
Deutsch-Chinesische Enzyklopädie, 德汉百科
 Germany
Germany



 Automobile
Automobile
 *Engine
*Engine



 Automobile
Automobile
 ***Technology
***Technology



 Automobile
Automobile
 Volkeswagen
Volkeswagen



 Automobile
Automobile
 *Hydrogen propulsion
*Hydrogen propulsion



 Automobile
Automobile
 *Electric car
*Electric car
 Germany
Germany

 Motorsport
Motorsport
 German Touring Car Masters
German Touring Car Masters

 Companies
Companies
 *Centuries-old companies in the world
*Centuries-old companies in the world

 Companies
Companies
 Germany, Austria, Switzerland
Germany, Austria, Switzerland


 Bavaria
Bavaria
 Germany
Germany
 Women's Soccer World Cup 2011
Women's Soccer World Cup 2011

 History
History

 Vacation and Travel
Vacation and Travel

 Cities founded by the Romans
Cities founded by the Romans

 World Heritage
World Heritage


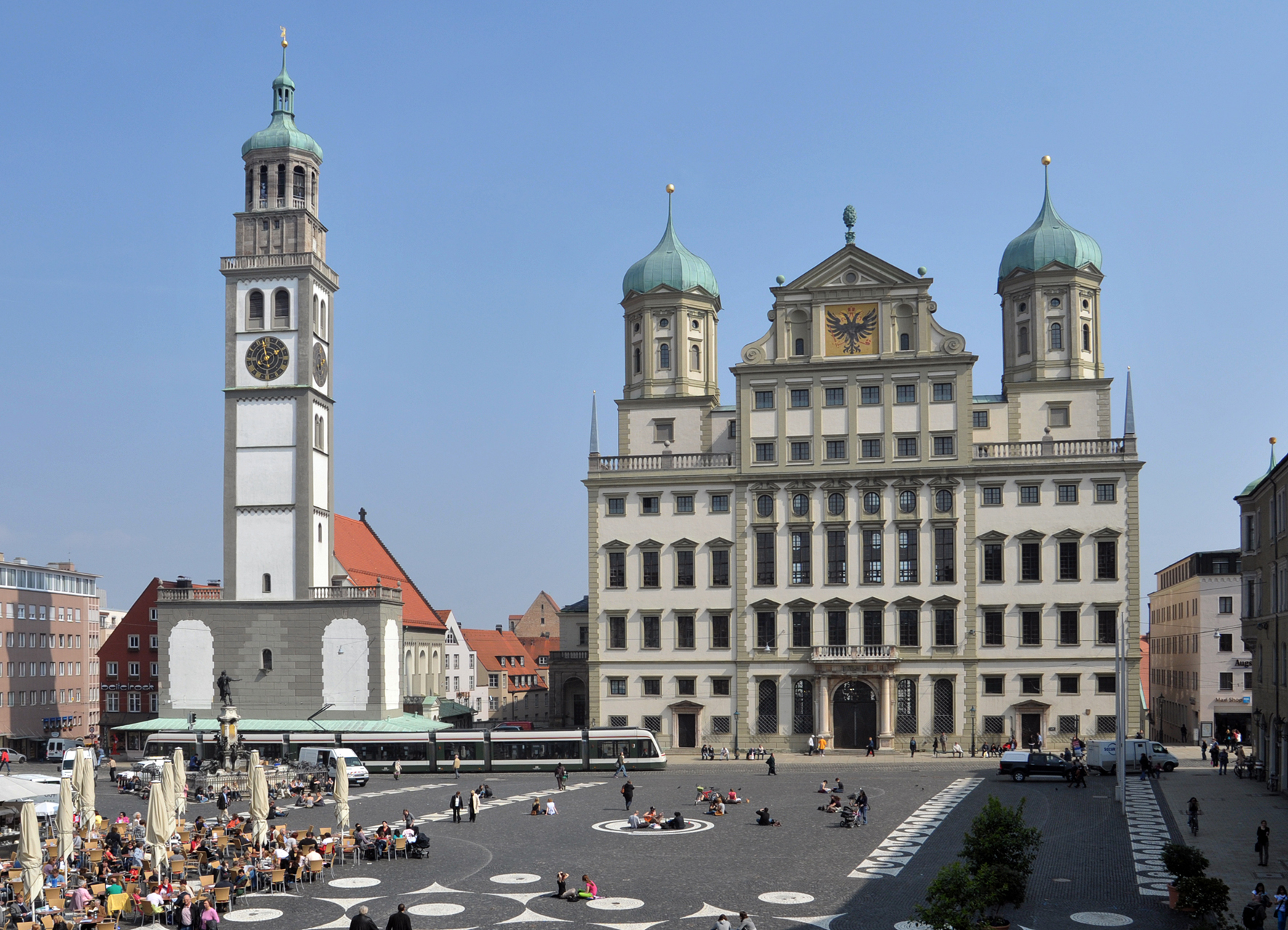
奥格斯堡(德语:Augsburg,又译奥古斯堡)是一座位于德国南部、巴伐利亚西南的城市。在神圣罗马帝国时代奥格斯堡就被划定是一帝国自由城市,直属于皇帝。今日的奥格斯堡除了是施瓦本行政区的地区政府所在地之外,也是奥格斯堡县的县府。
奥格斯堡自称是继特里尔之后德国第二古老的城市,其名称来源于前15年罗马皇帝屋大维统治时期建立的古罗马兵营奥古斯塔-温德利科伦(Augusta Vindelicorum),而该兵营的命名由来则是屋大维的称号“奥古斯都”。
2015年12月31日奥格斯堡有286,374名居民,是巴伐利亚州继慕尼黑和纽伦堡后第三大城市。1906年奥格斯堡的人口数量超过十万人,在德国属于大城市。它是巴伐利亚的23个地区中央之一。其附近的大城市有慕尼黑(东南约57千米)、纽伦堡(北约121千米)和斯图加特(西北约133千米)。奥格斯堡的都市地区在巴伐利亚也是第三大的,其总人口约为83万。
奥格斯堡是德国唯一一座有自己的官方节日的城市:8月8日是奥格斯堡和平节,因此奥格斯堡是德国节假日数量最高的城市。奥格斯堡是天主教主教的驻地。
Augsburg ist eine kreisfreie Großstadt im Südwesten Bayerns und zählt zu dessen drei Metropolen.[2] Sie ist Universitätsstadt und Sitz der Regierung und des Bezirks Schwaben sowie des Landratsamtes des die Stadt im Westen umgebenden Landkreises Augsburg.
Augsburg wurde 1909 zur Großstadt und ist mit knapp 300.000 Einwohnern nach München und Nürnberg die drittgrößte Stadt Bayerns. Der Ballungsraum Augsburg steht bezüglich Bevölkerung und Wirtschaftskraft in Bayern ebenfalls an dritter Stelle und ist Teil der Planungsregion Augsburg, in der etwa 885.000 Menschen leben. Augsburg hatte im Jahr 2017 die zweitgeringste Rate aller Straftaten unter den deutschen Großstädten über 200.000 Einwohnern.[3]
Der Name der Stadt, die zu den ältesten in Deutschland gehört, geht auf das 15 v. Chr. gegründete römische Heerlager und die spätere römische Provinzhauptstadt Augusta Vindelicum zurück. Im 13. Jahrhundert löste sich die Stadt von der Bischofsherrschaft, wurde spätestens 1316 zur Reichsstadt und häufiger Schauplatz von Reichstagen mit engen Verbindungen zu den Herrschern des Heiligen Römischen Reiches, die unter anderem von den Kaufmannsfamilien Welser und Fugger finanziert wurden („Fuggerstadt“). Nach der Reformation wurde Augsburg bikonfessionell; hier wurde der Augsburger Religionsfriede 1555 geschlossen. Seit Februar 2018 läuft eine Bewerbung zur Anerkennung als UNESCO-Welterbe.
Augsburg ist die einzige deutsche Stadt mit einem auf das Stadtgebiet beschränkten gesetzlichen Feiertag, dem Augsburger Hohen Friedensfest, das jedes Jahr am 8. August gefeiert wird. Damit hat sie mehr gesetzliche Feiertage als jede andere Region oder Stadt in Deutschland.
アウクスブルク(ドイツ語: Augsburg [ˈʔaʊ̯ksbʊʁk] (![]() 音声ファイル), アレマン語:Augschburg(アウクシュブルク))は、ドイツ連邦共和国バイエルン州南西部に位置する郡独立市である。
音声ファイル), アレマン語:Augschburg(アウクシュブルク))は、ドイツ連邦共和国バイエルン州南西部に位置する郡独立市である。
シュヴァーベン郡市連合、シュヴァーベン行政管区およびアウクスブルク郡の本部所在地であり、大学都市としても知られる。
アウクスブルクは1909年に大都市となり、26万人強の人口を有するこの街はミュンヘン、ニュルンベルクに次ぐバイエルン州第3の都市である。アウクスブルク都市圏はその人口、経済力ともに、やはりバイエルン州で3番目の規模であり、約83万人が住むアウクスブルク開発地域の一部である。
都市名はローマ属州時代のアウグスタ・ヴィンデリコルム (Augusta Vindelicorum) に由来し、紀元前15年にローマ皇帝アウグストゥスによって築かれた城にその起源を持つ。このため、アウクスブルクはドイツで最も古い都市の一つに数えられる。また、15世紀から16世紀に、フッガー家やヴェルザー家によって金融都市として繁栄を極めたことから、「フッガーシュタット」(フッガー都市)としばしば称される。
なお、標準ドイツ語では「アウクスブルク」と発音されるが、日本語では「g」を濁音で読み「アウグスブルク」「アウグスブルグ」などと表記される場合もある[2]。
Augsburg (German pronunciation: [ˈaʊ̯ksbʊʁk] ( listen); Austro-Bavarian: Augschburg) is a city in Swabia, Bavaria, Germany. It is a university town and regional seat of the Regierungsbezirk Schwaben. Augsburg is an urban district and home to the institutions of the Landkreis Augsburg. It is the third-largest city in Bavaria (after Munich and Nuremberg) with a population of 300,000 inhabitants, with 885,000 in its metropolitan area.[2]
listen); Austro-Bavarian: Augschburg) is a city in Swabia, Bavaria, Germany. It is a university town and regional seat of the Regierungsbezirk Schwaben. Augsburg is an urban district and home to the institutions of the Landkreis Augsburg. It is the third-largest city in Bavaria (after Munich and Nuremberg) with a population of 300,000 inhabitants, with 885,000 in its metropolitan area.[2]
After Neuss and Trier, Augsburg is Germany's third oldest city, founded in 15 BC by the Romans as Augusta Vindelicorum, named after the Roman emperor Augustus. It was a Free Imperial City from 1276 to 1803 and the home of the patrician Fugger and Welser families that dominated European banking in the 16th century. The city played a leading role in the Reformation as the site of the 1530 Augsburg Confession and 1555 Peace of Augsburg. The Fuggerei, the oldest social housing complex in the world, was founded in 1513 by Jakob Fugger.
Augsbourg (allemand Augsburg, prononcé en allemand : [ˈʔaʊ̯ksbʊʁk] Écouter ; latin Augusta Vindelicorum) est une ville allemande située dans le Land de Bavière, en Souabe bavaroise, sur la Route romantique.
Ville universitaire et industrielle, Augsbourg est le chef-lieu du district de Souabe (Regierungsbezirk Schwaben), de l'arrondissement d'Augsbourg (Landkreis) et le siège d'un diocèse catholique. Ses palais, ses églises et son hôtel de ville reflètent son âge d'or, lorsqu'elle était aux XVe et XVIe siècles une ville de premier rang en Europe.
La ville a actuellement environ 286 000 habitants (286 374 au 31 décembre 2015) et est ainsi, après Munich et Nuremberg, la troisième ville de Bavière. Son nom vient du latin Augusta Vindelicorum.
Augsbourg est une ville-arrondissement (Kreisfreie Stadt) et une des 82 grandes villes (Großstadt) allemandes depuis le début du XXe siècle ; le nombre de ses habitants a franchi la barre des 100 000 à la même époque.
Augusta (in tedesco: Augsburg, in bavarese Augschburg, in latino: Augusta Vindelicorum e anche Augusta Vindelicum) è una città extracircondariale della Germania, situata nella parte sud-occidentale della Baviera. È capoluogo del distretto governativo della Svevia ed è la sede amministrativa del circondario di Augusta.
Nel 2016 il Consiglio Federale Bavarese ha innalzato Augsburg a città metropolitana Con 300.000 abitanti[3] 885.000 abitanti nel Area Urbana è la terza città più popolosa della Baviera dopo Monaco e Norimberga. La città è sede vescovile della diocesi cattolica di Augusta e di un'università fondata nel 1970.
Fondata nel 15 a.C. durante il regno dell'imperatore Augusto, si contende, con altre città tedesche, il titolo di più antica città della Germania.
Augsburgo (en alemán: Augsburg  [ˈaʊ̯ksbʊʁk] (?·i)) es una ciudad metrópoli alemana. Es la capital de la región administrativa de Suabia del estado federado de Baviera. Augsburgo es ciudad independiente y al mismo tiempo capital del distrito homónimo.
[ˈaʊ̯ksbʊʁk] (?·i)) es una ciudad metrópoli alemana. Es la capital de la región administrativa de Suabia del estado federado de Baviera. Augsburgo es ciudad independiente y al mismo tiempo capital del distrito homónimo.
А́угсбург (нем. Augsburg, бав. Augschburg) — университетский город на юго-западе Баварии, столица Швабии. Считается наиболее древним городом Германии после Трира. С населением в 293.415 тысяч жителей является третьим по величине городом в Баварии (после Мюнхена и Нюрнберга). Крупный научный и промышленный центр; в 1997 году был назван самым «зелёным» городом в конкурсе, в котором участвовали девять европейских стран.


 Baden-Wuerttemberg
Baden-Wuerttemberg

 Bavaria
Bavaria

 Berlin
Berlin

 Brandenburg
Brandenburg

 Bremen
Bremen
 Germany
Germany
 Erneuerbare Energie
Erneuerbare Energie
 Windenergie
Windenergie

 Financial
Financial
 *Germany economic data
*Germany economic data

 Geography
Geography
 *World overview
*World overview

 Hamburg
Hamburg

 Hessen
Hessen

 Mecklenburg-Vorpommern
Mecklenburg-Vorpommern

 Lower Saxony
Lower Saxony

 North Rhine-Westphalia
North Rhine-Westphalia

 Rhineland-Palatinate
Rhineland-Palatinate

 Saarland
Saarland

 Saxony
Saxony

 Saxony-Anhalt
Saxony-Anhalt

 Schleswig-Holstein
Schleswig-Holstein

 Thuringia
Thuringia
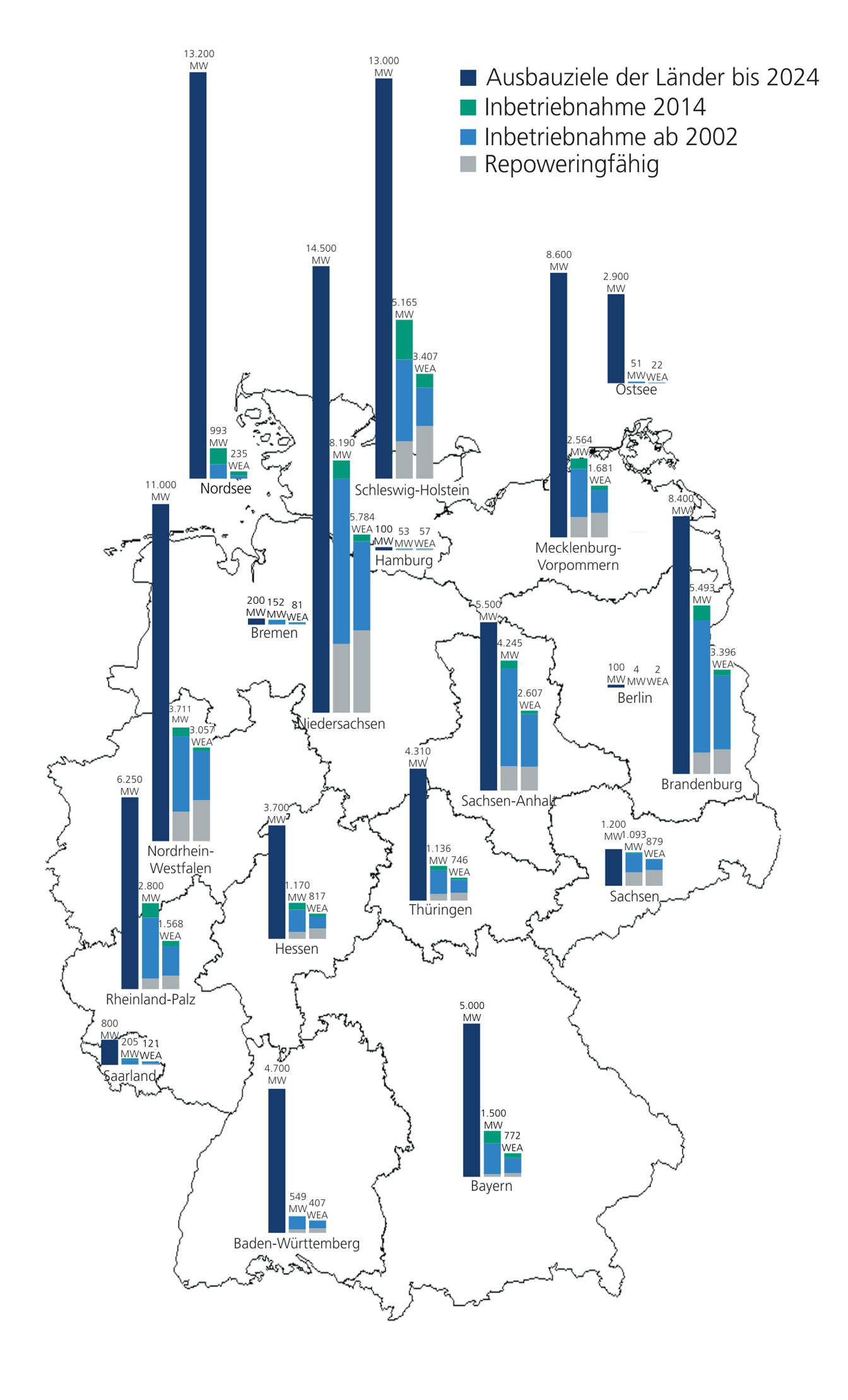
(Quelle:https://www.windkraft-journal.de/)
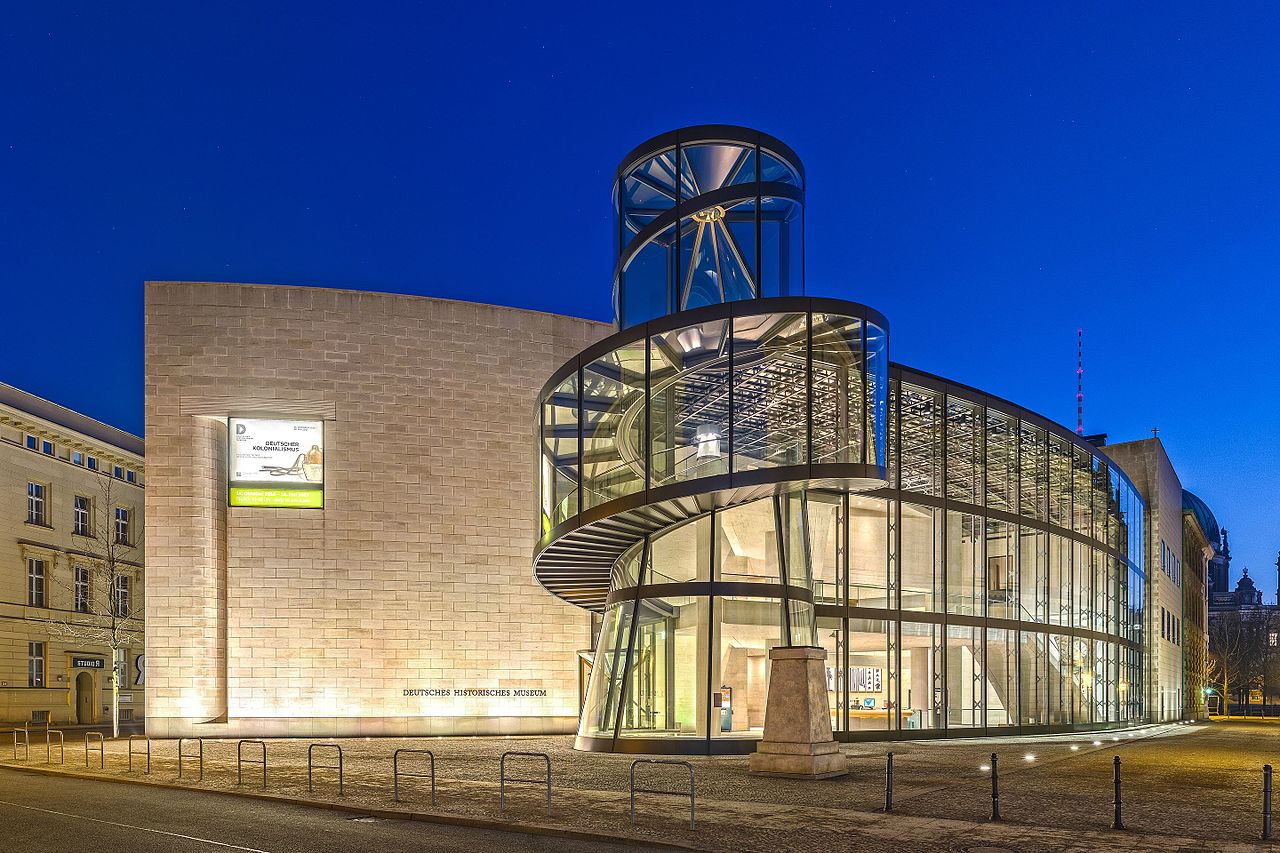



沃尔夫斯堡汽车城坐落在市区的东北部,是一个综合了大型建筑和小型展厅、桥梁、海洋、滩涂、山丘、绿地、市场服务区和便捷交通道路的工业区,占据了极佳的地理位置。精细而广泛的各种功能要素创造了活泼
的城市形象。铁路与航运、大众工厂与沃尔夫斯堡的城堡都使汽车城与城市建立起有机联系。汽车城的设计没有照搬书本上的建筑原理,而是和城市的规划理念“建筑群体与事件”紧密相关。
“建筑群体”由一组大型建筑组成,包括会展中心、酒店、博物馆、客户服务中心等;“事件”则是由附属于建筑群的许多独立品牌的小型展厅组成。这个城市实践颠覆了传统的“现代化过程”——个人模式决定了整个城市从房屋到室内装修的风格。“透明”是整个建筑群的表达方式,极富表现力的设计与永恒的材料创造了远远高于“时尚”的营造方式。材料反映出功能,加强了不同的建筑之间的联系。大众汽车城客户接待厅具有极高的透明度。玻璃立面与屋顶形成了开放的入口与玻璃塔的建筑形象。
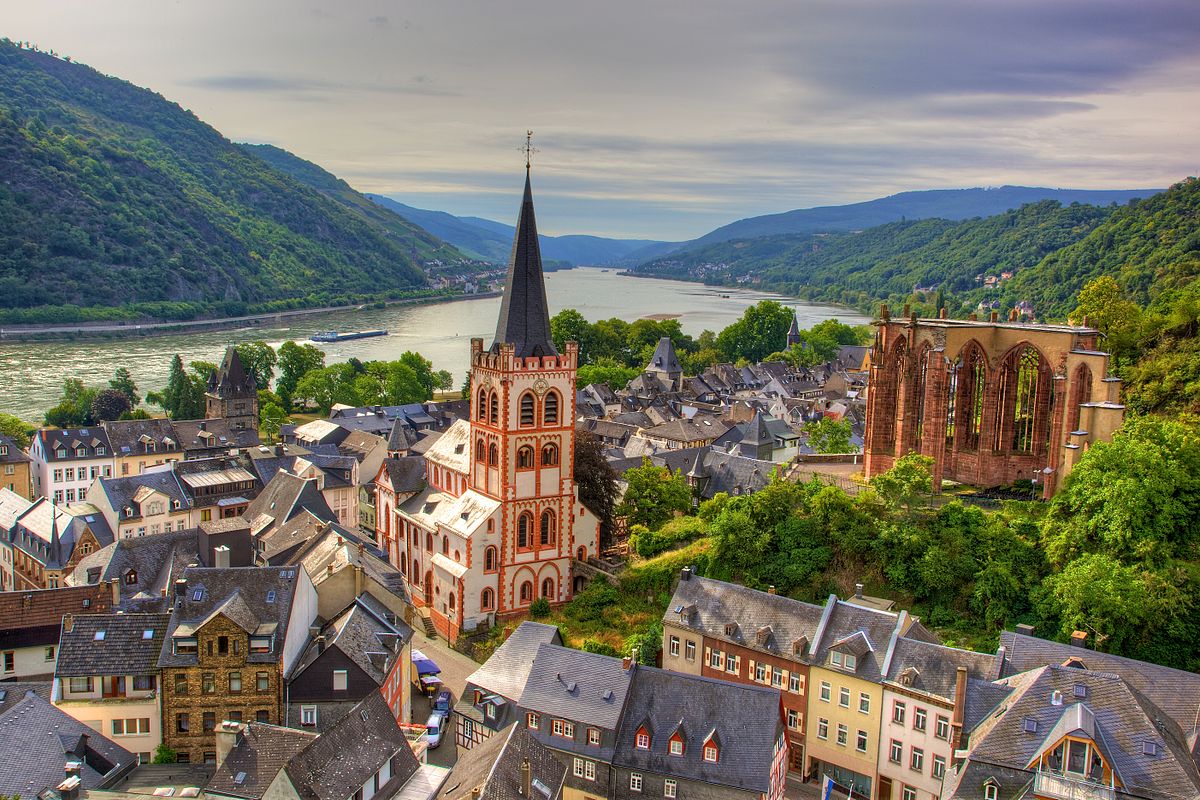




Bacharach [ˈbaxaʁax] (auch als Bacharach am Rhein bekannt) ist eine Stadt im UNESCO-Welterbe Oberes Mittelrheintal im Landkreis Mainz-Bingen in Rheinland-Pfalz. Der ursprüngliche Name Baccaracus deutet auf einen keltischen Ursprung hin. Oberhalb des Ortes erhebt sich die Burg Stahleck (heute eine Jugendherberge).
巴赫拉赫(Bacharach)(又称莱茵河畔巴赫拉赫)是莱茵兰-法尔茨州美因茨-宾根地区莱茵河中上游河谷中的一个小镇,位于联合国教科文组织世界遗产莱茵河中上游河谷。原名巴卡拉克斯(Baccaracus)表明其起源于凯尔特人。


巴赫音乐节(Bachfest)于每年基督升天节(Christi Himmelfahrt)期间在莱比锡举行,是为这座城市最著名的托马斯合唱团团长举行的纪念活动的高潮,吸引着各国的观众。
颇具气派的巴赫音乐传统
在莱比锡巴赫音乐节中,在最著名的托马斯合唱团团长的正式工作场所,国际知名音乐家们聚集于此诠释这位大师的作品。除了弥撒曲(Messen)以外,还演出管弦乐作品和合唱作品,也主办管风琴音乐会和交响乐音乐会,包括专题性展览和文化活动。(Quelle:http://www.germany-tourism.cn)
Das Bachfest Leipzig ist ein Musikfestival. Es fand in der Stadt Leipzig zum ersten Mal im Jahre 1908 statt.
Bereits 1904 hatte es das 2. deutsche Bachfest der Neuen Bachgesellschaft in der Messestadt gegeben. Das Bachfest fand in der Folgezeit in unregelmäßigen Abständen, zum Teil als Bachwochen oder Bachtage bezeichnet, statt.
Seit dem Jahre 1999 wird das Festival jedes Jahr vom Bach-Archiv im Auftrag der Stadt Leipzig organisiert, jedes Mal unter einem anderen Motto.
Zum Bachfest werden in verschiedenen Kontexten Werke von Johann Sebastian Bach aufgeführt, der von 1723 bis zu seinem Tode 1750 in Leipzig lebte und als Thomaskantor an der Thomaskirche wirkte. Ferner gehören Orgelfahrten in Mitteldeutschland zum regelmäßigen Programm.
Jedes Jahr finden etwa 100 einzelne Veranstaltungen im Rahmen des Bachfests statt, darunter ein Konzert unter der Leitung des Thomaskantors zur Eröffnung.
Seit 2011 finden im Rahmen des Festes die BachSpiele Leipzig statt.
 Belarus
Belarus

 Berlin
Berlin

 Brandenburg
Brandenburg

 Bremen
Bremen
 Denmark
Denmark
 Germany
Germany
 Estonia
Estonia
 Finland
Finland
 France
France

 Hamburg
Hamburg
 Italy
Italy
 Latvia
Latvia
 Lithuania
Lithuania

 Mecklenburg-Vorpommern
Mecklenburg-Vorpommern
 Netherlands
Netherlands

 Lower Saxony
Lower Saxony

 North Rhine-Westphalia
North Rhine-Westphalia
 Poland
Poland

 Review
Review
 Russia
Russia

 Saxony
Saxony

 Saxony-Anhalt
Saxony-Anhalt

 Schleswig-Holstein
Schleswig-Holstein
 Sweden
Sweden
 Switzerland
Switzerland

 Traditions
Traditions

 Vacation and Travel
Vacation and Travel
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom

 World Heritage
World Heritage

一种特别在德国北海和波罗的海海岸常见的哥特式建筑是用烤砖建造起来的建筑结构.这个十二世纪开始使用那红色的烤砖作为建筑材料的独特建筑风格之所以在北部德国低地如此普及是因为这块地区缺少天然石而且运输也非常困难,由于那片地区和汉萨盟的一 致性,因此它就成为了汉萨同盟的象征.有些历史悠久的建筑也就成了联合国教科文组织世界文化遗产项目之一。
Die Backsteingotik (englisch Brick Gothic, polnisch Gotyk ceglany) umfasst gotische Bauwerke, die aus oder mit sichtbarem Backstein errichtet wurden. Sie ist vor allem in Norddeutschland, dem Ostseeraum und den Niederlanden[1] verbreitet. Ihr Verbreitungsgebiet erstreckt sich im Westen bis an die Straße von Dover und im Südosten bis nach Galizien. Der auch oft verwendete Begriff Norddeutsche Backsteingotik erfasst daher nur einen Teil der gesamten Backsteingotik. Gotische Backsteinarchitektur in Italien und Südfrankreich wird in der Regel allein den dortigen Regionalstilen zugerechnet.
Die mittelalterliche Verwendung von Backstein als Baustoff setzte nördlich der Alpen im 12. Jahrhundert ein. Die ältesten Bauten gehören deshalb noch der so genannten Backsteinromanik an. Im 16. Jahrhundert ging die Backsteingotik in die Backsteinrenaissance über. Die geografische Verbreitung des Bauens aus Backstein und mit sichtbarem Backstein unterlag vom Beginn des Hochmittelalters bis in die frühe Neuzeit aber durchaus Veränderungen. So gab es in Teilen des Münsterlandes zwischen Pionierbauten der Romanik und dem starken Backsteineinsatz in Renaissance und Barock eine zeitliche Lücke.
Viele von der Backsteingotik geprägte Altstädte und Einzelbauten wurden in die Liste des UNESCO-Welterbes aufgenommen.
Brick Gothic (German: Backsteingotik, Polish: Gotyk ceglany, Dutch: Baksteengotiek) is a specific style of Gothic architecture common in Northwest and Central Europe especially in the regions in and around the Baltic Sea, which do not have resources of standing rock, but in many places a lot of glacial boulders. The buildings are essentially built using bricks. Buildings classified as Brick Gothic (using a strict definition of the architectural style based on the geographic location) are found in Belgium (and the very north of France), Netherlands, Germany, Poland, Lithuania, Latvia, Estonia, Kaliningrad (former East Prussia), Sweden and Finland.
As the use of baked red brick arrived in Northwestern and Central Europe in the 12th century, the oldest such buildings are classified as the Brick Romanesque. In the 16th century, Brick Gothic was superseded by Brick Renaissance architecture.
Brick Gothic is characterised by the lack of figural architectural sculpture, widespread in other styles of Gothic architecture. Typical for the Baltic Sea region is the creative subdivision and structuring of walls, using built ornaments and the colour contrast between red bricks, glazed bricks and white lime plaster. Nevertheless, these characteristics are neither omnipresent nor exclusive. Many of the old town centres dominated by Brick Gothic, as well as some individual structures, have been listed as UNESCO World Heritage sites.
The real extent and the real variety of this brick architecture has to be distinguished from the view of late 19th and early 20th century, especially the years around the end of World War I, when it was instrumentalized, politically.
Indeed, about a quarter of medieval Gothic brick architecture is standing in the Netherlands, in Flanders and in French Flanders. Some dominant buildings combinations of brick and stone. But the criterion "no stone at all" looks like a trick to exclude them.[according to whom?] The towers of St Mary church in Lübeck, the very top Brick Gothic church of the Baltic Sea region, have corners of granite ashley. And many village churches in northern Germany and Poland have Brick Gothic design, but most of their walls are formed by boulders.
L'architettura gotica dei paesi baltici è una varietà regionale dell'architettura gotica, in particolare del gotico tedesco. Le aree coinvolte in questa forma di architettura medievale si affacciano sul mar Baltico e sul Mare del Nord e, da un punto di vista politico, comprendevano gli stati settentrionali del Sacro Romano Impero, le città della Lega Anseatica, i possedimenti dell'Ordine Teutonico. Il periodo interessato va dal XIII secolo al XV secolo.
Le caratteristiche distintive sono che si tratta di un'architettura prevalentemente in laterizio e di una rielaborazione originale e per certi aspetti molto distante dall'iniziale gotico francese. I paesi europei attuali che hanno testimonianze di questa architettura sono Germania, Polonia, Lituania, Lettonia, Estonia, e nell'area della storica Prussia Orientale, (Oblast di Kaliningrad Russia); alcune testimonianze sono anche presenti in Scandinavia.
Le gothique de brique (allemand : Backsteingotik) est un style d´architecture gothique du Nord de l´Europe, et plus particulièrement du Nord de l'Allemagne et des régions autour de la mer Baltique. Il s'est surtout répandu dans les villes culturellement allemandes de l'ancienne Ligue Hanséatique à partir du XIIIe siècle, puis bien au-delà par influence (Scandinavie, Flandres, toute la Pologne, Allemagne du Sud). Les bâtiments sont essentiellement constitués de briques et le style de la décoration s'est adapté aux possibilités et aux limites de ce matériaux, conférant à cette architecture une identité bien particulière.
Il existe d'autres styles d'architecture gothique en brique en Europe, plus ou moins indépendants, comme en Italie et dans la région Toulousaine en France. Le style gothique baltique ne comprend pas tout le gothique en brique d'Europe.
El gótico báltico (en alemán, Norddeutsche Backsteingotik), forma la parte mayor del gótico de ladrillos (en alemán: Backsteingotik). Es una variante de la arquitectura gótica y neogótica que apareció en la Europa septentrional. Sin la especificación "Baltico" es estendido del estrecho de Calais a la Galicia de los Cárpatos. Con la especificación "Baltico" esta concentrada en el norte de Alemania y las zonas aledañas al mar Báltico. En todas estas regiones mancan recursos naturales para construir edificios de piedra. Se extendió principalmente en las ciudades culturalmente alemanas de la antigua Liga Hanseática desde el siglo XIII, y luego por influencia (Escandinavia, toda Polonia, el sur de Alemania). Los edificios son esencialmente de ladrillo y el estilo de decoración se ha adaptado a las posibilidades y límites de este material, dando a esta arquitectura una identidad muy particular.
Кирпичная, ганзейская или северогерманская готика — разновидность готического стиля архитектуры, распространённая в Северной Германии, Польше, Белоруссии и Прибалтике в XIII—XVI веках. Красный керамический кирпич как строительный материал стал использоваться в Северной Европе в XII веке, поэтому самые древние кирпичные образцы относятся ещё к так называемой «кирпичной романике». В XVI в. кирпичную готику сменил «кирпичный ренессанс».
Для кирпичной готики характерны, с одной стороны, отсутствие скульптурных украшений, которые невозможно выполнить из кирпича, и, с другой стороны, богатство орнаментальных деталей кладки и структуризация плоскостей за счёт чередования красного либо глазурованного кирпича и известковой побелки стен.
Многие города, внешний облик которых украшают готические сооружения из красного кирпича, являются объектами Всемирного культурного наследия ЮНЕСКО.


巴 登巴登坐落在德国西南部的黑森林边上,离法国和瑞士都很近。优雅的城市,依山傍水。起伏的群山,潺 潺的溪流瀑布与古老的城堡、修道院浑然一体;说它“满城泉水满城花”一点也不为过,汩汩喷涌的温泉与满眼的绿地花园,让这里充满了优雅浪漫的味道。德国的 高速列车ICE不曾在此停留,因为巴登巴登不想被打扰,就连它的城郊,也有个别致的名字叫Rebland(葡萄园区),在众多德国人的眼中,德国的春天就 从这里开始。
巴登在德语中就是洗澡的意思,巴登巴登———洗澡洗澡,直接道出了这是个国际知名的温泉疗养胜地,而用了两个巴登,有舍我 其谁的意 味。早在公元一世纪,古罗马人就在山谷里发现了温度高达69℃的矿泉,并用此泉水为军人治病疗伤,巴登温泉由此得名。罗马皇帝卡拉卡拉曾于公元213年到 此享受温泉。漫长岁月里,造访过巴登巴登的名人还有:拿破仑三世、俾斯麦、维多利亚女王、瓦格纳、拉姆斯……
(Quelle: http://ycwb.com/gb/content/2005-12/13/content_1036545.htm)
巴登-巴登(德语:Baden-Baden,国际音标:[ˈbaːdn̩ ˈbaːdn̩] (ⓘ)),德国巴登-符腾堡州的非县辖城市,位于德国的西南部,黑林山的西麓,奥斯河谷,邻近卡尔斯鲁厄。巴登-巴登是著名的温泉疗养地、旅游胜地和国际会议城市。
Baden-Baden (anhörenⓘ/?) ist eine Stadt im Westen des Landes Baden-Württemberg. Sie ist mit 57.420 Einwohnern (31. Dezember 2023) der bevölkerungsärmste Stadtkreis des Landes. Baden-Baden ist als Kur- und Bäderstadt sowie als Medien-, Kunst- und internationale Festspielstadt bekannt. Bereits die Römer nutzten die hier am Rand des Schwarzwalds entspringenden heißen Thermalquellen. Im Mittelalter war Baden-Baden Residenzstadt der Markgrafschaft Baden und somit auch namensgebend für das Land Baden. Nach dem katastrophalen Stadtbrand 1689 verlor sie den Status der Residenzstadt an Rastatt.
Im 19. Jahrhundert wurde die Bäderstadt wiederentdeckt und entwickelte sich, auch dank der Einnahmen aus der Spielbank, zu einem international bedeutsamen Treffpunkt von Adligen und wohlhabenden Bürgern. Aus dieser Blütezeit im 19. Jahrhundert ist ein reiches, gut erhaltenes materielles und immaterielles Erbe erhalten. Am 24. Juli 2021 nahm das Welterbekomitee der UNESCO Baden-Baden als eine der elf bedeutenden Kurstädte Europas in die Liste des Weltkulturerbes auf.
 International cities
International cities
 Architecture
Architecture
 Energy resource
Energy resource
 Museum
Museum
 Exhibition
Exhibition
 Media and press
Media and press
 Eat and Drink
Eat and Drink
 Music
Music
 Performing Arts
Performing Arts