
漢德百科全書 | 汉德百科全书
 Georgia
Georgia



 UEFA European Championship 2020
UEFA European Championship 2020
 Group D
Group D

 UEFA European Championship 2024
UEFA European Championship 2024
 Georgia
Georgia

 Sport
Sport
 (F)UEFA Nations League
(F)UEFA Nations League
 UEFA Nations League
UEFA Nations League
 UEFA Nations League D- Group 1
UEFA Nations League D- Group 1

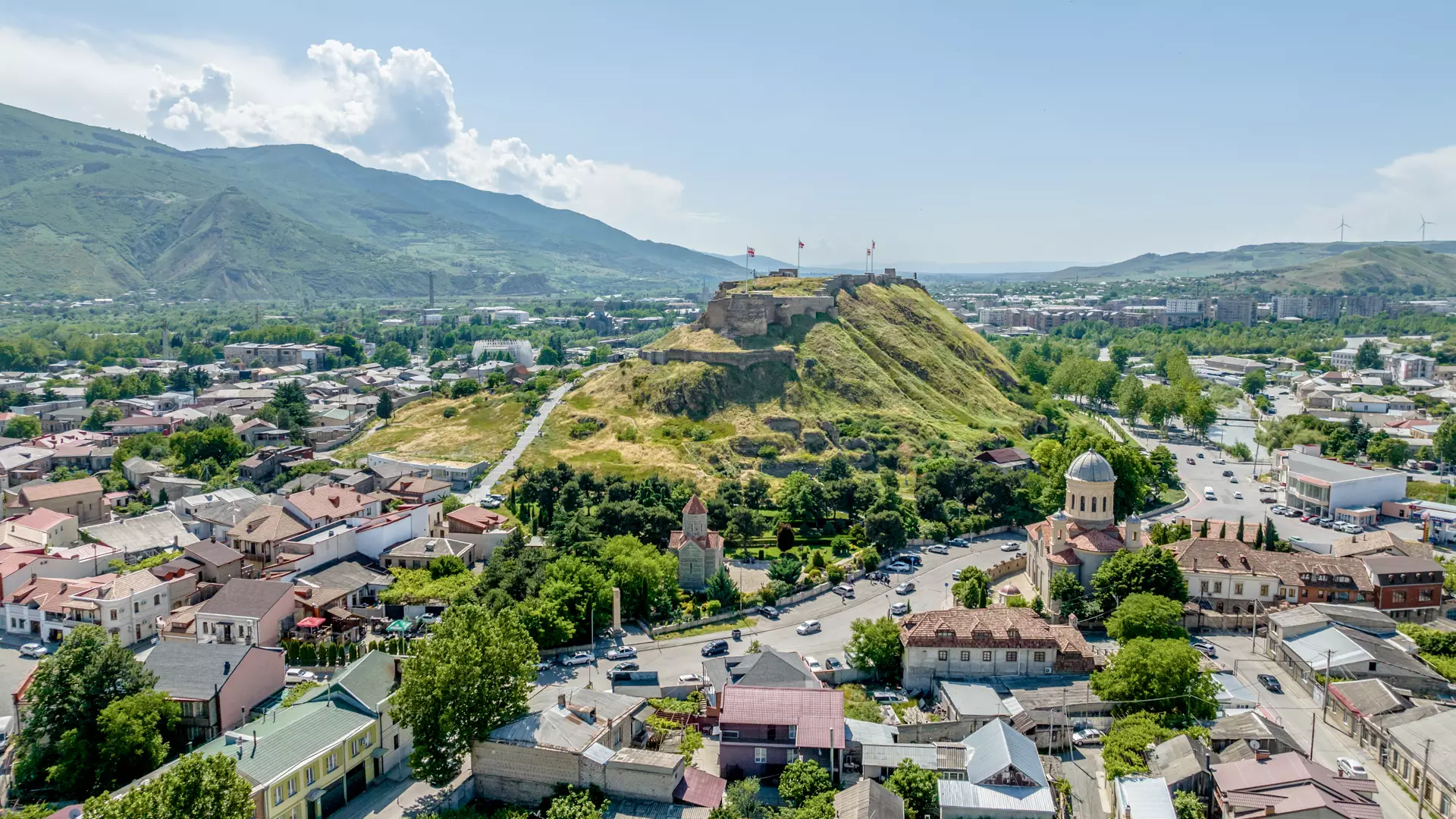
Georgien ([geˈɔrgi̯ən], georgisch საქართველო, Sakartwelo, IPA: [sɑkʰɑrtʰvɛlɔ] ), nach der russischen Bezeichnung Грузия (Grusija) früher gelegentlich auch Grusien oder Grusinien genannt, ist ein eurasischer Staat im Südkaukasus, östlich des Schwarzen Meeres und südlich des Großen Kaukasus gelegen. Im Norden wird er von Russland, im Süden von der Türkei und Armenien, im Osten von Aserbaidschan begrenzt. Die Landesteile Abchasien und Südossetien sind abtrünnig (abgefallen) und werden nur von Russland und einigen weiteren Staaten als souverän anerkannt.
Mit rund 3,7 Millionen Einwohnern (2019) auf einer Fläche von 57.215 km² (ohne die abtrünnigen Landesteile) ist Georgien eher dünn besiedelt. Mehr als ein Viertel der Bevölkerung lebt in der Hauptstadtregion um Tiflis, weitere große Städte sind Batumi, Kutaissi und Rustawi.
格鲁吉亚(格鲁吉亚语:საქართველო,ISO 9984:Sakartvelo,IPA:[sɑkʰɑrtʰvɛlɔ] (![]() 聆听))为跨洲国家,地跨欧亚两洲,但因文化上深受欧洲影响,故也被认为是欧洲国家[4][5][6][7]。它曾经是苏联加盟共和国,1991年4月9日正式独立,首任总统兹维亚德·加姆萨胡尔季阿。独立后法定国名为“格鲁吉亚共和国”,1995年8月24日该国通过新宪法,国名定为“格鲁吉亚”,曾为独立国家联合体成员。因为2008年南奥塞梯战争,格鲁吉亚根据议会2008年8月14日通过的决议做出退出独联体的决定,并于2009年8月18日完成手续,正式退出。[8]
聆听))为跨洲国家,地跨欧亚两洲,但因文化上深受欧洲影响,故也被认为是欧洲国家[4][5][6][7]。它曾经是苏联加盟共和国,1991年4月9日正式独立,首任总统兹维亚德·加姆萨胡尔季阿。独立后法定国名为“格鲁吉亚共和国”,1995年8月24日该国通过新宪法,国名定为“格鲁吉亚”,曾为独立国家联合体成员。因为2008年南奥塞梯战争,格鲁吉亚根据议会2008年8月14日通过的决议做出退出独联体的决定,并于2009年8月18日完成手续,正式退出。[8]
格鲁吉亚领土面积达69,700平方公里(包括阿布哈兹和南奥塞梯)[9];人口数量有4,352,224(2011年人口统计);主要民族为格鲁吉亚族(70.1%),其他主要少数民族有亚美尼亚族、俄罗斯族和阿塞拜疆族等;官方语言为格鲁吉亚语,当地居民亦多通晓俄语;多数人信仰东正教,少数信仰伊斯兰教。
格鲁吉亚位于地区的黑海沿岸,北邻俄罗斯,南部与土耳其、亚美尼亚、阿塞拜疆接壤。格鲁吉亚是苏联领导人斯大林的故乡,现在格鲁吉亚政治上倾向于欧盟和西方国家,甚至与俄罗斯爆发战争并断交,其最终目标是加入欧盟。
ジョージア(グルジア語: საქართველო, ラテン文字転写: sakartvelo, 英語: Georgia)は、南コーカサスにある共和制国家。首都はトビリシ。東ヨーロッパ[3][4][5]、もしくは西アジアに区分される[5][6]。北側にロシア、南側にトルコ、アルメニア、アゼルバイジャンと隣接する。
日本では2015年4月まで国名呼称にグルジア(ロシア語: Грузия, Gruziya)を使用していた。
Georgia (Georgian: საქართველო, Sakartvelo; IPA: [sɑkʰɑrtʰvɛlɔ] (![]() listen)) is a country located at the intersection of Eastern Europe and Western Asia. It is a part of the Caucasus region, bounded to the west by the Black Sea, to the north and east by Russia, to the south by Turkey and Armenia, and to the southeast by Azerbaijan. It covers 69,700 square kilometres (26,911 sq mi), and has a population of around 4 million.[11] Georgia is a representative democracy governed as a unitary parliamentary republic.[11] Tbilisi is the capital and largest city, home to roughly a quarter of the population.
listen)) is a country located at the intersection of Eastern Europe and Western Asia. It is a part of the Caucasus region, bounded to the west by the Black Sea, to the north and east by Russia, to the south by Turkey and Armenia, and to the southeast by Azerbaijan. It covers 69,700 square kilometres (26,911 sq mi), and has a population of around 4 million.[11] Georgia is a representative democracy governed as a unitary parliamentary republic.[11] Tbilisi is the capital and largest city, home to roughly a quarter of the population.
During the classical era, several independent kingdoms became established in what is now Georgia, such as Colchis and Iberia. Georgians officially adopted Christianity in the early fourth century, which contributed to the spiritual and political unification of early Georgian states. In the Middle Ages, the unified Kingdom of Georgia emerged and reached its Golden Age during the reign of King David the Builder and Queen Tamar the Great in the 12th and early 13th centuries. Thereafter, the kingdom declined and eventually disintegrated under the hegemony of various regional powers, including the Mongols, the Ottoman Empire and successive dynasties of Persia. In 1783, one of the Georgian kingdoms entered an alliance with the Russian Empire, which proceeded to annex the territory of modern Georgia in a piecemeal fashion throughout the 19th century.
After the Russian Revolution in 1917, Georgia emerged as an independent republic under German protection.[12] Following World War I, Georgia was forcibly annexed by the Soviet Union in 1922, becoming one of its fifteen constituent republics. By the 1980s, an independence movement emerged and grew quickly, leading to Georgia's secession from the Soviet Union in April 1991. For most of the subsequent decade, post-Soviet Georgia suffered from economic crisis, political instability, ethnic conflict, and secessionist wars in Abkhazia and South Ossetia. Following the bloodless Rose Revolution in 2003, Georgia strongly pursued a pro-Western foreign policy; it introduced a series of democratic and economic reforms aimed at integration into the European Union and NATO. The country's Western orientation soon led to worsening relations with Russia, at one point even resulting in a brief war in 2008.
Georgia is a developing country with "very high" Human Development, high levels of economic freedom and ease of doing business, as well as relatively low corruption indicators, although poverty and unemployment remain a challenge.[13] It is one of the first countries in the world to legalize cannabis, becoming the only former-communist state in the world to do so. The country is a member of international organizations across both Europe and Asia, such as Council of Europe, Organization of the Black Sea Economic Cooperation, OSCE, Eurocontrol, European Bank for Reconstruction and Development, and GUAM.
La Géorgie (en géorgien : საქართველო, translittéré en SakartveloÉcouter), en forme longue depuis 1995 la république de Géorgie, est un pays sur la côte est de la mer Noire dans le Caucase, situé à la fois en Europe de l'Est et en Asie de l'Ouest2,5,6. Elle est considérée comme faisant culturellement, historiquement et politiquement parlant partie de l'Europe7,8,9. Le pays est membre du Conseil de l'Europe, de l'OSCE, de Eurocontrol, de la Coopération économique de la mer Noire et de l'Alliance GUAM. Elle espère devenir un jour membre de l'OTAN et de l'Union européenne avec laquelle un accord d'association a été conclu en 201410.
L'histoire de la Géorgie remonte aux royaumes antiques de Colchide et d'Ibérie, qui furent ensuite unifiés. La Géorgie est l'une des premières nations à avoir adopté la religion chrétienne comme religion officielle, au début du IVe siècle : elle a rejoint l'orthodoxie après le schisme de 1054. Elle connaît son âge d'or au XIIe siècle, sous le règne de Tamar Ire. Confrontée tour à tour aux Romains, Perses, Mongols, Byzantins, et Ottomans11, la Géorgie est annexée au début du XIXe siècle par la Russie impériale sous Paul Ier, mais retrouve son indépendance de 1918 à 1921 et devient un protectorat allemand. Elle est ensuite intégrée en tant que république au sein de l'Union soviétique.
L'indépendance de la Géorgie est une nouvelle fois restaurée en 1991. Le pays accumule difficultés économiques et guerres de sécession ; l'Adjarie redevient totalement géorgienne en 2004, par contre l'Abkhazie et l'Ossétie du Sud proclament unilatéralement leur indépendance avec le soutien direct de la Russie après les combats des années 1990 et la deuxième guerre d'Ossétie du Sud en 2008. La Révolution des Roses, en 2004, pacifique, et l'alternance démocratique, en 2012, non moins pacifique, ont conduit le pays sur le chemin de la démocratie.
Le pays couvre un territoire de 69 700 km2 dont 12 560 km2, soit environ 18 %3, échappent à l’administration géorgienne. La Georgie possède des frontières avec la Russie au nord et nord-est, l'Arménie et la Turquie au sud, et l'Azerbaïdjan au sud-est. La population est de 3,7 millions d'habitants selon le recensement de novembre 2014.
La Georgia (in georgiano: საქართველო?, Sakartvelo; in russo: Грузия?, Gruzija) è uno Stato sulle rive del Mar Nero, situato su una[6] delle linee convenzionali di demarcazione che separano l'Europa dall'Asia[7][8][9]. Dal punto di vista geografico è considerato appartenente all'Asia[10] o anche un paese transcontinentale, mentre, dal punto di vista storico-culturale è spesso considerato appartenente all'Europa orientale.[8][11][12][13]
La Georgia fa parte del Consiglio d'Europa, dell'OSCE, di Eurocontrol, della Banca Europea per la Ricostruzione e lo Sviluppo, e del GUAM ed è compresa nel piano d'azione per l'adesione alla NATO.
Parte dell'impero russo dal 1801 fino alla rivoluzione del 1917, per buona parte del XX secolo fu una repubblica dell'Unione Sovietica; nel corso del 1991 proclamò la propria indipendenza che divenne formalmente riconosciuta il 25 dicembre di quello stesso anno.
Confina a nord e a nord-est con la Russia, a sud con la Turchia e l'Armenia, a sud-est con l'Azerbaigian, e a ovest col Mar Nero. Ha una popolazione di 3 716 858 abitanti e la sua capitale è Tbilisi[14].
Georgia (en georgiano, საქართველო, transliterado Sakartvelo) es un país soberano localizado en la costa del mar Negro,4en el límite entre Europa Oriental y Asia Occidental. Geográficamente su territorio ha sido clasificado como euroasiático o como bicontinental56 dependiendo de la correspondiente convención, aunque cultural, histórica y políticamente, Georgia se considera como parte de Europa.78910 Como RSS de Georgia, hasta 1991, formó parte de la Unión de Repúblicas Socialistas Soviéticas (URSS).11 Comparte fronteras con Rusia al norte y noreste, con Turquía y Armenia al sur, y con Azerbaiyán al sudeste.12 La capital es Tiflis (en georgiano: თბილისი, Tbilisi),12 aunque desde 2012 el Parlamento tiene su sede en la ciudad de Kutaisi.13
La Constitución de Georgia es la de una democracia representativa, organizada como un Estado unitario, República semipresidencialista. Georgia es actualmente miembro de las Naciones Unidas, el Consejo de Europa, la Organización Europea para la Seguridad de la Navegación Aérea (Eurocontrol), la Organización Mundial del Comercio, la Cooperación Económica del Mar Negro, la Organización para la Seguridad y la Cooperación en Europa, la Comunidad de Opción Democrática, y la GUAM. El país aspira a unirse a la Unión Europea y a la OTAN; en julio de 2016 la Unión Europea incorporó a Georgia como estado asociado.14
La historia de Georgia se remonta a los antiguos reinos de Cólquida e Iberia. Georgia llegó a la cima de su fuerza política y económica durante el reinado de David IV y la reina Tamar, en los siglos XI y XII. A principios del siglo XIX, Georgia fue anexionada por el Imperio ruso. Después de un breve período de independencia tras la revolución rusa de 1917, Georgia fue anexionada por la Rusia soviética en 1921. Desde 1922 hasta 1991 la República Socialista Soviética de Georgia fue una de las quince repúblicas federales de la Unión Soviética. El 9 de abril de 1991, poco antes del colapso de la Unión Soviética, Georgia declaró su independencia. Al igual que muchos países postcomunistas, Georgia sufrió los disturbios civiles y la crisis económica de la mayor parte de la década de 1990, pero a través de Revolución de las Rosas de 2003 el nuevo gobierno introdujo reformas democráticas y económicas.
Гру́зия (груз. საქართველო [sɑkʰɑrtʰvɛlɔ], Сакартве́ло) — государство, расположенное в западной части Закавказья на восточном побережье Чёрного моря[9][10][11][12]. Относится к Передней Азии; рассматривается часто как страна на стыке Европы и Азии, иногда — как часть современной Европы[* 7].
Население, по итогам официальной переписи 2014 года, составляет 3 713 804 человека[5][* 6] (по оценочным данным на начало 2021 года — 3 728 573 человека[4][* 6]), территория — 69 700[* 8] км². Занимает 131-е место в мире по численности населения и 119-е по территории.
Столица — Тбилиси. Государственный язык — грузинский.
Грузия — унитарное государство с парламентской формой правления. 16 декабря 2018 года пост президента Грузии заняла Саломе Зурабишвили, премьер-министром с 22 февраля 2021 года является Ираклий Гарибашвили.
Согласно Конституции, в состав Грузии входят 2 автономные республики, 9 краёв и приравненный к ним столичный город.
Грузия омывается водами Чёрного моря на западе; граничит с Россией на востоке и севере, Арменией и Турцией на юге и Азербайджаном на юго-востоке. Территории Абхазии и Цхинвальского региона де-факто не управляются грузинским правительством и расцениваются им, Парламентской Ассамблеей ОБСЕ, США и Европейской комиссией[25][* 9][27] как оккупированные Россией части Грузии. Россия, Никарагуа, Науру, Венесуэла[28][29] и Сирия[30][31] признают их независимыми от Грузии государствами Республика Абхазия и Республика Южная Осетия.



Das Schwarze Meer ist ein zwischen Südosteuropa, Osteuropa und Vorderasien gelegenes Binnenmeer, das über den Bosporus und die Dardanellen mit dem östlichen Mittelmeer verbunden ist. Es ist bis 2212 m tief[1] und hat (ohne das Asowsche Meer) eine Fläche von etwa 436.400 km².[2] Der Rauminhalt des Schwarzen Meeres beträgt 547.000 km³. Die durchschnittliche Wassertiefe beträgt 1253 Meter.
黑海是欧亚大陆的一个陆间海,被欧洲、高加索和安那托利亚半岛所包围[4]。黑海通过土耳其海峡与地中海的爱琴海区域相联。西亚和东欧被这一系列水体分隔开来。黑海在北面通过刻赤海峡与亚速海相连。流入黑海的主要河流有多瑙河和第聂伯河。沿海国家有土耳其、保加利亚、罗马尼亚、乌克兰、俄罗斯和格鲁吉亚。沿海重要城市有伊斯坦布尔、布尔加斯、瓦尔纳、康斯坦察、图尔恰、敖德萨、塞瓦斯托波尔、巴统等。
黑海的面积有436,400平方千米(168,500平方英里)(不包括亚速海)[1],最大深度为2,212米(7,257英尺)[2],体积为547,000立方千米(131,200立方英里)。[3]黑海形成一个东西向的椭圆形凹陷。[5]黑海的南面是本廷山脉,东面是高加索山脉,西北面是宽阔的低地。黑海东西向最宽有大约1,175千米(730英里)。
黒海(こっかい)は、ヨーロッパとアジアの間にある内海で、大西洋の縁海(地中海 (海洋学))の一つである。マルマラ海を経てエーゲ海、地中海に繋がる。
バルカン半島、アナトリア半島、コーカサスと南ウクライナ・クリミア半島に囲まれており、ドナウ川、ドニエストル川、ドニエプル川などの東ヨーロッパの大河が注ぐ。アナトリアとバルカンの間のボスポラス海峡、マルマラ海、ダーダネルス海峡を通じて地中海に繋がっており、クリミアの東にはケルチ海峡を隔ててアゾフ海がある。
黒海に面する国は、南岸がトルコで、そこから時計回りにブルガリア、ルーマニア、ウクライナ、ロシア、ジョージアである。
黒海に面する有名な港湾には、イスタンブール(ビュザンティオン、コンスタンティノープル)から時計回りにブルガス、ヴァルナ、コンスタンツァ、オデッサ、セヴァストポリ、ヤルタ、ガグラ、バトゥミ、トラブゾン、サムスンなどがある。
The Black Sea is a body of water and marginal sea of the Atlantic Ocean between the Balkans, Eastern Europe, the Caucasus, and Western Asia.[1] It is supplied by a number of major rivers, such as the Danube, Dnieper, Southern Bug, Dniester, Don, and the Rioni. About a third of Europe drains into the Black Sea,[2] including the countries of Austria, Belarus, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Croatia, Czech Republic, Georgia, Germany, Hungary, Moldova, Poland, Romania, Russia, Serbia, Slovakia, Slovenia, Turkey and Ukraine.
The Black Sea has an area of 436,400 km2 (168,500 sq mi) (not including the Sea of Azov),[3] a maximum depth of 2,212 m (7,257 ft),[4] and a volume of 547,000 km3 (131,000 cu mi).[5] It is constrained by the Pontic Mountains to the south, Caucasus Mountains to the east, Crimean Mountains to the north, Strandzha to the southwest, Dobrogea Plateau to the northwest, and features a wide shelf to the northwest.
The longest East-West extent is about 1,175 km (730 mi).[6]
Important cities along the coast include Batumi, Burgas, Constanța, Giresun, Istanbul, Kerch, Novorossiysk, Odessa, Ordu, Poti, Rize, Samsun, Sevastopol, Sochi, Sukhumi, Trabzon, Varna, Yalta, and Zonguldak.
The Black Sea has a positive water balance; that is, a net outflow of water 300 km3 (72 cu mi) per year through the Bosphorus and the Dardanelles into the Aegean Sea. Mediterranean water flows into the Black Sea as part of a two-way hydrological exchange. The Black Sea outflow is cooler and less saline, and floats over the warm, more saline Mediterranean inflow – as a result of differences in density caused by differences in salinity – leading to a significant anoxic layer well below the surface waters. The Black Sea drains into the Mediterranean Sea, via the Aegean Sea and various straits, and is navigable to the Atlantic Ocean. The Bosphorus Strait connects it to the Sea of Marmara, and the Strait of the Dardanelles connects that sea to the Aegean Sea region of the Mediterranean. These waters separate Eastern Europe, the Caucasus and Western Asia. The Black Sea is also connected, to the North, to the Sea of Azov by the Strait of Kerch.
The water level has varied significantly. Due to these variations in the water level in the basin, the surrounding shelf and associated aprons have sometimes been land. At certain critical water levels it is possible for connections with surrounding water bodies to become established. It is through the most active of these connective routes, the Turkish Straits, that the Black Sea joins the world ocean. When this hydrological link is not present, the Black Sea is an endorheic basin, operating independently of the global ocean system, like the Caspian Sea for example. Currently the Black Sea water level is relatively high, thus water is being exchanged with the Mediterranean. The Turkish Straits connect the Black Sea with the Aegean Sea, and comprise the Bosphorus, the Sea of Marmara and the Dardanelles.
La mer Noire est située entre l’Europe, le Caucase et l’Anatolie. Large d'environ 1 150 km d’ouest en est et de 600 km du nord au sud, elle s’étend sur une superficie de 413 000 km2. L'adjectif correspondant est « pontique », qui vient du nom antique de cette mer, le Pont Euxin.
Le terme océanographique d'« euxinisme » y fait également référence, il désigne une anoxie des eaux profondes, plus salées qu'en surface et provenant de la Méditerranée via la mer de Marmara par un courant de fond inverse de celui des eaux plus douces de la surface alimentées par les fleuves se jetant dans la mer Noire.
Elle communique au sud-ouest avec la mer Méditerranée par le Bosphore, la mer de Marmara et le détroit des Dardanelles. Sur ses côtes ouest et nord, elle communique avec de nombreux limans (lagunes navigables dont la salinité et la turbidité varient avec la saison, et qui servaient de frayères pour le poisson). Au nord-est, la mer d'Azov, reliée par le détroit de Kertch, est considérée comme le plus grand des limans. Son climat spécifique doux et humide, aux épais brouillards aux saisons intermédiaires, subit des influences méditerranéennes au sud-ouest et en été (chaud, sec et ensoleillé), continentales au nord et en hiver (froid glacial, la mer peut geler, les chutes de neige sont fréquentes), et subtropicales au sud-est. Pendant les tempêtes, surtout hivernales, les vagues sont courtes, mais hautes, et peuvent venir de plusieurs directions à la fois, rendant la navigation difficile.
Depuis 1996, le 31 octobre est la « journée internationale pour la protection de la mer Noire »1.
Il Mar Nero (in ucraino: Чорне море? Čorne more; in russo: Чёрное море? Čiornoje morie; in bulgaro: Черно море? Černo more; in rumeno: Marea Neagră; in turco: Karadeniz, in georgiano: შავი ზღვა, Shavi zghva, in greco moderno: Μαύρη Θάλασσα, Mávri Thálassa) è un mare situato tra l'Europa sud-orientale e l'Asia minore. È collegato al Mar d'Azov tramite lo stretto di Kerč e, tramite il Bosforo, al Mare di Marmara, che a sua volta, tramite lo stretto dei Dardanelli, è collegato con il mare Egeo che fa parte del Mediterraneo.
I flussi di acqua in ingresso, attraverso il Bosforo, sono di circa 200 km³ (200 miliardi di metri cubi) all'anno. Il suo bacino imbrifero è molto ampio (2 milioni di km²); dalle aree circostanti riceve acque dolci per un totale di circa 320 km³ all'anno. I fiumi più importanti che vi sfociano sono il Danubio, il Dnepr e il Buh Meridionale.
La sua superficie è pari a circa 436 400 km² (escludendo il Mar d'Azov)[1] con una salinità pari a circa il 17‰ (poco meno della metà della salinità media del Mare Mediterraneo). In profondità, oltre i 150 m, questo valore aumenta drasticamente. Il punto più profondo si trova a 2 212 m, mentre nel centro la profondità è di circa 1 830 m. [2]
El mar Negro es un mar interior ubicado entre Europa oriental y Asia occidental. Se encuentra encerrado entre los Balcanes, la estepa póntica, Crimea, el Cáucaso y la península de Anatolia. El estrecho del Bósforo lo conecta con el pequeño mar de Mármara, y el estrecho de los Dardanelos conecta al anterior mar con el mar Egeo, que es una división del mar Mediterráneo. También está conectado con el mar de Azov, situado al noreste, por el estrecho de Kerch. El mar Negro forma una depresión elíptica con una pendiente de este a oeste, y tiene una superficie de 436 400 km2 (sin incluir el mar de Azov),1 una profundidad máxima de 2212 m2 y un volumen de 547 000 km3.3 Los países ribereños del mar Negro son, empezando por el sur y en sentido horario, Turquía, Bulgaria, Rumania, Ucrania, Rusia y Georgia.4
Está delimitado por los montes Pónticos al sur y por las montañas del Cáucaso al este, y cuenta con una amplia meseta al noreste. Su mayor longitud de este a oeste es de 1 175 km. Entre las ciudades importantes de sus costas están: Batumi, Burgas, Constanza, Giresun, Hopa, Estambul, Kerch, Mangalia, Năvodari, Novorossiysk, Odesa, Ordu, Poti, Rize, Sinope, Samsun, Sevastopol, Sochi, Sozopol, Sujumi, Trabzon, Varna, Yalta y Zonguldak.
Existe una salida neta de agua de 300 km3 al año a través del Bósforo y del estrecho de Dardanelos hacia el mar Egeo, mientras que el agua del Mediterráneo discurre hacia el mar Negro como parte de un camino de ida y vuelta de intercambio hidrológico. El flujo que sale del mar Negro es más frío y menos salino, y el flujo que entra desde el Mediterráneo es más cálido y salino, por lo que este flujo es el resultado de los cambios de densidad causados por la diferente salinidad, lo que da lugar a una gran cantidad de agua anóxica a 150 m bajo la superficie, que tienen la particularidad de descomponer los barcos hundidos fabricados en hierro pero no así los barcos de madera.5 El mar Negro también recibe agua del gran sistema fluvial de Eurasia por el norte del mar. Los ríos que le aportan más agua son el Danubio, el Dniéster, el Dniéper y el Don.
Los niveles de agua de este mar han variado significativamente a lo largo de la historia. Debido a estas variaciones del nivel del agua en la cuenca, los límites actuales de este mar han sido a veces terrazas geológicas secas. Cuando se dan determinados niveles de agua elevados es posible que el mar se conecte con otras aguas cercanas para estabilizarse. Es a través de una de estas rutas de conexión más activas, el estrecho turco, donde este mar se conecta con los océanos del mundo. Cuando este enlace hidrológico no está presente, el mar Negro se transforma en una cuenca endorreica que opera de forma independiente del sistema global de los océanos, como es el caso del mar Caspio. El estrecho turco conecta el mar Negro con el Egeo, y abarca el Bósforo, el mar de Mármara y el estrecho de Dardanelos.
Чёрное мо́ре — внутреннее море бассейна Атлантического океана. Проливом Босфор соединяется с Мраморным морем, далее, через пролив Дарданеллы (эти проливы зачастую называют Черноморскими проливами) — с Эгейским и Средиземным морями. Керченским проливом соединяется с Азовским морем. С севера в море глубоко врезается Крымский полуостров. По поверхности Чёрного моря проходит водная граница между Европой и Азией.
Площадь Чёрного моря — 422 000 км²[1] (по другим данным — 436 400 км²[2]). Очертания Чёрного моря напоминают овал с наибольшей осью около 1150 км. Наибольшая протяжённость моря с севера на юг — 580 км. Наибольшая глубина — 2210 м[1], средняя — 1240 м. Объём воды в море составляет 555 тыс. км³[3]. Характерной особенностью Чёрного моря является полное (за исключением ряда анаэробных бактерий) отсутствие жизни на глубинах более 150—200 м из-за насыщенности глубинных слоёв воды сероводородом.
Море омывает берега России, Украины, Румынии, Болгарии, Турции, Грузии, Абхазии[4] (территории, расположенные вокруг моря, традиционно именуют термином «Причерноморье»).
Чёрное море — важный район транспортных перевозок. Помимо этого, Чёрное море сохраняет важное стратегическое и военное значение. В Севастополе и Новороссийске находятся основные военные базы российского Черноморского флота, в Синопе и Самсуне базируются корабли черноморской группировки ВМФ Турции, в Варне — ВМС Болгарии, в Поти и Батуми — корабельный состав департамента береговой охраны Пограничной полиции Грузии[5], в Констанце и Мангалии — ВМС Румынии. До марта 2014 года в Севастополе и Новоозёрном базировались части Военно-морских сил Украины, после присоединения Крыма к России переместившиеся в Одессу.

Die Black Sea Trade and Development Bank (BSTDB, dt, Schwarzmeer-Handels- und Entwicklungsbank) ist eine internationale Entwicklungsbank im Dienst der elf Gründungsmitglieder der Schwarzmeer-Wirtschaftskooperation, einer regionalen Wirtschaftsorganisation. Sie unterstützt die wirtschaftliche Entwicklung und die regionale Zusammenarbeit durch die Bereitstellung von Darlehen, Garantien und Eigenkapital für Entwicklungsprojekte und Handelsgeschäfte. Die BSTDB unterstützt sowohl öffentliche als auch private Unternehmen in den Mitgliedsländern und knüpft ihre Finanzierungen nicht an politische Bedingungen[2].
Zu den Zielen der Bank gehören die Förderung regionaler Handelsbeziehungen, länderübergreifender Projekte und ausländischer Direktinvestitionen sowie die Unterstützung von Aktivitäten, die zur nachhaltigen Entwicklung beitragen, wobei der Schwerpunkt auf der Schaffung von Arbeitsplätzen in den Mitgliedsländern liegt[3]. Die Bank verfügt über ein genehmigtes Kapital von 3,45 Mrd. EUR[4].
黑海贸易和开发银行(BSTDB)是一家国际开发银行,为区域经济组织黑海经济合作组织的 11 个创始成员提供服务。它通过为发展项目和贸易交易提供贷款、担保和股权来支持经济发展和区域合作。黑海经济合作银行为成员国的公共和私营公司提供支持,对其融资不附加任何政治条件。
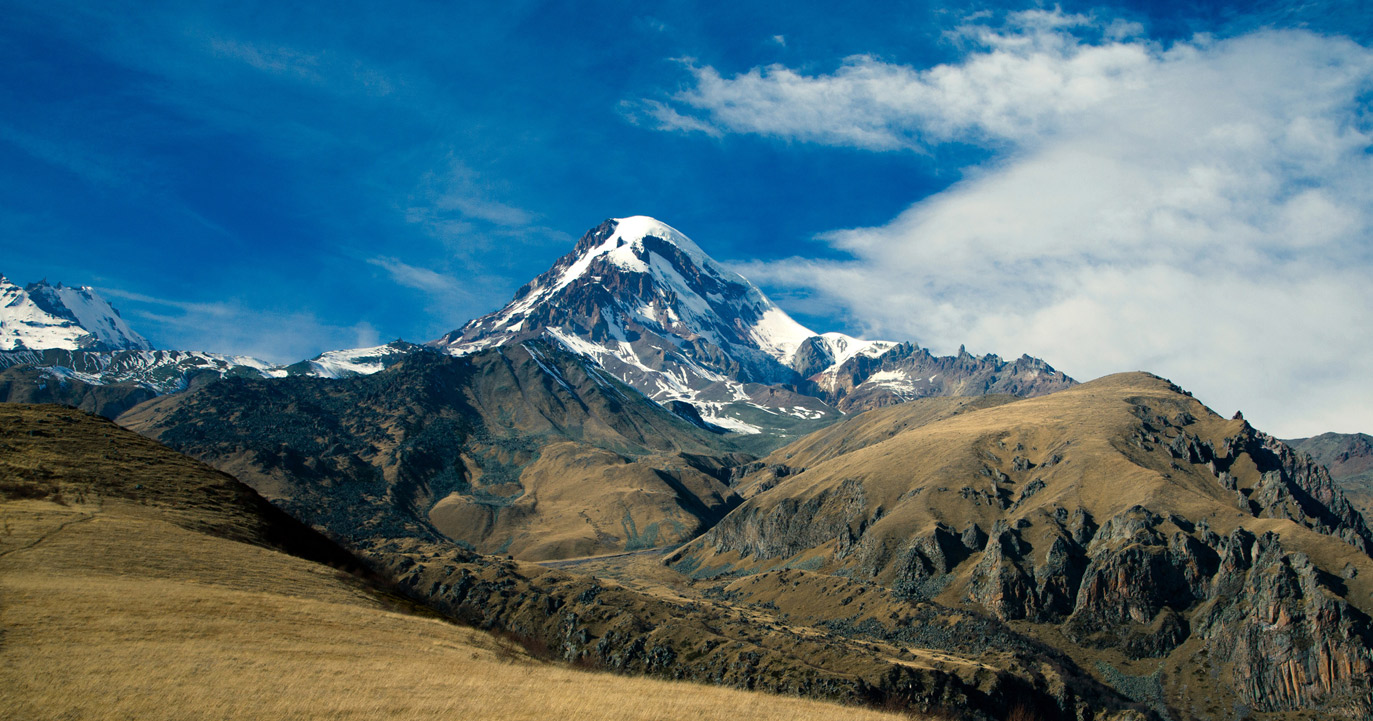


Die 1364 km lange Kura (dt. auch Kur; georgisch მტკვარი Mtkwari, aserbaidschanisch Kür, türkisch Kura) ist der größte Fluss im Kaukasus.
 Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan

 Bavaria
Bavaria
 Bourgogne-Franche-Comté
Bourgogne-Franche-Comté

 Bretagne
Bretagne

 Centre-Val de Loire
Centre-Val de Loire
 China
China
 Germany
Germany
 France
France
 Georgia
Georgia
 Kyrgyzstan
Kyrgyzstan
 Austria
Austria

 Pays-de-la-Loire
Pays-de-la-Loire
 Romania
Romania
 Switzerland
Switzerland
 Tajikistan
Tajikistan

 Tyrol
Tyrol
 Turkmenistan
Turkmenistan
 Hungary
Hungary
 Uzbekistan
Uzbekistan
 Xinjiang Uygur Zizhiqu-XJ
Xinjiang Uygur Zizhiqu-XJ
 Architecture
Architecture
 International cities
International cities
 States of Asia
States of Asia
 Geography
Geography
 States of Europe
States of Europe


 Eat and Drink
Eat and Drink
 Hand in Hand
Hand in Hand
 Financial
Financial
 Transport and traffic
Transport and traffic