
漢德百科全書 | 汉德百科全书
 克罗地亚
克罗地亚
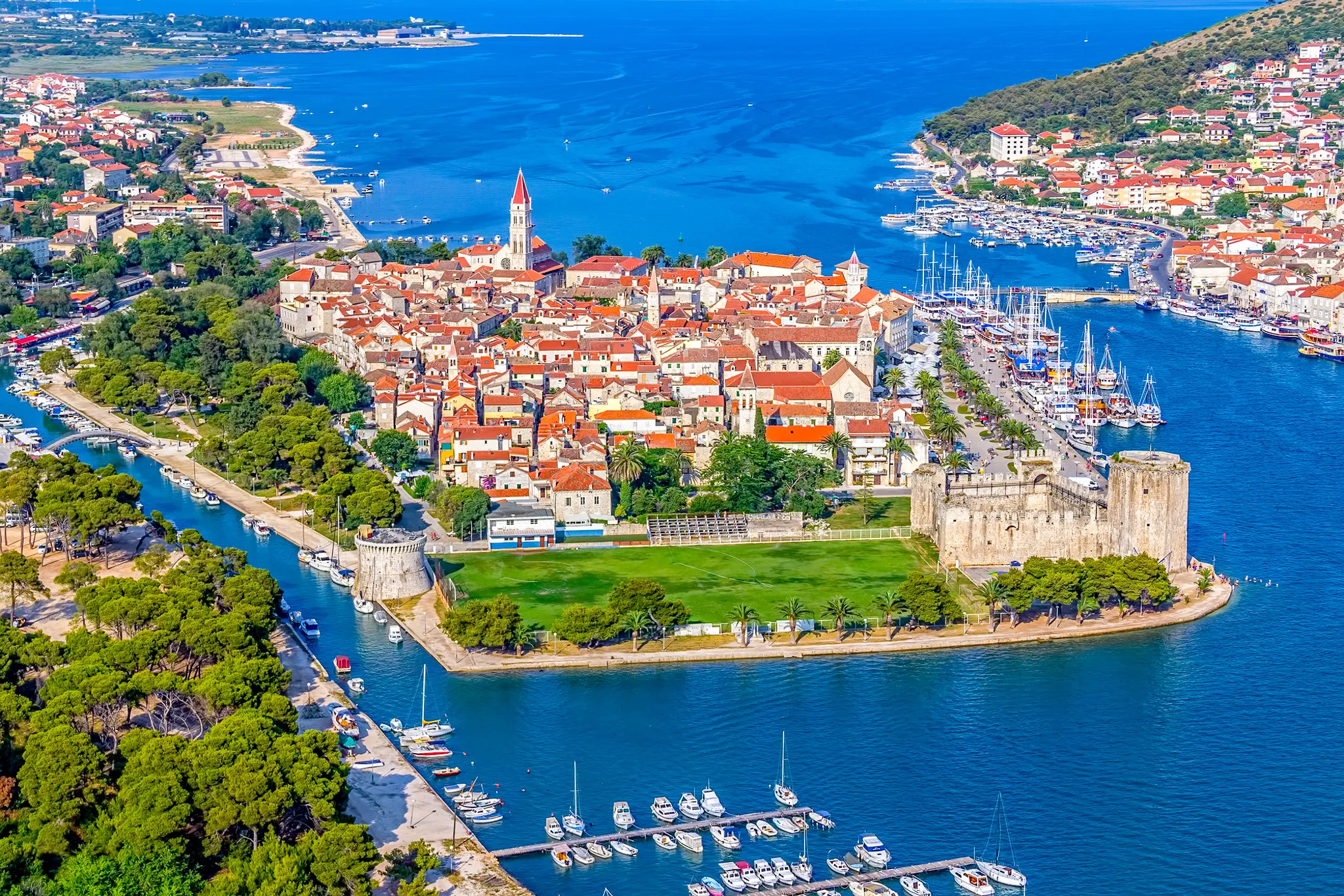

Trogir [ˈtrɔ.ɡiːr] (deutsch und ungarisch Trau, altgriechisch Τραγούριον Tragoúrion, lateinisch Tragurium, italienisch Traù) ist eine Hafenstadt in Kroatien. Sie liegt in Mitteldalmatien, etwa 15 Kilometer westlich von Split. Die gesamte Altstadt zählt seit 1997 zum Weltkulturerbe der UNESCO.
特罗吉尔(克罗地亚语:Trogir,意大利语、达尔马提亚语:Traù,拉丁语:Tragurium,希腊语:Tragurion,匈牙利语:Trau)是克罗地亚的一座古城,亚德里亚海港口,2001年人口 13,322人。特罗吉尔古城座落在克罗地亚大陆和契奥沃岛之间的一个小岛上。位在斯普利特以西27公里。

Der Golf von Venedig (italienisch: Golfo di Venezia, slowenisch: Beneški zaliv, kroatisch: Venecijanski zaljev) ist eine Meeresbucht im nördlichen Teil der Adria bzw. der Oberen Adria.
Die Küstenlinie des Golfs erstreckt sich vom Mündungsdelta des Po bis an das Kap Kamenjak in Istrien. In die Bucht münden neben dem Po weitere große Flüsse, wie der Tagliamento, der Piave, die Etsch und die Brenta. Ein bekannter Teil des Golfs ist die Lagune von Venedig. Sie entstand um 4000 v. Chr. durch Ablagerungen der Brenta und anderer Flüsse. In ihr liegt die namengebende Insel-Großstadt Venedig.
Der Golf von Triest ist ebenfalls Teil des Golfs von Venedig.
An die Meeresbucht grenzen die drei europäischen Staaten Italien, Slowenien und Kroatien.
威尼斯湾是欧洲南部的海湾,位于波河河口和伊斯特拉半岛之间的亚得里亚海北部,与意大利、斯洛文尼亚和克罗地亚接壤,宽120公里,平均水深38米。
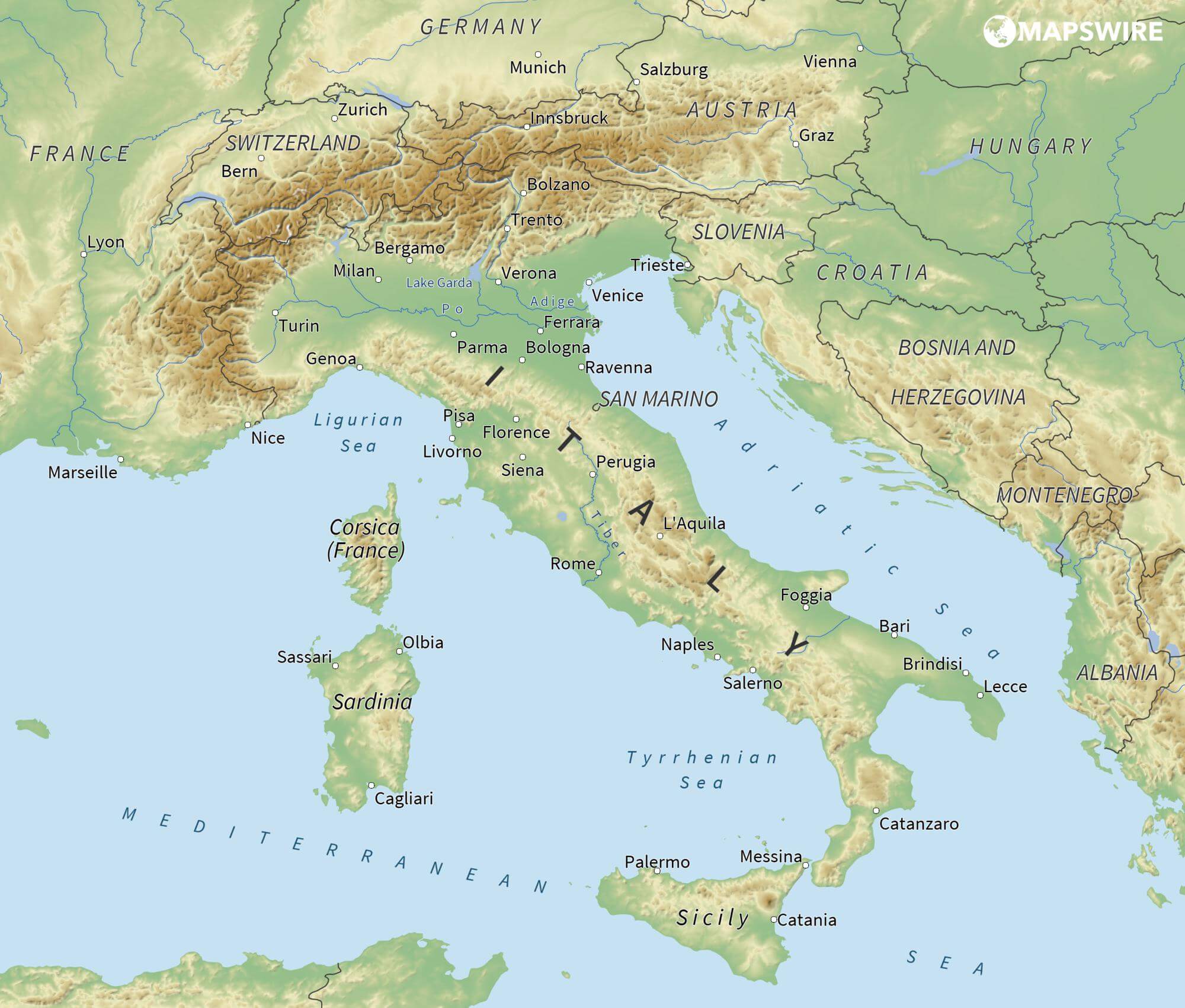
Das Adriatische Meer, kurz auch die Adria (lateinisch Mare Adriaticum; italienisch Mare Adriatico; bosnisch, kroatisch und serbisch Jadransko more oder kurz Jadran; slowenisch Jadransko morje; albanisch Deti Adriatik oder kurz Adriatiku), ist das lang gestreckte nördliche Seitenbecken des Mittelmeeres zwischen der Apenninhalbinsel und Balkanhalbinsel. Es ist nach der Stadt Adria in Italien (Provinz Rovigo) benannt. Zum Adriatischen Meer wird alles gerechnet, was nördlich der Straße von Otranto liegt.
亚得里亚海(意大利语:Mar Adriatico,斯洛文尼亚语:Jadransko morje,克罗地亚语:Jadransko more,阿尔巴尼亚语:Deti Adriatik),是地中海的一部分水域,分隔了意大利半岛(亚平宁半岛)和巴尔干半岛,也分隔了亚平宁山脉与狄那里克阿尔卑斯山脉及其临近地区。亚得里亚海西岸属于意大利,东岸则分别属于斯洛文尼亚、克罗地亚、波斯尼亚和黑塞哥维那、黑山和阿尔巴尼亚。亚得里亚海透过位于其南部的奥特朗托海峡与爱奥尼亚海相连。波河、阿迪杰河、奥凡托河等河流流入亚得里亚海;海中有近1200个岛屿,其中只有69个有人居住。
アドリア海(アドリアかい、英: Adriatic Sea ; イタリア語: Mar Adriatico ; クロアチア語: Jadransko more)は、地中海の海域の一つ。イタリア半島とバルカン半島に挟まれている。
The Adriatic Sea (/ˌeɪdriˈætɪk/) is a body of water separating the Italian Peninsula from the Balkans. The Adriatic is the northernmost arm of the Mediterranean Sea, extending from the Strait of Otranto (where it connects to the Ionian Sea) to the northwest and the Po Valley. The countries with coasts on the Adriatic are Albania, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croatia, Italy, Montenegro and Slovenia. The Adriatic contains over 1,300 islands, mostly located along the Croatian part of its eastern coast. It is divided into three basins, the northern being the shallowest and the southern being the deepest, with a maximum depth of 1,233 metres (4,045 ft). The Otranto Sill, an underwater ridge, is located at the border between the Adriatic and Ionian Seas. The prevailing currents flow counterclockwise from the Strait of Otranto, along the eastern coast and back to the strait along the western (Italian) coast. Tidal movements in the Adriatic are slight, although larger amplitudes are known to occur occasionally. The Adriatic's salinity is lower than the Mediterranean's because the Adriatic collects a third of the fresh water flowing into the Mediterranean, acting as a dilution basin. The surface water temperatures generally range from 30 °C (86 °F) in summer to 12 °C (54 °F) in winter, significantly moderating the Adriatic Basin's climate.
The Adriatic Sea sits on the Apulian or Adriatic Microplate, which separated from the African Plate in the Mesozoic era. The plate's movement contributed to the formation of the surrounding mountain chains and Apennine tectonic uplift after its collision with the Eurasian plate. In the Late Oligocene, the Apennine Peninsula first formed, separating the Adriatic Basin from the rest of the Mediterranean. All types of sediment are found in the Adriatic, with the bulk of the material transported by the Po and other rivers on the western coast. The western coast is alluvial or terraced, while the eastern coast is highly indented with pronounced karstification. There are dozens of marine protected areas in the Adriatic, designed to protect the sea's karst habitats and biodiversity. The sea is abundant in flora and fauna—more than 7,000 species are identified as native to the Adriatic, many of them endemic, rare and threatened ones.
The Adriatic's shores are populated by more than 3.5 million people; the largest cities are Bari, Venice, Trieste and Split. The earliest settlements on the Adriatic shores were Etruscan, Illyrian, and Greek. By the 2nd century BC, the shores were under Rome's control. In the Middle Ages, the Adriatic shores and the sea itself were controlled, to a varying extent, by a series of states—most notably the Byzantine Empire, the Croatian Kingdom, the Republic of Venice, the Habsburg Monarchy and the Ottoman Empire. The Napoleonic Wars resulted in the First French Empire gaining coastal control and the British effort to counter the French in the area, ultimately securing most of the eastern Adriatic shore and the Po Valley for Austria. Following Italian unification, the Kingdom of Italy started an eastward expansion that lasted until the 20th century. Following World War I and the collapse of Austria-Hungary and the Ottoman Empire, the eastern coast's control passed to Yugoslavia and Albania. The former disintegrated during the 1990s, resulting in four new states on the Adriatic coast. Italy and Yugoslavia agreed on their maritime boundaries by 1975 and this boundary is recognised by Yugoslavia's successor states, but the maritime boundaries between Slovenia, Croatia, Bosnia-Herzegovina, and Montenegro are still disputed. Italy and Albania agreed on their maritime boundary in 1992.
Fisheries and tourism are significant sources of income all along the Adriatic coast. Adriatic Croatia's tourism industry has grown faster economically than the rest of the Adriatic Basin's. Maritime transport is also a significant branch of the area's economy—there are 19 seaports in the Adriatic that each handle more than a million tonnes of cargo per year. The largest Adriatic seaport by annual cargo turnover is the Port of Trieste, while the Port of Split is the largest Adriatic seaport by passengers served per year.
La mer Adriatique (du latin : Mare Hadriaticum ou Mare Adriaticum) est une mer séparant la péninsule italienne de la péninsule balkanique. L'Adriatique est le bras de la Méditerranée situé le plus au nord en s'étendant du canal d'Otrante (où elle rejoint la mer Ionienne) jusqu'aux villes de Venise et de Trieste et à l'embouchure du Pô. Les pays côtiers sont l'Italie, la Slovénie, la Croatie, la Bosnie-Herzégovine, le Monténégro et l'Albanie, ainsi que la Grèce par l'île de Corfou.
Il mare Adriatico è l'articolazione del mar Mediterraneo orientale situata tra la penisola italiana e la penisola balcanica; suddiviso in Alto Adriatico, Medio Adriatico e Basso Adriatico, bagna sei Paesi: Italia, Slovenia, Croazia, Bosnia ed Erzegovina, Montenegro e Albania, confinando a sud-est con il Mar Ionio.
El mar Adriático (del latín, Mare Hadriaticum) es un golfo estrecho y alargado que forma parte del mar Mediterráneo. Se encuentra situado entre la península Itálica, al oeste, y la península de los Balcanes, al este, con una anchura máxima de unos 200 km, y una longitud de unos 800 km. Su extremo meridional limita con el mar Jónico, del que lo separa el canal de Otranto. Su superficie total es de, aproximadamente, 160 000 km².
Las costas occidental, septentrional, y parte de la oriental corresponden a Italia (60% de la longitud de costa del Adriático), mientras que el resto de la costa oriental corresponde a Croacia, Eslovenia, Bosnia y Herzegovina, Montenegro y Albania. Algunos de los ríos que desembocan en el Adriático son el Reno, el Po, el Adigio, el Brenta, el Piave y el Neretva.
La costa del Adriático concentra un gran número de centros turísticos, como Venecia, que recibe el nombre de «Reina del Adriático». Tras la división de Yugoslavia, la costa croata se ha convertido también en un destino turístico muy popular.
Sus aguas sostienen industria pesquera, y se llevan a cabo prospecciones petrolíferas en este mar. Durante los años 1990, varias investigaciones revelaron que sus niveles de contaminación son muy altos.
En las últimas décadas el gobierno de Italia ha intentado hacer de él una barrera contra la inmigración ilegal, en su mayor parte proveniente de Albania.
Адриати́ческое мо́ре (итал. mare Adriatico, эмил.-ром. Mèr Adriâtic, вен. Mar Adriàtico, неап. Mar Adriateco, словен. Jadransko morje, сербохорв. Jadransko more/Јадранско море, алб. Deti Adriatik, лат. mare Hadriaticum), также Адриатика — полузамкнутое море, часть Средиземного моря между Апеннинским и Балканским полуостровами. Омывает берега Италии (более 1000 км), Словении (47 км), Хорватии (1777 км), Боснии и Герцеговины (20 км), Черногории (200 км), Албании (472 км).

Istrien (kroatisch/slowenisch Istra, italienisch Istria, istriotisch Eîstria) ist mit einer Fläche von etwa 3500 km² die größte Halbinsel an der nördlichen Adria. Sie erstreckt sich zwischen dem Golf von Triest und der Kvarner-Bucht vor Rijeka, im Osten reicht sie bis zur rund 1400 m hohen Učka. An der Halbinsel haben drei Staaten Anteil. Der größte Flächenanteil befindet sich auf dem Gebiet Kroatiens, ein kleinerer im Norden gehört zu Slowenien, zu Italien gehört nur das Gebiet um Muggia und dessen Umland.
伊斯特拉半岛(克罗地亚语、斯洛文尼亚语:Istra),又称伊斯特里亚,(意大利语、威尼托语:Istria),是欧洲亚德里亚海东北岸的一个三角形半岛。西临威尼斯湾。
 比利时
比利时
 保加利亚
保加利亚
 丹麦
丹麦
 联邦德国
联邦德国
 爱沙尼亚
爱沙尼亚
 芬兰
芬兰
 法国
法国
 希腊
希腊
 爱尔兰
爱尔兰
 冰岛
冰岛
 以色列
以色列
 意大利
意大利
 克罗地亚
克罗地亚
 拉脱维亚
拉脱维亚
 立陶宛
立陶宛
 卢森堡
卢森堡
 马耳他
马耳他
 摩纳哥
摩纳哥
 黑山
黑山
 荷兰
荷兰
 北马其顿
北马其顿
 挪威
挪威
 奥地利
奥地利
 波兰
波兰
 葡萄牙
葡萄牙
 罗马尼亚
罗马尼亚
 俄罗斯
俄罗斯
 圣马力诺
圣马力诺
 瑞典
瑞典
 瑞士
瑞士
 塞尔维亚
塞尔维亚
 斯洛伐克
斯洛伐克
 斯洛文尼亚
斯洛文尼亚
 西班牙
西班牙
 捷克
捷克
 土耳其
土耳其
 乌克兰
乌克兰
 匈牙利
匈牙利
 英国
英国

 科学技术
科学技术
 塞浦路斯
塞浦路斯

Mittel- und osteuropäische Länder (MOEL), auch Mittel-/Osteuropa (MOE), steht für den gleichbedeutenden Begriff mittel- und osteuropäische Staaten (MOES). Der englische Ausdruck lautet CEE für englisch Central and Eastern Europe, der französische PECO für französisch Pays d’Europe centrale et orientale. Weitgehend identisch ist der EU-statistische Begriff Central and Eastern European Countries (CEC oder CEEC).
Welche Länder tatsächlich zu den mittel- und osteuropäischen Ländern gehören, ist unscharf abgegrenzt. Im engeren Sinn wird der Begriff für jene Länder gebraucht, die im Rahmen der EU-Erweiterung 2004 und 2007 in die Europäische Union aufgenommen wurden (EU-12), bzw. für jene Staaten des Westbalkans, die sich im Erweiterungsprozess befinden. Die ebenfalls unscharf abgegrenzte Großregion Ostmitteleuropa ist ein Teil der MOEL.
中东欧是一个欧洲大陆的地缘政治概念,包括冷战后影响力最大、统一后的德国,受德国影响及冷战时作为中立国的奥地利,冷战时期被苏联所控制的东欧卫星国,波罗的海三国(立陶宛、拉脱维亚、爱沙尼亚),再加上摩尔多瓦、白罗斯、乌克兰和俄罗斯。
为了避免意识形态和政治上的怀疑,同时为了弥补政治地理与自然地理的差距,中东欧是近年来兴起的一种称呼,特别是在冷战之后,大部分中东欧国家皆加入欧盟及北约,成为西方自由世界的一部分,中东欧的社会政治及经济发展日益受到西方自由阵营原有国家的关注。
欧盟统计局目前使用 CEC 或 CEEC(中欧和东欧国家)这一术语来指中欧和东欧地区寻求加入欧盟的下列国家:
阿尔巴尼亚
波斯尼亚和黑塞哥维那
科索沃
北马其顿
黑山共和国
塞尔维亚
土耳其
在 2004 年 5 月 1 日加入欧洲联盟之前,下列国家也属于这一类别:
爱沙尼亚
拉脱维亚
立陶宛
波兰
匈牙利
捷克共和国
斯洛伐克
斯洛文尼亚
在 2007 年 1 月 1 日加入欧盟之前,以下国家也属于这一类别:
罗马尼亚
保加利亚
在 2013 年 7 月 1 日加入欧盟之前,以下国家也属于此类国家:克罗地亚
克罗地亚
中東欧(ちゅうとうおう)は、ヨーロッパの区分で、様々に解釈されるが、主に二つの意味がある。
- 中欧(中央ヨーロッパ)と東欧(東ヨーロッパ)を合わせた地域。(この場合中・東欧とも書く。他のヨーロッパの区分と違い、「中東とヨーロッパ」と取られる可能性もあるため、中東ヨーロッパとはほとんど言わない)。
- 中欧のうち過去に東側諸国に組み込まれていた地域で、かつ2004年以降に欧州連合(EU)に加盟した諸国のみを指す。
日本では1.の意味で用いられることが多く、英語圏などではでは中東欧を一般に「CEE」と表記し、2.の意味で用いることも多い。
Central and Eastern Europe, abbreviated CEE, is a term encompassing the countries in Central Europe (the Visegrád Group), the Baltics, Eastern Europe, and Southeastern Europe (Balkans), usually meaning former communist states from the Eastern Bloc (Warsaw Pact) in Europe. Scholarly literature often uses the abbreviations CEE or CEEC for this term.[1][2][3] The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development also uses the term "Central and Eastern European Countries (CEECs)" for a group comprising some of these countries.
Depuis les années 1990, la plupart des pays européens dont la majeure partie du territoire s'étend à l'est du 15e degré de longitude Est sont parfois collectivement désignés sous l'appellation de pays de l'Europe centrale et orientale (PECO). Toutefois, la Suède, la Finlande, la Grèce et Chypre ne sont pas considérés dans cet ensemble malgré leur situation géographique, cette notion étant généralement réservée aux anciens pays du bloc de l'Est et aux États européens issus de la dislocation de l'URSS comme les pays baltes, ainsi que de la Tchécoslovaquie et de la Yougoslavie.
Europa centro-orientale è la designazione, usata soprattutto in ambito accademico, della regione d'Europa comprendente la parte orientale dell'Europa centrale. Ne fanno parte le seguenti nazioni che si estendono ad est della Germania e sono comprese fra il Mar Baltico al nord e la Grecia a sud[1]:
Центральная и Восточная Европа (ЦВЕ) (англ. Central and Eastern Europe, CEE) — бывшие социалистические государства Восточной Европы, не входящие в СНГ.
В литературе встречаются название — Восточно-Центральная Европа (ВЦЕ).
 国际城市
国际城市

 地理
地理
 弗留利-威尼斯朱利亚
弗留利-威尼斯朱利亚
 威尼托大区
威尼托大区
 建筑艺术
建筑艺术
 历史
历史
 文化遗产
文化遗产

 阿布鲁佐大区
阿布鲁佐大区
 艾米利亚-罗马涅大区
艾米利亚-罗马涅大区
 马尔凯大区
马尔凯大区
 莫利塞大区
莫利塞大区
 普利亚大区
普利亚大区

 欧洲联盟
欧洲联盟

 欧洲的高等院校
欧洲的高等院校
