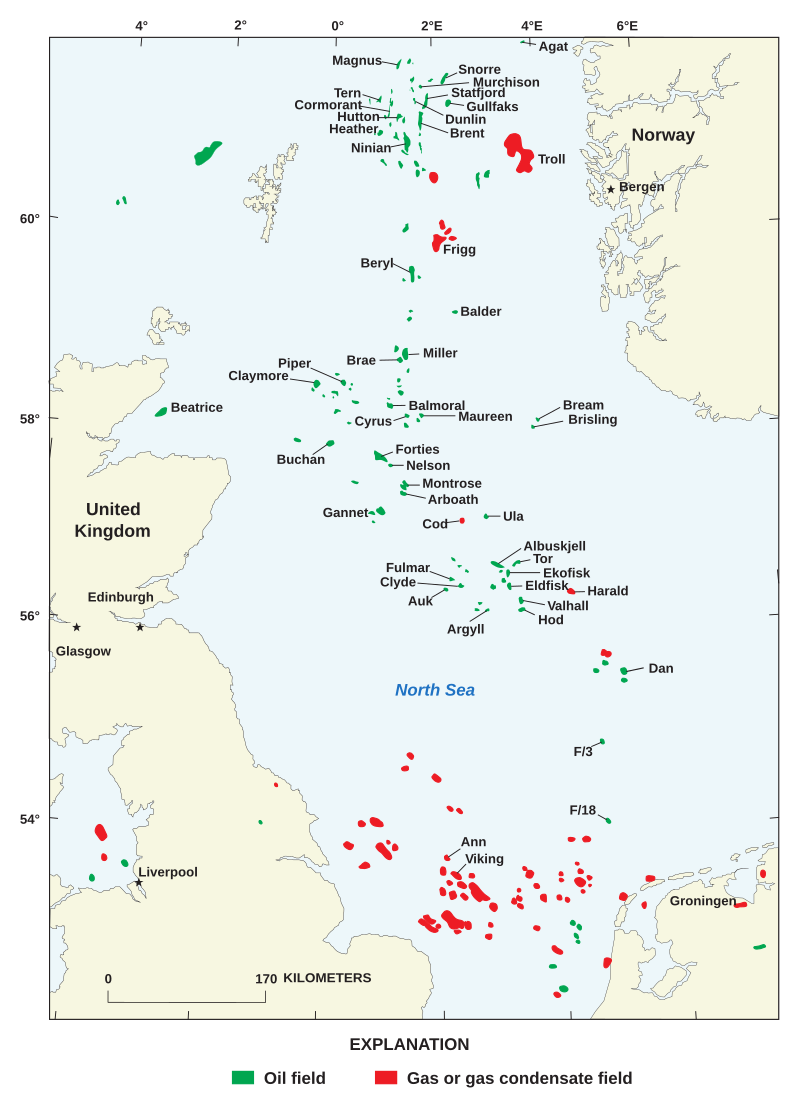
Mit Nordseeöl werden Kohlenwasserstoffe (Erdöl und -gas) bezeichnet, die unter dem Boden der Nordsee lagern. Anfang der 1960er-Jahre wurde Öl in der Nordsee entdeckt, die Förderung begann 1971. Nach der Ölpreiskrise von 1973 wurde die Nordseeförderung in großem Stil rentabel und ausgebaut (siehe unten). 1975 wurde eine Pipeline nach Teesside, Großbritannien, eröffnet.
Fünf Länder haben die Nordsee nach ihren Fördergebieten eingeteilt: Norwegen, Großbritannien, die Niederlande, Dänemark und Deutschland. Die Produktion von Nordseeöl hatte ihr Ölfördermaximum 1999, damals betrug die tägliche Ölproduktion knapp 6 Millionen Barrel (950.000 Kubikmeter). 2004 ging die Produktion von Nordseeöl um 10 Prozent (230.000 Barrel) zurück und im Jahr 2005 nochmals um 12,8 Prozent. Deshalb wurde Großbritannien 2006 vom Nettoölexporteur zur Importnation. Es wurde prognostiziert, dass die Ölproduktion der Nordsee bis 2020 auf 2 Millionen Barrel zurückgehen wird.
北海油田是世界著名的石油集中出产区,每日生产大约600万桶。位于大西洋的陆缘海——北海,它是介于欧洲大不列颠岛、挪威和欧洲大陆之间,所出产之石油为沿岸英国,挪威,丹麦, 德国和荷兰等国所享有,也是布兰特原油指数主要标的。


 Architecture
Architecture
 Financial
Financial
 Färöer
Färöer
 Art
Art
 Vacation and Travel
Vacation and Travel
 Energy resource
Energy resource
 Companies
Companies
 Medical, Pharmaceutical, Rehabilitation
Medical, Pharmaceutical, Rehabilitation