
漢德百科全書 | 汉德百科全书
 Geography
Geography

 Egypt
Egypt
 Algeria
Algeria
 Ethiopia
Ethiopia
 Bahrain
Bahrain

 Education and Research
Education and Research
 Djibouti
Djibouti
 Eritrea
Eritrea
 Gambia
Gambia

 Hand in Hand
Hand in Hand

 Hand in Hand
Hand in Hand
 Institute of Culture and Language
Institute of Culture and Language
 Iraq
Iraq
 Iran
Iran
 Israel
Israel
 Yemen
Yemen
 Jordan
Jordan
 Katar
Katar
 Comoros
Comoros
 Kuwait
Kuwait
 Libanon
Libanon
 Libya
Libya
 Literature
Literature
 Morocco
Morocco
 Mauritania
Mauritania
 Niger
Niger
 Nigeria
Nigeria
 Oman
Oman
 Palestine
Palestine
 Republic of the Sudan
Republic of the Sudan
 Republik Südsudan
Republik Südsudan
 Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia
 Senegal
Senegal
 Somalia
Somalia
 Syria
Syria
 Tansania
Tansania
 Tschad
Tschad
 Tunisia
Tunisia
 Turkey
Turkey
 United Arab Emirates
United Arab Emirates

 United Nations
United Nations
 Official languages
Official languages
 Cyprus
Cyprus
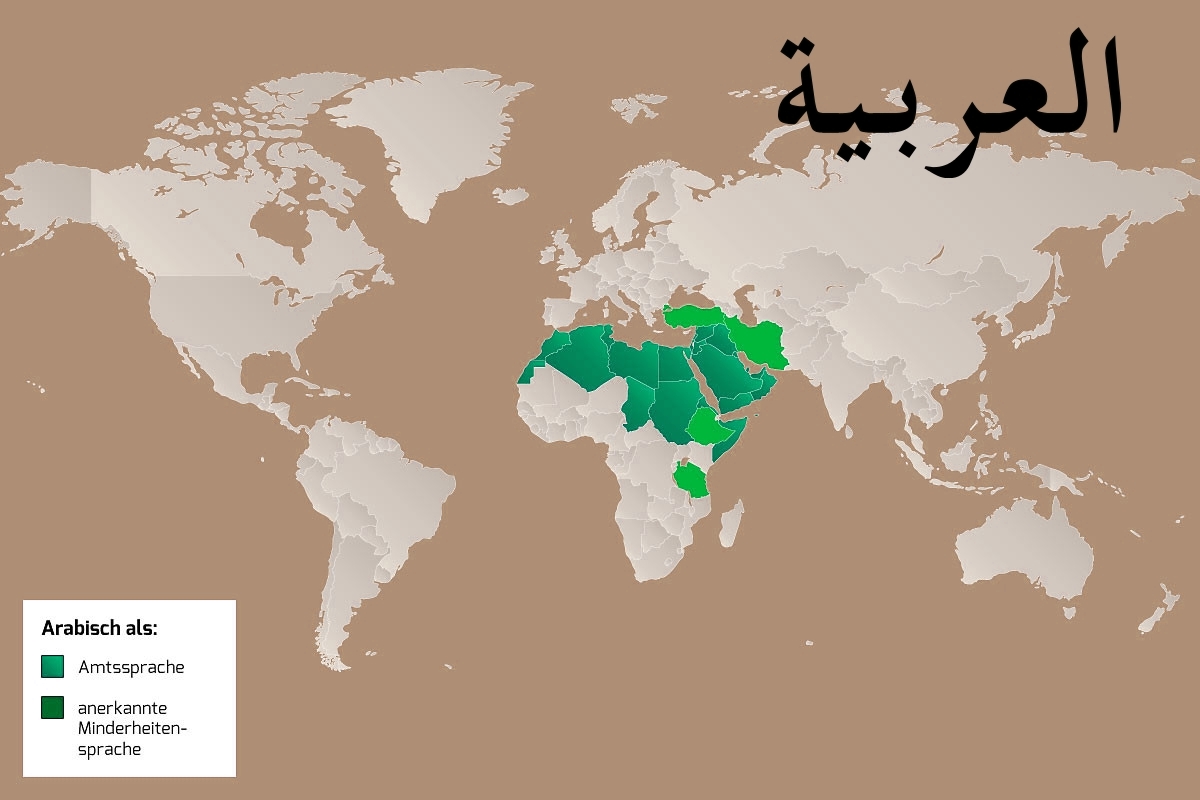
Die arabische Sprache (kurz Arabisch; Eigenbezeichnung اَللُّغَةُ اَلْعَرَبِيَّة, DMG al-luġatu l-ʿarabiyya ‚die arabische Sprache‘, kurz العربية, DMG al-ʿarabiyya ‚das Arabische‘, Ausspracheⓘ/?) ist die am weitesten verbreitete Sprache des semitischen Zweigs der afroasiatischen Sprachfamilie und in ihrer Hochsprachform الفصحى / al-Fuṣḥā eine der sechs Amtssprachen der Vereinten Nationen. Schätzungsweise wird Arabisch von 313 Millionen Menschen als Muttersprache und von weiteren 424 Millionen als Zweit- oder Fremdsprache gesprochen.[2][3] Auch durch seine Rolle als Sakralsprache entwickelte sich das Arabische zur Weltsprache.[4] Die moderne arabische Standardsprache beruht auf dem klassischen Arabischen, der Sprache des Korans und der Dichtung, und unterscheidet sich stark von den gesprochenen Varianten des Arabischen.
Aus dem klassischen Arabisch hat sich in den letzten anderthalb Jahrtausenden eine Vielzahl von Dialekten entwickelt. Für alle Sprecher dieser Sprache, außer den Sprechern des Maltesischen, ist Hocharabisch Schrift- und Dachsprache. Das Maltesische ist mit den maghrebinisch-arabischen Dialekten stark verwandt, wurde jedoch im Gegensatz zu den anderen gesprochenen Formen des Arabischen zu einer eigenständigen Standardsprache ausgebaut. Ob Hocharabisch als moderne Standardsprache zu betrachten ist, ist umstritten (siehe auch Ausbausprache). Es fehlt oft an einem einheitlichen Wortschatz für viele Begriffe der modernen Welt sowie am Fachwortschatz in vielen Bereichen moderner Wissenschaften. Darüber hinaus ist Hocharabisch innerhalb der einzelnen arabischen Länder relativ selten ein Mittel zur mündlichen Kommunikation.
Die einzelnen arabischen Dialekte in den verschiedenen Ländern unterscheiden sich teilweise sehr stark voneinander, wenn auch meist nur in der Aussprache, und sind bei vorliegender geographischer Distanz gegenseitig nicht oder nur schwer verständlich. So werden beispielsweise algerische Filme, die im dortigen Dialekt gedreht worden sind, zum Teil hocharabisch untertitelt, wenn sie in den Golfstaaten ausgestrahlt werden.
阿拉伯语(اَلْعَرَبِيَّةُ,al-ʿarabiyyah [al ʕaraˈbijːa] (ⓘ)或者 عربي/عربى,ʿarabīy [ˈʕarabiː] (ⓘ)或 [ʕaraˈbij]),书写形式也称阿拉伯文,是除了英语和法语之外最多国家使用的官方语言。阿拉伯语源自公元6世纪的古典阿拉伯语。它包括书面语及流通于中东、北非和非洲之角(即索马里半岛)的各种口语。阿拉伯语属于亚非语系。

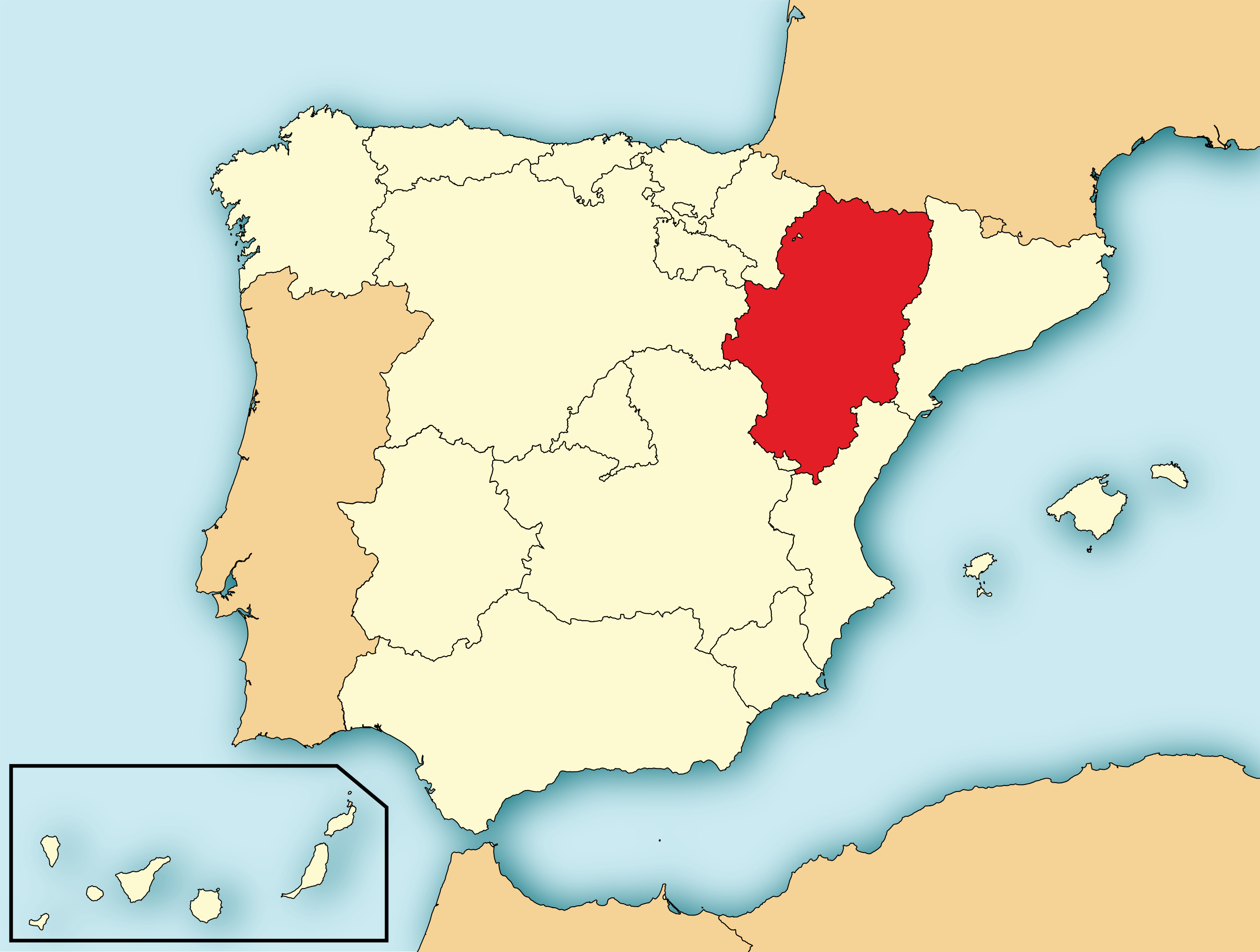


Aragonien oder Aragon (spanisch und aragonesisch Aragón, katalanisch Aragó) ist eine autonome Gemeinschaft im Nordosten Spaniens. Sie grenzt im Norden auf dem Hauptkamm der Pyrenäen an Frankreich, im Osten an Katalonien, im Südosten an Valencia und im Westen an Kastilien-La Mancha, Kastilien und León, La Rioja sowie Navarra. Hauptstadt ist Saragossa.
Das Gebiet der heutigen autonomen Gemeinschaft entspricht dem früheren Königreich Aragonien im engeren Sinne, das seinen Namen wiederum dem Fluss Aragón verdankte.
阿拉贡(西班牙语:Aragón;加泰罗尼亚语:Aragó;阿拉贡语:Aragón)是西班牙东北部的一个自治区,面积47,719平方公里,人口1,277,471(2003年)。
阿拉贡向北与法国相邻,向东是加泰罗尼亚,向南是巴伦西亚省,向西是卡斯蒂利亚-拉曼恰、卡斯蒂利亚-莱昂、拉里奥哈和纳瓦拉。萨拉戈萨省、韦斯卡省和特鲁埃尔省属于阿拉贡自治地区。阿拉贡的首府是萨拉戈萨。

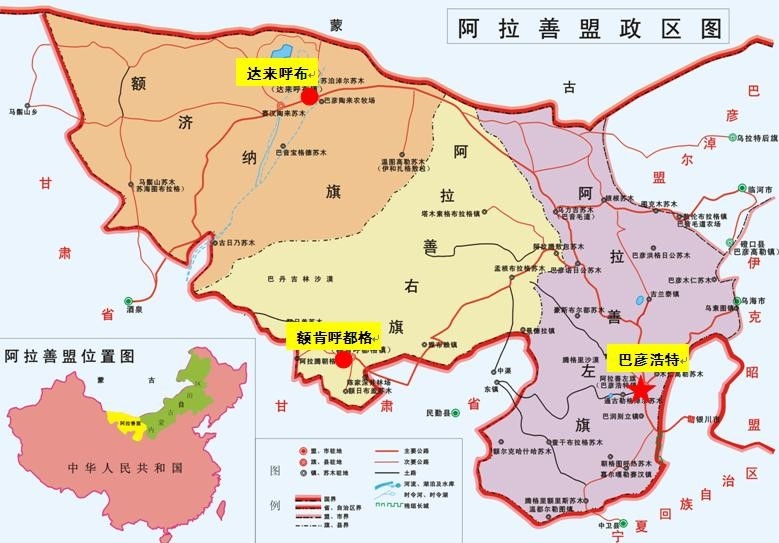


Der Aras, Araks oder Arax, aserbaidschanisch Araz, persisch ارس (rud-e) Aras, armenisch Արաքս Araks, kurdisch Erez, urartäisch Muna,[2] griechisch Araxes, türkisch Aras Nehri) ist mit 1072 km Länge der längste Nebenfluss der Kura in Vorderasien. Er wird von den Brücken von Choda Afarin gequert.
阿拉斯河[1](土耳其语:Aras Nehri,亚美尼亚语:Արաքս,罗马化:Araks,阿塞拜疆语:ارس,آراز,波斯语:ارس),亚美尼亚称之为阿拉克斯河[2][3],是欧亚大陆高加索地区的河流,流经土耳其、亚美尼亚、阿塞拜疆和伊朗,河道全长1,072公里,流域面积102,000平方公里,为库拉河的最大支流。
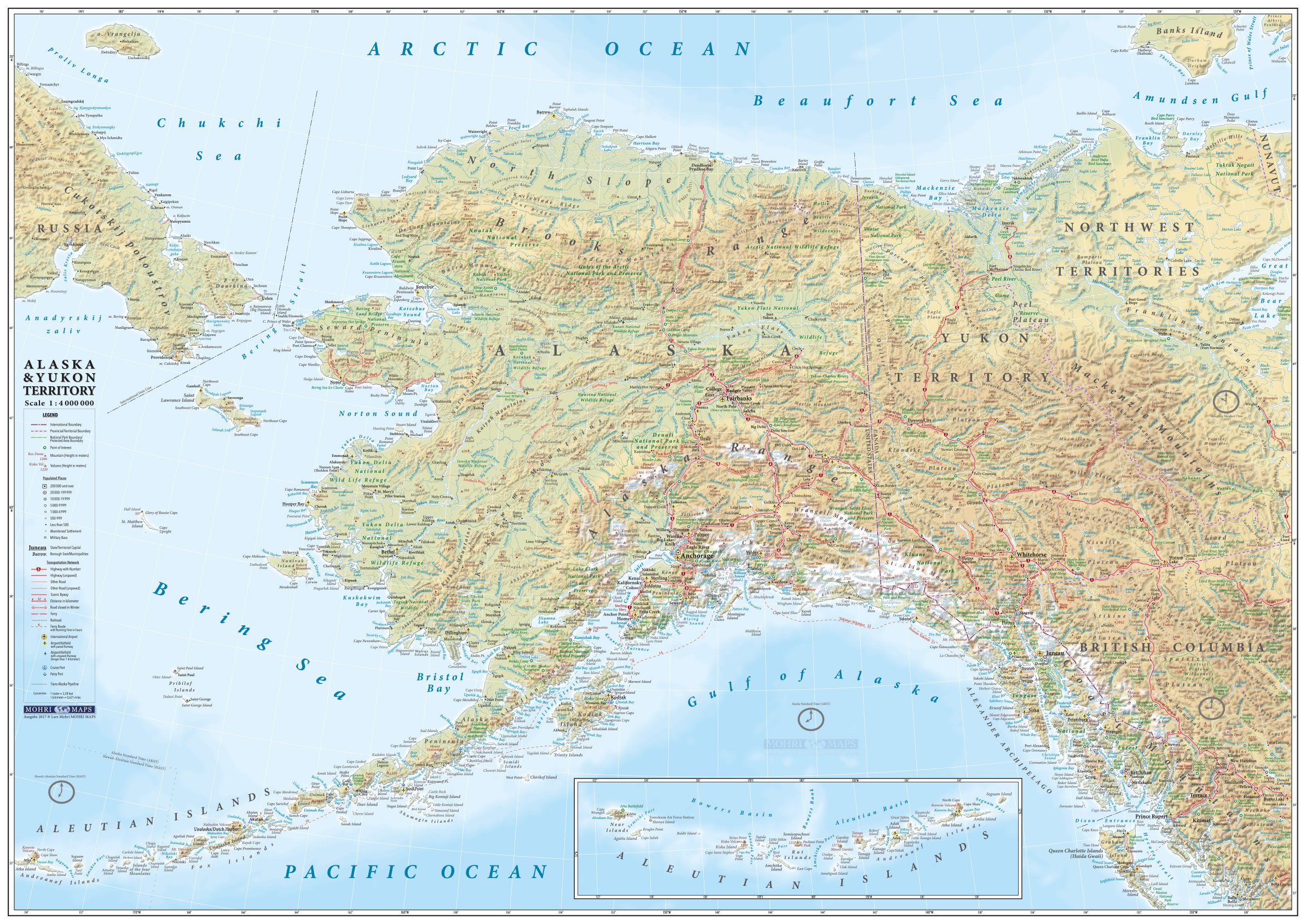
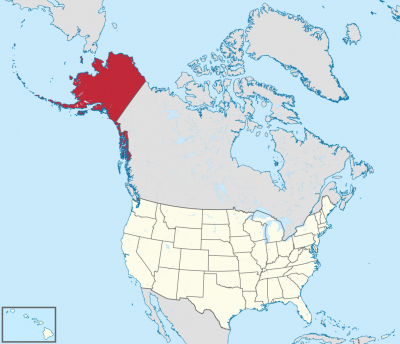


アラスカ州(英: State of Alaska [əˈlæskə] (![]() 音声ファイル))は、アメリカ合衆国最北端にある州。アリューシャン列島を含む。北アメリカ大陸北西の端にあり、合衆国本土とはカナダを挟んで飛地になっている。アラスカでは、合衆国本土を"lower 48"(直訳:南方の48州。アメリカ50州からアラスカ州とハワイ州を除いたもの)と呼ぶことがある[2]。
音声ファイル))は、アメリカ合衆国最北端にある州。アリューシャン列島を含む。北アメリカ大陸北西の端にあり、合衆国本土とはカナダを挟んで飛地になっている。アラスカでは、合衆国本土を"lower 48"(直訳:南方の48州。アメリカ50州からアラスカ州とハワイ州を除いたもの)と呼ぶことがある[2]。
アメリカ合衆国の州の中では面積最大、東はカナダ、北は北極海、西と南は太平洋と接し、西のベーリング海を隔ててロシアとも海上の国境がある。2010年国勢調査による人口は710,231人であり[3]、その約半分はアンカレッジ都市圏に居住。州都はジュノー市で、最大都市はアンカレッジ市である。海港アンカレッジはかつてアジアとアメリカおよびヨーロッパを結ぶ航空路線の寄港地として知られた。アメリカ合衆国の州の中では人口密度が最小の州でもある[4]。
アラスカは1867年3月30日にロシア帝国からアメリカ合衆国が買収した。その後幾つかの管理形態の変遷を経て、1912年5月11日にアラスカ準州、1959年1月3日にアラスカ州となった。
Alaska (/əˈlæskə/ (![]() listen); Aleut: Alax̂sxax̂; Inupiaq: Alaasikaq; Alutiiq: Alas'kaaq; Tlingit: Anáaski; Russian: Аля́ска, romanized: Alyáska) is a U.S. state located on the northwest extremity of the country's West Coast, just across the Bering Strait from Asia. An exclave of the U.S., it borders the Canadian province of British Columbia and territory of Yukon to the east and southeast and has a maritime border with Russia's Chukotka Autonomous Okrug to the west. To the north are the Chukchi and Beaufort seas of the Arctic Ocean, while the Pacific Ocean lies to the south and southwest.
listen); Aleut: Alax̂sxax̂; Inupiaq: Alaasikaq; Alutiiq: Alas'kaaq; Tlingit: Anáaski; Russian: Аля́ска, romanized: Alyáska) is a U.S. state located on the northwest extremity of the country's West Coast, just across the Bering Strait from Asia. An exclave of the U.S., it borders the Canadian province of British Columbia and territory of Yukon to the east and southeast and has a maritime border with Russia's Chukotka Autonomous Okrug to the west. To the north are the Chukchi and Beaufort seas of the Arctic Ocean, while the Pacific Ocean lies to the south and southwest.
Alaska is the largest U.S. state by area and the seventh-largest subnational division in the world. It is the third-least populous and the most sparsely populated state, but by far the continent's most populous territory located mostly north of the 60th parallel, with an estimated population of 738,432 as of 2015—more than quadruple the combined populations of Northern Canada and Greenland.[3] Approximately half of Alaska's residents live within the Anchorage metropolitan area. The state capital of Juneau is the second-largest city in the United States by area, comprising more territory than the states of Rhode Island and Delaware.
Alaska was occupied by various indigenous peoples for thousands of years before the arrival of Europeans. The state is considered the entry point for the settlement of North America by way of the Bering land bridge. The Russians were the first Europeans to settle the area beginning in the 18th century, eventually establishing Russian America, which spanned most of the current state. The expense and difficulty of maintaining this distant possession prompted its sale to the U.S. in 1867 for US$7.2 million, or approximately two cents per acre ($4.74/km2). The area went through several administrative changes before becoming organized as a territory on May 11, 1912. It was admitted as the 49th state of the U.S. on January 3, 1959.[4]
While it has one of the smallest state economies in the country, Alaska's per capita income is among the highest, owing to a diversified economy dominated by fishing, natural gas, and oil, all of which it has in abundance. United States armed forces bases and tourism are also a significant part of the economy; more than half the state is federally owned public land, including a multitude of national forests, parks, and wildlife refuges.
Alaska's indigenous population is proportionally the highest of any U.S. state, at over 15 percent.[5] Close to two dozen native languages are spoken, and Alaskan Natives exercise considerable influence in local and state politics.
L’Alaska (prononcé /a.las.ka/ Écouter (Fr.) en français et /ə.ˈlæs.kə/ Écouter (É.-U.A) en anglais) est le 49e État des États-Unis, dont la capitale est Juneau et la plus grande ville Anchorage, où habite environ 40 % de la population de l'État. Avec une superficie totale de 1 717 854 km2, il est l'État le plus étendu et le plus septentrional du pays, mais l'un des moins peuplés, ne comptant que 731 545 habitants en 20191.
Comme Hawaï, l'Alaska est séparé des États-Unis contigus et se situe au nord-ouest du Canada. Bordé par l'océan Arctique au nord et la mer de Béring et l'océan Pacifique au sud, ce territoire est séparé de l'Asie par le détroit de Béring. En outre, ses divisions administratives ne sont pas des comtés mais des boroughs.
Alaska signifie « grande Terre » ou « continent » en aléoute3. Cette région, que l'on appelait au XIXe siècle l'« Amérique russe », tire son nom d'une longue presqu'île, au nord-ouest du continent américain, à environ 1 000 kilomètres au sud du détroit de Bering, et qui se lie, vers le sud, aux îles Aléoutiennes. Le surnom de l'Alaska est « la dernière frontière » ou « la terre du soleil de minuit ».
Peuplé par des Aléoutes, Esquimaux (notamment Iñupiak et Yupiks) et peut-être d'autres Amérindiens depuis plusieurs millénaires, le territoire est colonisé par des trappeurs russes à la fin du XVIIIe siècle. Les ressources de l'Alaska proviennent alors essentiellement du commerce du bois et de la traite des fourrures. Le 30 mars 1867, les États-Unis l'achètent à la Russie pour la somme de 7,2 millions de dollars (environ 120 millions de dollars actuels), et celui-ci adhère à l'Union le 3 janvier 1959. Les secteurs économiques prédominants aujourd'hui sont la pêche, le tourisme, et surtout la production d'hydrocarbures (pétrole, gaz) depuis la découverte de gisements à Prudhoe Bay dans les années 1970.
Le Denali (6 190 mètres d'altitude), point culminant des États-Unis, se trouve dans la chaîne d'Alaska et constitue le cœur du parc national et réserve du Denali.
Le climat y est de type polaire, et la faune caractéristique des milieux froids (grizzli, caribou, orignal, ours blanc).
Les territoires limitrophes sont le territoire du Yukon et la province de Colombie-Britannique au Canada. Le Kraï du Kamtchatka et le district autonome de Tchoukotka en Russie se trouvent à quelques dizaines de kilomètres, de l'autre côté du détroit de Bering.
Bastion du Parti républicain, l'Alaska est gouverné depuis 2018 par Mike Dunleavy.
L'Alaska (pron. /aˈlaska/[3]; in inglese , /əˈlæskə/), italianizzata in Alasca[4][5] (in aleutino Alax̂sxax̂; in inupiaq Alaasikaq; in alutiiq Alas'kaaq; in tlingit Anáaski; in russo Аляска, Aljaska), è uno Stato federato degli Stati Uniti d'America. Situato nella estremità nordoccidentale del continente nordamericano è separato da qualsiasi altro stato degli USA, confina a est con il Canada ed è bagnato a nord dal Mar Glaciale Artico e a sud dall'oceano Pacifico; a ovest lo stretto di Bering lo separa dalla Čukotka, nella regione storica della Siberia. Con 1717854 km² è lo Stato più grande degli Stati Uniti ma, visto il clima rigido, è scarsamente popolato: nel 2019 la popolazione dello Stato era di 731 545 abitanti[1]; il dato lo rende il 47º stato per popolazione. Circa la metà di questi abitanti vive nell'area metropolitana di Anchorage, centro principale dello Stato. L'economia dell'Alaska è dominata dalle riserve di petrolio, gas naturale e dall'industria della pesca, risorse di cui dispone in abbondanza. Anche il turismo occupa una parte significativa dell'economia.
Anche se era stato occupato per migliaia di anni dalle popolazioni indigene, dal XVIII secolo in poi le potenze europee considerarono il territorio dell'Alaska pronto per essere sfruttato. Gli Stati Uniti acquistarono l'Alaska dalla Russia il 30 marzo 1867, per 7,2 milioni di dollari (120 milioni di dollari al netto dell'inflazione), a circa due centesimi per acro (4,74 $/km²). L'area ha attraversato diversi cambiamenti amministrativi prima di essere organizzata come un territorio l'11 maggio 1912. È stato ammesso come 49º Stato degli Stati Uniti d'America il 3 gennaio 1959.
Il toponimo Alaska è derivato dalla parola alaxsxaq che ha come significato «grande paese» o «terraferma» nella lingua degli Aleutini o Unangan (come essi si chiamavano nella propria lingua)[6].
Il soprannome dell'Alaska è The Last Frontier (usato anche nelle targhe automobilistiche), e l'animale scelto come simbolo dello Stato è l'alce.
Alaska es uno de los cincuenta estados que forman los Estados Unidos de América. Su capital es Juneau y su ciudad más poblada es Anchorage. Está ubicado en el extremo noroeste de América del Norte, en la región Oeste del país, división Pacífico. Limita al norte con el océano Ártico, al este con Canadá, al sur con el océano Pacífico y al oeste con el mar de Bering (océano Pacífico). Con 1 717 856 km² es el estado más extenso del país y la séptima entidad subnacional más grande del mundo, por detrás de la república de Sajá (Rusia), Australia Occidental, Krai de Krasnoyarsk (Rusia), Groenlandia (Dinamarca), Nunavut (Canadá) y Queensland (Australia); con 710 231 habs. en 2010, el cuarto menos poblado —por delante de Dakota del Norte, Vermont y Wyoming, el menos poblado— y con 0,41 hab/km², el menos densamente poblado. Fue el penúltimo en ser admitido en la Unión, el 3 de enero de 1959, como el estado número 49, solo antes que Hawái. Es el estado con mayor proporción de empleados públicos respecto de la población.4
Alaska recibe el nombre del vocablo aleutiano alyeska o alaxsxaq, que significa «tierra grande», o más literalmente, «el objeto contra el que la acción del mar es dirigida».5 La bandera de Alaska representa, sobre fondo azul, las estrellas que forman la constelación de la Osa Mayor y, en la esquina superior derecha, la estrella polar.
El 30 de marzo de 1867, Estados Unidos compró Alaska del Imperio ruso, por 7 200 000 dólares.6 Estados Unidos trató, durante las primeras décadas del siglo XX, de mejorar las comunicaciones (sobre todo para conectar Alaska con el resto de los Estados Unidos por ferrocarril), y promover la colonización del valle de Matanuska. Sin embargo, la Segunda Guerra Mundial y las batallas navales en las islas Aleutianas con Japón cambiaron el rumbo de la política de los EE. UU. en los asuntos de Alaska. Así, en 1942, se construyó en meses una carretera de comunicación (la Autopista Alaska) para garantizar la defensa del Territorio de Alaska, a la vez que establecieron nuevas bases militares (por ejemplo, de radares) y se promovieron asentamientos civiles. El final de la guerra mundial y el comienzo de la Guerra Fría aceleraron la necesidad de integrar este territorio a la Unión. En 1959, Alaska fue finalmente aceptada como el 49.º estado de los Estados Unidos de América.
El descubrimiento de yacimientos petrolíferos ha permitido un enorme crecimiento económico en Alaska durante las últimas décadas, pese al aislamiento geográfico y a las duras condiciones de vida. El mayor hito de su desarrollo ha sido la construcción, a partir de 1974, del Trans-Alaska Pipeline, un oleoducto de 1269 km que une la Bahía Prudhoe con el puerto de Valdez. Pero el petróleo también ha sido el origen de ciertos desastres, como el accidente ocurrido en 1989 cuando el superpetrolero Exxon Valdez encalló en las aguas de Alaska y provocó una marea negra que ha sido calificada como uno los mayores desastres ecológicos de la historia, el desastre del Exxon Valdez.
Аля́ска[2][3] (англ. Alaska [əˈlæskə], эским. Alaskaq, Aqłuq) — самый северный и крупнейший по территории штат[4] США; расположен на северо-западе Северной Америки. В Беринговом проливе имеет морскую границу с Россией.
Включает территорию Северной Америки западнее 141-го меридиана западной долготы, в том числе одноимённый полуостров с прилегающими островами, Алеутские острова и собственно территорию Северной Америки к северу от полуострова, а также узкую полосу тихоокеанского побережья вместе с островами архипелага Александра вдоль западной границы Канады.
Площадь территории — 1 717 854 км², из которых 236 507 км² приходится на водную поверхность. Население — 737 438[1] чел. (2018). Столица штата — город Джуно.



 Aragón
Aragón
 Alaska-AK
Alaska-AK
 Animal world
Animal world