
漢德百科全書 | 汉德百科全书
 FIFA
FIFA


 Alberta-AB
Alberta-AB

 British Columbia-BC
British Columbia-BC
 FIFA
FIFA
 Women's Soccer World Cup 2015
Women's Soccer World Cup 2015
 Canada
Canada
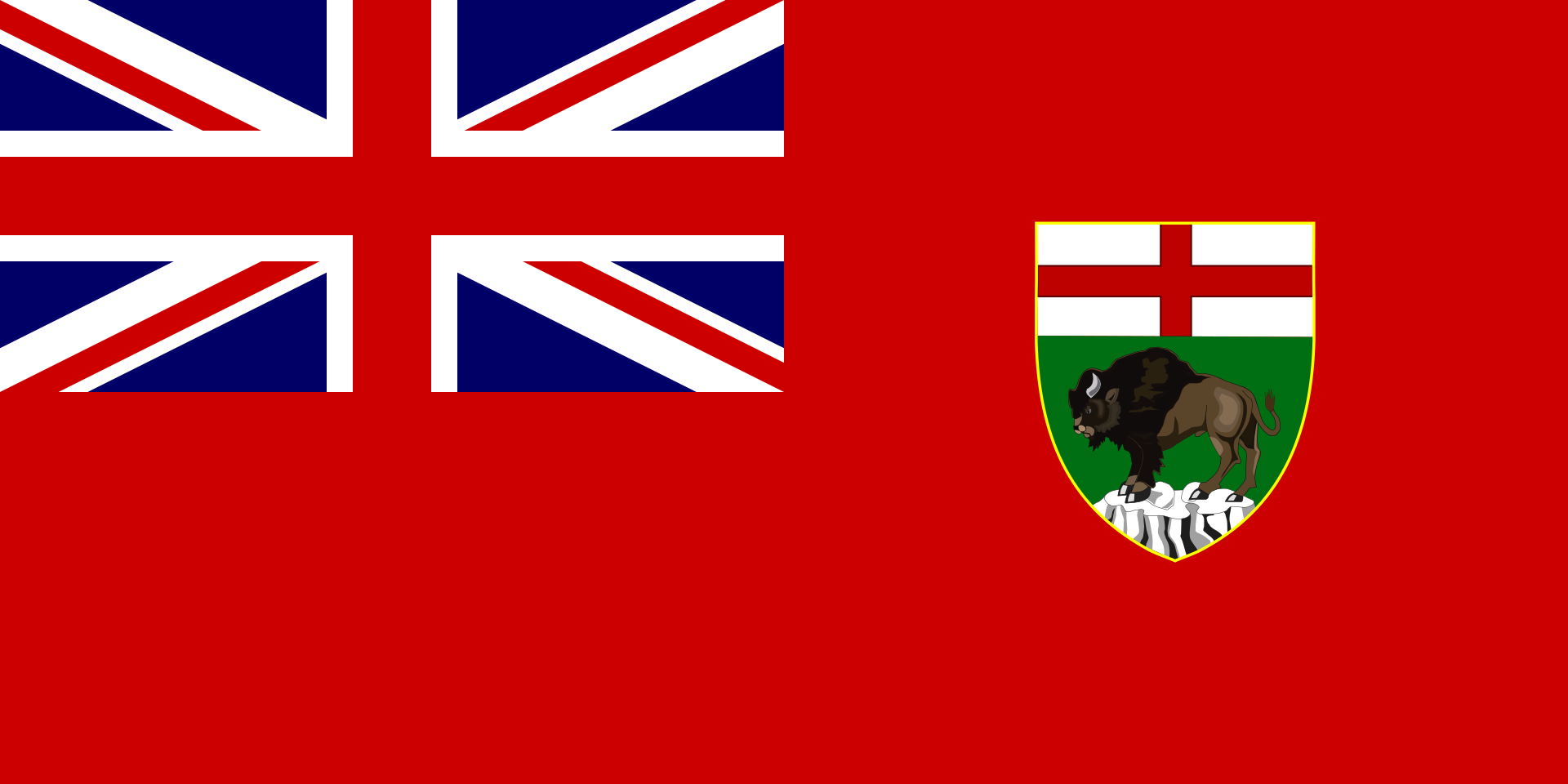
 Manitoba-MB
Manitoba-MB

 New Brunswick-NB
New Brunswick-NB

 Ontario-ON
Ontario-ON

 Quebec-QC
Quebec-QC

 Sport
Sport
 (F)Football World Cup
(F)Football World Cup


 Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes
Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes

 Bretagne
Bretagne
 FIFA
FIFA
 France
France
 Women's Soccer World Cup 2019
Women's Soccer World Cup 2019

 Grand Est
Grand Est

 Ile-de-France
Ile-de-France

 Normandie
Normandie

 Occitania
Occitania

 Provence-Alpes-Côte d´Azur
Provence-Alpes-Côte d´Azur

 Sport
Sport
 (F)Football World Cup
(F)Football World Cup


 Confederation of African Football
Confederation of African Football
 FIFA
FIFA

 Sport
Sport
 (F)International soccer leagues
(F)International soccer leagues

 Sport
Sport
 (F)African Cup of Nations
(F)African Cup of Nations

 FIFA
FIFA
 FIFA Club World Cup
FIFA Club World Cup

 Sport
Sport
 (F)AFC Champions League
(F)AFC Champions League

 Sport
Sport
 (F)CAF Champions League
(F)CAF Champions League

 Sport
Sport
 (F)CONCACAF Champions League
(F)CONCACAF Champions League

 Sport
Sport
 (F)Copa Libertadores
(F)Copa Libertadores

 Sport
Sport
 (F)UEFA Champions League
(F)UEFA Champions League


国际足联俱乐部世界杯(英语:FIFA Club World Cup),或译为世界俱乐部杯、俱乐部冠军杯,简称世俱杯。由该项赛事的前身国际足联俱乐部世锦赛(英语:FIFA Club World Championship)与洲际杯(又名丰田杯,英语:Intercontinental Cup)合并而来[1][2]。是一项由国际足联主办,来自六大洲最顶级俱乐部参与的国际足球锦标赛。
Die FIFA-Klub-Weltmeisterschaft ist die offizielle Weltmeisterschaft für Fußball-Vereinsmannschaften, bei der die Sieger der sechs kontinentalen Meisterwettbewerbe im Vereinsfußball gegeneinander antreten. Nach einem ersten Versuch im Jahr 2000 in Brasilien wird sie seit 2005 regelmäßig gegen Ende des Jahres ausgespielt. Sie gilt als Nachfolger des Weltpokals, der auf europäische und südamerikanische Mannschaften begrenzt war.
Startberechtigt sind sieben Klubs, neben den Gewinnern der UEFA Champions League (Europa) und der Copa Libertadores (Südamerika) auch die Gewinner der CAF Champions League (Afrika), der AFC Champions League (Asien), des CONCACAF Champions Cups (Nord- und Mittelamerika) und der OFC Champions League (Ozeanien) sowie ein Team aus dem Gastgeberland.
 Germany
Germany
 Germany
Germany
 FIFA
FIFA
 Women's Soccer World Cup 2015
Women's Soccer World Cup 2015
 Women's Soccer World Cup 2019
Women's Soccer World Cup 2019
 Women's Soccer World Cup 2023
Women's Soccer World Cup 2023
 Japan
Japan
 Norwegen
Norwegen
 Spain
Spain
 United States
United States
 United States
United States
 United States
United States

 AFC Champions League 2015
AFC Champions League 2015
 AFC Champions League 2017
AFC Champions League 2017
 AFC Champions League 2017
AFC Champions League 2017
 AFC Champions League 2018
AFC Champions League 2018
 AFC Champions League 2019
AFC Champions League 2019
 Asian Football Confederation
Asian Football Confederation
 CONCACAF
CONCACAF
 Confederación Sudamericana de Fútbol
Confederación Sudamericana de Fútbol
 Confederation of African Football
Confederation of African Football
 FIFA
FIFA
 FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 1990
FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 1990
 FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 1994
FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 1994
 FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 1998
FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 1998
 FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 2002
FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 2002
 FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 2006
FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 2006
 FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 2010
FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 2010
 FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 2014
FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 2014
 FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 2018
FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 2018
 FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 2022
FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 2022

 FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 2026
FIFA Fussball-Weltmeisterschaft 2026
 FIFA-Konföderationen-Pokal 2013
FIFA-Konföderationen-Pokal 2013
 FIFA-Konföderationen-Pokal 2017
FIFA-Konföderationen-Pokal 2017
 Women's Soccer World Cup 1991
Women's Soccer World Cup 1991
 Women's Soccer World Cup 1995
Women's Soccer World Cup 1995
 Women's Soccer World Cup 1999
Women's Soccer World Cup 1999
 Women's Soccer World Cup 2003
Women's Soccer World Cup 2003
 Women's Soccer World Cup 2007
Women's Soccer World Cup 2007
 Women's Soccer World Cup 2011
Women's Soccer World Cup 2011
 Women's Soccer World Cup 2015
Women's Soccer World Cup 2015
 Women's Soccer World Cup 2019
Women's Soccer World Cup 2019
 Oceania Football Confederation
Oceania Football Confederation
 Switzerland
Switzerland
 Zurich
Zurich

 Sport
Sport
 (F)Football Women's World Cup
(F)Football Women's World Cup

 Sport
Sport
 (F)International soccer leagues
(F)International soccer leagues

 Sport
Sport
 (F)AFC Champions League
(F)AFC Champions League

 Sport
Sport
 (F)CAF Champions League
(F)CAF Champions League

 Sport
Sport
 (F)CONCACAF Champions League
(F)CONCACAF Champions League

 Sport
Sport
 (F)Copa Libertadores
(F)Copa Libertadores

 Sport
Sport
 (F)UEFA Champions League
(F)UEFA Champions League

 Sport
Sport
 (F)European football championship
(F)European football championship

 Sport
Sport
 (F)FIFA U-20 World Cup
(F)FIFA U-20 World Cup

 Sport
Sport
 (F)FIFA Confederations Cup
(F)FIFA Confederations Cup

 Sport
Sport
 (F)Soccer Asia Cup
(F)Soccer Asia Cup

 Sport
Sport
 (F)African Cup of Nations
(F)African Cup of Nations
 UEFA Champions League 2015/16
UEFA Champions League 2015/16
 UEFA Champions League 2016/17
UEFA Champions League 2016/17
 UEFA Champions League 2017/18
UEFA Champions League 2017/18
 UEFA Champions League 2018/19
UEFA Champions League 2018/19
 UEFA Champions League 2019/20
UEFA Champions League 2019/20
 UEFA Europa League 2017/18
UEFA Europa League 2017/18
 UEFA Europa League 2018/19
UEFA Europa League 2018/19
 UEFA Europa League 2019/20
UEFA Europa League 2019/20
 UEFA Nations League
UEFA Nations League
 Union of European Football Associations
Union of European Football Associations

 Important International Organizations
Important International Organizations

Die Fédération Internationale de Football Association (deutsch Internationaler Verband des Association Football), kurz FIFA oder Fifa, ist ein privater Verband, der „die Kontrolle des Association Football in all seinen Formen“ zum Zweck hat.[3] Der Weltfußballverband ist ein gemeinnütziger Verein im Sinne der Artikel 60 ff. des Schweizerischen Zivilgesetzbuches mit Sitz in Zürich und im Handelsregister eingetragen.[4][5][6] Die FIFA muss als nicht steuerbefreiter Verein im Kanton Zürich eine reduzierte Gewinnsteuer von 4 % entrichten.[1][2]
Die FIFA erwirtschaftet in ihrer aktuellen Vierjahresertragsperiode 5,66 Milliarden Dollar, die zu 89 % aus der Vermarktung der von ihr organisierten Männer-Fußball-WM stammen. Darüber hinaus organisiert sie auch die Frauen-Fußball-WM und zahlreiche weitere Turniere. Ihr Präsident ist Gianni Infantino.
国际足球联合会(法语:Fédération Internationale de Football Association;英语:International Federation of Association Football[注 1]),简称国际足联(FIFA),是管理英式足球、室内五人足球和沙滩足球的国际体育组织,下辖211个会员协会。总部设于瑞士苏黎世。现任主席为吉安尼·因凡蒂诺。国际足联负责组织世界重大足球赛事,当中最著名的是4年举行一次的世界杯。[3]
国際サッカー連盟(こくさいサッカーれんめい、仏: Fédération Internationale de Football Association)は、サッカー(アソシエーション式フットボール)の国際競技連盟であり、スイスの法律に基づいた自立法人である。略称はFIFA(フランス語発音: [fifa] フィファ、英語発音: [ˈfiːfə] フィーファ)。本部はスイスのチューリッヒに置かれている。
2018年時点で全211の国内競技連盟が加盟し[1]、国際競技連盟としては世界最大である[3]。FIFAワールドカップ・FIFA女子ワールドカップの主催が、もっとも大きな任務となっている。
The Fédération Internationale de Football Association[a] (FIFA /ˈfiːfə/ FEE-fə; French for International Federation of Association Football; Spanish: Federación Internacional de Fútbol Asociación; German: Internationaler Verband des Association Football) is a non-profit organization which describes itself as an international governing body of association football, fútsal, beach soccer, and efootball. It is the highest governing body of football.
FIFA was founded in 1904[3] to oversee international competition among the national associations of Belgium, Denmark, France, Germany, the Netherlands, Spain, Sweden, and Switzerland. Headquartered in Zürich, its membership now comprises 211 national associations. Member countries must each also be members of one of the six regional confederations into which the world is divided: Africa, Asia, Europe, North & Central America and the Caribbean, Oceania, and South America.
Today, FIFA outlines a number of objectives in the organizational Statues, including growing football internationally, providing efforts to ensure football is accessible to everyone, and advocating for integrity and fair play.[4] FIFA is responsible for the organization and promotion of football's major international tournaments, notably the World Cup which commenced in 1930 and the Women's World Cup which commenced in 1991. Although FIFA does not solely set the rules of football, that being the responsibility of the International Football Association Board of which FIFA is a member, it applies and enforces the rules across all FIFA competitions.[5] All FIFA tournaments generate revenue from sponsorship; in 2018, FIFA had revenues of over US $4.6 billion, ending the 2015–2018 cycle with a net positive of US$1.2 billion, and had cash reserves of over US$2.7 billion.[6]
Reports by investigative journalists have linked FIFA leadership with corruption, bribery, and vote-rigging related to the election of FIFA president Sepp Blatter and the organization's decision to award the 2018 and 2022 World Cups to Russia and Qatar, respectively. These allegations led to the indictments of nine high-ranking FIFA officials and five corporate executives by the U.S. Department of Justice on charges including racketeering, wire fraud, and money laundering. On 27 May 2015, several of these officials were arrested by Swiss authorities, who were launching a simultaneous but separate criminal investigation into how the organization awarded the 2018 and 2022 World Cups. Those among these officials who were also indicted in the U.S. are expected to be extradited to face charges there as well.[7][8][9] Many officials were suspended by FIFA's ethics committee including Sepp Blatter[10] and Michel Platini.[11] In early 2017 reports became public about FIFA president Gianni Infantino attempting to prevent the re-elections[12] of both chairmen of the ethics committee, Cornel Borbély and Hans-Joachim Eckert, during the FIFA congress in May 2017.[13][14] On 9 May 2017, following Infantino's proposal,[15] FIFA Council decided not to renew the mandates of Borbély and Eckert.[15] Together with the chairmen, 11 of 13 committee members were removed.[16]
La Fédération internationale de football association2 (souvent désignée par l'acronyme FIFA) est la fédération sportive internationale du football, du futsal et du football de plage. Association des fédérations nationales fondée le 21 mai 1904 à Paris, elle a pour vocation de gérer et de développer le football dans le monde. La Coupe du monde de football est créée en 1924 par Jules Rimet3, président de la fédération internationale de 1920 à 1954. Le terme Football Association est le nom originel du football, utilisé pour le distinguer des autres sports de ballon.
Fondée par les fédérations d'Allemagne, de Belgique, du Danemark, d'Espagne, de France, des Pays-Bas, de Suède et de Suisse, elle compte au 13 mai 2016 211 associations nationales affiliées à travers le monde, qui doivent être reconnues par l'une des six confédérations continentales. Son siège est situé depuis 1932 à Zurich, en Suisse.
Bien qu'étant officiellement une association à but non lucratif, la FIFA brasse un chiffre d'affaires très important du fait de l'organisation des compétitions et de leur sponsoring. En 2013, la FIFA génère 1,3 milliard de dollars de chiffre d'affaires, et dispose de réserves évaluées à 1,4 milliard de dollars4. La FIFA est chargée de l'organisation des grands tournois mondiaux, et notamment des Coupes du monde masculines, depuis le 13 juillet 1930, et féminines, depuis le 30 novembre 1991.
Après plusieurs années de rumeurs et d'enquêtes de journalistes sur les affaires financières au sein de la FIFA, notamment autour de l'attribution de l'organisation des Coupes du monde de 2018 et 2022 à la Russie et au Qatar, une enquête lancée par le département de la Justice des États-Unis pour des faits de corruption aboutit à un grand scandale en 2015, à la suite duquel le président Sepp Blatter, le 2 juin 2015, trois jours après sa réélection pour un cinquième mandat, annonce qu'il convoque un congrès extraordinaire, prévu en février 2016, afin de remettre son mandat de président à disposition. Le 8 octobre 2015, la commission d'éthique de la FIFA suspend Sepp Blatter de manière provisoire, pendant 90 jours5. Le 21 décembre 2015, la commission suspend Sepp Blatter pour 8 ans6. Cette suspension est ramenée à six ans le 24 février 2016, peu avant l'élection de son successeur, Gianni Infantino, le 26 février 2016.
La Fédération Internationale de Football Association (in italiano "Federazione internazionale di calcio"[Nota 1]), più nota con l'acronimo FIFA, è la federazione internazionale che governa gli sport del calcio, del calcio a 5 e del beach soccer. La sua sede si trova a Zurigo, in Svizzera, e il presidente è Gianni Infantino, eletto nel 2016.
La federazione fu fondata a Parigi il 21 maggio 1904 e si occupa dell'organizzazione di tutte le manifestazioni intercontinentali degli sport sopraccitati, tra le quali la più importante è sicuramente il Campionato mondiale di calcio, che premia il vincitore con il trofeo della Coppa del Mondo. Tale torneo viene disputato ogni quattro anni dal 1930, eccetto che per il 1942 e il 1946 a causa della Seconda guerra mondiale, e la federazione ha il compito di scegliere il paese organizzatore che ospita la fase finale della manifestazione.
La Fédération Internationale de Football Association2 (en español: Federación Internacional de Fútbol Asociación),3 universalmente conocida por sus siglas FIFA, es la institución que gobierna las federaciones de fútbol en todo el planeta. Se fundó el 21 de mayo de 1904 y tiene su sede en Zúrich, Suiza. Forma parte del IFAB, organismo encargado de modificar las reglas del juego. Además, la FIFA organiza la Copa Mundial de Fútbol, los otros campeonatos del mundo en sus distintas categorías, ramas y variaciones de la disciplina, y los Torneos Olímpicos a la par del COI.
La FIFA agrupa 211 asociaciones o federaciones de fútbol de distintos países, contando con 17 países afiliados más que la Organización de las Naciones Unidas, tres menos que la Asociación Internacional de Federaciones de Atletismo y dos menos que la Federación Internacional de Baloncesto.45
Междунаро́дная федера́ция футбо́ла[1] (фр. Fédération Internationale de Football Association, сокращённо FIFA, в русской транслитерации — ФИФА́) — главная футбольная организация, являющаяся крупнейшим международным руководящим органом в футболе, мини-футболе и пляжном футболе. Штаб-квартира ФИФА находится в швейцарском городе Цюрихе.
Под эгидой ФИФА проходят все футбольные турниры всемирного масштаба, в числе которых чемпионат мира ФИФА, аналогичный турнир среди женщин, молодёжные и юношеские турниры, Кубок конфедераций и клубный чемпионат мира.

 FIFA
FIFA
 UEFA European Championship 2016
UEFA European Championship 2016
 UEFA European Championship 2020
UEFA European Championship 2020

 UEFA European Championship 2024
UEFA European Championship 2024
 Switzerland
Switzerland

 Sport
Sport
 (F)International soccer leagues
(F)International soccer leagues

 Sport
Sport
 (F)European football championship
(F)European football championship

 Sport
Sport
 (F)UEFA Women's Champions League
(F)UEFA Women's Champions League

 Sport
Sport
 (F)UEFA Youth League
(F)UEFA Youth League

 Sport
Sport
 (F)UEFA Futsal Cup
(F)UEFA Futsal Cup

 Sport
Sport
 (F)UEFA Nations League
(F)UEFA Nations League
 UEFA Champions League 2015/16
UEFA Champions League 2015/16
 UEFA Champions League 2016/17
UEFA Champions League 2016/17
 UEFA Champions League 2017/18
UEFA Champions League 2017/18
 UEFA Champions League 2018/19
UEFA Champions League 2018/19
 UEFA Champions League 2019/20
UEFA Champions League 2019/20
 UEFA Europa League 2017/18
UEFA Europa League 2017/18
 UEFA Europa League 2018/19
UEFA Europa League 2018/19
 UEFA Europa League 2019/20
UEFA Europa League 2019/20
 Union of European Football Associations
Union of European Football Associations

Die Union of European Football Associations (offiziell französisch Union des Associations Européennes de Football[1] [ˈɥɛfa]; deutsch Union Europäischer Fußballverbände [uˈeːfa] genannt), kurz UEFA [juːˈeɪfə], ist der europäische Fußballverband. Die UEFA ist ein gemeinnütziger Verein[2][3][4] im Sinne der Artikel 60 ff.[5] des Schweizerischen Zivilgesetzbuches[6] und im Handelsregister eingetragen.
Die UEFA ist eine der sechs Kontinental-Konföderationen des Weltfußballverbandes FIFA und umfasst 55 nationale Fußballverbände einzelner Länder und Gebiete, die nicht alle innerhalb der geografischen Grenzen Europas liegen.
欧洲足球联合会联盟(英语:Union of European Football Associations,首字母缩写为UEFA),官方简称欧洲足联或欧足联,港澳地区简称欧洲足协,台湾简称欧洲足总[3][4],是负责管理欧洲区各项足球事务,并代表欧洲的足球机构(包括所有的欧洲国家以及俄罗斯、土耳其、以色列、格鲁吉亚、亚美尼亚、阿塞拜疆、塞浦路斯和哈萨克等亚洲或跨欧亚两洲的国家)。
欧足联是国际足联底下六个洲别足球联会之一。由于世界上许多顶尖球员因为欧洲五大足球联赛(英超、西甲、德甲、意甲、法甲)的高竞技水平和高薪和而齐聚于欧洲,使得欧足联在世界上的影响力高居六大足联之首。世界上许多足球强国也均是欧足联的成员国,在2006年世界杯32强中,有14支国家队来自欧洲,在国际足联世界排名中,也有13个国家排在前20名。
欧洲足联于1954年6月15日在瑞士巴塞尔成立,成立时总部设于法国巴黎,1959年移往瑞士伯尔尼。埃贝·施瓦泽(Ebbe Schwartz)成为第一任欧洲足联主席,而欧洲足球锦标赛创办人亨利·德劳内(Henri Delaunay)则为秘书长。1995年总部移至瑞士尼永。成立之初只有25个成员协会,目前欧洲足联已有55个成员协会。现任主席是亚历山大·切费林(Aleksander Čeferin)。
欧州サッカー連盟(おうしゅうサッカーれんめい、英: Union of European Football Associations、仏: Union des associations européennes de football[4][5])は、ヨーロッパの各国・地域サッカー協会を統括する、国際サッカー連盟(FIFA)傘下のサッカーの大陸連盟である。
頭字語(略称)のUEFA(日本語発音:ウエファ、英語発音: [juːˈeifə] ユーエイファ)で呼ばれることが多い。
UEFAは、イタリア、フランス、ベルギー協会間での協議の後、1954年6月15日にスイスのバーゼルで設立された。当初は、25の協会からなっていたが、1990年代初めまでに加盟協会は倍に増加した。ヨーロッパの全ての主権国の協会がUEFAの会員となっているわけではないが、非会員の国家は全てミニ国家である。以前はアジアサッカー連盟(AFC)に加盟していたいくつかのアジアの国も、政治的理由などによりUEFAへの加盟が認められている(イスラエル(政治的理由)とカザフスタンはAFCから転籍した)。
UEFA本部は1959年までは、フランスのパリに位置し、後にスイスのベルンに移転。1995年から、同じくスイスのニヨンへ移転した。
The Union of European Football Associations (UEFA /juːˈeɪfə/ yoo-AY-fə; French: Union des Associations Européennes de Football;[a] German: Vereinigung Europäischer Fußballverbände)[b] is the administrative body for association football, futsal and beach soccer in Europe, although several member states are primarily or entirely located in Asia. It is one of six continental confederations of world football's governing body FIFA. UEFA consists of 55 national association members.
UEFA represents the national football associations of Europe, runs nation and club competitions including the UEFA European Championship, UEFA Nations League, UEFA Champions League, UEFA Europa League, and UEFA Super Cup, and controls the prize money, regulations, and media rights to those competitions.
Henri Delaunay was the first general secretary and Ebbe Schwartz the first president. The current president is Aleksander Čeferin, a former Football Association of Slovenia president, who was elected as UEFA's seventh president at the 12th Extraordinary UEFA Congress in Athens in September 2016, and automatically became a vice-president of the world body FIFA.[3]
L'Union des associations européennes de football, plus connue sous son sigle UEFA (correspondant à son nom en anglais Union of European Football Associations, parfois traduit en « Union européenne de Football-Association ») est une association regroupant et représentant les fédérations nationales de football d'Europe.
Fondée en 1954, l'UEFA a pour rôle de gérer et développer le football à l'échelon continental, sous l'égide de la FIFA. Elle organise et administre les principales compétitions continentales, qu'elles soient destinées aux sélections, comme le Championnat d'Europe et la Ligue des nations, ou aux clubs, comme la Ligue des champions, la Ligue Europa et la Supercoupe de l'UEFA. Elle est aussi responsable des compétitions de football féminin.
L'UEFA rassemble 55 fédérations depuis l'admission du Kosovo en 2016. Basée en Suisse depuis 1959, c'est une association au sens du droit suisse, neutre sur le plan politique et religieux. Son président actuel est le juriste slovène Aleksander Čeferin, élu le 14 septembre 2016 après l'intérim de onze mois de l'ancien footballeur espagnol Ángel María Villar Llona qui remplaçait alors Michel Platini, suspendu par la Commission d'éthique de la FIFA.
La Union of European Football Associations (in italiano: Unione delle associazioni calcistiche europee, in francese: Union des associations européennes de football),[1] meglio nota con l'acronimo di UEFA, è l'organo amministrativo, organizzativo e di controllo del calcio europeo con sede a Nyon (Svizzera).
La Unión de Asociaciones Europeas de Fútbol1 (en francés, Union des Associations Européennes de Football),2 referida comúnmente por su acrónimo UEFA, es la confederación europea de asociaciones nacionales de fútbol y máximo ente de este deporte en el continente. Agrupa en la actualidad a 55 asociaciones y es una de las seis confederaciones pertenecientes a la Federación Internacional de Fútbol Asociación (FIFA), máximo rector en el mundo.3
Fundada el 15 de junio de 1954, su sede central se encuentra en Nyon, Suiza, y es la encargada de organizar los distintos campeonatos de naciones de Europa, además de promover, desarrollar, controlar y velar por el fútbol, sus cometidos, finanzas, reglamentos y medios del mismo, siendo la Eurocopa, oficialmente Campeonato de Europa de Naciones, su principal torneo masculino, y la Eurocopa Femenina, oficialmente Campeonato de Europa Femenino, su homólogo de mujeres. De igual modo es quien trata las diferentes cuestiones de las federaciones nacionales del territorio europeo, así como su fútbol de formación organizando también competiciones para dichas categorías conformando un total de 15 torneos entre todas las disciplinas.4
Es la asociación continental más laureada del ámbito FIFA pues suma entre todas las selecciones de sus miembros un total de 223 títulos oficiales, donde destacan 41 títulos mundiales, además de ser la más reconocida.n 1 Entre ellas destaca Alemania (DFB),5 que es de ser la más galardonada de Europa con 34 títulos; España (RFEF), que es su miembro más premiado en el continente con 29 títulos6n 2; y Francia (FFF), que es la vigente campeona del mundo y la más condecorada en competiciones mundiales con seis trofeos.7
La principal competición en lo que se refiere a los clubes es la Liga de Campeones, tanto en categoría masculina —disputada por primera vez en 1955—, como en femenina —establecida en 2001—. En ellas dominan los clubes españoles con 18 títulos y los alemanes con 9 respectivamente.
Es la tercera confederación continental más antigua, y la que más miembros posee siendo el último en incorporarse la Federación de Fútbol de Kosovo (FFK) —como estado parcialmente reconocido internacionalmente— el 3 de mayo de 2016.8
Сою́з европе́йских футбо́льных ассоциа́ций (англ. Union of European Football Associations, сокращённо UEFA, в русской транслитерации УЕФА) — спортивная организация, управляющая футболом в Европе и некоторых западных регионах Азии. Она объединяет национальные футбольные ассоциации европейских стран и организует все европейские соревнования футбольных клубов и сборных команд, а также распределяет доходы от рекламы и трансляций между клубами и национальными ассоциациями, входящими в её состав.
УЕФА — одна из шести континентальных конфедераций, входящих в Международную федерацию футбола (ФИФА), причём УЕФА из них наиболее влиятельна и богата. Почти все сильнейшие футболисты мира играют в Европе из-за того, что именно в ней самые большие зарплаты, особенно в Англии, Франции, Италии, Испании и Германии[1]. Также УЕФА представляют многие сильные сборные мира, что предопределяет большое представительство стран этой конфедерации на мировых первенствах: так, из 32 команд на чемпионате мира 2006 года УЕФА представляли 14.
УЕФА был основан 15 июня 1954 года в Базеле (Швейцария) после консультаций, начатых федерациями футбола Франции, Италии и Бельгии. Первоначально УЕФА насчитывал 25 стран, сейчас их 55. Штаб-квартира УЕФА располагалась в Париже до 1959 года, когда она переехала в Берн. С 1995 года она базируется в швейцарском Ньоне. Первым генеральным секретарём УЕФА был Анри Делоне, а президентом — Эббе Шварц.
УЕФА часто имел конфликты с Еврокомиссией, организовывавшей интересы национальных ассоциаций. В 1990-х годах разногласия касались прав на телетрансляции и особенно трансферного регламента (правило Босмана).
 AFC Champions League 2015
AFC Champions League 2015
 AFC Champions League 2016
AFC Champions League 2016
 AFC Champions League 2017
AFC Champions League 2017
 AFC Champions League 2018
AFC Champions League 2018
 AFC Champions League 2019
AFC Champions League 2019
 Asian Football Confederation
Asian Football Confederation
 FIFA
FIFA

 Sport
Sport
 (F)International soccer leagues
(F)International soccer leagues

 Sport
Sport
 (F)Soccer Asia Cup
(F)Soccer Asia Cup

